Lake Phenology of Freeze-Thaw Cycles Using Random Forest: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
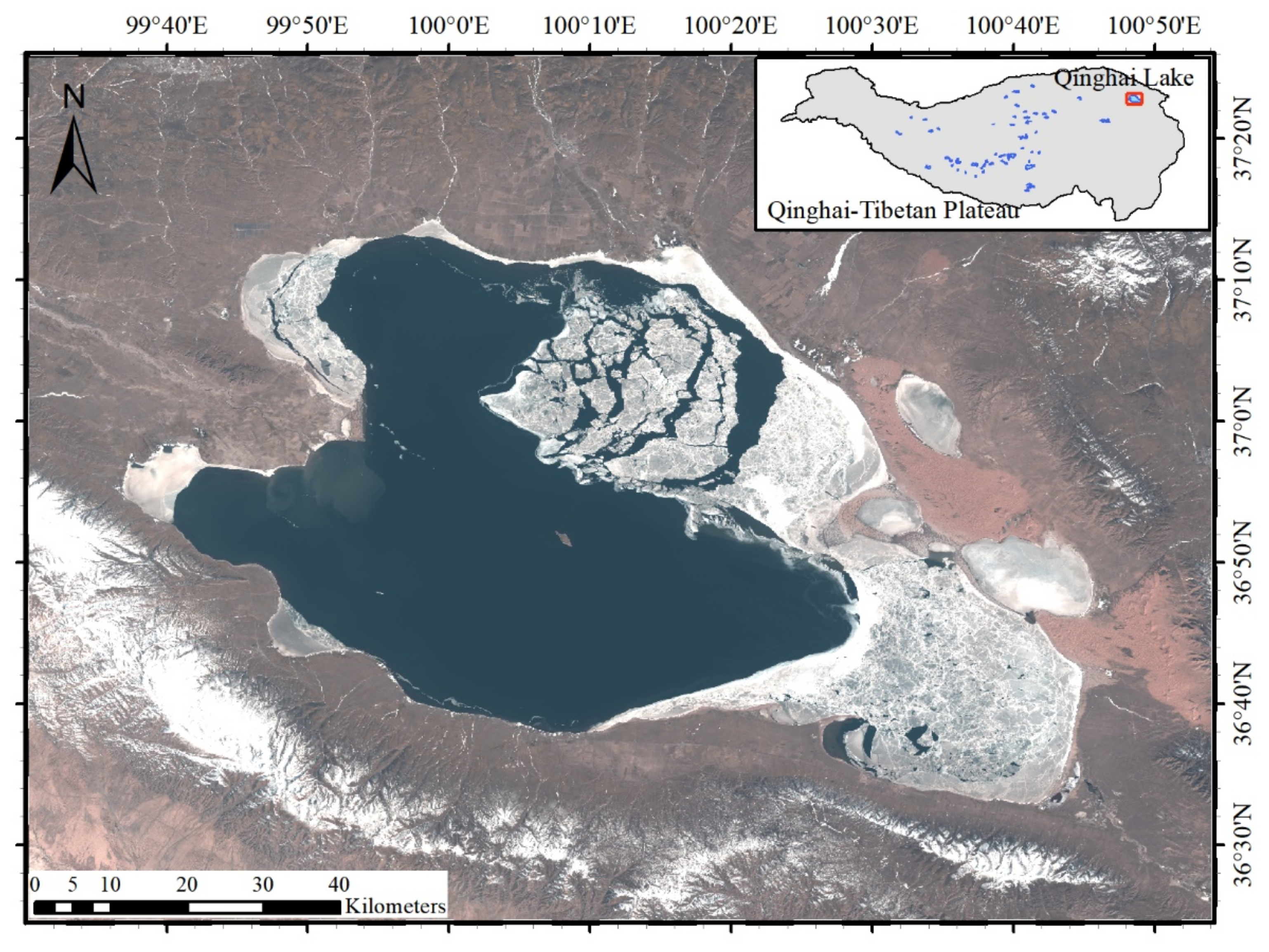
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Surface Reflectance
2.2.2. Training Data and Testing Data
2.2.3. Land Surface Temperature
2.2.4. Water Mask and SRTM
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. RF Algorithm
2.3.2. Lake Ice Threshold Value
2.3.3. Water Index
2.3.4. Postprocessing
3. Results
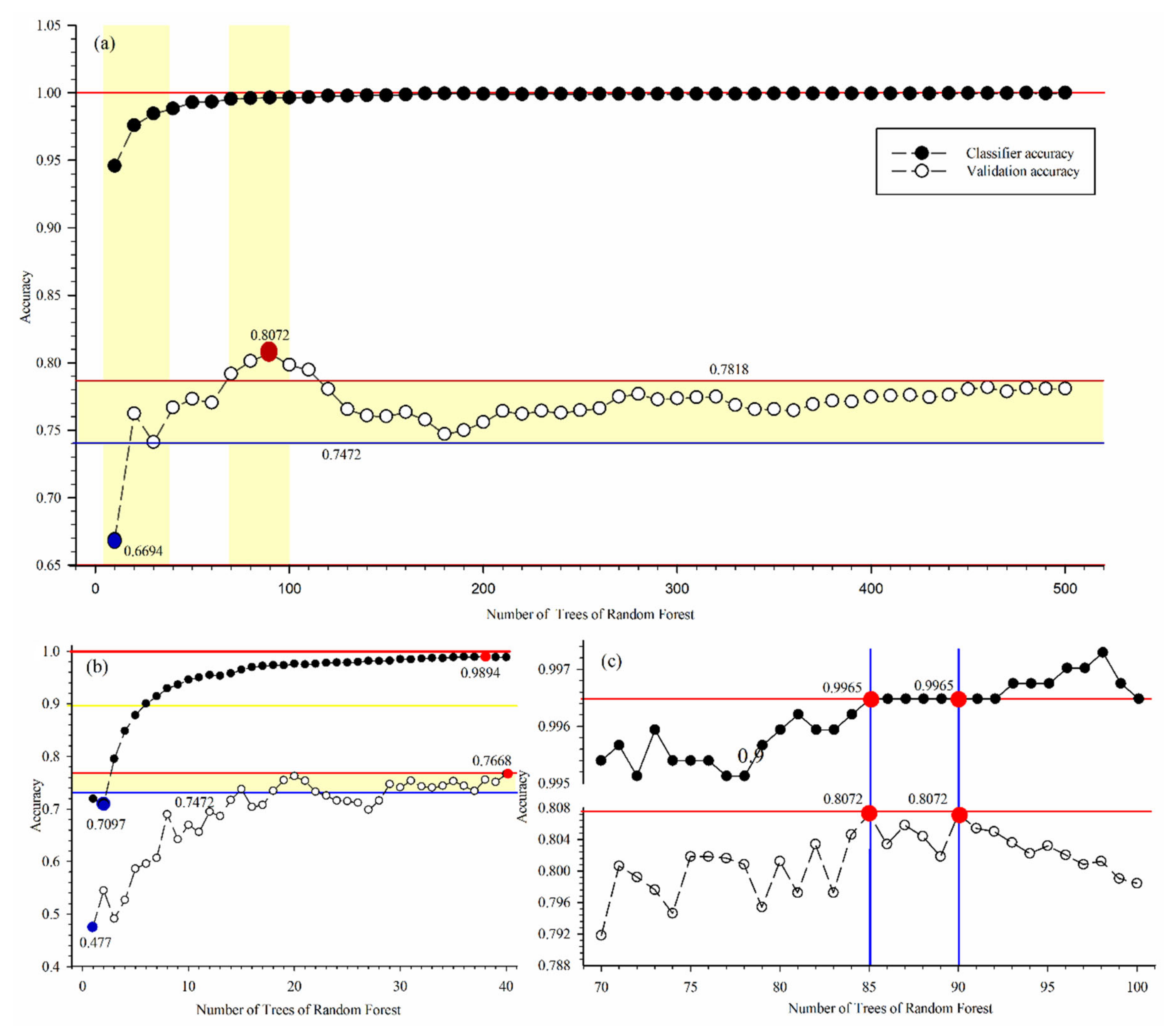
3.1. Accuracy of RF Algorithm
3.2. Classification of RF
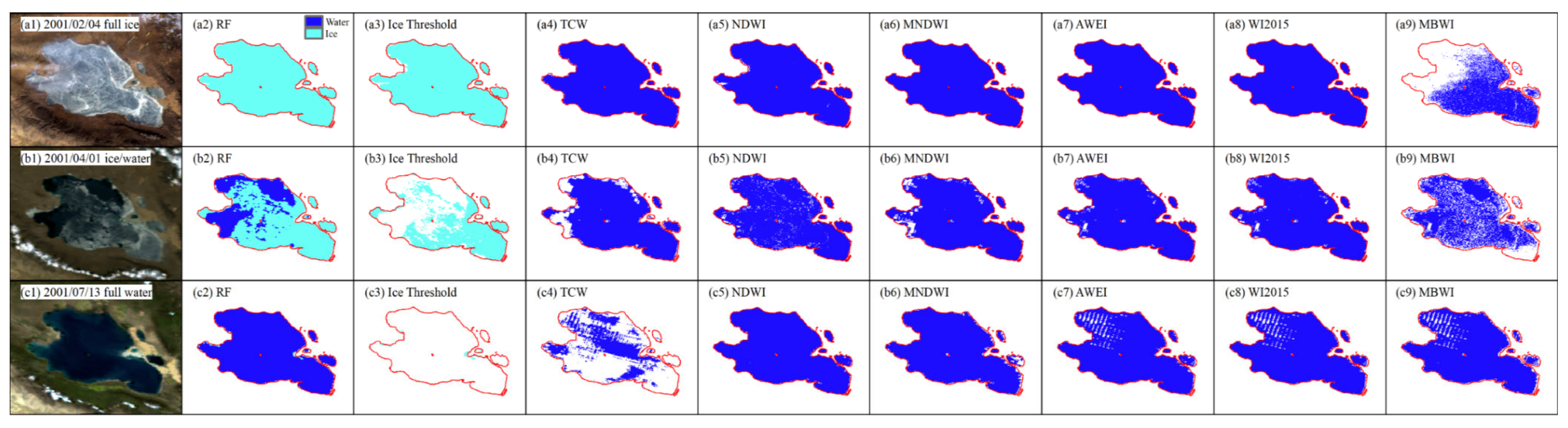
3.3. Comparison of RF and Water/Ice Extraction Methods
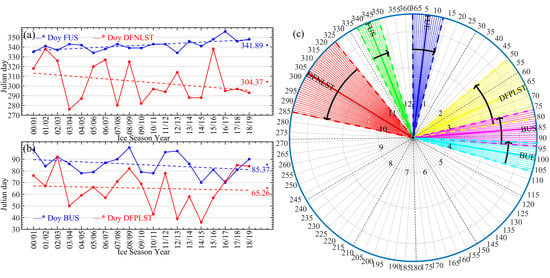
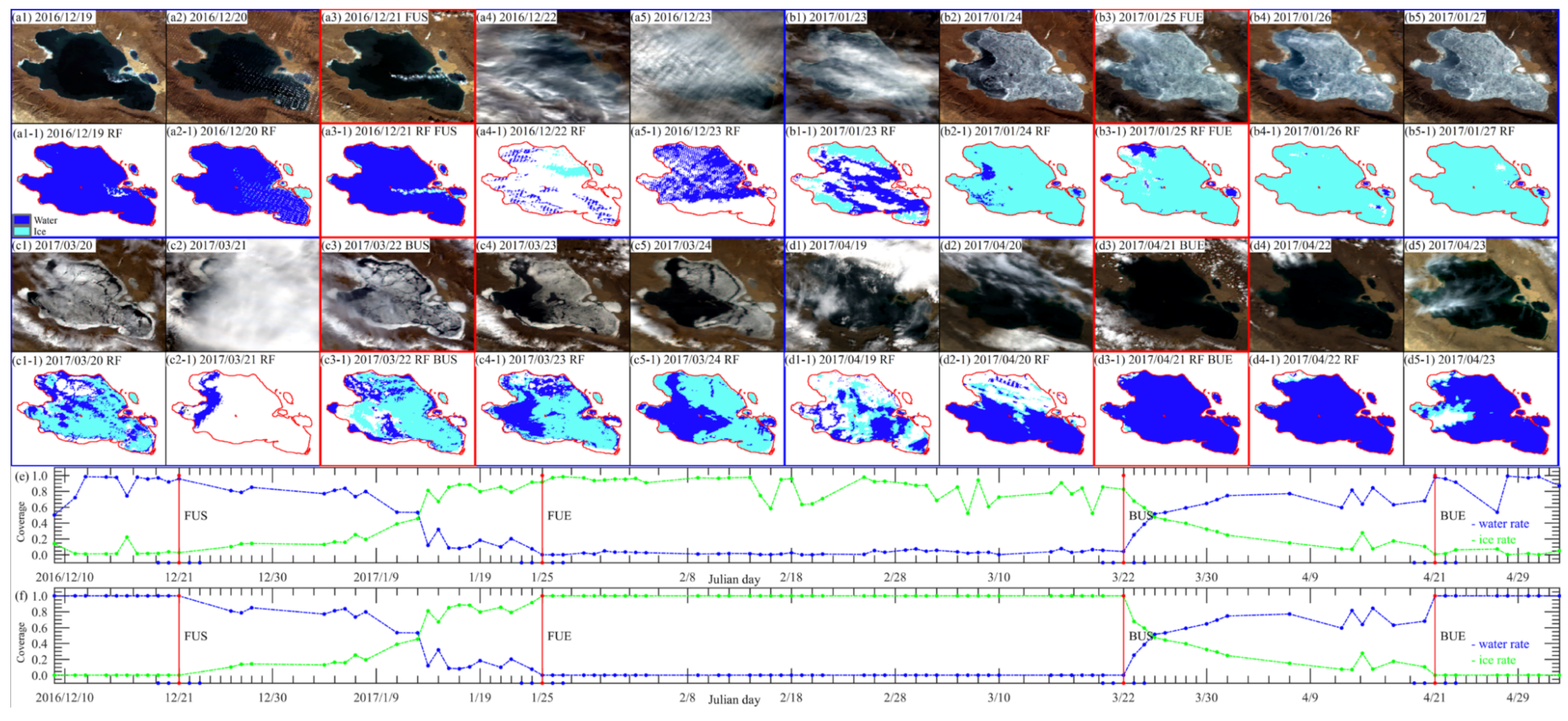
3.4. Lake Phenology
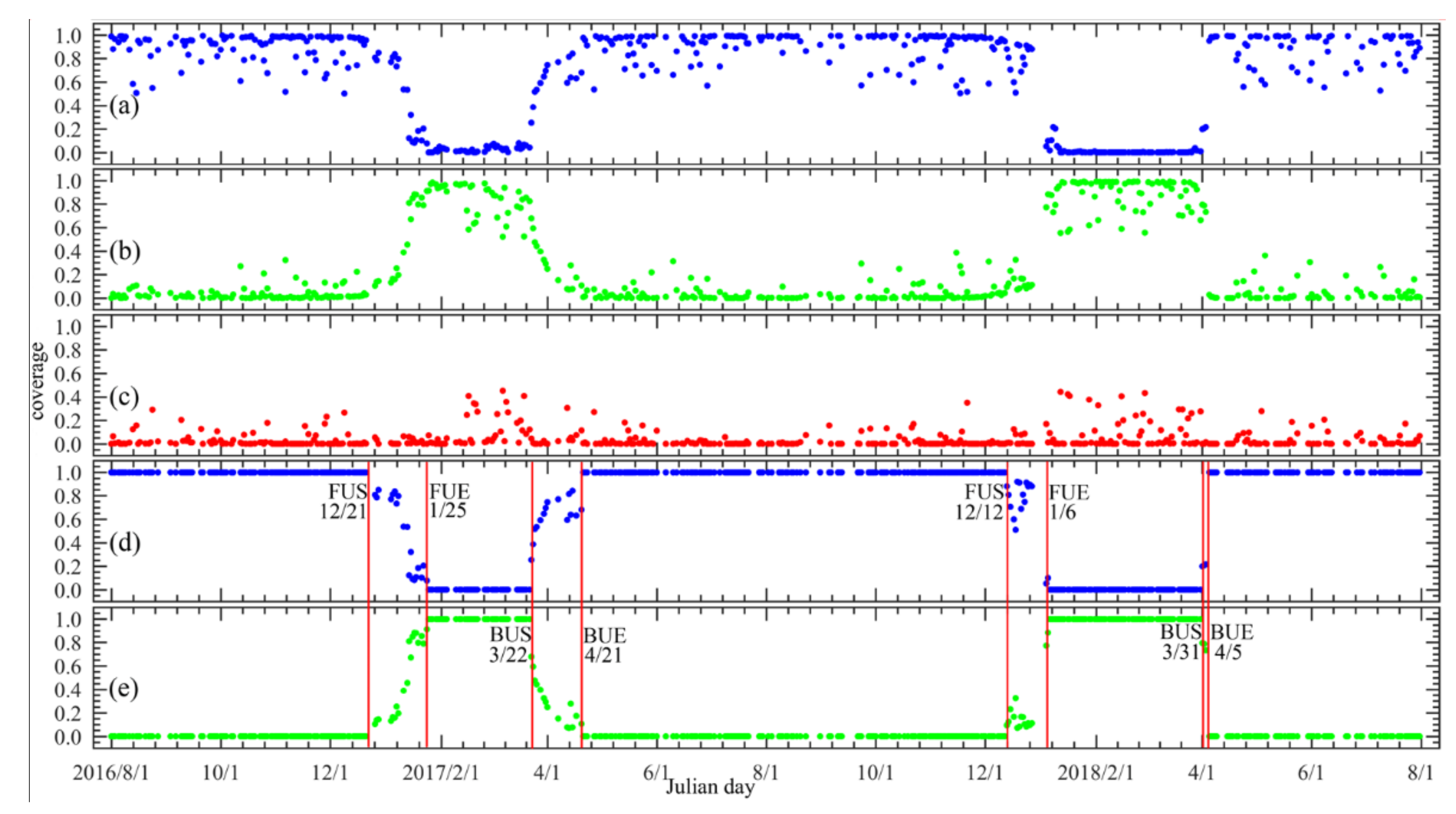
3.4.1. Lake Phenology for the 2016–2018 Ice Season
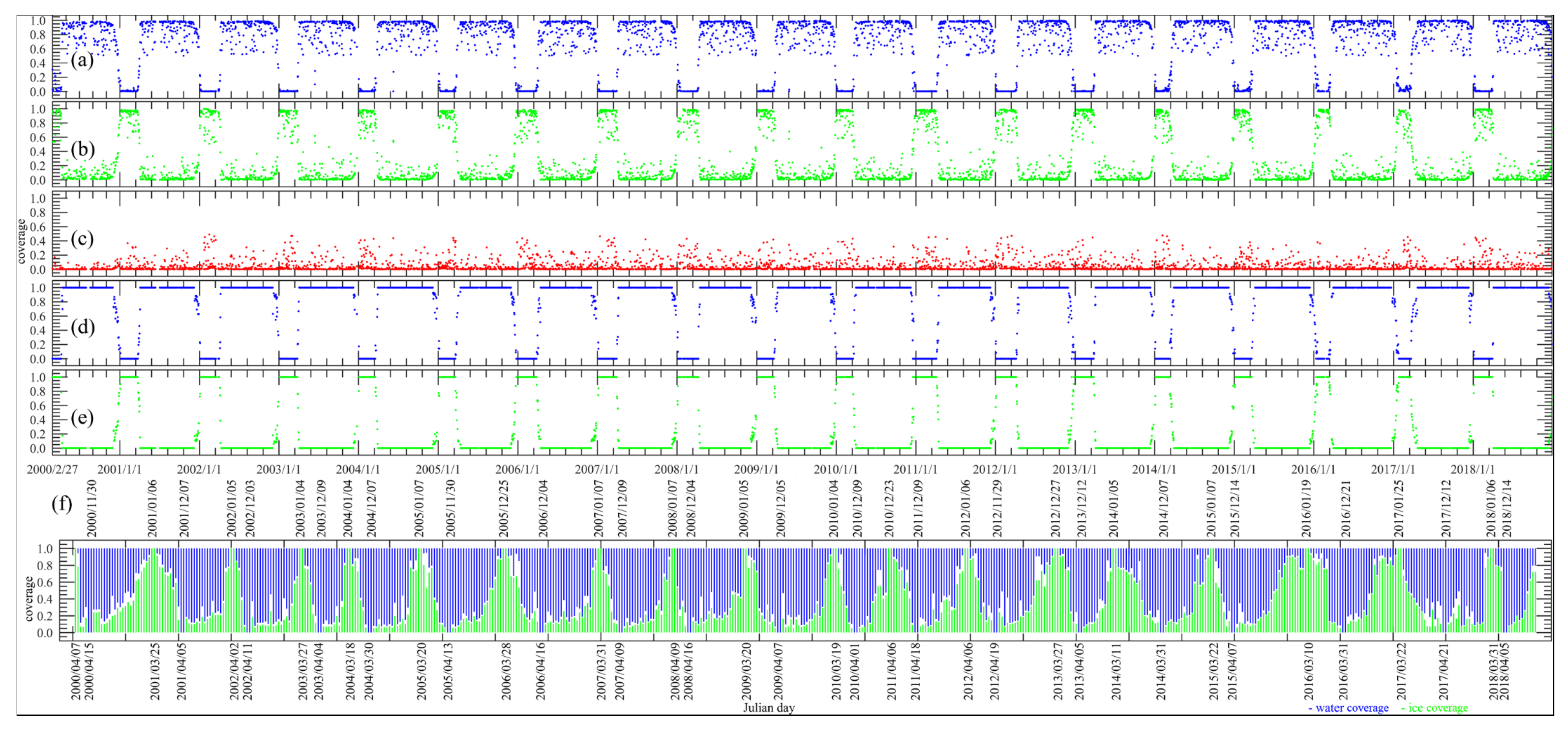
3.4.2. Lake Phenology for the 2000–2018 Ice Season
3.5. Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Trends in Lake Phenology
4.2. LST and Lake Phenology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Predicted | Producer Accuracy/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Ice | Land | Cloud | |||
| Actual | Water | 1537 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 99.48 |
| Ice | 2 | 909 | 0 | 1 | 99.67 | |
| Land | 1 | 0 | 1871 | 2 | 99.84 | |
| Cloud | 0 | 2 | 2 | 779 | 99.49 | |
| Overall accuracy: 99.65 | ||||||
| Kappa coefficient: 99.51 | ||||||
| Predicted | Producer Accuracy/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Ice | Land | Cloud | |||
| Actual | Water | 684 | 33 | 53 | 35 | 84.97 |
| Ice | 31 | 424 | 61 | 38 | 76.53 | |
| Land | 49 | 50 | 762 | 49 | 83.74 | |
| Cloud | 30 | 25 | 59 | 279 | 70.99 | |
| Overall accuracy: 80.72 | ||||||
| Kappa coefficient: 73.45 | ||||||
| Ice Season | FUS | FUE | BUS | BUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999/2000 | 2000/04/07 | 2000/04/15 | ||
| 2000/2001 | 2000/11/30 | 2001/01/06 | 2001/03/25 | 2001/04/05 |
| 2001/2002 | 2001/12/07 | 2002/01/05 | 2002/04/02 | 2002/04/11 |
| 2002/2003 | 2002/12/03 | 2003/01/04 | 2003/03/27 | 2003/04/04 |
| 2003/2004 | 2003/12/09 | 2004/01/04 | 2004/03/18 | 2004/03/30 |
| 2004/2005 | 2004/12/07 | 2005/01/07 | 2005/03/20 | 2005/04/13 |
| 2005/2006 | 2005/11/30 | 2005/12/25 | 2006/03/28 | 2006/04/16 |
| 2006/2007 | 2006/12/04 | 2007/01/07 | 2007/03/31 | 2007/04/09 |
| 2007/2008 | 2007/12/09 | 2008/01/07 | 2008/04/09 | 2008/04/16 |
| 2008/2009 | 2008/12/04 | 2009/01/05 | 2009/03/20 | 2009/04/07 |
| 2009/2010 | 2009/12/05 | 2010/01/04 | 2010/03/19 | 2010/04/02 |
| 2010/2011 | 2010/12/09 | 2010/12/23 | 2011/04/06 | 2011/04/18 |
| 2011/2012 | 2011/12/09 | 2012/01/06 | 2012/04/06 | 2012/04/19 |
