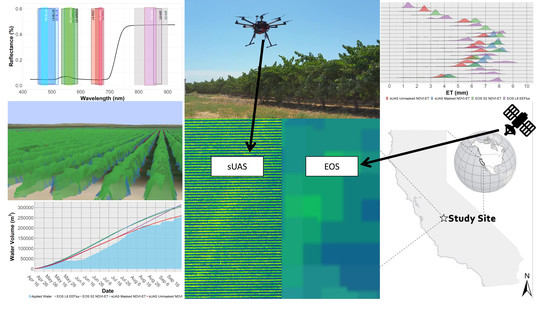
sUAS Remote Sensing of Vineyard Evapotranspiration Quantifies Spatiotemporal Uncertainty in Satellite-Borne ET Estimates
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Evapotranspiration in Water Management
1.2. Remote Sensing of Evapotranspiration
1.3. Research Questions
- Do EOS and sUAS ET estimates fundamentally differ over same period of time? In other words, over the course of the growing season, does either the mean or variance of sUAS and EOS ET estimates differ? While we expect that ET estimates to similarly track the growing season (e.g., peak ET demand in mid-summer), it remains unknown if the variance in ET estimates also track either the growing season or each other, sUAS compared to EOS. By using the fixed temporal domain of the growing season and coincident measurements, we can compare upscaled sUAS ET to EOS ET estimates to determine if temporal variance is uniformly distributed or varies across time.
- Do EOS and sUAS ET estimates fundamentally differ over the same study domain and same period of time? While we expect that the mean ET should be comparable from pixel to pixel, it remains unknown if the variance will differ in either within an EOS pixel or across the pixel domain. By using the fixed spatial domain of the vineyard block and by comparing upscaled sUAS ET to EOS ET estimates within and across pixels, we can retain the spatial variance of sUAS to determine if sUAS spatial variance is greater than EOS pixel to pixel variance.
- Do “mixed pixels” inherent in EOS data obscure important signals in ET estimation? Over the course of a growing season, biomass and leaf area index can change, altering reflectance and ultimately energy balance models. We evaluated the canopy fraction using high spatial resolution sUAS imagery and vineyard canopy structure to determine if unobscured plant reflectance values were better proxies for ET estimation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.2.1. Reference Evapotranspiration
2.2.2. Earth Engine Flux
2.2.3. OpenET
2.3. Data Products
2.3.1. Satellite Imagery
2.3.2. sUAS Imagery and Ancillary Data
3. Results
3.1. Irrigation Delivery and Canopy Growth
3.2. Remote Sensing of Evapotranspiration
Seasonal Evapotranspiration
4. Discussion
4.1. Viticultural Considerations
4.2. RSE Considerations
4.3. Land Use Considerations
4.4. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Sahagian, D. Anthropogenic disturbance of the terrestrial water cycle. Bioscience 2000, 50, 753–765. [Google Scholar]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R.B. Global water resources: Vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, P.J.F.; Famiglietti, J. Regional terrestrial water storage change and evapotranspiration from terrestrial and atmospheric water balance computations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisser, D.; Frolking, S.; Douglas, E.M.; Fekete, B.M.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Schumann, A.H. Global irrigation water demand: Variability and uncertainties arising from agricultural and climate data sets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni, J.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Suárez, L.; González-Dugo, V.; Fereres, E. Remote sensing of vegetation from UAV platforms using lightweight multispectral and thermal imaging sensors. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inform. Sci. 2009, 38, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kovacs, J.M. The application of small unmanned aerial systems for precision agriculture: A review. Precis. Agric. 2012, 13, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.; Torres-Rua, A.; Kustas, W.; Nieto, H.; McKee, M.; Hipps, L.; Stevens, D.; Alfieri, J.; Prueger, J.; Alsina, M.M.; et al. Influence of Model Grid Size on the Estimation of Surface Fluxes Using the Two Source Energy Balance Model and sUAS Imagery in Vineyards. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, B.G.; Messina, J.P.; Carroll, J.W.; Zhi, J.; Chimonyo, V.; Lin, S.; Snapp, S.S. Multi-Spatial Resolution Satellite and sUAS Imagery for Precision Agriculture on Smallholder Farms in Malawi. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2020, 86, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Water Use and Stress. Our World in Data. 2017. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/water-use-stress (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Underwood, E.C.; Viers, J.H.; Klausmeyer, K.R.; Cox, R.L.; Shaw, M.R. Threats and biodiversity in the mediterranean biome. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, T.E.; Viers, J.H. 100 years of California’s water rights system: Patterns, trends and uncertainty. