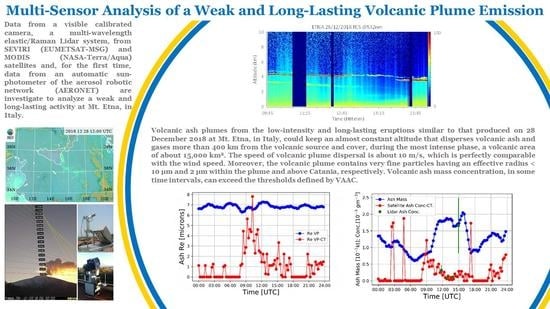
Multi-Sensor Analysis of a Weak and Long-Lasting Volcanic Plume Emission
Abstract
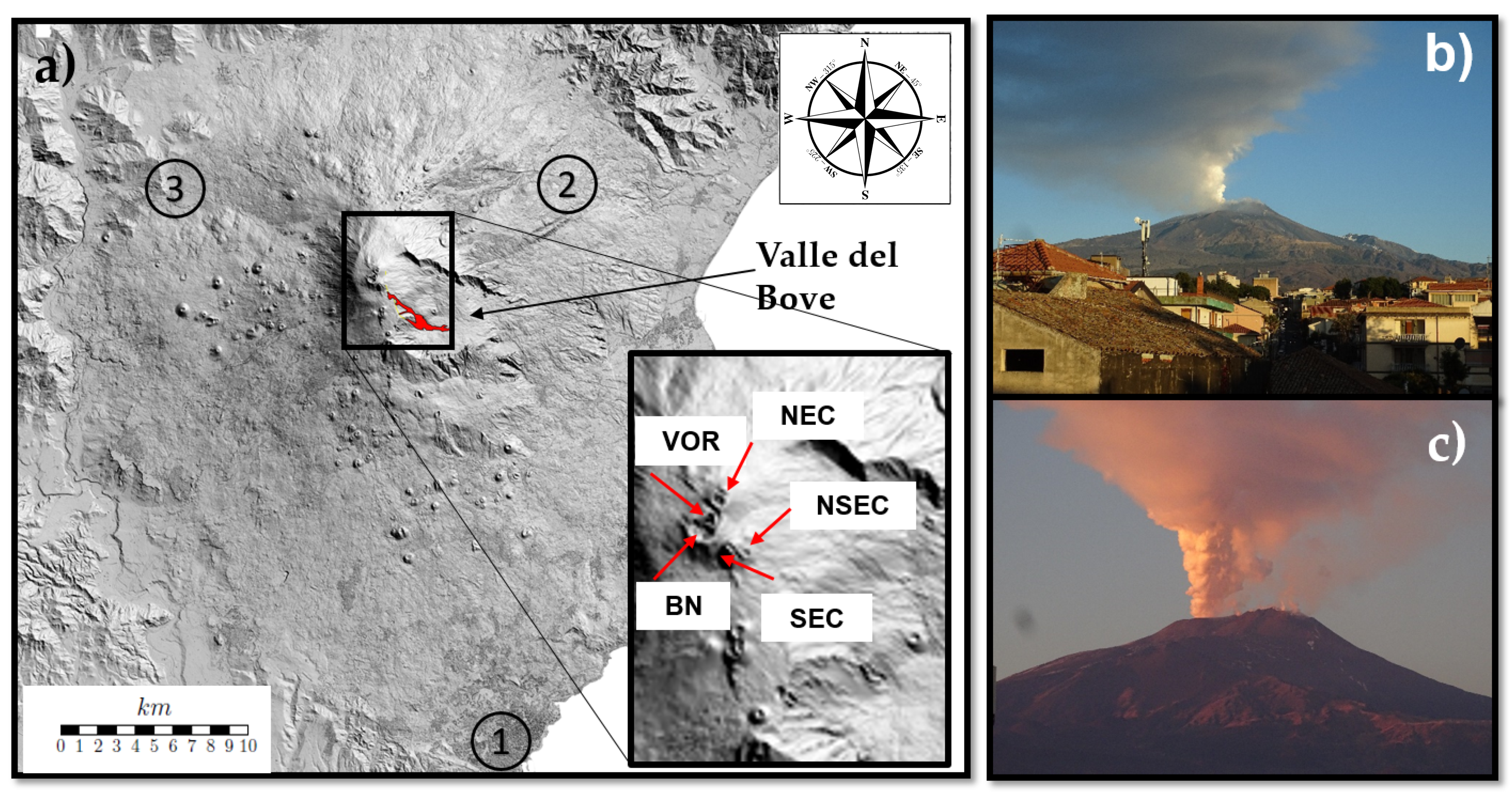
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
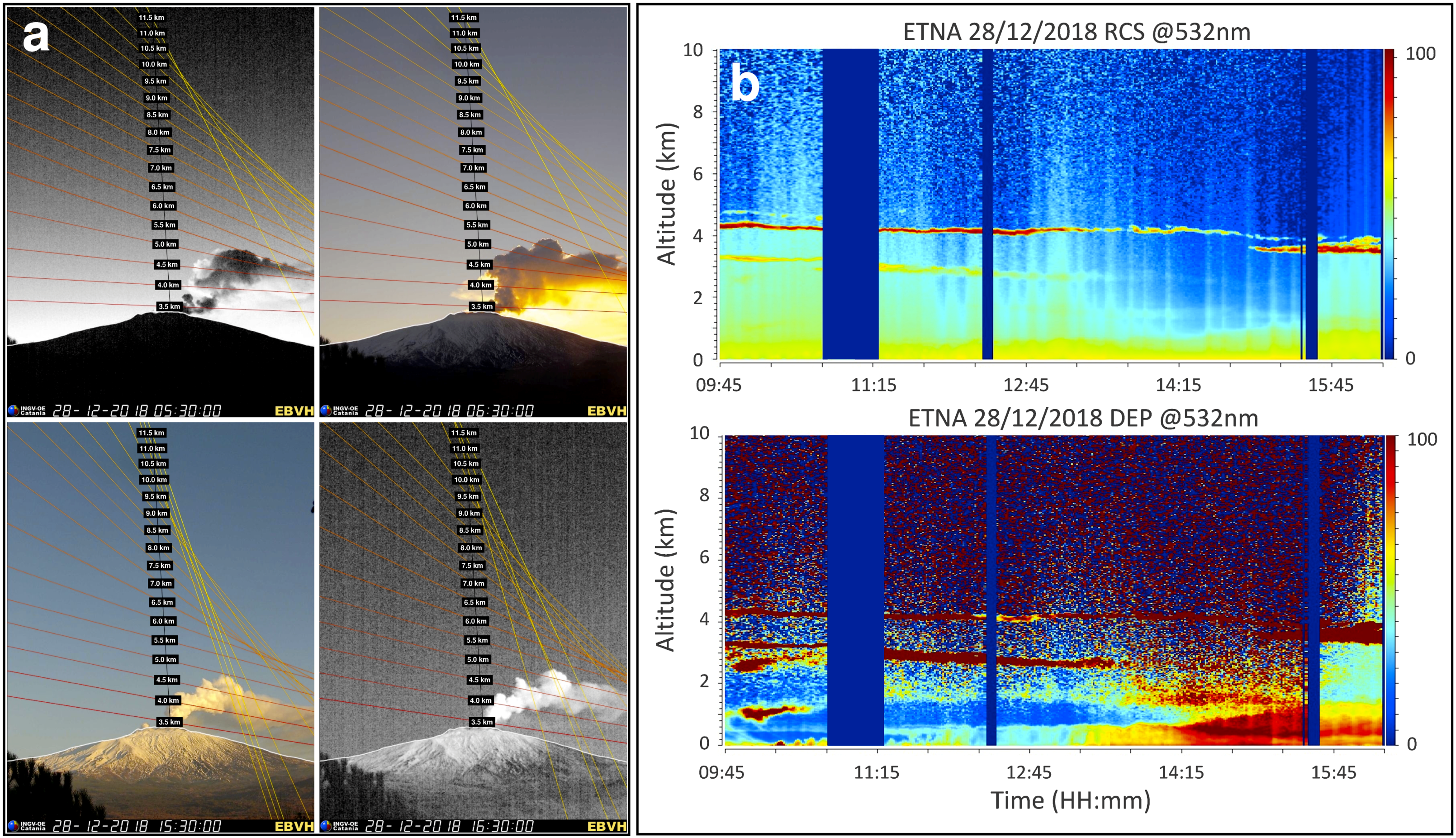
2.1. Visible Calibrated Images
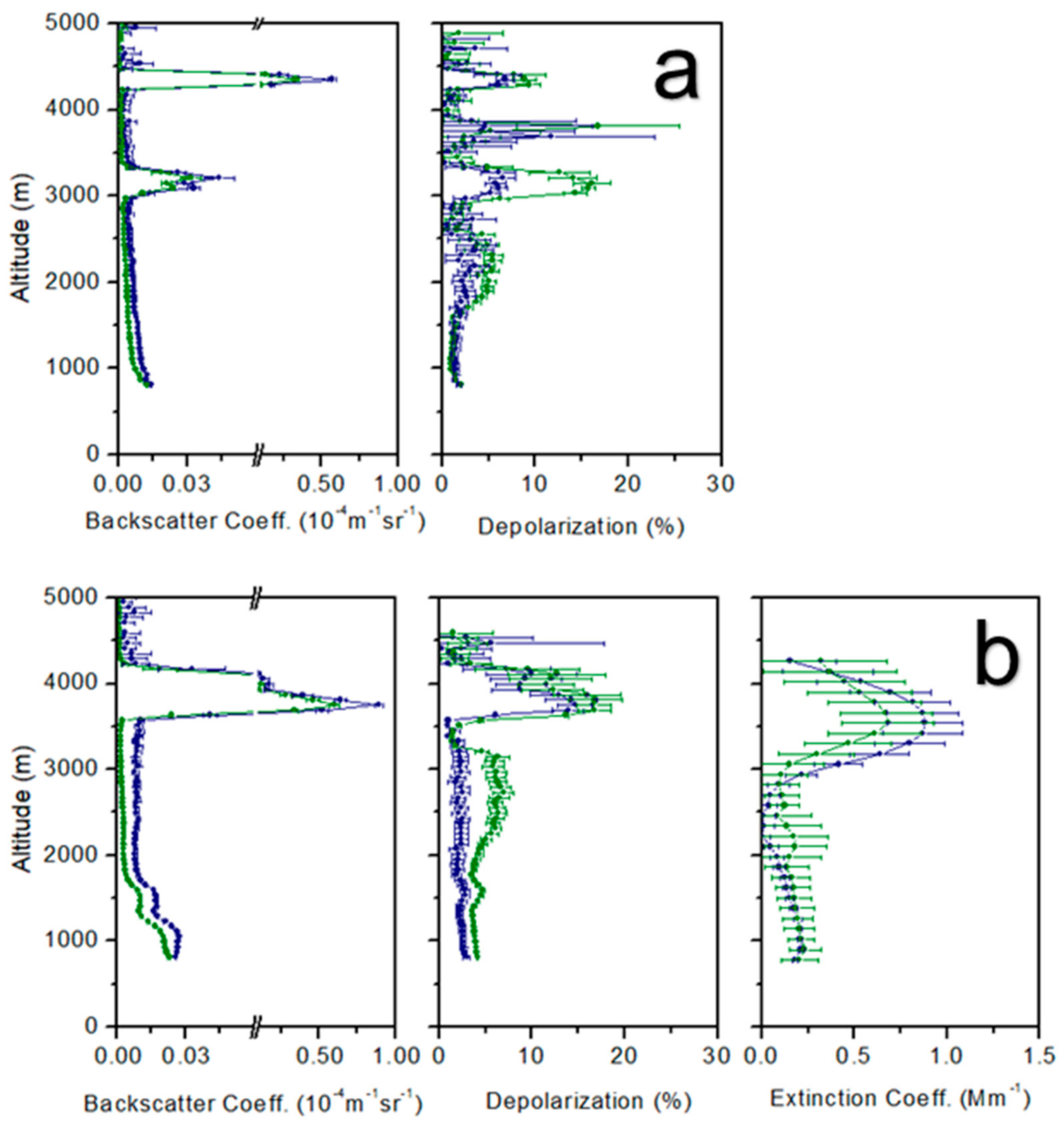
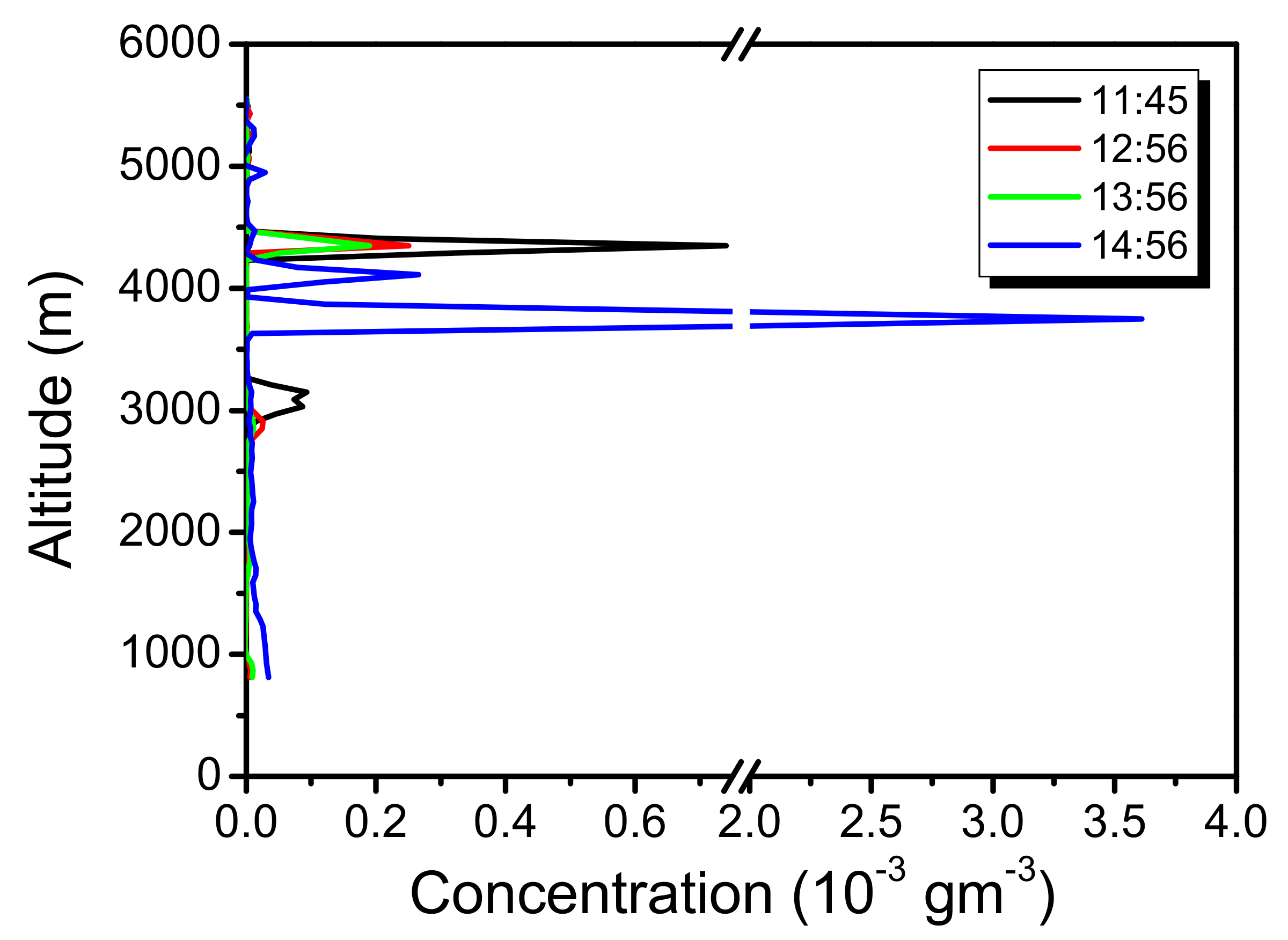
2.2. Lidar Measurements
2.3. Satellite Measurements
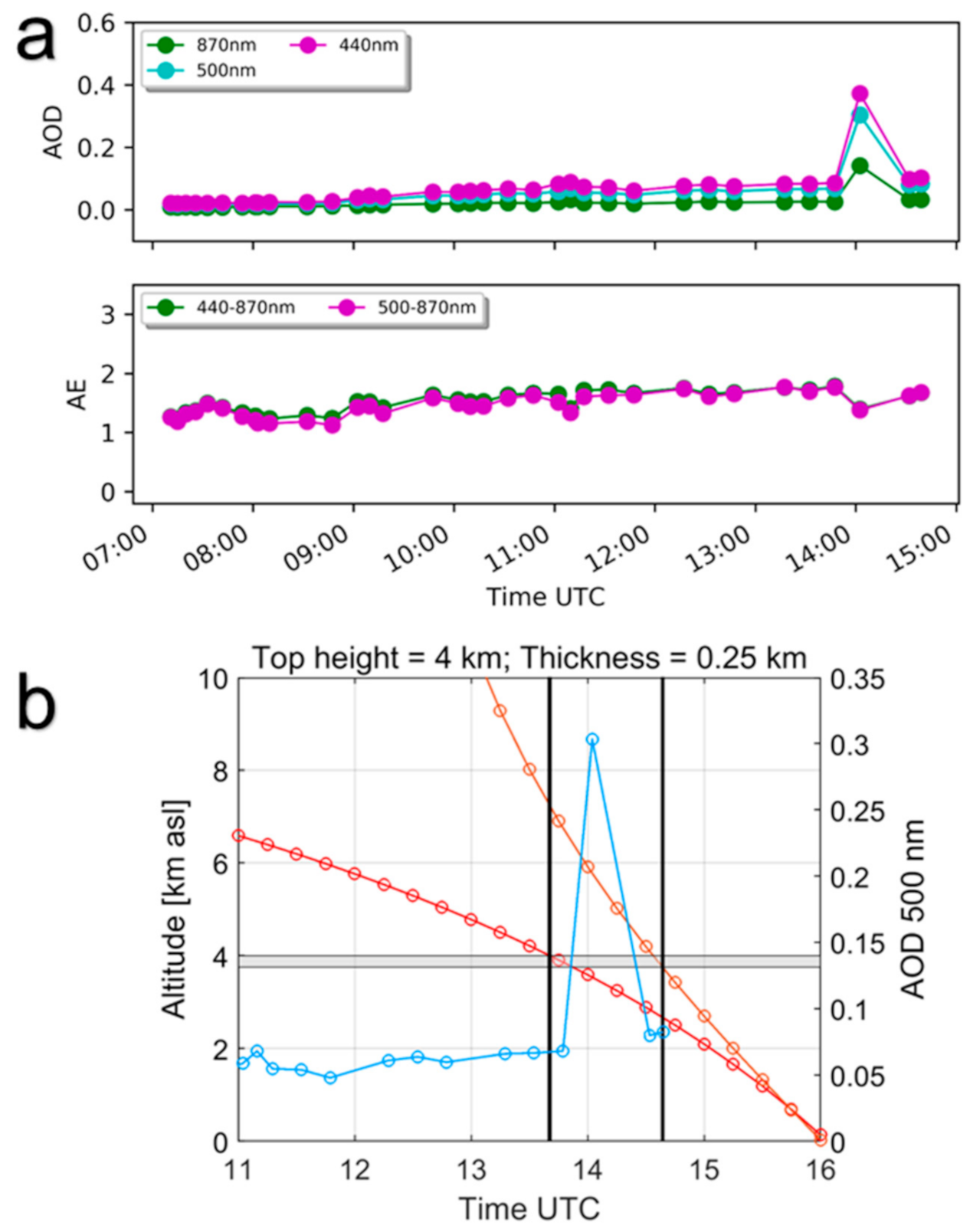
2.4. Photometer Data
3. Results and Discussion
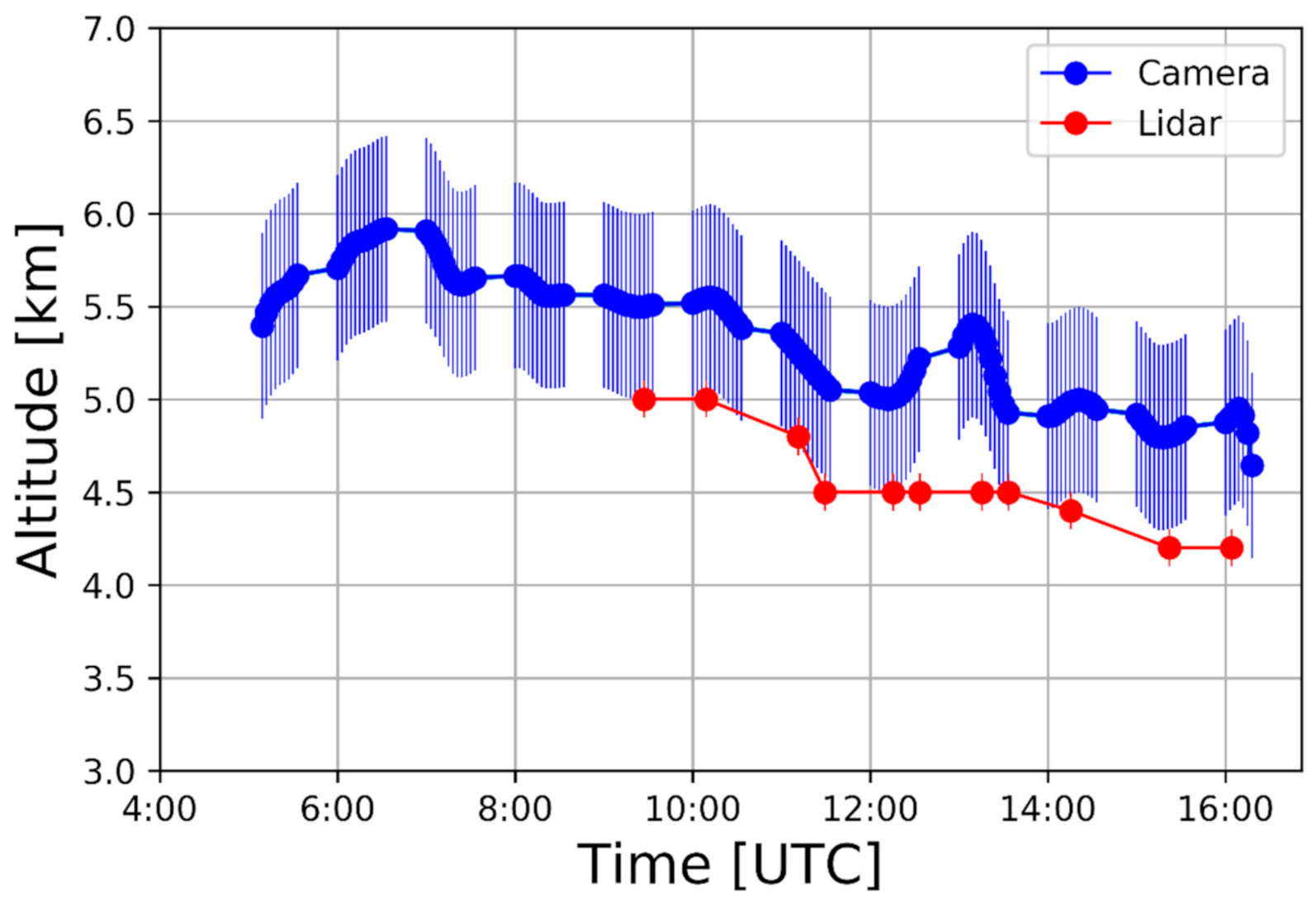
3.1. Volcanic Plume Height
3.2. Volcanic Plume Thickness
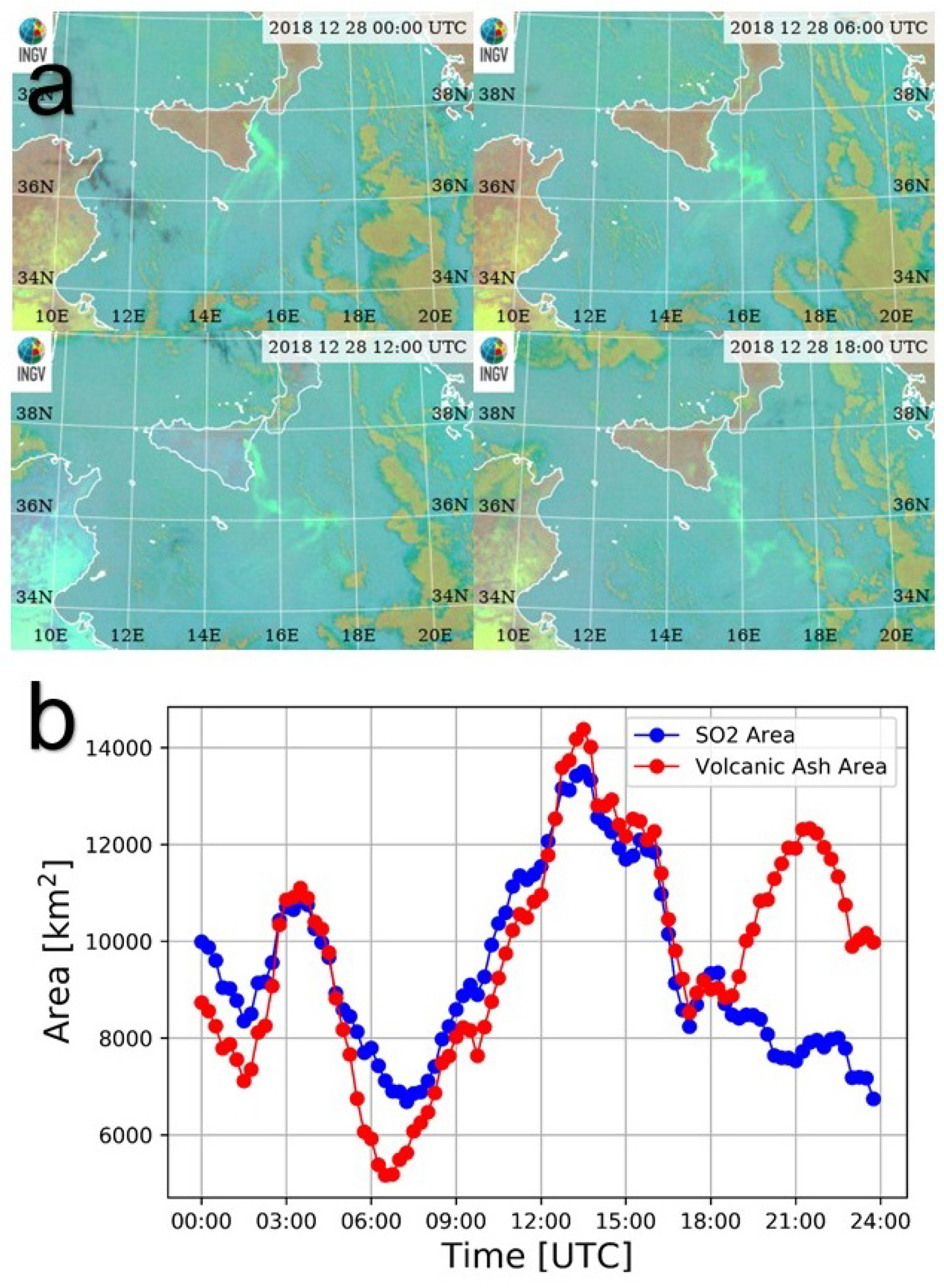
3.3. Volcanic Plume Dispersal
3.4. Volcanic Aerosol Properties
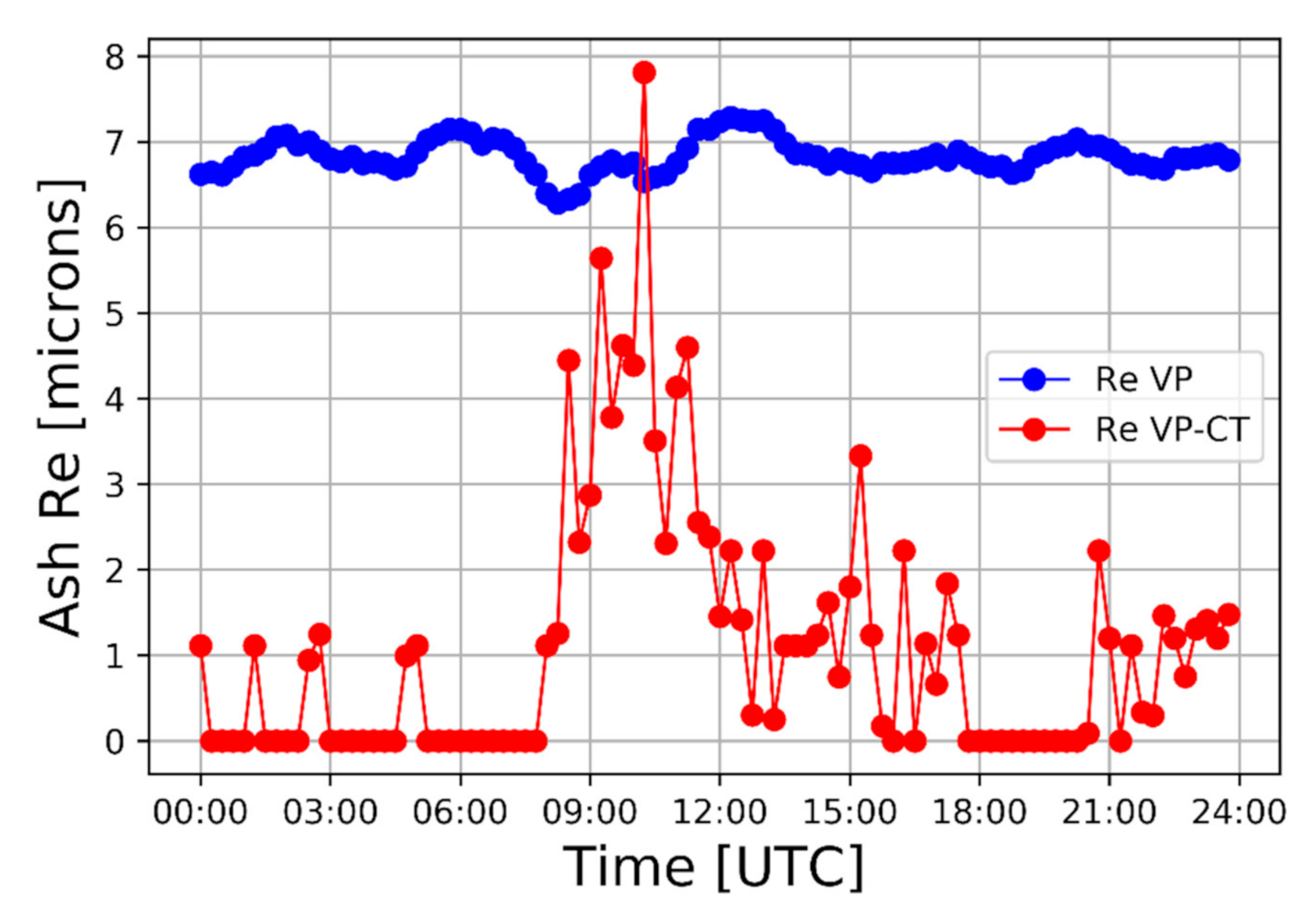
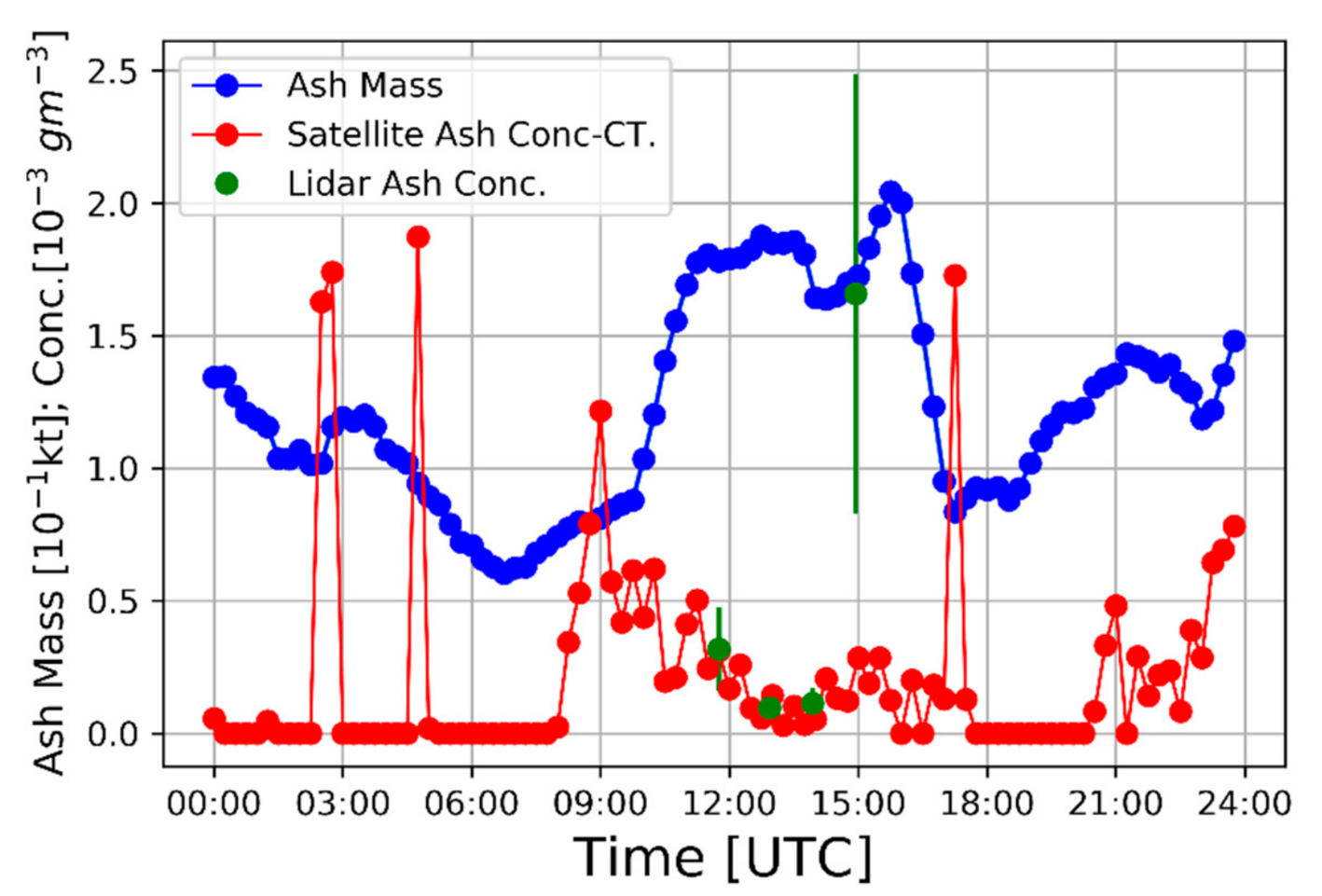
3.5. Volcanic Ash Mass Concentration and Total Mass
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Branca, S.; Carlo, P. Types of eruptions of Etna volcano AD 1670–2003: Implications for short-term eruptive behaviour. Bull. Volcanol. 2005, 67, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarini, F.; Giammanco, S.; Behncke, B.; Acocella, V.; Neri, M.; Rust, D. Structural analysis of the eruptive fissures at Mount Etna (Italy). Ann. Geophys. 2011, 54, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavo’, F.; Sciotto, M.; Cannata, A.; Di Grazia, G. An integrated geophysical approach to track magma intrusion: The 2018 Christmas Eve eruption at Mount Etna. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 8009–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonforte, A.; Guglielmino, F.; Puglisi, G. Large dyke intrusion and small eruption: The December 24, 2018 Mt. Etna eruption imaged by Sentinel-1 data. Terra Nova 2019, 31, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvari, S.; Bilotta, G.; Bonaccorso, A.; Caltabiano, T.; Cappello, A.; Corradino, C.; del Negro, C.; Ganci, G.; Neri, M.; Pecora, E.; et al. The VEI 2 Christmas 2018 Etna eruption: A small but intense eruptive event or the starting phase of a larger one? Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiolo, M.; Ripepe, M.; Cigolini, C.; Coppola, D.; della Schiava, M.; Genco, R.; Innocenti, L.; Lacanna, G.; Marchetti, E.; Massimetti, F.; et al. Space- and ground-based geophysical data tracking of magma migration in shallow feeding system of Mount Etna volcano. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercatanti, L.; Sabato, G. Volcanic risk and the role of the media. A case study in the Etna area. AIMS Geosci. 2019, 5, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastin, L.G.; Guffanti, M.; Servranckx, R.; Webley, P.; Barsotti, S.; Dean, K.; Durant, A.; Ewert, J.W.; Neri, A.; Rose, W.I.; et al. A multidisciplinary effort to assign realistic source parameters to models of volcanic ash-cloud transport and dispersion during eruptions (Book review). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2009, 186, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollo, S.; Boselli, A.; Coltelli, M.; Leto, G.; Pisani, G.; Prestifilippo, M.; Spinelli, N.; Wang, X. Volcanic ash concentration during the 12 August 2011 Etna eruption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, H.N.; Devenish, B.J.; Mastin, L.G.; Thomson, D.J.; van Eaton, A.R. Operational modelling of umbrella cloud growth in a lagrangian volcanic ash transport and dispersion model. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eaton, A.R.; Mastin, L.G.; Herzog, M.; Schwaiger, H.F.; Schneider, D.J.; Wallace, K.L.; Clarke, A.B. Hail formation triggers rapid ash aggregation in volcanic plumes. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellitto, P.; Zanetel, C.; Di Sarra, A.; Salerno, G.; Tapparo, A.; Meloni, D.; Pace, G.; Caltabiano, T.; Briole, P.; Legras, B. The impact of Mount Etna sulfur emissions on the atmospheric composition and aerosol properties in the central Mediterranean: A statistical analysis over the period 2000–2013 based on observations and Lagrangian modelling. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, D.; Solomon, S.; Barnes, J.; Burlakov, V.; Deshler, T.; Dolgii, S.; Herber, A.; Nagai, T.; Neely, R.; Nevzorov, A.; et al. Total volcanic stratospheric aerosol optical depths and implications for global climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 7763–7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, A.; Goloub, P.; Podvin, T.; Deroo, C.; Chaikovsky, A.; Ajtai, N.; Blarel, L.; Tanre, D.; Derimian, Y. Detection and characterization of volcanic ash plumes over Lille during the Eyjafjallajökull eruption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3705–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.J.; Pioli, L.; Harris, A.J.L.; Gurioli, L.; Thivet, S. Magma fragmentation and particle size distributions in low intensity mafic explosions: The July/August 2015 Piton de la Fournaise eruption. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronico, D.; del Carlo, P. PM10 measurements in urban settlements after lava fountain episodes at Mt. Etna, Italy: Pilot test to assess volcanic ash hazard to human health. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurioli, L.; Harris, A.J.L.; Houghton, B.F.; Polacci, M.; Ripepe, M. Textural and geophysical characterization of explosive basaltic activity at Villarrica volcano. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2008, 113, B08206–n/a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnadieu, F.; Freville, P.; Hervier, C.; Coltelli, M.; Scollo, S.; Prestifilippo, M.; Valade, S.; Rivet, S.; Cacault, P. Near-source Doppler radar monitoring of tephra plumes at Etna. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 312, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollo, S.; Boselli, A.; Coltelli, M.; Leto, G.; Pisani, G.; Spinelli, N.; Wang, X. Monitoring Etna volcanic plumes using a scanning LiDAR. Bull. Volcanol. 