| 2012/2013 | 2012/11/29 | 2012/12/27 | 2013/03/27 | 2013/04/05 |
| 2013/2014 | 2013/12/12 | 2014/01/05 | 2014/03/11 | 2014/03/31 |
| 2014/2015 | 2014/12/07 | 2015/01/07 | 2015/03/22 | 2015/04/07 |
| 2015/2016 | 2015/12/14 | 2016/01/19 | 2016/03/10 | 2016/03/31 |
| 2016/2017 | 2016/12/21 | 2017/01/25 | 2017/03/22 | 2017/04/21 |
| 2017/2018 | 2017/12/12 | 2018/01/06 | 2018/03/31 | 2018/04/05 |
| 2018/2019 | 2018/12/14 |

References
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Grill, G.; Nedeva, I.; Schmitt, O. Estimating the volume and age of water stored in global lakes using a geo-statistical approach. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolway, R.I.; Merchant, C.J. Intralake Heterogeneity of Thermal Responses to Climate Change: A Study of Large Northern Hemisphere Lakes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3087–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrahan, J.L.; Kravtsov, S.V.; Roebber, P.J. Connecting past and present climate variability to the water levels of Lakes Michigan and Huron. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-Q.; Tao, A.-Q.; Jin, X. Variability in the ice phenology of Nam Co Lake in central Tibet from scanning multichannel microwave radiometer and special sensor microwave/imager: 1978 to 2013. J. Appl. Remote. Sens. 2013, 7, 073477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Duan, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Kong, F.; Xue, B.; Wu, J. China’s lakes at present: Number, area and spatial distribution. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. China: The third pole. Nature 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, G.; Hayhoe, K.; Johnson, L.; Magnuson, J.; Polassky, S.; Robinson, S.; Shuter, B.; Wander, M.; Wubbles, D.; Zak, D. Confronting Climate Change in the Great Lakes Region: Impacts on Our Communities and Ecosystems; The Union of Concerned Scientists and The Ecological Society of America: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Xie, M.; Wu, Y. Quantitative analysis of lake area variations and the influence factors from 1971 to 2004 in the Nam Co basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Xue, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Lake records and LGM climate in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2000, 45, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong-jian, D.; Shi-yin, L.; Bai-sheng, Y.; Lin, Z. Climatic implications on variations of lakes in the cold and arid regions of China during the recent 50 years. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2006, 28, 623–632. [Google Scholar]
