Abstract
Single-pair differential synthetic aperture radar interferometry (DInSAR) as well as more advanced methods, such as persistent scatterer interferometry (PSI), allow vertical displacements to be detected at the sub-centimeter level. Since 2014 free SAR data—Sentinel-1—have been collected systematically under the COPERNICUS program at a high temporal resolution and with global coverage. Such an open-access policy greatly helps build a wide user-community and develop diverse SAR-based applications. In this study conventional single-pair DInSAR and the PSI techniques were employed to monitor the vertical displacements of the newly constructed D8 highway, more specifically the part passing through the České Středohoří Mountains, where, during highway construction, a massive landslide occurred in June 2013. For both DInSAR and PSI, free Sentinel-1 radar data were used; moreover, the conventional single-pair DInSAR workflow was processed using freely available SNAP software. Results from the radar interferometry were validated using in situ techniques, such as geodetic measurements, 3D inclinometers, and laser scanning. Both approaches proved their ability to achieve reliable results in detecting vertical displacement “hotspots”. Additionally, in terms of absolute values, the PSI interferometry corresponds very well with the in situ measurements. This study also shows that open-source solutions (free data and SW) provided under the COPERNICUS program bring a great potential for monitoring vertical displacements.
1. Introduction
Landslides are prominent geohazards affecting not only the natural environment, but also human settlements and infrastructure. Detection and continuous monitoring of landslide-prone areas is, therefore, crucial for its prevention and prediction [1,2]. Such monitoring is usually focused on continuous surface deformation and displacement detection which serve as indicators of a possible sudden slip with further damages. In the last decade modern remote sensing data and methods (e.g., synthetic aperture radar: SAR) have been used more and more often as new means to detect landslide-prone areas before a disaster happens and, also, to monitor vertical displacements in case the disaster has already happened [3,4,5,6,7].
SAR radar data analysis could be either amplitude- or phase-based. Amplitude change is usually used for fast-motion landslides, while the phase component serves for tracing slow motions [1]. One of the most exploited phase-related techniques enabling surface displacement to be measured is differential SAR interferometry (DInSAR) [8]. Under suitable conditions DInSAR can achieve millimeter accuracy, thus, it is a very powerful tool for land subsidence/uplift measurements [9]. Due to its ability to identify deformations from millimeters to centimeters, DinSAR is a suitable method for monitoring slow-moving landslides.
The goal of DinSAR is to obtain the most precise measurements of a surface deformation, this means removing or diminishing all the contributors to the interferometric phase (1) except the displacement. To do so, interferogram flattening and topographic phase removal is performed during the simple single-pair interferometric process (also known as conventional DInSAR, [10]). Therefore, DInSAR is usually limited by temporal and geometrical decorrelation and atmospheric delay anomalies. It only works properly in areas where the interferograms that are generated are characterized by high coherence, as an insufficient coherence value of corresponding pixels causes unreliable phase difference values [6]. Among typical surfaces with low coherence are forests and other densely vegetated areas. In addition, snow and near-surface moisture changes can also cause coherence losses [11]. In spite of the afore-mentioned limitations, several studies have demonstrated that single-pair interferometry can be employed successfully for landslide analysis [12,13,14,15,16].
Multi-temporal DInSAR (MT DInSAR) techniques, known as Advanced-DInSAR, can partly overcome the DInSAR limitations [17]. MT DInSAR techniques use large stacks composed of many SAR images collected with the same sensor under the same geometry and remove the redundant information of phase difference, particularly the atmospheric contribution [18]. MT DInSAR includes two approaches—persistent scatterers interferometry (PSI) [19] and small baseline subset (SBAS)—originally proposed by [20]. The main difference between SBAS and PSI technique is that they use a different approach for stacking differential interferograms and in the use of either persistent or distributed scatterers [21,22,23,24,25].
The SBAS technique [20,26] is based on the use of multiple small perpendicular baseline acquisition subsets via an easy and effective combination of all the available interferograms [20]. It deals with multi-master, short time interferograms, and investigates the distributed pixels. The singular value decomposition (SVD) method is applied in order to link independent SAR acquisitions, separated by large baselines, thus, it increases the temporal sampling rate of the dataset. The SBAS has been used for instance by [27,28,29,30] for detecting and monitoring ground surface deformations related to landslides.
PSI, presented by [19], requires at least 20 SAR images to perform the analysis in the C-band data [31]. PSI measures the surface deformation over months or years, removing the effects of atmosphere, topography, and signal noise. The PSI technique’s potential for landslide assessment has been demonstrated in numerous studies (e.g., [2,18,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]).
As already explained, employing DInSAR techniques in predominantly vegetated areas is still not easy. Especially when using frequencies in the C band (e.g., free Sentinel-1 data) and X band (e.g., TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X), insufficient coherence is the main limitation. So far, the potential of Sentinel-1 C band data to monitor land deformation connected with landslides and subsidence has been demonstrated in several studies [16,31,39,40,41,42]. However, for vegetated areas it still might be challenging to use COPERNICUS Sentinel-1 SAR data working in the C band.
In this study the surface vertical displacements of the newly-built D8 highway in the Czech Republic was analyzed, more specifically the Hodkovičky area, which was affected by a massive landslide in June 2013. The intention was to test whether Sentinel-1 C band data can be successfully used to detect vertical displacements even in the conditions of Central Europe-mainly covered by dense vegetation. Furthermore, using the in situ data and techniques, such as geodetic measurements, 3D inclinometers, and laser scanning, it was possible to validate and compare the results for two scenarios: (i) the open-access data and freeware-based Scenario 1: DinSAR employed to Sentinel-1 data using SNAP freeware, and (ii) Scenario 2: more advanced PSI techniques employed to Sentinel-1 data when using a commercial SW [43]. Scenario 1 was intended to determine whether the vertical displacement can be detected by using not only the freely available data but also the freely accessible technology. The aim of Scenario 2 was to get accurate values of ground subsidence/uplift by means of the robust PSI technique that combines a large number of SAR scenes, thus reducing possible errors. Robust PSI tools are currently only available in commercial SW. The results obtained by both approaches are compared and discussed in detail in this study.
2. Study Area
The study area is located in the northern part of the Czech Republic, approx. 60 km from Prague. In this area, a newly built, 16 km long section of the D8 highway passes through the České Středohoří Mountains (Figure 1). During the highway construction a massive landslide occurred in June 2013 when 370,000 m3 of soil slid down over the newly built D8 highway. The progress of this landslide is described in detail in [44].
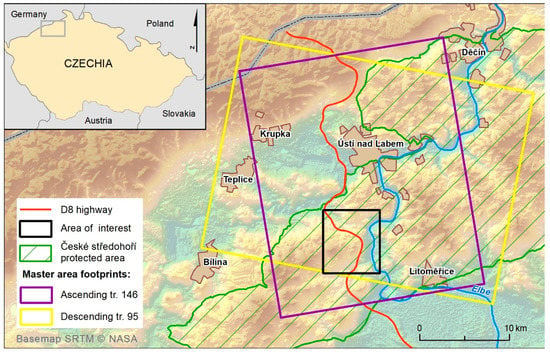
Figure 1.
