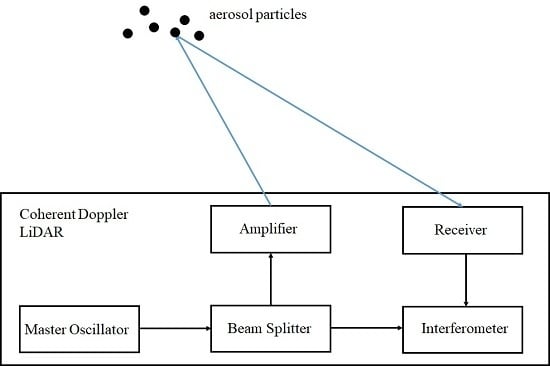
A Review of Progress and Applications of Pulsed Doppler Wind LiDARs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals of Coherent Doppler Wind LiDAR
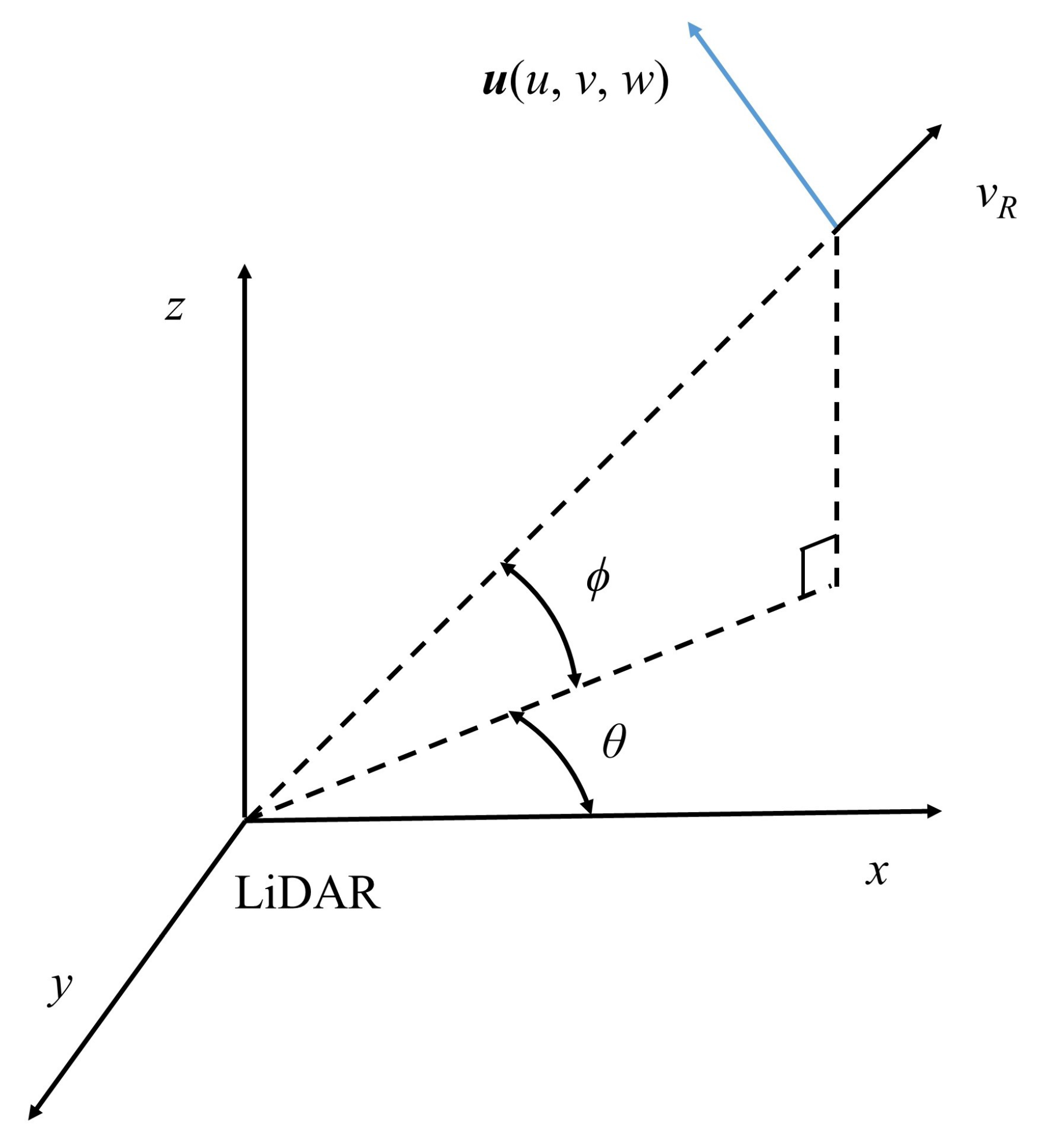
2.1. Measurement Principles and Uncertainties
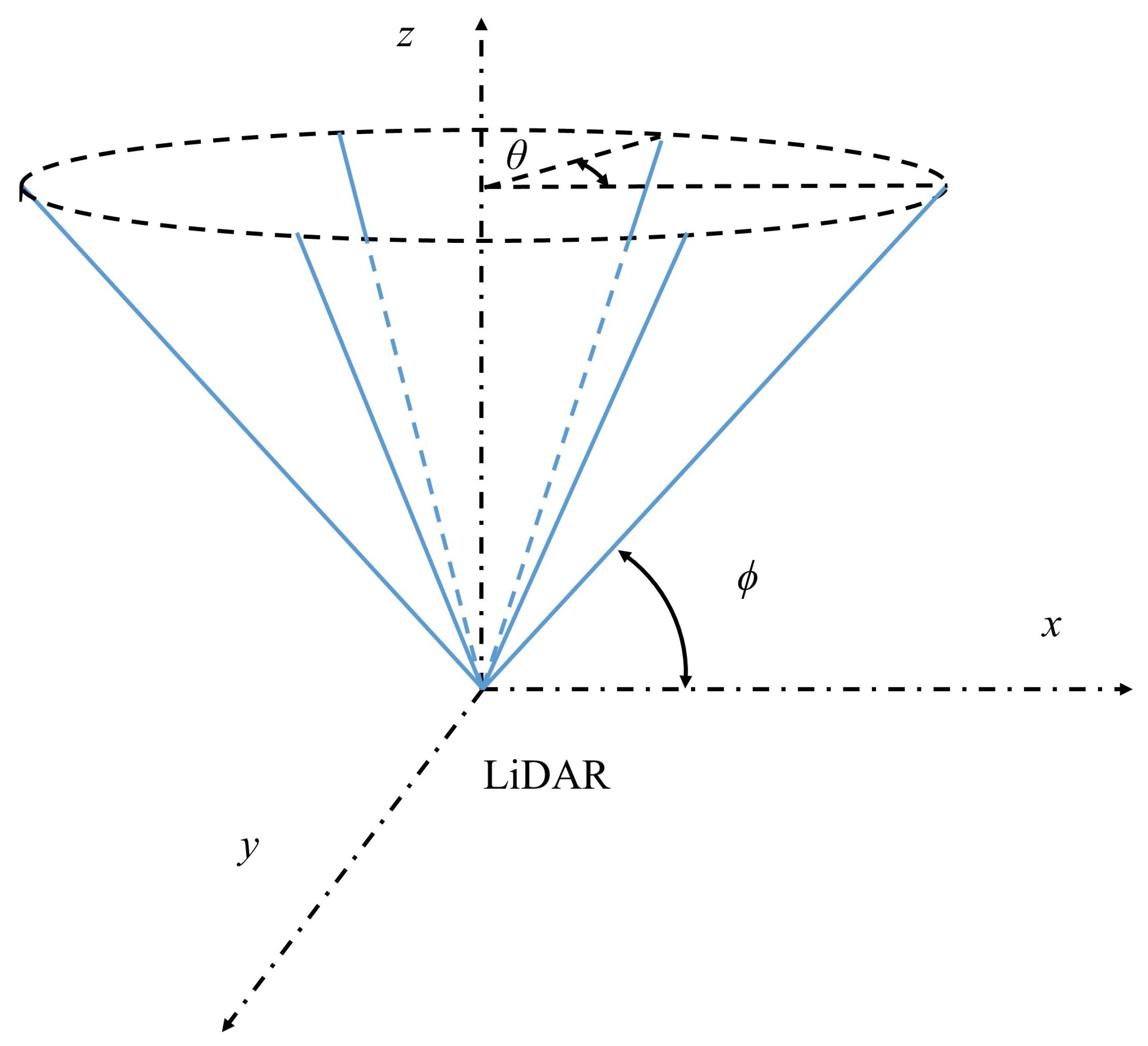
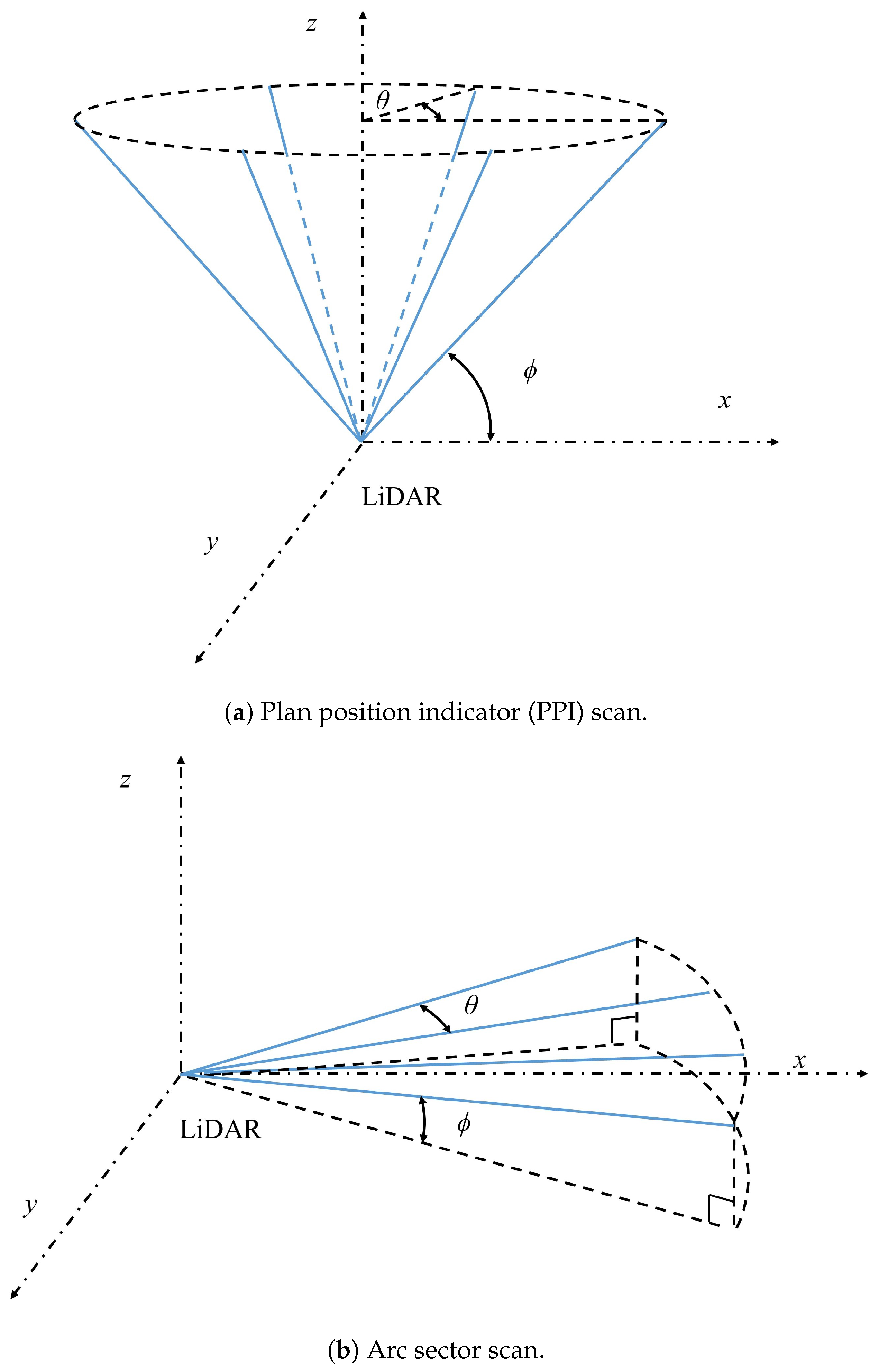
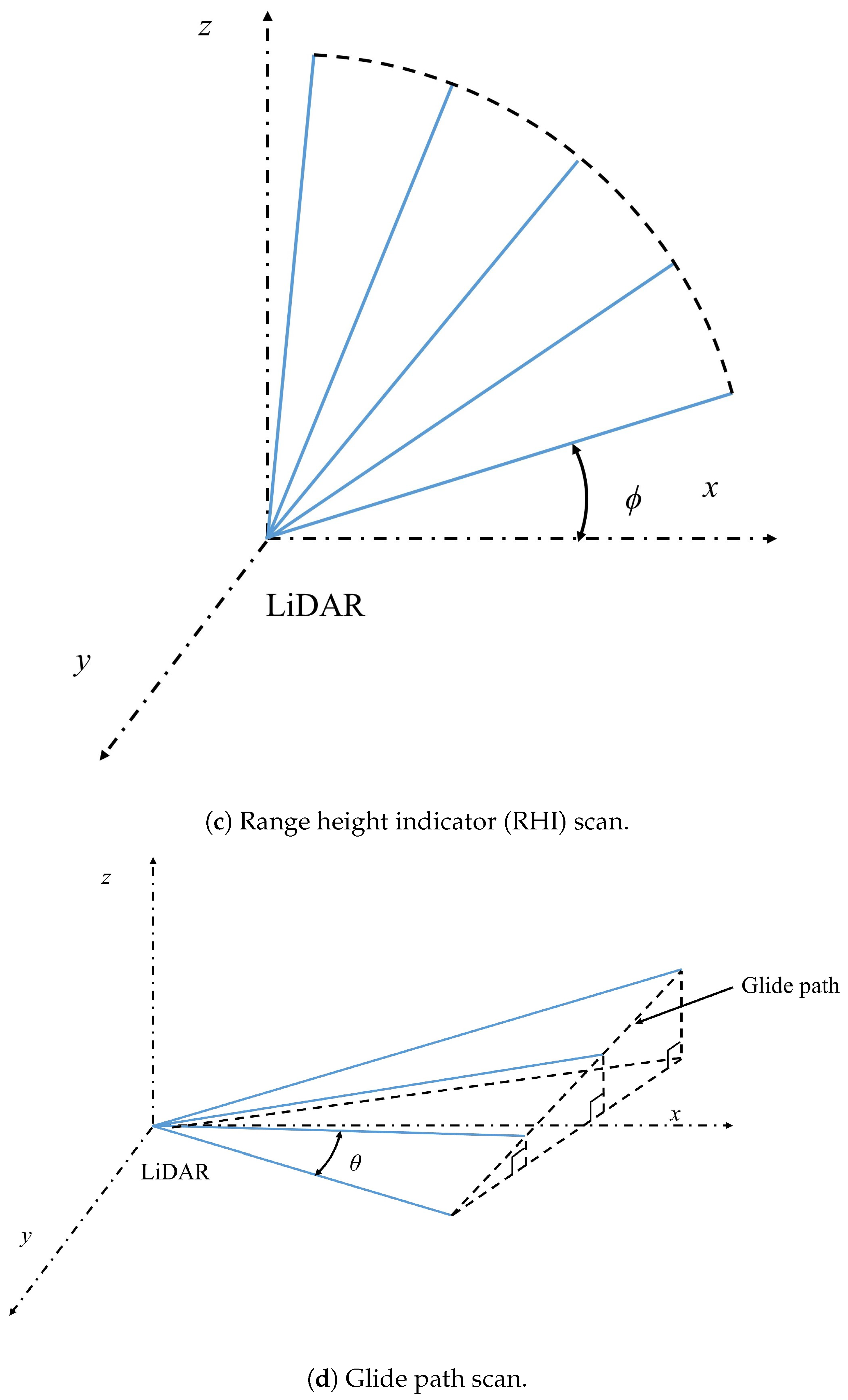
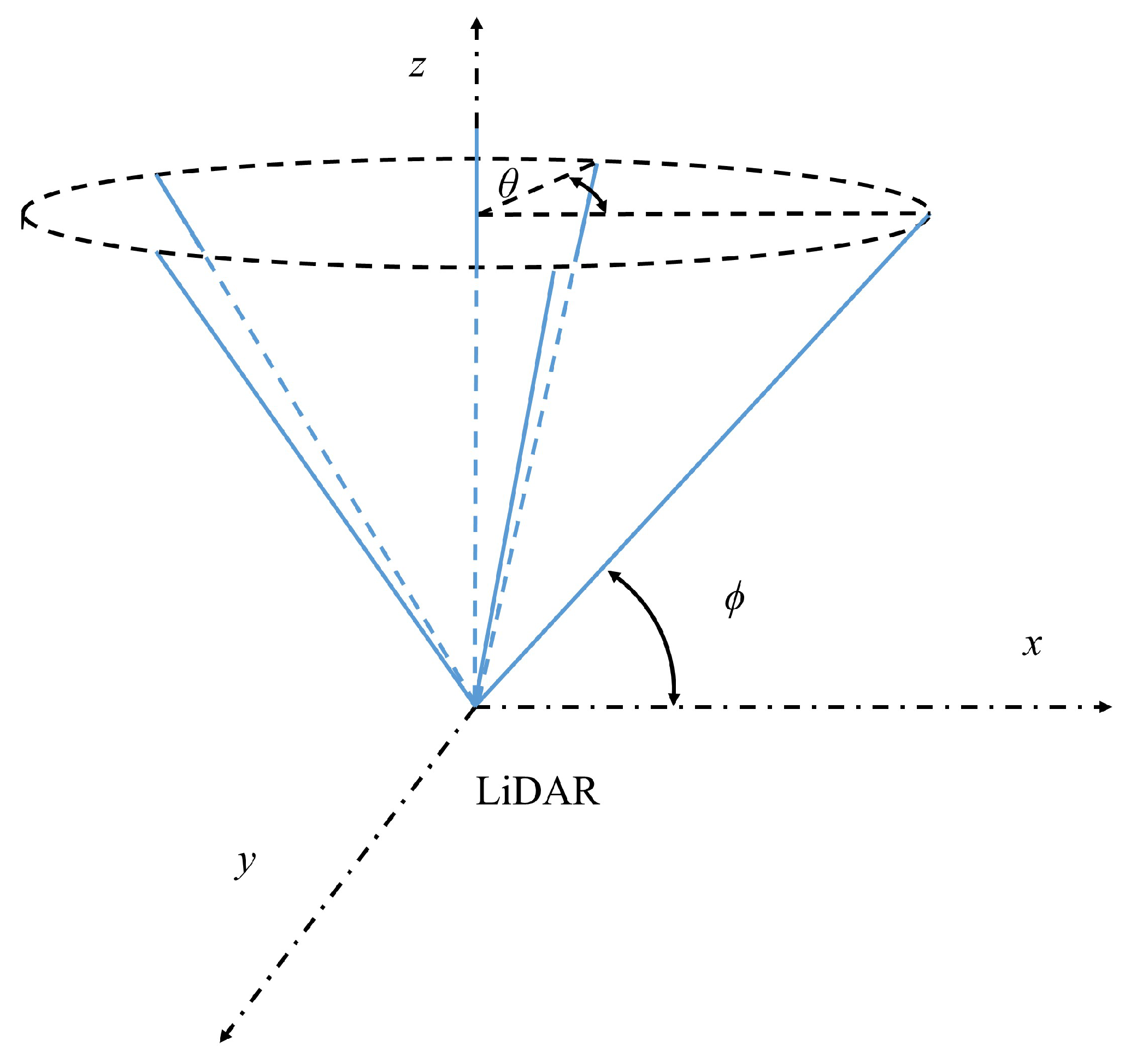
2.2. Scan Patterns
2.3. Methods for Wind Field Retrieval
2.4. Limitations and Precautions
3. Applications of Doppler Wind LiDARs
3.1. Aviation Safety
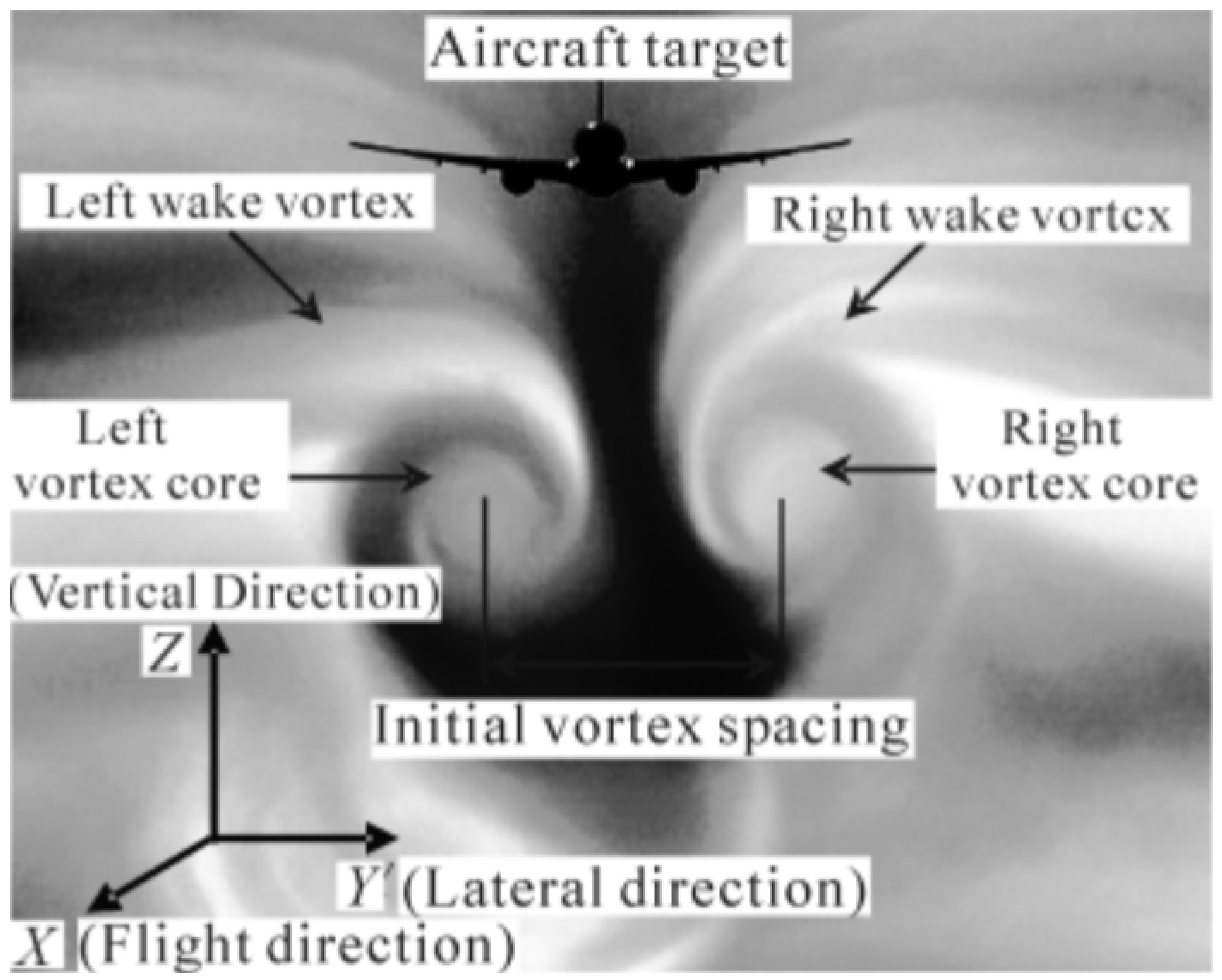
3.1.1. Aircraft Wake Vortex
3.1.2. Low Level Wind Shear
3.2. Wind Energy
3.2.1. Wind Resource Assessment
3.2.2. Turbine Wake
3.2.3. Turbine Control
3.3. Meteorological Research
3.3.1. Boundary Layer
3.3.2. Urban Meteorology
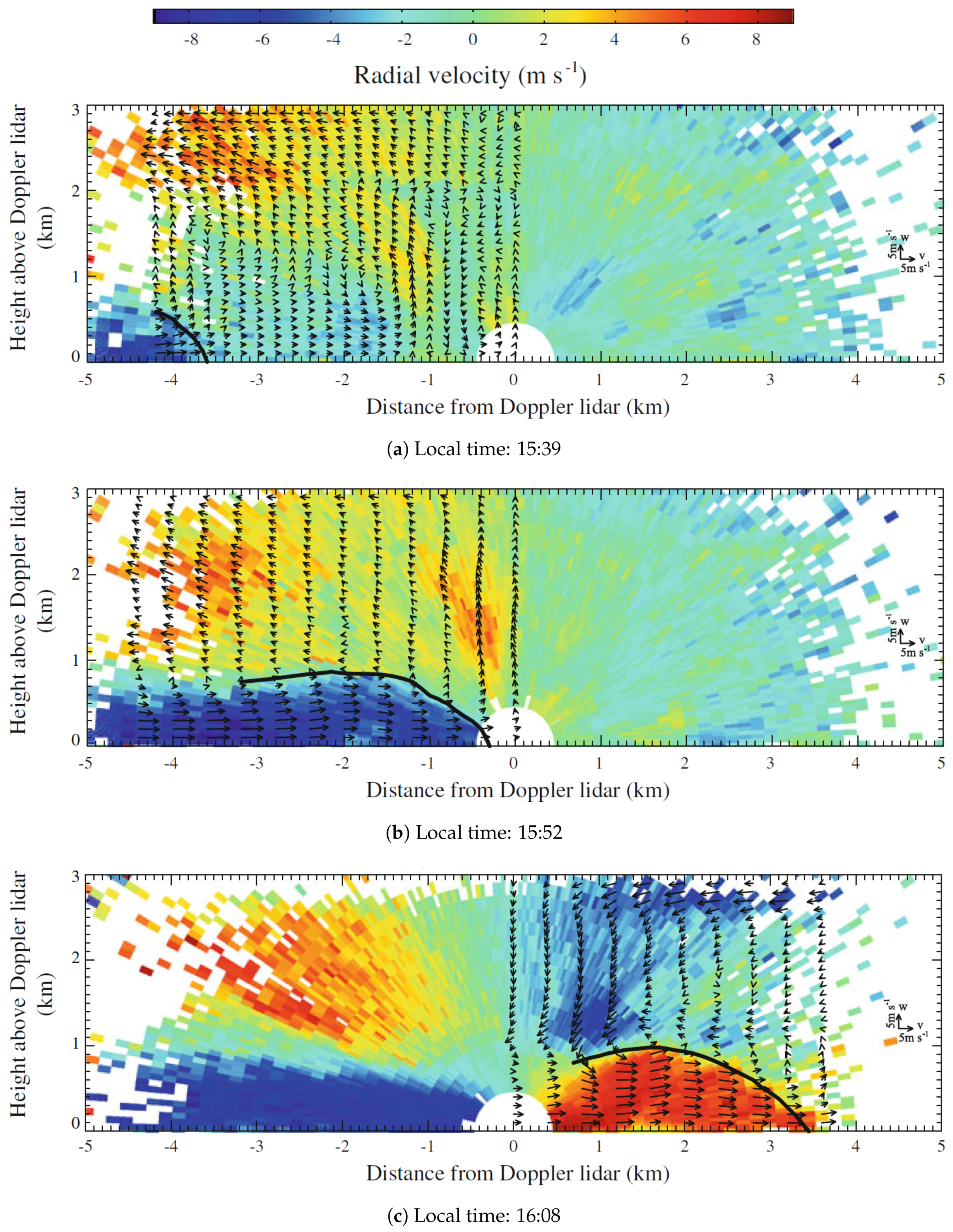
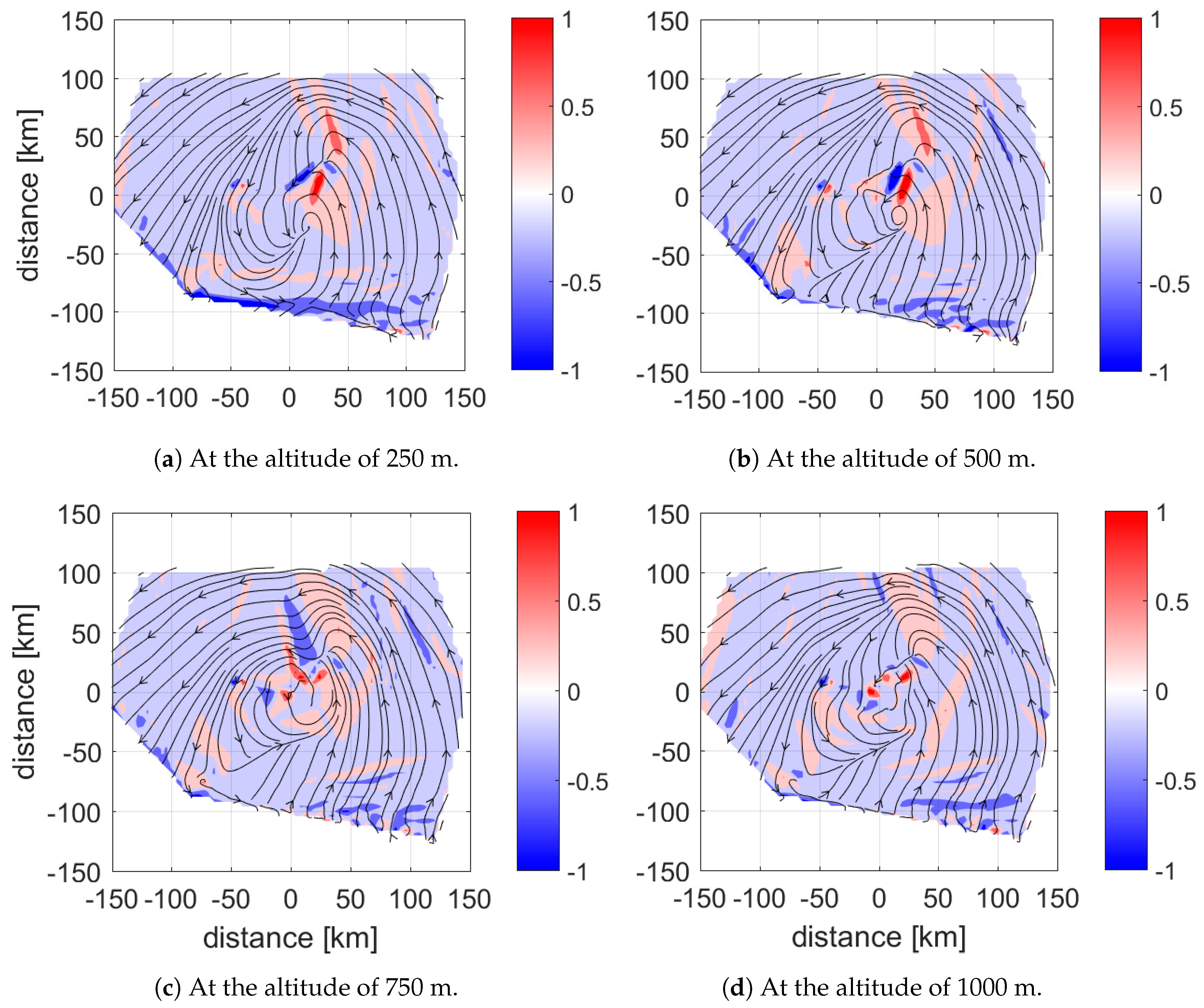
3.3.3. Tracking Atmospheric Flows
3.3.4. Model Validation and Improvement
4. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D | two-dimensional |
| 3D | three-dimensional |
| 4DVAR | four-dimensional variational data assimilation |
| CFD | computational fluid dynamics |
| CW | continuous wave |
| CWEX | Crop Wind Energy Experiment |
| DBS | doppler beam swinging |
| DLR | Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt |
| DOF | degree of freedom |
| ECMWF | Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| ESDU | Engineering Sciences Data Unit |
| ICAO | International Civil Aviation Organization |
| LiDAR | Light Detection And Ranging |
| MLH | mixed layer height |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| OI | optimal interpolation |
| PPI | plan position indicator |
| RHI | range height indicator |
| RUNW | Reducing Uncertainty of Near-shore wind resource Estimates |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| SODAR | Sound Detection and Ranging Device |
| TWICS | Turbine Wake and Inflow Characterization Study |
| VAD | velocity azimuth display |
| VVP | volume velocity processing |
Appendix A. Wind Retrieval Methods
Appendix A.1. Velocity Azimuth Display
Appendix A.2. Volume Velocity Processing
Appendix A.3. Optimal Interpolation

Appendix A.4. Variational Methods
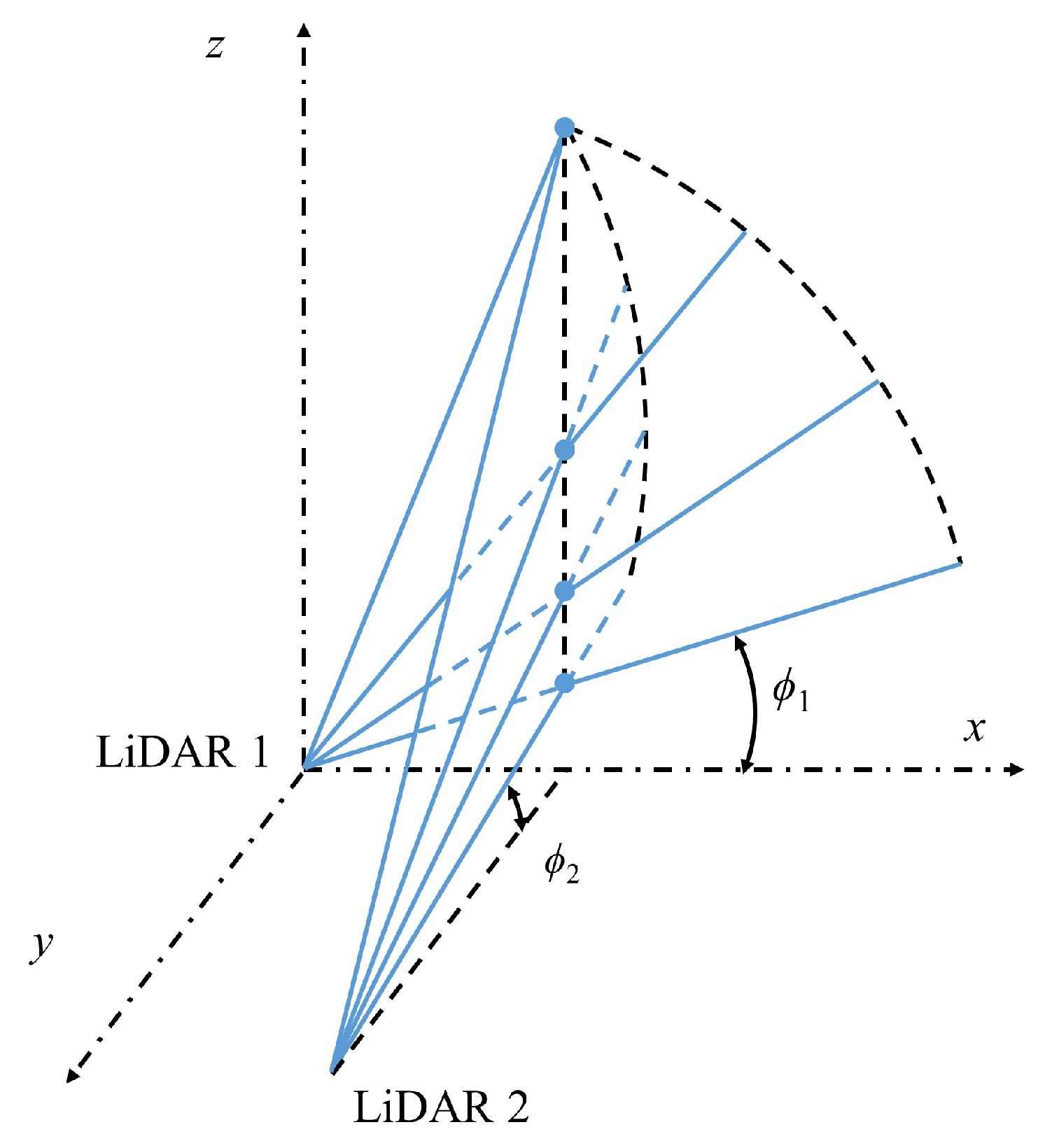
Appendix A.5. Retrieval Methods of Multiple LiDARs
Appendix B. Summary of Literature on Pulsed Doppler Wind LiDARs
| Author | Location | Time | Manufacturer | Scan pattern | Instruments | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chai et al. (2004) [197] | Leon | 24 Oct 1999 | NOAA | PPI | NA | 4DVAR |
| Köpp et al. (2004) [77] | Tarbes | Jun 2002 | DLR | RHI | NA | Aircraft wake vortices |
| Newsom & Banta (2004) [189] | Kansas | 25 Oct 1999 | NOAA | PPI | NA | 4DVAR |
| Collier et al. (2005) [190] | London | 23 Jul 2003 | University of Salford | PPI and RHI | NA | Dual LiDAR |
| Ishii et al. (2005) [198] | Wakkanai | 3 and 4 Sep 2002 | Lockheed Martin Coherent Technologies | PPI | Radiosondes and radar | Airborne |
| Köpp et al. (2005) [86] | Tarbes | Jun 2002 | DLR | RHI | NA | Aircraft wake vortices |
| Newsom et al. (2005) [188] | Oklahoma | 28 Jun to 31 Jul 2003 | CLR Photonics | RHI | NA | 4DVAR |
| Smalikho et al. (2005) [199] | Tarbes | 27 and 28 Aug 2003 | DLR | RHI | NA | Turbulence |
| Weissmann et al. (2005) [168] | Southern Germany | 19 Jul 2002 | DLR | PPI | Dropsonde | Airborne |
| Wulfmeyer & Janjić (2005) [41] | Pacific | 23 Jun 1999 | NOAA | Staring and PPI | Radiosonde | Shipborne, Boundary layer |
| Calhoun et al. (2006) [48] | Oklahoma | 9 Jul 2003 | Lockheed Martin Coherent Technologies | RHI | SODAR and radar | Dual LiDAR |
| Chan & Shao (2007) [93] | Hong Kong | 2002 to 2006 | NA | PPI and RHI | Anemometer and weather buoy | Two-step variational method |
| Davies et al. (2007) [42] | Northolt | 3 weeks in Jul 2003 | University of Salford | Staring | NA | Boundary layer |
| Weissmann & Cardinali (2007) [173] | north Atlantic | 14 to 28 Nov 2003 | DLR | PPI | Dropsonde | Airborne |
| Xia et al. (2007) [49] | Oklahoma | 28 Jun to 31 Jul 2003 | CLR Photonics | RHI | NA | Dual LIDAR, 4DVAR |
| Drechsel et al. (2008) [50] | Owens Valley | 14 Mar to 25 Apr 2006 | Lockheed Martin Coherent Technologies | PPI and RHI | Radiosonde and wind profiler | Dual LiDAR |
| Shun & Chan (2008) [55] | Hong Kong | 2003 to 2006 | NA | PPI, RHI and glide patch scan | Quick access recorder | Airport wind shear |
| Pearson et al. (2009) [37] | Cardington | 51 days in 2007 | Halo Photonics | PPI | Radiosonde, radar and ultrasonic anemometer | Boundary layer |