- Palecki, M.A.; Barry, R.G. Freeze-up and Break-up of Lakes as an Index of Temperature Changes during the Transition Seasons: A Case Study for Finland. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Leppäranta, M.; Li, Z.; Cheng, B.; Lin, Z. Thermal structure and water-ice heat transfer in a shallow ice-covered thermokarst lake in central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouch, N.; Temimi, M.; Romanov, P.; Cabrera, R.; McKillop, G.; Khanbilvardi, R. An automated algorithm for river ice monitoring over the Susquehanna River using the MODIS data. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifovic, R.; Pouliot, D. Analysis of climate change impacts on lake ice phenology in Canada using the historical satellite data record. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropáček, J.; Maussion, F.; Chen, F.; Hoerz, S.; Hochschild, V. Analysis of ice phenology of lakes on the Tibetan Plateau from MODIS data. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, L.; Cribb, M. Cloud detection for Landsat imagery by combining the random forest and superpixels extracted via energy-driven sampling segmentation approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 112005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, S.A.; Kuvatov, M.; Sreerekha, T.R.; John, V.O.; Rydberg, B.; Eriksson, P.; Notholt, J. A cloud filtering method for microwave upper tropospheric humidity measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 5531–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay, C.R.; Bernier, M.; Gauthier, Y.; Kouraev, A. Remote sensing of lake and river ice. Remote Sens. Cryosphere 2015, 12, 273–306. [Google Scholar]
- Qiufang, W.; Qinghua, Y. Review of lake ice monitoring by remote sensing. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 29, 803–810. [Google Scholar]
- Dorofy, P.; Nazari, R.; Romanov, P. Application of dynamic threshold in a lake ice detection algorithm. Am. J. Rem. Sens. 2018, 6, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Wang, R. Automatic identification of the lake area at Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau using remote sensing images. Quat. Int. 2019, 503, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, E.P. A TM Tasseled Cap equivalent transformation for reflectance factor data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1985, 17, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhan, W.; Sun, C.; Duan, Y. Landsat 8 OLI image based terrestrial water extraction from heterogeneous backgrounds using a reflectance homogenization approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Liu, Y.; Haoren, W.; Zhang, W. Analysis of Dynamic Change of Hongjiannao Lake Based on MNDWI; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; Volume 57, p. 012005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Guo, H.; Du, J.; Duan, Z. A robust Multi-Band Water Index (MBWI) for automated extraction of surface water from Landsat 8 OLI imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing Landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R.; Hastie, T. A working guide to boosted regression trees. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps-Valls, G. Machine learning in remote sensing data processing. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, Grenoble, France, 1–4 September 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pavelsky, T.M.; Smith, L.C. Spatial and temporal patterns in Arctic river ice breakup observed with MODIS and AVHRR time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, R.H.; Magnuson, J.J.; Clayton, M.K.; Lillesand, T.M.; Rodman, D.C. Determinants of temporal coherence in the satellite-derived 1987–1994 ice breakup dates of lakes on the Laurentian Shield. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, R.H.; Lillesand, T.M. Satellite observation of lake ice as a climate indicator-initial results from statewide monitoring in Wisconsin. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1993, 59, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Maslanik, J.A.; Barry, R.G. Lake ice formation and breakup as an indicator of climate change: Potential for monitoring using remote sensing techniques. In The influence of climate change and climatic variability on the hydrologic regime and water resources. In Proceedings of the Vancouver Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–22 August 1987; pp. 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Duan, S.; Tian, M.; Yi, D. Water level variation of Lake Qinghai from satellite and in situ measurements under climate change. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2011, 5, 053532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ke, C.-Q.; Duan, Z. Monitoring ice variations in Qinghai Lake from 1979 to 2016 using passive microwave remote sensing data. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, D.L.; An, D. Response of water level in Qinghai Lake to climate change in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau (in Chinese). Plat. Meteorol 2012, 31, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-Y.; Xu, H.-Y.; Sun, Y.-L.; Zhang, D.-S.; Yang, Z.-P. Lake-Level Change and Water Balance Analysis at Lake Qinghai, West China during Recent Decades. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhode, D.; Haizhou, M.; Madsen, D.B.; Brantingham, P.J.; Forman, S.L.; Olsen, J.W. Paleoenvironmental and archaeological investigations at Qinghai Lake, western China: Geomorphic and chronometric evidence of lake level history. Quat. Int. 2010, 218, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Gu, J. Study on the Area Variation of Qinghai Lake Based on Long-Term Landsat 5/8 Multi-Band Remote Sensing Imagery. Adv. Earth Sci. 2019, 34, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.J.; Liu, F.J. Estimating on water balance elements in the drainage basin of Qinghai Lake. Arid Land Geogr. 