Orange Snow—A Saharan Dust Intrusion over Romania During Winter Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. Meteorological Data
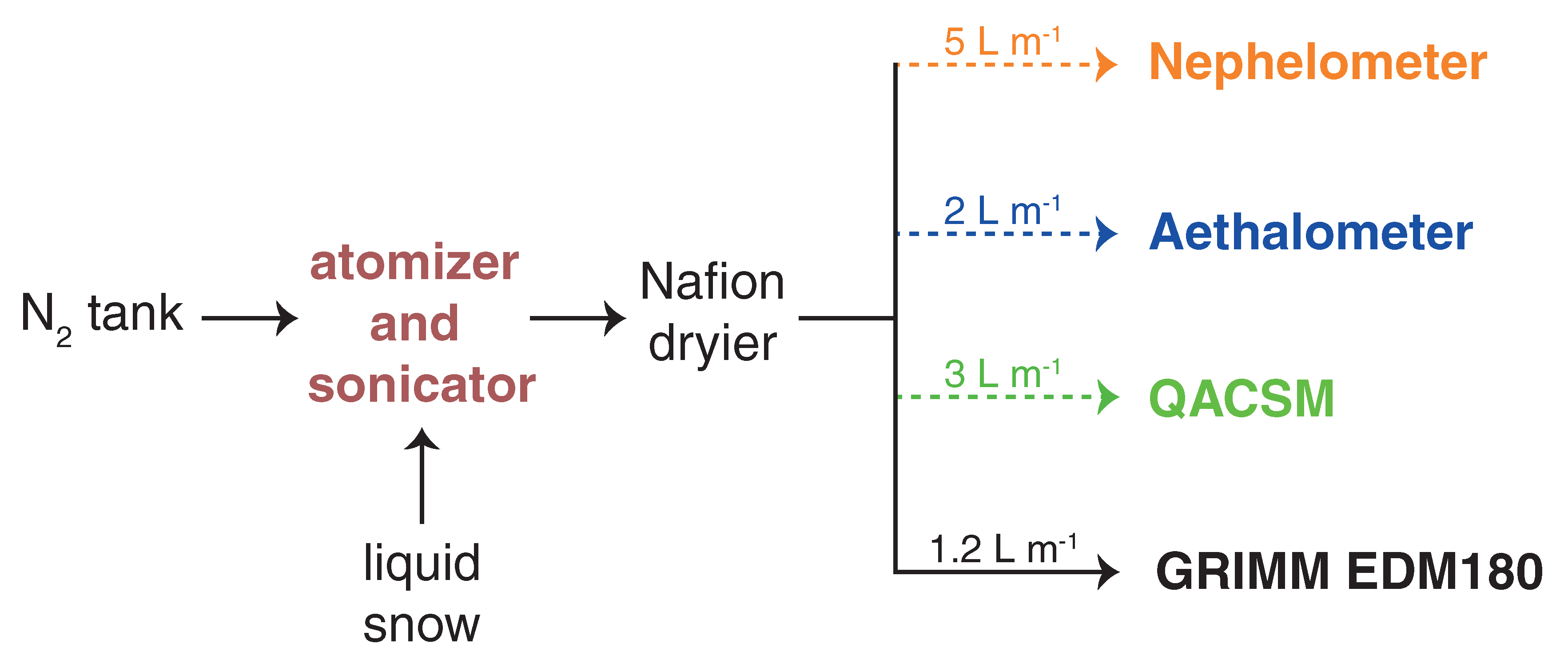
2.3. Ambient Aerosols Measurements before Dust Snow Event
2.4. Dust Deposition Measurements
3. Results
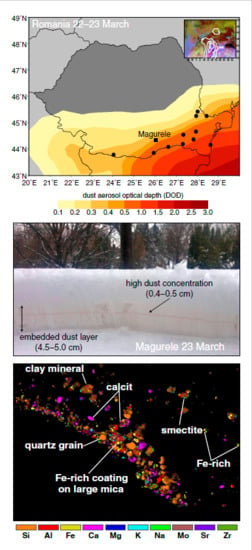
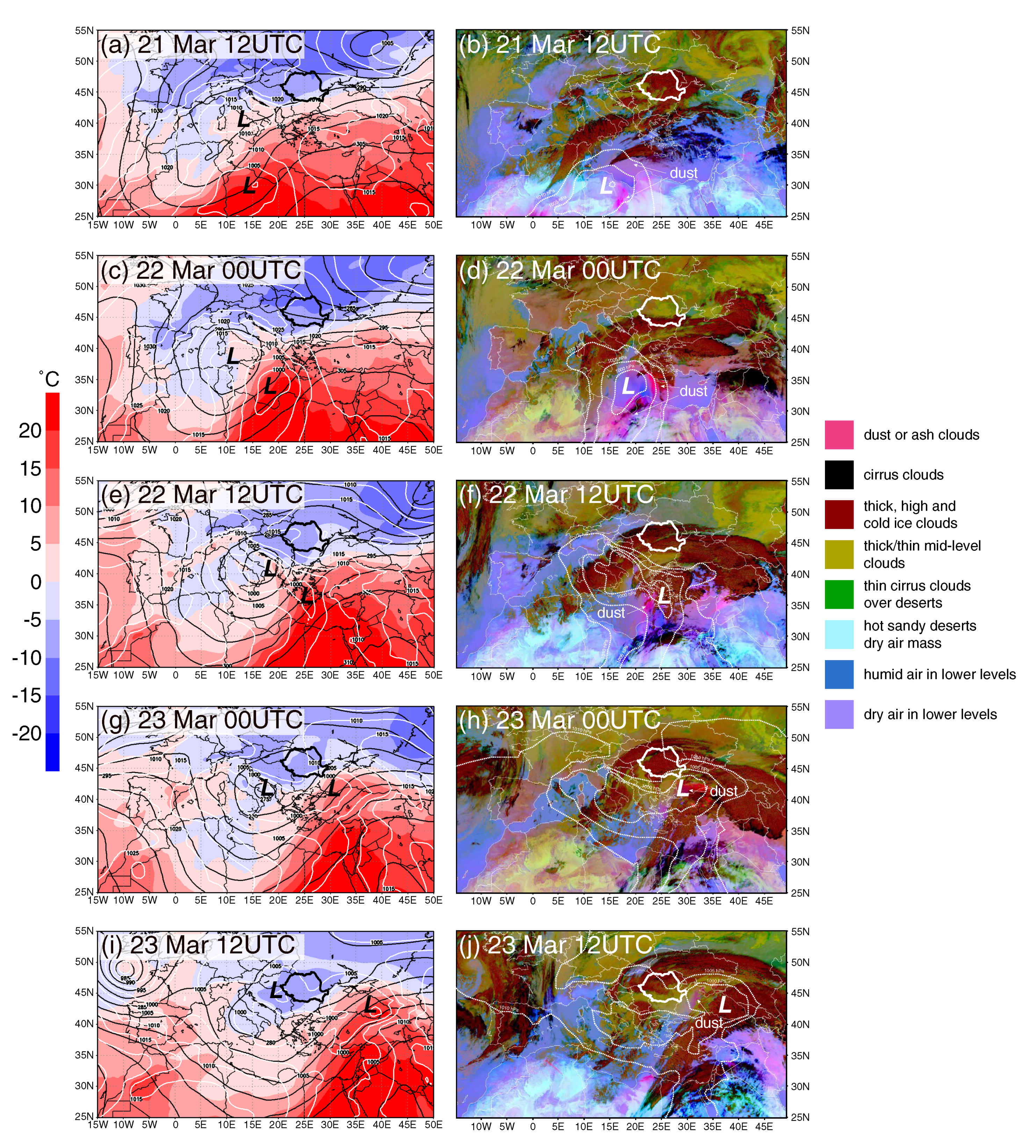
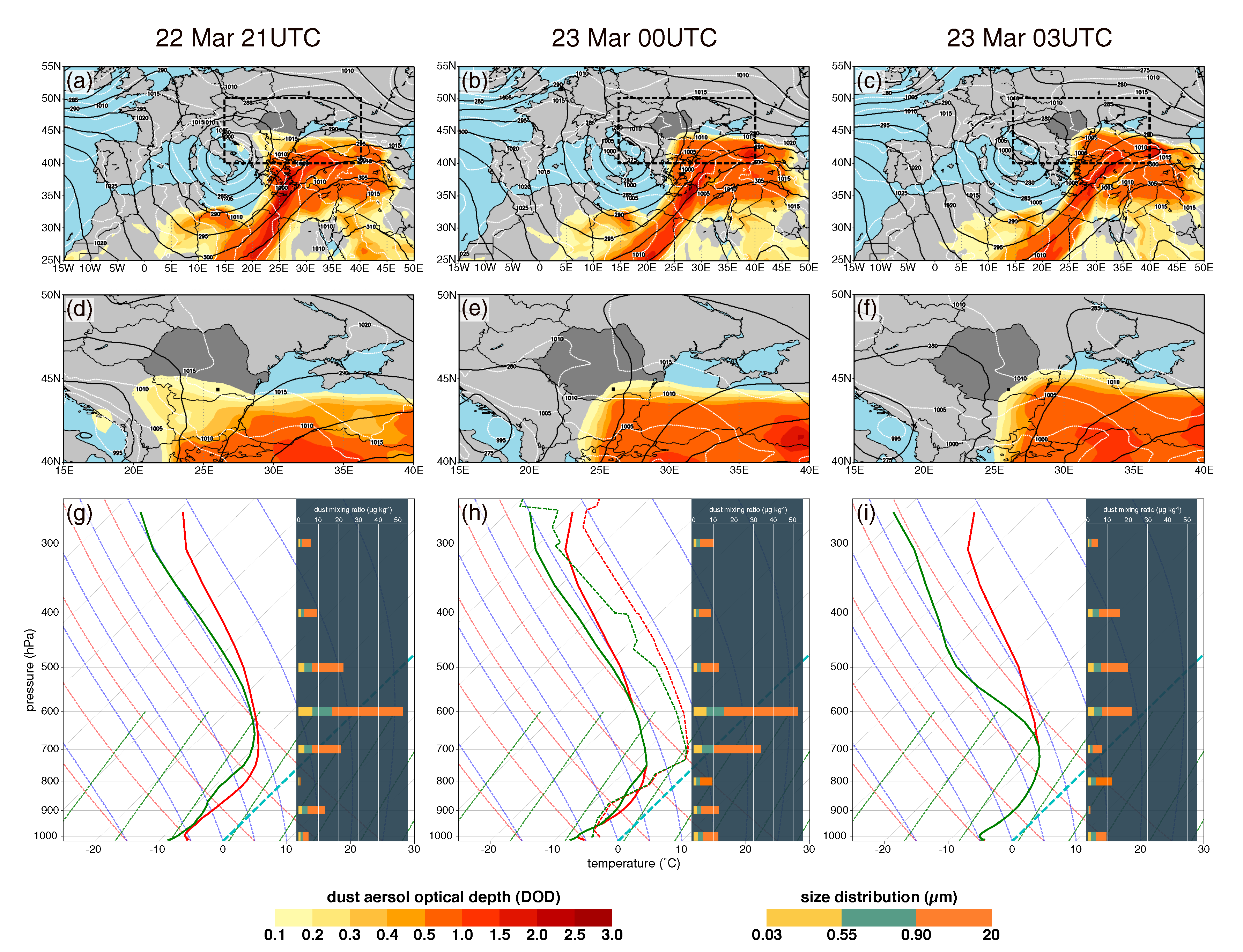
3.1. Synoptic Context
3.2. Local Conditions before Dust Snow Event
3.3. Saharan Dust Signature in Snow Layer
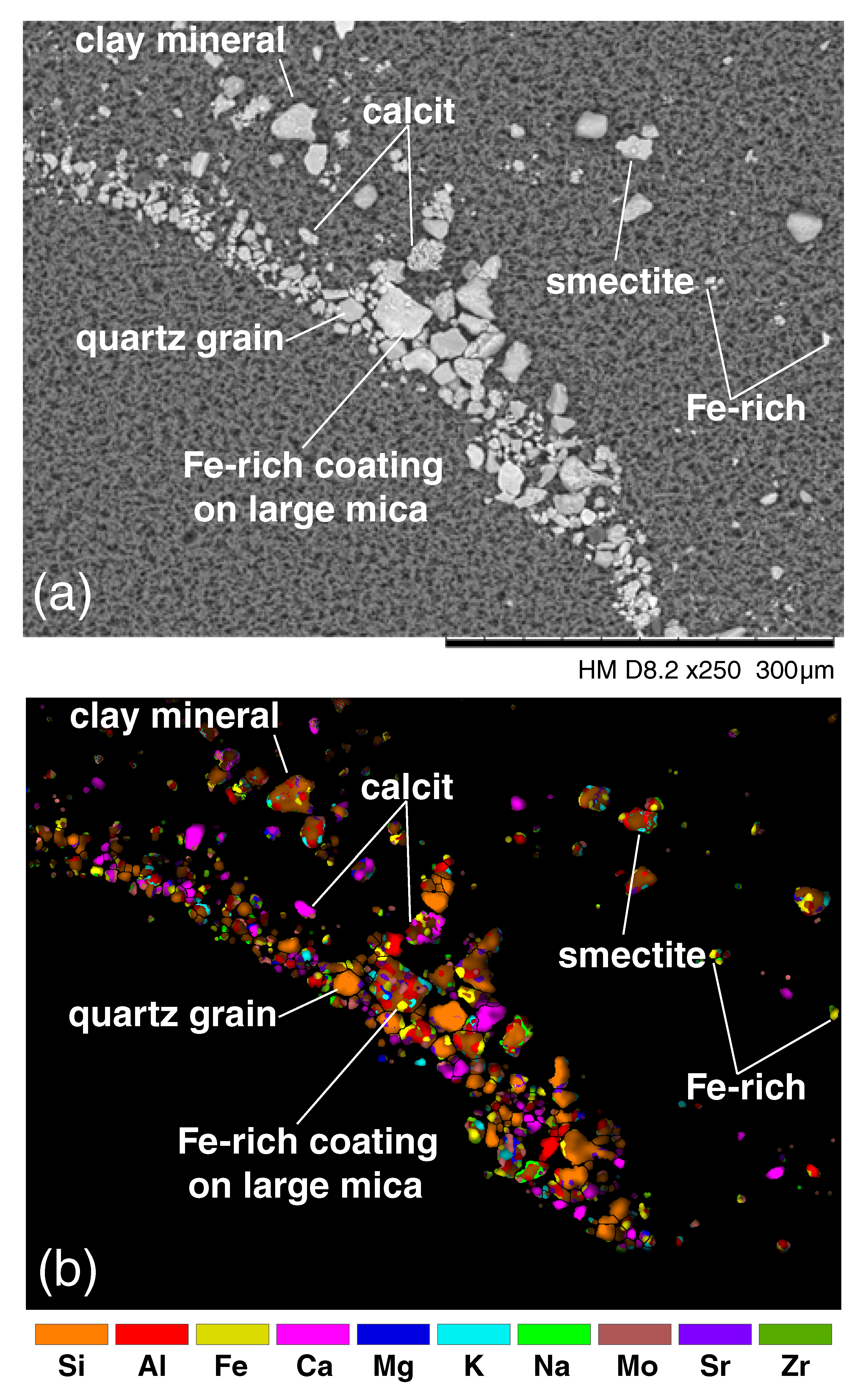
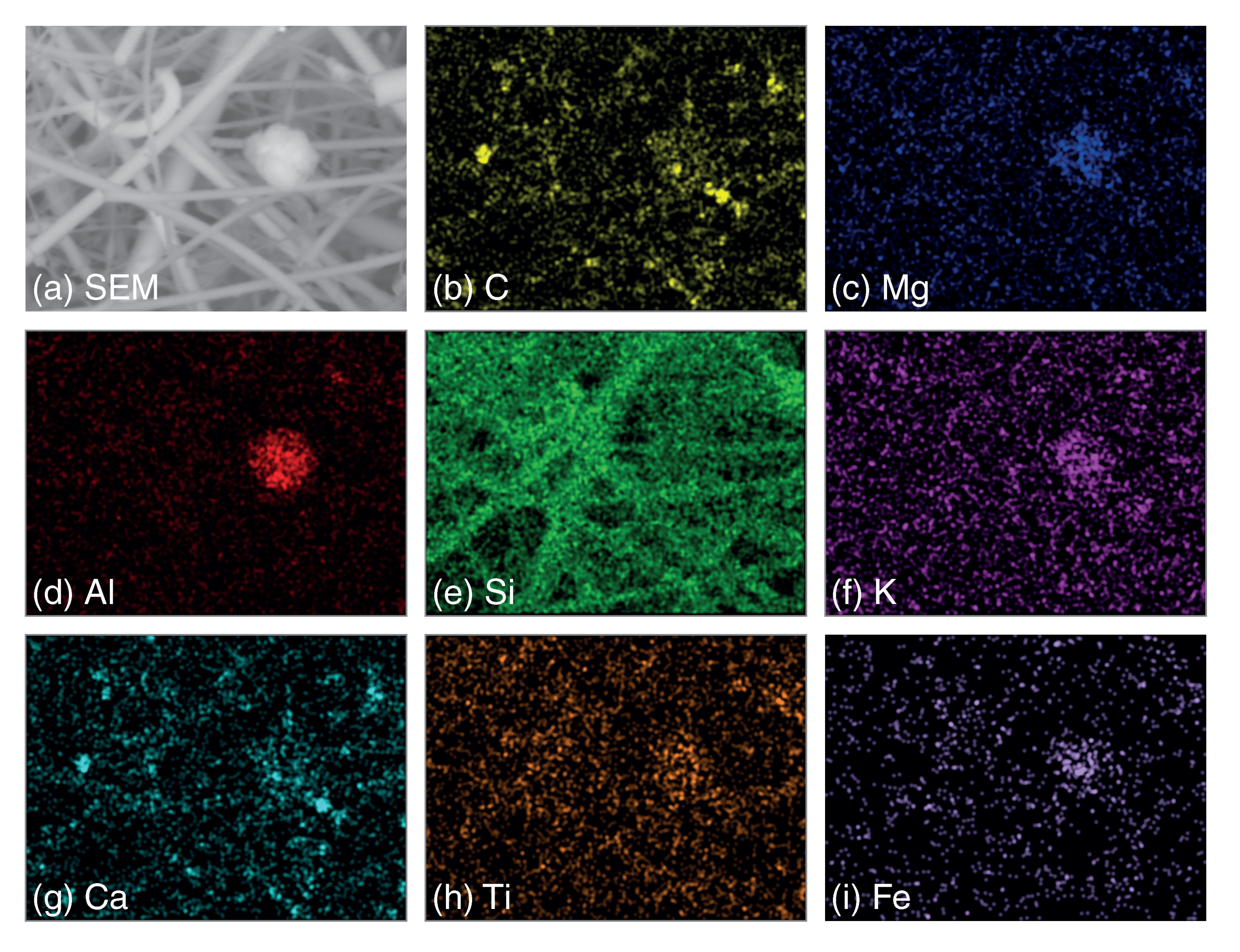
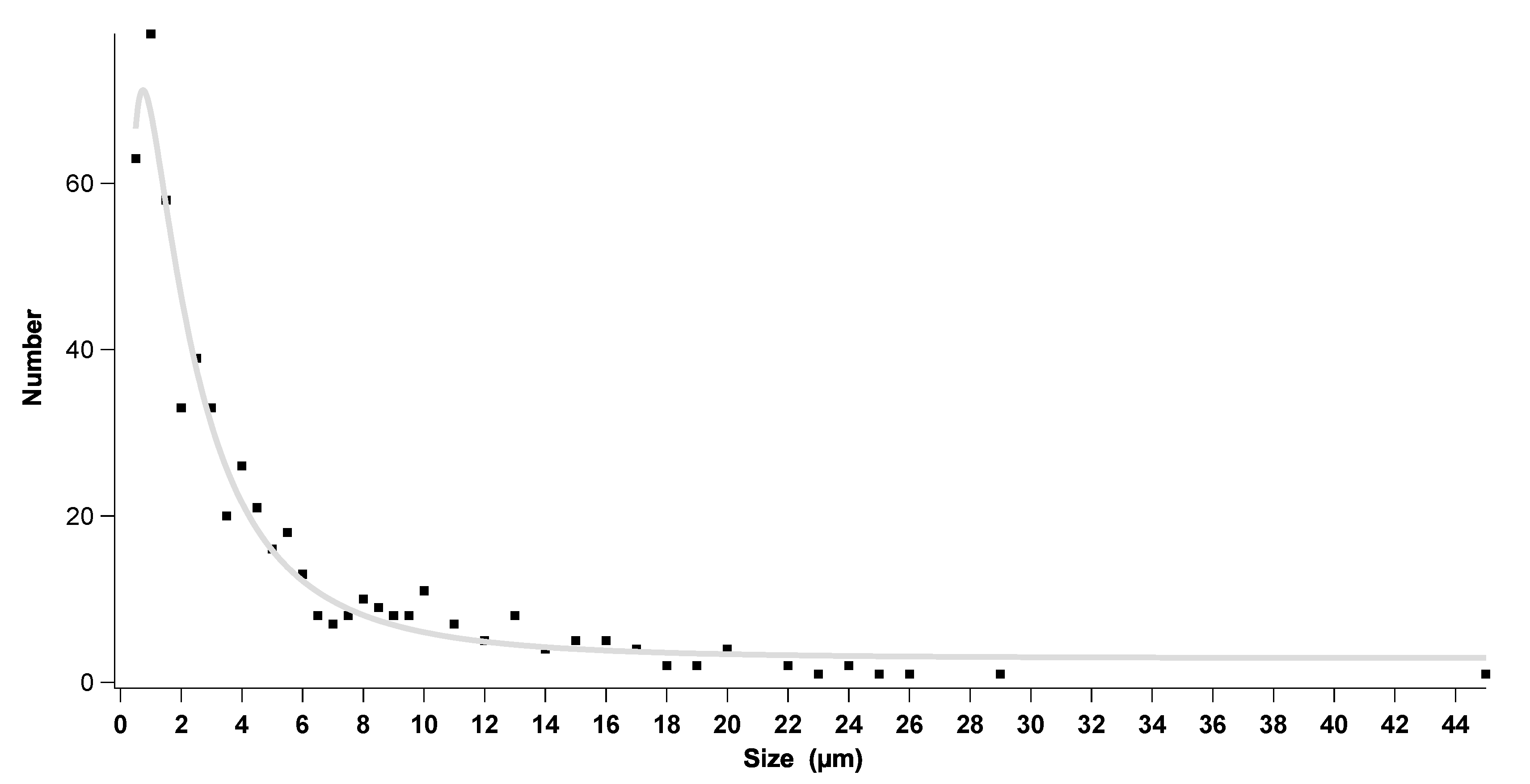
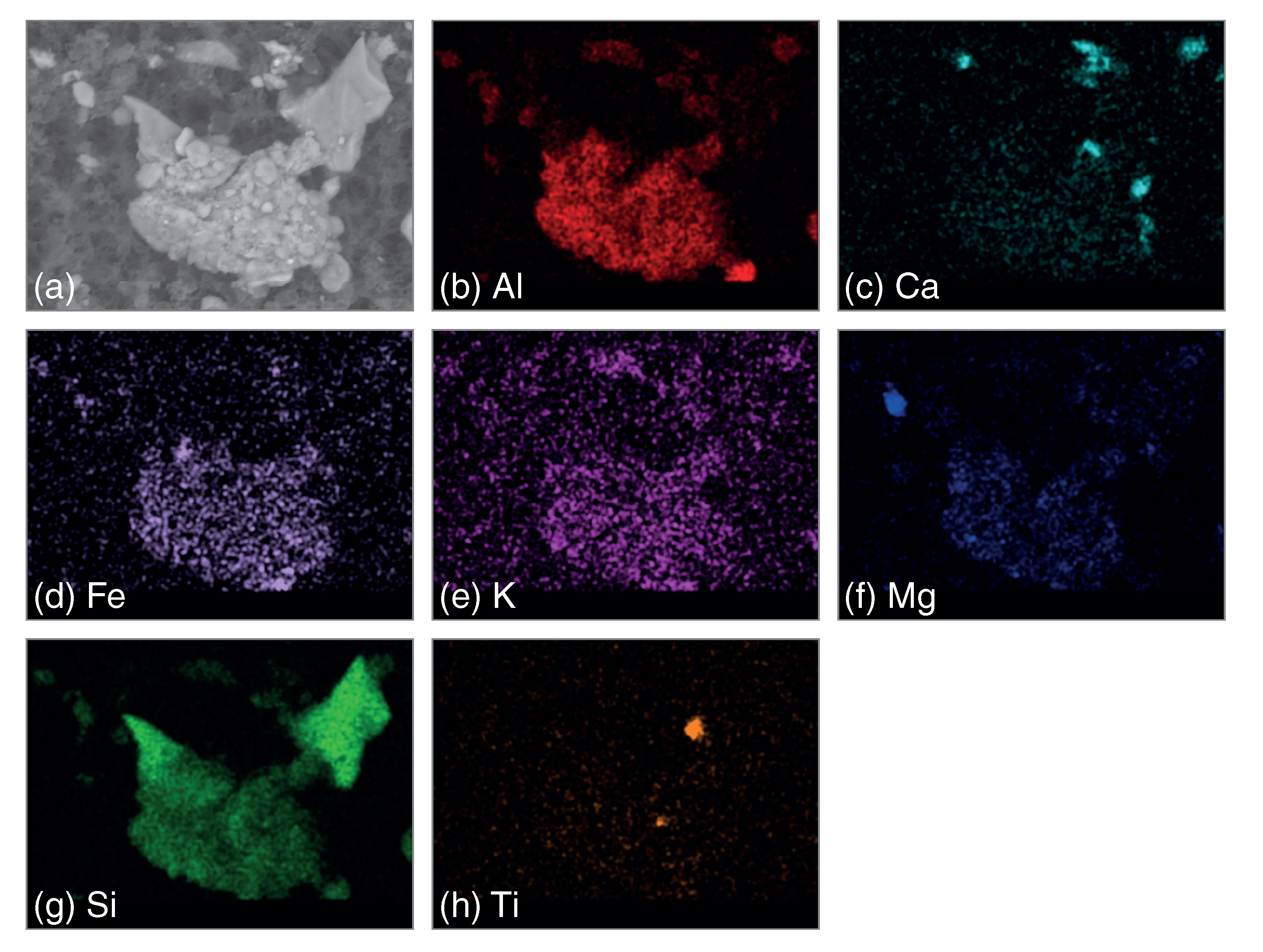
3.3.1. Particle Morphology and Chemical Composition
3.3.2. The Optical Parameters of Re-Suspended Transported Dust Particles
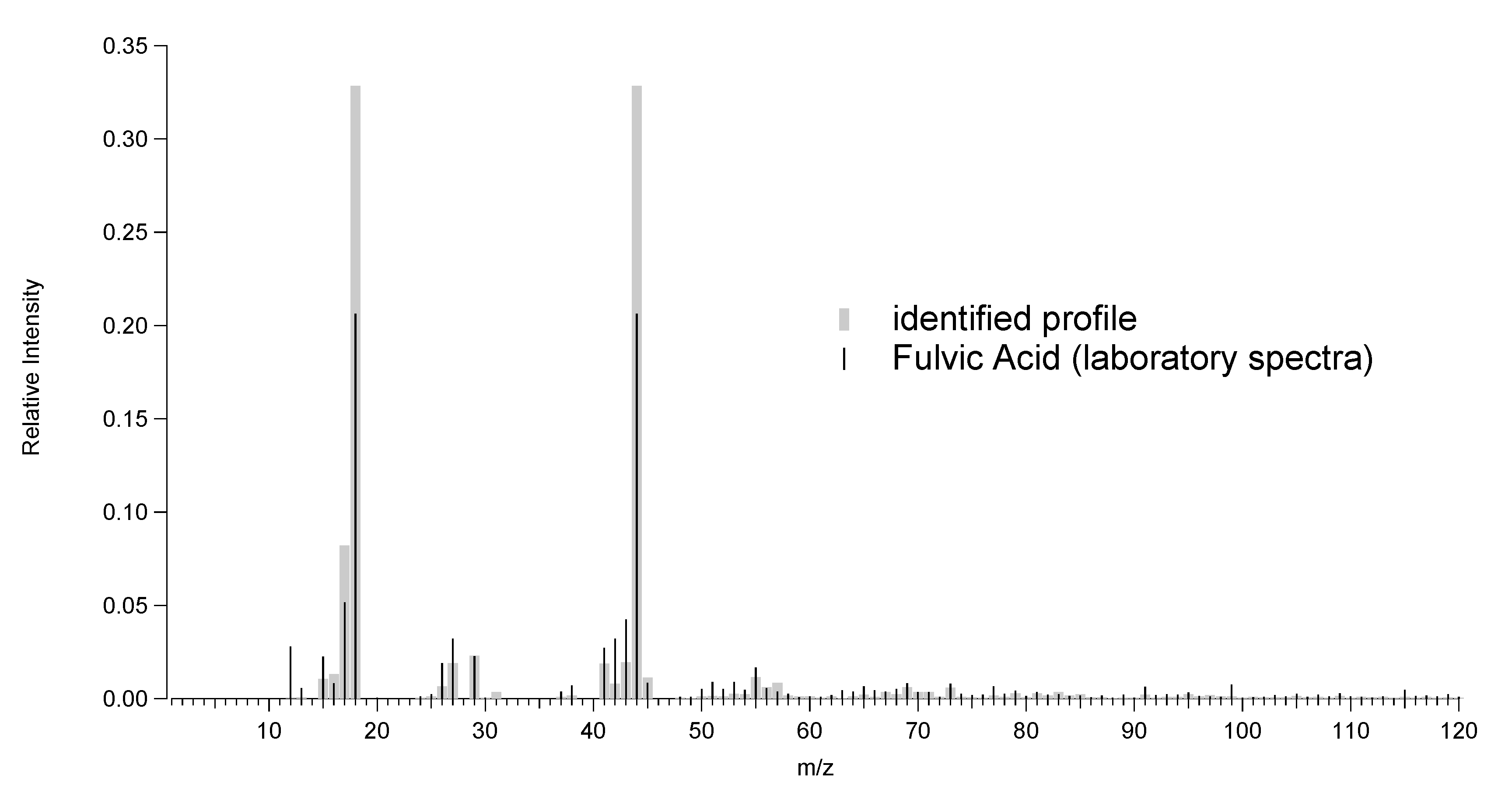
3.3.3. Nonrefractory Mass Fraction Signature of Transported Dust Particles
4. Conclusions
- The chemical analyses and the ratios computed from elemental concentrations (confirmed by the synoptic scale circulations) allowed the identification of the dust origin as the north Sahara; for example, the ratio between (Ca+Mg)/Fe was 1.39 for the sample analyzed in this article, values greater that 1.20 being characteristics for Algeria, Libya or Egypt as shown in previous studies. Other ratios between elemental concentrations (e.g., Ca/Al, Mg/Al) supported this conclusion,
- The presence of biological markers (i.e., diatoms), characteristics for Bodélé Depression, indicate the possible contamination of the dust from our sample with particles from the Sub-Saharan belt area during our event or during previous dust storms,
- A new approach was developed to highlight different mineral associations. In this approach, images for each elemental compound are merged; the presence of clay minerals, quartz or calcite were evidenced through this analyses,
- Optical parameters were measured for re-suspended Saharan dust fine fraction; the obtained values are similar with that obtain in the Iberian Peninsula regularly affected by dust intrusions,
- The pattern of organic spectra obtained, indicates the possible contamination of the dust with marine aerosols due to presence of highly oxidized organics as HULIS-like compounds.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Querol, X.; Tobías, A.; Pérez, A.; Karanasioua, A.; Amato, F.; Stafoggia, M.; García-Pando, C.P.; Ginoux, P.; Forastiere, F.; Gumy, S.; et al. Monitoring the impact of desert dust outbreaks for air quality for health studies. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Almeida, G.A. A model for saharan dust transport. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1986, 25, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Blades, E.; Mathison, G.; Naidu, R. Interhemispheric transport of viable fungi and bacteria from Africa to the Caribbean with soil dust. Aerobiologia 2005, 21, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Binietoglou, I.; Tsikerdekis, A.; Solomos, S.; Proestakis, E.; Konsta, D.