2012, 74, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollo, S.; Prestifilippo, M.; Pecora, E.; Corradini, S.; Merucci, L.; Spata, G.; Coltelli, M. Eruption column height estimation of the 2011–2013 Etna lava fountains. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, S.; Montopoli, M.; Guerrieri, L.; Ricci, M.; Scollo, S.; Merucci, L.; Marzano, F.; Pugnaghi, S.; Prestifilippo, M.; Ventress, L.; et al. A multi-sensor approach for volcanic ash cloud retrieval and eruption characterization: The 23 November 2013 Etna lava fountain. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, S.; Guerrieri, L.; Lombardo, V.; Merucci, L.; Musacchio, M.; Prestifilippo, M.; Scollo, S.; Silvestri, M.; Spata, G.; Stelitano, D. Proximal monitoring of the 2011–2015 Etna lava fountains using MSG-SEVIRI data. Geosciences 2018, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollo, S.; Prestifilippo, M.; Bonadonna, C.; Cioni, R.; Corradini, S.; Degruyter, W.; Rossi, E.; Silvestri, M.; Biale, E.; Carparelli, G.; et al. Near-real-time tephra fallout assessment at Mt. Etna, Italy. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, S.; Guerrieri, L.; Stelitano, D.; Salerno, G.; Scollo, S.; Merucci, L.; Prestifilippo, M.; Musacchio, M.; Silvestri, M.; Lombardo, V.; et al. Near real-time monitoring of the Christmas 2018 Etna eruption using SEVIRI and products validation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boselli, A.; Scollo, S.; Leto, G.; Sanchez, R.Z.; Sannino, A.; Wang, X.; Coltelli, M.; Spinelli, N. First volcanic plume measurements by an elastic/raman lidar close to the Etna summit craters. