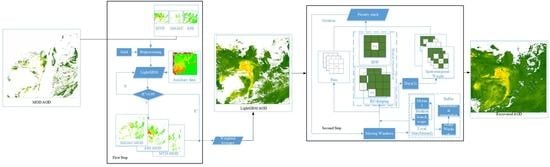
Handling Missing Data in Large-Scale MODIS AOD Products Using a Two-Step Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. AOD Products
2.2.2. AERONET Data
2.2.3. Auxiliary Data
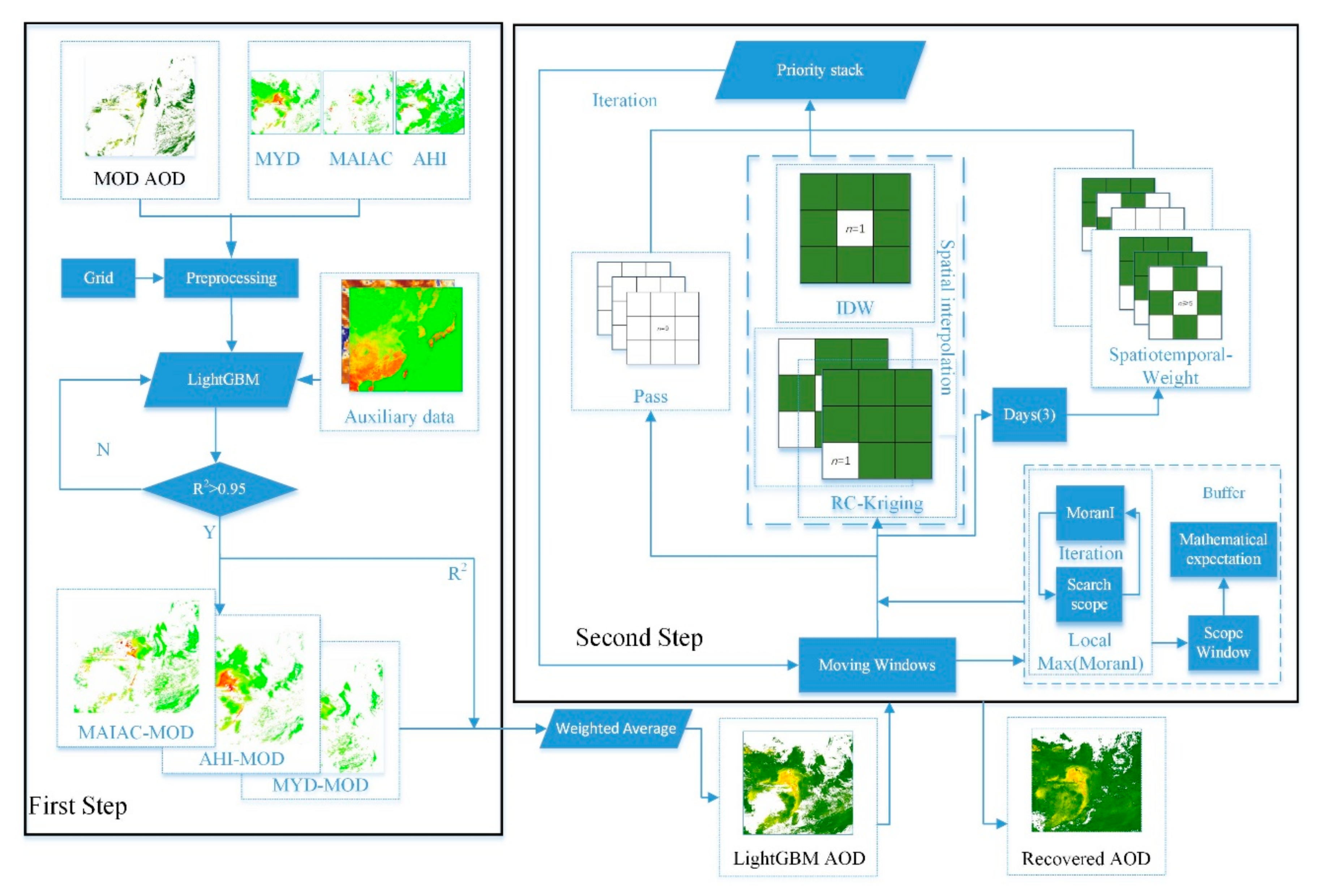
3. Methods
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. First Step of TWS
3.3. Second Step of TWS
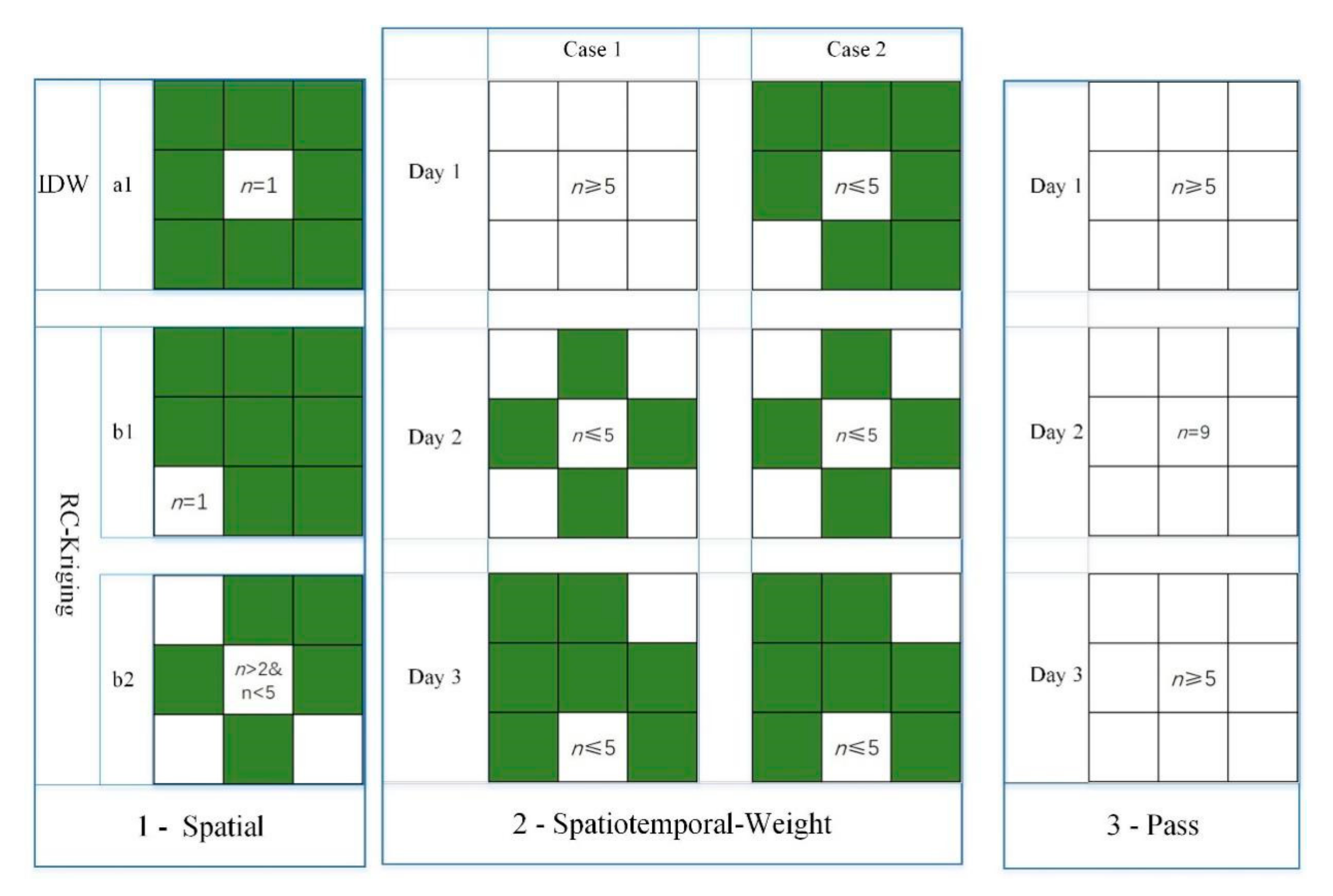
3.3.1. Design of Moving Window Size and Selection of Interpolation Mode
3.3.2. Buffer Factor
3.3.3. Spatial Interpolation Method (IDW and RC Kriging)
3.3.4. Spatiotemporal Weight Interpolation (STW)
3.3.5. Priority Setting of Overlapping Pixels
3.3.6. Validation Methodology
4. Results
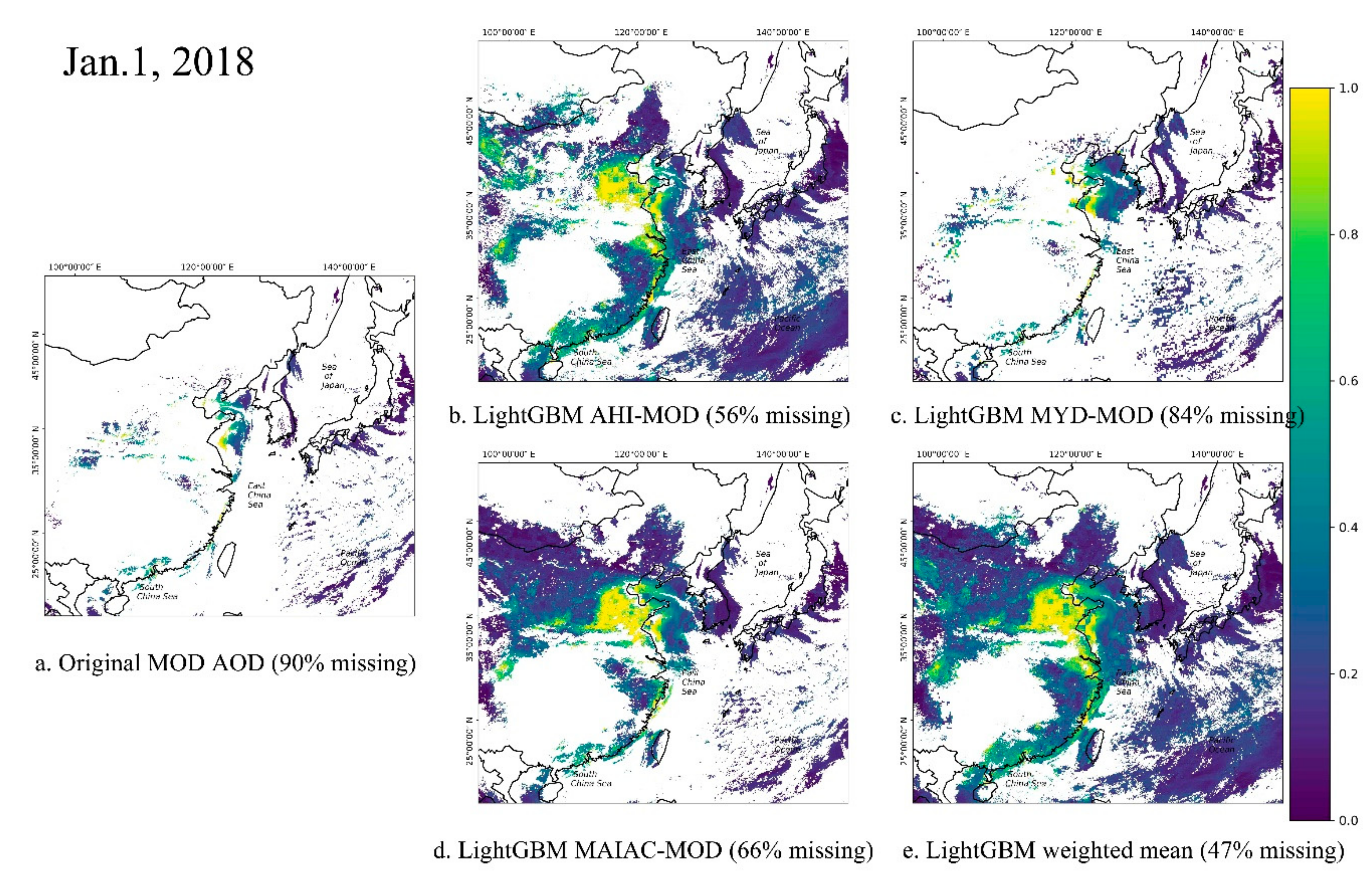
4.1. LightGBM Training and Processing Results
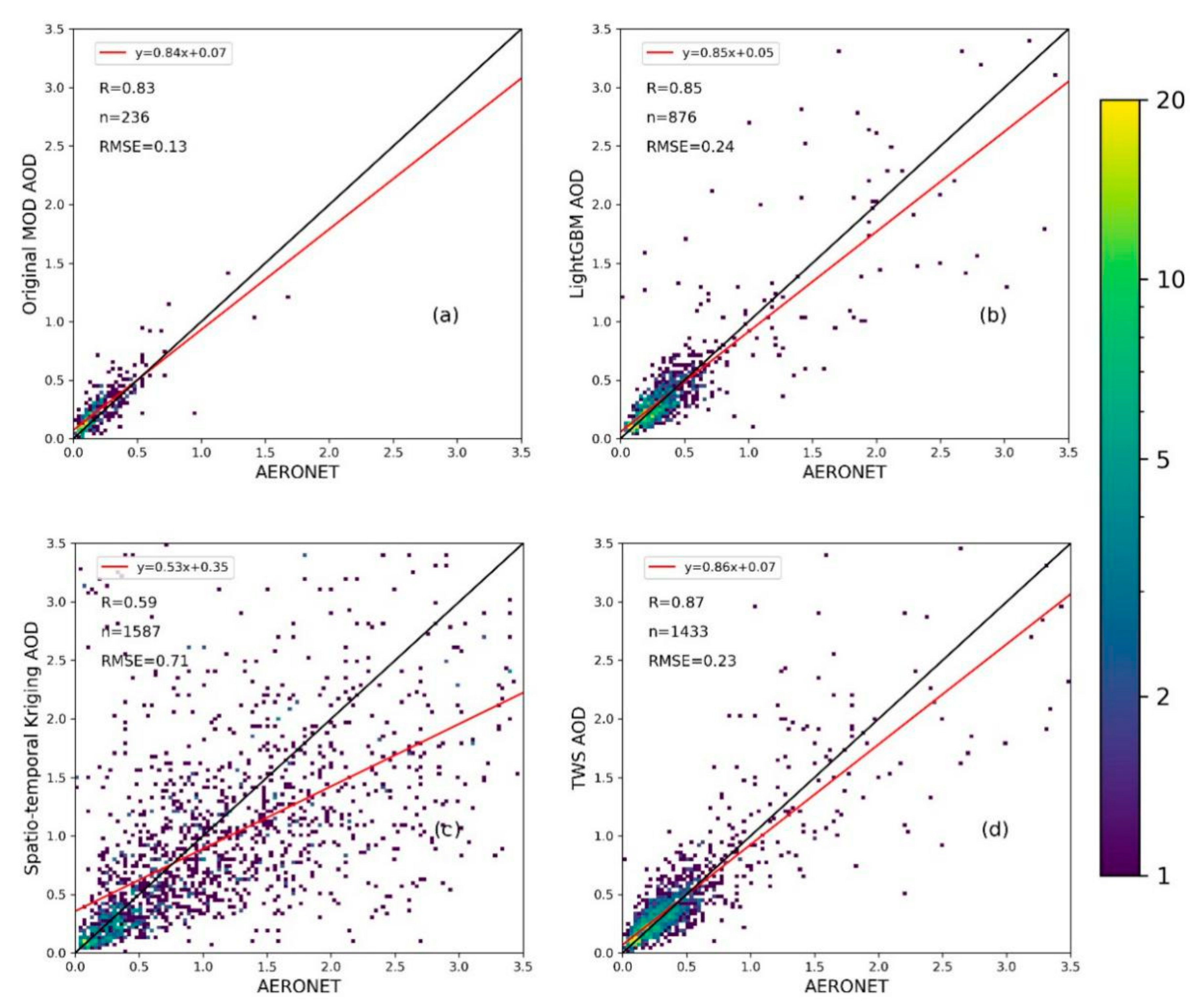
4.2. Comparison between MOD AOD Recovered by Different Methods and AERONET
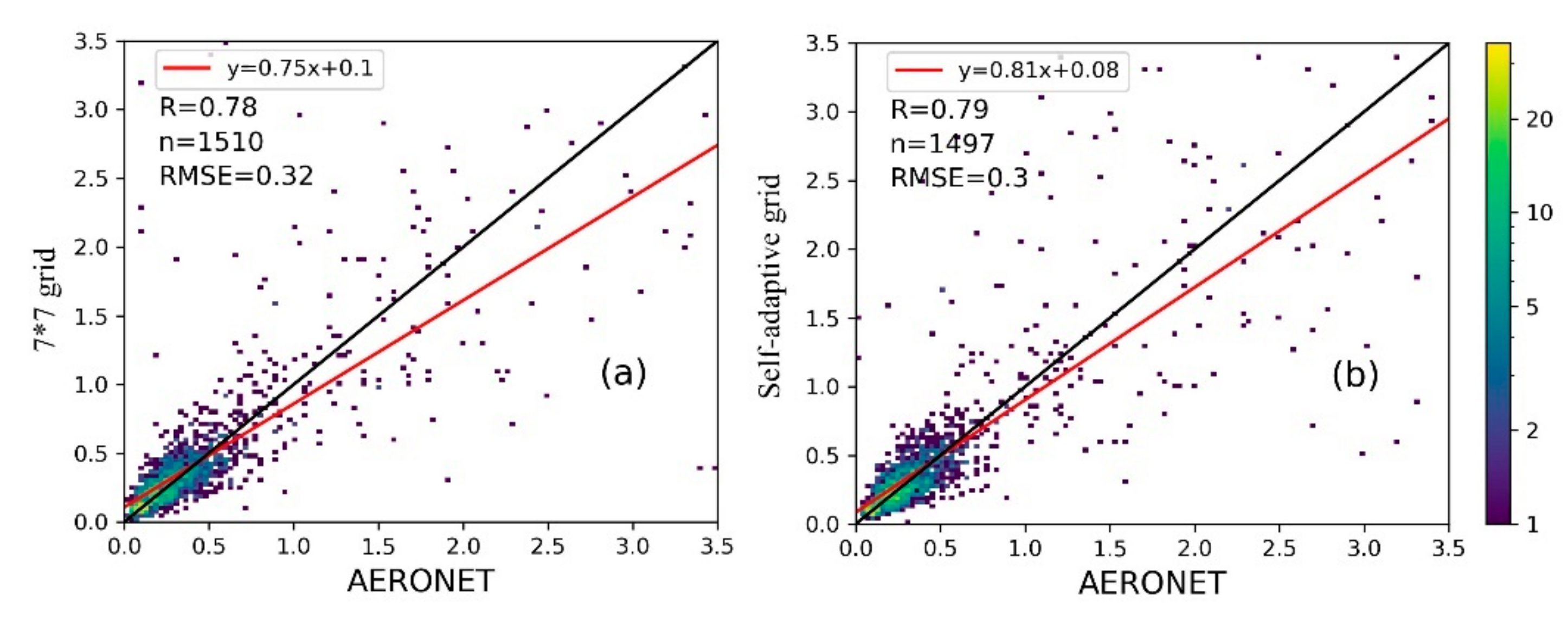
4.3. TWS Recovered the Performance with Different Moving Windows
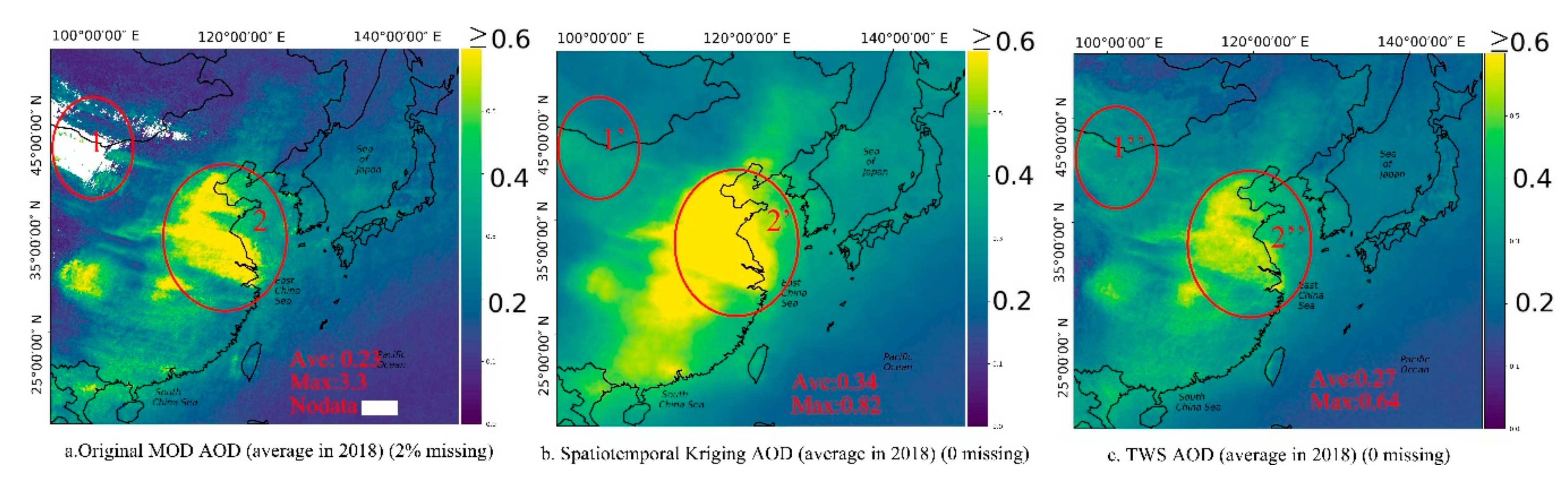
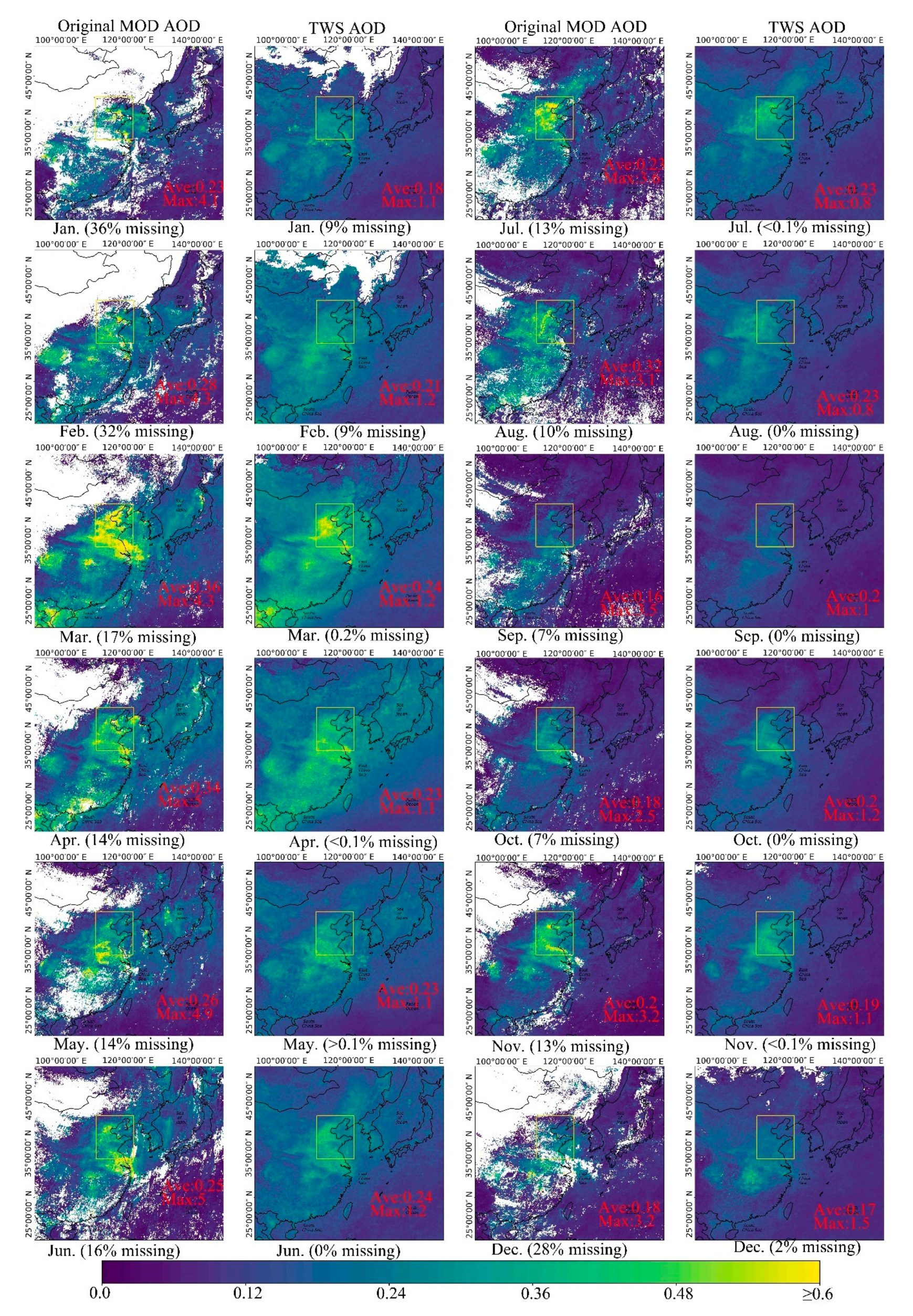
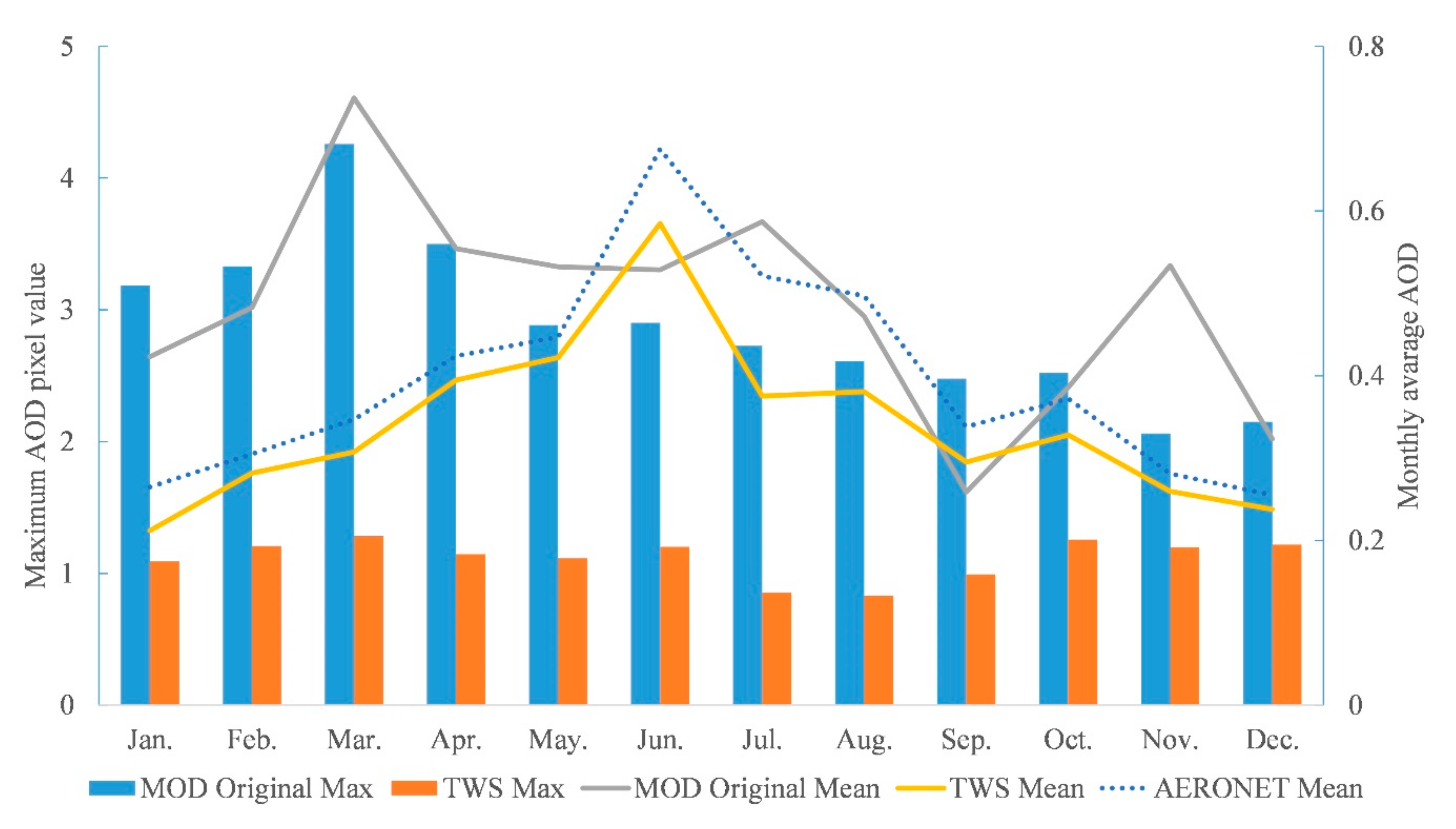
4.4. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Characteristics of MOD AOD Recovered by TWS
5. Discussion
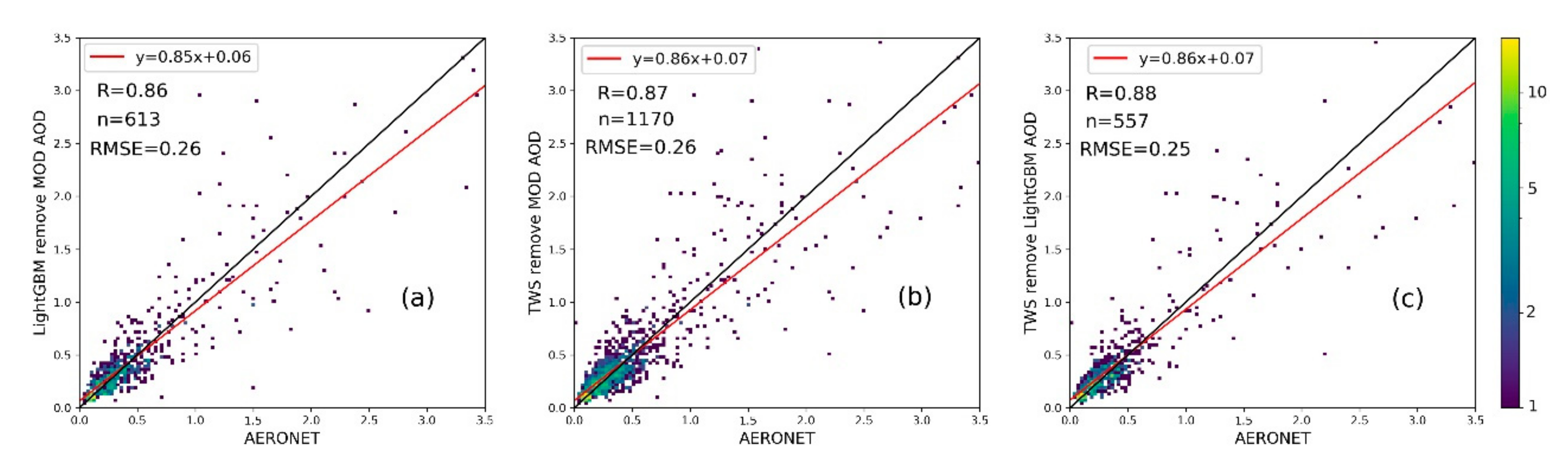
5.1. Comparison of TWS and Other MOD AOD Recovery Models
5.2. TWS Recovery MOD AOD Performance Discussion
5.3. TWS Recovery MOD AOD
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallquist, M.; Wenger, J.C.; Baltensperger, U.; Rudich, Y.; Simpson, D.; Claeys, M.; Dommen, J.; Donahue, N.M.; George, C.; Goldstein, A.H.; et al. The formation, properties and impact of secondary organic aerosol: Current and emerging issues. