TWC-Net: A SAR Ship Detection Using Two-Way Convolution and Multiscale Feature Mapping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To solve the problem that the traditional backbone has insufficient ability to extract SAR features and make the network extract SAR features more effectively, a convolution model based on a two-way structure is designed. The model makes the feature be used more effectively in the model through the information exchange between the upper and lower channels, reduces the loss of information, realizes the use of fewer parameters to learn more useful information, and reduces the overfitting of the model.
- We design a multi-scale mapping output structure to make more effective use of feature information at different scales. The different outputs of the structure correspond to the results of the feature maps of different positions of the backbones. After simple processing of feature maps, the next step of detection can be conducted, which improves the detection ability of the model for ships of different sizes.
2. Related Work
3. Methods
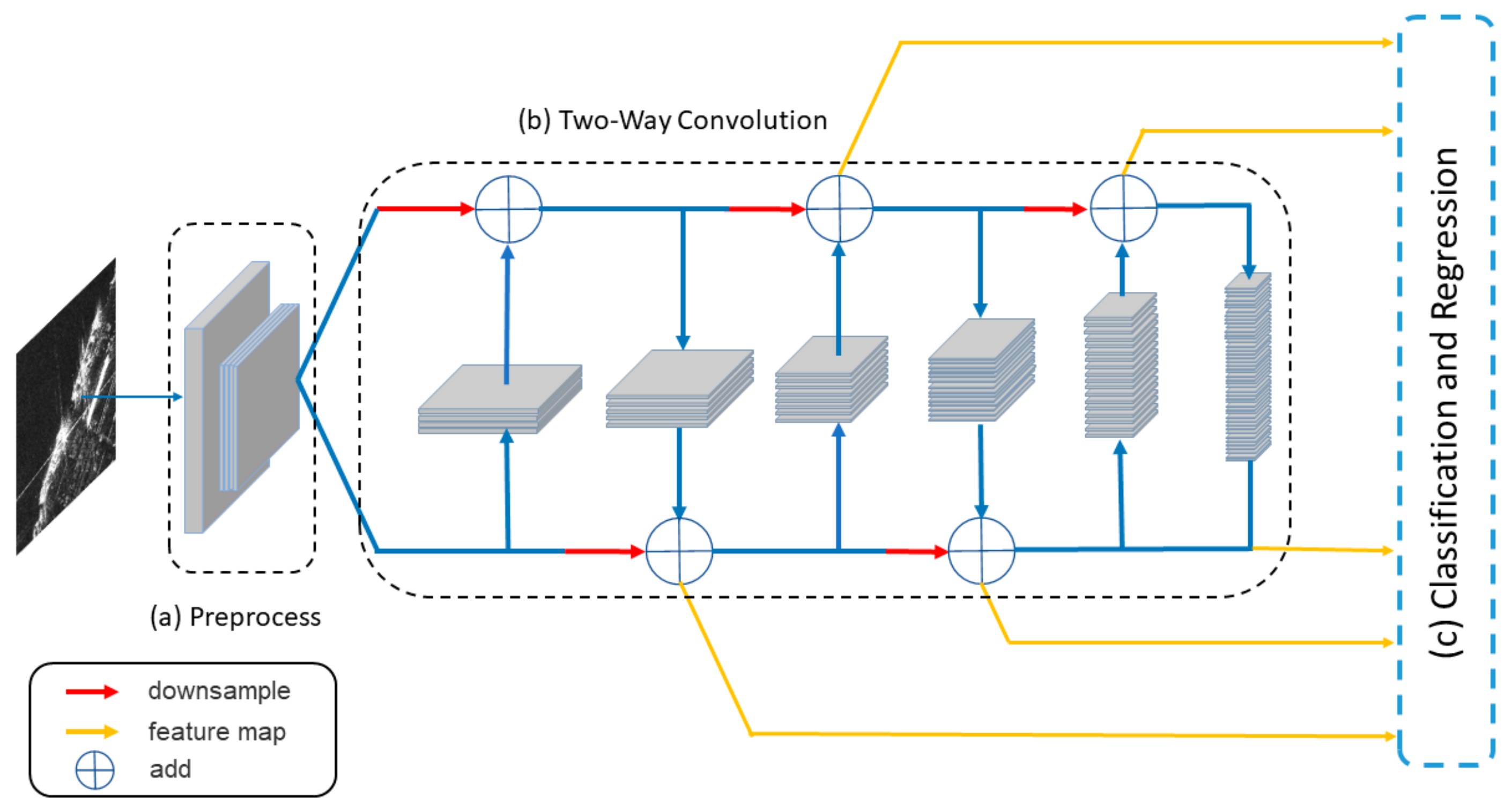
3.1. Network Architecture
3.2. Preprocess, Two-Way Convolution Structure, and Multi Scale Feature Extraction
3.3. Classification and Regression
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Indicators
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Comparative Experiment
4.5. Generating Heatmap
4.6. Generalized Performance Test
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stasolla, M.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Margarit, G.; Santamaria, C.; Walker, N. A Comparative Study of Operational Vessel Detectors for Maritime Surveillance Using Satellite-Borne Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 2687–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Ma, L.; Chen, H. Arbitrary-Oriented Ship Detection Framework in Optical Remote-Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Lu, Y.; Easterbrook, S.; Fidler, S. Efficient and Information-Preserving Future Frame Prediction and Beyond. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Qu, C.; Shao, J. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 13–14 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xianxiang, Q.; Shilin, Z.; Huanxin, Z.; Gui, G. A CFAR Detection Algorithm for Generalized Gamma Distributed Background in High-Resolution SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frery, A.C.; Muller, H.J.; Yanasse, C.C.F.; Sant’Anna, S.J.S. A model for extremely heterogeneous clutter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Wei, L.; Yangqing, J.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Diao, W.; Wang, P.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, X. PCAN—Part-Based Context Attention Network for Thermal Power Plant Detection in Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, N. Dense Attention Pyramid Networks for Multi-Scale Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8983–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmin Duta, I.; Liu, L.; Zhu, F.; Shao, L. Pyramidal Convolution: Rethinking Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11538. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.03144. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.-Y.; Pang, R.; Le, Q.V. NAS-FPN: Learning Scalable Feature Pyramid Architecture for Object Detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.07392. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.08083. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, J.; Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, J. R-FCN: Object Detection via Region-based Fully Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.06409. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollar, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.-W.; Tao, C.-S.; Wang, X.-S.; Xiao, S.-P. Polarimetric SAR Targets Detection and Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS-Toyama), Toyama, Japan, 1 August 2018; pp. 2227–2234. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Fan, W.; Sheng, Q.; Tao, M. Ship Detection Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Polsar Images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 681–684. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Zhuge, Y.; Claramunt, C.; Men, S. N-YOLO: A SAR Ship Detection Using Noise-Classifying and Complete-Target Extraction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, W.; Deng, D. Improved YOLOv3 Based on Attention Mechanism for Fast and Accurate Ship Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z. SDGH-Net: Ship Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images Based on Gaussian Heatmap Regression. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, D.; di Martino, G.; Poggi, G.; Verdoliva, L. A fully convolutional neural network for low-complexity single-stage ship detection in Sentinel-1 SAR images. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 886–889. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, K.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. A Patch-to-Pixel Convolutional Neural Network for Small Ship Detection with PolSAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6623–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-L.; Anagaw, A.; Chang, L.; Wang, Y.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Lee, W.-H. Ship Detection Based on YOLOv2 for SAR Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Ji, K.; Leng, X.; Kuang, G. Squeeze and Excitation Rank Faster R-CNN for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Ji, K.; Leng, X.; Lin, Z. Contextual Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network with Multilayer Fusion for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.06993. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, IT, USA, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Zeng, X.; Qu, Q.; Wang, M.; Su, H.; Shi, J. HRSID: A High-Resolution SAR Images Dataset for Ship Detection and Instance Segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 120234–120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Wei, S. A SAR Dataset of Ship Detection for Deep Learning under Complex Backgrounds. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Methods | Recall (%) | Precision (%) | F-Measure (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TWC-Net | 82.67 | 81.36 | 82.01 |
| Methods | Recall (%) | Precision (%) | F-Measure (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RetinaNet+Res50+FPN | 81.28 | 92.11 | 86.36 |
| YOLOv4 | 82.14 | 91.90 | 86.75 |
| SSD+Res50 | 95.21 | 89.03 | 92.01 |
| Faster RCNN+Res50+FPN | 79.76 | 88.28 | 83.80 |
| TWC-Net | 95.28 | 91.44 | 93.32 |
| Methods | Recall (%) | Precision (%) | F-Measure (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RetinaNet+Res50+FPN | 55.00 | 53.30 | 54.14 |
| YOLOv4 | 37.37 | 21.82 | 27.55 |
| SSD+Res50 | 56.19 | 46.20 | 50.71 |
| Faster RCNN+Res50+FPN | 32.84 | 36.02 | 34.36 |
| TWC-Net | 62.75 | 53.05 | 57.49 |
| Backbones | Model Size (MB) | FLOPs (G) | Parameter (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VGG19 | 549 | 62.26 | 143.73 |
| ResNet50 | 98 | 13.29 | 25.67 |
| DenseNet201 [33] | 78 | 13.75 | 20.21 |
| EfficientNet B7 [9] | 256 | 255.83 | 66.72 |
| Two-way Convolution | 77 | 5.80 | 19.54 |
| Methods | Model size (MB) | FLOPs (G) | Parameter (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RetinaNet+Res50+FPN | 143 | 12.58 | 35.17 |
| YOLOv4 | 251 | 29.88 | 63.94 |
| SSD+Res50 | 122 | 16.23 | 15.43 |
| Faster RCNN+Res50+FPN | 324 | 134.25 | 41.35 |
| TWC-Net | 104 | 9.39 | 26.36 |
| Methods | Recall (%) | Precision (%) | F-Measure (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RetinaNet+Res50+FPN | 70.55 | 66.93 | 67.23 |
| YOLOv4 | 63.99 | 58.03 | 60.86 |
| SSD+Res50 | 82.57 | 66.75 | 72.37 |
| Faster RCNN+Res50+FPN | 61.87 | 60.37 | 61.11 |
| TWC-Net | 85.72 | 64.90 | 73.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Wu, H.; Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Deng, Q.; Hu, H. TWC-Net: A SAR Ship Detection Using Two-Way Convolution and Multiscale Feature Mapping. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132558
Yu L, Wu H, Zhong Z, Zheng L, Deng Q, Hu H. TWC-Net: A SAR Ship Detection Using Two-Way Convolution and Multiscale Feature Mapping. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(13):2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132558
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Lei, Haoyu Wu, Zhi Zhong, Liying Zheng, Qiuyue Deng, and Haicheng Hu. 2021. "TWC-Net: A SAR Ship Detection Using Two-Way Convolution and Multiscale Feature Mapping" Remote Sensing 13, no. 13: 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132558
APA StyleYu, L., Wu, H., Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Deng, Q., & Hu, H. (2021). TWC-Net: A SAR Ship Detection Using Two-Way Convolution and Multiscale Feature Mapping. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132558