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Riebesell, M.; Wandinger, U.; Weitkamp, C.; Voss, E.; Lahmann, W.; Michaelis, W. Combined raman elastic-backscatter LIDAR for vertical profiling of moisture, aerosol extinction, backscatter, and LIDAR ratio. Appl. Phys. B 1992, 55, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Riebesell, M.; Weitkamp, C. Measurement of atmospheric aerosol extinction profiles with a Raman lidar. Opt. Lett. 1990, 15, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J.D. Stable analytical inversion solution for processing lidar returns. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: Some comments. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biele, J.; Beyerle, G.; Baumgarten, G. Polarization lidar: Correction of instrumental effects. Opt. Express 2000, 7, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freudenthaler, V.; Esselborn, M.; Wiegner, M.; Heese, B.; Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; MüLLER, D.; Althausen, D.; Wirth, M.; Fix, A.; et al. Depolarization ratio profiling at several wavelengths in pure Saharan dust during SAMUM 2006. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2017, 61, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Tesche, M.; Seifert, P.; Groß, S.; Freudenthaler, V.; Apituley, A.; Wilson, K.M.; Serikov, I.; Linné, H.; Heinold, B.; et al. Ash and fine-mode particle mass profiles from EARLINET-AERONET observations over central Europe after the eruptions of the Eyjafjallajökull volcano in 2010. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D00U02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, G.; Boselli, A.; Coltelli, M.; Leto, G.; Pica, G.; Scollo, S.; Spinelli, N.; Wang, X. Lidar depolarization measurement of fresh volcanic ash from Mt. Etna, Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereu, L.; Scollo, S.; Mori, S.; Boselli, A.; Leto, G.; Marzano, F.S. Maximum-likelihood retrieval of volcanic ash concentration and particle size from ground-based scanning lidar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5824–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrieri, L.; Merucci, L.; Corradini, S.; Pugnaghi, S. Evolution of the 2011 Mt. Etna ash and SO2 lava fountain episodes using SEVIRI data and VPR retrieval approach. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2015, 291, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugnaghi, S.; Guerrieri, L.; Corradini, S.; Merucci, L. Real time retrieval of volcanic cloud particles and SO2 by satellite using an improved simplified approach. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 3053–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugnaghi, S.; Guerrieri, L.; Corradini, S.; Merucci, L.; Arvani, B. A new simplified approach for simultaneous retrieval of SO2 and ash content of tropospheric volcanic clouds: An application to the Mt Etna volcano. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, S. Mt. Etna tropospheric ash retrieval and sensitivity analysis using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer measurements. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, S.; Pugnaghi, S.; Piscini, A.; Guerrieri, L.; Merucci, L.; Picchiani, M.; Chini, M. Volcanic Ash and SO2 retrievals using synthetic MODIS TIR data: Comparison between inversion procedures and sensitivity analysis. Ann. Geophys. 2015, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylling, A.; Kahnert, M.; Lindqvist, H.; Nousiainen, T. Volcanic ash infrared signature: Porous non-spherical ash particle shapes compared to homogeneous spherical ash particles. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Muñoz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, N.T.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Thulasiraman, S. Spectral discrimination of coarse and fine mode optical depth. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, D11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, N.T.; Dubovik, O.; Eck, T.F. Modified angström exponent for the characterization of submicrometer aerosols. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Draxler, R.; Rolph, G.; Stunder, B.; Cohen, M.; Ngan, F. NOAA’S HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, T.; Davis, C. Forecasting volcanic ash deposition using HYSPLIT. J. Appl. Volcanol. 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollo, S.; Prestifilippo, M.; Spata, G.; D’Agostino, M.; Coltelli, M. Monitoring and forecasting Etna volcanic plumes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.; Tupper, A. Aviation hazards from volcanoes: The state of the science. Nat. Hazards 2009, 51, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D. Volcanic ash in the atmosphere and risks for civil aviation: A study in European crisis management. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2013, 4, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, I.; Oppenheimer, C. Particle size distributions of Mount Etna’s aerosol plume constrained by Sun photometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 9823–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, I.M.; Oppenheimer, C. Photometric observations of Mt. Etna’s different aerosol plumes. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 3561–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselovskii, I.; Kolgotin, A.; Griaznov, V.; Müller, D.; Franke, K.; Whiteman, D.N. Inversion of multiwavelength Raman lidar data for retrieval of bimodal aerosol size distribution. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 1180–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, L.M.; Francis, P.N.; Watson, I.M.; Mackie, S. Inferring the size distribution of volcanic ash from IASI measurements and optimal estimation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2016, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.; Rose, W. Estimating particle sizes, concentrations, and total mass of ash in volcanic clouds using weather radar. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1983, 88, 10969–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioli, L.; Harris, A. Real-time geophysical monitoring of particle size distribution during volcanic explosions at Stromboli volcano (Italy). Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scollo, S.; Baratta, G.A.; Palumbo, M.E.; Corradini, S.; Leto, G.; Strazzulla, G. Linking the IR transmittance to size and type of volcanic ash particles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12207–12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonadonna, C.; Phillips, J.C.; Houghton, B.F. Modeling tephra sedimentation from a Ruapehu weak plume eruption. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2005, 110, B08209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scollo, S.; Boselli, A.; Corradini, S.; Leto, G.; Guerrieri, L.; Merucci, L.; Prestifilippo, M.; Sanchez, R.Z.; Sannino, A.; Stelitano, D. Multi-Sensor Analysis of a Weak and Long-Lasting Volcanic Plume Emission. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233866
Scollo S, Boselli A, Corradini S, Leto G, Guerrieri L, Merucci L, Prestifilippo M, Sanchez RZ, Sannino A, Stelitano D. Multi-Sensor Analysis of a Weak and Long-Lasting Volcanic Plume Emission. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(23):3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233866
Chicago/Turabian StyleScollo, Simona, Antonella Boselli, Stefano Corradini, Giuseppe Leto, Lorenzo Guerrieri, Luca Merucci, Michele Prestifilippo, Ricardo Zanmar Sanchez, Alessia Sannino, and Dario Stelitano. 2020. "Multi-Sensor Analysis of a Weak and Long-Lasting Volcanic Plume Emission" Remote Sensing 12, no. 23: 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233866
APA StyleScollo, S., Boselli, A., Corradini, S., Leto, G., Guerrieri, L., Merucci, L., Prestifilippo, M., Sanchez, R. Z., Sannino, A., & Stelitano, D. (2020). Multi-Sensor Analysis of a Weak and Long-Lasting Volcanic Plume Emission. Remote Sensing, 12(23), 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233866