Area of interest with delineated Master areas footprints of ascending and descending pass.
The České středohoří is one of the areas in the Czech Republic that is highly landslide-susceptible. The whole area along the D8 highway section passing the particular part shown in Figure 2 is historically known for the presence of documented and in situ verified landslides of various types and age (fossil stable block deformations, approx. 40 m thick; older dormants of various shapes; young active landslides) [45]. Figure 2a shows the landslides documented in the Ground Instabilities Registry of the Czech Geological Survey; some of these landslides are still active.
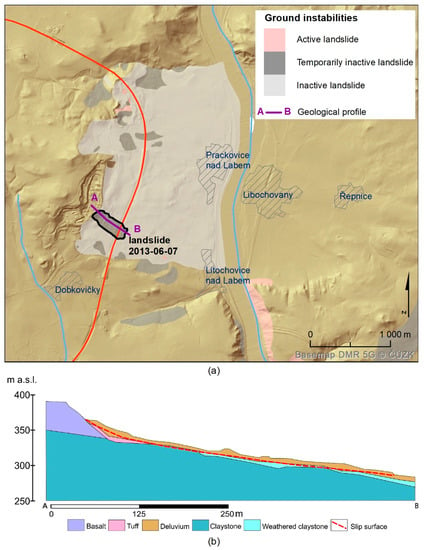
Figure 2.
(a) Ground instabilities in the area of interest [46], and (b) geological profile, adapted by [44].
From the geological point of view, the slopes in these particular areas are formed by chalky clays and other quaternary sediments which are represented by old slope deformation accumulations. Solid or more compact volcanic rock outcrops could only be found in the upper part of the landslide scarp with the presence of the lava flow relicts (Figure 2b). The geological development of the test area is well presented in an animation in [47]. The geological situation is further complicated by intensive tectonic processes which created plenty of tectonic blocks with a large relative uplift (approx. hundreds of meters). Major morphological lineaments, probably predisposed by the tectonic faults, have a SW–NE (following the Ore Mountains’ morphological direction) and a NW–SE (following the Sudetic fault system) direction.
3. Dataset Description
The SAR data used in this study were acquired by Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-1B satellites, which have been freely available through the COPERNICUS Programme since 2014. The shorter revisit time (six days) is expected to enhance the coherence value of interferometric pairs. Other S-1 advantages come from its wide range coverage (250 km in an interferometric wide swath mode) and sufficient spatial resolution (5 m × 20 m in range vs. azimuth). Furthermore, the TOPSAR (Terrain Observation with Progressive Scans SAR) technique ensures homogeneous image quality throughout the swath [48].
For conventional DInSAR (Scenario 1, where data are processed using the freeware SNAP), several pairs of images in Single Look Complex (SLC) format were used. The selection of the appropriate data pair is a crucial task, because the success of the method applied is highly dependent on coherence values. Therefore, attention was paid to several parameters that influence coherence preservation, such as the perpendicular baseline between the satellites’ orbits, the temporal baseline between acquisition dates, and the overall coherence estimation of the pair. To minimize the effect of the atmosphere, weather conditions on dates of acquisition were checked and only days without precipitation were chosen. In addition, despite careful pair selection, the interferometric process did not always come up with satisfactory results. Phase unwrapping proved a critical step of the workflow, because many promising datasets failed at this stage of the processing chain. After running different DInSAR combinations, the best results were obtained from the pair of the descending pass at the beginning of 2017 (from 22 February 2017 to 17 May 2017), perpendicular baseline: −7.98 m, track 95).
The PSI technique requires at least 20 SAR time-series images to obtain reliable results. Therefore for Scenario 2, when the PSI is employed to Sentinel-1 data, four different time series with more than 30 images for an ascending and descending pass were used (Table 1, Figure 1). These consist of two time series for each descending and ascending pass geometry, the longer one comprising the whole year and the shorter one that includes just the part of the year without snow cover. The purpose of this selection was to test the influence of possible snow cover or moisture on the PSI method. For every data stack of the time-series the perpendicular (Bp) and temporal baselines were analyzed to make sure that the Bps of the time-series did not exceed the critical value, which is about 200 m for Sentinel-1. A Bp longer than the critical value causes geometrical decorrelation, and, in such a case, the interferometric phase is not usable. As can be seen in Figure 3, the Bps of both longer time-series (A, C) did not generally exceed 200 m.

Table 1.
Analyzed datasets.
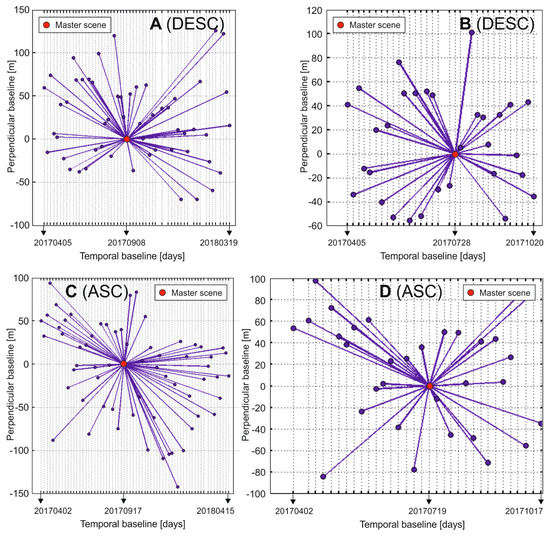
Figure 3.
Images of star graphs depicting the temporal and perpendicular baselines of time series (A–D).
4. Methodology
DInSAR, as a general technique, includes methods from single-pair interferometry to more advanced approaches. However, what all of them have in common is that they exploit the information contained in the interferometric phase calculated as the phase difference between two images acquired at two different times from almost the same satellite position [49]. The interferometric phase comprises the following contributions [49]:
where Δφflat is the phase contribution of the flat earth, Δφheight represents topography Δφdisplacement is the part of the phase which represents the ground deformation measured along the line of sight (LOS), Δφatmosphere is the contribution of the phase caused by the delay of radar wave propagation through the atmosphere and Δφnoise is residual noise.
Δφ = Δφflat + Δφheight + Δφdisplacement + Δφatmosphere + Δφnoise,
As mentioned above, the goal of DInSAR is to remove all the contributors to the interferometric phase except displacement. Conventional DInSAR (used in Scenario 1) is able to cope with the most of them. But the last two terms of Equation (1)—atmosphere and noise—can be resolved only when employing more robust MT DInSAR techniques, such as the PSI used in Scenario 2.
4.1. Scenario 1: The Single Pair DInSAR
A conventional DInSAR was conducted in the SNAP software (Sentinel-1 Toolbox) developed by the European Space Agency (ESA). It is freely available and is designed mainly for processing Sentinel’s data. A simple workflow of single-pair DInSAR is shown in Figure 4.