| Tucker et al. (2009)[146] | Houston | Jul 2006 | NOAA | Staring, PPI and RHI | Radiosonde | Shipborne, Boundary layer |
| Hill et al. (2010) [51] | Owens Valley | 25 Mar 2006 | Lockheed Martin Coherent Technologies | RHI | NA | Dual LiDAR |
| Käsler et al. (2010) [46] | Bremerhaven | NA | DLR | Arc sector and RHI | NA | Turbine wake |
| Pu et al. (2010) [163] | Pacific | 16 to 17 Aug 2008 | NA | NA | Dropsonde | Airborne, Typhoon |
| Barlow et al. (2011) [145] | London | 25 Oct to 13 Nov 2007 | Halo Photonics | Staring | Sonic anemometer | Turbulence |
| Iwai et al. (2011) [161] | Tokyo | 14 May to 15 Jun 2008 | NICT | PPI and RHI | Ceilometer | Sea breeze |
| Kiemle et al. (2011) [73] | Rhine valley | 30 Jul 2007 | DLR | PPI | In-situ sensors | Airborne, Complex terrain |
| Sathe et al. (2011) [200] | Høvsøre | Jan to Apr 2009 | Leosphere | PPI | Sonic anemometers | Turbulence |
| Schumann et al. (2011) [169] | Southern Germany and Iceland | 19 April to 18 May 2010 | DLR | PPI | In-situ aerosol instrumentation | Airborne, Valcano plume |
| Tang et al. (2011) [54] | Hong Kong | Apr 2008 to Feb 2009 | NA | PPI and RHI | NA | Two-step variational method |
| Aitken et al. (2012) [67] | Boulder and central Iowa | Jun to Aug 2010 | Leosphere | PPI | Ceilometer | LiDAR performance assessment |
| Koch et al. (2012) [113] | Virginia Beach | 4 Oct to 17 Oct 2011 | NA | Arc sector | In-situ anemometer | Offshore wind measurement |
| Kongara et al. (2012) [62] | Oklahoma | 28 Jun to 31 Jul 2003 | CLR Photonics | PPI | NA | Optimal interpolation method |
| Pichugina et al. (2012) [111] | New England | 9 Jul to 12 Aug 2004 | NOAA | PPI and RHI | NA | Shipborne |
| Weissmann et al. (2012) [164] | Pacific | 11 to 21 Sep 2008 | DLR | PPI | Dropsonde | Airborne, Typhoon |
| Drew et al. (2013) [155] | London | 22 May 2011 to 6 Jan 2012 | Halo Photonics | DBS | Sonic anemometer | Urban flow |
| Harvey et al. (2013) [151] | Southern England | 2009 | Halo photonics | Staring | NA | Boundary layer |
| Iungo et al. (2013) [44] | Canton de Valais | Jun to Aug 2011 | Halo Photonics | Staring, RHI | NA | Dual LiDAR, Turbine wake |
| Krishnamurthy et al. (2013) [103] | NA | Jun to Jul 2007 | Lockheed Martin Coherent Technologies | PPI | Cup anemometers and vanes | Wind farm optimization |
| Lane et al. (2013) [201] | London | 06 Jul 2010 to 11 Jan 2012 | Halo Photonics | DBS | Sonic anemometer | Urban flow |
| Rajewski et al. (2013) [122] | Central Iowa | 2010 and 2011 | Leosphere | NA | NA | Turbine wake |
| Smalikho et al. (2013) [119] | Boulder | Apr 2011 | NOAA | Arc sector and PPI | Sonic anemometer | Turbine wake |
| Aitken et al. (2014) [120] | Boulder | 5 Apr to 3 May 2011 | NOAA | Arc sector and RHI | NA | Turbine wake |
| Bluestein et al. (2014) [202] | Oklahoma, Texas Panhandle, Kansas and Colorado | May to Jun 2010 | Lockheed Martin Coherent Technologies | Arc sector | X-band Doppler radar | Truck-mounted, Tornado |
| Fuertes et al. (2014) [194] | Cabauw | Dec 2012 | Halo Photonics | Staring | Sonic anemometer | Trinal LiDAR, Turbulence |
| Iungo et al. (2014) [116] | Collonges | Jun to Oct 2012 | Halo Photonics | Staring, PPI and RHI | Sonic anemometer | Turbine wake |
| Kavaya et al. (2014) [165] | Atlantic | Aug to Sep 2010 | NA | Arc sector | Dropsonde | Airborne, Hurricane |
| Koch et al. (2014) [112] | Virginia and Maryland | 2012 and 2013 | NA | Arc sector and RHI | NA | Airborne, Offshore wind measurement |
| Schween et al. (2014)[69] | Jülich | Dec 2011 to Nov 2012 | Halo Photonics | NA | Radiosondes | Boundary layer |
| Achtert et al. (2015) [72] | Arctic | 5 Jul to 5 Oct 2014 | Halo Photonics | PPI | Radiosonde | Shipborne |
| Banta et al. (2015) [121] | Boulder | Mar to Apr 2011 | NOAA | Arc sector and RHI | NA | Turbine wake |
| Bastine et al. (2015) [127] | North Sea | NA | Leosphere | Staring | Ultrasonic anemometer | Turbine wake |
| Berg et al. (2015) [193] | Høvsøre | Jun 2013 | Technical University of Denmark | Sonic anemometers | Arc sector and RHI | Trinal LiDAR |
| Devara et al. (2015) [154] | Pune | 2009 and 2010 | Leosphere | PPI and DBS | Radiosonde | Boundary layer |
| Klaas et al. (2015) [203] | Kassel | NA | Leosphere | PPI | Cup and ultrasonic anemometers | Complex terrain |
| Newsom et al. (2015) [192] | Oklahoma | 21 Oct to 22 Nov 2010 | Halo Photonics | PPI and RHI | Sonic anemometer, wind profiler and radiosonde | Dual LiDAR |
| Päschke et al. (2015) [34] | Tauche | 2 Oct 2012 to 2 Oct 2013 | Halo Photonics | PPI | Radar and radiosonde | LiDAR performance assessment |
