Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Their Driving Factors in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau Based on Geographical Detectors and Google Earth Engine: A Case Study in Gannan Prefecture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Preparation
2.2.1. Satellite Imagery
2.2.2. Training and Validation Sample Selection
2.2.3. Anthropogenic and Natural Data
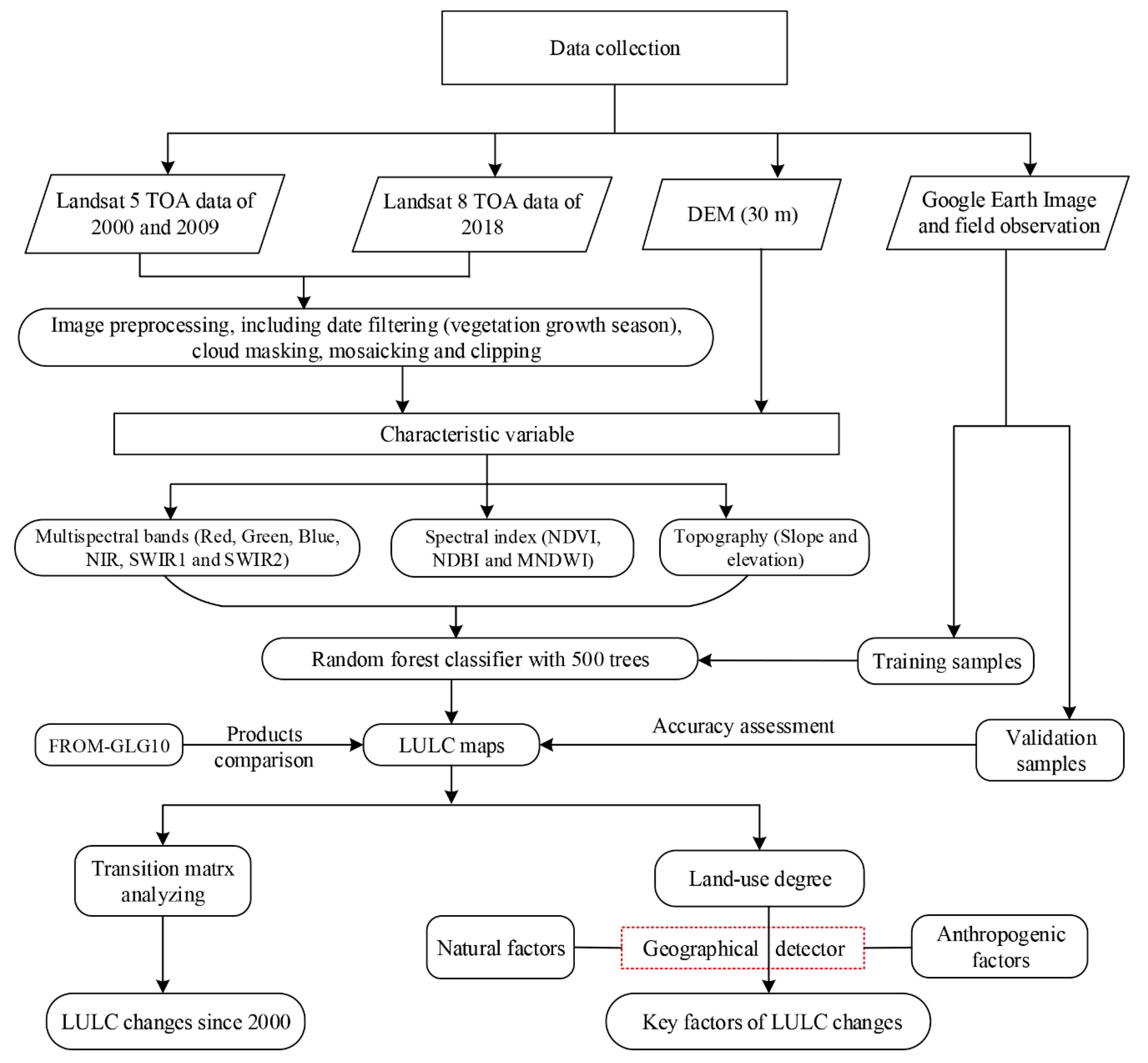
2.3. Methods
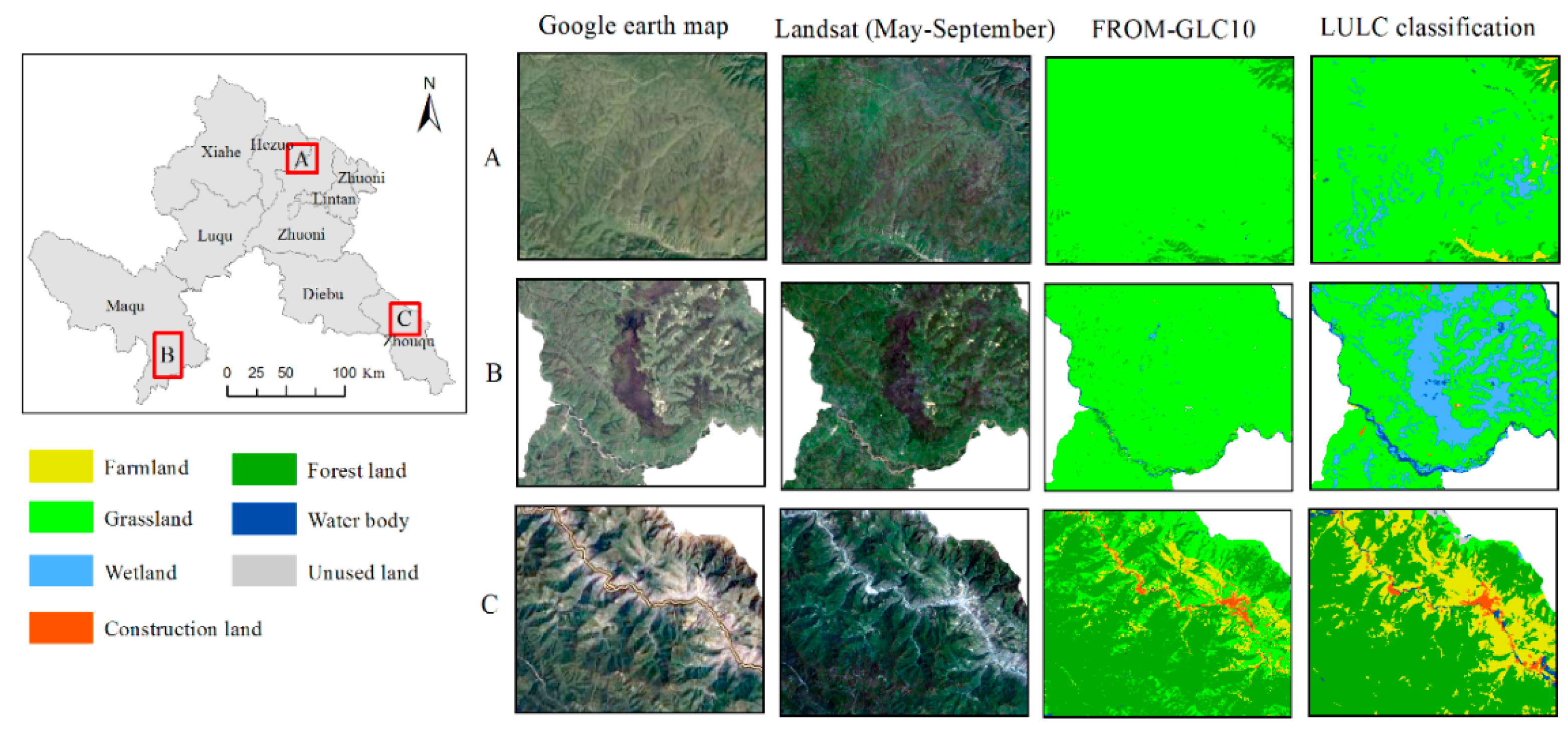
2.3.1. LULC Classification and Accuracy Assessment
2.3.2. Land Use Degree Index
2.3.3. Geographical Detector
3. Results
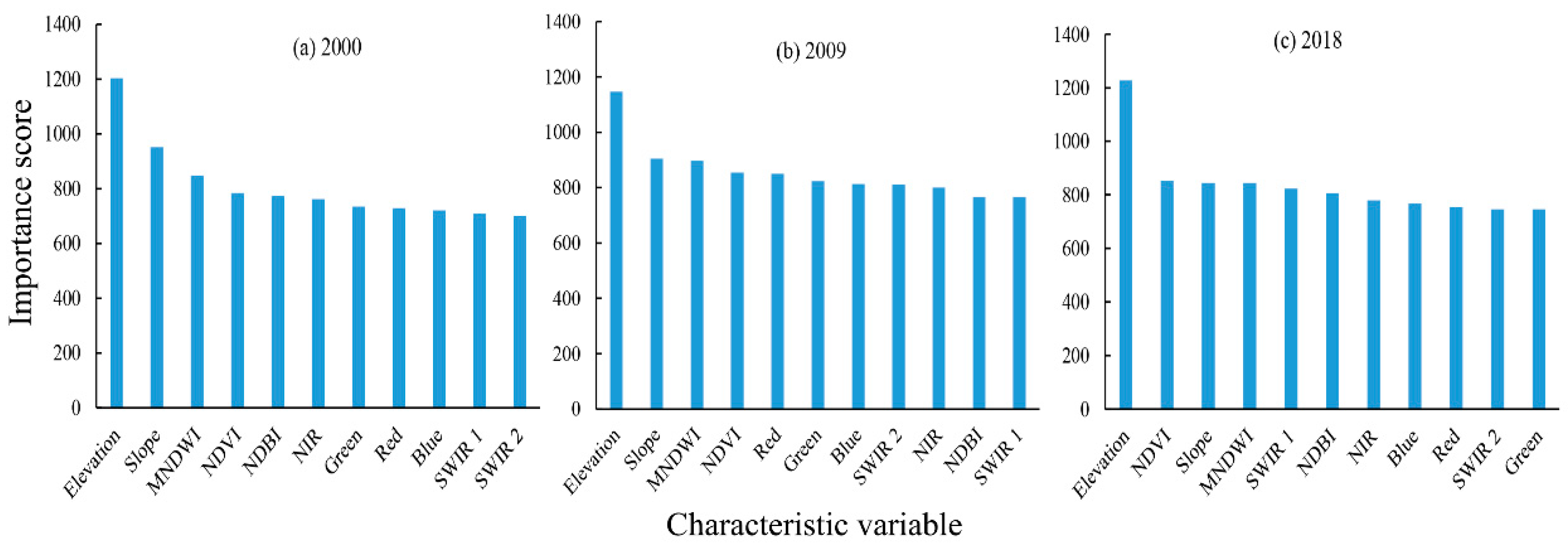
3.1. Variable Importance Analysis and Accuracy Assessment of LULC Classification
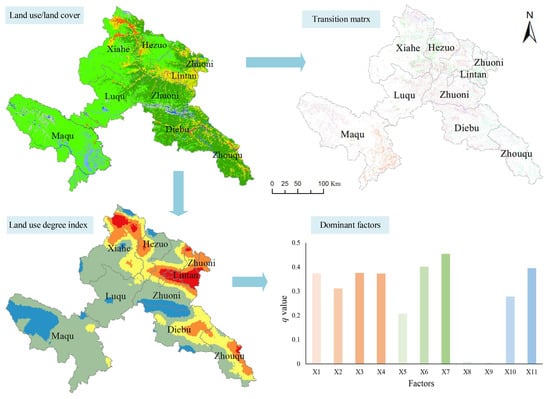
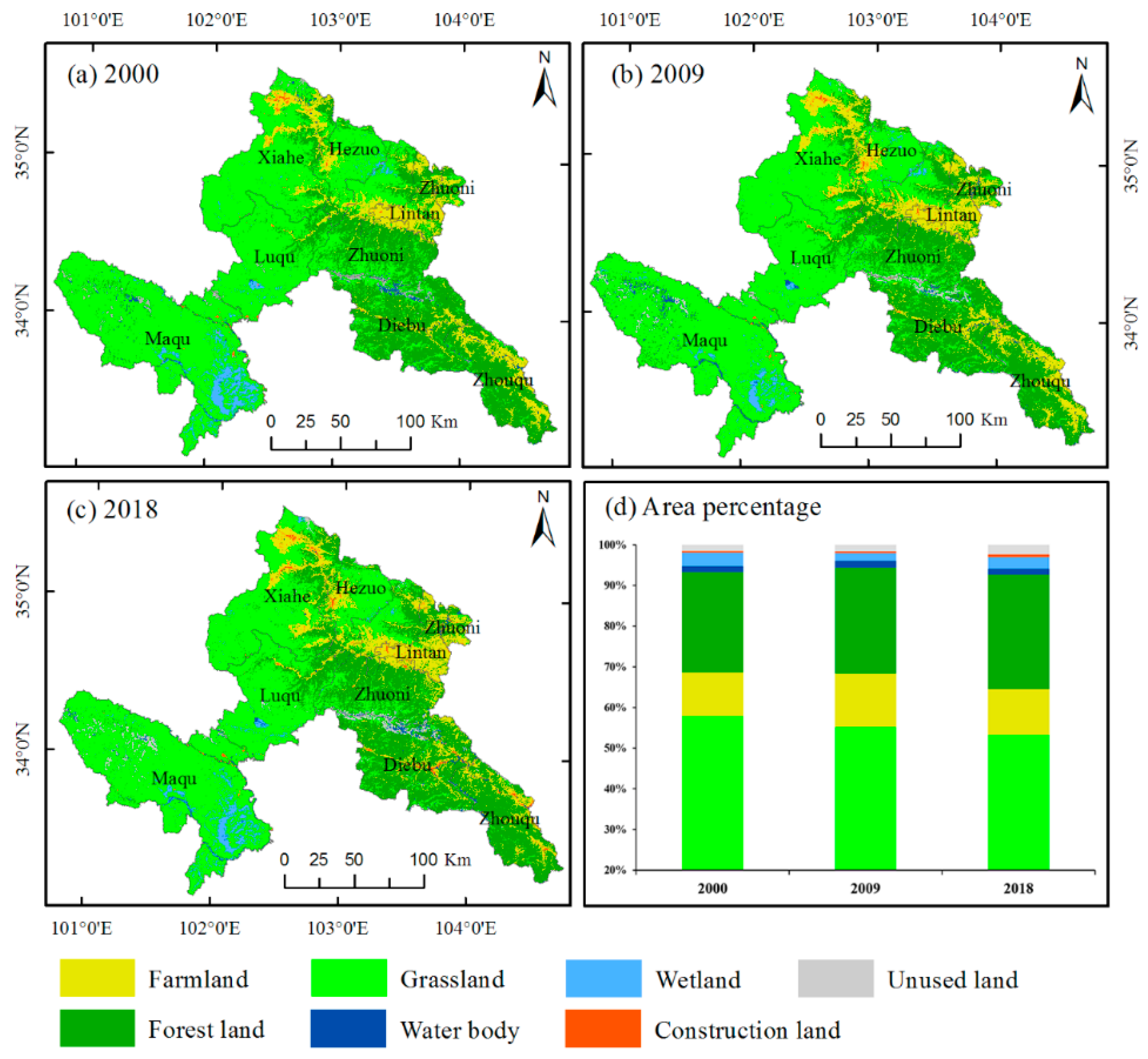
3.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of LULC Changes
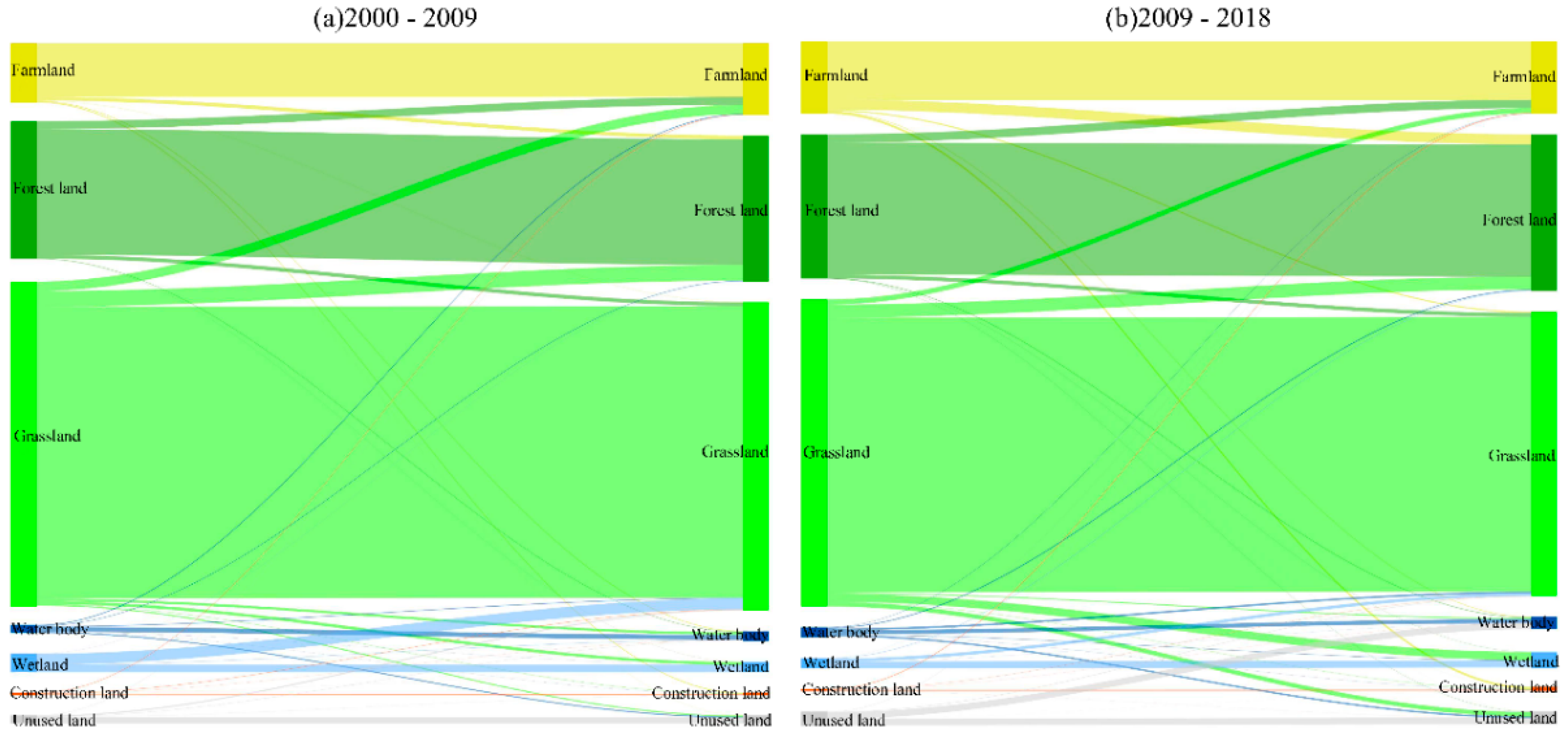
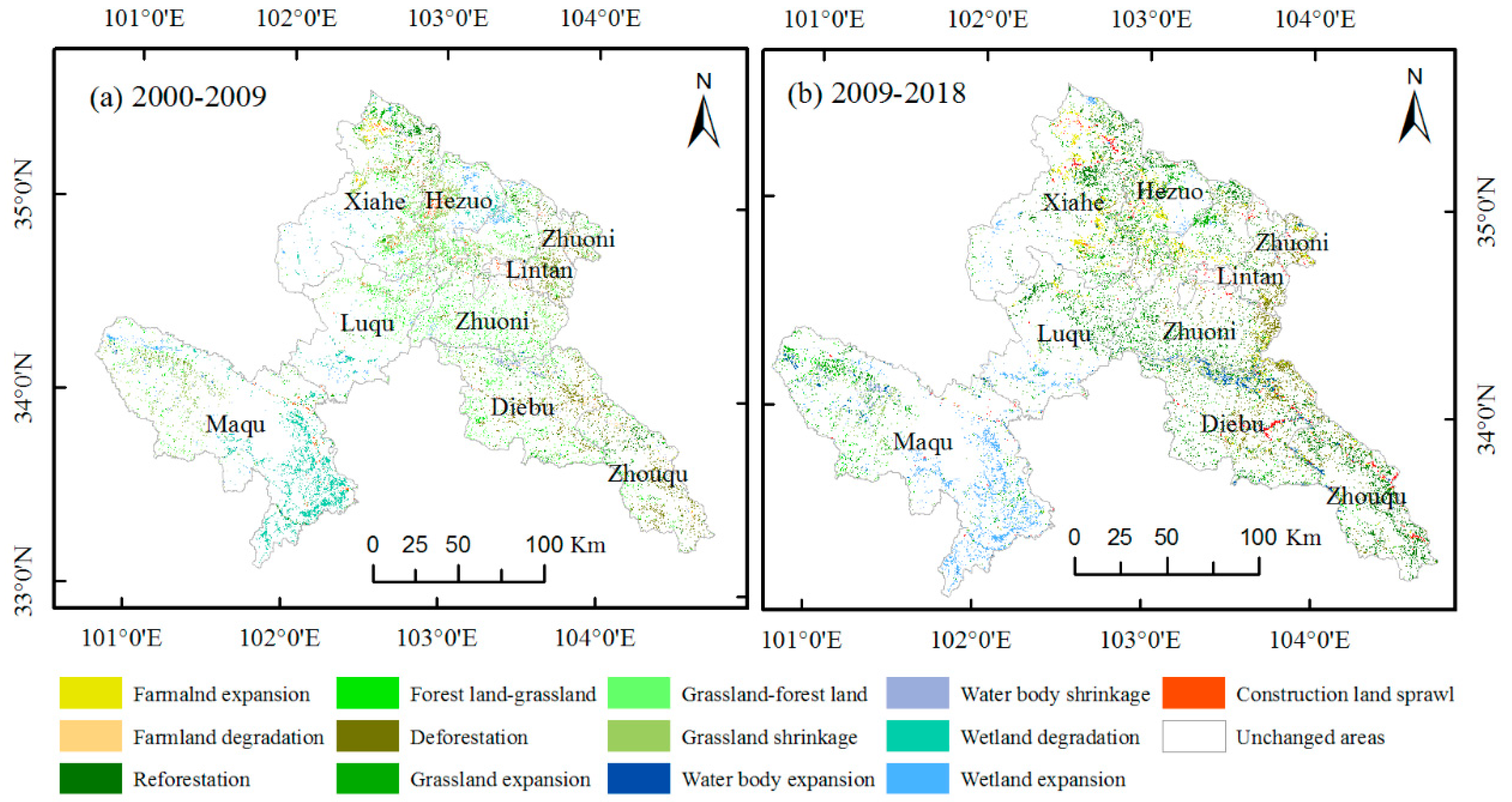
3.3. LULC Transformation
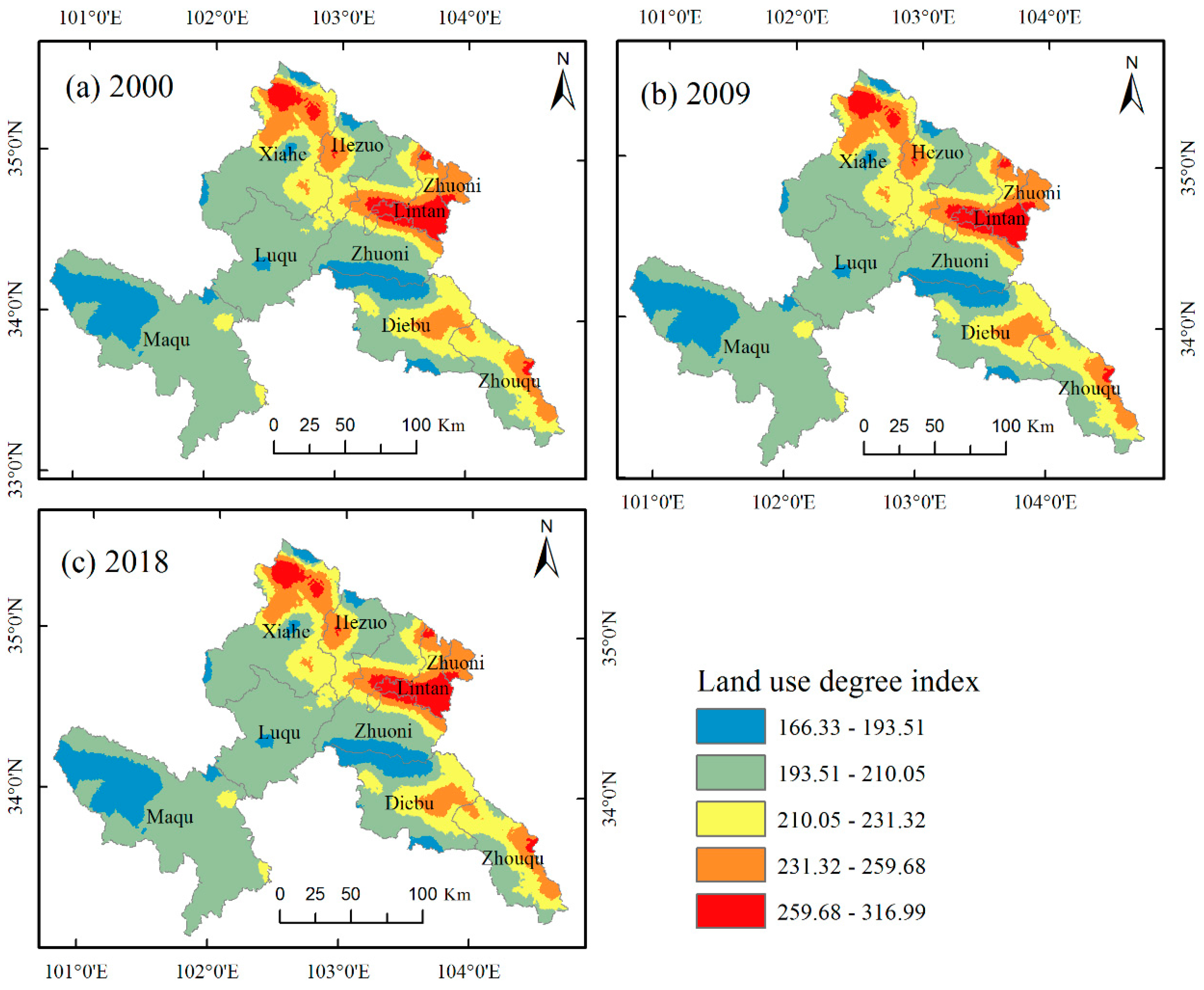
3.4. Degree of Land Use Change
3.5. Analysis of Driving Mechanisms in LULC Changes
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of LULC Classification Variable Importance and Result Verification
4.2. Temporal-Spatial Variation of LULC Changes
4.3. Major Drivers of LULC Changes
4.4. Advantages and Limitations of the Current Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quintero-Gallego, M.E.; Quintero-Angel, M.; Vila-Ortega, J.J. Exploring land use/land cover change and drivers in Andean mountains in Colombia: A case in rural Quindio. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Yi, Y.H.; Kimball, J.S.; Kim, Y.; Song, K.C. Climatic controls on spring onset of the Tibetan Plateau Grasslands from 1982 to 2008. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16607–16622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Yu, M. Quantifying trends of land change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during 2001-2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.L.; Cui, M.D.; Chen, A.P.; Wang, X.H.; Ciais, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.H. Altitude and temperature dependence of change in the spring