1993, 16, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.J.; Yang, Y.L. Remote sensing monitoring of Lake Qinghai based on EOS/MODIS data (in Chinese). J. Lake Sci. 2005, 17, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Che, T.; Li, X.; Jin, R. Monitoring the frozen duration of Qinghai Lake using satellite passive microwave remote sensing low frequency data (in Chinese). Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewer, M.J.; Gough, W.A. Lake Ontario ice coverage: Past, present and future. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, J. Overview of NASA’s Terra Satellite. 2001. Available online: http://www2.hawaii.edu/~jmaurer/terra/ (accessed on 13 December 2020).
- Shen, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Tao, D.; Zeng, C. Compressed Sensing-Based Inpainting of Aqua Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Band 6 Using Adaptive Spectrum-Weighted Sparse Bayesian Dictionary Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, P.; Vermote, E.; Ray, J. MODIS Surface Reflectance User’s Guide; Collection 6: 2015. Available online: http://modis-sr.ltdri.org (accessed on 13 December 2020).
- Duan, S.-B.; Li, Z.-L.; Li, H.; Göttsche, F.-M.; Wu, H.; Zhao, W.; Leng, P.; Zhang, X.; Coll, C. Validation of Collection 6 MODIS land surface temperature product using in situ measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekertekin, A.; Inyurt, S.; Yaprak, S. Pre-seismic ionospheric anomalies and spatio-temporal analyses of MODIS Land surface temperature and aerosols associated with Sep, 24 2013 Pakistan Earthquake. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2020, 200, 105218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, M.L.; DiMiceli, C.M.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Sohlberg, R.A.; Elders, A.I.; Devadiga, S.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.C. Development of an operational land water mask for MODIS Collection 6, and influence on downstream data products. Int. J. Digit. Earth. 2017, 10, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, H.; Feng, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. DEM generation from contours and a low-resolution DEM. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 134, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-filled seamless SRTM data V4. In International Centre for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT). 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 13 December 2020).
