Tropospheric Delay Correction Based on a Three-Dimensional Joint Model for InSAR
Abstract
1. Introduction
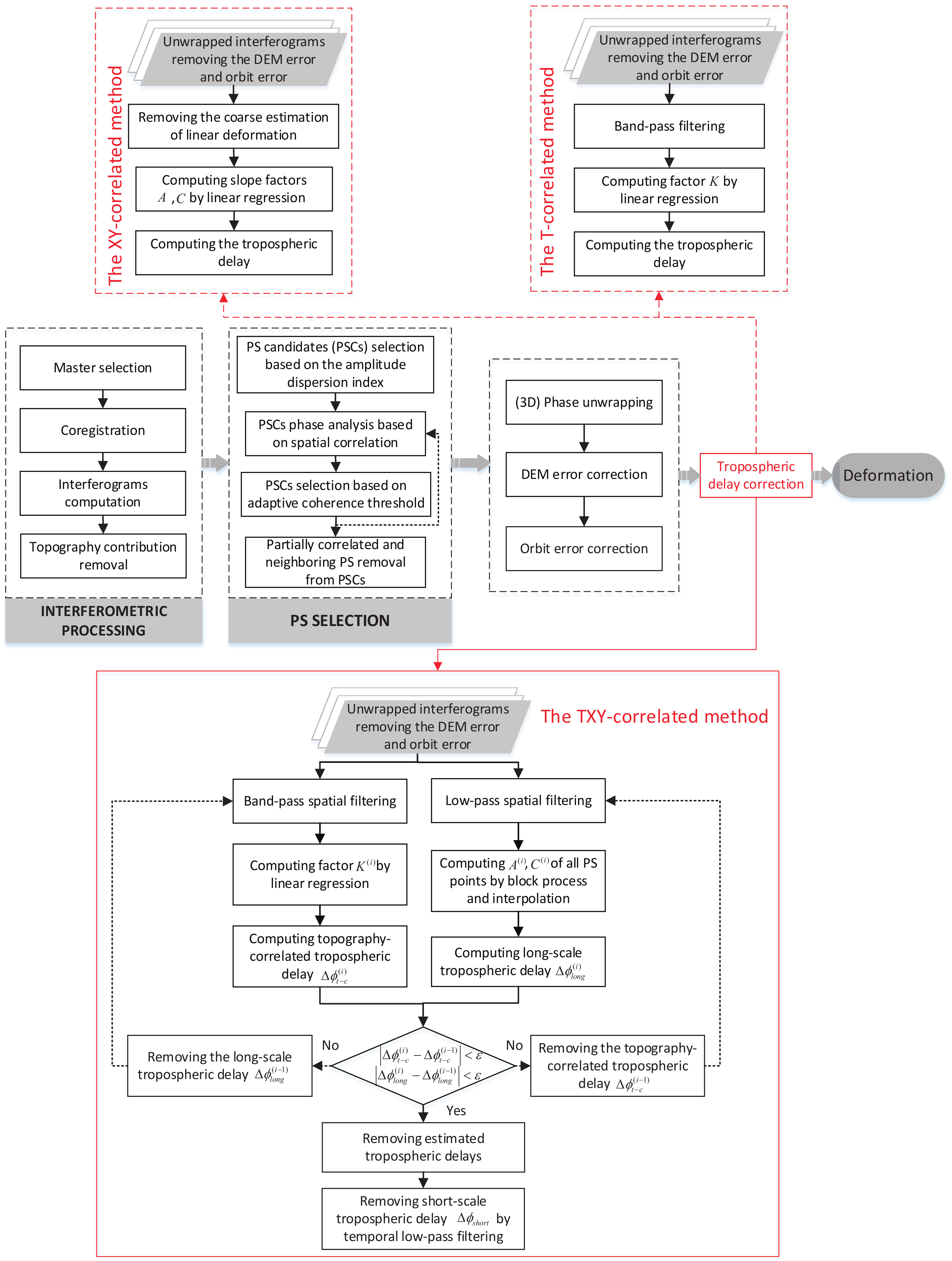
2. Methodology
2.1. The Three-Dimensionally Joint Model
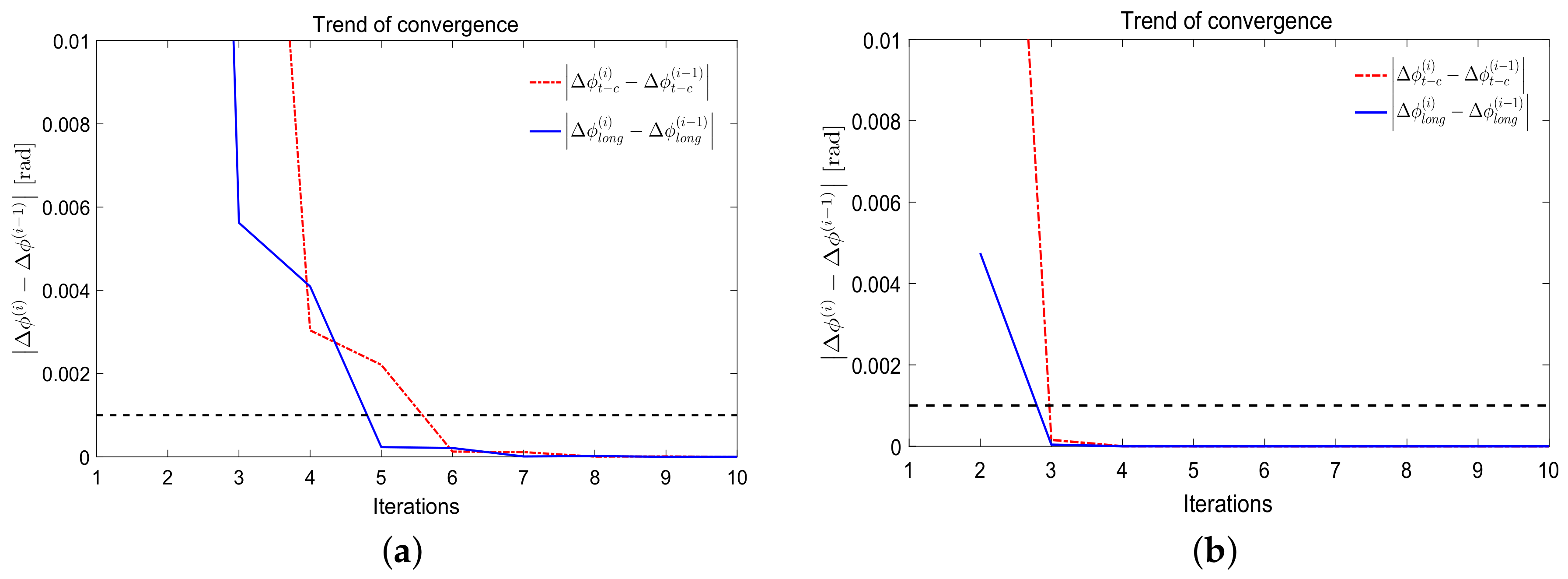
2.2. The TXY-Correlated Method
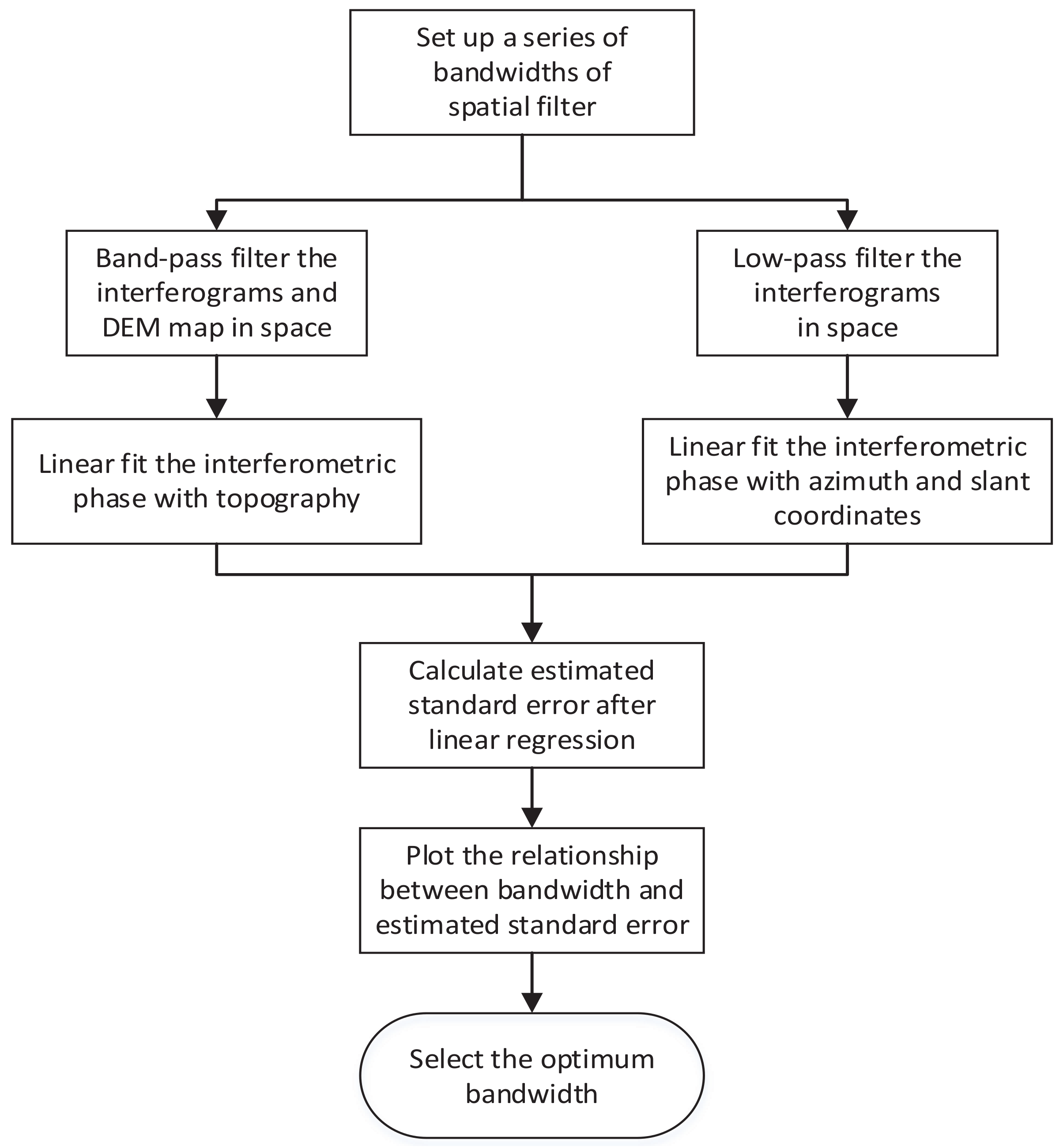
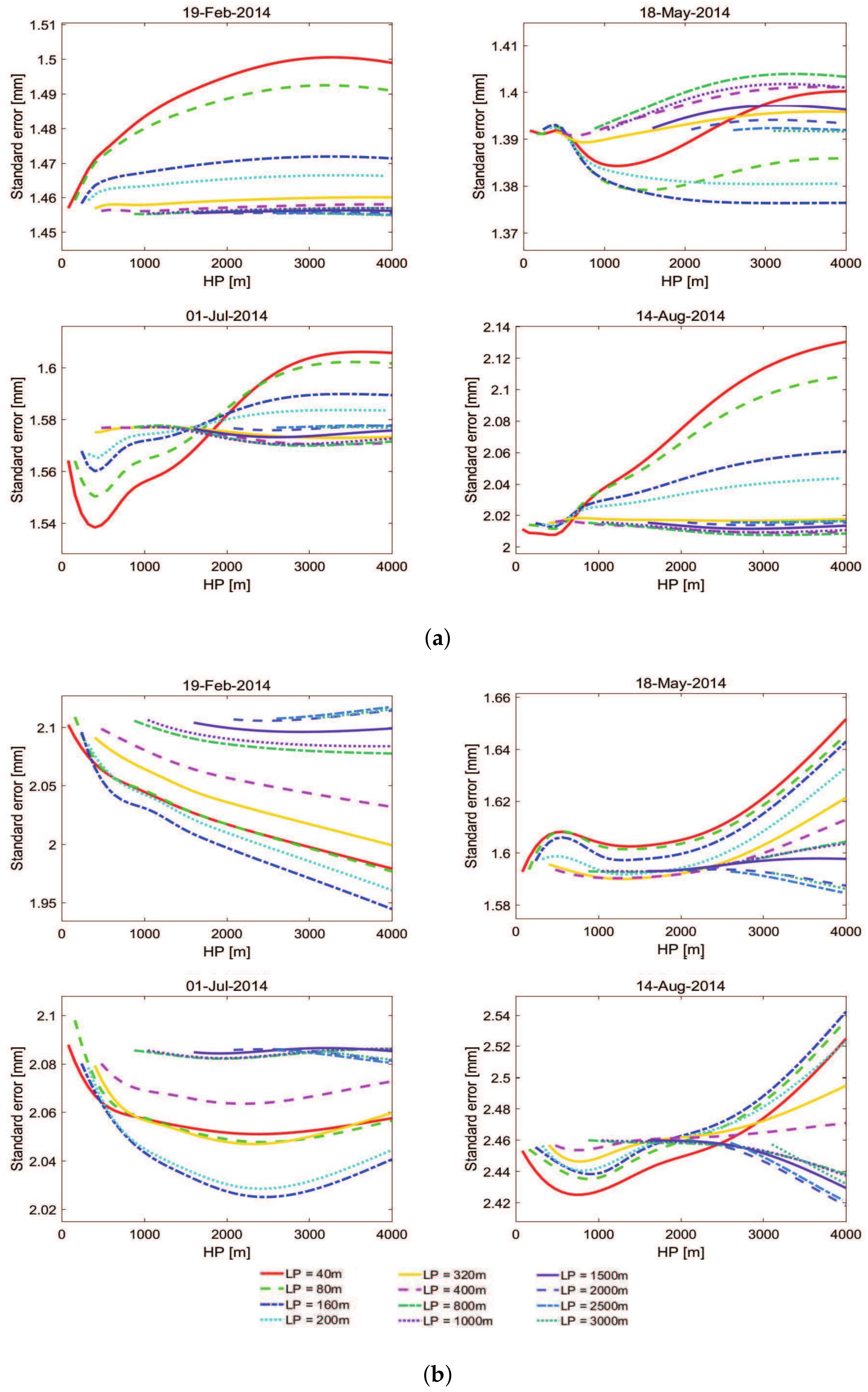
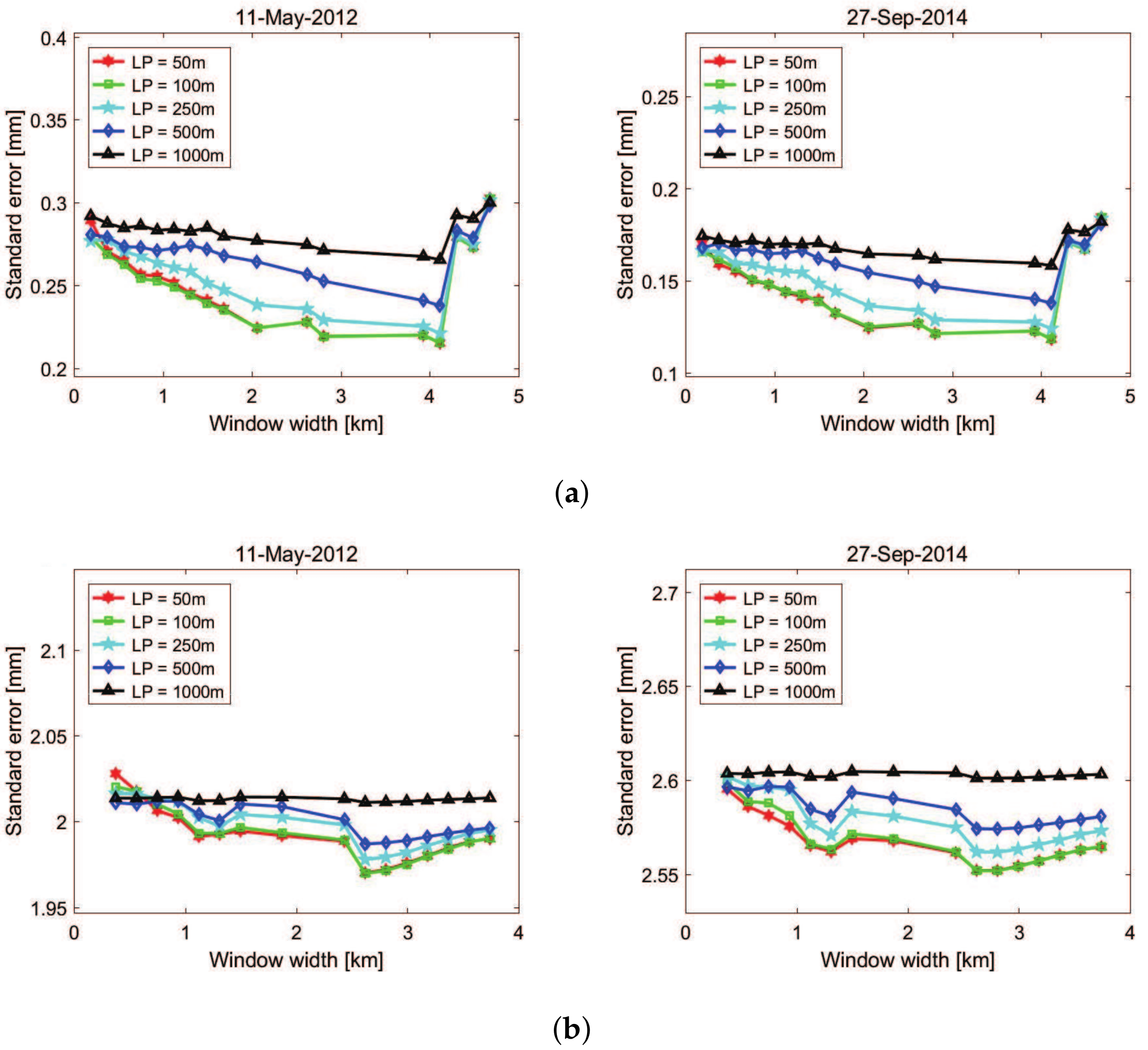
2.3. Selection of Spatial Filter Bandwidth
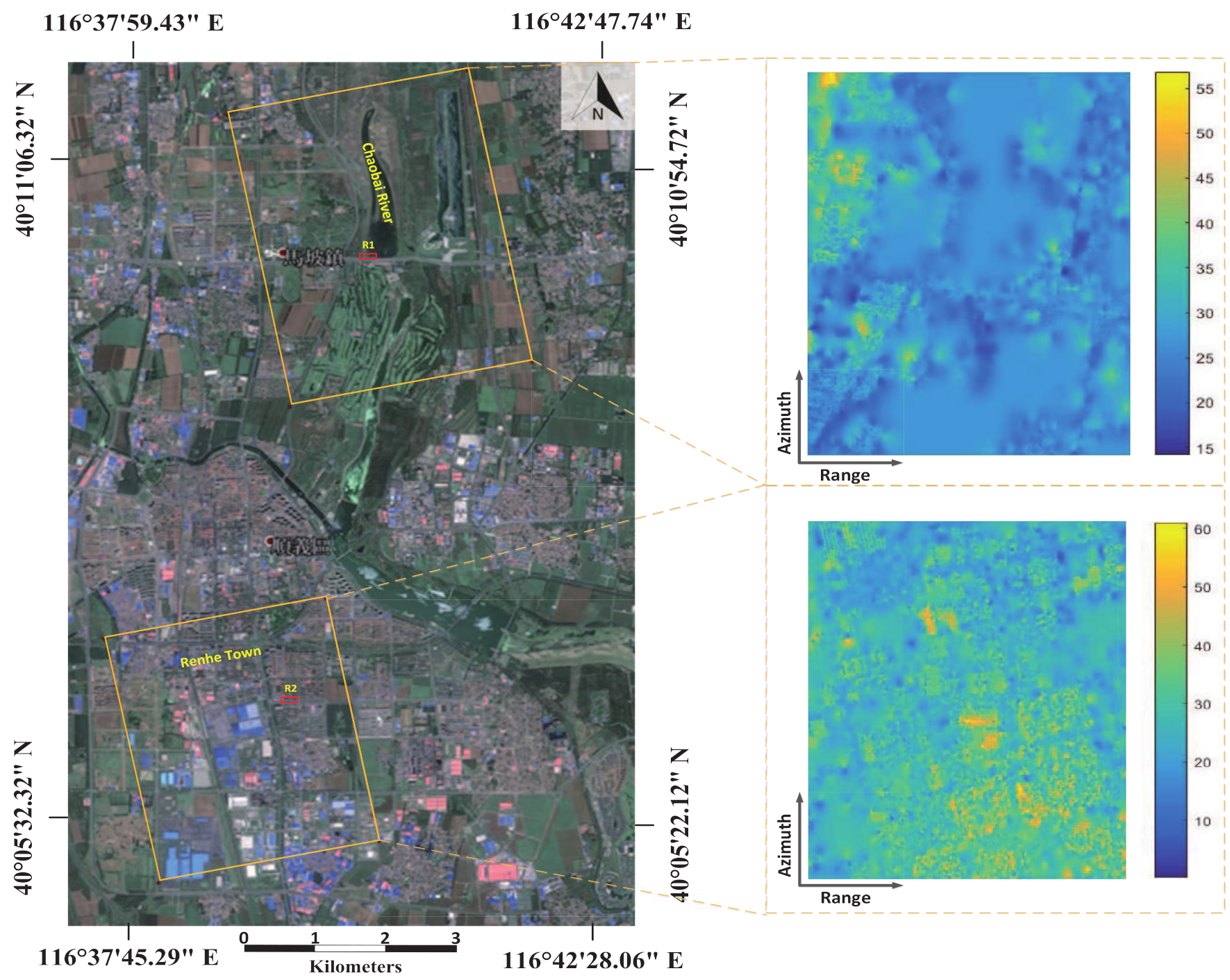
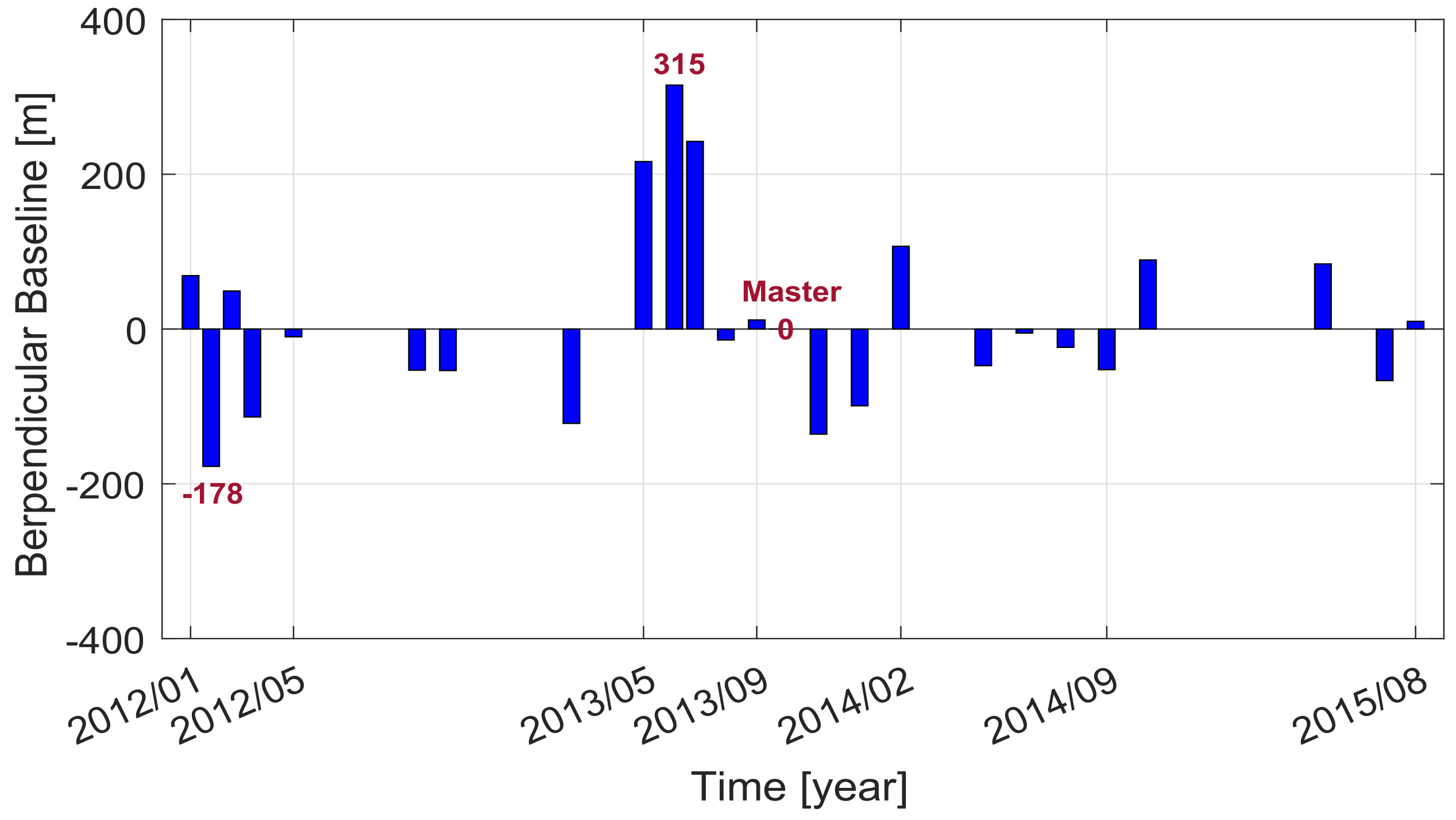
3. Study Area and Dataset Used
4. Results
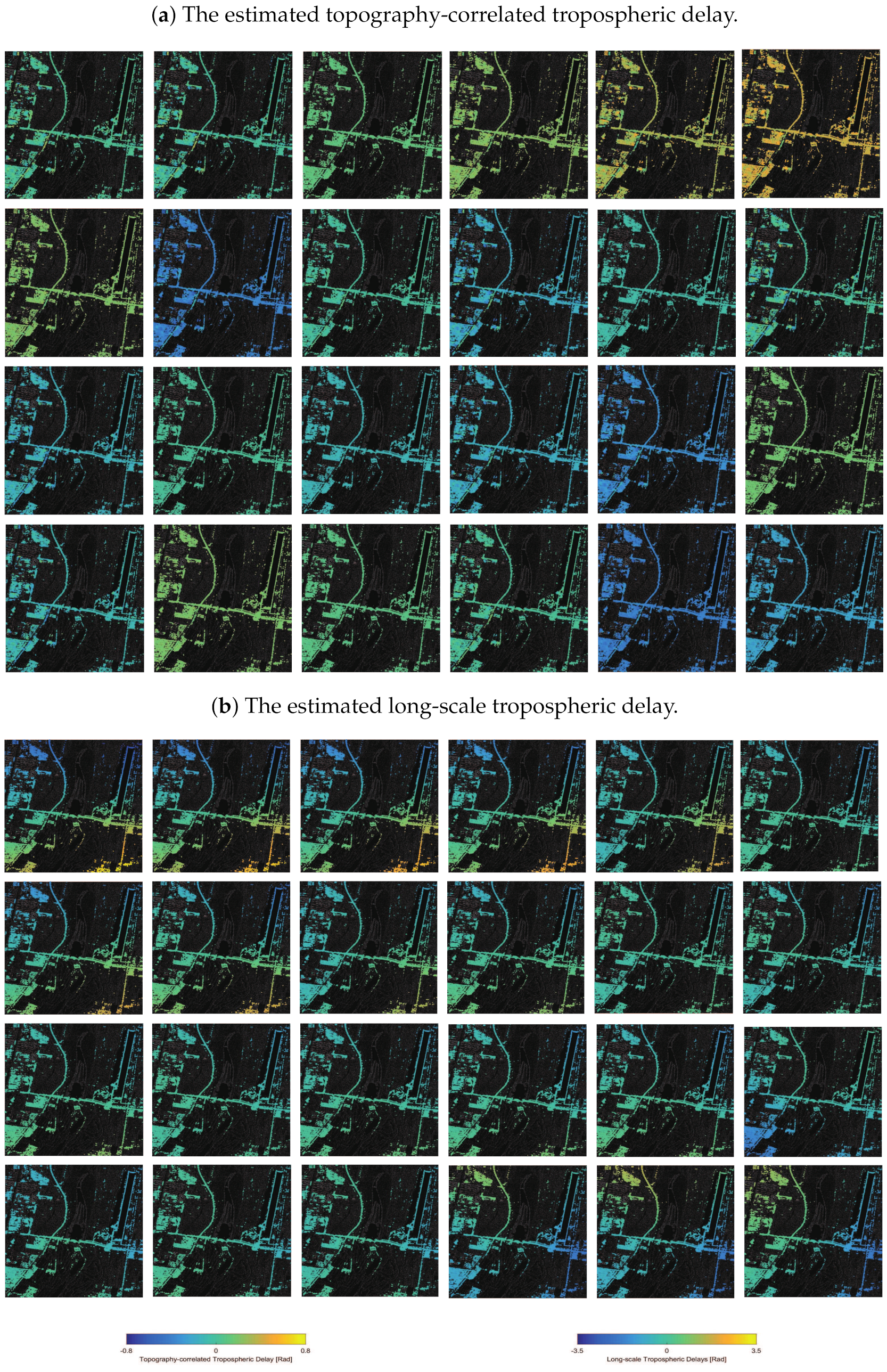
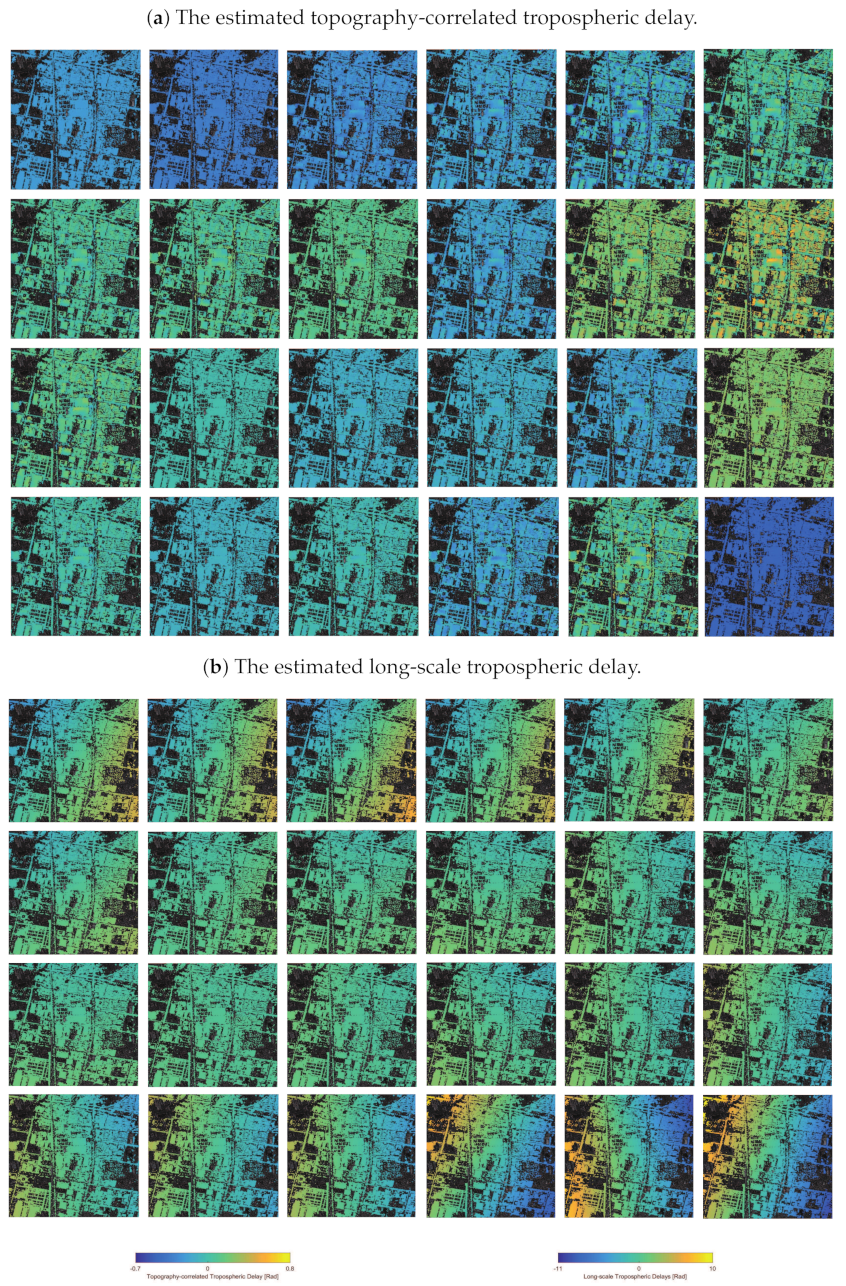
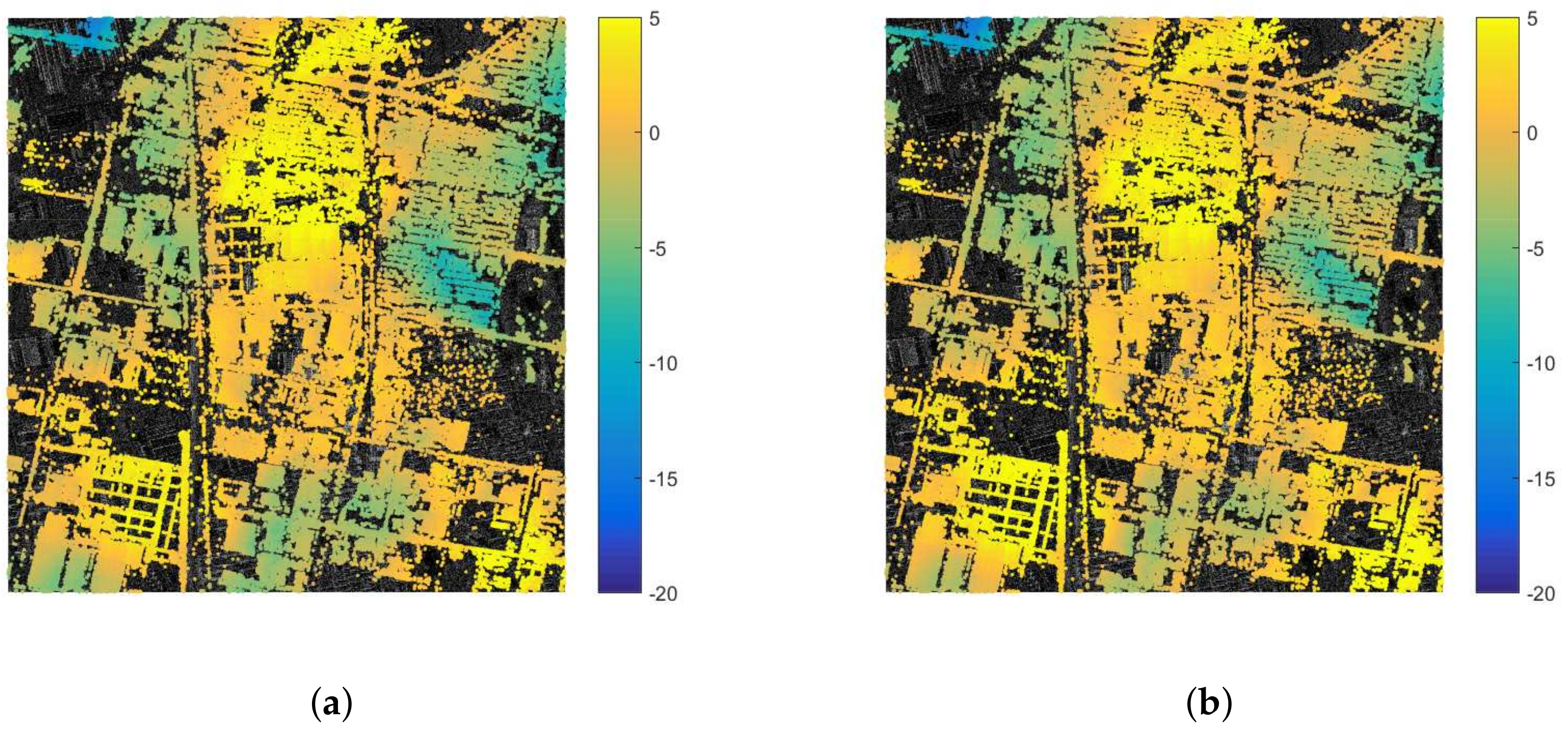
4.1. Estimated Tropospheric Delays
4.2. Residual Tropospheric Delays
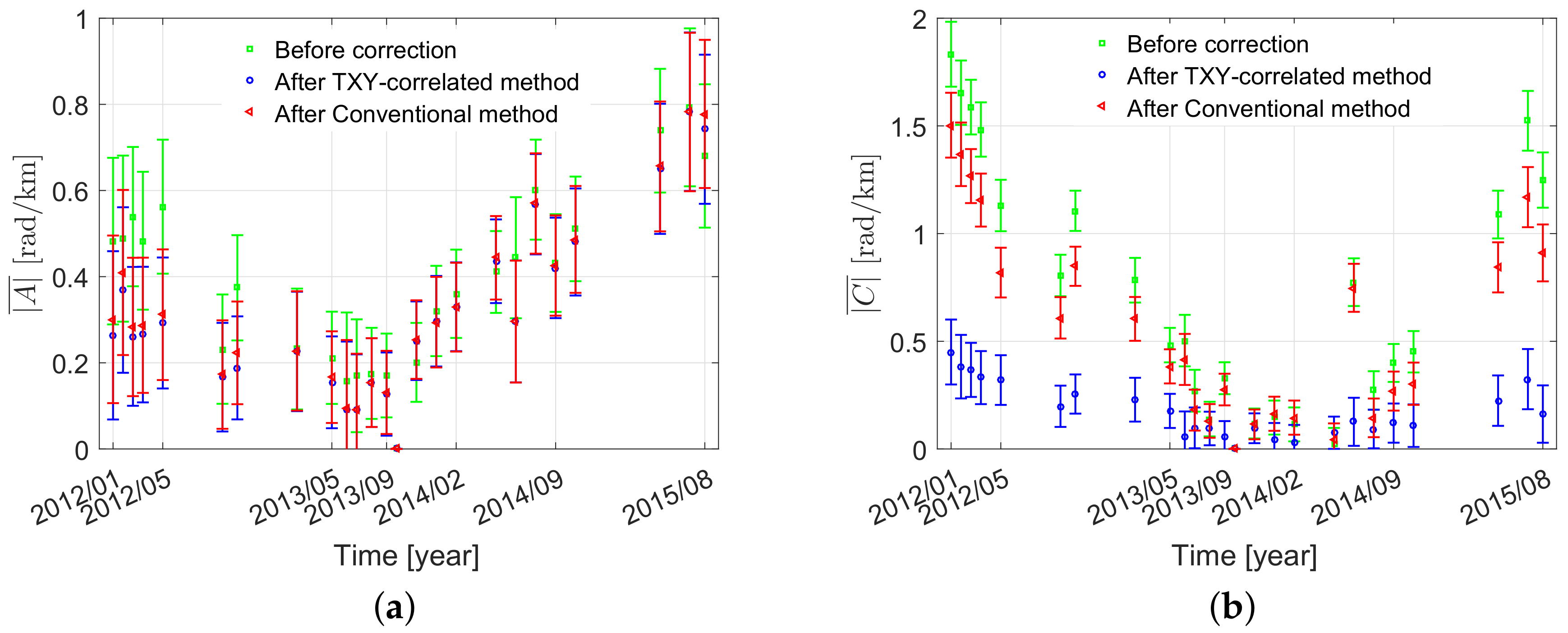
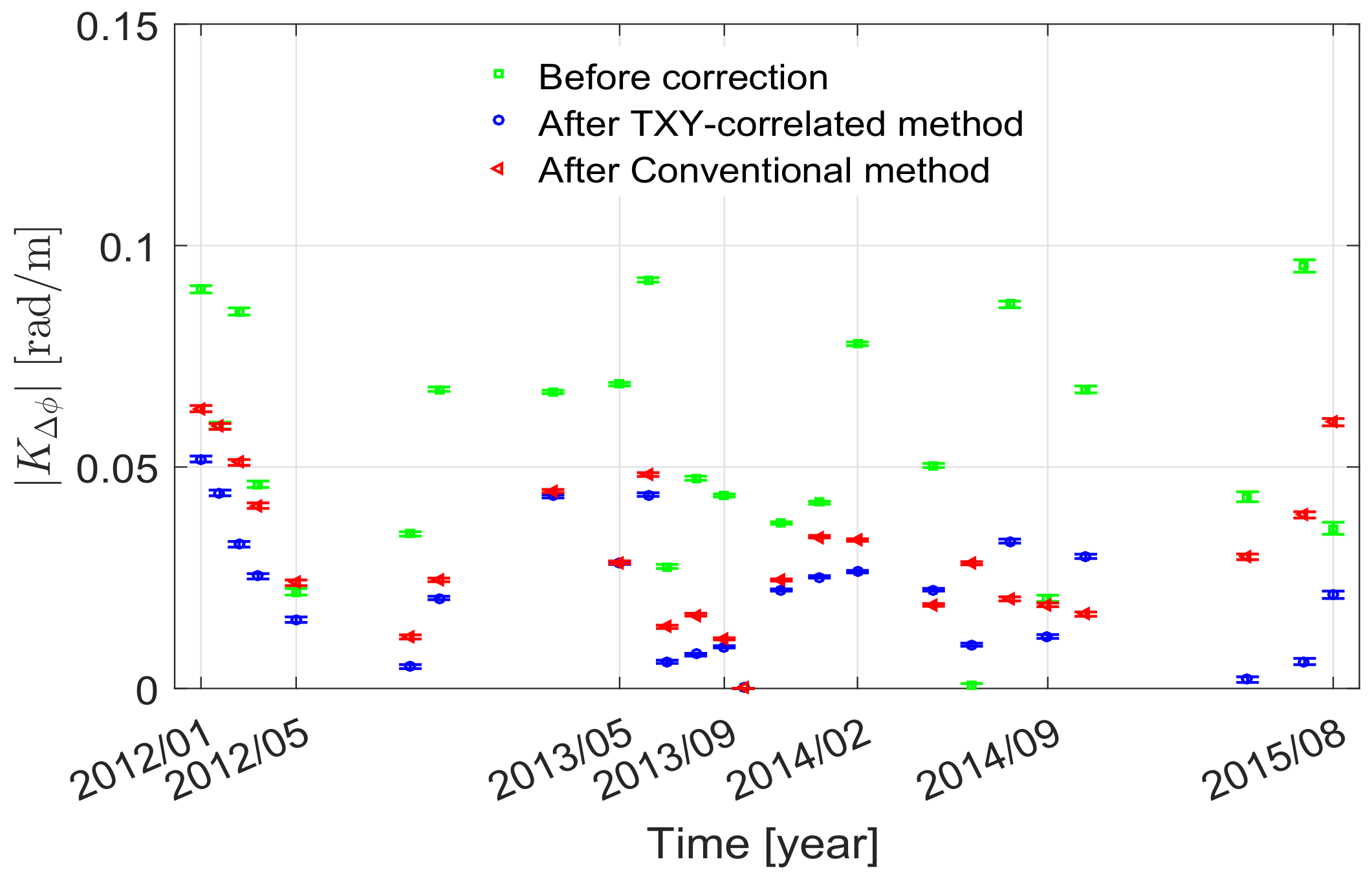
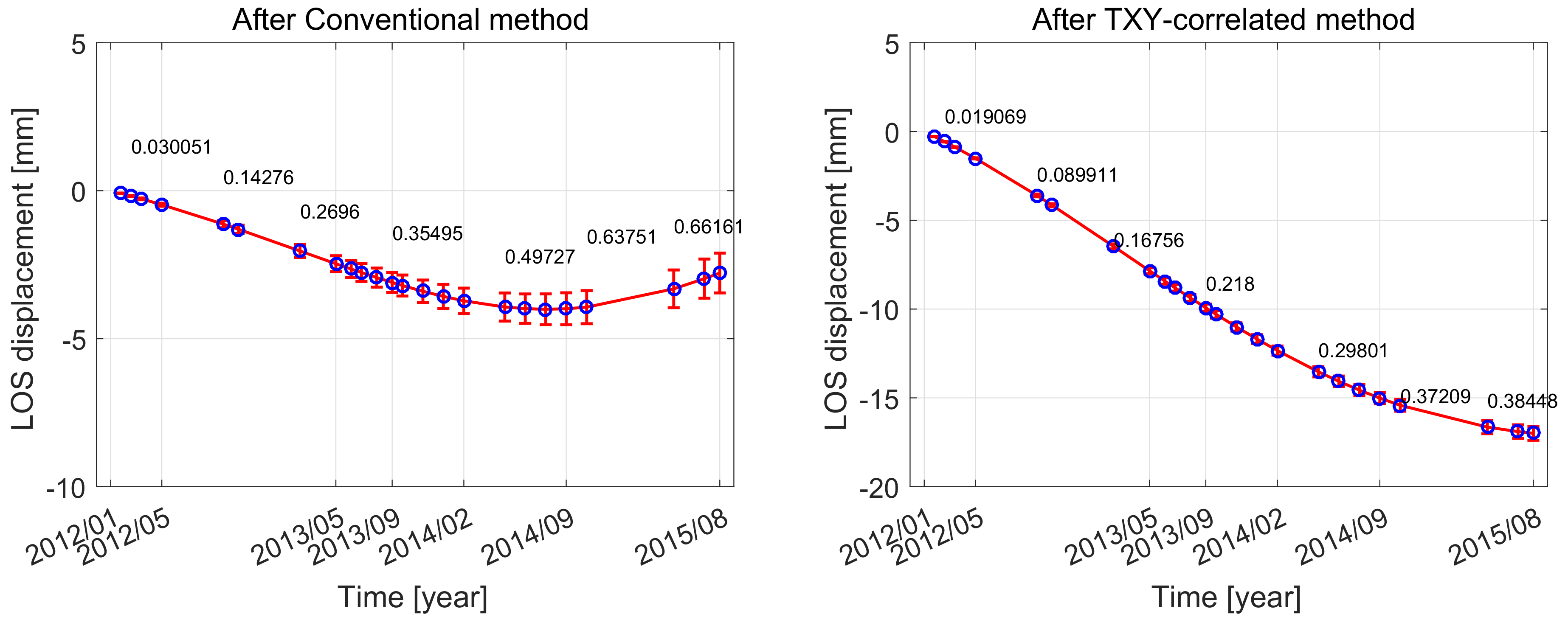
4.2.1. The Chaobai River Site
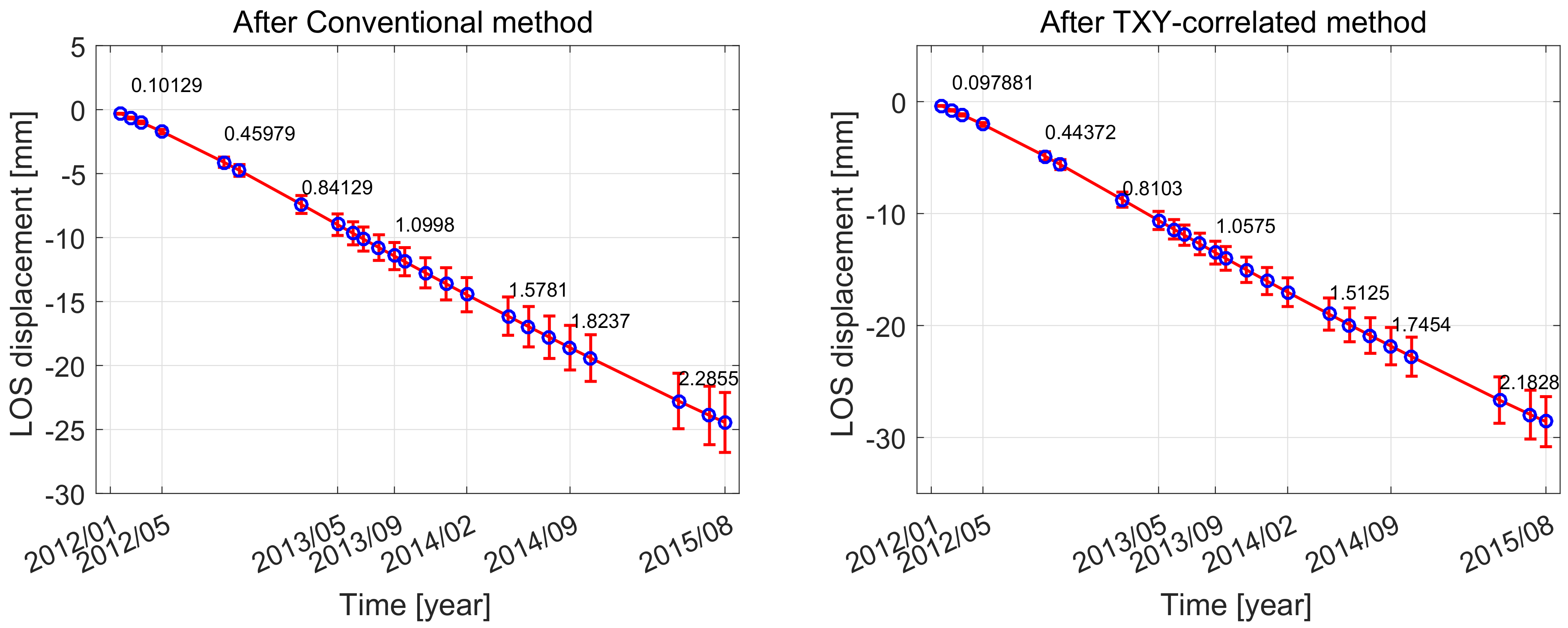
4.2.2. The Renhe Town
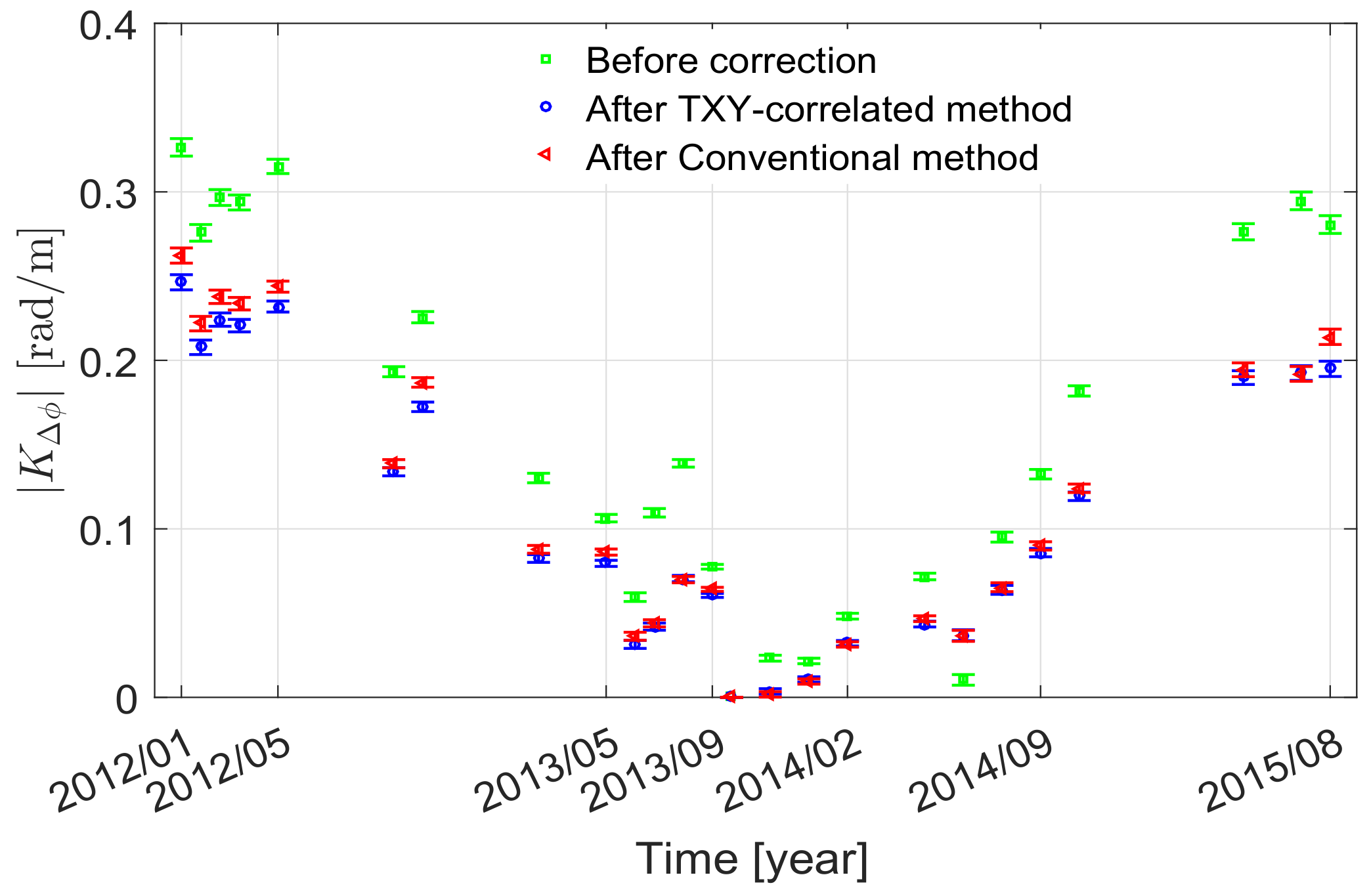
4.3. Deformation Estimation Accuracy
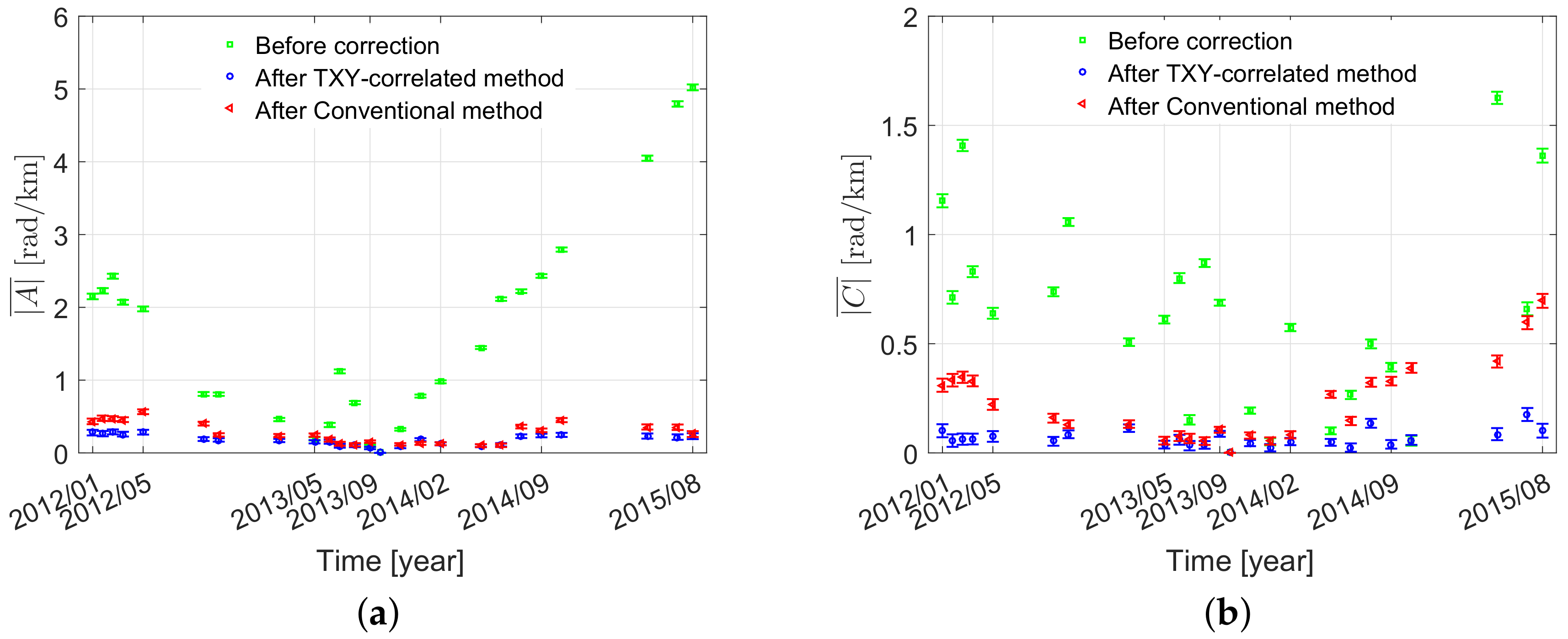
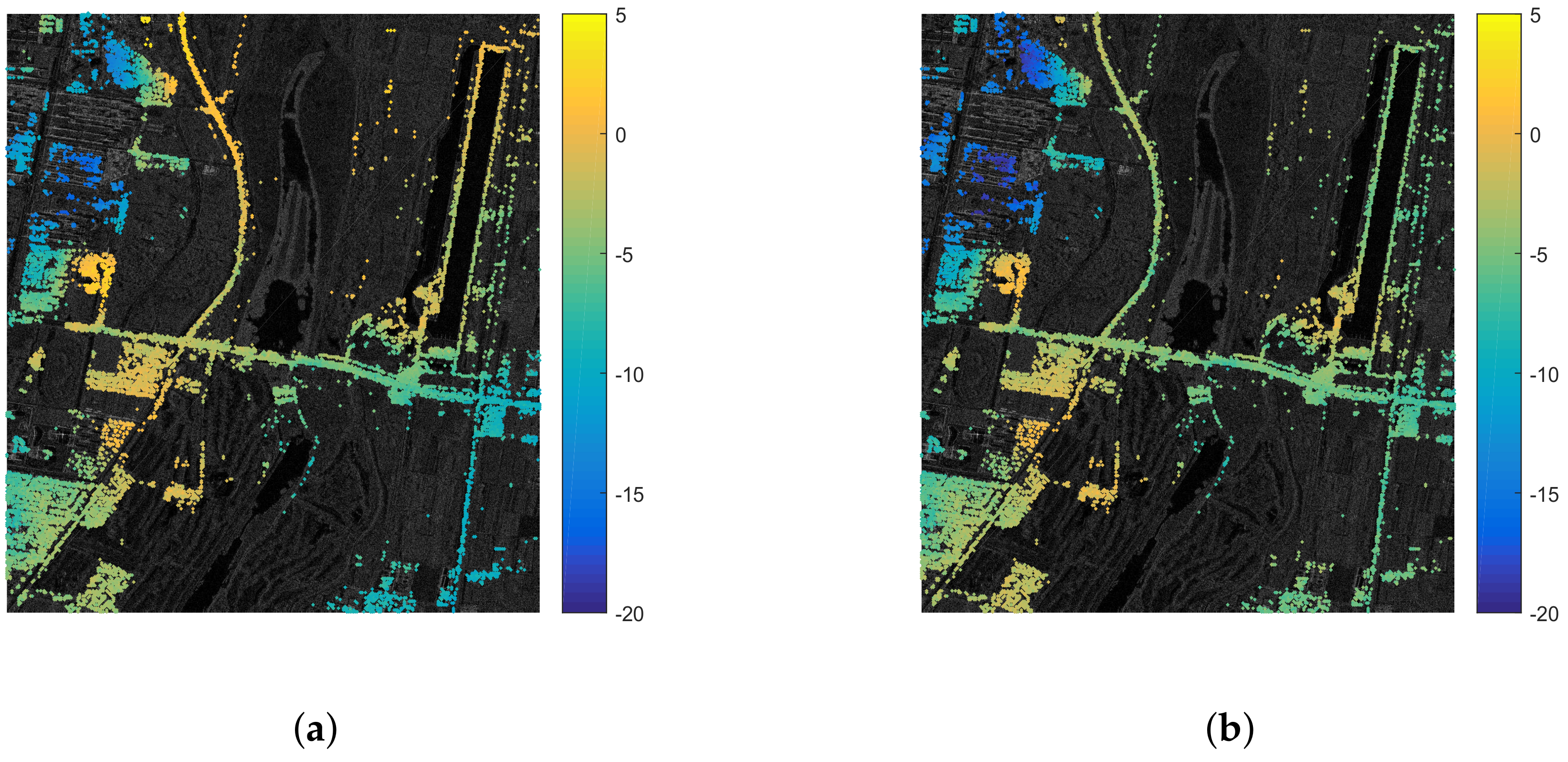
4.3.1. The Chaobai River Site
4.3.2. The Renhe Town
