Constructing a Finer-Resolution Forest Height in China Using ICESat/GLAS, Landsat and ALOS PALSAR Data and Height Patterns of Natural Forests and Plantations
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- What is the accuracy of the finer-resolution forest height map of China generated by the combination of GLAS, Landsat imagery, L-band SAR, topographical data and tree cover?
- (2)
- What is the difference between forest heights in natural forests and those in plantations?
- (3)
- To what extent can the addition of L-band SAR data improve the accuracy of extrapolated forest heights on a large scale?
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Height Extraction from Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS) Footprints
2.2. The Greenest Compositions from Landsat 5 Thematic Mapper (TM)
2.3. Landsat Vegetation Continuous Fields (VCF) Tree Cover and Topographic Data
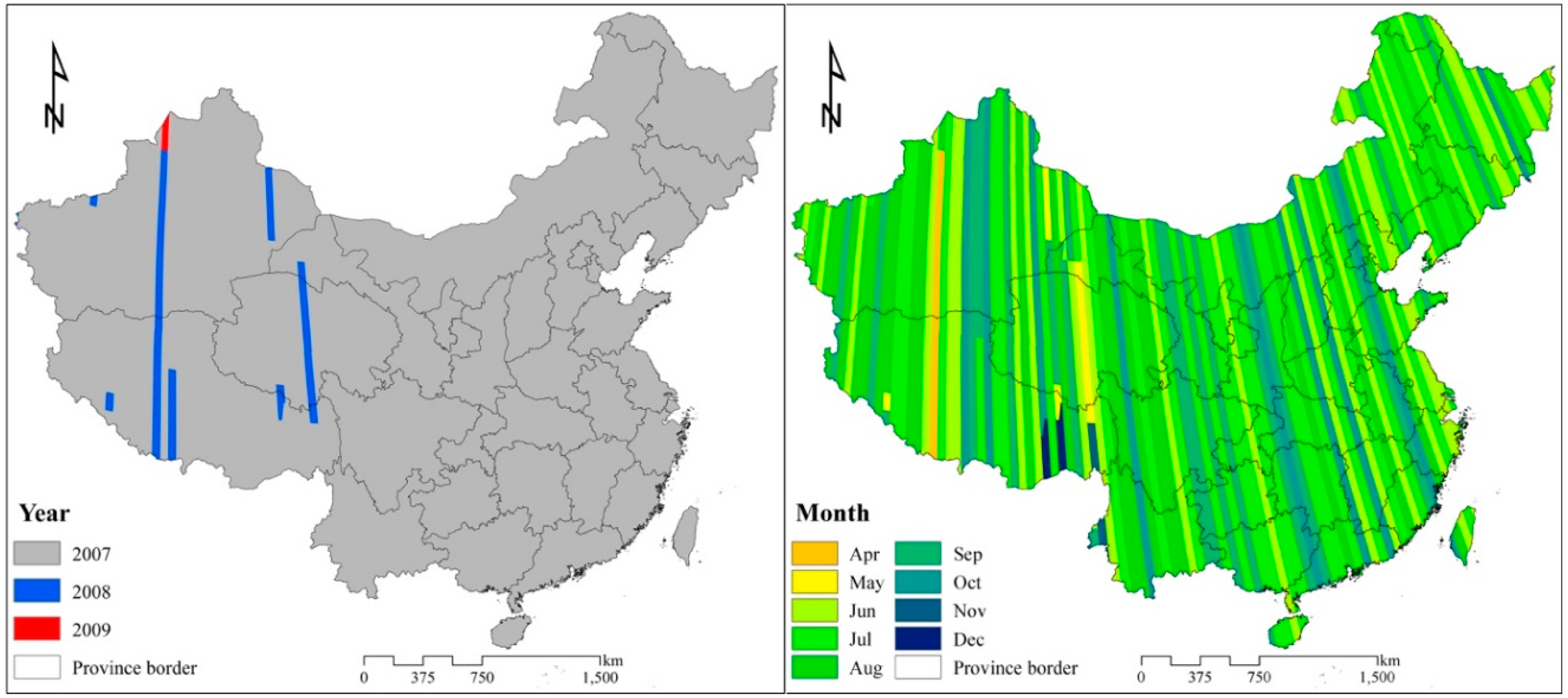
2.4. Phased Array L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR-2/PALSAR) Mosaic Dataset
2.5. Sampling Selection for Natural Forests and Plantations
2.6. Wall-to-Wall Forest Height Estimation
2.7. Assessment of Accuracy and Prediction of Uncertainty
3. Results and Discussion
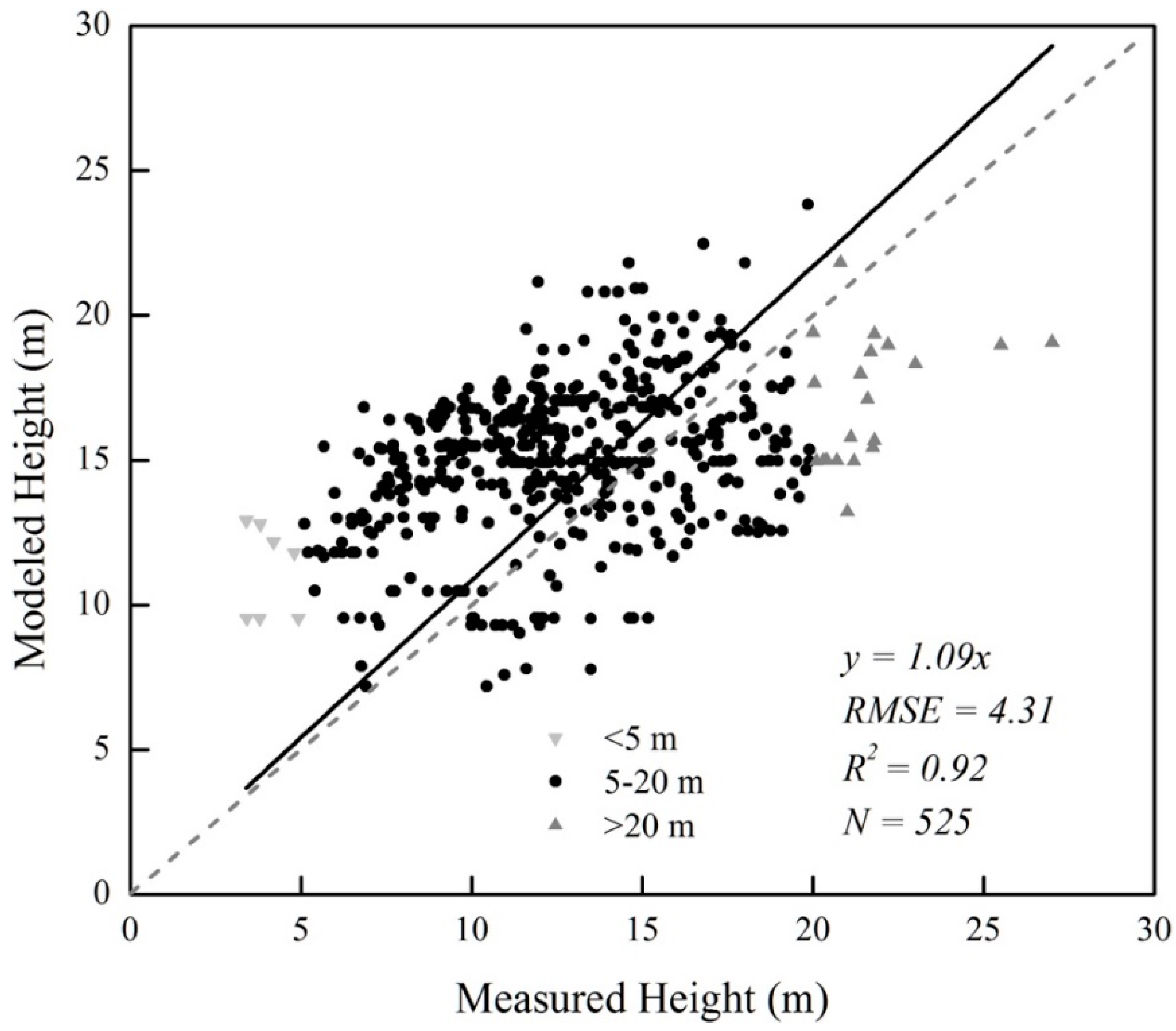
3.1. Accuracy and Spatial Patterns of Forest Height in China
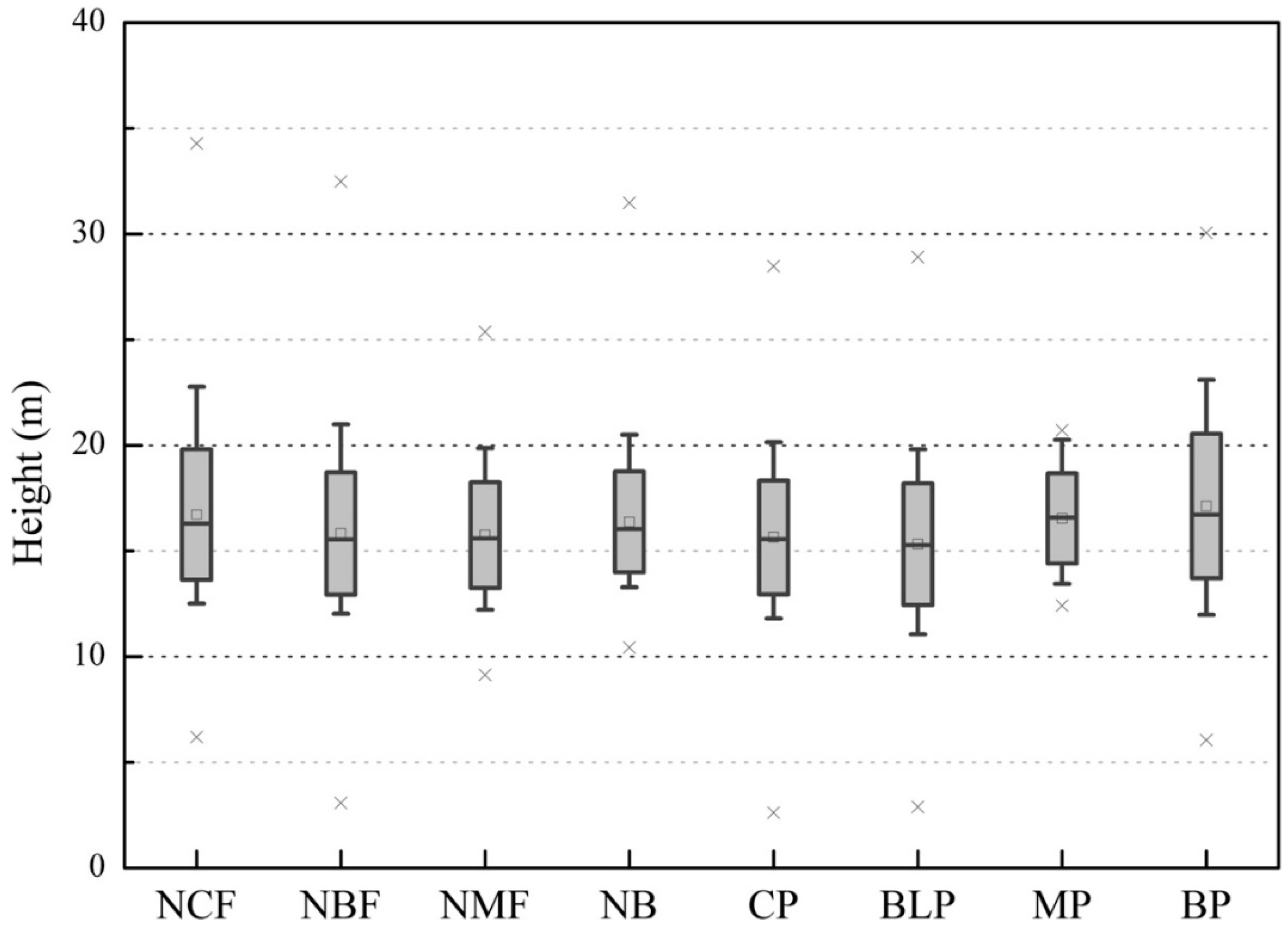
3.2. Height Differences between Natural Forests and Plantations
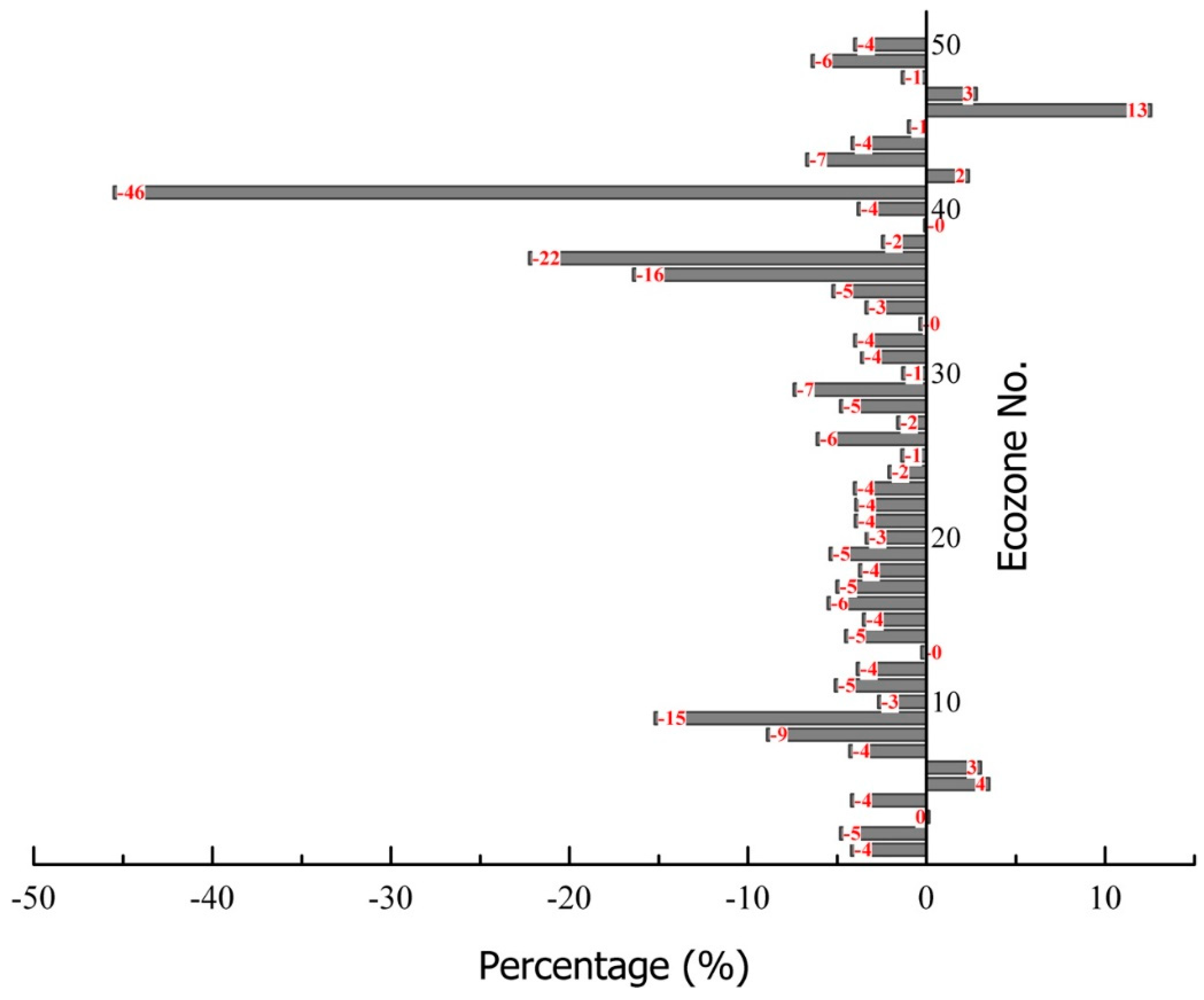
3.3. Improvement after Integrating PALSAR Data
3.4. Importance of Predictors to Model Wall-to-Wall Forest Height
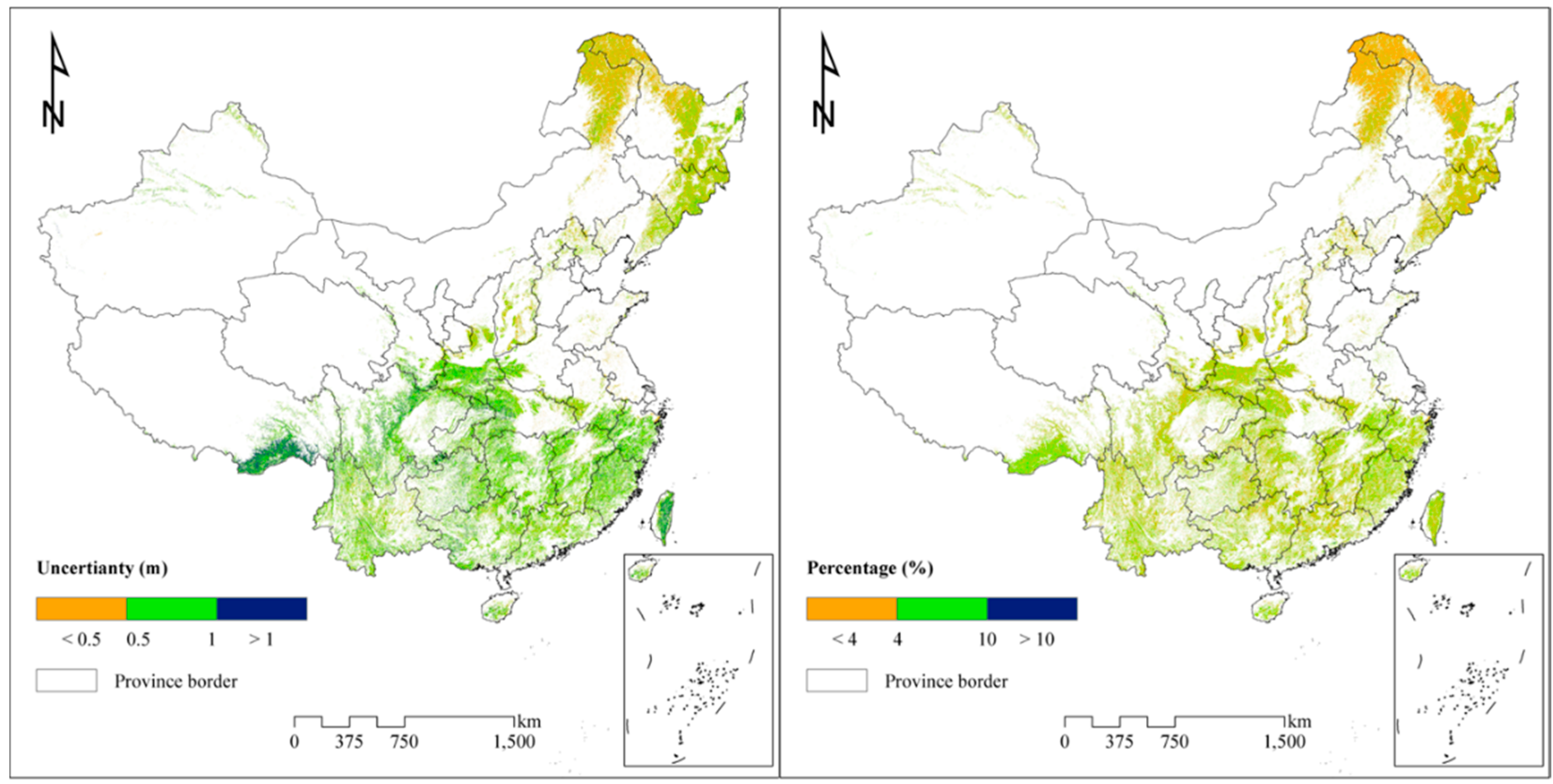
3.5. Quantifying Uncertainty Caused by Footprints Space in Modeled Forest Heights
3.6. Comparisons with Published Forest Heights
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, P. Remote sensing of environmental change over China: A review. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorelli, N.; Wegmann, M.; Skidmore, A.; Mücher, S.; Dawson, T.P.; Fernandez, M.; Lucas, R.; Schaepman, M.E.; Wang, T.; O’Connor, B.; et al. Framing the concept of satellite remote sensing essential biodiversity variables: Challenges and future directions. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 2, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontemps, S.D.P.; Van Bogaert, E.; Arino, O.; Kalogirou, V.; Ramos, P.; Jose, J. GLOBCOVER 2009 Products Description and Validation Report; Université catholique de Louvain (UCL) & European Space Agency (esa): Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Tomppo, E.; Healey, S.; Gadow, K. The national forest inventory in China: History-results-international context. For. Ecosyst. 2015, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shao, G.; Zhao, G.; Le Master, D.C.; Parker, G.R.; Dunning, J.B.; Li, Q. China’s Forest Policy for the 21st Century. Science 2000, 288, 2135–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefsky, M.A.; Cohen, W.B.; Parker, G.G.; Harding, D.J. LiDAR Remote Sensing for Ecosystem Studies. Bioscience 2002, 52, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Knapp, D.E.; Kennedy-Bowdoin, T.; Jones, M.O.; Martin, R.E.; Boardman, J.; Field, C.B. Carnegie Airborne Observatory: In-flight fusion of hyperspectral imaging and waveform light detection and ranging (wLiDAR) for three-dimensional studies of ecosystems. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2007, 1, 013536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwally, H.J.; Schutz, B.; Abdalati, W.; Abshire, J.; Bentley, C.; Brenner, A.; Bufton, J.; Dezio, J.; Hancock, D.; Harding, D.; et al. ICESat’s laser measurements of polar ice, atmosphere, ocean, and land. J. Geodyn. 2002, 34, 405–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ranson, K.J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Montesano, P.; Kimes, D. Forest biomass mapping from lidar and radar synergies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2906–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, X.; Gong, P.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, X. Earth science applications of ICESat/GLAS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 8837–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, B.E.; Zwally, H.J.; Shuman, C.A.; Hancock, D.; DiMarzio, J.P. Overview of the ICESat Mission. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 32, L21S01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefsky, M.A. A global forest canopy height map from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer and the Geoscience Laser Altimeter System. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L15401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, M.; Pinto, N.; Fisher, J.B.; Baccini, A. Mapping forest canopy height globally with spaceborne lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116, G04021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Ding, J.; Guo, Z.; Tang, S.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.; Liu, R.; Chen, J.M. A combined GLAS and MODIS estimation of the global distribution of mean forest canopy height. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, S.O.; Rosette, J.A.B.; Kljun, N.; North, P.R.J.; Chasmer, L.; Suárez, J.C.; Hopkinson, C.; Hill, R.A.; van Gorsel, E.; Mahoney, C.; et al. Vegetation height and cover fraction between 60° S and 60° N from ICESat GLAS data. Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 5, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Park, T.; Choi, S.; Myneni, R. Mapping Forest Canopy Height over Continental China Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8436–8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarth, P.; Armston, J.; Lucas, R.; Bunting, P. A Structural Classification of Australian Vegetation Using ICESat/GLAS, ALOS PALSAR, and Landsat Sensor Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Guo, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Fang, J. Global patterns and determinants of forest canopy height. Ecology 2016, 97, 3265–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, S.R.J.; Eriksson, M.; Halldin, S. Tree-heights derived from radar profiles over boreal forests. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 98, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.G.; Bergen, K.; Blair, J.B.; Dubayah, R.; Houghton, R.; Hurtt, G.; Kellndorfer, J.; Lefsky, M.; Ranson, J.; Saatchi, S.; et al. Characterizing 3D vegetation structure from space: Mission requirements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2753–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, C.; Schmullius, C. The potential of ALOS PALSAR backscatter and InSAR coherence for forest growing stock volume estimation in Central Siberia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 173, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchard, E.T.A.; Saatchi, S.S.; Woodhouse, I.H.; Nangendo, G.; Ribeiro, N.S.; Williams, M.; Ryan, C.M.; Lewis, S.L.; Feldpausch, T.R.; Meir, P. Using satellite radar backscatter to predict above-ground woody biomass: A consistent relationship across four different African landscapes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L23401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Mitchard, E.; Schumacher, J.; Johannsen, V.; Saatchi, S.; Fensholt, R. L-Band SAR Backscatter Related to Forest Cover, Height and Aboveground Biomass at Multiple Spatial Scales across Denmark. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4442–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, D.J.; Carabajal, C.C. ICESat waveform measurements of within-footprint topographic relief and vegetation vertical structure. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 32, L21S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Biging, G.S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Gong, P. Mapping vegetation heights in China using slope correction ICESat data, SRTM, MODIS-derived and climate data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 129, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, H.; Gong, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Li, Z. Joint Use of ICESat/GLAS and Landsat Data in Land Cover Classification: A Case Study in Henan Province, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Gong, P.