Assessment of Irrigation Performance in Large River Basins under Data Scarce Environment—A Case of Kabul River Basin, Afghanistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
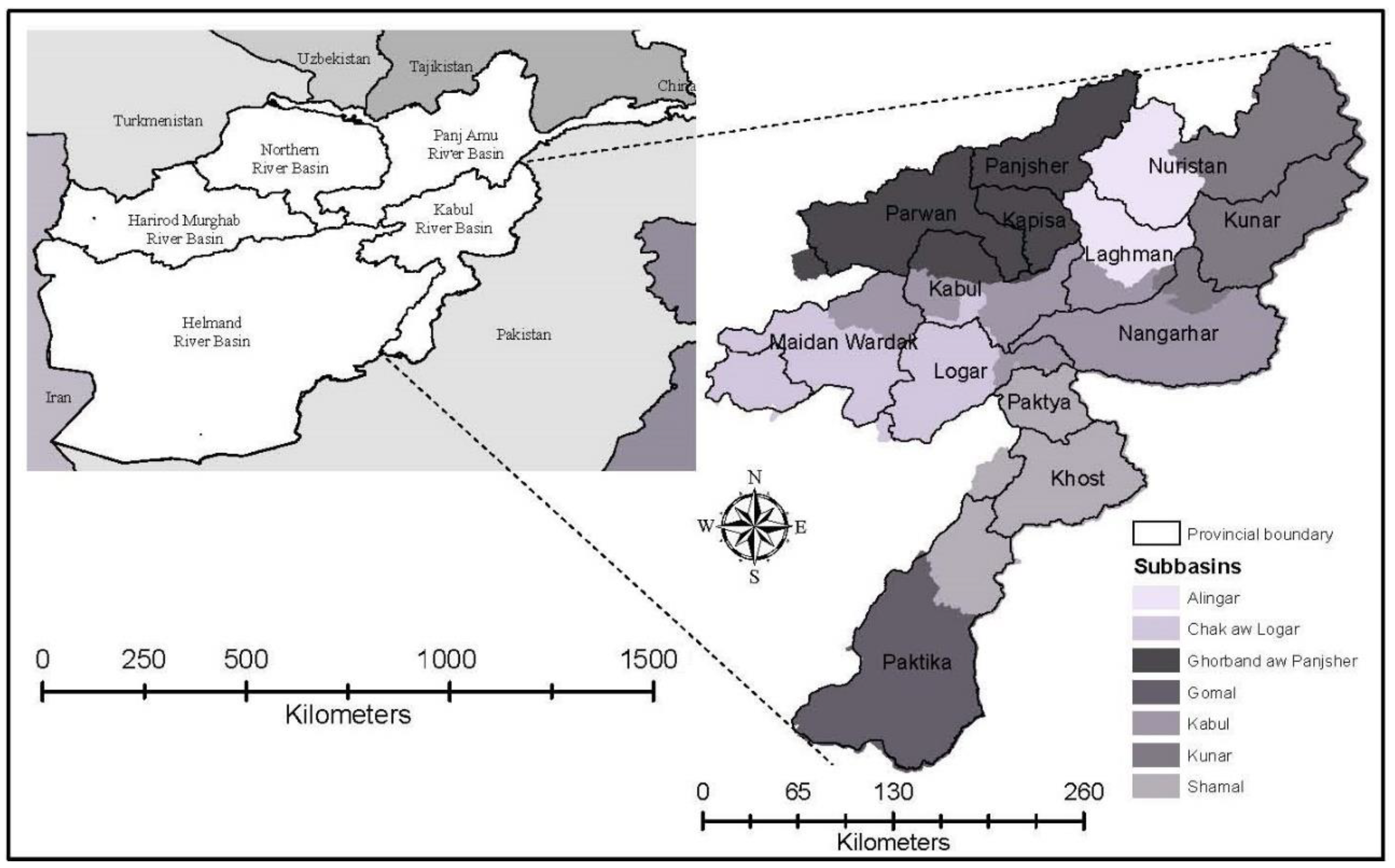
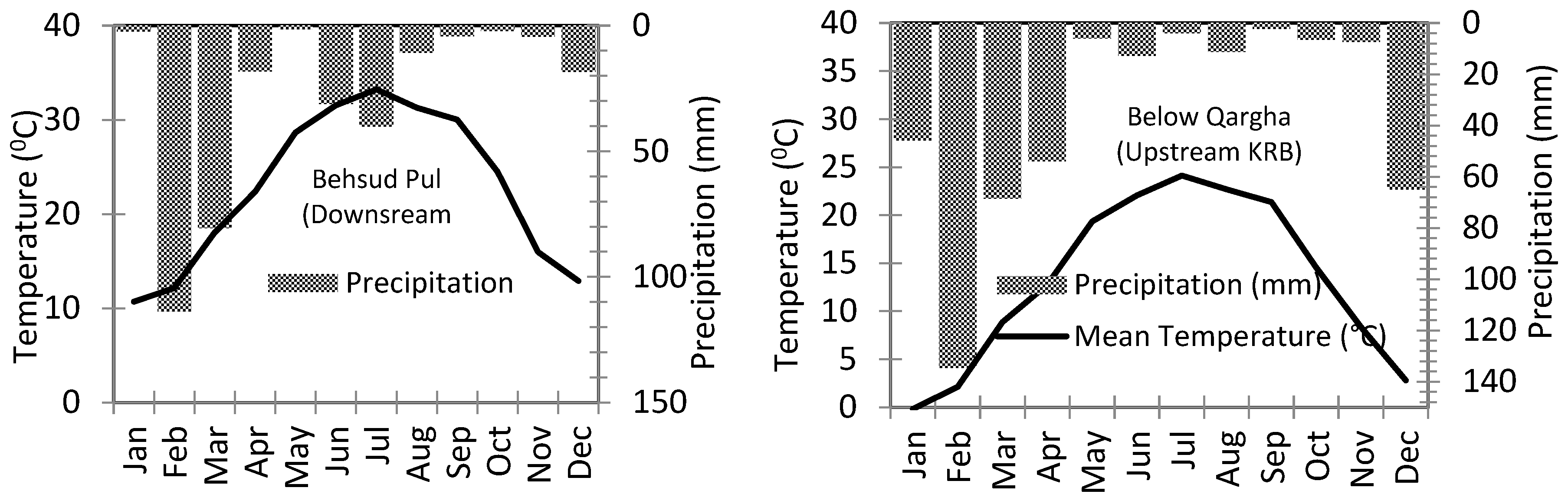
2.1. Description of the Study Site
2.2. Diagnosis of the Irrigation System Performance of the KRB
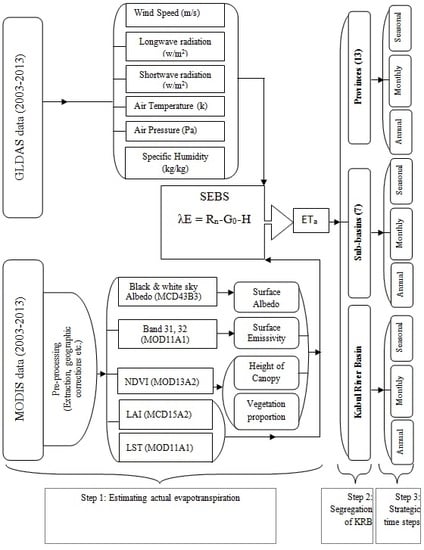
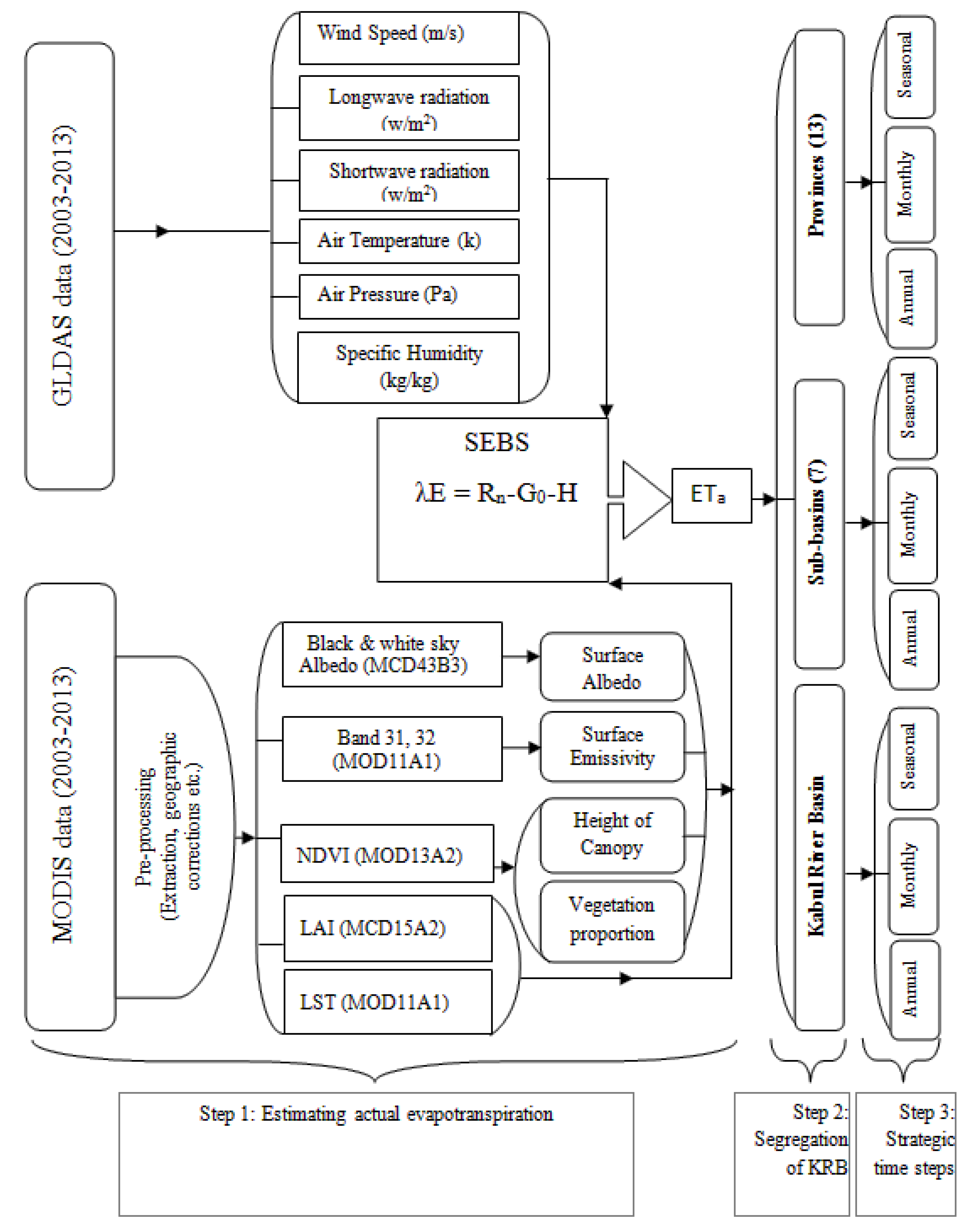
2.3. Actual Evapotranspiration Estimated by Remote Sensing
Main Input Data Characteristics for the SEBS
2.4. Evaluation of the SEBS Actual Evapotranspiration through Advection-Aridity Model (AA)
2.5. Mann-Kendall Test for Monotonic Trend in Temperature
| for l ≤ k | |
3. Results and Discussion
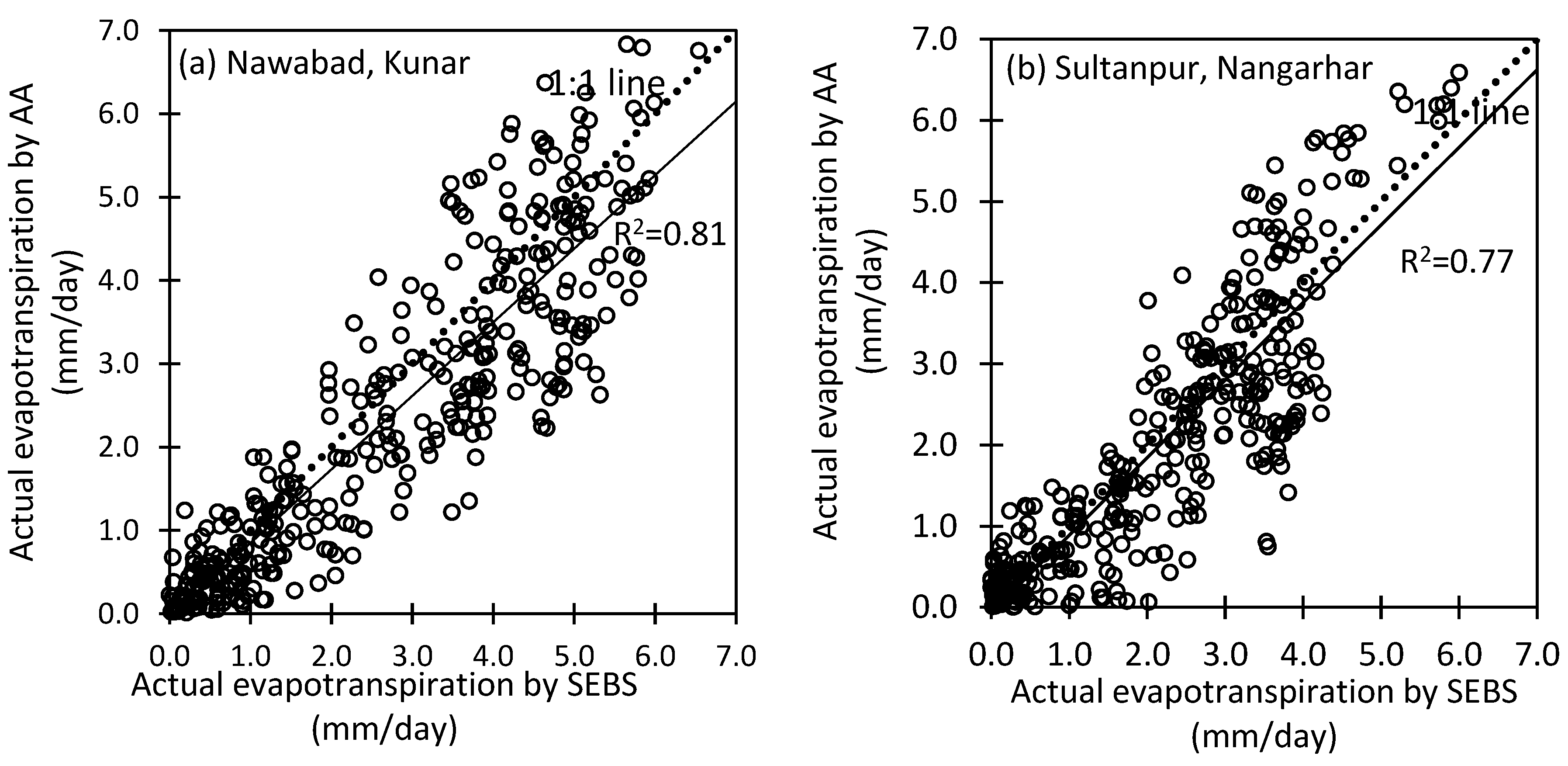
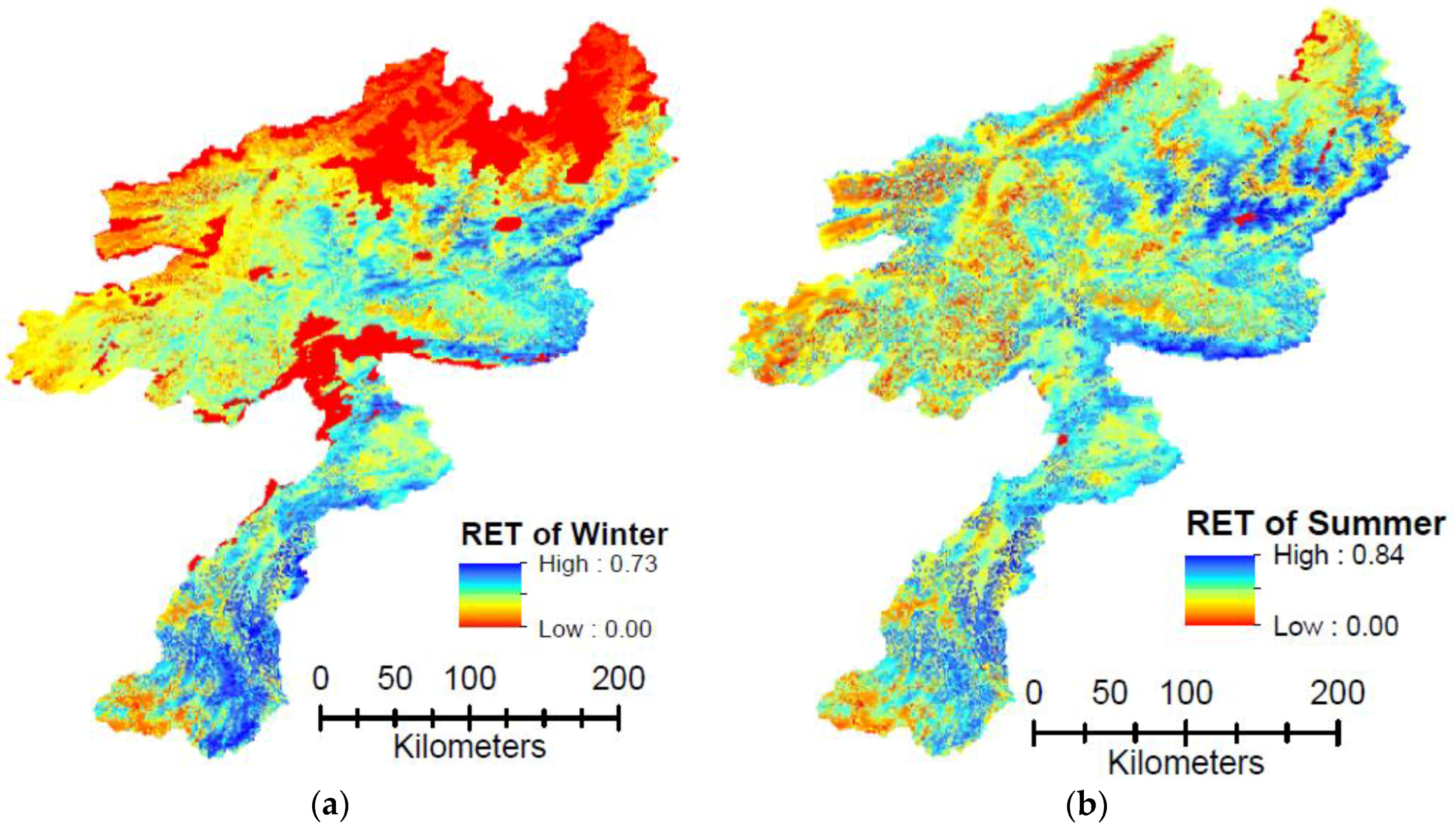
3.1. Validation of the ETa Estimated through SEBS with AA Model Estimates
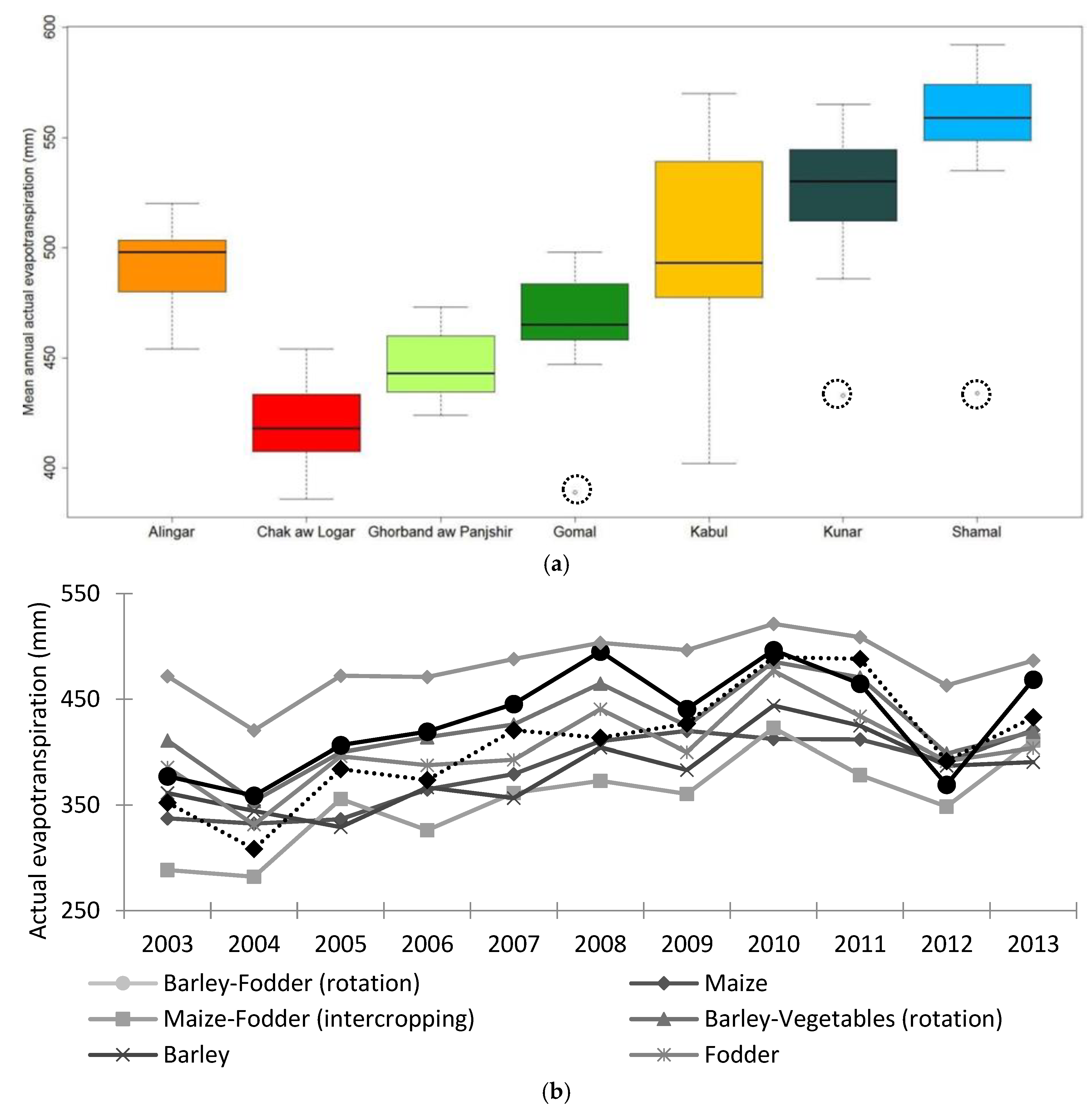
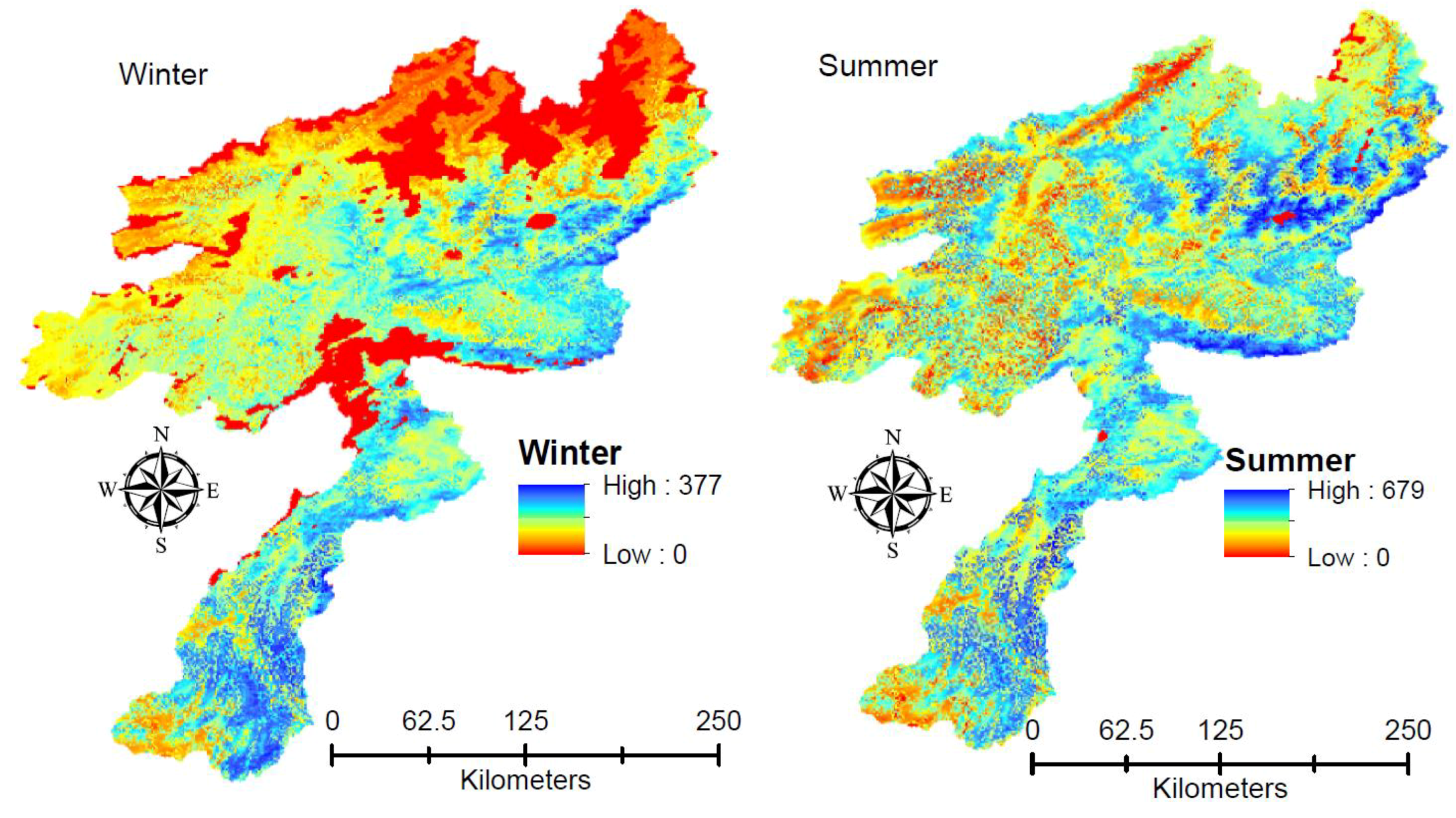
3.2. Annual Distribution of Actual Evapotranspiration across the KRB, Constituent Sub-Basins and Provinces
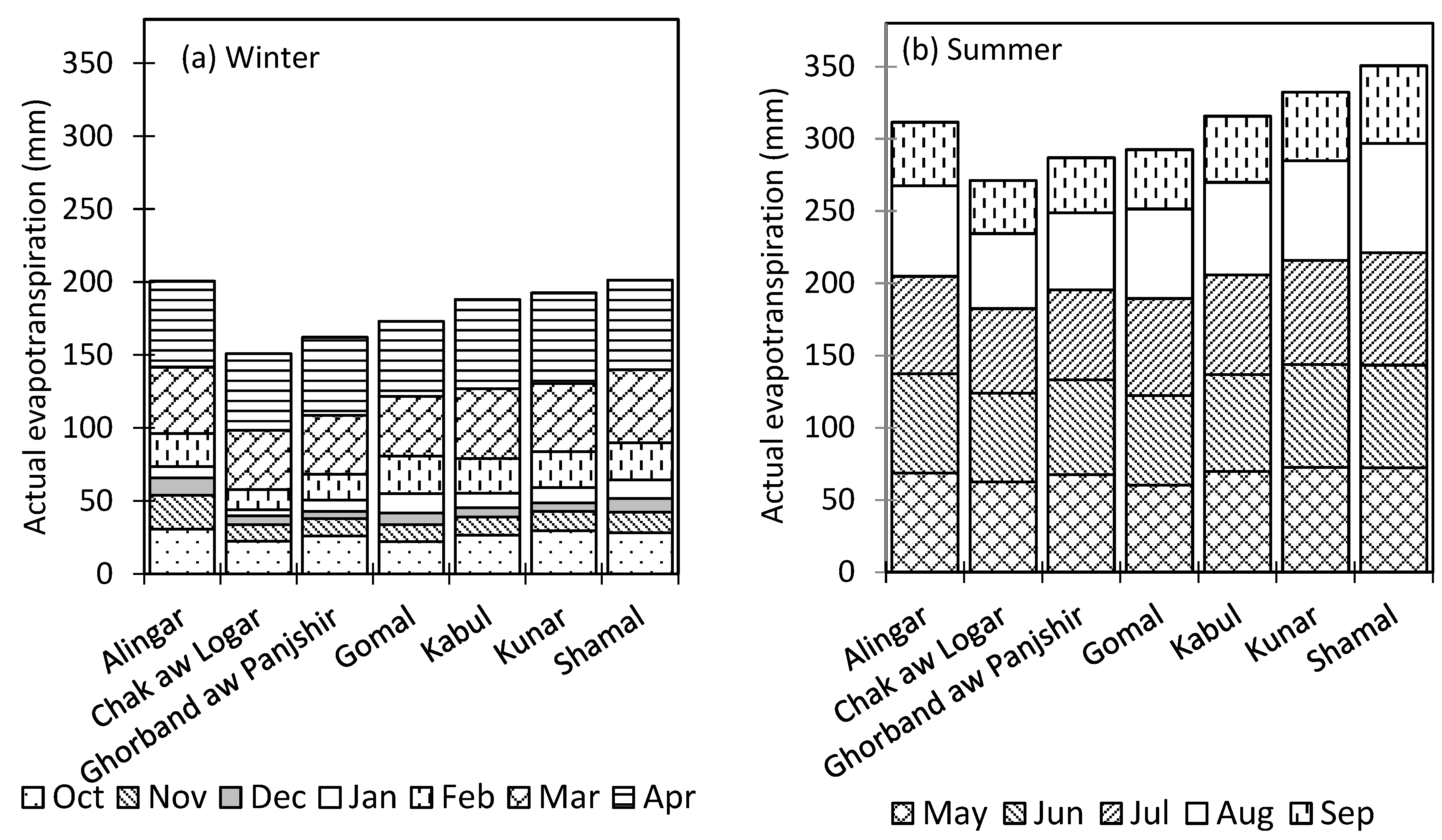
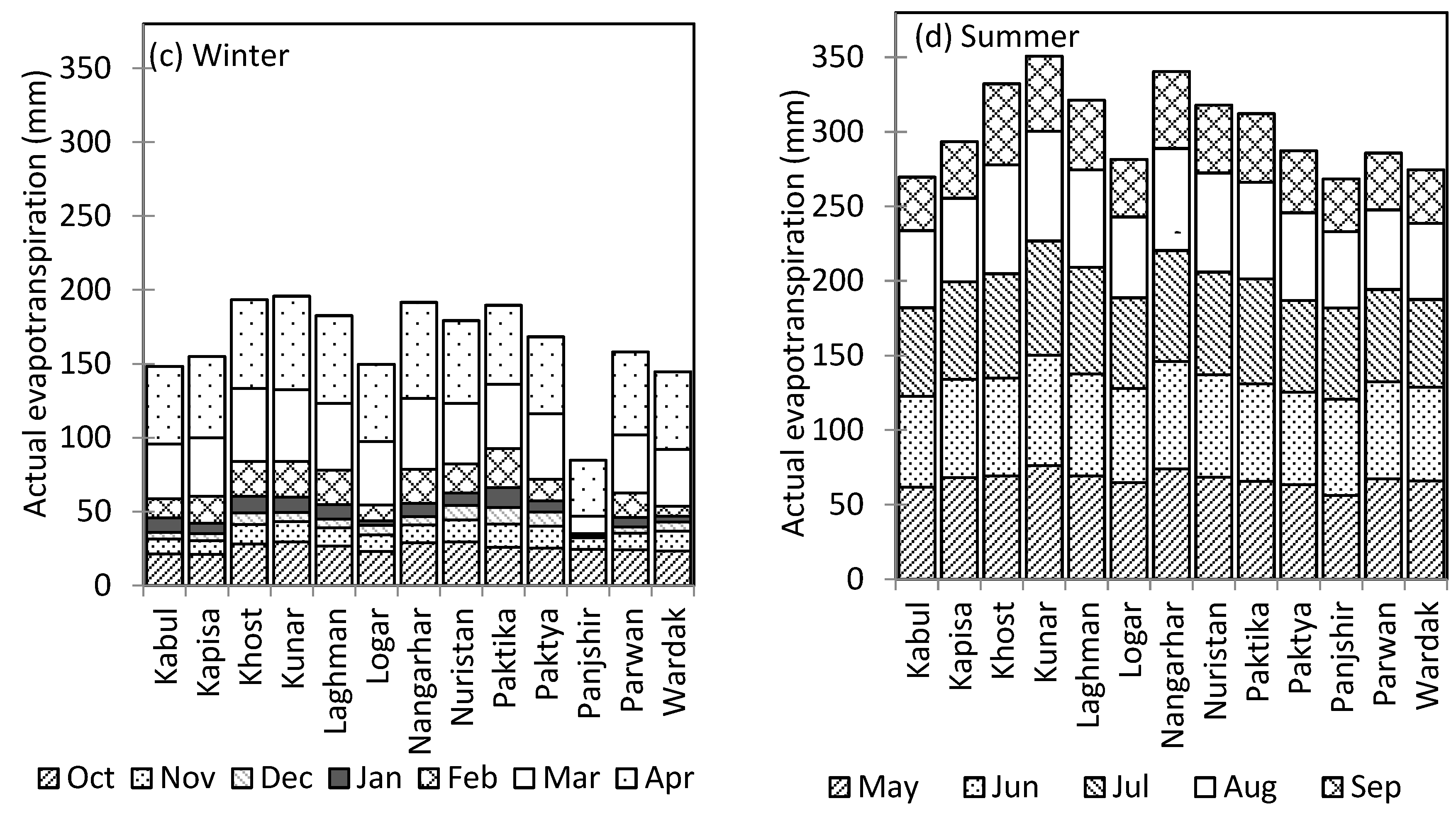
3.3. Monthly Distribution of Actual Evapotranspiration Across the KRB, Constituent Sub-Basins and Provinces
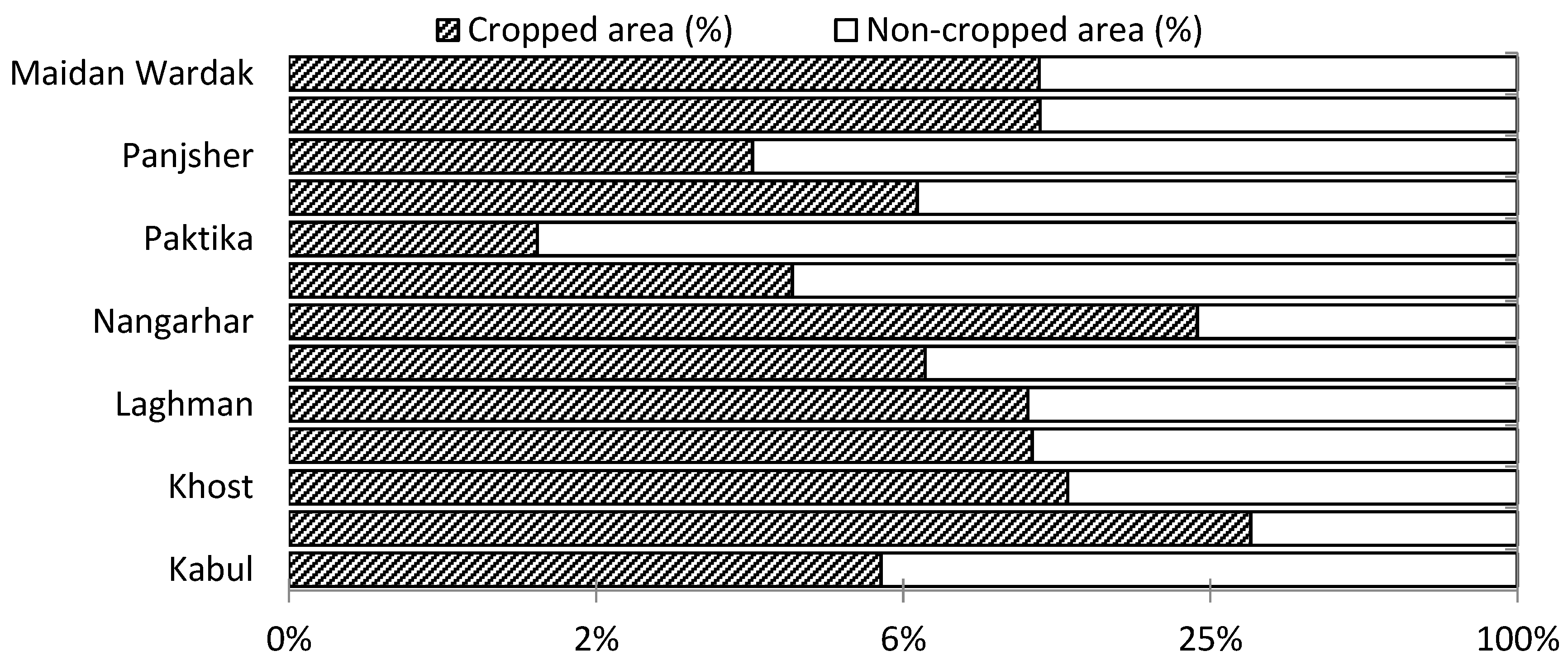
3.4. Land Cover Based Variation of ETa Across the KRB
3.5. Evaluation of the Results of Mann-Kendall Test for Monotonic Trend in Temperature
3.6. Evaluation of the Irrigation Performance
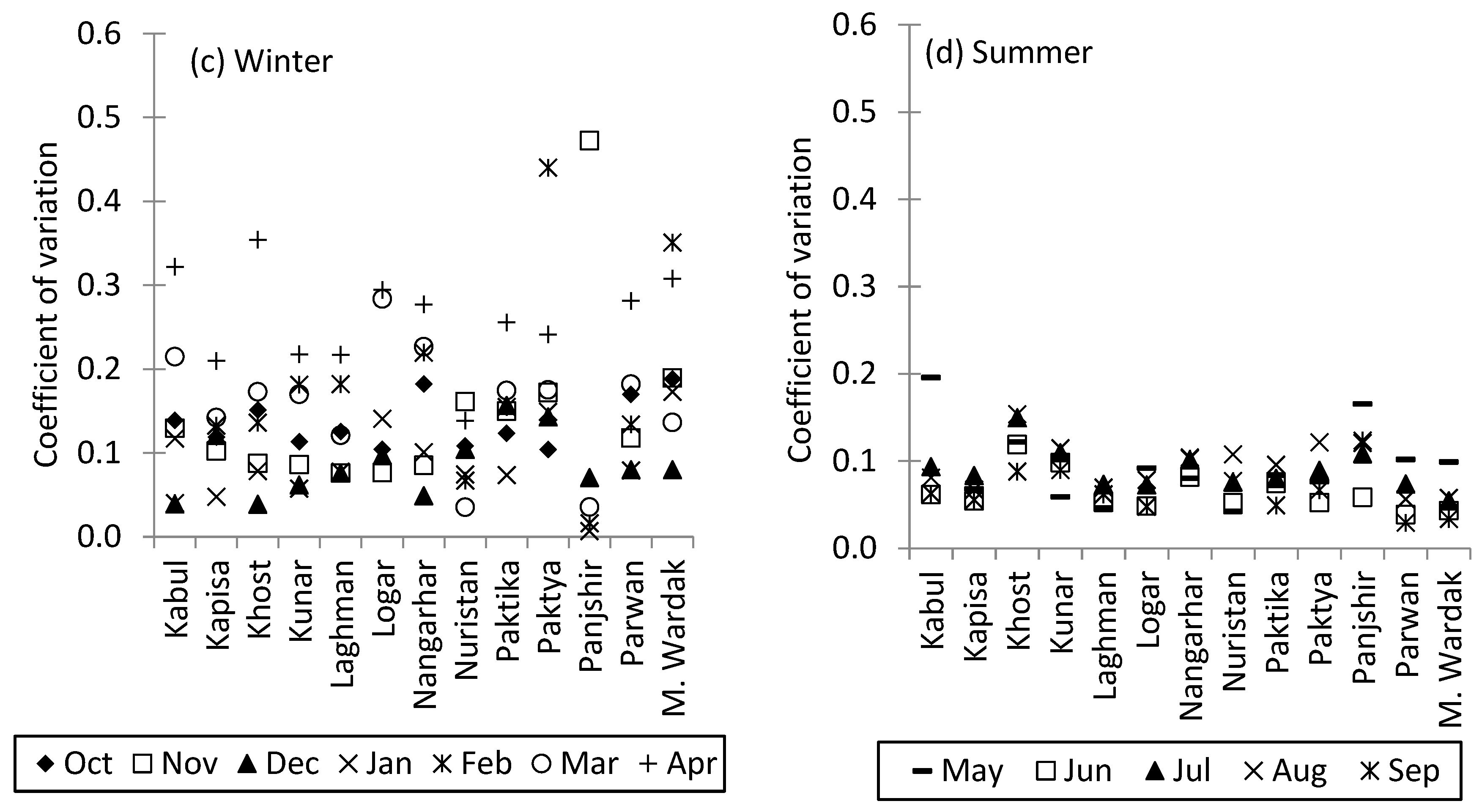
3.6.1. Analysis of Spatial Equity
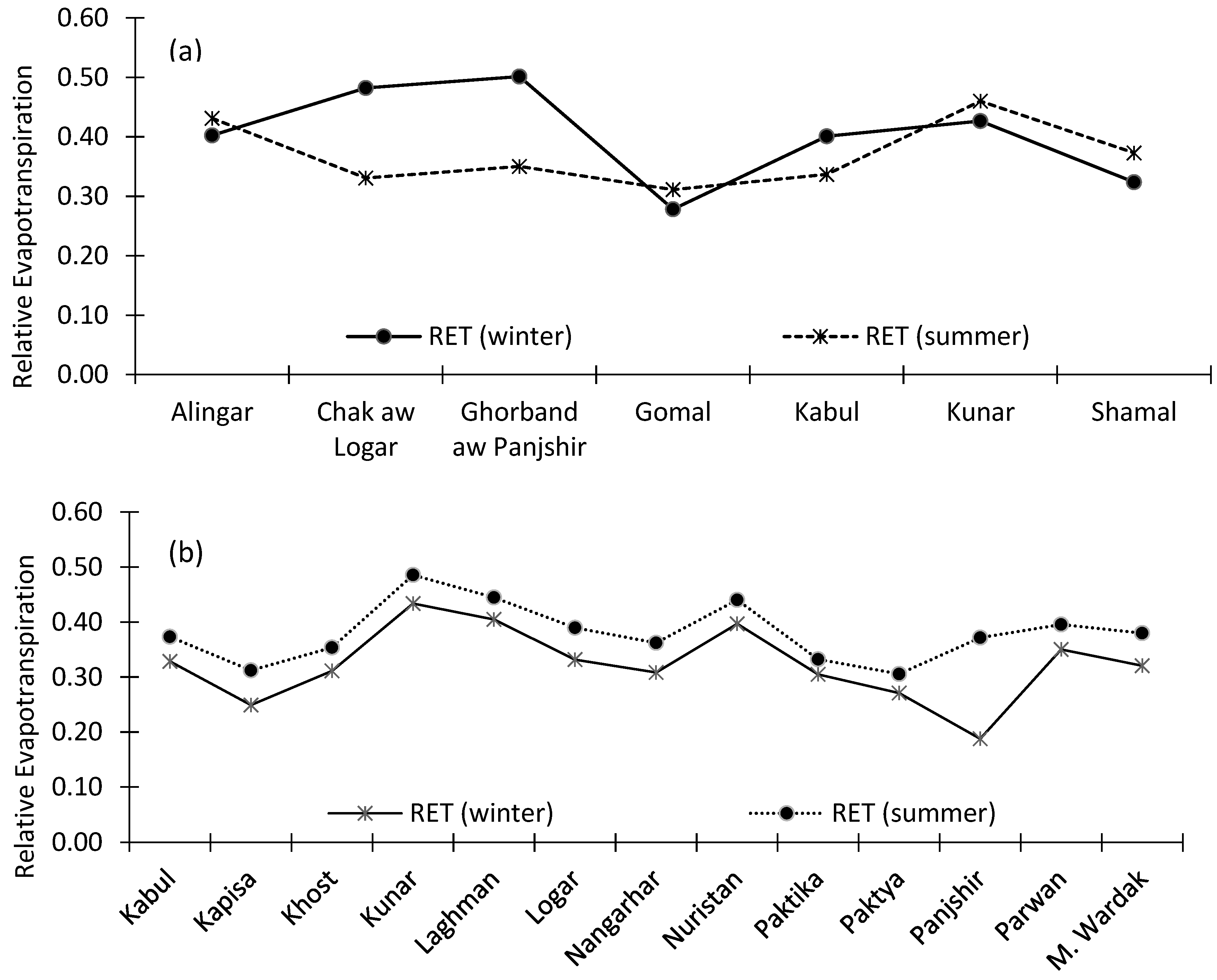
3.6.2. Analysis of Seasonal Adequacy
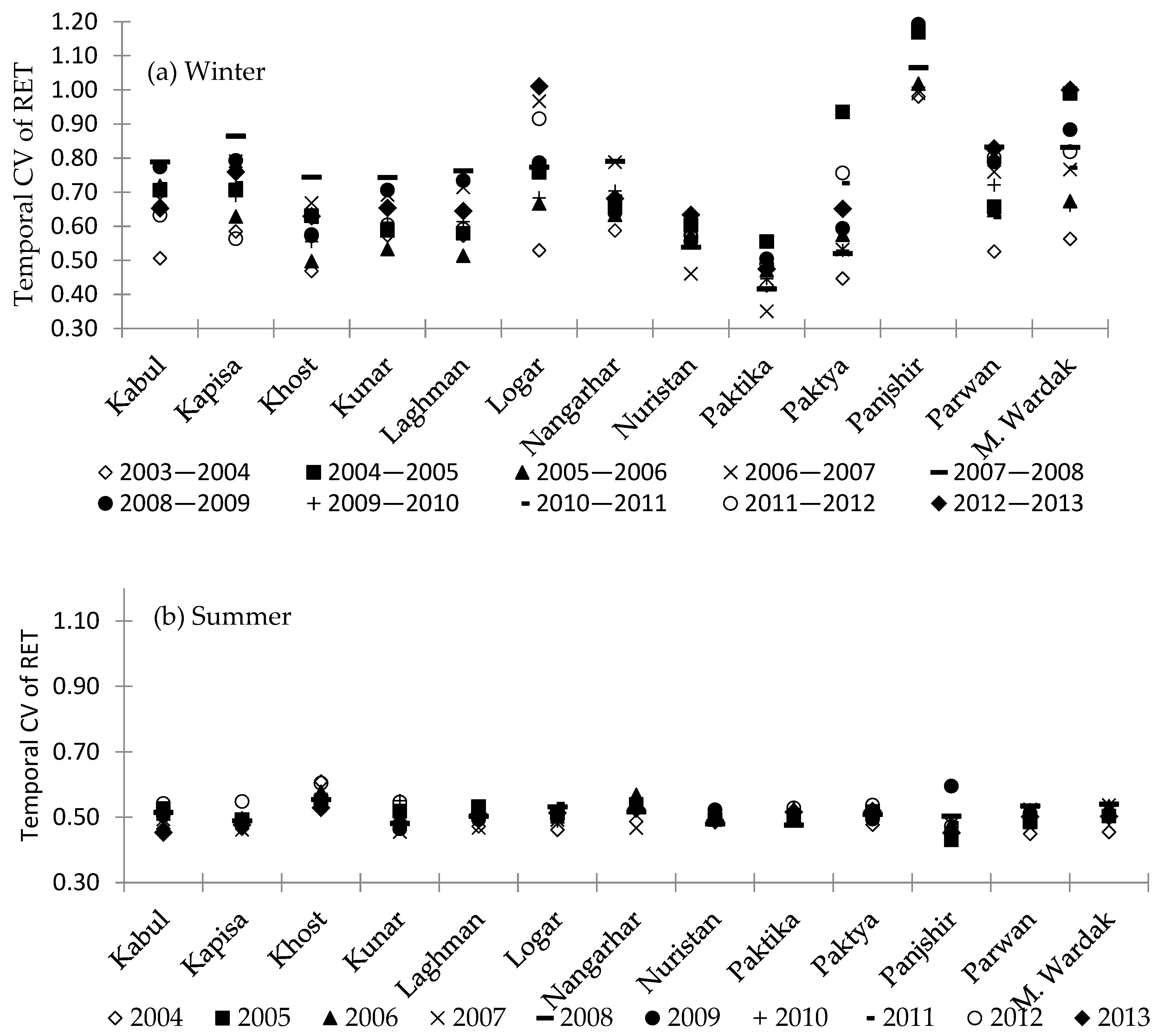
3.6.3. Analysis of Temporal Reliability
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qureshi, A.S. Water Resources in Afghanistan: Issues and Options (Working Paper 49). 2002. Available online: http://www.iwmi.cgiar.org/Publications/Working_Papers/working/WOR49.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2015).
