Abstract
Accurate representation of the ocean-atmosphere coupling in weather, wave and climate models requires reliable estimates of air-sea surface fluxes of momentum, heat and mass. Whitecap fraction (W) usually quantifies the enhancement of the surface fluxes due to wave breaking. Satellite-based passive remote sensing of W from ocean surface brightness temperatures (s) observes open ocean surface fluxes at low spatial resolution. Radiometric surface observations at higher resolution are necessary to monitor the complex environment in the coastal zone and in polar regions. We assess the feasibility of using the millimeter-wave frequencies (89 to 150 GHz) to observe whitecaps. We evaluate the derivative of the with respect to W as a measure for the observation of W. We describe the models and data used to evaluate the sensitivity to W for different instrumental and environmental conditions. Atmospheric absorption limits the ability to observe the surface at millimeter-wave frequencies. We find that the sensitivity to W at 89 GHz may be sufficient to support limited W retrieval from observations at altitudes below 1 km and that the sensitivity at 113 and 150 GHz is not sufficient. Clear skies, and low to moderate atmospheric humidity favor whitecap observations.
1. Introduction
Air-sea surface fluxes of momentum, heat and mass serve as boundary conditions for weather, wave and climate models. Accurate observations and parameterizations of surface fluxes are required for accurate weather forecasting and wave model predictions [1,2]. Breaking of ocean waves with air entrainment enhances the interfacial surface fluxes [3]. Sea foam (whitecaps) on the ocean surface is the most direct expression of breaking waves. Whitecap fraction (W) quantifies the presence of sea foam and is widely used to parameterize and evaluate the enhancement of the air-sea transfer [4,5,6,7]. The high reflectivity of whitecaps at visible wavelengths has been traditionally used to estimate the amount of sea foam on the ocean surface from photographic data of the sea state [8,9,10]. However, we have demonstrated that the high emissivity of foam at microwave frequencies enables retrieval of W from passive satellite observations [11]. Our retrievals of W using WindSat brightness temperatures (s) provide data to evaluate and parameterize the variability of W and the possibility to improve the modeling of surface fluxes via global mapping and monitoring of whitecaps in the open ocean [12,13,14].
Anguelova and Bettenhausen [11] combined the geophysical model function developed for WindSat retrievals and physical models for the specular, wind-induced roughness and foam contributions to the ocean surface emissivity to develop parameterized expressions for W. The input data for this algorithm includes the WindSat retrievals [11,15] for wind speed and direction, the sea surface temperature (SST), precipitable water vapor and columnar cloud liquid water along with the WindSat s. Models for the dielectric permittivity of seawater, surface roughness and wave spectrum are used to obtain the emissivity of foam-free sea surface. The adjustable parameters in the algorithm include parameters in the wave spectrum model used to obtain roughness emissivity with the two-scale model and the foam void fraction and foam layer thickness in the foam emissivity model.
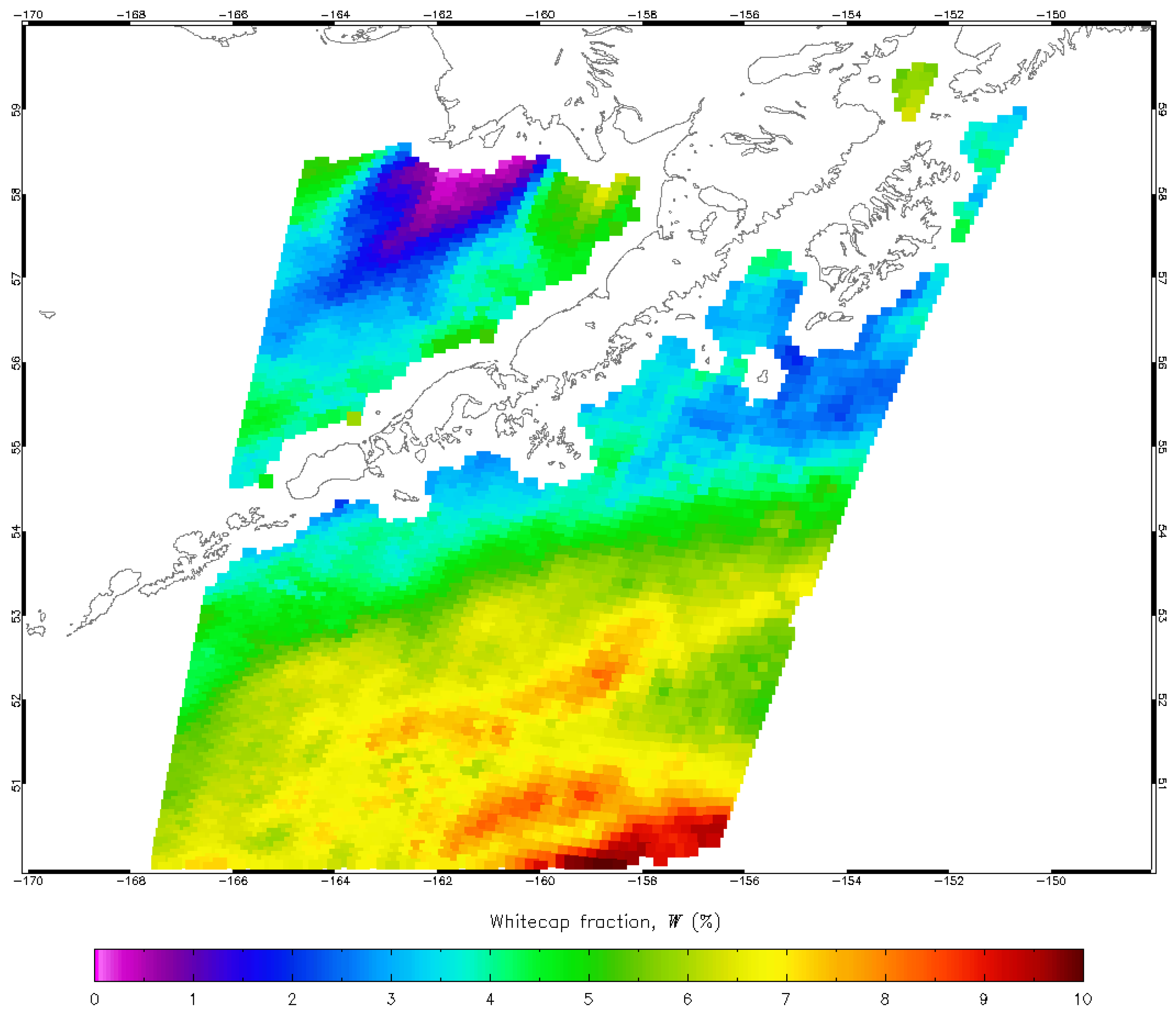
WindSat operates at five nominal frequency bands from 6.8 to 37 GHz [16]. We use 10.7, 18.7 and 37 GHz data to retrieve W at spatial resolutions as high as 25 km × 35 km (half-power contour of the footprint). This resolution is sufficient over most of the open ocean where conditions are homogeneous over large areas but limits observations and predictions of surface processes in the coastal zone and marine areas confined by land, including polar regions. Figure 1 illustrates this with a map of W retrieval from WindSat around a portion of southern Alaska. The figure shows that retrievals are discarded in the coastal zone to avoid land contamination [15] due to the much higher emissivity of land relative to the ocean. There are no retrievals at a distance below 30–50 km from the shore line depending on the orientation of the elliptical footprint. Similar restrictions would prevent measurements either close to the ice edge in polar regions or along new Arctic routes [17] (Figure 5 there). Radiometric surface observations at higher spatial resolution are necessary to monitor and study the complex, highly variable environment in the coastal zone and in polar regions.