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Tsekeri, A.; Vlastou, G.; et al. Three-dimensional evolution of Saharan dust transport towards Europe based on a 9-year EARLINET-optimized CALIPSO dataset. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5893–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S. Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ. Int. 2014, 63, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in Earth system science. Aeolian Res. 2005, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telloli, C.; Chicca, M.; Pepi, S.; Vaccaro, C. Saharan dust particles in snow samples of Alps and Apennines during an exceptional event of transboundary air pollution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, B.; Garzonio, R.; Rossini, M.; Filippa, G.; Pogliotti, P.; Galvagno, M.; di Cella, U.M.; Migliavacca, M.; Baccolo1, G.; Clemenza, M.; et al. Saharan dust events in the European Alps: Role in snowmelt and geochemical characterization. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 1147–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Tong, D.Q.; Wu, G.; Dan, M.; Teng, B. A systematic review of global desert dust and associated human health effects. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meola, M.; Lazzaro, A.; Zeyer, J. Bacterial composition and survival on Sahara dust particles transported to the European Alps. Front Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Engelbrecht, J.P.; Skiba, M.; Frey, G.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Arnott, W.P. Single scattering albedo of fine mineral dust aerosols controlled by iron concentration. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, L.; Amodeo, A.; Pandolfi, M.; Pappalardo, G. Saharan dust intrusions in the Mediterranean area: Three years of Raman lidar measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannis, A.; Amiridis, V.; Mona, L.; Tsaknakis, G.; Balis, D.; Bösenberg, J.; Chaikovski, A.; De Tomasi, F.; Grigorov, I.; Mattis, I.; et al. Systematic lidar observations of Saharan dust over Europe in the frame of EARLINET (2000–2002). J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Ansmann, A.; Freudenthaler, V.; Kandler, K.; Toledano, C.; Hiebsch, A.; Gasteiger, J.; Esselborn, M.; Tesche, M.; Heese, B.; et al. Mineral dust observed with AERONET Sun photometer, Raman lidar, and in situ instruments during SAMUM 2006: Shape-dependent particle properties. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D11207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binietoglou, I.; Basart, S.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Amiridis, V.; Argyrouli, A.; Baars, H.; Baldasano, J.M.; Balis, D.; Belegante, L.