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Li, W. Forest Canopy Height Extraction in Rugged Areas With ICESat/GLAS Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4650–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Sun, G.; Wang, L. ICESat GLAS Data for Urban Environment Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1158–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Gong, P. Integration of multi-resource remotely sensed data and allometric models for forest aboveground biomass estimation in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arino, O.; Ramos Perez, J.J.; Kalogirou, V.; Bontemps, S.; Defourny, P.; Van Bogaert, E. Global land cover map for 2009 (GlobCover 2009). In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Symposium, Bergen, Norway, 28 June–2 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: First mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Liu, G.H.; Lü, Y.H.; Chen, L.D.; Ma, K.M. Ecoregions and ecosystem management in China. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2004, 11, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Woodcock, C.E. Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: Cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, J.O.; Song, X.-P.; Feng, M.; Noojipady, P.; Anand, A.; Huang, C.; Kim, D.-H.; Collins, K.M.; Channan, S.; DiMiceli, C.; et al. Global, 30-m resolution continuous fields of tree cover: Landsat-based rescaling of MODIS vegetation continuous fields with lidar-based estimates of error. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 427–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Jarvis, A. An evaluation of void-filling interpolation methods for SRTM data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2007, 21, 983–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D.; Grayson, R.B.; Ladson, A.R. Digital terrain modelling: A review of hydrological, geomorphological, and biological applications. Hydrol. Process. 1991, 5, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Itoh, T.; Motooka, T.; Watanabe, M.; Shiraishi, T.; Thapa, R.; Lucas, R. New global forest/non-forest maps from ALOS PALSAR data (2007–2010). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Shimada, M.