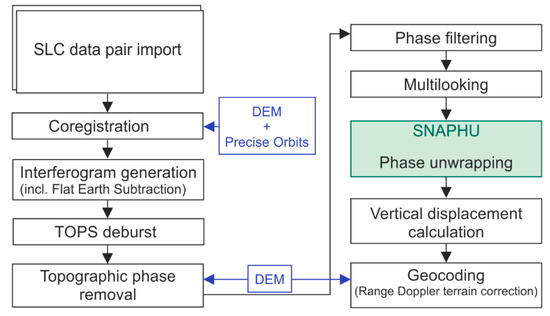
Figure 4.
Single-pair DInSAR workflow in SNAP.
The conversion of unwrapped phases to displacement values, preferentially in a vertical direction instead of a line-of-sight (LOS) direction, was carried out according to the formula [50]:
where ϕunw is the unwrapped phase, λ is the radar wavelength, and θinc is the incidence angle. Since the calculated vertical displacement values are relative, the stable areas in the resulting raster were identified first, then the mean value of displacement in these areas was derived. Subsequently, this offset value (1.425 cm) was used to adjust the whole dataset. After that the final raster was geocoded via a Range Doppler terrain correction and places of low coherence (>0.7) were masked out.
vert_displ = (ϕunw·λ)/(−4π(cos θinc))
4.2. Scenario 2: The PSI
The PSI [21] requires at least 20 SAR images to perform the analysis in C-band data [51]. The PSI measures surface deformation over months or years, removing the effects of the atmosphere, topography, and signal noise. The PSI exploits interferograms with a single master scene (Figure 3). In this technique, only the coherent pixels with stable phase or amplitude are processed. The number of resulting points can be rather low in vegetated areas. In this study the highway surface was large enough to be represented by tens of S-1 pixels, therefore, there were enough coherent PSI pixels.
SARPROZ software was used for the PSI [43] allowing huge datasets to be processed. SARPROZ has been successfully used, e.g., by [52] to make a displacement map of Hong Kong proving the accuracy of the PSI is at the level of one millimeter. It uses the principles of the PSInSAR©TM approach described in detail by [19,53], therefore, the general workflow (Figure 5) and the specifics of the setup for the particular datasets used in this study are briefly described in this section.
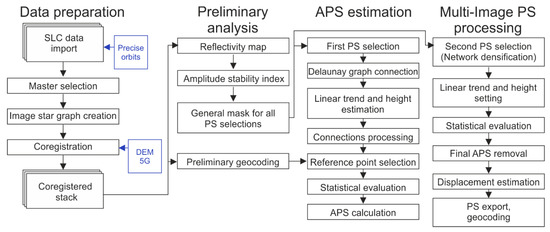
Figure 5.
Simplified workflow of PSI Processing in SARPROZ.
Before deriving interferograms, a crucial step is the coregistration of all images into a single master stack. It is very important to choose a proper master scene which must meet the following specifications:
- It must be acquired under good weather conditions (no rain); and
- It has a suitable position (approximately in the middle) in the image star graph considering the perpendicular and temporal baseline [54].
The SARPROZ SW is able to download weather data from the Weather Underground database, but the data are related to the whole subscene. Therefore, another source for detailed information about weather conditions during image acquisitions was used. The nearest meteorological station Milešovka (6 km away) was chosen as a reference weather point. The acquisition dates of the selected master images for four time series are given in Table 1. On these days no rain occurred and there was a certain amount of sunny hours. To speed up the following procedures the smaller area of interest (AOI) was defined (Figure 1). Then the master and slave images were all extracted and coregistered on the basis of precision orbits and the digital elevation model (DEM) DMR 5G ©ČÚZK with submeter accuracy.
While phase stability can be assessed only after estimating and removing different phase contributions (atmospheric phase screen (APS), DEM errors, orbit inaccuracies), absolute amplitude values are almost insensitive to most of these phenomena. Thus, a pixel that constantly has similar amplitude during all acquisitions is expected to have small phase dispersion. In SARPROZ SW the Amplitude Stability Index (ASI) is used to select the permanent scatterers (PS):
where DA represents the amplitude dispersion, mA is the mean deviation of amplitude in time, and σA is the standard deviation of amplitude in time. An example of the ASI of time series A is given in Figure 6.
ASI = 1 − DA = 1 − (σA/mA)
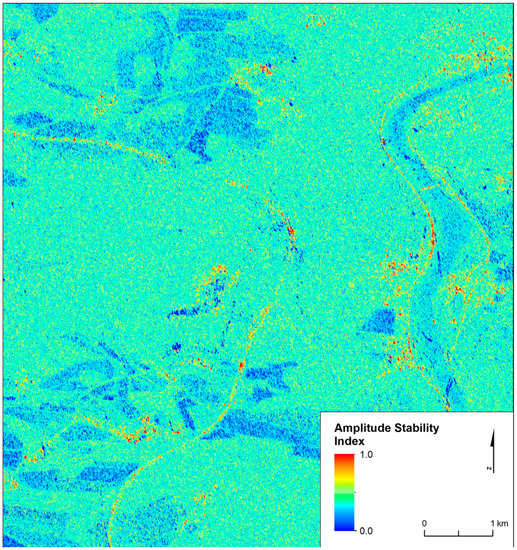
Figure 6.
An example of Amplitude Stability Index (ASI) in the area of interest, time series A.
Ferretti et al. [19] recommended a suitable threshold to select the first PSs when ASI > 0.75 (DA < 0.25). In this study ASI > 0.8 was set for the first PS selection. Only a small number of points satisfy this strict parameter, however, this condition is necessary to obtain correct APS estimations. An overview of ASI values is given in Figure 6. It is evident that there are only a few places with sufficiently high ASI values, thus, fewer points (2526 from approx. 40,000) were chosen for further processing.
After selecting the first order PS, a reference network needs to be established by connecting the PSs by Delaunay triangulation. The differential deformation velocity and differential residual topographic error (RTE) are computed for each edge. Then the estimated linear model (linear displacement velocities and residual height) is subtracted and the APS is estimated from the phase residuals by graph inversion. During this step it is necessary to fix the velocity value of at least one pixel (reference point). The APS estimation quality was assessed by an analysis of the temporal coherence of PSs after graph inversion and APS removal, which gave satisfactory results: most of the selected PSs had a coherence value higher than 0.9 (Figure 7).
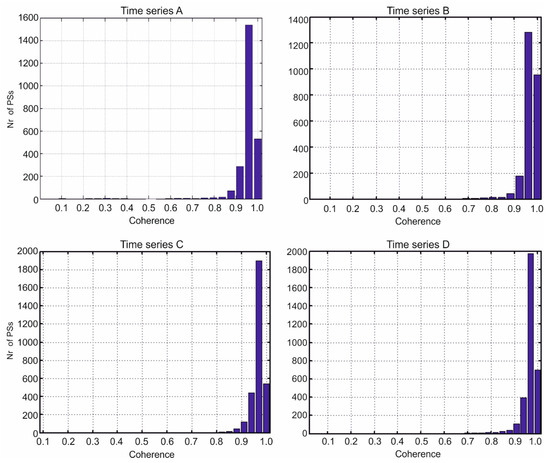
Figure 7.