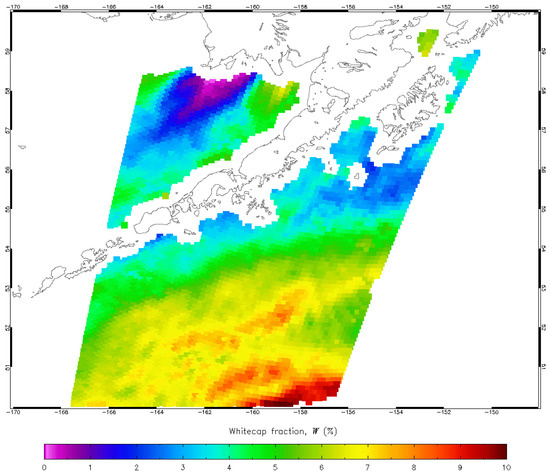
Figure 1.
WindSat whitecap retrievals on 9 February 2014.
Microwave radiometers deployable on low-flying small airplanes or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can provide passive remote sensing of surface processes at higher resolutions compared to satellite-borne radiometers. However, the radiometric systems at frequencies below 37 GHz are bulky and heavy due to the inverse relationships between frequency and antenna size [18]. Bulky and heavy instrumentation also limits the deployment of radiometers on oceanographic platforms [19].
The spatial resolution of radiometric systems can be improved significantly by operating at higher frequencies for two reasons. First, for a fixed antenna size, the sensor footprint gets smaller as the frequency increases. Second, at shorter wavelengths, electronics and antennas can be made much smaller. Recent technological advances in miniaturization of microwave and millimeter- wave radiometers [20,21] and the maturing of UAV technology [22] further enable high resolution observations at millimeter-wave frequencies.
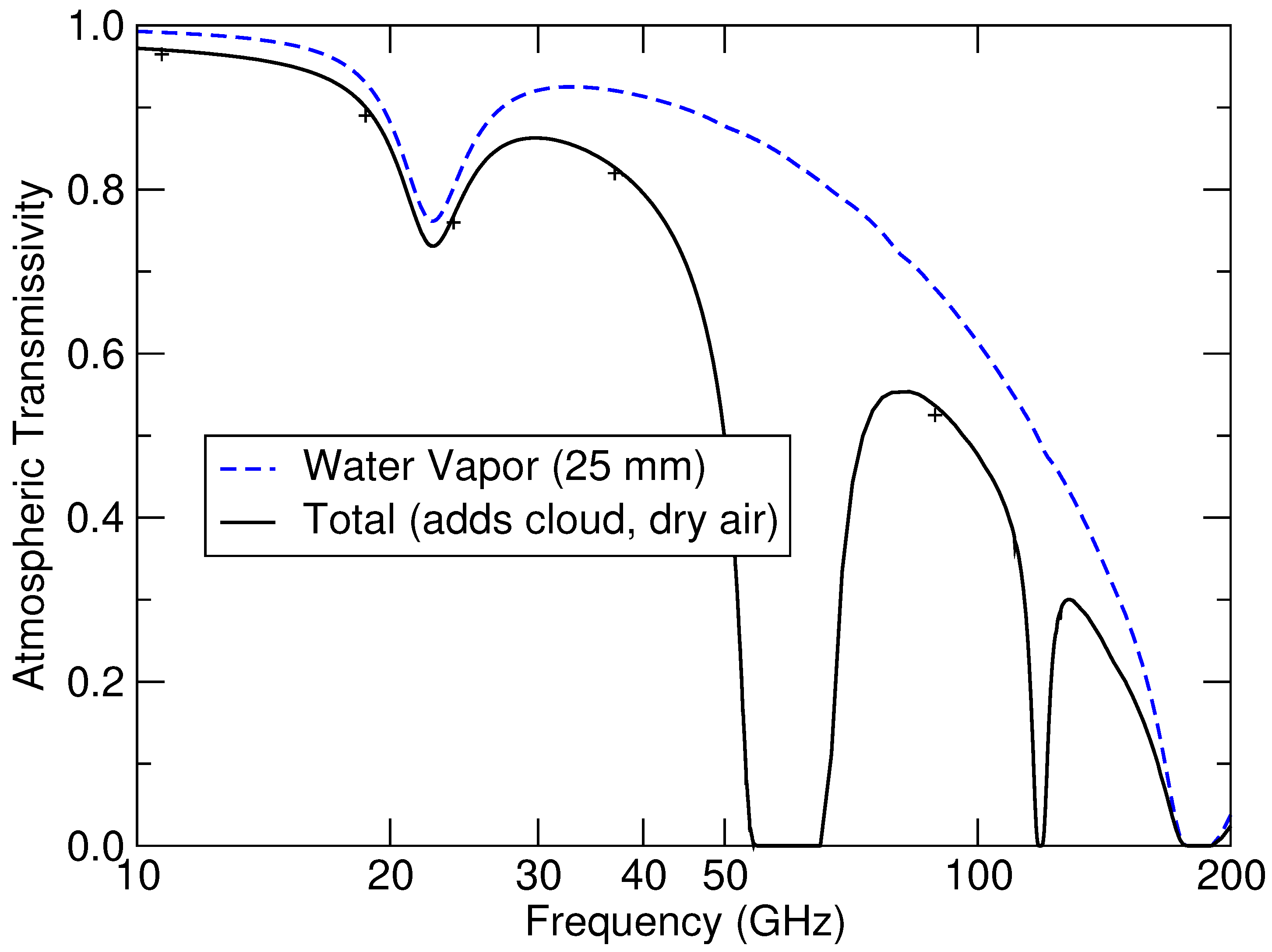
The gains from operating at millimeter-wave frequencies come, however, with a trade-off. A major advantage of the microwave systems at frequencies below 40 GHz is the relative transparency of the atmosphere. Figure 2 shows atmospheric transmissivity above 0.80 for humid air with clouds for the WindSat frequencies from 10 to 37 GHz that we use in our W retrieval algorithm. For higher frequencies, we have to contend with increasing atmospheric attenuation. The atmospheric transmissivity for the parameters considered in Figure 2 is about 0.5 and 0.3 in the imaging windows of 90 and 140–170 GHz, respectively. The atmospheric transmissivity is further decreased as the water vapor increases.