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Kou, W.; Moore, B., III. Forest cover maps of China in 2010 from multiple approaches and data sources: PALSAR, Landsat, MODIS, FRA, and NFI. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 109, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Isoguchi, O.; Tadono, T.; Isono, K. PALSAR Radiometric and Geometric Calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3915–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Ministry of Forestry. Forest Resource Report of China for Periods 2009–2013; Department of Forest Resource and Management, Chinese Ministry of Forestry: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Van Beijma, S.; Comber, A.; Lamb, A. Random forest classification of salt marsh vegetation habitats using quad-polarimetric airborne SAR, elevation and optical RS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Clinton, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Gong, P.; Yang, J.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Mapping major land cover dynamics in Beijing using all Landsat images in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Clinton, N.; Ji, L.; Li, W.; Bai, Y.; et al. Stable classification with limited sample: transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Yu, L.; Clinton, N.; Huang, H.; Yang, J.; Gong, P. A Circa 2010 Thirty Meter Resolution Forest Map for China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5325–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; Zhu, B.; Tan, K. Forest biomass carbon stocks in China over the past 2 decades: Estimation based on integrated inventory and satellite data. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2005, 110, G01006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ju, W.; Chen, J.M.; Zan, M.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X. China’s forest biomass carbon sink based on seven inventories from 1973 to 2008. Clim. Chang. 