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 084012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. 2017 Census of Agriculture, United States Summary and State Data; Volume 1, Geographic Area Series, Part 51, AC-17-A-51; Technical Report; National Agricultural Statistics Service (USDA): Washington, DC, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Publications/AgCensus/2017/Full_Report/Volume_1,_Chapter_1_US/ (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Sabo, J.L.; Sinha, T.; Bowling, L.C.; Schoups, G.H.; Wallender, W.W.; Campana, M.E.; Cherkauer, K.A.; Fuller, P.L.; Graf, W.L.; Hopmans, J.W.; et al. Reclaiming freshwater sustainability in the Cadillac Desert. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21263–21269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Chapagain, A.K.; Mathews, R.E.; Richter, B.D. Global Monthly Water Scarcity: Blue Water Footprints versus Blue Water Availability. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, D.L.; Tsiang, M.; Haugen, M.; Singh, D.; Charland, A.; Rajaratnam, B.; Diffenbaugh, N.S. The extraordinary California drought of 2013/2014: Character, context, and the role of climate change. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, S3–S7. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, D.L.; Langenbrunner, B.; Neelin, J.D.; Hall, A. Increasing precipitation volatility in twenty-first-century California. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nover, D.; Dogan, M.; Ragatz, R.; Booth, L.; Medellín-Azuara, J.; Lund, J.; Viers, J. Does More Storage Give California More Water? JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2019, 55, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín-Azuara, J.; Paw, U.K.T.; Jin, Y.; Jankowski, J.; Bell, A.; Kent, E.; Clay, J.; Wong, A.; Alexander, N.; Santos, N.; et al. A Comparative Study for Estimating Crop Evapotranspiration in the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta; Technical Report; Center for Watershed Sciences, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2018; Available online: https://watershed.ucdavis.edu/delta-et (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- Gleick, P.H. Roadmap for sustainable water resources in southwestern North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21300–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, A.B.; Araghinejad, S.; Nejadhashemi, A.P.; Tabrizi, M.S. Optimal water allocation in irrigation networks based on real time climatic data. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zaks, D.P.; Kucharik, C.J. Data and monitoring needs for a more ecological agriculture. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 014017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: Observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, Y.A.; Kar, S.K. Evapotranspiration estimation with remote sensing and various surface energy balance algorithms—A review. Energies 2014, 7, 2821–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Running, S.W. A review of remote sensing based actual evapotranspiration estimation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2016, 3, 834–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.; Holtslag, A. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Pelgrum, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Moreno, J.; Roerink, G.; Van der Wal, T. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL): Part 2: Validation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.; Noordman, E.; Pelgrum, H.; Davids, G.; Thoreson, B.; Allen, R. SEBAL model with remotely sensed data to improve water-resources management under actual field conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC)—Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, A.; Allen, R.G.; Kjaersgaard, J.; Huntington, J.; Kamble, B.; Trezza, R.; Ratcliffe, I. Operational Remote Sensing of ET and Challenges. In Evapotranspiration; Irmak, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Chapter 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, C.; Harding, J.; Erickson, T. OpenET: Filling the Biggest Gap in Water Management. Available online: https://github.com/Open-ET (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Mitchell, K.E.; Lohmann, D.; Houser, P.R.; Wood, E.F.; Schaake, J.C.; Robock, A.; Cosgrove, B.A.; Sheffield, J.; Duan, Q.; Luo, L.; et al. The multi-institution North American Land Data Assimilation System (NLDAS): Utilizing multiple GCIP products and partners in a continental distributed hydrological modeling system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Mitchell, K.; Ek, M.; Sheffield, J.; Cosgrove, B.; Wood, E.; Luo, L.; Alonge, C.; Wei, H.; Meng, J.; et al. Continental-scale water and energy flux analysis and validation for the North American Land Data Assimilation System project phase 2 (NLDAS-2): 1. Intercomparison and application of model products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T. Development of gridded surface meteorological data for ecological applications and modelling. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, B.; Smith, B.; Chen, Y. Survey of thermal infrared remote sensing for Unmanned Aerial Systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Orlando, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1294–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Niu, H.; Anderson, A.; Chen, Y.; Viers, J. A detailed study on accuracy of uncooled thermal cameras by exploring the data collection workflow. In Proceedings of the Autonomous Air and Ground Sensing Systems for Agricultural Optimization and Phenotyping III. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–17 April 2018; Volume 10664, p. 106640F. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Rua, A. Vicarious calibration of sUAS microbolometer temperature imagery for estimation of radiometric land surface temperature. Sensors 2017, 17, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J.W.; Ma, Q.; Rungee, J.; Bales, R.C. Evapotranspiration Mapping for Forest Management in California’s Sierra Nevada. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2020, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffler, D.; Frantz, D.; Segl, K. Spectral harmonization and red edge prediction of Landsat-8 to Sentinel-2 using land cover optimized multivariate regressors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, Q.J.; Brugnach, M.; Temesgen, B.; Rueda, C.; Ustin, S.L.; Frame, K. Daily reference evapotranspiration for California using satellite imagery and weather station measurement interpolation. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2009, 26, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigollier, C.; Lefèvre, M.; Cros, S.; Wald, L. Heliosat 2: An improved method for the mapping of the solar radiation from Meteosat imagery. In Proceedings of the EUMETSAT Meteorological Satellite Conference, Dublin, Ireland, 1–6 September 2002; EUMETSAT: Darmstadt, Germany, 2002; pp. 585–592. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, I.A.; Allen, R.G.; Elliott, R.; Jensen, M.E.; Itenfisu, D.; Mecham, B.; Howell, T.A.; Snyder, R.; Brown, P.; Echings, S.; et al. The ASCE Standardized Reference Evapotranspiration Equation; Rep. 0-7844-0805-X, ASCE Task Committee on Standardization of Reference Evapotranspiration; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Claverie, M.; Ju, J.; Masek, J.G.; Dungan, J.L.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.C.; Skakun, S.V.; Justice, C. The Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance data set. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Wan, P.; Wang, H.; Xie, D.; Wang, X.; Yan, G. An easy-to-use airborne LiDAR data filtering method based on cloth simulation. Remote. Sens. 2016, 8, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viers, J.H.; Williams, J.N.; Nicholas, K.A.; Barbosa, O.; Kotzé, I. Vinecology: Pairing wine with nature. Conserv. Lett. 2013, 6, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, C.; Darriet, P. The impact of climate change on viticulture and wine quality. J. Wine Econ. 2016, 11, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.V.; White, M.A.; Cooper, O.R.; Storchmann, K. Climate change and global wine quality. Clim. Chang. 2005, 73, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, K.A.; Durham, W.H. Farm-scale adaptation and vulnerability to environmental stresses: Insights from winegrowing in Northern California. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Vaz, M.; Escalona, J.; Egipto, R.; Lopes, C.; Medrano, H.; Chaves, M. Modern viticulture in southern Europe: Vulnerabilities and strategies for adaptation to water scarcity. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 164, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, I.; Green, S.; Singh, R.; Horne, D.; van der Zijpp, S.; Clothier, B. Water footprinting of agricultural products: A hydrological assessment for the water footprint of New Zealand’s wines. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Agam, N.; Ortega-Farias, S. Forward to the GRAPEX special issue. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Brown, I.; Metcalfe, A.; Jerram, C.; Collins, C. Sustainability assessment in wine-grape growing in the new world: Economic, environmental, and social indicators for agricultural businesses. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8178–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazar, A.; Krueger, R.; Corwin, D.; Pourreza, A.; Little, C.; Rios, S.; Snyder, R.L. Determination of Actual Evapotranspiration and Crop Coefficients of California Date Palms Using the Residual of Energy Balance Approach. Water 2020, 12, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, P.H.; Chávez, J.L.; Howell, T.A.; Marek, T.H.; New, L.L. Surface energy balance based evapotranspiration mapping in the Texas high plains. Sensors 2008, 8, 5186–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Tang, R.; Wan, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, B.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. A review of current methodologies for regional evapotranspiration estimation from remotely sensed data. Sensors 2009, 9, 3801–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín-Azuara, J.; MacEwan, D.; Howitt, R.E.; Koruakos, G.; Dogrul, E.C.; Brush, C.F.; Kadir, T.N.; Harter, T.; Melton, F.; Lund, J.R. Hydro-economic analysis of groundwater pumping for irrigated agriculture in California’s Central Valley, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, T.; Liptzin, D.; Dzurella, K.; Fryjoff-Hung, A.; Hollander, A.; Jensen, V.; King, A.; Kourakos, G.; McNally, A.; Stuart Pettygrove, G.; et al. Agriculture’s contribution to nitrate contamination of Californian groundwater (1945–2005). J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, K.M.; King, A.M.; Harter, T. Identifying sources of groundwater nitrate contamination in a large alluvial groundwater basin with highly diversified intensive agricultural production. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 151, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhao, S.; Kang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhou, M.; Lyu, J. Control and remediation methods for eutrophic lakes in the past 30 years. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín-Azuara, J.; Rosenstock, T.S.; Howitt, R.E.; Harter, T.; Jessoe, K.K.; Dzurella, K.; Pettygrove, S.; Lund, J.R. Agroeconomic analysis of nitrate crop source reductions. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayzelle, M.; Viers, J.; Medellín-Azuara, J.; Harter, T. Economic feasibility of irrigated agricultural land use buffers to reduce groundwater nitrate in rural drinking: Water sources. Water 2015, 7, 12–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welle, P.; Medellín-Azuara, J.; Viers, J.; Mauter, M. Economic and policy drivers of agricultural water desalination in California’s central valley. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, E.; Hutchinson, R.; Viers, J.; Kelsey, T.; Distler, T.; Marty, J. Quantifying trade-offs among ecosystem services, biodiversity, and agricultural returns in an agriculturally dominated landscape under future land-management scenarios. San Franc. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Zhou, M.; Deng, H.; Lyu, J.; Cao, W.; Takara, K.; Nover, D.; Geoffrey Schladow, S. Impact of forest maintenance on water shortages: Hydrologic modeling and effects of climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, P.J.; Lulla, V.; Jensen, R.R.; Jensen, J.R. Small Unmanned Aerial Systems (sUAS) for environmental remote sensing: Challenges and opportunities revisited. GIScience Remote. Sens. 2019, 56, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandé, J.; Stockert, C.; Liles, G.; Williams, J.; Smart, D.; Viers, J. From berries to blocks: Carbon stock quantification of a California vineyard. Carbon Balance Manag. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| 2018 Flight Dates | sUAS Platform | sUAS Sensor | EOS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 April | Finwing Sabre | Parrot Sequoia | N/A |
| 7 May | Finwing Sabre | Parrot Sequoia | Sentinel 2 |
| 6 June | DJI S1000 | Micasense RedEdge-M | Sentinel 2 |
| 21 June | DJI S1000 | Micasense RedEdge-M | Sentinel 2 |
| 5 July | DJI S1000 | Micasense RedEdge-M | Landsat 8 |
| 16 July | DJI S1000 | Micasense RedEdge-M | Sentinel 2 |
| 26 July | DJI S1000 | Micasense RedEdge-M | Sentinel 2 |
| 6 August | DJI S1000 | Micasense RedEdge-M | Landsat 8 |
| 20 August | DJI S1000 | Micasense RedEdge-M | Sentinel 2 |
| 19 September | DJI S1000 | Micasense RedEdge-M | Sentinel 2 |
| Date | Method | Mean | Median | Std Dev | Var | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 April | EOS L8 EEFlux | 1.448 | 1.375 | 0.340 | 0.116 | 0.930 | 3.265 |
| 20 April | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 2.450 | 2.524 | 0.418 | 0.175 | 0.102 | 3.688 |
| 22 April | EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 3.258 | 3.339 | 0.427 | 0.182 | 1.227 | 4.765 |
| 2 May | EOS L8 EEFlux | 3.889 | 4.016 | 0.467 | 0.218 | 2.376 | 4.559 |