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.; Rossi, M.; Adragna, F. Radar interferometric mapping of deformation in the year after the Landers earthquake. Nature 1994, 369, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry to measure Earth’s surface topography and its deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S. Atmospheric effects in interferometric synthetic aperture radar surface deformation and topographic maps. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 7547–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Pietrzak, J.; Simons, W.; Cui, H.; Riva, R.; Naeije, M.; van Scheltinga, A.T.; Schrama, E.; Stelling, G.; Socquet, A. Importance of horizontal seafloor motion on tsunami height for the 2011 Mw= 9.0 Tohoku-Oki earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 361, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.L.; Mattar, K.E.; Sofko, G. Influence of ionospheric electron density fluctuations on satellite radar interferometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.; Hooper, A.; Wright, T. Reassessing the 2006 Guerrero slow-slip event, Mexico: Implications for large earthquakes in the Guerrero Gap. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 1357–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bekaert, D.; Walters, R.; Wright, T.; Hooper, A.; Parker, D. Statistical comparison of InSAR tropospheric correction techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doin, M.; Lasserre, C.; Peltzer, G.; Cavalié, O.; Doubre, C. Estimating tropospheric phase delay in SAR interferograms using Global Atmospheric Models. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–19 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jolivet, R.; Grandin, R.; Lasserre, C.; Doin, M.P.; Peltzer, G. Systematic InSAR tropospheric phase delay corrections from global meteorological reanalysis data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, R.; Agram, P.S.; Lin, N.Y.; Simons, M.; Doin, M.P.; Peltzer, G.; Li, Z. Improving InSAR geodesy using global atmospheric models. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 2324–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hanssen, R.; Mika, Á. On the value of high-resolution weather models for atmospheric mitigation in SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 2, pp. 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- Bennartz, R.; Fischer, J. Retrieval of columnar water vapour over land from backscattered solar radiation using the Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 78, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fielding, E.J.; Cross, P.; Muller, J.P. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar atmospheric correction: Medium resolution imaging spectrometer and advanced synthetic aperture radar integration. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fielding, E.J.; Cross, P.; Muller, J.P. InSAR water vapour correction models: GPS, MODIS, MERIS and InSAR integration. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Fielding, E.; Cross, P.; Preusker, R. Advanced InSAR atmospheric correction: MERIS/MODIS combination and stacked water vapour models. Int. J. Remote Sen. 2009, 30, 3343–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Bock, Y.; Fang, P. Integrated satellite interferometry: Tropospheric noise, GPS estimates and implications for interferometric synthetic aperture radar products. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 27051–27067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuveni, Y.; Bock, Y.; Tong, X.; Moore, A.W. Calibrating interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) images with regional GPS network atmosphere models. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 202, 2106–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H. GPS meteorology: Remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 15787–15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.; Hooper, A.; Wright, T. A spatially variable power law tropospheric correction technique for InSAR data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, R.; Elliott, J.; Li, Z.; Parsons, B. Rapid strain accumulation on the Ashkabad fault (Turkmenistan) from atmosphere-corrected InSAR. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 3674–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.; Kealy, J.; Cherubini, T.; Businger, S.; Lu, Z.; Murphy, M. The utility of atmospheric analyses for the mitigation of artifacts in InSAR. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.L.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J.; Feng, G.C.; Long, J.P. Atmospheric effects on InSAR measurements and their mitigation. Sensors 2008, 8, 5426–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, J.; Tang, W. Correcting InSAR Topographically Correlated Tropospheric Delays Using a Power Law Model Based on ERA-Interim Reanalysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, J.; Chu, Z.; Tang, W.; Wang, B.; Li, D. A robust and multi-weighted approach to estimating topographically correlated tropospheric delays in radar interferograms. Sensors 2016, 16, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacourt, C.; Briole, P.; Achache, J. Tropospheric corrections of SAR interferograms with strong topography. Application to Etna. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 2849–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, C.W., Jr.; Dzurisin, D.; Ingebritsen, S.; Thatcher, W.; Lu, Z.; Iverson, J. Magmatic activity beneath the quiescent Three Sisters volcanic center, central Oregon Cascade Range, USA. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 26-1–26-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.n.N.; Simons, M.; Hetland, E.A.; Muse, P.; DiCaprio, C. A multiscale approach to estimating topographically correlated propagation delays in radar interferograms. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrada Baby, H.; Gole, P.; Lavergnat, J. A model for the tropospheric excess path length of radio waves from surface meteorological measurements. Radio Sci. 1988, 23, 1023–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.K.; Weintraub, S. The constants in the equation for atmospheric refractive index at radio frequencies. Proc. IRE 1953, 41, 1035–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.J. Persistent Scatter Radar Interferometry for Crustal Deformation Studies and Modeling of Volcanic Deformation. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University of Geophysics, Stanford, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis, with application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doin, M.; Cavalié, O.; Laserre, C.; Briole, P. Ground Motion Measurement in the Lake Mead Area (Nevada, USA), by DinSAR Time Series Analysis: Probing of the Lithosphere Rheological Structure. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- DiCaprio, C.J.; Simons, M. Importance of ocean tidal load corrections for differential InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, H. Research of features related to land subsidence and ground fissure disasters in the Beijing Plain. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 372, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lin, P.; Liu, J.; Xing, L.; Gao, Z. Restudy of the storage and migration model of the Quaternary groundwater in Beijing Plain area. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Zhou, C.; Chen, W.; Liang, Y.; Shi, M.; Si, Y. InSAR time-series investigation of long-term ground displacement at Beijing Capital International Airport, China. Tectonophysics 2016, 691, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitz, W.; Miller, D. The TerraSAR-X satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.J.; Hooper, A.J.; Hanssen, R.F.; Bastos, L.C.; Ruiz, A.M. Persistent scatterer InSAR: A comparison of methodologies based on a model of temporal deformation vs. spatial correlation selection criteria. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Biggs, J.; Parsons, B.; Wright, T. InSAR slip rate determination on the Altyn Tagh Fault, northern Tibet, in the presence of topographically correlated atmospheric delays. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Strategy | (rad/m) | (rad/km) | (rad/km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before correction | 0.16 ± 0.0031 | 0.39 ± 0.1293 | 0.73 ± 0.0992 |
| Conventional methods | 0.12 ± 0.0028 | 0.33 ± 0.1294 | 0.58 ± 0.0990 |