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5155–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N. Aerosol Indirect Effect on Biogeochemical Cycles and Climate. Science 2011, 334, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of Absorption and Optical Properties of Key Aerosol Types Observed in Worldwide Locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikary, B.; Kulkarni, S.; Dallura, A.; Tang, Y.; Chai, T.; Leung, L.R.; Qian, Y.; Chung, C.E.; Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G.R. A regional scale chemical transport modeling of Asian aerosols with data assimilation of AOD observations using optimal interpolation technique. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8600–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Hao, W.; Nordgren, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Wen, T.; et al. Aerosol optical depth (AOD) and Ångström exponent of aerosols observed by the Chinese Sun Hazemeter Network from August 2004 to September 2005. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ban, J.; Chen, N.X.; Li, T. High-resolution daily AOD estimated to full coverage using the random forest model approach in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.A.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.C.; Kleidman, R.G.; et al. The MODIS Aerosol Algorithm, Products, and Validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyer, E.J.; Reid, J.S.; Zhang, J. An over-land aerosol optical depth data set for data assimilation by filtering, correction, and aggregation of MODIS Collection 5 optical depth retrievals. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 379–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS Collection 6 MAIAC algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Laszlo, I.; Kahn, R.; Korkin, S.; Remer, L.; Levy, R.; Reid, J.S. Multiangle implementation of atmospheric correction (MAIAC): 2. Aerosol algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Peng, Y.; Sun, L.; Cribb, M. Estimating 1-km-resolution PM2.5 concentrations across China using the space-time random forest approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, M.; Murakami, H.; Suzuki, K.; Nagao, T.M.; Higurashi, A. Improved Hourly Estimates of Aerosol Optical Thickness Using Spatiotemporal Variability Derived From Himawari-8 Geostationary Satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3442–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Nagao, T.M.