Temporal coherence of selected PSs of time series (A–D) after graph inversion and APS removal.
According to the workflow (Figure 5), the next step was second order PS selection. This time the criterion was less strict (ASI > 0.6) in order to obtain a densified PS collection. Then the final processing with APS removal was conducted using the same parameters and the reference point as for APS estimation. The final set of PS was then geocoded and exported to GIS. Similarly to [55], only PSs with a high coherence were selected (γ < 0.7) and were used in the final vertical displacement maps (Figures 10, 13, 15 and 16).
5. Results
In this section, the results obtained from Scenario 1 (single pair DInSAR) and 2 (PSI analyses) are presented and compared to each other.
5.1. Scenario 1: Single Pair DInSAR Results
The final raster of vertical displacement was statistically evaluated via histogram and basic statistical parameters. As Figure 8 shows, the histogram has an asymmetric shape and the mean value is about −8 mm, whereas the mode is 4 mm higher. This means that most of the displacement values are negative. This can be due to the atmospheric effect, which is not removed during the single-pair interferometric process. The dataset was not further corrected, and it must be taken into account that the resulting absolute values may have a greater error.
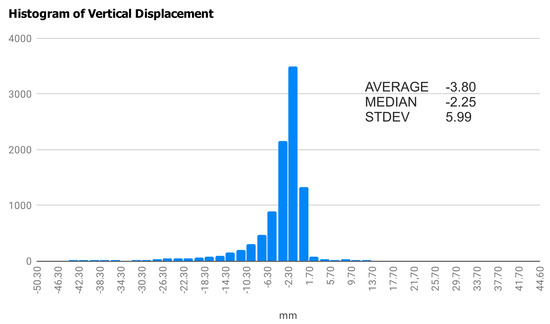
Figure 8.
Histogram of vertical displacement dataset during the period from 22 February 2017 to 17 May 2017 complemented by descriptive statistics.
To be able to compare the results of the single-pair DInSAR with the PSI, the raster of vertical displacement was recalculated to the displacement velocity (mm/year). The resulting map of the cumulative displacement and adequate velocity during the given period, from 22 February 2017 to 17 May 2017, is shown in Figure 9. Vertical displacements ranging between −5 and −50 mm were detected in four different areas during this nearly three-month period.
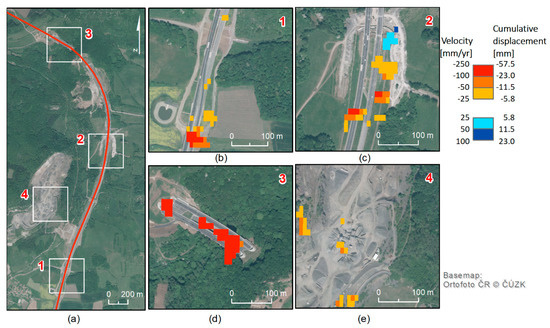
Figure 9.
(a) Overview of the four sites with detected subsidence: 1: Area of highway embankment between Ječky Bridge and Dobkovičky Bridge; 2: Prackovice Bridge; 3: Area between two highway tunnels (“Prackovice” and “Radejčín”); 4: Dobkovičky quarry. (b–e) Cumulative vertical displacement (mm) during the given period from 22 February 2017 to 17 May 2017 and the recalculated subsidence/uplift velocity (mm/year) obtained by using single-pair DInSAR.
5.2. Scenario 2: The PSI Results
Four maps of surface deformation velocity represent the basic results of PSI analysis for each time series (Figure 10).
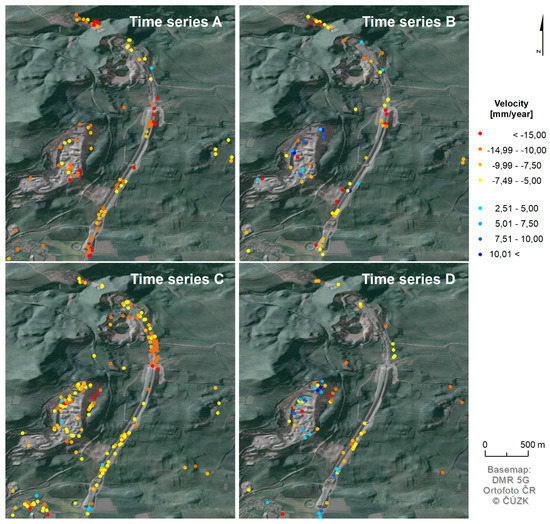
Figure 10.
Displacement velocity (in LOS) of all processed time series (A–D).
The results of shorter periods (Figure 10B,D) show a lot of noise, especially in the case of an ascending pass where there are many mixed pixels of subsidence and uplift. In comparison with longer periods (Figure 10A,C) it can be seen that the number of processed images was, in this case, more important for PSI analysis than the possible presence of snow cover. This is in accordance with the study performed by [56] according to their findings the best results are obtained from datasets with more than 50 images. Therefore, only results from time series A and C were used for further evaluation.
The deformation velocity values of PSI are measured along satellites in terms of LOS. Although it is possible to retrieve an estimation of true vertical and horizontal motion components from a descending and ascending track [57]; in this case it is not technically feasible. The main reason for not processing the datasets this way was the fact that the resulting PSs were rather sparse and those from an ascending track usually did not overlap with points of the descending pass.
Histograms and basic statistics have been calculated for datasets A and C (Figure 11).
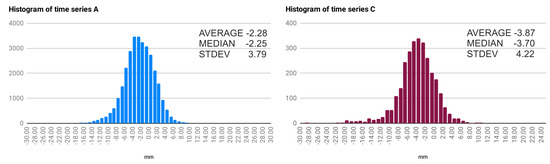
Figure 11.
Histograms and basic statistics for time series (A) and (C).
As can be seen in Figure 11, the histograms of time series A and C show that the whole dataset has a shift towards negative values with an average velocity of −2.28 and −3.87 mm/year, respectively. To make these values more comparable they were classified using standard deviation thresholding. Deformation values converted to standard deviation intervals allow the relative extreme values to be found independently of absolute numbers. Original velocity values and their standard deviation intervals are given in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
Values used for thresholding the PSI data of time series A.

Table 3.
Values used for thresholding the PSI data of time series C.
More detailed maps of time series A and C, where the PS points were classified using standard deviation thresholds, are presented in Figures 13, 15 and 16. In accordance with the single-pair DInSAR map (Figure 9) the four identical areas of subsidence were defined. The subsidence is more pronounced in the case of descending track results. In this case, viewing geometry influences the location of PSs, because of the eastward orientation of the slope on which the motorway is built. The Time series of the selected points (on maps highlighted with white backgrounds) are plotted in the graphs that complement the detailed maps (Figures 13, 15 and 16).