| TXY-correlated method | 0.11 ± 0.0027 | 0.31 ± 0.1296 | 0.18 ± 0.0991 |
| Strategy | (rad/m) | (rad/km) | (rad/km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before correction | 0.055 ± 0.00063 | 1.70 ± 0.0265 | 0.64 ± 0.0208 |
| Conventional methods | 0.031 ± 0.00045 | 0.23 ± 0.0264 | 0.23 ± 0.0207 |
| TXY-correlated method | 0.021 ± 0.00044 | 0.18 ± 0.0263 | 0.07 ± 0.0206 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Luo, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Tropospheric Delay Correction Based on a Three-Dimensional Joint Model for InSAR. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212542
Xu H, Luo Y, Yang B, Li Z, Liu W. Tropospheric Delay Correction Based on a Three-Dimensional Joint Model for InSAR. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(21):2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212542
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Huaping, Yao Luo, Bo Yang, Zhaohong Li, and Wei Liu. 2019. "Tropospheric Delay Correction Based on a Three-Dimensional Joint Model for InSAR" Remote Sensing 11, no. 21: 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212542
APA StyleXu, H., Luo, Y., Yang, B., Li, Z., & Liu, W. (2019). Tropospheric Delay Correction Based on a Three-Dimensional Joint Model for InSAR. Remote Sensing, 11(21), 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212542