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; et al. A methodology for investigating dust model performance using synergistic EARLINET/AERONET dust concentration retrievals. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 3577–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ealo, M.; Alastuey, A.; Ripoll, A.; Pérez, N.; Minguillón, M.; Querol, X.; Pandolfi, M. Detection of Saharan dust and biomass burning events using near-real-time intensive aerosol optical properties in the north-western Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12567–12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogren, J.A.; Andrews, E.; McComiskey, A.; Sheridan, P.; Jefferson, A.; Fiebig, M. New insights into aerosol asymmetry parameter. In Proceedings of the 16th ARM Science Team Meeting, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 27–31 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Barnaba, F.; Gobbi, G.P. Aerosol seasonal variability over the Mediterranean region and relative impact of maritime, continental and Saharan dust particles over the basin from MODIS data in the year 2001. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 2367–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marey, H.S.; Gille, J.C.; El-Askary, H.M.; Shalaby, E.A.; El-Raey, M.E. Aerosol climatology over Nile Delta based on MODIS, MISR and OMI satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10637–10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Schepanski, K.; Heinold, B. Comparing two years of Saharan dust source activation obtained by regional modelling and satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.R.; Schepanski, K.; Heinold, B.; Hünerbein, A.; Brindley, H.E. The influence of dust optical properties on the colour of simulated MSG-SEVIRI Desert Dust imagery. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9681–9703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandija, F.; Chavez-Perez, V.M.; Nieto, R.; Sicard, M.; Danylevsky, V.; Añel, J.A.; Gimeno, L. The climatology of dust events over the European continent using data of the BSC-DREAM8b model. Atmos. Res. 2018, 209, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomos, S.; Kalivitis, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Amiridis, V.; Kouvarakis, G.; Gkikas, A.; Binietoglou, I.; Tsekeri, A.; Kazadzis, S.; Kottas, M.; et al. From tropospheric folding to Khamsin and Foehn winds: How atmospheric dynamics advanced a record-breaking dust episode in Crete. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemuc, A.; Vasilescu, J.; Talianu, C.; Belegante, L.; Nicolae, D. Assessment of aerosol’s mass concentrations from measured linear particle depolarization ratio (vertically resolved) and simulations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3243–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, G.; Cserháti, C.; Kovács, J.; Szeberényi, J.; Bradák, B. Saharan dust deposition in the Carpathian Basin and its possible effects on interglacial soil formation. Aeolian Res. 2016, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaud Coen, M.; Weingartner, E.; Schaub, D.; Hueglin, C.; Corrigan, C.; Henning, S.; Schwikowski, M.; Baltensperger, U. Saharan dust events at the Jungfraujoch: Detection by wavelength dependence of the single scattering albedo and first climatology analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 2465–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cârstea, E.; Fragkos, K.; Siomos, N.; Antonescu, B.; Belegante, L. Columnar aerosol measurements in a continental southeastern Europe site: Climatology and trends. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 3149–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkos, K.; Antonescu, B.; Giles, D.M.; Ene, E.; Boldeanu, M.; Efstathiou, G.A.; Belegante, L.; Nicolae, D. Assessment of the total precipitable water from a sun photometer, microwave radiometer and radiosondes at a continental site in southeastern Europe. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 1979–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.A.; Mărmureanu, L.; Radu, C.; Dandocsi, A.; Stan, C.; Ţoancă, F.; Preda, L.; Antonescu, B. Wintertime variations of gaseous atmospheric constituents in Bucharest peri-Urban area. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ţoancă, F.; Ştefan, S. Temporal variability of atmospheric aerosols (PM10) in Magurele during 2006 and 2007. In Book of Abstracts, Annual Scientific Conference; University of Bucharest: Bucharest, Romania, 2012; pp. 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mărmureanu, L.; Vasilescu, J.; Nemuc, A.; Nicolae, D.; Belegante, L. Aerosol characterization based on chemical composition and optical properties. Rom. Journ. Phys. 2016, 61, 1635–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, C.; Mărmureanu, L.; Vasilescu, J. Seasonal variability of submicronic aerosols in Romania. Eur. Aerosol Conf. 2017, 16, 2491–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lensky, I.M.; Rosenfeld, D. Clouds-Aerosols-Precipitation Satellite Analysis Tool (CAPSAT). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6739–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcrette, J.J.; Boucher, O.; Jones, L.; Salmond, D.; Bechtold, P.; Benedetti, A.; Bonet, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Razinger, M.; Schulz, M.; et al. Aerosol analysis and forecast in the ECMWF integrated forecast system: Forward modelling. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D06206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, A.; Morcrette, J.J.; Boucher, O.; Dethof, A.; Engelen, R.J.; Fisher, M.; Flentjes, H.; Huneeus, N.; Jones, L.; Kaiser, J.W.; et al. The GEMS-AER team. Aerosol analysis and forecast in the ECMWF Integrated Forecast System: 2. Data assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D13205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.; Crewell, S.; Löhnert, U.; Simmer, C. A network suitable microwave radiometer for operational monitoring of the cloudy atmosphere. Atmos. Res. 2005, 75, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, S.; Müller, T.; Weinhold, K.; Zikova, N.; dos Santos, S.M.; Marinoni, A.; Bischof, O.F.; Kykal, C.; Ries, L.; Meinhardt, F.; et al. Intercomparison of 15 aerodynamic particle size spectrometers (APS 3321): Uncertainties in particle sizing and number size distribution. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Che, H.Z.; Li, Y. Spatial and temporal variations of the concentrations of PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13585–13598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; White, D.J.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L.; Ogren, J.A. Determining Aerosol Radiative Properties Using the TSI 3563 Integrating Nephelometer. Aerosol. Sci. Tech. 1998, 29, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingartner, E.; Saathoff, H.; Schnaiter, M.; Streit, N.; Bitnar, B.; Baltensperger, U. Absorption of light by soot particles: Determination of the absorption coefficient by means of aethalometers. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinovec, L.; Močnik, G.; Zotter, P.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Ruckstuhl, C.; Coz, E.; Rupakheti, M.; Sciare, J.; Müller, T.; Wiedensohler, A.; et al. The “dual-spot” Aethalometer: An improved measurement of aerosol black carbon with real-time loading compensation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, N.L.; Herndon, S.C.; Trimborn, A.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Croteau, P.L.; Onasch, T.B.; Sueper, D.; Worsnop, D.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.L.; et al. An aerosol chemical speciation monitor (ACSM) for routine monitoring of the composition and mass concentrations of ambient aerosol. Aerosol. Sci. Tech. 2011, 45, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguillón, M.C.; Ripoll, A.; Pérez, N.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Canonaco, F.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Chemical characterization of submicron regional background aerosols in the western Mediterranean using an Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6379–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.E.; Favez, O.; Sciare, J.; Crenn, V.; Sarda-Estève, R.; Bonnaire, N.; Močnik, G.; Dupont, J.C.; Haeffelin, M.; Leoz-Garziandia, E. Two years of near real-time chemical composition of submicron aerosols in the region of Paris using an Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitor (ACSM) and a multi-wavelength Aethalometer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2985–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freney, E.; Zhang, Y.; Croteau, P.; Amodeo, T.; Williams, L.; Truong, F.; Petit, J.; Sciare, J.; Sarda-Esteve, R.; Bonnaire, N.; et al. The second ACTRIS inter-comparison (2016) for Aerosol Chemical Speciation Monitors (ACSM): Calibration protocols and instrument performance evaluations. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheras, P.; Flocas, H.; Patrikas, I.; Anagnostopoulou, C. A 40 year objective climatology of surface cyclones in the Mediterranean region: Spatial and temporal distribution. Int. J. Clim. 2001, 21, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepanski, K.; Knippertz, P. Soudano-Saharan depressions and their importance for precipitation and dust: A new perspective on a classical synoptic concept. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2011, 137, 1431–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, P.; Ziv, B. The Sharav cyclone: Observations and some theoretical considerations. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 18495–18514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkan, J.; Alpert, P.; Kutiel, H.; Kishcha, P. Synoptics of dust transportation days from Africa toward Italy and central Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D07208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, S.; Schepanski, K.; Knippertz, P.; Heinold, B.; Tegen, I. How important are atmospheric depressions and mobile cyclones for emitting mineral dust aerosol in North Africa? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8983–9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmala, M.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Laaksonen, A. Cluster activation theory as an explanation of the linear dependence between formation rate of 3nm particles and sulphuric acid concentration. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.; Albani, S.; Kok, J.F.; Engelstaeder, S.; Scanza, R.; Ward, D.S.; Flanner, M.G. The size distribution of desert dust aerosols and its impact on the Earth system. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Lacis, A.A. Modeling of particle size distribution and its influence on the radiative properties of mineral dust aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 19237–19244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Does, M.; Knippertz, P.; Zschenderlein, P.; Harrison, R.; Stuut, J.B.W. The mysterious long-range transport of giant mineral dust particles. Sci. Adv. 2018, 12, eaau2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, P.; Schütz, L.; Balkanski, Y.; Desboeufs, K.; Ebert, M.; Kandler, K.; Petzold, A.; Scheuvens, D.; Weinbruch, S.; Zhang, D. Recent progress in understanding physical and chemical properties of African and Asian mineral dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8231–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuvens, D.; Schütz, L.; Kandler, K.; Ebert, M.; Weinbruch, S. Bulk