| Sathe et al. (2015) [56] | Høvsøre | 1 to 28 Jul 2013 | Technical University of Denmark | PPI and DBS | Cup anemometer | Turbulence |
| Smalikho et al. (2015) [79] | Tomsk | Summer 2014 | Halo Photonics | RHI | NA | Aircraft wake vortices |
| Vakkari et al. (2015) [147] | Limassol and Loviisa | 22 Aug to 15 Oct 2013 and 10 Dec 2013 to 17 Mar 2014 | Halo Photonics | PPI | NA | Boundary layer |
| Wang et al. (2015) [47] | Colorado | 15 to 25 Feb 2013 | SgurrEnergy | Arc sector | Cup and sonic anemometers and wind vanes | LiDAR performance assessment |
| Aubrun et al. (2016) [117] | Ablaincourt-Pressoir | Nov to Dec 2015 | Leosphere | Arc sector | NA | Multiple turbine wakes |
| Choukulkar et al. (2016) [63] | Lamar | 2 weeks in Sep 2003 | NOAA | PPI | NA | Prediction for power generated by a wind turbine |
| Floors et al. (2016) [106] | Denmark | Nov 2015 to Feb 2016 | Leosphere | PPI, RHI and arc sector | NA | Dual LIDAR |
| Kim et al. (2016) [101] | Jeju Island | 4 Feb to 23 Mar 2015 | Leosphere | PPI | Cup anemometer and wind vane | Influence of terrain complexity |
| Pauscher et al. (2016) [105] | Kassel | 3 Jul to 17 Aug 2014 | Leosphere | Staring and DBS | Sonic anemometer | Trinal LiDAR, Complex terrain |
| Van Dooren et al. (2016) [128] | North Sea | NA | Leosphere | Arc sector | NA | Dual LiDAR, Turbine wake |
| Wu et al. (2016) [53] | Longgang and Rudong | 2013 to 2015 | Seaglet Environmental Technology | PPI and RHI | Wind mast | Turbine wake |
| Bonin et al. (2017) [70] | Erie | 15 to 31 May 2015 | Leosphere | Staring, PPI, RHI and DBS | Sonic anemometer | Turbulence |
| Bodini et al. (2017) [118] | Central Iowa | June to September 2013 | Leosphere | Arc sector, PPI and RHI | NA | Multiple turbine wakes |
| Chen (2017) [170] | Tainan | 28 Jul 2015 | Leosphere | DBS | NA | Building wake |
| Cherukuru et al. (2017) [186] | North Sea | 31 Aug 2016 | Leosphere | PPI | Cup and vane anemometer | Two-dimensional variational data assimilation |
| Cheynet et al. (2017) [191] | Bjørnafjord | May to Jun 2016 | Technical University of Denmark | Staring and arc sector | Sonic Anemometer | Dual LiDAR |
| Huang et al. (2017) [143] | Beijing | Jun to Sep 2015 | Leosphere | DBS | Sonic anemometers and open-path gas analyzers | Boundary layer |
| Kawamoto (2017) [162] | Fukuoka | 11 Sep 2015 | Leosphere | DBS | NA | Sea breeze and urban heat island |
| Kikumoto et al. (2017) [159] | Tokyo | Sep to Dec 2013 and Apr to Jun 2014 | NA | PPI | ultrasonic anemometer | Urban flow |
| Lim et al. (2017) [158] | Tokyo | 1 Sep 2013 to 30 Jun 2014 | Leosphere | PPI | NA | Urban flow |
| Newsom et al. (2017) [204] | Oklahoma | 6 Mar to 16 Apr 2015 | Halo Photonics | PPI | Sonic anemometer | LiDAR performance assessment |
| Suomi et al. (2017) [39] | Høvsøre | 10 and 11 Oct 2015 | Leosphere | DBS | Sonic anemometer | Wind gusts |
| Thobois et al. (2017) [52] | Paris | NA | Leosphere | RHI | NA | Aircraft wake vortices |
| Vasiljević et al. (2017) [195] | Perdigão | 4 May to 29 Jun 2015 | Technical University of Denmark | Staring and RHI | NA | Trinal LiDAR |
| Zhai et al. (2017) [129] | Shandong, Jiangsu and Xinjiang | 2013 to 2015 | Seaglet Environmental Technology | PPI, arc sector and RHI | NA | Turbine wake |
| Bonin et al. (2018) [148] | Indianapolis | 2016 | Halo Photonics | Staring, PPI and RHI | NA | Boundary layer |
| Bucci et al. (2018) [71] | East Pacific | 2, 3, 8 and 9 Aug 2016 | NA | PPI | Dropsonde | Airborne, Tropical cyclones |
| Gao et al. (2018) [88] | Hong Kong | 2014 | Lockheed Martin Coherent Technologies | RHI | NA | Aircraft wake vortices |
| Gottschall et al. (2018) [108] | Southern Baltic Sea | 7 Feb to 8 Jun 2017 | Leosphere | DBS | NA | Shipborne |
| Halios & Barlow (2018) [149] | London | 2011 and 2012 | Halo Photonics | Staring and DBS | NA | Boundary layer |
| Karagali et al. (2018) [107] | Northern Denmark | Apr to Aug 2016 | Leosphere | RHI and arc sector | NA | Dual LiDAR, Complex terrain |
| Kotthaus et al. (2018) [153] | London | 21 Sep 2010 to 2 Mar 2011 | Halo Photonics | Staring, DBS and RHI | NA | Boundary layer |
| Manninen et al. (2018) [152] | Hyytiälä and Jülich | 1 May 2015 to 31 Dec 2016 | Halo Photonics | Staring, PPI and DBS | NA | Boundary layer |
| Pantillon et al. (2018) [167] | Karlsruhe | Dec 2016 to Mar 2017 | Lockheed Martin Coherent Technologies | PPI and RHI | Doppler C-band radar and instrumented tower | Extratropical cyclones |