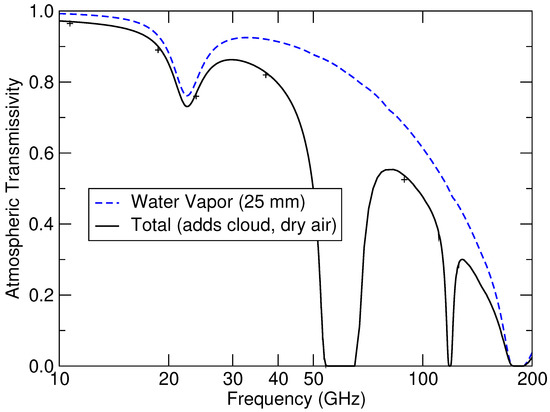
Figure 2.
Atmospheric transmissivity as a function of frequency spanning the range from 10 to 200 GHz. The blue line is the water vapor absorption contribution for humid air containing 25 mm columnar water vapor. The black line includes absorption due to water vapor, clouds (0.1 mm columnar cloud liquid water) and dry air.
The atmospheric attenuation is the reason that the millimeter-wave frequencies are primary for remote sensing of the atmosphere [20,21] but not for remote sensing of near-surface variables. However, Rosenkranz [23] has shown that the millimeter-wave frequencies are affected by sea state. Rosenkranz’s results suggested that the surface contributions should be accounted for when satellite millimeter-wave measurements are interpreted or used in numerical models. Indeed, the radiative transfer (RT) model RTTOV [24], developed for both microwave and millimeter-wave frequencies, accounts for the surface signal.
We would like to assess the feasibility of using the surface signal at millimeter-wave frequencies to detect whitecaps at high spatial resolution. If feasible, such a new remote sensing capability has the potential to extend existing observations of surface variables and air-sea fluxes in coastal zones and polar regions. Our approach to investigate the feasibility is to: (1) Evaluate the sensitivity of foam-covered surface signal to the atmospheric signal; (2) Evaluate the performance of existing models in representing the rough sea surface; (3) Develop a model for the emissivity of sea foam at millimeter-wave frequencies that accounts for both absorption and scattering. The work presented here focuses on the first aspect of this feasibility study.
2. Methods
2.1. Whitecap Fraction Sensitivity Model
The whitecap fraction sensitivity model is based on the RT equation for microwave and millimeter-wave frequencies [18]. The measured brightness temperature is
where is atmospheric upwelling brightness temperature, is atmospheric downwelling brightness temperature, e is sea surface emissivity, r is sea surface reflectivity, T is SST, (≈2.7 K) is cosmic background temperature, is the atmospheric transmissivity from the surface to the point of observation and is the atmospheric transmissivity from the top of the atmosphere (TOA) to the surface. The form of (1) is consistent with the form used in the fast radiative transfer model RTTOV [24]. The emissivity is modeled with specular (), roughness () and foam () components:
The reflectivity is presented as:
where is a correction for non-specular reflection. Reflection from foam is neglected here because it is small (<3%) at the frequencies and earth incidence angles (EIAs) considered herein.
We use the derivative of the with respect to W as a measure of the sensitivity needed to detect and estimate whitecap fraction. From (1)–(3), we have:
We completed RT simulations to obtain the variables used in (4). Our calculations of and assume that , and are independent of W which is consistent with the models we use:
Descriptions of the models and data used for the simulations follow.
2.2. Radiative Transfer Models
We calculate the atmospheric parameters , , , and in (4) using the monochromatic RT model MonoRTM, version 5.4, developed by Atmospheric and Environmental Research, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA [25] with customized input and output routines. We use MonoRTM here to be consistent with our previous development of a geophysical model for the WindSat s. The atmospheric absorption varies primarily with water vapor and clouds at the frequencies considered here. Absorption due to oxygen, nitrogen and ozone is also included in our calculations.
FASTEM is a fast, generic all-surface semi-empirical model [26,27,28,29,30]. We used FASTEM to model the ocean surface emissivity variables , , and . A model for W is not needed to calculate the derivatives because both e and r are linear in W. We neglected the wind direction effect on the emissivity since model evaluation was limited to frequencies above 37 GHz and the effect is much smaller than the specular and wind speed dependent contributions to the emissivity. We adapted the FASTEM source code distributed with RTTOV version 12.3 [24] for our simulations. We used the FASTEM-5 version which is equivalent to the latest FASTEM-6 version for our purposes because the differences between the two versions are in the parameterizations of the wind direction effect on the emissivity. Some elements of FASTEM are physically-based (e.g., modeling surfaces as dielectric media), FASTEM also features data-based parameterizations (e.g., surface roughness expressions derived from modeling or observations of radiances) for speedy computations.
FASTEM-5 employs a double Debye model [28] for the seawater permittivity which is used to calculate . The excess emissivity due to ocean surface roughness, , includes small-scale roughness, as a multiplicative correction of the Fresnel reflection coefficients, and a large-scale contribution with additive correction terms specific for each polarization. The correction terms are regressions in terms of wind speed and frequency, as well as EIA for the large-scale corrections. The regressions are fit to roughness values obtained with a two-scale roughness model [28] and the wave spectrum of Durden and Vesecky [31]. The model for foam emissivity is based on the empirical model of Stogryn [32] with modifications justified by the foam emissivity measurements of Rose et al. [33]. Calculation of the nonspecular reflection correction term, , follows the method developed for FASTEM-2 [27].