vegetation green-up date from 1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate change will affect the asian water towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.W.; Hao, Y.B.; Xia, A.Q.; Liu, W.J.; Hu, R.H.; Cui, X.Y.; Xue, K.; Song, X.N.; Xu, C.; Ding, B.Y.; et al. Quantitative assessment of the impact of physical and anthropogenic factors on vegetation spatial-temporal variation in Northern Tibet. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Gang, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.L.; An, R.; Wang, K.; Odeh, I.; et al. Quantitative assess the driving forces on the grassland degradation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, in China. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 33, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyland, K.E.; Gunn, G.E.; Shiklomanov, N.I.; Engstrom, R.N.; Streletskiy, D.A. Land cover change in the Lower Yenisei River using dense stacking of landsat imagery in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, L.L.; Stow, D.A.; Tsai, Y.H.; Ibanez, N.; Shih, H.C.; Kerr, A.; Benza, M.; Weeks, J.R.; Mensah, F. Classification and assessment of land cover and land use change in southern Ghana using dense stacks of Landsat 7 ETM + imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Cohen, W.B.; Schroeder, T.A. Trajectory-based change detection for automated characterization of forest disturbance dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedano, F.; Molini, V.; Azad, M.A.K. A Mapping framework to characterize land use in the Sudan-Sahel region from dense stacks of landsat data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, H.; Qi, S.H.; Tao, S.Q.; Xu, H.Z.Y.; Yao, Y. An efficient approach to capture continuous impervious surface dynamics using spatial-temporal rules and dense Landsat time series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutanga, O.; Kumar, L. Google Earth Engine applications. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Hu, Y. Land cover changes and their driving mechanisms in Central Asia from 2001 to 2017 Supported by Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijani, Z.; Hosseinali, F.; Biswas, A. Spatio-temporal evolution of agricultural land use change drivers: A case study from Chalous region, Iran. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, T.; Mengistu, D.A. Land use and land cover dynamics and drivers in the Muga watershed, Upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Feng, M.; Biswas, A.; Su, H.; Niu, Y.; Cao, J. Driving factors and future prediction of land use and cover change based on satellite remote sensing data by the LCM model: A case study from Gansu Province, China. Sensors 2020, 20, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berihun, M.L.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Meshesha, D.T.; Adgo, E.; Tsubo, M.; Masunaga, T.; Fenta, A.A.; Sultan, D.; Yibeltal, M. Exploring land use/land cover changes, drivers and their implications in contrasting agro-ecological environments of Ethiopia. Land Use Pol. 2019, 87, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, D.; Morgenroth, J.; Xu, C. Long-term land cover change in Zambia: An assessment of driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, L.; Yang, D.Y.; Liu, Y.B. Quantifying the spatial heterogeneity influences of natural and socioeconomic factors and their interactions on air pollution using the geographical detector method: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.F.; Kuang, T.T.; Tao, S. Quantifying influences of natural factors on vegetation NDVI changes based on geographical detector in Sichuan, western China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.H.; Pan, Z.Z.; Liu, D.F.; Guo, X.N. Exploring the regional differences of ecosystem health and its driving factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, B.P.; Gao, J.L.; Liang, T.G.; Cui, X.; Ge, J.; Yin, J.P.; Feng, Q.S.; Xie, H.J. Modeling of alpine grassland cover based on unmanned aerial vehicle technology and multi-factor methods: A case study in the East of Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, Q.S.; Wang, C.G.; Tang, Z. A risk-based model for grassland management using MODIS data: The case of Gannan region, China. Land Use Pol. 2018, 72, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Guo, Z.G.; Liang, T.G.; Shen, Y.