6. Validation
The study area was divided into four specific locations (Figure 12), where subsidence was detected using DInSAR and PSI. Three sites are located directly on the highway lanes, while one site is located in the Dobkovičky quarry. Results from the radar interferometry were validated using in situ techniques, such as geodetic measurements [58] and 3D inclinometers [59], both under continuous operation since December, 2016, and laser scanning [60], which have been employed at the second test site (Figure 12). In the following section the validation results are discussed in detail.
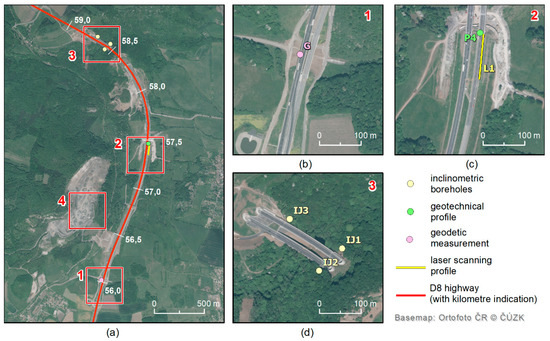
Figure 12.
(a) Overview of the four sites with detected subsidence: 1: Area of the highway embankment between Ječky Bridge and Dobkovičky Bridge at km 55,700−56,000; 2: Prackovice Bridge, 57,300–57,500 km; 3: Area between two highway tunnels (“Prackovice” and “Radejčín”) at km 58,400; 4: Dobkovičky quarry. (b–d) Localization of in situ measurements in polygons 1–3: inclinometers (IJ1-3), laser scanning (L1), and geodetic measurements (G, P4).
6.1. Area 1: Highway Embankment Between Ječky Bridge and Dobkovičky Bridge at km 55.700–56.000
The embankment between two bridges (Ječky and Dobkovičky) has been monitored for about five years using geodetic measurements, while its gradual consolidation was measured repeatedly within the landslide remediation project. Based on the geodetic measurements conducted in 2017, subsidence of the embankment is approximately 10 mm/year [59]. In 2018, the maximum subsidence was up to 6 mm which corresponds to a typical consolidation of the embankment. The conventional DinSAR shows the subsidence ranging between 20–50 mm per a three-month period (Figure 9). For the PSI, the subsidence was detected only by the descending geometry (see Figure 13). The maximum subsidence detected by the PSI (descending pass) was around 17 mm, while the average subsidence of all the PS points was around 11 mm for the observed period (April 2017–March 2018).
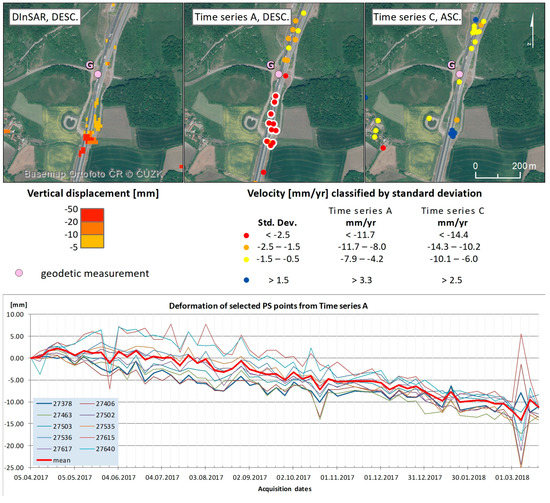
Figure 13.
Combined outcomes of the methods used for detecting land subsidence/uplift in area No. 1. From the left: the single-pair DInSAR and the PSI results (time series A and C), and a graph of the deformation of selected PS points from time series A, highlighted with white background on maps.
6.2. Area 2: Prackovice Bridge, 57,300–57,500 km
Due to extensive construction prior to opening the highway, this highway and its surroundings are very prone to vertical settling. In situ measurements in this part of the highway were made in an hour-interval using total station [59] in eight geotechnical profiles. One of them, P4, was chosen for validation (location of the profile, see Figures 12 and 15). Geotechnical profile P4 consists of nine points that are located at a very short distance (40 cm) from each other, therefore they are shown as a point on the map (Figure 12). Measurements taken at two points (No. 3 and No. 9) out of these nine points of profile P4 from April 2017 to April 2018 are plotted in a separate graph (Figure 14). Subsidence values measured in situ at point Nos. 3 and 9 in the P4 profile were 18 and 17 mm, respectively, between April 2017 and April 2018 (Figure 14).
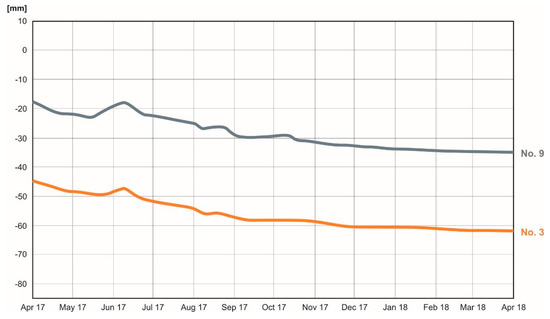
Figure 14.
Subsidence of the “Prague bridge abutment” of the Prackovice overpass at km 57,450, measured in situ by total station in the period between April 2017 and April 2018. The most significant subsidence was 18 and 17 mm at points No. 3 and No. 9 of the geotechnical profile P4.
The values derived from both scenarios correspond well with these in situ measurements. In the case of the PSI, significant subsidence was detected in both ascending and descending datasets (Figure 15). The conventional DInSAR method shows a subsidence for most of the coherent pixels varying between 10 and 20 mm within the three-month time period, for a few pixels a subsidence of up to 50 mm was detected. The average subsidence detected by the PSI was 20 mm/year for both descending and ascending datasets. Most vertical changes were observed for 2017, while in 2018 the gradual stabilization was confirmed by both PSI and in situ measurements (Figure 15).
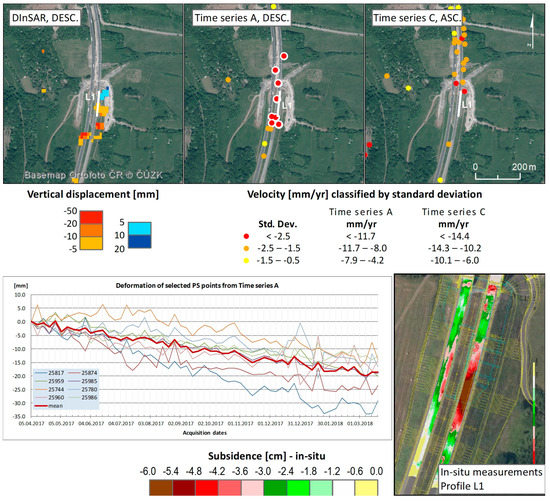
Figure 15.
Combined outcomes of the methods used for detecting land subsidence/uplift in area no. 3. In order from the left: the single-pair DInSAR and the PSI results (time series A and C) together with a graph of the deformation of selected PS points from time series A, highlighted with white background on maps. Subsidence measured using laser scanning between December 2016 and May 2017 on profile L1 (Fuchs, 2017).