| Risan et al. (2018) [43] | Central Norway | 13 Apr to 11 Jun 2015 | Halo Photonics | Staring | Sonic anemometer | Complex terrain |
| Sepe et al. (2018) [157] | Aversa | 9 Oct 2015 to 27 Jul 2016 | Leosphere | PPI | NA | Urban flow |
| Shimada et al. (2018) [110] | Hazaki | Oct 2015 to Dec 2016 | Leosphere | Staring | NA | Fetch effect |
| Thobois et al. (2018) [27] | Lanzhou | 9 months in 2016 | Leosphere | PPI and RHI | NA | Airport wind shear. Aircraft wake vortices |
| Wildmann et al. (2018) [196] | Central Portugal | 8 May to 14 Jun 2017 | Leosphere | PPI and RHI | Sonic anemometer | Trinal LiDAR, Turbine wake |
| Zhang et al. (2018) [166] | Atlantic | 26 August 2015 | Lockheed Martin Coherent Technologies | Arc sector | Dropsonde and Doppler radar | Airborne, Tropical cyclone |
| Fernando et al. (2019) [109] | Perdigão | 1 May to 15 Jun 2017 | NA | PPI and RHI | NA | Trinal LiDAR, Complex terrain |
| Palma et al. (2019) [205] | Perdigão | 2017 | NA | RHI | NA | Complex terrain |
| Wu et al. (2019) [75] | Beijing | 2017 | QINGDAO Leice Transient Technology | RHI | NA | Aircraft wake vortices |
| Yoshino (2019) [97] | Narita | 20 Jun 2012 | NA | PPI and RHI | NA | Airport wind shear |
| Zhang et al. (2019) [91] | Beijing | 2015 and 2016 | NA | Arc sector, RHI and DBS | NA | Airport wind shear |
References
- Laughton, J.K. Historical sketch of anemometry and anemometers. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1882, 8, 161–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, S. Lidar-Based Reconstruction of Wind Fields and Application for Wind Turbine Control. Ph.D. Thesis, Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Oldenburg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pardyjak, E.R.; Stoll, R. Improving measurement technology for the design of sustainable cities. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 092001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuerva, A.; Sanz-Andrés, A. On sonic anemometer measurement theory. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2000, 88, 25–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, T.; Semmer, S.; Maclean, G. Correction of a non-orthogonal, three-component sonic anemometer for flow distortion by transducer shadowing. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2015, 155, 371–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeon, B.; Comte-Bellot, G.; Foss, J.; Westerweel, J.; Scarano, F.; Tropea, C.; Meyers, J.; Lee, J.; Cavone, A.; Schodl, R.; et al. Velocity, vorticity, and mach number. In Springer Handbook of Experimental Fluid Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 215–471. [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen, N. Wind measurements for wind energy applications. A review. In Proceedings of the 16th British Wind Energy Association Conference, Stirling, UK, 15–17 June 1994; Mechanical Engineering Publications Limited: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, S.; McKeogh, E. LIDAR and SODAR Measurements of Wind Speed and Direction in Upland Terrain for Wind Energy Purposes. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1871–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenti, G.H. The degradation of doppler sodar performance due to noise: A review. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Fukuchi, T. Laser Remote Sensing; Optical Science and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Emeis, S.; Harris, M.; Banta, R.M. Boundary-layer anemometry by optical remote sensing for wind energy applications. Meteorol. Z. 2007, 16, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindelöw, P. Fiber Based Coherent Lidars for Remote Wind Sensing. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pitter, M.; Slinger, C.; Harris, M. Introduction to continuous-wave Doppler lidar. In Chapter 4 in Remote Sensing for Wind Energy; Technical Report, DTU Wind Energy-E-Report-0029(EN); DTU Wind Energy: Roskilde, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp, C. Lidar: Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere; Springer Science & Business: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 102. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz Porcar, C. Analysis and Design of an Edge-Technique-Based Doppler Wind Lidar: Practical Assessment of a Laboratory Prototype. Ph.D. Thesis, Departament de Teoria del Senyal i Comunicacions, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, W.R.; Hays, P.B. A Comparative Study of Coherent & Incoherent Doppler Lidar Techniques; Technical Report; Marshall Space Flight Center: Huntsville, AL, USA, 1994.