2.3. Data
We used a global set of atmospheric profiles over the ocean and corresponding surface parameters from the ERA-Interim Project [34] for 15 January, 15 April, 15 July and 15 October 2009 at analysis times of 0, 6, 12, and 18 h. We exclude profiles near land or sea ice or that include precipitation or heavy clouds (columnar cloud liquid water > 0.3 mm). The final set includes more than one million profiles. The atmospheric profiles, sea surface temperature and wind speed for the RT model are taken from this ERA-Interim data. Sea surface salinity is obtained from the NOAA World Ocean Atlas [35] mapped at 0.25 longitude-latitude grid cells.
3. Results
We used (4) to evaluate the sensitivity to foam-covered sea surface for frequencies of 37, 89, 113 and 150 GHz at vertical (V) and horizontal (H) polarizations. The WindSat frequency of 37 GHz is used for comparison of the millimeter-wave results to those at microwave frequencies. We used EIAs of 53 and nadir.
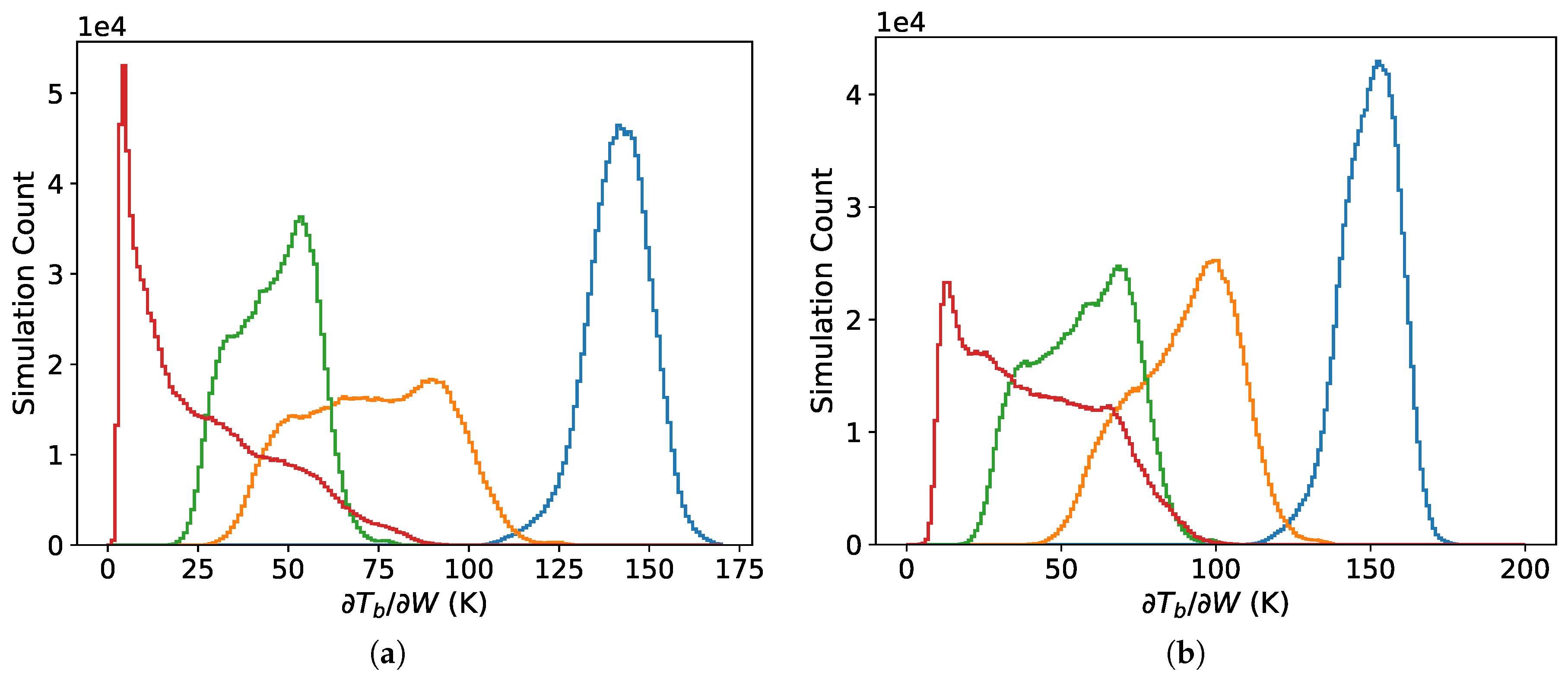
We present the sensitivity to signals from foam-covered sea surface with distributions (simulation counts) of the derivative where each simulation used one atmospheric profile and corresponding surface parameters from the ERA-Interim dataset. A sensitivity of 100 K means that a change of the whitecap fraction by 1% would change the brightness temperature by 1 K. The parameterization of W as a function of wind speed given by Brumer et al. [10] shows that wind speeds of 10, 15 and 20 m/s give W values of about 0.9%, 2.2% and 3.7%, respectively. This indicates that a change in W of 1% is a substantial fraction of the range in W. Meanwhile, a change of by 1 K is a relatively small change compared with the effects of instrument noise and changes due to other geophysical parameters such as water vapor and wind speed.