The new landfill body of the embankment was constructed of lightweight ceramic gravel (Liapor) in winter 2016. Due to the completion of the structures in December 2016, it is obvious that consolidation of the embankment had to take place over the next few months, which was also proven by the DInSAR and in situ measurements. Further remediation interventions took place in the area around the embankment. Along the embankment, underground drainage gravel walls were excavated to a depth of 16 m in 2016 using drilled piles. Another construction element was an anchored pile wall beneath the embankment. Following completion of all these constructions at the end of 2016, it is logical that the surrounding land mass gradually settled to the stabilized state in the following years.
Other in situ measurements were done by laser-scanning on the highway surface (profile L1 in Figure 12 and Figure 15). A maximum subsidence value of 60 mm during the period between December 2016 and May 2017 was detected in the eastern lane [60].
Subsidence values obtained using laser scanning (L1) are higher than those obtained by the PSI. This fact may have different causes. Laser-scanning measurements predate the PSI by three months (December 2016–May 2017) and the subsidence could have been more significant in this period than in subsequent months. This is confirmed by the gradual stabilization in Figure 14. Another reason why the subsidence values are not equal could be the low density of PS points. It is possible that none of the PS points are located precisely at places with the highest subsidence rate according to the in situ measurements.
6.3. Area 3: Part between Two Highway Tunnels (“Prackovice” and “Radejčín”) at km 58,400
For polygon no. 3—the area connecting the Prackovice and Radejčín highway tunnels—single pair DinSAR indicated movements between 20 and 110 mm over a three-month period. PSI analysis indicated subsidence with average subsidence up to 15 mm in the descending geometry and 9 mm in the ascending geometry (Figure 16). However, due to the coherence issue, there were only three PS points for time series A (ascending geometry). The bridge’s pile foundation and slopes are monitored using borehole inclinometers (IJ1, IJ2, and IJ3, [60]) and these showed zero motion values in 2018. On the other hand, geodetic measurements [58] show subsidence of up to several centimeters for the valley surface. Such movements can be interpreted as a result of the volume changes in clay soils in the valley beneath the bridge. Due to rather dry weather conditions in 2017 and 2018, the clay soils were shrinking and losing their volume. The presence of soil compaction was also indicated by numerous shrinking cracks and subsequent exposed borehole heads in the valley (Figure 17).
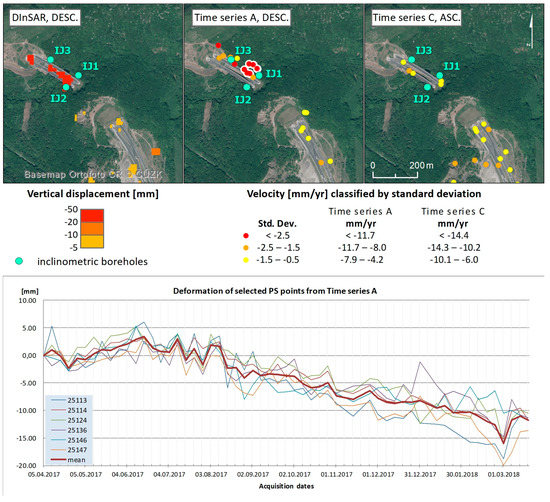
Figure 16.
Combined outcomes of the methods used for detecting land subsidence/uplift in area no. 3. In order from left: the single-pair DInSAR and the PSI results (time series A and C) together with a graph of deformation of selected PS points from time series A, highlighted with a white background on maps.
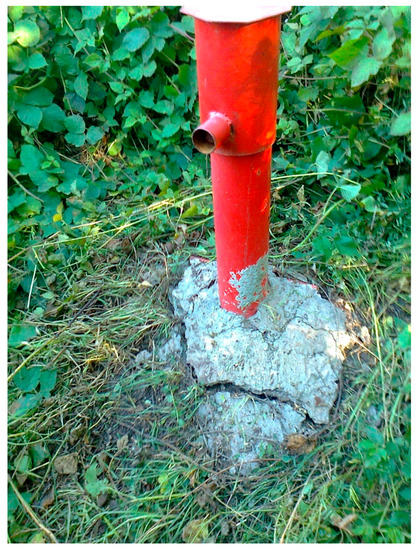

Figure 17.
Cracks on concrete at the borehole inclinometer IJ3. The picture shows the ground subsidence of the lower part of the column holding the instrument. Photo: Jan Suchý.
6.4. Area 4: Vertical Changes in the Dobkovičky Quarry
For the Dobkovičky quarry (the owner is Kámen Zbraslav a. s.) we did not have access to any in situ data. It is still an active quarry where basalt is mined. Therefore, the vertical surface changes identified by both scenarios can be linked with the on-going mining activities.
7. Discussion
The newly constructed highway D8 suffered a major landslide in 2013. This occurred in an area historically and geologically prone to land compaction and landslides. In this study, combined InSAR PSI analysis and DInSAR analysis applied to Sentinel-1 data (C band SAR) was assessed in order to detect ongoing subsidence indicated by the in situ measurements in several parts of the D8 highway in the area of the České Středohoří Mountains, Czech Republic in 2018. Both methods provided consistent results with the in situ measurements and proved its usability in densely vegetated landscapes.
PSI and DInSAR methods were combined in order to improve results and thus overcome the coherence limitations (citace) of each respective method in densely vegetated areas, such as the České Středohoří Mountains. Combining different SAR analysis approaches (e.g., DSM change detection or offset tracking) has been used in previous studies [61] in order to improve overall subsidence detection capabilities. Both DInSAR and PSI proved their usability in such a case study, however, a few specific features should be considered. As was shown in Figure 10, Figure 13, Figure 15 and Figure 16, thanks to the different viewing geometry, PSI analysis produces spatially different PS sets based on ascending (time series C) and descending (time series A) geometries. The primary PS point network is defined at the local maxima of average backscatter intensity [43] and, thus, can spatially differ in an ascending and descending pass. In the case of the D8 highway, the average distance of the detected descending and ascending-based subsidence was up to 100 meters, which is insignificant in respect to the size of the studied unstable area around the highway. Secondly, as described by [39], the PS measurements indicate ground displacement along the satellite LOS, therefore, the deformation values can indicate opposite movement directions if the ground moves away (descending pass) or towards the satellite (ascending pass). This particular case is notable in Area 1 (highway embankment between Ječky-Dobkovičky bridge) where the points of time series C show uplift, whereas the points of time series A show subsidence in southern part of the embankment.