- Karlsson, C.J.; Olsson, F.Å.A.; Letalick, D.; Harris, M. All-fiber multifunction continuous-wave coherent laser radar at 1.55 µm for range, speed, vibration, and wind measurements. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 3716–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, P.J.; Pedersen, C. Field performance of an all-semiconductor laser coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 2277–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, V.; Smalikho, I. Coherent Doppler Wind Lidars in a Turbulent Atmosphere; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cariou, J.P.; Sauvage, L.; Thobois, L.; Gorju, G.; Machta, M.; Lea, G.; Duboué, M. Long range scanning pulsed Coherent Lidar for real time wind monitoring in the Planetary Boundary Layer. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Coherent Laser Radar, Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, M.; Hand, M.; Wright, A. Lidar for Turbine Control; Report No. NREL/TP-500-39154; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2006.
- Richmond, R.D.; Cain, S.C. Introduction to LADAR Systems. In Direct-Detection LADAR Systems; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Chapter 1; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Emeis, S. Surface-Based Remote Sensing of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2010; Volume 40. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolae, D.; Talianu, C.; Nemuc, A.; Carstea, E. Benefits and drawbacks of laser remote sensing in atmospheric research. Sci. Bull. J. Politeh. Univ. Buchar. 2008, 70, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bilbro, J.W.; Vaughan, W.W. Wind field measurement in the nonprecipitous regions surrounding severe storms by an airborne pulsed Doppler lidar system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1978, 59, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitebuch, O. Wind lidar for atmospheric research. In Atmospheric Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 487–507. [Google Scholar]
- Thobois, L.; Cariou, J.P.; Gultepe, I. Review of Lidar-Based Applications for Aviation Weather. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 1959–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, S.; Ando, T.; Asaka, K.; Hirano, Y.; Wadaka, S. Performance of Discrete-Fourier-Transform-Based Velocity Estimators for a Wind-Sensing Coherent Doppler Lidar System in the Kolmogorov Turbulence Regime. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3560–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xia, H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, S.; Dou, X. Spatial resolution enhancement of coherent Doppler wind lidar using joint time–frequency analysis. Opt. Commun. 2018, 424, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, A.; Hasager, C. (Eds.) Remote Sensing for Wind Energy; Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy, Technical University of Denmark: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2011.
- Lindelöw, P.; Courtney, M.; Parmentier, R.; Cariou, J.P. Wind shear proportional errors in the horizontal wind speed sensed by focused, range gated lidars. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindelöw-Marsden, P. UpWind D1. Uncertainties in Wind Assessment with LIDAR; Technical Report, Risø-R-1681(EN); Risø National Laboratory (Den.), Technical University of Denmark: Roskilde, Denmark, 2009.
- Frehlich, R.G.; Yadlowsky, M.J. Performance of Mean-Frequency Estimators for Doppler Radar and Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1994, 11, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Päschke, E.; Leinweber, R.; Lehmann, V. An assessment of the performance of a 1.5 μm Doppler lidar for operational vertical wind profiling based on a 1-year trial. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 2251–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryning, S.E.; Floors, R.; Peña, A.; Batchvarova, E.; Brümmer, B. Weibull Wind-Speed Distribution Parameters Derived from a Combination of Wind-Lidar and Tall-Mast Measurements Over Land, Coastal and Marine Sites. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2016, 159, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rye, B.J.; Hardesty, R.M. Discrete spectral peak estimation in incoherent backscatter heterodyne lidar. I. Spectral accumulation and the Cramer-Rao lower bound. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.; Davies, F.; Collier, C. An Analysis of the Performance of the UFAM Pulsed Doppler Lidar for Observing the Boundary Layer. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, E.J.; Illingworth, A.J.; Brooks, I.M.; Westbrook, C.D.; Hogan, R.J.; Davies, F.; Brooks, B.J. A method for estimating the turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate from a vertically pointing Doppler lidar, and independent evaluation from balloon-borne in situ measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 1652–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suomi, I.; Gryning, S.E.; O’Connor, E.J.; Vihma, T. Methodology for obtaining wind gusts using Doppler lidar. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, A.; Boquet, M.; Burin Des Roziers, E.; Westerhellweg, A.; Hofsass, M.; Klaas, T.; Vogstad, K.; Clive, P.; Harris, M.; Wylie, S.; et al. Remote Sensing of Complex Flows by Doppler Wind Lidar: Issues and Preliminary Recommendations; Technical Report; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2015.
- Wulfmeyer, V.; Janjić, T. Twenty-Four-Hour Observations of the Marine Boundary Layer Using Shipborne NOAA High-Resolution Doppler Lidar. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 1723–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, F.; Middleton, D.; Bozier, K. Urban air pollution modelling and measurements of boundary layer height. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4040–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risan, A.; Lund, J.A.; Chang, C.Y.; Sætran, L. Wind in Complex Terrain—Lidar Measurements for Evaluation of CFD Simulations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iungo, G.V.; Wu, Y.T.; Porté-Agel, F. Field Measurements of Wind Turbine Wakes with Lidars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, V.A.; Smalikho, I.N.; Köpp, F.; Werner, C. Representativeness of wind measurements with a cw Doppler lidar inthe atmospheric boundary layer. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käsler, Y.; Rahm, S.; Simmet, R.; Kühn, M. Wake Measurements of a Multi-MW Wind Turbine with Coherent Long-Range Pulsed Doppler Wind Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Barthelmie, R.J.; Clifton, A.; Pryor, S.C. Wind Measurements from Arc Scans with Doppler Wind Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, R.; Heap, R.; Princevac, M.; Newsom, R.; Fernando, H.; Ligon, D. Virtual Towers Using Coherent Doppler Lidar during the Joint Urban 2003 Dispersion Experiment. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2006, 45, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Lin, C.L.; Calhoun, R.; Newsom, R.K. Retrieval of Urban Boundary Layer Structures from Doppler Lidar Data. Part I: Accuracy Assessment. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsel, S.; Mayr, G.J.; Chong, M.; Weissmann, M.; Dörnbrack, A.; Calhoun, R. Three-Dimensional Wind Retrieval: Application of MUSCAT to Dual-Doppler Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.; Calhoun, R.; Fernando, H.J.S.; Wieser, A.; Dörnbrack, A.; Weissmann, M.; Mayr, G.; Newsom, R. Coplanar Doppler Lidar Retrieval of Rotors from T-REX. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 713–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thobois, L.; Cariou, J.P. Next generation scanning Lidar systems for optimizing wake turbulence separation minima. J. Radar 2017, 6, 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhai, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; et al. Wind turbine wake visualization and characteristics analysis by Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2016, 24, A762–A780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Chan, P.W.; Haller, G. Lagrangian Coherent Structure Analysis of Terminal Winds Detected by Lidar. Part I: Turbulence Structures. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 50, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun, C.M.; Chan, P.W. Applications of an Infrared Doppler Lidar in Detection of Wind Shear. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Mann, J.; Vasiljevic, N.; Lea, G. A six-beam method to measure turbulence statistics using ground-based wind lidars. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, K.A.; Wexler, R. The Determination of Kinematic Properties of a Wind Field Using Doppler Radar. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1968, 7, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koscielny, A.J.; Doviak, R.J.; Rabin, R. Statistical Considerations in the Estimation of Divergence from Single-Doppler Radar and Application to Prestorm Boundary-Layer Observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1982, 21, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caya, D.; Zawadzki, I. VAD Analysis of Nonlinear Wind Fields. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1992, 9, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejka, T.; Srivastava, R.C. An Improved Version of the Extended Velocity-Azimuth Display Analysis of Single-Doppler Radar Data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1991, 8, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Gong, J. Background error covariance functions for Doppler radial-wind analysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 129, 1703–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongara, S.; Calhoun, R.; Choukulkar, A.; Boldi, M.O. Velocity retrieval for coherent Doppler lidar. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 3596–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukulkar, A.; Pichugina, Y.; Clack, C.T.M.; Calhoun, R.; Banta, R.; Brewer, A.; Hardesty, M. A new formulation for rotor equivalent wind speed for wind resource assessment and wind power forecasting. Wind Energy 2016, 19, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pailleux, J. Data assimilation: Optimum interpolation approach/Variational approach. In Proceedings of the ECMWF Seminar “Ten Years of Medium-Range Weather Forecasting”, Shinfield Park, Reading, UK, 4–8 September 1989; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, C.J.; Xu, Q. A Simple Adjoint Method of Wind Analysis for Single-Doppler Data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1992, 9, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Flicker, D.W.; Lilly, D.K. Recovery of Three-Dimensional Wind and Temperature Fields from Simulated Single-Doppler Radar Data. J. Atmos. Sci. 1991, 48, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.L.; Rhodes, M.E.; Lundquist, J.K. Performance of a Wind-Profiling Lidar in the Region of Wind Turbine Rotor Disks. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization, W.M. Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation; Secretariat of the World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schween, J.H.; Hirsikko, A.; Löhnert, U.; Crewell, S. Mixing-layer height retrieval with ceilometer and Doppler lidar: From case studies to long-term assessment. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3685–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, T.A.; Choukulkar, A.; Brewer, W.A.; Sandberg, S.P.; Weickmann, A.M.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Banta, R.M.; Oncley, S.P.; Wolfe, D.E. Evaluation of turbulence measurement techniques from a single Doppler lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3021–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, L.R.; O’Handley, C.; Emmitt, G.D.; Zhang, J.A.; Ryan, K.; Atlas, R. Validation of an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar in Tropical Cyclones. Sensors 2018, 18, 4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achtert, P.; Brooks, I.M.; Brooks, B.J.; Moat, B.I.; Prytherch, J.; Persson, P.O.G.; Tjernström, M. Measurement of wind profiles by motion-stabilised ship-borne Doppler lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4993–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiemle, C.; Wirth, M.; Fix, A.; Rahm, S.; Corsmeier, U.; Di Girolamo, P. Latent heat flux measurements over complex terrain by airborne water vapour and wind lidars. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suharev, A.; Shestakov, V.; Stefanski, K. Analysis of the affecting factors on aircraft takeoff and landing ground path length. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Chongqing, China, 30–31 May 2019; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2077, p. 020056. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhai, X.; Liu, B. Aircraft wake vortex and turbulence measurement under near-ground effect using coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 1142–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Dai, D. Design of airport wake vortex monitoring system based on 1.5-μm pulsed coherent Doppler lidar. Optoelectron. Lett. 2011, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köpp, F.; Rahm, S.; Smalikho, I. Characterization of Aircraft Wake Vortices by 2-μm Pulsed Doppler Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalikho, I.N.; Banakh, V.A. Estimation of aircraft wake vortex parameters from data measured with a 1.5-μm coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 3408–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalikho, I.; Banakh, V.; Holzäpfel, F.; Rahm, S. Method of radial velocities for the estimation of aircraft wake vortex parameters from data measured by coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A1194–A1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frehlich, R.; Sharman, R. Maximum Likelihood Estimates of Vortex Parameters from Simulated Coherent Doppler Lidar Data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallermeyer, A.; Dolfi-Bouteyre, A.; Valla, M.; Le Brusquet, L.; Fleury, G.; Thobois, L.P.; Cariou, J.P.; Duponcheel, M.; Winckelmans, G. Development and assessment of a wake vortex characterization algorithm based on a hybrid LIDAR signal processing. In Proceedings of the 8th AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 June 2016; p. 3272. [Google Scholar]
- Besson, C.; Dolfi-Bouteyre, A.; Canat, G.; Cézard, N.; Augère, B.; Durecu, A.; Lombard, L.; Valla, M.; Hallermeyer, A. Doppler LIDAR Developments for Aeronautics. Aerosp. Lab J. 2016, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzäpfel, F.; Dengler, K.; Gerz, T.; Schwarz, C. Prediction of Dynamic Pairwise Wake Vortex Separations for Approach and Landing; Technical Report; DLR: Bonn, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Körner, S.; Holzäpfel, F. Assessment of the Wake-Vortex Proximity to Landing Aircraft Exploiting Field Measurements. J. Aircr. 2019, 56, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruis, M.J.; Delisi, D.P.; Jacob, D.; Lai, D. Summary of NASA Wake and Weather Data Collection at Memphis International Airport: 2013–2015. In Proceedings of the 8th AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 June 2016; p. 3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köpp, F.; Rahm, S.; Smakikho, I.; Dolfi, A.; Cariou, J.P.; Harris, M. Comparison of Wake-Vortex Parameters Measured by Pulsed and Continuous-Wave Lidars. J. Aircr. 2005, 42, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzäpfel, F.; Misaka, T.; Hennemann, I. Wake-Vortex Topology, Circulation, and Turbulent Exchange Processes. In Proceedings of the AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–5 August 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, H.; Li, J.; Chan, P.W.; Hon, K.K.; Wang, X. Parameter-retrieval of dry-air wake vortices with a scanning Doppler Lidar. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 16377–16392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzäpfel, F.; Stephan, A.; Heel, T.; Körner, S. Enhanced wake vortex decay in ground proximity triggered by plate lines. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2016, 88, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallock, J.N.; Holzäpfel, F. A review of recent wake vortex research for increasing airport capacity. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2018, 98, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B.; Yin, B.; Zhai, X. Airport low-level wind shear lidar observation at Beijing Capital International Airport. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 96, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.W.; Shun, C.M.; Wu, K.C. Operational LIDAR-based system for automatic windshear alerting at the Hong Kong International Airport. In Proceedings of the 12th Conference on Aviation, Range, and Aerospace Meteorology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 28 January–2 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, P.W.; Shao, A.M. Depiction of complex airflow near Hong Kong International Airport using a Doppler LIDAR with a two-dimensional wind retrieval technique. Meteorol. Z. 2007, 16, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.W.; Hon, K.K.; Shin, D.K. Combined use of headwind ramps and gradients based on LIDAR data in the alerting of low-level windshear/turbulence. Meteorol. Z. 2011, 20, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.W. Application of LIDAR-based F-factor in windshear alerting. Meteorol. Z. 2012, 21, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.F.; Chan, P.W. LIDAR-based F-factor for wind shear alerting: Different smoothing algorithms and application to departing flights. Meteorol. Appl. 2014, 21, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K. Low-Level Wind Shear Induced by Horizontal Roll Vortices at Narita International Airport, Japan. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2019, 97, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Nijhuis, A.C.P.; Thobois, L.P.; Barbaresco, F.; De Haan, S.; Dolfi-Bouteyre, A.; Kovalev, D.; Krasnov, O.A.; Vanhoenacker-Janvier, D.; Wilson, R. Wind Hazard and Turbulence Monitoring at Airports with Lidar, Radar, and Mode-S Downlinks: The UFO Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 2275–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.W. Severe wind shear at Hong Kong International Airport: Climatology and case studies. Meteorol. Appl. 2017, 24, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Antoniou, I.; Pedersen, S.M.; Courtney, M.S.; Jørgensen, H.E. The influence of the wind speed profile on wind turbine performance measurements. Wind Energy 2009, 12, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, T.; Oh, G.; Huh, J.; Ko, K. A comparison of ground-based LiDAR and met mast wind measurements for wind resource assessment over various terrain conditions. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2016, 158, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, A.J.; Mortensen, N.G. WAsP Prediction Errors Due to Site Orography; Technical Report Risø-R-995(EN); Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 2004.