- Farrell, G.; Thorne, J. Where have all the flowers gone? Evaluation of the Taliban crackdown against opium poppy cultivation in Afghanistan. Int. J. Drug Policy 2004, 16, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, A. Swords into plowshares? Accessing natural resources and securing agricultural livelihoods in rural Afghanistan. In Livelihoods, Natural Resources, and Post-Conflict Peacebuilding; Routledge: London, UK, 2015; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Lin, D.; Wu, Y. Mapping Drought Risk (Maize) of the World. In World Atlas of Natural Disaster Risk; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 211–226. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, F.; Tischbein, B.; Awan, U.K. Optimizing Deficit Irrigation Scheduling under Shallow Groundwater Conditions in Lower Reaches of Amu Darya River Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3165–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, M.G.; Murray-Rust, D.H.; Merrey, D.J.; Johnson, H.G.; Snellen, W.B. Methodologies for assessing performance of irrigation and drainage management. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1994, 7, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhungel, R.; Allen, R.G.; Trezza, R.; Robison, C.W. Evapotranspiration between satellite overpasses: Methodology and case study in agricultural dominant semi-arid areas. Meteorol. Appl. 2016, 23, 714–730. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.D.; Turral, H.; Nazeer, A. Diagnosing irrigation performance and water productivity through satellite remote sensing and secondary data in a large irrigation system of Pakistan. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Bos, M.G. Irrigation Performance Indicators Based on Remotely Sensed Data: A Review of Literature. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1999, 13, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Toomanian, N.; Droogers, P.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Gieske, A. Monitoring irrigation performance in Esfahan, Iran, using NOAA satellite imagery. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, S.J.; Leclert, L.M.C. A remote sensing-based irrigation performance assessment: A case study of the Office du Niger in Mali. Irrig. Sci. 2010, 28, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwasoka, D.T.; Gumindoga, W.; Gwenzi, J. Estimation of actual evapotranspiration using the Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) algorithm in the upper Manyame catchment in Zimbabwe. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, U.W.; Choi, M.; Awan, U.K. Spatio-temporal distribution of actual evapotranspiration in the Indus Basin Irrigation System. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 2613–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Liedl, R.; Awan, U.K. Spatio-temporal estimation of consumptive water use for assessment of irrigation system performance and management of water resources in irrigated Indus Basin, Pakistan. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, U.K.; Tischbein, B.; Conrad, C.; Martius, C.; Hafeez, M. Remote Sensing and Hydrological Measurements for Irrigation Performance Assessments in a Water User Association in the Lower Amu Darya River Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 2467–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, F.; Awan, U.K.; Tischbein, B.; Liaqat, U.W. A phenology based geo-informatics approach to map land use and land cover (2003–2013) by spatial segregation of large heterogenic river basins. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 88, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.; Sturtewagen, B. Making the Most of Afghanistan’s River Basins: Opportunities for Regional Cooperation; EastWest Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, C.; Mansfield, D.; Oldham, P.; Byrd, W. Afghanistan: Economic Incentives and Development Initiatives to Reduce Opium Production; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, M.G.; Nugteren, J. On Irrigation Efficiencies; ILRI: Nairobi, Kenya, 1990; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Brito, R.A.L.; Bos, M.G.; Souza, R.A.; Cavalcanti, E.B.; Bakker, M.M. Low cost satellite data for monthly irrigation performance monitoring: Benchmarks from Nilo Coelho, Brazil. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2001, 15, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.J. Quantification and Measurement of a Minimum Set of Indicators of the Performance of Irrigation Systems; International Irrigation Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, K.M.P.S. Monitoring irrigation performance in Sri Lanka with high-frequency satellite measurements during the dry season. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 58, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, M.; Small, L.E. Farmer’s perspective on irrigation performance. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1990, 4, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorenbos, J.; Kassam, A.H. Yield response to water. Irrig. Drain. Paper 1979, 33, 257. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 56. [Google Scholar]
- Asaana, J.; Sadick, A. Assessment of Irrigation Performance Using Remote Sensing Technique at Tono irrigation Area in the Upper East Region of Ghana. Int. Res. J. Agric. Food Sci. 2016, 1, 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Roerink, G.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.; Chambouleyron, J.; Menenti, M. Relating Crop Water Consumption to Irrigation Water Supply by Remote Sensing. Water Resour. Manag. 1997, 11, 445–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, K.M.P.S. Assessing Irrigation Performance by Using Remote Sensing; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006; p. 156. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, L.; Nott, D.; Sharma, A.C.W. Hydrological model selection: A Bayesian alternative. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, N.; Sánchez, M.L.; Timmermans, J.; Su, Z.; Pérez, I.A.; García, M.A. SEBS validation in a Spanish rotating crop. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 195, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hafeez, M.; Rabbani, U.; Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Y. Retrieved actual ET using SEBS model from Landsat-5 TM data for irrigation area of Australia. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, A.S.; Obukhov, A. Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the surface layer of the atmosphere. Contrib. Geophys. Inst. Acad. Sci. USSR 1954, 151, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert, W. Aspects of bulk atmospheric boundary layer similarity under free—Convective conditions. Rev. Geophys. 1999, 37, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Xi, G.; Liu, S.; Huang, C.; Yan, Y.; Liu, G. Regional estimation of daily to annual regional evapotranspiration with MODIS data in the Yellow River Delta wetland. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Jia, G.; Zhao, T.; Wang, H.; Tang, B. Satellite-based estimation of daily average net radiation under clear-sky conditions. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Brutsaert, W. Daily evaporation over a region from lower boundary layer profiles measured with radiosondes. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.E.A.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The Global Land Data Assimilation System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Yang, S.; Zhao, C.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, Q. Estimation of daily average temperature using multisource spatial data in data sparse regions of Central Asia. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 073478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiptala, J.K.; Mohamed, Y.; Mul, M.L.; Zaag, P. Mapping evapotranspiration trends using MODIS and SEBAL model in a data scarce and heterogeneous landscape in Eastern Africa. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 8495–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W.; Stricker, H. An advection-aridity approach to estimate actual regional evapotranspiration. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hao, X.; Zhang, H. Evaluation of evapotranspiration models over semi-arid and semi-humid areas of China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 4292–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilagyi, J.; Hobbins, M.T.; Jozsa, J. Modified advection-aridity model of evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W. Hydrology: An Introduction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Crago, R.D.; Brutsaert, W. A comparison of several evaporation equations. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, Z.; Sun, R.; Zhang, X. Comparison of Different Complementary Relationship Models for Regional Evapotranspiration Estimation. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2004, 59, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchet, R.J. Evapotranspiration Réelle et Potentielle, Signification Climatique; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, UK, 1963; Volume 62, pp. 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Koffi, D.; Komla, G. Trend analysis in reference evapotranspiration and aridity index in the context of climate change in Togo. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2015, 6, 848–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Cavadias, G. Power of the Mann–Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J. Hydrol. 2002, 259, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric test against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Fatima, A.; Awan, U.K.; Anwar, A. Analysis of long term meteorological trends in the middle and lower Indus Basin of Pakistan—A non-parametric statistical approach. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 122, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.M.; Slack, J.R.; Smith, R.A. Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, E.S.; Hartley, H.O. Biometrika Tables for Statisticians; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.Y.; Singh, V.P. Evaluation of three complementary relationship evapotranspiration models by water balance approach to estimate actual regional evapotranspiration in different climatic regions. J. Hydrol. 2005, 308, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSO-IRoA. Agriculture Development. 2014. Available online: http://cso.gov.af/Content/files/Agriculture%20Development%281%29.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2015).
- Senay, G.B.; Budde, M.; Verdin, J.P.; Melesse, A.M. A coupled remote sensing and simplified surface energy balance approach to estimate actual evapotranspiration from irrigated fields. Sensors 2007, 7, 979–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maupin, M.A.; Senay, G.B.; Kenny, J.F.; Savoca, M.E. A Comparison of Consumptive-Use Estimates Derived from the Simplified Surface Energy Balance Approach and Indirect Reporting Methods; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2012.