The comparison of absolute ground deformation values obtained by the single-pair DInSAR (Scenario 1) and the PSI (Scenario 2, time series A) shows a big difference in absolute values. The maximal detected subsidence by the DInSAR procedure was approx. 50 mm in area Nos. 1, 2, and 3 (Figure 9, Figure 13, Figure 15 and Figure 16), whereas subsidence values achieved by the PSI approach do not exceed 20 mm (Figure 13, Figure 15 and Figure 16). This difference is even higher if the shorter time period of Scenario 1 is taken into account. In addition to DEM inaccuracy and sensor noise, atmospheric path delay (APD) is considered to be the major reason for such inconsistency. APD is driven mainly by changes in pressure, temperature, and water vapor in the troposphere between acquisitions [62], introducing uncertainty up to several centimeters [63]. As was pointed out by [64], the differential radar phase delays caused by APD can be comparable to or even higher than those expected from surface deformations [64]. It is for these reasons that the use of single-pair DInSAR should be considered as an indication of the monitored phenomena rather than an exact quantification of the subsidence process. The DInSAR method can also improve information on ground deformation in areas where only a reduced number of SAR data with irregular acquisition dates is available [65]. One of the major limitations of the single-pair DInSAR approach is the relatively difficult search for a suitable SAR-pair. This problem also occurred during the monitored period, where there was no suitable ascending pair and, therefore, only a descending pair was used for the analysis.
However, concerning spatial patterns, it was shown that both methods detected subsidence at the highway body in a similar manner. One of the major advantages of the conventional DInSAR is its accessibility in free software (e.g., SNAP with extensive user-community support), which allows SAR data to be processed even by less experienced users. The PSI approach could also be carried using freeware, however, it requires extensive knowledge of the technique [66].
8. Conclusions
The presented study demonstrated that both PSI and DInSAR techniques could be used for investigating slope movements along the newly constructed highway D8 in the densely vegetated area of the České Středohoří Mountains. The analysis of subsidence along the highway revealed the same spatial distribution as ground measurements, however, it also showed differences between the respective methods and their results, leading to different numerical results for the subsidence detected. The DInSAR method, though very simple, proved its ability to identify possible phenomena and to support other means of measurement. Based on a 12-month Sentinel-1 continuous PSI time series from both geometries, covering in situ displacement variation detected in the sensing period, it was possible to obtain a more detailed insight into the land deformation process. The maximum subsidence detected at the highway body came to 20 mm over the measured period. The successful utilization of InSAR techniques in a densely vegetated area proved its potential for further exploitation in monitoring the construction of linear structures. Sentinel-1 based analysis provides an unparalleled source of information in terms of data availability, revisiting a time period and the best compromise between spatial resolution and coherence features in vegetated areas, such as those examined. These attributes could have a positive influence on adopting DInSAR methods as a standard approach for validating in situ highway monitoring over a longer time range and larger areas in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: J.J., V.K.-S. and K.F.; methodology: K.F.; software: K.F. and J.J.; validation: P.K.; formal analysis: J.J. and V.K.-S.; investigation: K.F. and J.J.; resources: K.F. and J.J.; data curation: K.F.; writing—original draft preparation: K.F. and J.J.; writing—review and editing: V.K.-S. and P.K.; visualization: K.F. and J.J.; supervision: V.K.-S.; project administration: J.J.; funding acquisition: J.J.
Funding
This research was funded by the Czech Geological Survey´s internal project No. 321610.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like thank to Danielle Perissin for providing the license of SARPROZ and Matúš Bakoň for his instant help with this software.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chae, B.G.; Park, H.J.; Catani, F.; Simoni, A.; Berti, M. Landslide prediction, monitoring and early warning: A concise review of state-of-the-art. Geosci. J. 2017, 21, 1033–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Notti, D.; Mateos, R.M.; Ezquerro, P.; Centolanza, G.; Herrera, G.; Bru, G.; Sanabria, M.; Solari, L.; Duro, J.; et al. Mapping Vulnerable Urban Areas Affected by Slow-Moving Landslides Using Sentinel-1 InSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, A.; Malet, J.P.; Delacourt, C. Correlation of satellite image time-series for the detection and monitoring of slow-moving landslides. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Ciampalini, A.; Del Conte, S.; Lombardi, L.; Nocentini, M.; Gigli, G.; Ferretti, A.; Casagli, N. Exploitation of Amplitude and Phase of Satellite SAR Images for Landslide Mapping: The Case of Montescaglioso (South Italy). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14576–14596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, A.; Li, Z.; Hoey, T.; Muller, J.-P. Evaluating sub-pixel offset techniques as an alternative to D-InSAR for monitoring episodic landslide movements in vegetated terrain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaioni, M.; Longoni, L.; Melillo, V.; Papini, M. Remote Sensing for Landslide Investigations: An Overview of Recent Achievements and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9600–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Cigna, F.; Bianchini, S.; Hölbling, D.; Füreder, P.; Righini, G.; Del Conte, S.; Friedl, B.; Schneiderbauer, S.; Iasio, C.; et al. Landslide mapping and monitoring by using radar and optical remote sensing: Examples from the EC-FP7 project SAFER. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2016, 4, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Bardi, F.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Del Ventisette, C.; Farina, P.; Ferrigno, F.; Solari, L.; Casagli, N. The contribution of satellite SAR-derived displacement measurements in landslide risk management practices. Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 327–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przyłucka, M.; Herrera, G.; Graniczny, M.; Colombo, D.; Béjar-Pizarro, M. Combination of Conventional and Advanced DInSAR to Monitor Very Fast Mining Subsidence with TerraSAR-X Data: Bytom City (Poland). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5300–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; De, J. Large-area landslide detection and monitoring with ALOS / PALSAR imagery data over Northern California and Southern Oregon, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Iodice, A.; Magnapane, L.; Pietranera, L. Monitoring terrain movements by means of sparse SAR differential interferometric measurements. In Proceedings of the 20th IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 July 2000; pp. 3225–3227. [Google Scholar]
- Strozzi, T.; Farina, P.; Corsini, A.; Ambrosi, C.; Thüring, M.; Zilger, J.; Wiesmann, A.; Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C. Survey and monitoring of landslide displacements by means of L-band satellite SAR interferometry. Landslides 2005, 2, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catani, F.; Farina, P.; Moretti, S.; Nico, G.; Strozzi, T. On the application of SAR interferometry to geomorphological studies: Estimation of landform attributes and mass movements. Geomorphology 2005, 66, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabro, M.D.; Schmidt, D.A.; Roering, J.J. An examination of seasonal deformation at the Portuguese Bend landslide, southern California, using radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, F02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; Mazzanti, P.; Esposito, C.; Crosetto, M.; Mugnozza, G.S. First insights on the potential of Sentinel-1 for landslides detection. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasowski, J.; Bovenga, F. Investigating landslides and unstable slopes with satellite multitemporal interferometry: Current issues and future perspectives. Eng. Geol. 2014, 174, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlögel, R.; Thiebes, B.; Mulas, M.; Cuozzo, G.; Notarnicola, C.; Schneiderbauer, S.; Crespi, M.; Mazzoni, A.; Mair, V.; Corsini, A. Multi-Temporal X-Band Radar Interferometry Using Corner Reflectors: Application and Validation at the Corvara Landslide (Dolomites, Italy). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Broquetas, A. Linear and Nonlinear Terrain Deformation Maps from a Reduced Set of Interferometric SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A New Method for Measuring Deformation on Volcanoes and Other Natural Terrains Using Insar Persistent Scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent Scatterer InSAR for Crustal Deformation Analysis, with Application to Volcán Alcedo, Galapagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Biescas, E.; Duro, J.; Closa, J.; Arnaud, A. Generation of Advanced ERS and Envisat Interferometric SAR Products Using the Stable Point Network Technique. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, T. Repeat-pass SAR Interferometry with Partially Coherent Targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Lundgren, P.; Manzo, M.; Casu, F. Satellite radar interferometry time series analysis of surface deformation for Los Angeles, California. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L23–L613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Manunta, M.; Ardizzone, F.; Pepe, A.; Cardinali, M.; Zeni, G.; Reichenbach, P.; Lanari, R. Analysis of Ground Deformation Detected Using the SBAS-DInSAR Technique in Umbria, Central Italy. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2009, 166, 1425–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; García-Davalillo, J.C.; Guerrero, J.; Notti, D.; Galve, J.P.; Fernández-Merodo, J.A.; Cooksley, G. Multi-sensor advanced DInSAR monitoring of very slow landslides: the Tena Valley case study (Central Spanish Pyrenees). Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Castaldo, R.; Lollino, P.; Tizzani, P.; Guzzetti, F.; Lanari, R.; Angeli, M.-C.; Pontoni, F.; Manunta, M. Enhanced landslide investigations through advanced DInSAR techniques: The Ivancich case study, Assisi, Italy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 142, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Li, Z.; Tomás, R.; Liu, G.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Chen, J.; Stockamp, J. Monitoring activity at the Daguangbao mega-landslide (China) using Sentinel-1 TOPS time series interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Devanthery, N.; Cuevas-Gonzalez, M.; Barra, A.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Using Sentinel-1 Data. In Proceedings of the XXIII ISPRS Congress International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–19 July 2016; Volume XLI-B7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuti, P.; Casagli, N.; Ermini, L.; Fanti, R.; Farina, P. Landslide activity as a geoindicator in Italy: Significance and new perspectives from remote sensing. Environ Geol. 2004, 45, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Wasowski, J. Investigating landslides with space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) interferometry. Eng. Geol. 2006, 88, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovenga, F.; Wasowski, J.; Nitti, D.O.; Nutricato, R.; Chiaradia, M.T. Using COSMO/SkyMed X-band and ENVISAT C-band SAR interferometry for landslides analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofani, V.; Raspini, F.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) Technique for Landslide Characterization and Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1045–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Ventisette, C.; Righini, G.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Multitemporal landslides inventory map updating using spaceborne SAR analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O. Persistent scatterer interferometry: Potentials and limits. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Hannover Workshop: High-Resolution Earth Imaging for Geospatial Information, Hannover, Germany, 2–5 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Czikhardt, R.; Papco, J.; Bakon, M.; Liscak, P.; Ondrejka, P.; Zlocha, M. Ground Stability Monitoring of Undermined and Landslide Prone Areas by Means of Sentinel-1 Multi-Temporal InSAR, Case Study from Slovakia. Geosciences 2017, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.; Solari, L.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Monserrat, O.; Bianchini, S.; Herrera, G.; Crosetto, M.; Sarro, R.; González-Alonso, E.; Mateos, R.M.; et al. A Methodology to Detect and Update Active Deformation Areas Based on Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Farolfi, G.; Rosi, A.; Raspini, F.; Casagli, N. Subsidence Evolution of the Firenze–Prato–Pistoia Plain (Central Italy) Combining PSI and GNSS Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Klimeš, J.; Frey, H.; Caduff, R.; Huggel, C.; Wegmüller, U.; Rapre, A.C. Satellite SAR interferometry for the improved assessment of the state of activity of landslides: A case study from the Cordilleras of Peru. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Del Soldato, M.; Solari, L.; Novali, F.; Del Conte, S.; Rucci, A.; Ferretti, A.; Casagli, N. Continuous, semi-automatic monitoring of ground deformation using Sentinel-1 satellites. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T. SARPROZ InSAR Tool for Urban Subsidence/manmade Structure Stability Monitoring in China. Proc. of ISRSE 2011, Sydney (Australia). Available online: http://www.isprs:proceedings/2011/ISRSE-34/211104015Final00632.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- Roháč, J.; Scaringi, G.; Boháč, J.; Kycl, P.; Najser, J. Revisiting strength concepts and correlations with soil index properties: insights from the Dobkovičky landslide in Czech Republic. Landslides 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasek, J.; Janek, J. Engineering Geological Survey of D8 Motorway in part Chotiměř –Radejčín, km 62.2–67.8., I. stage. In Final Report of Geological Institute of Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences; Geological Institude: Prague, Czech Republic, 1972. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Ground Instabilities Map. Praha, Czech Geological Survey. Available online: https://mapy.geology.cz/svahove_nestability/ (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Lisec, M.; Kycl, P.; Rapprich, V. Landslide on D8 highway at Dobkovičky–the animation. Czech Geological Survey, 2018 (in Czech). Available online: https://youtu.be/S9hyHsatu18?list=PLaDi6UUdmA3TlddYfbmochSYerTUxa_Py (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- ESA Sentinel Online. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/ (accessed on 11 November 2018).
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis. Kluwer Academic; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, D. Surface subsidence monitoring with NEST. SAR-EDU Tutorial ID 3102. Available online: https://eo-college:resources/insar_deformation/ (accessed on 5 December 2018).
- Crosetto, M.; Devanthery, N.; Cuevas-Gonzalez, M.; Monserrat, O.; Crippa, B. Exploitation of the full potential of PSI data for subsidence monitoring. Proc. IAHS 2015, 372, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Perissin, D. Monitoring Ground Subsidence in Hong Kong via Spaceborne Radar: Experiments and Validation. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10715–10736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in Interferometric Radar Echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Rocca, F. High Accuracy Urban DEM Using Permanent Scatterers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3338–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. SAR monitoring of progressive and seasonal ground deformation using the permanent scatterers technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1685–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 133, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, J. Geodetic protocol No. 2.Trimble DiNi, D0805 km 57.250–57.450. RIDGES s. r. o. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- SG Geotechnika. Available online: https://www.barab.eu (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- Automatic Sensing. Available online: https://app.automaticsensing.com (accessed on 28 October 2018).
- Kyriou, A.; Nikolakopoulos, K. Assessing the suitability of Sentinel-1 data for landslide mapping. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R. Atmospheric limitations to repeat-track interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 2517–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, N.F.; Wadge, G. Towards Operational Repeat-Pass SAR Interferometry at Active Volcanoes. Nat. Hazards 2004, 33, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Peduto, D. Analysis at medium scale of low-resolution DInSAR data in slow-moving landslide-affected areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Foumelis, M.; Stewart, C.; Hooper, A. Measuring Urban Subsidence in the Rome Metropolitan Area (Italy) with Sentinel-1 SNAP-StaMPS Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).