- Krishnamurthy, R.; Choukulkar, A.; Calhoun, R.; Fine, J.; Oliver, A.; Barr, K. Coherent Doppler lidar for wind farm characterization. Wind Energy 2013, 16, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Angelou, N.; Arnqvist, J.; Callies, D.; Cantero, E.; Arroyo, R.C.; Courtney, M.; Cuxart, J.; Dellwik, E.; Gottschall, J.; et al. Complex terrain experiments in the New European Wind Atlas. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. and Eng. Sci. 2017, 375, 20160101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauscher, L.; Vasiljevic, N.; Callies, D.; Lea, G.; Mann, J.; Klaas, T.; Hieronimus, J.; Gottschall, J.; Schwesig, A.; Kühn, M.; et al. An Inter-Comparison Study of Multi-and DBS Lidar Measurements in Complex Terrain. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floors, R.; Peña, A.; Lea, G.; Vasiljević, N.; Simon, E.; Courtney, M. The RUNE Experiment—A Database of Remote-Sensing Observations of Near-Shore Winds. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagali, I.; Mann, J.; Dellwik, E.; Vasiljević, N. New European Wind Atlas: The Østerild balconies experiment. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1037, 052029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschall, J.; Catalano, E.; Dörenkämper, M.; Witha, B. The NEWA Ferry Lidar Experiment: Measuring Mesoscale Winds in the Southern Baltic Sea. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, H.J.S.; Mann, J.; Palma, J.M.L.M.; Lundquist, J.K.; Barthelmie, R.J.; Belo-Pereira, M.; Brown, W.O.J.; Chow, F.K.; Gerz, T.; Hocut, C.M.; et al. The Perdigão: Peering into Microscale Details of Mountain Winds. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Takeyama, Y.; Kogaki, T.; Ohsawa, T.; Nakamura, S. Investigation of the Fetch Effect Using Onshore and Offshore Vertical LiDAR Devices. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichugina, Y.L.; Banta, R.M.; Brewer, W.A.; Sandberg, S.P.; Hardesty, R.M. Doppler Lidar–Based Wind-Profile Measurement System for Offshore Wind-Energy and Other Marine Boundary Layer Applications. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 327–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.J.; Beyon, J.Y.; Cowen, L.J.; Kavaya, M.J.; Grant, M.S. Three-dimensional wind profiling of offshore wind energy areas with airborne Doppler lidar. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.J.; Beyon, J.Y.; Modlin, E.A.; Petros, M.; Yu, J.; Petzar, P.J.; Woll, S.; Kavaya, M.J. Side-scan Doppler lidar for offshore wind energy applications. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsuan, C.Y.; Tasi, Y.S.; Ke, J.H.; Prahmana, R.A.; Chen, K.J.; Lin, T.H. Validation and measurements of floating LiDAR for nearshore wind resource assessment application. Energy Procedia 2014, 61, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, A.; Smith, A.; Fields, M. Wind Plant Preconstruction Energy Estimates. Current Practice and Opportunities; Technical Report; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2016.
- Iungo, G.V.; Porté-Agel, F. Volumetric Lidar Scanning of Wind Turbine Wakes under Convective and Neutral Atmospheric Stability Regimes. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 2035–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrun, S.; Garcia, E.T.; Boquet, M.; Coupiac, O.; Girard, N. Wind turbine wake tracking and its correlations with wind turbine monitoring sensors. Preliminary results. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 753, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodini, N.; Zardi, D.; Lundquist, J.K. Three-dimensional structure of wind turbine wakes as measured by scanning lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2881–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalikho, I.N.; Banakh, V.A.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Brewer, W.A.; Banta, R.M.; Lundquist, J.K.; Kelley, N.D. Lidar Investigation of Atmosphere Effect on a Wind Turbine Wake. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 2554–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.L.; Banta, R.M.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Lundquist, J.K. Quantifying Wind Turbine Wake Characteristics from Scanning Remote Sensor Data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 765–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Brewer, W.A.; Lundquist, J.K.; Kelley, N.D.; Sandberg, S.P.; Alvarez, R.J., II; Hardesty, R.M.; Weickmann, A.M. 3D Volumetric Analysis of Wind Turbine Wake Properties in the Atmosphere Using High-Resolution Doppler Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajewski, D.A.; Takle, E.S.; Lundquist, J.K.; Oncley, S.; Prueger, J.H.; Horst, T.W.; Rhodes, M.E.; Pfeiffer, R.; Hatfield, J.L.; Spoth, K.K.; et al. Crop Wind Energy Experiment (CWEX): Observations of Surface-Layer, Boundary Layer, and Mesoscale Interactions with a Wind Farm. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, M.E.; Lundquist, J.K. The Effect of Wind-Turbine Wakes on Summertime US Midwest Atmospheric Wind Profiles as Observed with Ground-Based Doppler Lidar. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2013, 149, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirocha, J.D.; Rajewski, D.A.; Marjanovic, N.; Lundquist, J.K.; Kosović, B.; Draxl, C.; Churchfield, M.J. Investigating wind turbine impacts on near-wake flow using profiling lidar data and large-eddy simulations with an actuator disk model. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2015, 7, 043143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, L.P.; Porté-Agel, F. A Wind-Tunnel Investigation of Wind-Turbine Wakes: Boundary-Layer Turbulence Effects. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2009, 132, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Porté-Agel, F. Large-Eddy Simulation of Wind-Turbine Wakes: Evaluation of Turbine Parametrisations. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2011, 138, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastine, D.; Wächter, M.; Peinke, J.; Trabucchi, D.; Kühn, M. Characterizing Wake Turbulence with Staring Lidar Measurements. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 625, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dooren, M.F.; Trabucchi, D.; Kühn, M. A Methodology for the Reconstruction of 2D Horizontal Wind Fields of Wind Turbine Wakes Based on Dual-Doppler Lidar Measurements. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, B. Doppler lidar investigation of wind turbine wake characteristics and atmospheric turbulence under different surface roughness. Opt. Express 2017, 25, A515–A529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, L.Y.; Johnson, K.E. A tutorial on the dynamics and control of wind turbines and wind farms. In Proceedings of the 2009 American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–12 June 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 2076–2089. [Google Scholar]
- Simley, E.; Fürst, H.; Haizmann, F.; Schlipf, D. Optimizing Lidars for Wind Turbine Control Applications—Results from the IEA Wind Task 32 Workshop. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossanyi, E.A.; Kumar, A.; Hugues-Salas, O. Wind turbine control applications of turbine-mounted LIDAR. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 555, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, T.; Hansen, K.H.; Angelou, N.; Sjöholm, M.; Harris, M.; Hadley, P.; Scullion, R.; Ellis, G.; Vives, G. Lidar wind speed measurements from a rotating spinner. In Proceedings of the 2010 European Wind Energy Conference and Exhibition, Warsaw, Poland, 20–23 April 2010; European Wind Energy Association (EWEA): Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schlipf, D.; Fleming, P.; Haizmann, F.; Scholbrock, A.; Hofsäß, M.; Wright, A.; Cheng, P.W. Field Testing of Feedforward Collective Pitch Control on the CART2 Using a Nacelle-Based Lidar Scanner. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 555, 012090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, P.A.; Scholbrock, A.K.; Jehu, A.; Davoust, S.; Osler, E.; Wright, A.D.; Clifton, A. Field-test results using a nacelle-mounted lidar for improving wind turbine power capture by reducing yaw misalignment. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 524, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simley, E.; Pao, L.Y.; Frehlich, R.; Jonkman, B.; Kelley, N. Analysis of light detection and ranging wind speed measurements for wind turbine control. Wind Energy 2014, 17, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholbrock, A.; Fleming, P.; Schlipf, D.; Wright, A.; Johnson, K.; Wang, N. Lidar-enhanced wind turbine control: Past, present, and future. In Proceedings of the 2016 American Control Conference (ACC), Boston, MA, USA, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlipf, D.; Haizmann, F.; Cosack, N.; Siebers, T.; Cheng, P.W. Detection of Wind Evolution and Lidar Trajectory Optimization for Lidar-Assisted Wind Turbine Control. Meteorol. Z. 2015, 24, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlipf, D.; Kapp, S.; Anger, J.; Bischoff, O.; Hofsäß, M.; Rettenmeier, A.; Kühn, M. Prospects of optimization of energy production by lidar assisted control of wind turbines. In Proceedings of the EWEA 2011 Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 November–1 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schlipf, D.; Fleming, P.; Kapp, S.; Scholbrock, A.; Haizmann, F.; Belen, F.; Wright, A.; Cheng, P.W. Direct Speed Control using LIDAR and turbine data. In Proceedings of the 2013 American Control Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 17–19 June 2013; pp. 2208–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, F.; Schlipf, D.; Pao, L.; Wright, A.; Jonkman, B.; Kelley, N.; Simley, E. Comparison of two independent lidar-based pitch control designs. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Nashville, TE, USA, 9–12 January 2012; p. 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Delaval, A.; Loth, C.; Garnier, A.; Flamant, P.H. 0.355-micrometer direct detection wind lidar under testing during a field campaign in consideration of ESA’s ADM-Aeolus mission. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3349–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Gao, Z.; Miao, S.; Chen, F.; LeMone, M.A.; Li, J.; Hu, F.; Wang, L. Estimate of Boundary-Layer Depth Over Beijing, China, Using Doppler Lidar Data During SURF-2015. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2017, 162, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Träumner, K.; Kottmeier, C.; Corsmeier, U.; Wieser, A. Convective Boundary-Layer Entrainment: Short Review and Progress using Doppler Lidar. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2011, 141, 369–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.F.; Dunbar, T.; Nemitz, E.; Wood, C.R.; Gallagher, M.; Davies, F.; O’Connor, E.; Harrison, R. Boundary layer dynamics over London, UK, as observed using Doppler lidar during REPARTEE-II. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2111–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, S.C.; Senff, C.J.; Weickmann, A.M.; Brewer, W.A.; Banta, R.M.; Sandberg, S.P.; Law, D.C.; Hardesty, R.M. Doppler Lidar Estimation of Mixing Height Using Turbulence, Shear, and Aerosol Profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakkari, V.; O’Connor, E.J.; Nisantzi, A.; Mamouri, R.E.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Low-level mixing height detection in coastal locations with a scanning Doppler lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, T.A.; Carroll, B.J.; Hardesty, R.M.; Brewer, W.A.; Hajny, K.; Salmon, O.E.; Shepson, P.B. Doppler Lidar Observations of the Mixing Height in Indianapolis Using an Automated Composite Fuzzy Logic Approach. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halios, C.H.; Barlow, J.F. Observations of the Morning Development of the Urban Boundary Layer Over London, UK, Taken During the ACTUAL Project. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2018, 166, 395–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, R.J.; Grant, A.L.; Illingworth, A.J.; Pearson, G.N.; O’Connor, E.J. Vertical velocity variance and skewness in clear and cloud-topped boundary layers as revealed by Doppler lidar. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 135, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.J.; Hogan, R.J.; Dacre, H.F. A method to diagnose boundary-layer type using Doppler lidar. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 1681–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manninen, A.J.; Marke, T.; Tuononen, M.; O’Connor, E.J. Atmospheric Boundary Layer Classification with Doppler Lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8172–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthaus, S.; Halios, C.H.; Barlow, J.F.; Grimmond, C. Volume for pollution dispersion: London’s atmospheric boundary layer during ClearfLo observed with two ground-based lidar types. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 190, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devara, P.C.S.; Jaya Rao, Y.; Sonbawne, S.M.; Manoj, M.G.; Dani, K.K.; Saha, S.K. First results of compact coherent Doppler wind lidar and its validation at IITM, Pune, India. Meteorol. Appl. 2015, 22, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.R.; Barlow, J.F.; Lane, S.E. Observations of wind speed profiles over Greater London, UK, using a Doppler lidar. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 121, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, C.W.; Grimmond, C.; Gatey, D.; Barlow, J.F. Assessing methods to extrapolate the vertical wind-speed profile from surface observations in a city centre during strong winds. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 173, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Rizzo, F.; Ricciardelli, F.; Avossa, A. Characterization of Mean Wind Profiles and Surface Roughness Assessment from Wind LIDAR Measurements. In Proceedings of the Conference of the Italian Association for Wind Engineering, Naples, Italy, 9–12 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 689–702. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Akashi, Y.; Ooka, R.; Kikumoto, H.; Choi, Y. A probabilistic approach to the energy-saving potential of natural ventilation: Effect of approximation method for approaching wind velocity. Build. Environ. 2017, 122, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikumoto, H.; Ooka, R.; Sugawara, H.; Lim, J. Observational study of power-law approximation of wind profiles within an urban boundary layer for various wind conditions. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2017, 164, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.; Pauscher, L.; Ward, H.; Kotthaus, S.; Barlow, J.; Gouvea, M.; Lane, S.; Grimmond, C. Wind observations above an urban river using a new lidar technique, scintillometry and anemometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, H.; Murayama, Y.; Ishii, S.; Mizutani, K.; Ohno, Y.; Hashiguchi, T. Strong Updraft at a Sea-Breeze Front and Associated Vertical Transport of Near-Surface Dense Aerosol Observed by Doppler Lidar and Ceilometer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2011, 141, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, Y. Effect of Land-Use Change on the Urban Heat Island in the Fukuoka–Kitakyushu Metropolitan Area, Japan. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Emmitt, G.D. Impact of airborne Doppler wind lidar profiles on numerical simulations of a tropical cyclone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, M.; Langland, R.H.; Cardinali, C.; Pauley, P.M.; Rahm, S. Influence of airborne Doppler wind lidar profiles near Typhoon Sinlaku on ECMWF and NOGAPS forecasts. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 138, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavaya, M.J.; Beyon, J.Y.; Koch, G.J.; Petros, M.; Petzar, P.J.; Singh, U.N.; Trieu, B.C.; Yu, J. The Doppler Aerosol Wind (DAWN) Airborne, Wind-Profiling Coherent-Detection Lidar System: Overview and Preliminary Flight Results. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 826–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.A.; Atlas, R.; Emmitt, G.D.; Bucci, L.; Ryan, K. Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar Observations of the Tropical Cyclone Boundary Layer. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantillon, F.; Wieser, A.; Adler, B.; Corsmeier, U.; Knippertz, P. Overview and first results of the Wind and Storms Experiment (WASTEX): A field campaign to observe the formation of gusts using a Doppler lidar. Adv. Sci. Res. 2018, 15, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, M.; Braun, F.J.; Gantner, L.; Mayr, G.J.; Rahm, S.; Reitebuch, O. The Alpine Mountain–Plain Circulation: Airborne Doppler Lidar Measurements and Numerical Simulations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 3095–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, U.; Weinzierl, B.; Reitebuch, O.; Schlager, H.; Minikin, A.; Forster, C.; Baumann, R.; Sailer, T.; Graf, K.; Mannstein, H.; et al. Airborne observations of the Eyjafjalla volcano ash cloud over Europe during air space closure in April and May 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2245–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W. Comparison of Field Measurements and Numerical Simulations for Atmospheric Boundary Layer Flow over a Cylindrical Building. Master’s Thesis, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, W.E.; Atlas, R.; Cardinali, C.; Clement, A.; Emmitt, G.D.; Gentry, B.M.; Hardesty, R.M.; Källén, E.; Kavaya, M.J.; Langland, R.; et al. Lidar-Measured Wind Profiles: The Missing Link in the Global Observing System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 2; Technical Report; National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder Co Mesoscale and Microscale: Boulder, CO, USA, 2005.