- Awan, U.; Tischbein, B.; Martius, C. A GIS-based approach for up-scaling capillary rise from field to system level under soil-crop-groundwater mix. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| S. No. | Data Type | Source | Variables | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Temporal Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GLDAS | NOAH | Wind Speed (m/s) | 25 km | 3-h | 2003–2013 |
| 2 | Long-wave Radiation (W/m2) | 25 km | 3-h | 2003–2013 | ||
| 3 | Air Temperature (K) | 25 km | 3-h | 2003–2013 | ||
| 4 | Short-wave Radiation (W/m2) | 25 km | 3-h | 2003–2013 | ||
| 5 | Air Pressure (Pa) | 25 km | 3-h | 2003–2013 | ||
| 6 | Specific Humidity (Kg/Kg) | 25 km | 3-h | 2003–2013 |
| S. No. | Data Type | Source | Variables | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Granularity | Temporal Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Satellite Land Surface Data | MODIS | Emissivity/LST (MOD11A1) | 1 km | Instantaneous | 2003–2013 |
| 2 | NDVI (MOD13A2) | 1 km | 16-day | 2003–2013 | ||
| 3 | LAI (MCD15A2) | 1 km | 8-day | 2003–2013 | ||
| 4 | Albedo (MCD43B3) | 1 km | 8-day | 2003–2013 | ||
| 5 | Land Cover (MCD12Q1) | 500 m | Yearly | 2003–2013 |
| Observations | Std. Deviation | Kendall’s Tau | S | Var (S) | p-Value (Two-Tailed) | Alpha (α) | ZMK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | 11 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 9.0 | 165.0 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 0.70 |
| Feb | 11 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 5.0 | 165.0 | 0.76 | 0.05 | 0.39 |
| Mar | 11 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 5.0 | 165.0 | 0.76 | 0.05 | 0.39 |
| Apr | 11 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 3.0 | 165.0 | 0.88 | 0.05 | 0.23 |
| May | 11 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 13.0 | 165.0 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 1.01 |
| Jun | 11 | 1.5 | −0.1 | −5.0 | 165.0 | 0.76 | 0.05 | 0.39 |