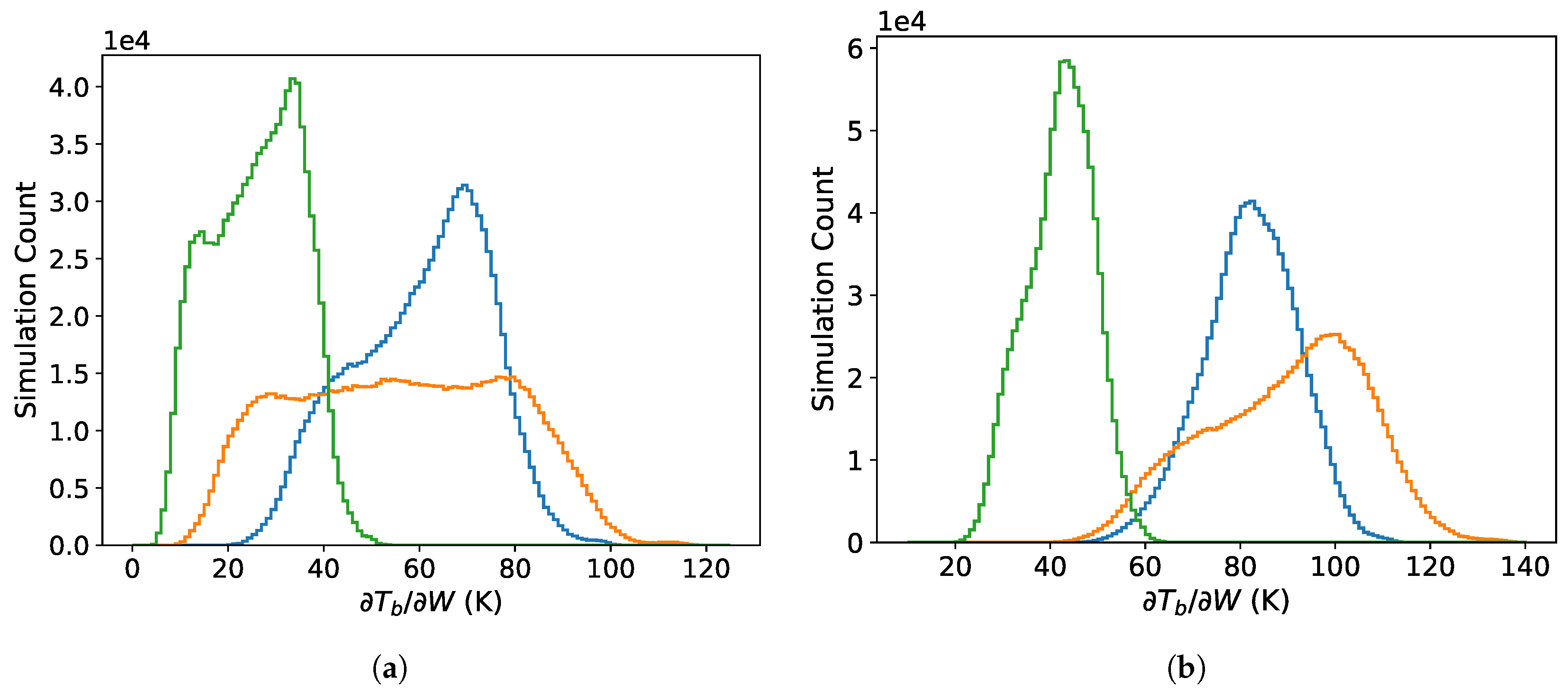
The distributions in Figure 3 show results for both the TOA (Figure 3a) and at the surface (Figure 3b). The TOA results presented in this section indicate the expected sensitivity for satellite observations. Our results for altitudes of 1 km or less indicate possible sensitivity for radiometers deployed on aircraft at low altitude or UAV. The results are given for 89 GHz at nadir and V and H polarizations at 53 EIA. Figure 3 shows that the sensitivity to the whitecap fraction increases at lower altitude compared to that at the TOA because increases with increasing . This effect is larger at the 53 EIA because of the increased path length through the atmosphere for a fixed altitude. The sensitivity is substantially larger for H polarization than for V polarization which is consistent with the larger sensitivity to wind speed changes for H versus V polarization [36]. The polarization differences are greater at lower altitudes due to the increase in the atmospheric transmissivity (increasing and ). The difference between changes in the of the two polarizations due to wind speed induced roughness and whitecaps is the reason that off-nadir viewing is important for accurate retrieval of surface geophysical variables. Thus, in the following, we focus on the results for altitudes at and below 1 km height, at EIA = 53 and H polarization. The H-pol is also more sensitive to changes in because is larger ( V-pol H-pol in (6)).
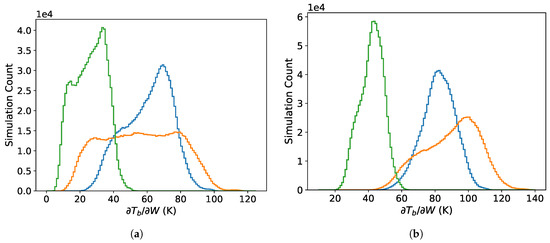
Figure 3.
Distributions (simulation counts) of the sensitivity measure for 89 GHz at nadir (blue) and at EIA of 53 for V polarization (green) and H polarization (orange): (a) at the top of the atmosphere and (b) at the sea surface.
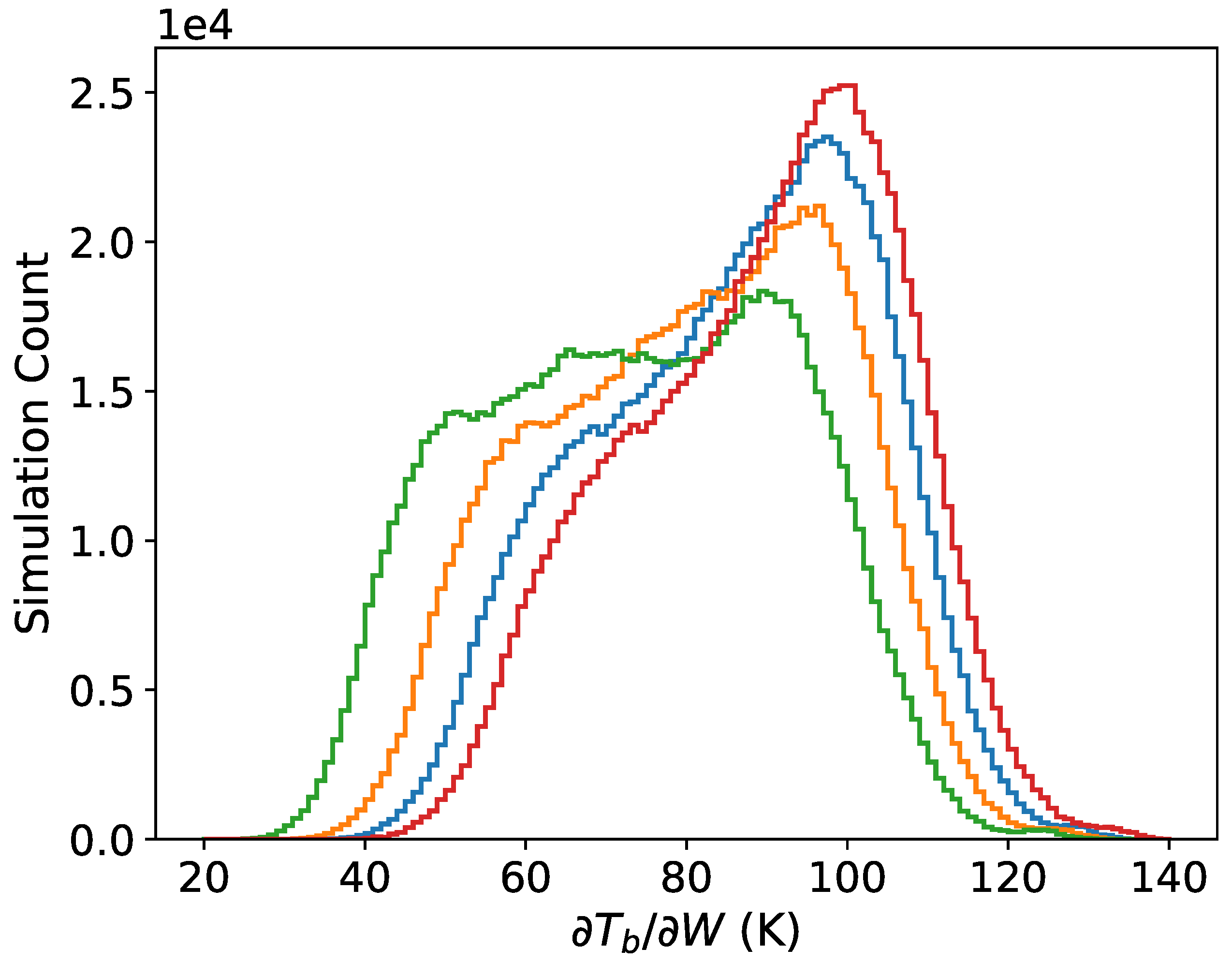
Figure 4 further demonstrates the altitude dependence of the sensitivity . The sensitivity increases by about 15% at the surface versus 1 km based on the modes of the distributions. The change in versus frequency is shown in Figure 5. The sensitivity decreases with increasing frequency with the effect being stronger at higher altitude.