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, Y. Classification management for grassland using MODIS data: A case study in the Gannan region, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 3156–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, A.; Flessa, H.; Grabe, M.; Kazansky, O.A.; Shibistova, O.; Guggenberger, G. Organic carbon and total nitrogen variability in permafrost-affected soils in a forest tundra ecotone. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 1260–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Fu, J.E.; Wu, Z.T.; Pang, Z.G. Spatiotemporal variation of NDVI in the vegetation growing season in the source region of the Yellow River, China. ISPRS Int. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.G.; Yuan, L.H.; Wang, W.J.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.F.; Shen, W.M. Spatio-temporal analysis of vegetation variation in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Odeh, I.O.A.; Han, C.F. Bi-temporal characterization of land surface temperature in relation to impervious surface area, NDVI and NDBI, using a sub-pixel image analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.C.; Zhang, W. 40-Year (1978–2017) human settlement changes in China reflected by impervious surfaces from satellite remote sensing. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Kuang, W.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Xu, X.L.; Qin, Y.W.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.C.; Zhang, S.W.; Li, R.D.; Yan, C.Z.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.G.; Huang, X.M.; Fu, H.H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: First mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, M. Spatially differentiated trends in urbanization, agricultural land abandonment and reclamation, and woodland recovery in Northern China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, L. Land cover change in the central region of the Lower Yangtze River based on landsat imagery and the Google Earth Engine: A case study in Nanjing, China. Sensors 2020, 20, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L. Applying geodetector to disentangle the contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to NDVI