| Jul | 11 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 13.0 | 165.0 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 1.01 |
| Aug | 11 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 25.0 | 165.0 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 1.95 |
| Sep | 11 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 7.0 | 165.0 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.54 |
| Oct | 11 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 13.0 | 165.0 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 1.01 |
| Nov | 11 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 11.0 | 165.0 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 0.86 |
| Dec | 11 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 11.0 | 165.0 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 0.86 |
| Mean | 1.3 | 0.2 | 9.17 | 165.0 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 0.78 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhtar, F.; Awan, U.K.; Tischbein, B.; Liaqat, U.W. Assessment of Irrigation Performance in Large River Basins under Data Scarce Environment—A Case of Kabul River Basin, Afghanistan. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060972
Akhtar F, Awan UK, Tischbein B, Liaqat UW. Assessment of Irrigation Performance in Large River Basins under Data Scarce Environment—A Case of Kabul River Basin, Afghanistan. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(6):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060972
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhtar, Fazlullah, Usman Khalid Awan, Bernhard Tischbein, and Umar Waqas Liaqat. 2018. "Assessment of Irrigation Performance in Large River Basins under Data Scarce Environment—A Case of Kabul River Basin, Afghanistan" Remote Sensing 10, no. 6: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060972
APA StyleAkhtar, F., Awan, U. K., Tischbein, B., & Liaqat, U. W. (2018). Assessment of Irrigation Performance in Large River Basins under Data Scarce Environment—A Case of Kabul River Basin, Afghanistan. Remote Sensing, 10(6), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060972