- Segal, M.R. Machine learning benchmarks and random forest regression. UCSF Center Bioinform. Mol. Biostat. 2004, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Karlson, M.; Ostwald, M.; Reese, H.; Sanou, J.; Tankoano, B.; Mattsson, E. Mapping tree canopy cover and aboveground biomass in Sudano-Sahelian woodlands using Landsat 8 and random forest. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10017–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajdak, M.; Piotrowski, O. C&RT model application in classification of biomass for energy production and environmental protection. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2013, 11, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.D. Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Stone, C.J.; Olshen, R.A. Classification and Regression Trees; Chapman and Hall/CRC Press: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden, C. An improved Random Forests approach with application to the performance prediction challenge datasets. Hands Pattern Recognit. Microtom. 2009, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, A.C.-C. Decision Tree Complexity and Betti Numbers. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1997, 55, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, G.V. An Exploratory Technique for Investigating Large Quantities of Categorical Data. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C 1980, 29, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ture, M.; Tokatli, F.; Kurt, I. Using Kaplan–Meier analysis together with decision tree methods (C&RT, CHAID, QUEST, C4.5 and ID3) in determining recurrence-free survival of breast cancer patients. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 2017–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anqi, T. Research on the Variation of Namco Lake Ice by Passive Microwave Remote Sensing; Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhija, S.; Krishnan, N.C.; Singh, G. Supervised Heterogeneous Domain Adaptation via Random Forests. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2016; pp. 2039–2045. [Google Scholar]
- Qui, M.; Yao, X.; Li, X.; An, L., Gong; Gao, Y.; Liu, J. Spatial-temporal characteristics of ice phenology of Qinghai Lake from 2000 to 2016. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 932–944. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zou, B. Satellite-based estimation of the aerosol forcing contribution to the global land surface temperature in the recent decade. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, B.J.; Magnuson, J.J.; Jensen, O.P.; Card, V.M.; Hodgkins, G.; Korhonen, J.; Livingstone, D.M.; Stewart, K.M.