variations in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Tian, J.; Sun, Q. Random forest classification of wetland landcovers from multi-sensor data in the arid region of Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Clinton, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, C.X.; Gong, P.; Yang, J.; Bai, Y.Q.; Zheng, Y.M.; et al. Mapping major land cover dynamics in Beijing using all Landsat images in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Dragut, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teluguntla, P.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Oliphant, A.; Xiong, J.; Gumma, M.K.; Congalton, R.G.; Yadav, K.; Huete, A. A 30-m landsat-derived cropland extent product of Australia and China using random forest machine learning algorithm on Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, X.D.; Zhang, S.Q.; Li, X.F.; Yu, H.A.; Liu, C.Y. Improved land cover mapping using random forests combined with landsat thematic mapper imagery and ancillary geographic data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiminia, H.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.; Adeli, S.; Brisco, B. Google Earth Engine for geo-big data applications: A meta-analysis and systematic review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Ghimire, B.; Rogan, J.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damtea, W.G.; Kim, D.; Im, S. Spatiotemporal analysis of land cover changes in the Chemoga Basin, Ethiopia, using landsat and Google Earth images. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhling, I.; Broll, G.; Trautz, D. Spatio-temporal analysis of agricultural land-use intensity across the Western Siberian grain belt. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Liu, J. Study on the model of regional differentiation of land use degree in China. J. Nat. Res. 1997, 12, 10–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Y.; Zheng, M.R.; Liu, J.Y.; Zheng, X.Q. Sustainable land use in the trans-provincial marginal areas in China. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurqani, H.A.; Post, C.J.