- Weissmann, M.; Cardinali, C. The impact of airborne Doppler lidar observations on ECMWF forecasts. ECMWF Tech. Memo. 2007, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, S.; Strehz, A.; Emeis, S. Remote sensing winds in complex terrain—A review. Meteorol. Z. 2015, 24, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Menke, R.; Vasiljević, N.; Berg, J.; Troldborg, N. Challenges in using scanning lidars to estimate wind resources in complex terrain. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1037, 072017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, S.T.; Warden, M.; Macarthur, J.; Silver, M.; Holtom, T.C.; McDonald, C.; Clive, P.; Bookey, H.T. Advances in Doppler Lidar for Accurate 3D Wind Measurements. In Imaging and Applied Optics 2018 (3D, AO, AIO, COSI, DH, IS, LACSEA, LS& C, MATH, pcAOP); OSA Publishing: Washington DC, USA, 2018; p. AM2A-3. [Google Scholar]
- Oertel, S.; Eggert, M.; Gutsmuths, C.; Wilhelm, P.; Müller, H.; Többen, H. Validation of three-component wind lidar sensor for traceable highly resolved wind vector measurements. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2019, 8, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, A.; Clive, P.; Gottschall, J.; Schlipf, D.; Simley, E.; Simmons, L.; Stein, D.; Trabucchi, D.; Vasiljevic, N.; Würth, I. IEA Wind Task 32: Wind Lidar Identifying and Mitigating Barriers to the Adoption of Wind Lidar. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Mann, J. A review of turbulence measurements using ground-based wind lidars. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3147–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Droegemeier, K.K.; Gong, J.; Xu, Q. A Method for Retrieving Mean Horizontal Wind Profiles from Single-Doppler Radar Observations Contaminated by Aliasing. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccippio, D.J. A Diagnostic Analysis of the VVP Single-Doppler Retrieval Technique. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, S.; Xue, M. Background error covariance functions for vector wind analyses using Doppler-radar radial-velocity observations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 132, 2887–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Nai, K.; Wei, L. An innovation method for estimating radar radial-velocity observation error and background wind error covariances. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 133, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenc, A.C. Atmospheric Data Assimilation; Meteorological Office: Berkshire, UK, 1995.
- Choukulkar, A.; Calhoun, R.; Billings, B.; Doyle, J.D. A Modified Optimal Interpolation Technique for Vector Retrieval for Coherent Doppler LIDAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuru, N.W.; Calhoun, R.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Benny, S.; Reuder, J.; Flügge, M. 2D VAR single Doppler lidar vector retrieval and its application in offshore wind energy. Energy Procedia 2017, 137, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.J.; Shao, A.M.; Liu, S.; Xu, Q. A two-step variational method for three-dimensional wind retrieval from single Doppler radar. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2006, 91, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, R.K.; Ligon, D.; Calhoun, R.; Heap, R.; Cregan, E.; Princevac, M. Retrieval of Microscale Wind and Temperature Fields from Single- and Dual-Doppler Lidar Data. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 1324–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, R.K.; Banta, R.M. Assimilating Coherent Doppler Lidar Measurements into a Model of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Part I: Algorithm Development and Sensitivity to Measurement Error. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 1328–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, C.G.; Davies, F.; Bozier, K.E.; Holt, A.R.; Middleton, D.R.; Pearson, G.N.; Siemen, S.; Willetts, D.V.; Upton, G.J.G.; Young, R.I. Dual-Doppler Lidar Measurements for Improving Dispersion Models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheynet, E.; Jakobsen, J.B.; Snæbjörnsson, J.; Mann, J.; Courtney, M.; Lea, G.; Svardal, B. Measurements of Surface-Layer Turbulence in a Wide Norwegian Fjord Using Synchronized Long-Range Doppler Wind Lidars. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, R.K.; Berg, L.K.; Shaw, W.J.; Fischer, M.L. Turbine-scale wind field measurements using dual-Doppler lidar. Wind Energy 2015, 18, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.; Vasiljevíc, N.; Kelly, M.; Lea, G.; Courtney, M. Addressing Spatial Variability of Surface-Layer Wind with Long-Range WindScanners. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, F.C.; Iungo, G.V.; Porté-Agel, F. 3D Turbulence Measurements Using Three Synchronous Wind Lidars: Validation against Sonic Anemometry. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljević, N.; Palma, J.M.L.M.; Angelou, N.; Carlos Matos, J.; Menke, R.; Lea, G.; Mann, J.; Courtney, M.; Frölen Ribeiro, L.; Gomes, V.M.M.G.C. Perdigão 2015: Methodology for atmospheric multi-Doppler lidar experiments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3463–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildmann, N.; Vasiljevic, N.; Gerz, T. Wind turbine wake measurements with automatically adjusting scanning trajectories in a multi-Doppler lidar setup. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3801–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Lin, C.L.; Newsom, R.K. Retrieval of Microscale Flow Structures from High-Resolution Doppler Lidar Data Using an Adjoint Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 1500–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; MizutaniI, K.; Aoki, T.; Sasano, M.; Murayama, Y.; Itabe, T.; Asai, K. Wind Profiling with an Eye-Safe Coherent Doppler Lidar System: Comparison with Radiosondes and VHF Radar. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2005, 83, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalikho, I.; Köpp, F.; Rahm, S. Measurement of Atmospheric Turbulence by 2-μm Doppler Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 1733–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Mann, J.; Gottschall, J.; Courtney, M.S. Can Wind Lidars Measure Turbulence? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.; Barlow, J.; Wood, C. An assessment of a three-beam Doppler lidar wind profiling method for use in urban areas. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 119, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestein, H.B.; Houser, J.B.; French, M.M.; Snyder, J.C.; Emmitt, G.D.; PopStefanija, I.; Baldi, C.; Bluth, R.T. Observations of the Boundary Layer near Tornadoes and in Supercells Using a Mobile, Collocated, Pulsed Doppler Lidar and Radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaas, T.; Pauscher, L.; Callies, D. LiDAR-mast deviations in complex terrain and their simulation using CFD. Meteorol. Z. 2015, 24, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, R.K.; Brewer, W.A.; Wilczak, J.M.; Wolfe, D.; Oncley, S.; Lundquist, J.K. Validating precision estimates in horizontal wind measurements from a Doppler lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, J.; Lopes, A.S.; Gomes, V.C.; Rodrigues, C.V.; Menke, R.; Vasiljević, N.; Mann, J. Unravelling the wind flow over highly complex regions through computational modeling and two-dimensional lidar scanning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1222, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

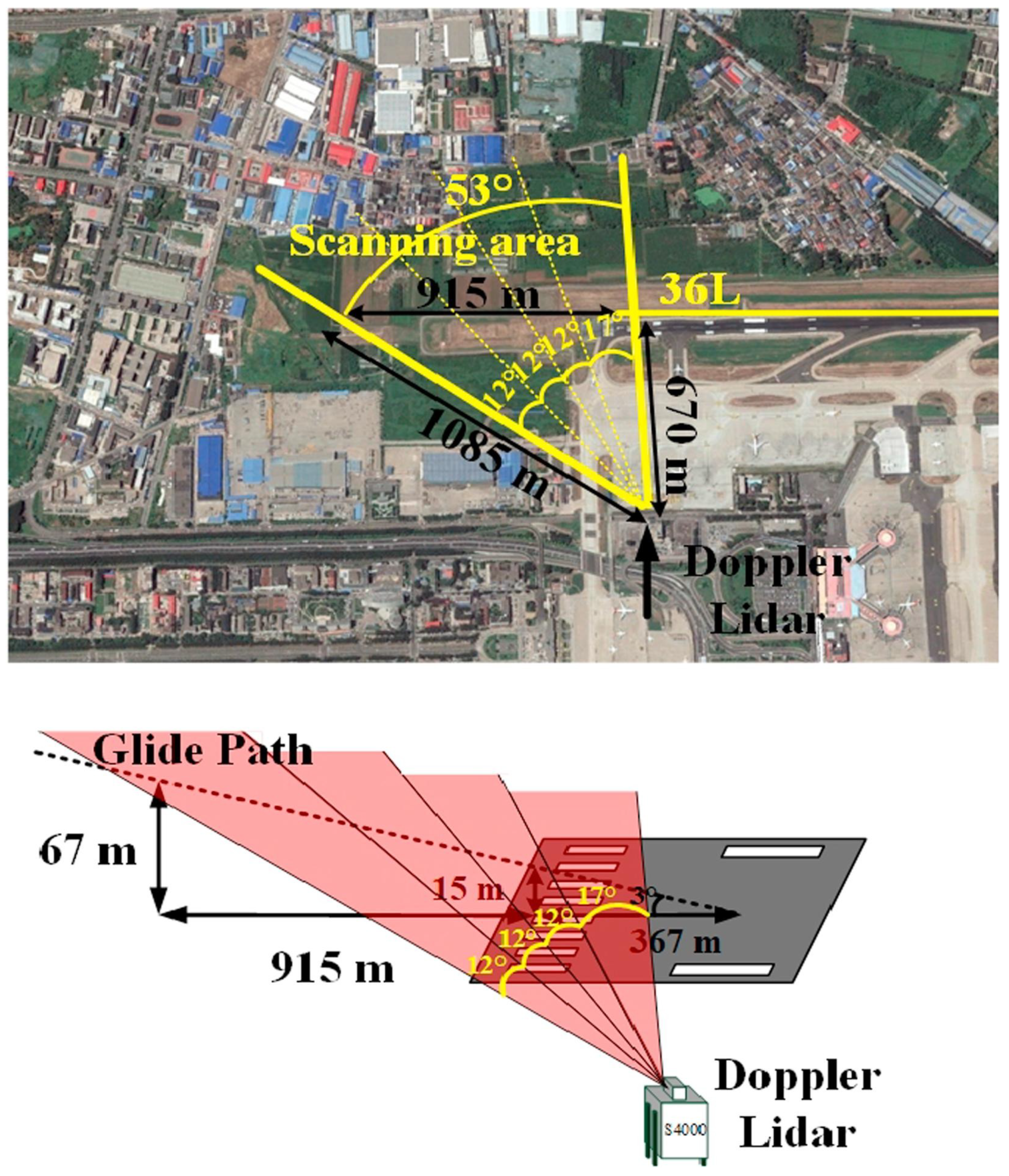
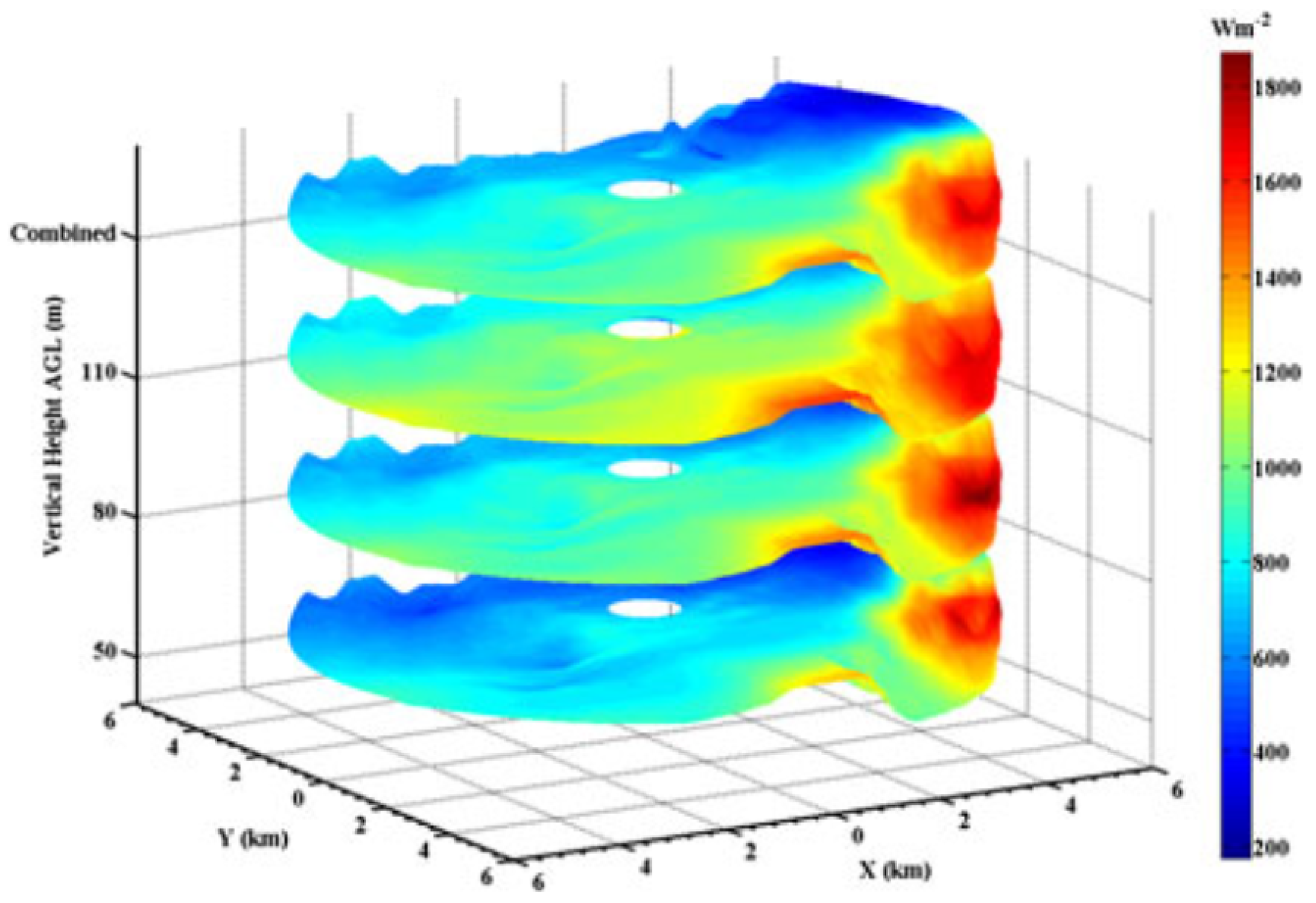
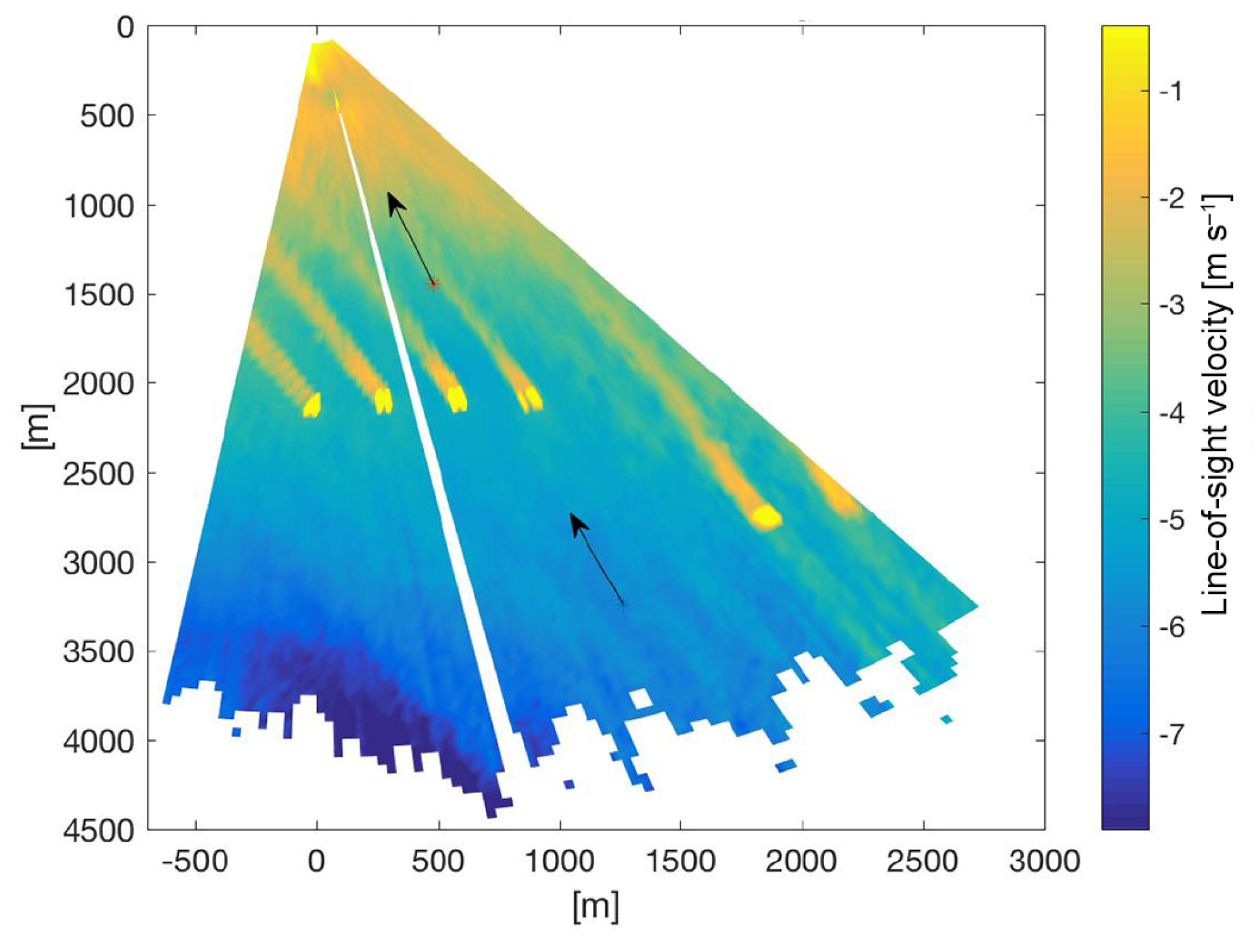

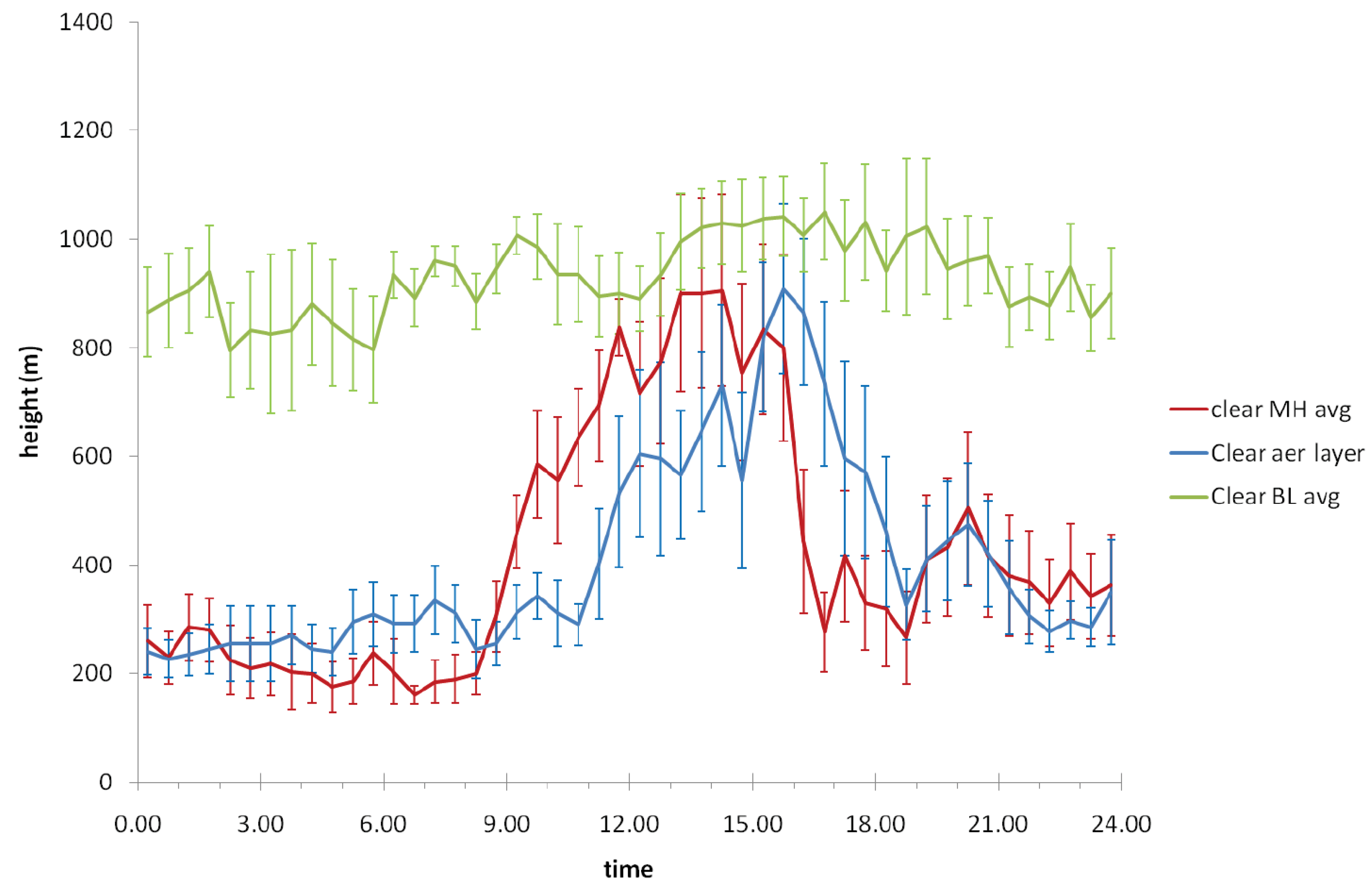
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical anemometers (e.g., cup anemometers) | Extremely robust and easy to maintain [2]. | Insufficient to measure weak and unsteady wind field [3]. |
| Sonic anemometer | High sampling frequency (e.g., 100 Hz) [4]. Able to measure 3-dimensional (3D) wind vector field [5]. Most widely used technique in turbulence measurements [3]. | Unable to measure the dissipation range of turbulence accurately [6]. Additional errors may be introduced to sonic measurements due to sensor wake effects [3]. Sensitive to temperature changes [7]. |
| Sound detection and ranging devices (SODARs) | Able to measure 3D wind vector [8]. Low sampling rate (e.g., 0.1 Hz) [2]. | Generating audible acoustic noise. Measurements may be polluted by ambient noise [9], e.g., noise from construction activities. |
| Doppler wind LiDARs | Able to measure 3D wind vector field. Maximum measurement distance up to 10 km and beyond [10]. | Ineffective under adverse weather conditions such as rainfall and fog. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Barlow, J.F.; Chan, P.-W.; Fung, J.C.H.; Li, Y.; Ren, C.; Mak, H.W.L.; Ng, E. A Review of Progress and Applications of Pulsed Doppler Wind LiDARs. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212522
Liu Z, Barlow JF, Chan P-W, Fung JCH, Li Y, Ren C, Mak HWL, Ng E. A Review of Progress and Applications of Pulsed Doppler Wind LiDARs. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(21):2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212522
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhengliang, Janet F. Barlow, Pak-Wai Chan, Jimmy Chi Hung Fung, Yuguo Li, Chao Ren, Hugo Wai Leung Mak, and Edward Ng. 2019. "A Review of Progress and Applications of Pulsed Doppler Wind LiDARs" Remote Sensing 11, no. 21: 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212522
APA StyleLiu, Z., Barlow, J. F., Chan, P.-W., Fung, J. C. H., Li, Y., Ren, C., Mak, H. W. L., & Ng, E. (2019). A Review of Progress and Applications of Pulsed Doppler Wind LiDARs. Remote Sensing, 11(21), 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212522