| 7 May | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 5.154 | 5.421 | 0.972 | 0.944 | 0.485 | 6.400 |
| EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 5.908 | 6.197 | 0.925 | 0.855 | 1.635 | 6.963 | |
| 18 May | EOS L8 EEFlux | 6.017 | 6.194 | 0.582 | 0.338 | 4.030 | 6.654 |
| 27 May | EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 6.570 | 6.931 | 1.051 | 1.104 | 1.659 | 7.425 |
| 3 June | EOS L8 EEFlux | 7.581 | 7.805 | 0.719 | 0.516 | 4.946 | 8.398 |
| 6 June | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 6.465 | 6.807 | 1.14 | 1.299 | 0.568 | 7.496 |
| sUAS Masked NDVI-ET | 7.308 | 7.533 | 0.809 | 0.654 | 0.523 | 7.824 | |
| EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 7.567 | 7.966 | 1.070 | 1.145 | 2.58 | 8.465 | |
| 19 June | EOS L8 EEFlux | 5.373 | 5.521 | 0.549 | 0.301 | 2.856 | 6.035 |
| 21 June | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 6.192 | 6.493 | 1.062 | 1.127 | 1.171 | 7.803 |
| sUAS Masked NDVI-ET | 7.771 | 7.886 | 0.590 | 0.348 | 1.704 | 8.423 | |
| EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 7.430 | 7.790 | 1.106 | 1.223 | 1.666 | 9.743 | |
| 5 July | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 5.743 | 6.025 | 0.983 | 0.966 | 1.143 | 6.829 |
| sUAS Masked NDVI-ET | 7.343 | 7.444 | 0.554 | 0.307 | 0.842 | 7.884 | |
| EOS L8 EEFlux | 6.142 | 6.307 | 0.663 | 0.440 | 3.669 | 6.959 | |
| 16 July | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 6.291 | 6.608 | 1.105 | 1.220 | 1.134 | 7.801 |
| sUAS Masked NDVI-ET | 8.038 | 8.127 | 0.505 | 0.255 | 1.022 | 8.788 | |
| EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 7.47 | 7.822 | 1.07 | 1.144 | 2.29 | 8.695 | |
| 21 July | EOS L8 EEFlux | 6.787 | 6.917 | 0.682 | 0.465 | 4.488 | 7.783 |
| 26 July | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 5.624 | 5.925 | 1.036 | 1.074 | 0.899 | 6.816 |
| sUAS Masked NDVI-ET | 6.821 | 7.035 | 0.871 | 0.758 | 0.809 | 7.562 | |
| EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 5.941 | 6.183 | 0.734 | 0.539 | 2.364 | 6.817 | |
| 6 August | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 5.372 | 5.633 | 1.002 | 1.005 | 0.768 | 6.753 |
| sUAS Masked NDVI-ET | 6.609 | 6.76 | 0.694 | 0.482 | 0.872 | 7.326 | |
| EOS L8 EEFlux | 8.135 | 8.264 | 0.675 | 0.455 | 5.597 | 9.18 | |
| 20 August | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 4.906 | 5.146 | 0.875 | 0.765 | 0.881 | 6.739 |
| sUAS Masked NDVI-ET | 6.08 | 6.191 | 0.584 | 0.342 | 0.83 | 7.297 | |
| EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 5.931 | 6.151 | 0.797 | 0.635 | 2.049 | 8.094 | |
| 22 August | EOS L8 EEFlux | 6.799 | 6.707 | 0.541 | 0.293 | 5.612 | 8.111 |
| 7 September | EOS L8 EEFlux | 7.043 | 7.231 | 0.728 | 0.530 | 4.496 | 8.328 |
| 19 September | sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 3.577 | 3.750 | 0.677 | 0.458 | 0.614 | 4.641 |
| sUAS Masked NDVI-ET | 4.066 | 4.198 | 0.613 | 0.376 | 0.733 | 4.968 | |
| EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 4.088 | 4.239 | 0.665 | 0.443 | 1.082 | 5.636 | |
| 23 September | EOS L8 EEFlux | 7.466 | 7.706 | 0.628 | 0.394 | 4.998 | 8.165 |
| Method | Lower Bound | Mean | Upper Bound |
|---|---|---|---|
| sUAS Unmasked NDVI-ET | 237.29 | 259.81 | 282.32 |
| sUAS Masked NDVI-ET | 267.64 | 308.13 | 348.62 |
| EOS S2 NDVI-ET | 249.61 | 303.21 | 356.81 |
| EOS L8 EEFlux | 266.83 | 313.63 | 360.44 |
| Applied Irrigation | 264.34 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalua, M.; Rallings, A.M.; Booth, L.; Medellín-Azuara, J.; Carpin, S.; Viers, J.H. sUAS Remote Sensing of Vineyard Evapotranspiration Quantifies Spatiotemporal Uncertainty in Satellite-Borne ET Estimates. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193251
Kalua M, Rallings AM, Booth L, Medellín-Azuara J, Carpin S, Viers JH. sUAS Remote Sensing of Vineyard Evapotranspiration Quantifies Spatiotemporal Uncertainty in Satellite-Borne ET Estimates. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(19):3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193251
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalua, Michael, Anna M. Rallings, Lorenzo Booth, Josué Medellín-Azuara, Stefano Carpin, and Joshua H. Viers. 2020. "sUAS Remote Sensing of Vineyard Evapotranspiration Quantifies Spatiotemporal Uncertainty in Satellite-Borne ET Estimates" Remote Sensing 12, no. 19: 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193251
APA StyleKalua, M., Rallings, A. M., Booth, L., Medellín-Azuara, J., Carpin, S., & Viers, J. H. (2020). sUAS Remote Sensing of Vineyard Evapotranspiration Quantifies Spatiotemporal Uncertainty in Satellite-Borne ET Estimates. Remote Sensing, 12(19), 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193251