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Schlautman, M.A.; Sharp, J.L. Geospatial analysis of land use change in the Savannah River Basin using Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 69, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshikawa, K.; Umezaki, M. Effects of terrain-induced shade removal using global DEM data sets on land-cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 1331–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.J.; Ge, J.; Gao, J.L.; Meng, B.P.; Li, Y.C.; Yin, J.P.; Liu, J.; Feng, Q.S.; Liang, T.G. Ecological Risk Assessment and Impact Factor Analysis of Alpine Wetland Ecosystem Based on LUCC and Boosted Regression Tree on the Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Meng, B.P.; Liang, T.G.; Feng, Q.S.; Gao, J.L.; Yang, S.X.; Huang, X.D.; Xie, H.J. Modeling alpine grassland cover based on MODIS data and support vector machine regression in the headwater region of the Huanghe River, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 218, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M.; Worqlul, A.W.; Tolessa, T.; Kindu, M. Estimating the impacts of land use/land cover changes on ecosystem service values: The case of the Andassa watershed in the Upper Blue Nile basin of Ethiopia. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubako, S.; Belhaj, O.; Heyman, J.; Hargrove, W.; Reyes, C. Monitoring of land use/land-cover changes in the arid transboundary Middle Rio Grande Basin using remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.J.; Lu, Y.H.; Comber, A.; Fu, B.J.; Harris, P.; Wu, L.H. Spatially explicit simulation of land use/land cover changes: Current coverage and future prospects. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Li, X.B. Spatial correlation between type of mountain area and land use degree in Guizhou Province, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Li, X. Rapid urbanization and its driving mechanism in the Pan-Third Pole region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.J.; Zhu, H.M.; Yang, S.W.; Ma, S.J.; Zhou, J.W.; Chu, B.; Hua, R.; Hua, L.M. Overgrazing leads to soil cracking that later triggers the severe degradation of alpine meadows on the Tibetan Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Zang, F.; Yang, J.; Li, N.; Rong, Z.; Zhao, C. Impacts of topography on the land cover classification in the Qilian Mountains, Northwest China. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 46, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xystrakis, F.; Psarras, T.; Koutsias, N. A process-based land use/land cover change assessment on a mountainous area of Greece during 1945-2009: Signs of socio-economic drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; He, M.; Niu, Z.G. Responses of alpine wetlands to climate changes on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau based on remote sensing. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Factors Types | Code | Index | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic factors | X1 | Population density | people/km2 |
| X2 | Gross domestic product (GDP) | yuan | |
| X3 | Livestock quantity | sheep | |
| X4 | Chemical fertilizer consumption | ton | |
| Natural factors | X5 | Annual mean temperature | °C |
| X6 | Annual mean precipitation | mm | |
| X7 | Elevation | m | |
| X8 | Slope degree | ° | |
| X9 | Aspect | ° | |
| X10 | Vegetation type | / | |
| X11 | Soil type | / |
| Type of Land | Uncultivated Land | Ecological Land | Agricultural Land | Construction Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LULC types | Unused land (sand and bare land) | Forest land, grassland, wetland, and water body | Farmland | Urban, residential area, traffic land, and industrial land |
| Index of Classification | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| LULC Types | 2000 | 2009 | 2018 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User’s Accuracy | Producer’s Accuracy | User’s Accuracy | Producer’s Accuracy | User’s Accuracy | Producer’s Accuracy | |
| Farmland | 75 | 79.41 | 78.68 | 90.56 | 83.33 | 84.67 |
| Grassland | 87.64 | 93.97 | 90.27 | 91.54 | 90 | 84.70 |
| Forest | 99 | 98.01 | 94.62 | 94.62 | 96.77 | 97.27 |
| Water | 92.85 | 84.41 | 95.23 | 88.49 | 93.25 | 93.78 |
| Wetland | 86.48 | 82.05 | 86.66 | 92.85 | 91.89 | 82.92 |
| Construction land | 86.36 | 90.47 | 91.22 | 77.61 | 91.87 | 93.03 |
| Unused land | 88.88 | 100 | 83.33 | 83.33 | 69.23 | 90 |
| Overall accuracy | 90.35 | 89.14 | 91.41 | |||