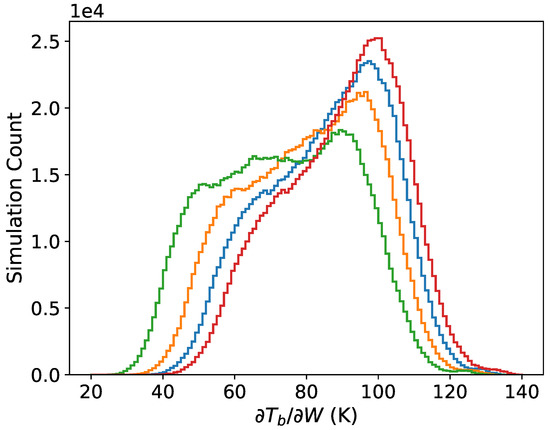
Figure 4.
Distributions of at the surface (red) and at altitudes of 0.2 (blue), 0.5 (orange) and 1 km (green) for H polarization at 89 GHz and 53 EIA.
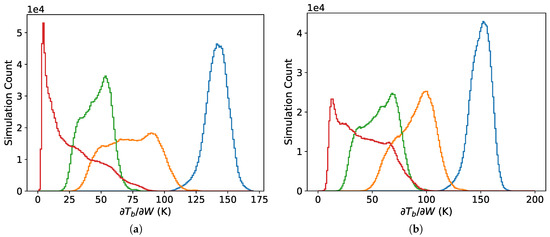
Figure 5.
Distributions of at 1 km altitude (a) and the surface (b) H polarization and 53 EIA at frequencies of 37 (blue), 89 (orange), 113 (green) and 150 GHz (red).
Table 1 summarizes the dependence of on changes in frequency, altitude and EIA. The values listed in the table are the median values of over the distribution of all the simulation profiles. The results in Table 1 are consistent with the variations of with changes in observation altitude and frequency illustrated in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5.

Table 1.
Median for different frequencies, altitudes and two EIAs and H polarization.
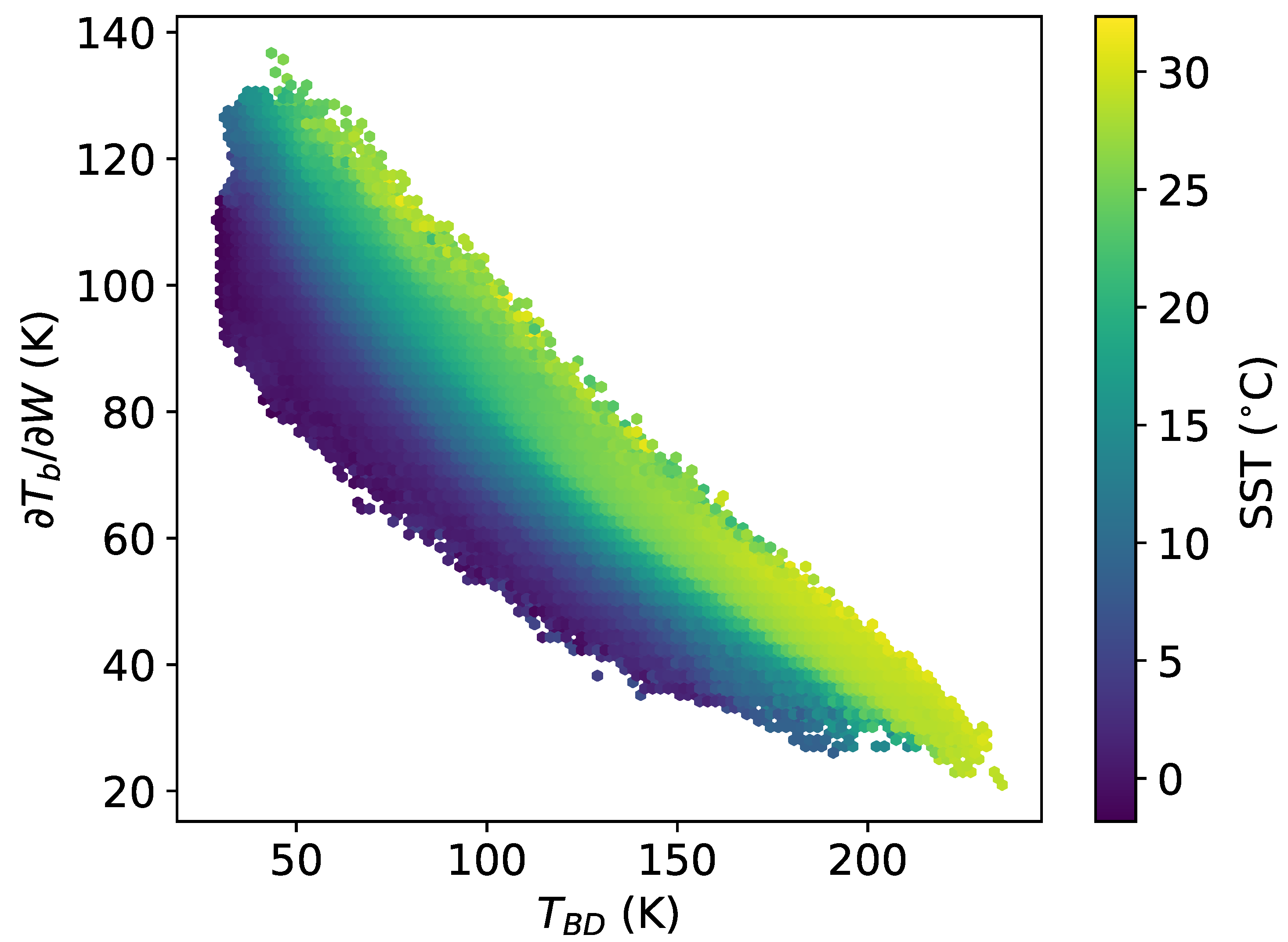
Figure 6 shows the dependence of the sensitivity on the and SST. The color in the figure represents the average value of for given values of and SST. Sensitivity to W is reduced for low SST even for clear sky and low water vapor conditions (high ). This follows from (4) which shows that the SST dependence increases with increasing .