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Riedi, J.; Ishimoto, H.; Baran, A.J.; Shang, H.; Sekiguchi, M.; Kikuchi, M. Ice Cloud Properties From Himawari-8/AHI Next-Generation Geostationary Satellite: Capability of the AHI to Monitor the DC Cloud Generation Process. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3229–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Shen, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, M. Spatiotemporal prediction of continuous daily PM2.5 concentrations across China using a spatially explicit machine learning algorithm. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 155, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M.; Huang, W.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Improved 1 km resolution PM2.5 estimates across China using enhanced space–time extremely randomized trees. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghotbi, S.; Sotoudeheian, S.; Arhami, M. Estimating urban ground-level PM10 using MODIS 3km AOD product and meteorological parameters from WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Broday, D.M.; Misra, A.; Tripathi, S.N. Evaluation of MODIS Collection 6 aerosol retrieval algorithms over Indo-Gangetic Plain: Implications of aerosols types and mass loading. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Di, B.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Wang, Z.; Yao, G.; Zhan, Y. A nonparametric approach to filling gaps in satellite-retrieved aerosol optical depth for estimating ambient PM2.5 levels. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, B.; Hu, Y.; Chang, H.H.; Russell, A.G.; Bai, Y. Improving the Accuracy of Daily PM2.5 Distributions Derived from the Fusion of Ground-Level Measurements with Aerosol Optical Depth Observations, a Case Study in North China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4752–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; Zuo, S.; Ren, Y.; Chen, K. The Spatiotemporal Pattern of the Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) on the Canopies of Various Forest Types in the Exurban National Park: A Case in Ningbo City, Eastern China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Fu, D.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Xia, X. MODIS AOD sampling rate and its effect on PM2.5 estimation in North China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Hu, S.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, T. Spatiotemporal Variability and Influencing Factors of Aerosol Optical Depth over the Pan Yangtze River Delta during the 2014–2017 Period. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Qureshi, S.; Blaschke, T. Monitoring spatio-temporal aerosol patterns over Pakistan based on MODIS, TOMS and MISR satellite data and a HYSPLIT model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4641–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Levy, R.C.; da Silva, A.M.; Krzyzanowski, M.; Chubarova, N.E.; Semutnikova, E.; Cohen, A.J. Satellite-based estimates of ground-level fine particulate matter during extreme events: A case study of the Moscow fires in 2010. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6225–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Goward, S.N.; Masek, J.G.; Thomas, N.; Zhu, Z.; Vogelmann, J.E. An automated approach for reconstructing recent forest disturbance history using dense Landsat time series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wang, X.; Shao, M.; Chen, W.; Chang, M. Aerosol optical depth assimilation for a modal aerosol model: Implementation and application in AOD forecasts over East Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zeng, C.; Gong, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, K.; Shen, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, Z. Improving