composition of northern African dust and its source sediments—A compilation. Earth. Sci. Rev. 2013, 16, 170–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journet, E.; Balkanski, Y.; Harrison, S.P. A new data set of soil mineralogy for dust-cycle modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3801–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; Tomasi, F.D.; Filippo, E.; Manno, D.; Perrone, M.R.; Serra, A.; Tafuro, A.M.; Tepore, A. Characterization of African dust over southern Italy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafon, S.; Sokolik, I.N.; Rajot, J.L.; Caquineau, S.; Gaudichet, A. Characterization of iron oxides in mineral dust aerosols: Implications for light absorption. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D21207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desboeufs, K.V.; Cautenet, G. Transport and mixing zone of desert dust and sulphate over tropical Africa and the Atlantic Ocean region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2005, 5, 5615–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, R.; Desboeufs, K.V. Effect of atmospheric organic complexation on iron-bearing dust solubility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, M.; Sferlazzo, D.M.; Becagli, S.; Bommarito, C.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; di Sarra, A.; Ghedini, C.; Gómez-Amo, J.L.; Lucarelli, F.; et al. Saharan dust aerosol over the central Mediterranean Sea: PM10 chemical composition and concentration versus optical columnar measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, P.; Elbert, W.; Maenhaut, W.; Haywood, J.; Andreae, M. Chemical composition of mineral dust aerosol during the Saharan Dust Experiment (SHADE) airborne campaign in the Cape Verde region. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallar, A.G.; Petersen, R.; Andrews, E.; Michalsky, J.; McCubbin, I.B.; Ogren, J.A. Contributions of dust and biomass burning to aerosols at a Colorado mountain-top site. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13665–13679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, E.; Sheridan, P.J.; Fiebig, M.; McComiskey, A.; Ogren, J.A.; Arnott, P.; Covert, D.; Elleman, R.; Gasparini, R.; Collins, D.; et al. Comparison of methods for deriving aerosol asymmetry parameter. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D05S04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donateo, A.; Feudo, T.L.; Marinoni, A.; Dinoi, A.; Avolio, E.; Merico, E.; Calidonna, C.; Contini, D.; Bonasoni, P. Characterization of In Situ Aerosol Optical Properties at Three Observatories in the Central Mediterranean. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, C.D.; Gierlus, K.M.; amd, V.H. Grassian, J.D. Water adsorption and cloud condensation nuclei activity of calcite and calcite coated with model humic and fulvic acids. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5672–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Alfarra, M.R.; Worsnop, D.R.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Jimenez, J.L. Deconvolution and quantification of hydrocarbon-like and oxygenated organic aerosols based on aerosol mass Sspectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4938–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarra, M.R.; Paulsen, D.; Gysel, M.; Garforth, A.A.; Dommen, J.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Worsnop, D.R.; Baltensperger, U.; Coe, H. A mass spectrometric study of secondary organic aerosols formed from the photooxidation of anthropogenic and biogenic precursors in a reaction chamber. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 5279–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Gros, V.; Atlas, E.; Maciejczyk, K.; Batsaikhan, A.; Schöler, H.F.; Forster, C.; Quack, B.; Yassaa, N.; Sander, R.; et al. Possible evidence for a connection between methyl iodide emissions and Saharan dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D07302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element Ratio | ICP-OES | SEM/EDX | [59,61] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Si/Al | - | 2.91 | 2.5–7 |
| (Ca+Mg)/Fe | 1.31 | 0.98 | 0.8–2.2 |
| Fe/Al | 0.89 | 0.72 | 0.5–2.5 |
| K/Al | 0.231 | 0.30 | 0.1–0.5 |
| Ca/Al | 0.76 | 0.53 | >0.5 |
| Na/Al | 0.12 | 0.29 | <0.45 |
| Ti/Al | - | 0.006 | <0.1 |
| Mg/Al | 0.41 | 0.17 | 0.34–1.54 |
| K/Ca | 0.303 | 0.57 | 0.73–1.25 |
| Fe/Ca | 1.17 | 1.35 | 0.6 -0.83 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mărmureanu, L.; Marin, C.A.; Andrei, S.; Antonescu, B.; Ene, D.; Boldeanu, M.; Vasilescu, J.; Viţelaru, C.; Cadar, O.; Levei, E. Orange Snow—A Saharan Dust Intrusion over Romania During Winter Conditions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212466
Mărmureanu L, Marin CA, Andrei S, Antonescu B, Ene D, Boldeanu M, Vasilescu J, Viţelaru C, Cadar O, Levei E. Orange Snow—A Saharan Dust Intrusion over Romania During Winter Conditions. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(21):2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212466
Chicago/Turabian StyleMărmureanu, Luminiţa, Cristina Antonia Marin, Simona Andrei, Bogdan Antonescu, Dragoş Ene, Mihai Boldeanu, Jeni Vasilescu, Cătălin Viţelaru, Oana Cadar, and Erika Levei. 2019. "Orange Snow—A Saharan Dust Intrusion over Romania During Winter Conditions" Remote Sensing 11, no. 21: 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212466
APA StyleMărmureanu, L., Marin, C. A., Andrei, S., Antonescu, B., Ene, D., Boldeanu, M., Vasilescu, J., Viţelaru, C., Cadar, O., & Levei, E. (2019). Orange Snow—A Saharan Dust Intrusion over Romania During Winter Conditions. Remote Sensing, 11(21), 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212466