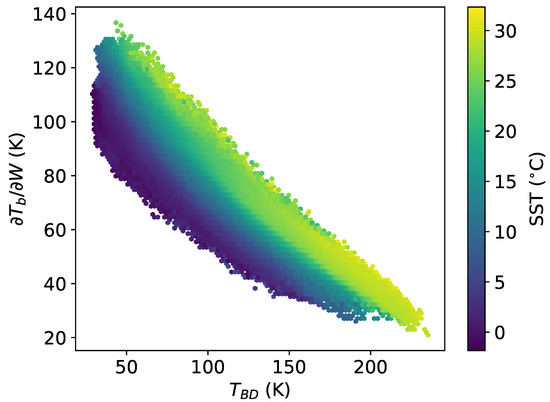
Figure 6.
Whitecap fraction sensitivity, , as a function of and SST for 89 GHz H-polarization at 1 km altitude and 53 EIA. The color represents the average SST for a given two-dimensional bin in and .
4. Discussion
A simplified form of (4) can be obtained by neglecting and using the approximations and in (5) and (6):
This form is useful for interpreting the effects of changes in the observation frequency and geophysical parameters on the sensitivity to W. The atmospheric absorption for the frequencies considered here increases with both increasing frequency and observation altitude. With increasing atmospheric absorption, decreases and increases both of which result in reduced sensitivity to W. Surface effects on are through the SST and the specular and wind-induced roughness contributions to the emissivity ( and ). These emissivity terms increase with increasing frequency which also contributes to reducing at the higher frequencies. Observation altitude affects the sensitivity to W by increasing as the altitude decreases.
We have previously demonstrated retrieval of W using WindSat 37 GHz observations [11]. To obtain sensitivity to W comparable to these 37 GHz TOA observations will require lower observation altitudes with millimeter-wave frequencies such as from an airplane or a UAV. The results in Table 1 indicate that for 89, 113 and 150 GHz at all altitudes are lower than for 37 GHz at TOA. Figure 5 shows that for 89 GHz there are a significant number of cases, particularly at lower altitudes, where is on the order of 100 K. We conclude that obtaining an estimate of W using passive observations at frequencies of 89 GHz and above will not provide the same sensitivity. The sensitivity to W at 89 GHz may be sufficient to support W retrieval from observations at low altitudes. Our results for 113 and 150 GHz suggest that the sensitivity to a 1% change in W is on the order of the instrument noise for a typical radiometer. Therefore, it is unlikely that useful estimates of W can be obtained using measurement at those frequencies.
The results in Section 3 are based on simulations which do not account for modeling and observation errors. Modeling errors include errors in the FASTEM parameterizations of , and , and errors in the MonoRTM atmospheric radiative transfer model. Errors in the values of surface and atmospheric geophysical parameters used in the model and observation errors due to, for example, instrument noise and pointing knowledge errors also contribute to W retrieval uncertainty. For the three emissivity components modeled using FASTEM, the largest uncertainty comes from . Roughness emissivity is difficult to model and the uncertainty of the input wave spectrum is high. Some uncertainty for is related to the relationship between sea foam thickness and the fact that foam emissivity varies with frequency [37] but this will have less impact on the sensitivity to whitecap coverage.
Therefore, the greatest potential for modeling improvements is in the surface emissivity model. While FASTEM performance is adequate to evaluate the sensitivity to W, more refined modeling is necessary in order to use the relatively weak signal from a foam-covered surface to retrieve W. The modeling of surface roughness, the choice of wave spectrum, and the account of all processes in modeling the foam emissivity all call for more involved effort to modify and improve existing models.
Our analysis begins with the assumption that (1)–(3) accurately account for the whitecap contribution to the brightness temperature for microwave and millimeter-wave radiation. This effectively assumes that there is a threshold level of air entrainment (bubbles) near the ocean surface; above the threshold the surface is highly emissive foam layer and below the threshold the emissivity is unaffected by the air entrainment. We expect that this assumption will be less accurate for millimeter-wave radiation because it will be more sensitive to both the emissivity of and the surface scattering from the foam layers. Indeed, the high frequency wavelengths become sensitive to the emissivity of even thin foam layers [37] and to the surface roughness created by the bubble caps [38]. This would mean that the effective coverage of the ocean surface with greater contribution from bubble formations would increase. Because thin foam layers are less turbulent, the increased effective coverage may not have a substantial impact on air-sea fluxes. However, it could affect the overall ocean surface emissivity, and the observed brightness temperature, at millimeter-wave frequencies because foam-covered areas start to contribute not only via foam emissivity but also via foam surface scattering. Experimental measurements with millimeter-wave radiometers could assist investigation of roughness emissivity from both foam-free and foam-covered areas.
Author Contributions
M.B. contributed with methodology, software, data curation, analysis, visualization, writing. M.A. contributed with conceptualization, interpretation, original draft preparation, review and editing.