Spatial Coverage for Aqua MODIS AOD using NDVI-Based Multi-Temporal Regression Analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, L. Large-scale MODIS AOD products recovery: Spatial-temporal hybrid fusion considering aerosol variation mitigation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2019, 157, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Venkatachalam, P.; Gautam, R. Geostatistical Methods for Filling Gaps in Level-3 Monthly-Mean Aerosol Optical Depth Data from Multi-Angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1963–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, M. Filling the missing data gaps of daily MODIS AOD using spatiotemporal interpolation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Bo, Y.; Zhu, Y. Spatiotemporal fusion of multiple-satellite aerosol optical depth (AOD) products using Bayesian maximum entropy method. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4034–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, R.J.; Park, J.-S.; Park, S.S. Changes in column aerosol optical depth and ground-level particulate matter concentration over East Asia. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Choi, M.; Li, S.; Kondragunta, S.; Kim, J.; Holben, B.; Levy, R.C.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of VIIRS, GOCI, and MODIS Collection 6 AOD retrievals against ground sunphotometer observations over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Si-Chee, T.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. 2004, 42, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Min, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, F.; Yang, C.; Sun, Z. Assimilating Himawari-8 AHI aerosol observations with a rapid-update data assimilation system. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 215, 116866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.H.; Su, H.; Zhai, C.; Wu, L.; Minschwaner, K.; Molod, A.M.; Tompkins, A.M. An assessment of upper troposphere and lower stratosphere water vapor in MERRA, MERRA2, and ECMWF reanalyses using Aura MLS observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, K.W.; Bhaduri, B.L.; Bright, E.A.; Cheriyadat, A.; Karnowski, T.P.; Palathingal, P.J.; Potok, T.E.; Price, J.R. Automated Feature Generation in Large-Scale Geospatial Libraries for Content-Based Indexing. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Rasmussen, K.; Nielsen, T.T.; Mbow, C. Evaluation of earth observation based long term vegetation trends—Intercomparing NDVI time series trend analysis consistency of Sahel from AVHRR GIMMS, Terra MODIS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1886–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Su, T.; Feng, L.; Cai, Z.; Wu, H. Evaluation and uncertainty estimate of next-generation geostationary meteorological Himawari-8/AHI aerosol products. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; Tegen, I. Climate Response to Soil Dust Aerosols. J. Climate 1998, 11, 3247–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mucs, D.; Norinder, U.; Svensson, F. LightGBM: An Effective and Scalable Algorithm for Prediction of Chemical Toxicity–Application to the Tox21 and Mutagenicity Data Sets. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2019, 59, 4150–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 3149–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.Y.; Wong, D.W. An adaptive inverse-distance weighting spatial interpolation technique. Comput. Geosci. UK 2008, 34, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requia, W.J.; Dalumpines, R.; Adams, M.D.; Arain, A.; Ferguson, M.; Koutrakis, P. Modeling spatial patterns of link-based PM2.5 emissions and subsequent human exposure in a large canadian metropolitan area. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 158, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, R.; Delicado, P.; Mateu, J. Ordinary kriging for function-valued spatial data. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2011, 18, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.W.; Zhu, P.; Liew, K.M. Thermal buckling of functionally graded plates using a local Kriging meshless method. Compos. Struct. 2014, 108, 472–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addesso, P.; Longo, M.; Montone, R.; Restaino, R.; Vivone, G. Interpolation and combination rules for the temporal and spatial enhancement of SEVIRI and MODIS thermal image sequences. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2017, 38, 1889–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Xia, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Synergy of AERONET and MODIS AOD products in the estimation of PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing. Sci. Rep. UK 2018, 8, 10174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Fu, D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xia, X.; He, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, R.; Che, H. Diurnal and seasonal variability of PM2.5 and AOD in North China plain: Comparison of MERRA-2 products and ground measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.T.; Trinh, T.T.; Le, T.T.; Nguyen, T.D.H.; Tu, B.M. Temperature inversion and air pollution relationship, and its effects on human health in Hanoi City, Vietnam. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Yoon, S.-C.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.-Y. Seasonal and monthly variations of columnar aerosol optical properties over east Asia determined from multi-year MODIS, LIDAR, and AERONET Sun/sky radiometer measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y. Tracking the PM2.5 inventories embodied in the trade among China, Japan and Korea. J. Econ. Issues 2017, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| R | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| MOD AOD spatial correlation | R = 0.92 (n = 13,489,645) | ||
| MOD AOD time correlation | R = 0.57 (n = 15,895,438) | ||