| Kappa coefficient | 87.97 | 86.55 | 89.40 | |||
| Year | Anthropogenic Factors | Natural Factors | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Factor | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 |
| q | 0.4062 | 0.2231 | 0.1930 | 0.3071 | 0.3575 | 0.0509 | 0.4689 | 0.0062 | 0.0041 | 0.2690 | 0.3848 | |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 2009 | q | 0.3796 | 0.2601 | 0.1137 | 0.3904 | 0.3103 | 0.2432 | 0.4486 | 0.0083 | 0.0029 | 0.2572 | 0.3604 |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 2018 | q | 0.3740 | 0.3117 | 0.3757 | 0.3731 | 0.2077 | 0.4013 | 0.4544 | 0.0086 | 0.0023 | 0.2780 | 0.3952 |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, H.; Yan, H.; Xue, P. Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Their Driving Factors in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau Based on Geographical Detectors and Google Earth Engine: A Case Study in Gannan Prefecture. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193139
Liu C, Li W, Zhu G, Zhou H, Yan H, Xue P. Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Their Driving Factors in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau Based on Geographical Detectors and Google Earth Engine: A Case Study in Gannan Prefecture. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(19):3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193139
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chenli, Wenlong Li, Gaofeng Zhu, Huakun Zhou, Hepiao Yan, and Pengfei Xue. 2020. "Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Their Driving Factors in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau Based on Geographical Detectors and Google Earth Engine: A Case Study in Gannan Prefecture" Remote Sensing 12, no. 19: 3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193139
APA StyleLiu, C., Li, W., Zhu, G., Zhou, H., Yan, H., & Xue, P. (2020). Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Their Driving Factors in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau Based on Geographical Detectors and Google Earth Engine: A Case Study in Gannan Prefecture. Remote Sensing, 12(19), 3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193139