Funding
This research was funded by the Office of Naval Research, NRL program element 61153N.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Berry, D.I.; Kent, E.C. A New Air–Sea Interaction Gridded Dataset from ICOADS With Uncertainty Estimates. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.B.; Zanna, L. Drivers of uncertainty in simulated ocean circulation and heat uptake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, C.W.; Bradley, E.F.; Hare, J.E.; Grachev, A.A.; Edson, J.B. Bulk Parameterization of Air–Sea Fluxes: Updates and Verification for the COARE Algorithm. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 571–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.A. Bubble clouds and the dynamics of the upper ocean. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 118, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, E.L.; Mahrt, L.; Vickers, D. An improved bulk air–sea surface flux algorithm, including spray-mediated transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninkhof, R.; Asher, W.E.; Ho, D.T.; Sweeney, C.; McGillis, W.R. Advances in Quantifying Air-Sea Gas Exchange and Environmental Forcing. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 213–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leeuw, G.; Andreas, E.L.; Anguelova, M.D.; Fairall, C.W.; Lewis, E.R.; O’Dowd, C.; Schulz, M.; Schwartz, S.E. Production flux of sea spray aerosol. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C. Oceanic Whitecaps. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1971, 1, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, A.H.; White, M. Automated Processing of Sea Surface Images for the Determination of Whitecap Coverage. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumer, S.E.; Zappa, C.J.; Brooks, I.M.; Tamura, H.; Brown, S.M.; Blomquist, B.W.; Fairall, C.W.; Cifuentes-Lorenzen, A. Whitecap Coverage Dependence on Wind and Wave Statistics as Observed during SO GasEx and HiWinGS. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 2211–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelova, M.D.; Bettenhausen, M.H. Whitecap Fraction From Satellite Measurements: Algorithm Description. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 1827–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, D.J.; Anguelova, M.D.; Brooks, I.M. On the variability of whitecap fraction using satellite-based observations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 6201–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, D.J.; Anguelova, M.D.; Brooks, I.M. Global distribution and seasonal dependence of satellite-based whitecap fraction. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.F.; Anguelova, M.D.; Manders, A.M.; Schaap, M.; De Leeuw, G. Parameterization of oceanic whitecap fraction based on satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13725–13751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettenhausen, M.H.; Smith, C.K.; Bevilacqua, R.M.; Wang, N.Y.; Gaiser, P.W.; Cox, S. A Nonlinear Optimization Algorithm for WindSat Wind Vector Retrievals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiser, P.W.; St. Germain, K.M.; Twarog, E.M.; Poe, G.A.; Purdy, W.; Richardson, D.; Grossman, W.; Jones, W.L.; Spencer, D.; Golba, G.; et al. The WindSat Spaceborne Polarimetric Microwave Radiometer: Sensor Description and Early Orbit Performance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2347–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenert, J.W. The United States Navy Arctic Roadmap for 2014 to 2030; Office of the Chief of Naval Operations: Washington DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.; Moore, R.; Fung, A. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive, Volume 1: Microwave Remote Sensing: Fundamentals and Radiometry; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1981; pp. 344–427. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, H.; Smith, G.B.; Snow, C.M.; Dowgiallo, D.J.; Bobak, J.P.; Anguelova, M.D. Whitecap lifetime stages from infrared imagery with implications for microwave radiometric measurements of whitecap fraction. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 7521–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturbide-Sanchez, F.; Reising, S.C.; Padmanabhan, S. A Miniaturized Spectrometer Radiometer Based on MMIC Technology for Tropospheric Water Vapor Profiling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaretin, I.A.; Shields, M.W.; Lorenzo, J.A.M.; Blackwell, W.J. A Compact 118-GHz Radiometer Antenna for the Micro-Sized Microwave Atmospheric Satellite. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned aerial systems for photogrammetry and remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, P.W. Rough-sea microwave emissivities measured with the SSM/I. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.; Hocking, J.; Turner, E.; Rayer, P.; Rundle, D.; Brunel, P.; Vidot, J.; Roquet, P.; Matricardi, M.; Geer, A.; et al. An update on the RTTOV fast radiative transfer model (currently at version 12). Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 2717–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, V.H.; Mlawer, E.J.; Cady-Pereira, K.E.; Moncet, J.L. Water Vapor Continuum Absorption in the Microwave. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2194–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, S.J.; Hewison, T.J. Fast generic millimeter-wave emissivity model. Proc. SPIE 1998, 3503, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblonde, D.; English, S.J. Evaluation of the FASTEM2 fast microwave oceanic surface emissivity model. In Technical Proceedings of the Eleventh International ATOVS Study Conference; Le Marshall, J.F., Jasper, J.D., Eds.; Australia Bureau of Meteorology: Budapest, Hungary, 2000; pp. 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Weng, F.; English, S.J. An Improved Fast Microwave Water Emissivity Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, N.; Geer, A.; English, S.J. Evaluation of The Microwave Ocean Surface Emissivity Model FASTEM-5 in the IFS; Technical Report Technical Memorandum 667; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kazumori, M.; Shibata, A.; English, S.J. Asymmetric Features of Oceanic Microwave Brightness Temperature in HighSurface Wind Speed Condition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5901–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durden, S.L.; Vesecky, J.F. A Physical Radar Cross-Section Model for a Wind-Driven Sea with Swell. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1985, 10, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogryn, A. The emissivity of sea foam at microwave frequencies. J. Geophys. Res. (1896–1977) 1972, 77, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, L.A.; Asher, W.E.; Reising, S.C.; Gaiser, P.W.; Germain, K.M.S.; Dowgiallo, D.J.; Horgan, K.A.; Farquharson, G.; Knapp, E.J. Radiometric Measurements of the Microwave Emissivity of Foam. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2619–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts. ERA-Interim Project; Research Data Archive at the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Computational and Information Systems Laboratory: Boulder, CO, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zweng, M.; Reagan, J.; Antonov, J.; Locarnini, R.; Mishonov, A.; Boyer, T.; Garcia, H.; Baranova, O.; Johnson, D.; Seidov, D.; et al. World Ocean Atlas 2013, Volume 2: Salinity; Technical Report 74; NOAA Atlas NESDIS: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger, J.P. Passive Microwave Measurements of Sea Surface Roughness. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron. 1971, 9, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelova, M.D.; Gaiser, P.W. Skin depth at microwave frequencies of sea foam layers with vertical profile of void fraction. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelova, M.D.; Gaiser, P.W. Dielectric and Radiative Properties of Sea Foam at Microwave Frequencies: Conceptual Understanding of Foam Emissivity. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1162–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).