2013, 118, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, J.G. Regression through the Origin. Teach. Stat. 2003, 25, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.A.; Thiel, C.; Schmullius, C. Growing stock volume estimation from L-band ALOS PALSAR polarimetric coherence in Siberian forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.; Saatchi, S.; Ustin, S.; Balzter, H. Modelling forest canopy height by integrating airborne LiDAR samples with satellite Radar and multispectral imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 66, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Turubanova, S.; Tyukavina, A.; Krylov, A.; Kommareddy, A.; Egorov, A. Mapping tree height distributions in Sub-Saharan Africa using Landsat 7 and 8 data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Shen, Z.; Tang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Feng, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Wu, X.; Zheng, C. Forest community survey and the structural characteristics of forests in China. Ecography 2012, 35, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, X. Constructing a Finer-Resolution Forest Height in China Using ICESat/GLAS, Landsat and ALOS PALSAR Data and Height Patterns of Natural Forests and Plantations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151740
Huang H, Liu C, Wang X. Constructing a Finer-Resolution Forest Height in China Using ICESat/GLAS, Landsat and ALOS PALSAR Data and Height Patterns of Natural Forests and Plantations. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(15):1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151740
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Huabing, Caixia Liu, and Xiaoyi Wang. 2019. "Constructing a Finer-Resolution Forest Height in China Using ICESat/GLAS, Landsat and ALOS PALSAR Data and Height Patterns of Natural Forests and Plantations" Remote Sensing 11, no. 15: 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151740
APA StyleHuang, H., Liu, C., & Wang, X. (2019). Constructing a Finer-Resolution Forest Height in China Using ICESat/GLAS, Landsat and ALOS PALSAR Data and Height Patterns of Natural Forests and Plantations. Remote Sensing, 11(15), 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11151740