| Time correlation of multisource AOD data (compared with MOD AOD) | MYD | MAIAC | AHI |
| R = 0.56 (n = 7,746,528) | R = 0.77 (n = 10,125,868) | R = 0.56 (n = 15,256,795) | |
| Group | Auxiliary Independent Variables | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOD AOD-MYD AOD | TLML, SPEED, ZM, QSH, PBLH, NDVI, POP, RLG, DOY, Slope, Aspect and Elevation | 2,112,108 | 0.964 |
| MOD AOD-MAIAC AOD | 4,226,536 | 0.975 | |
| MOD AOD-AHI AOD | 5,784,070 | 0.956 |
| Windows | R (Total) | Incompleteness (%) | Time Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 × 3 grid | 0.85 | 10 | 100 |
| 7 × 7 grid | 0.78 | 6 | 225 |
| Self-adaption grid | 0.79 | 8 | 423 |
| Method | Original Missing Rate (%) | Improved Missing Rate (%) | Decreased Missing Rate Difference (%) | Original R | Improved R | Improved Difference (R) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST-AVM | 80 | 60 | 20 | 0.89 | 0.87 | −0.02 | [34] |
| NWRL | ~70 | ~60 | ~10 | 0.77 | 0.78 | +0.01 | [33] |
| * | 89 | 75 | 14 | 0.93 | 0.91 | −0.02 | [28] |
| TWS (3 × 3) | 88 | 10 | 78 | 0.83 | 0.87 | +0.04 | Our paper |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liao, K.; Ren, Y. Handling Missing Data in Large-Scale MODIS AOD Products Using a Two-Step Model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223786
Chi Y, Wu Z, Liao K, Ren Y. Handling Missing Data in Large-Scale MODIS AOD Products Using a Two-Step Model. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(22):3786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223786
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Yufeng, Zhifeng Wu, Kuo Liao, and Yin Ren. 2020. "Handling Missing Data in Large-Scale MODIS AOD Products Using a Two-Step Model" Remote Sensing 12, no. 22: 3786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223786
APA StyleChi, Y., Wu, Z., Liao, K., & Ren, Y. (2020). Handling Missing Data in Large-Scale MODIS AOD Products Using a Two-Step Model. Remote Sensing, 12(22), 3786. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223786