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Granin, N.G. Extreme events, trends, and variability in Northern Hemisphere lake-ice phenology (1855–2005). Clim. Chang. 2012, 112, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global lake responses to climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsal, B.R.; Prowse, T.D. Trends and Variability in Spring and Autumn 0 °C-Isotherm Dates over Canada. Clim. Chang. 2003, 57, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay, C.R.; Prowse, T.D.; Bonsal, B.R.; Brown, R.D.; Lacroix, M.P.; Ménard, P. Recent trends in Canadian lake ice cover. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 781–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, A.; Carvalho, A.C.; Nunes, J.P.; Carvalhais, N.; Santos, A. Estimating air surface temperature in Portugal using MODIS LST data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Blagrave, K.; Magnuson, J.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Oliver, S.; Batt, R.D.; Magee, M.R.; Straile, D.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Winslow, L.; et al. Widespread loss of lake ice around the Northern Hemisphere in a warming world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Peylin, P.; Reichstein, M.; Luyssaert, S.; Margolis, H.; Fang, J.; Barr, A.; Chen, A.; et al. Net carbon dioxide losses of northern ecosystems in response to autumn warming. Nature 2008, 451, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ciais, P.; Viovy, N.; Demarty, J. Growing season extension and its impact on terrestrial carbon cycle in the Northern Hemisphere over the past 2 decades. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yao, F.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Shen, Z.; Wang, C.; Song, C. Recent dynamics of alpine lakes on the endorheic Changtang Plateau from multi-mission satellite data. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Drought under global warming: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Jones, C.D.; Cox, P.M. Strong present-day aerosol cooling implies a hot future. Nature 2005, 435, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Dickinson, R.E.; Chameides, W.L. Impact of aerosol indirect effect on surface temperature over East Asia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Band. | Spectral | Wavelength (nm) | Resolution (m) | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * 1 | Red | 620–670 | 250 | Land/Cloud/Aerosols Boundaries |
| * 2 | Near Infrared | 841–876 | 250 | |
| ** 3 | Blue | 459–479 | 500 | Land/Cloud/Aerosols Properties |
| ** 4 | Green | 545–565 | 500 | |
| ** 5 | Short Wave Infrared 1 | 1230–1250 | 500 | |
| ** 6 | Short Wave Infrared 2 | 1628–1652 | 500 | |
| ** 7 | Short Wave Infrared 3 | 2105–2155 | 500 |
| Year | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 10/15 | |
| 2001 | 1/15 | 4/16 | 7/15 | 10/15 |
| 2002 | 1/13 | 4/16 | 7/18 | 10/15 |
| 2003 | 1/15 | 4/15 | 7/13 | 10/15 |
| 2004 | 1/13 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 10/17 |
| 2005 | 1/15 | 4/15 | 7/16 | 10/15 |
| 2006 | 1/15 | 4/16 | 7/15 | 10/15 |
| 2007 | 1/15 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 10/15 |
| 2008 | 1/14 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 10/15 |
| 2009 | 1/14 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 10/15 |
| 2010 | 1/15 | 4/16 | 7/18 | 10/15 |
| 2011 | 1/15 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 10/15 |
| 2012 | 1/16 | 4/14 | 7/15 | 10/15 |
| 2013 | 1/15 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 10/15 |
| 2014 | 1/15 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 10/16 |
| 2015 | 1/15 | 4/15 | 7/16 | 10/16 |
| 2016 | 1/15 | 4/16 | 7/16 | 10/16 |
| 2017 | 1/15 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 10/14 |
| 2018 | 1/14,12/23 | 4/15 | 7/15 | 1015 |
| Water Index | Equation | No |
|---|---|---|
| TCW | (2) | |
| NDWI | (3) | |
| MNDWI | (4) | |
| AWEI | (5) | |
| WI2015 | (6) | |
| MBWI | (7) |
| Methods | 20010204 | 20010401 | 20010713 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Area/km2 | Ice Area/km2 | Water Area/km2 | Ice Area/km2 | Water Area/km2 | Ice Area/km2 | |
| RF | 0 | 4217 | 1769 | 2431 | 4202 | 22 |
| Ice Threshold | - | 4146 | - | 2115 | - | 45 |
| TCW | 4223 | - | 3742 | - | 1391 | - |
| NDWI | 4222 | - | 4136 | - | 4214 | - |
| MNDWI | 4295 | - | 4069 | - | 3889 | - |
| AWEI | 4288 | - | 4166 | - | 4048 | - |
| WI2015 | 4286 | - | 4165 | - | 4051 | - |
| MBWI | 2254 | - | 2866 | - | 3889 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, W.; Huang, C.; Duan, H.; Gu, J.; Hou, J. Lake Phenology of Freeze-Thaw Cycles Using Random Forest: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4098. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244098
Han W, Huang C, Duan H, Gu J, Hou J. Lake Phenology of Freeze-Thaw Cycles Using Random Forest: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(24):4098. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244098
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Weixiao, Chunlin Huang, Hongtao Duan, Juan Gu, and Jinliang Hou. 2020. "Lake Phenology of Freeze-Thaw Cycles Using Random Forest: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake" Remote Sensing 12, no. 24: 4098. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244098
APA StyleHan, W., Huang, C., Duan, H., Gu, J., & Hou, J. (2020). Lake Phenology of Freeze-Thaw Cycles Using Random Forest: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake. Remote Sensing, 12(24), 4098. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12244098