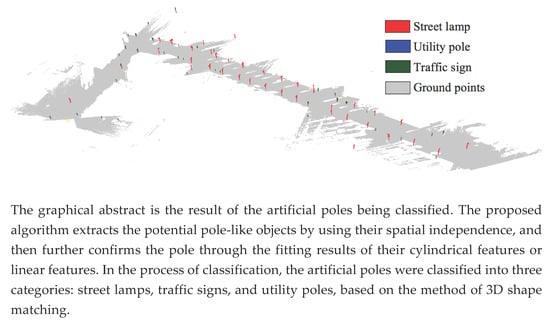
Automatic Recognition of Pole-Like Objects from Mobile Laser Scanning Point Clouds
Abstract
1. Introduction
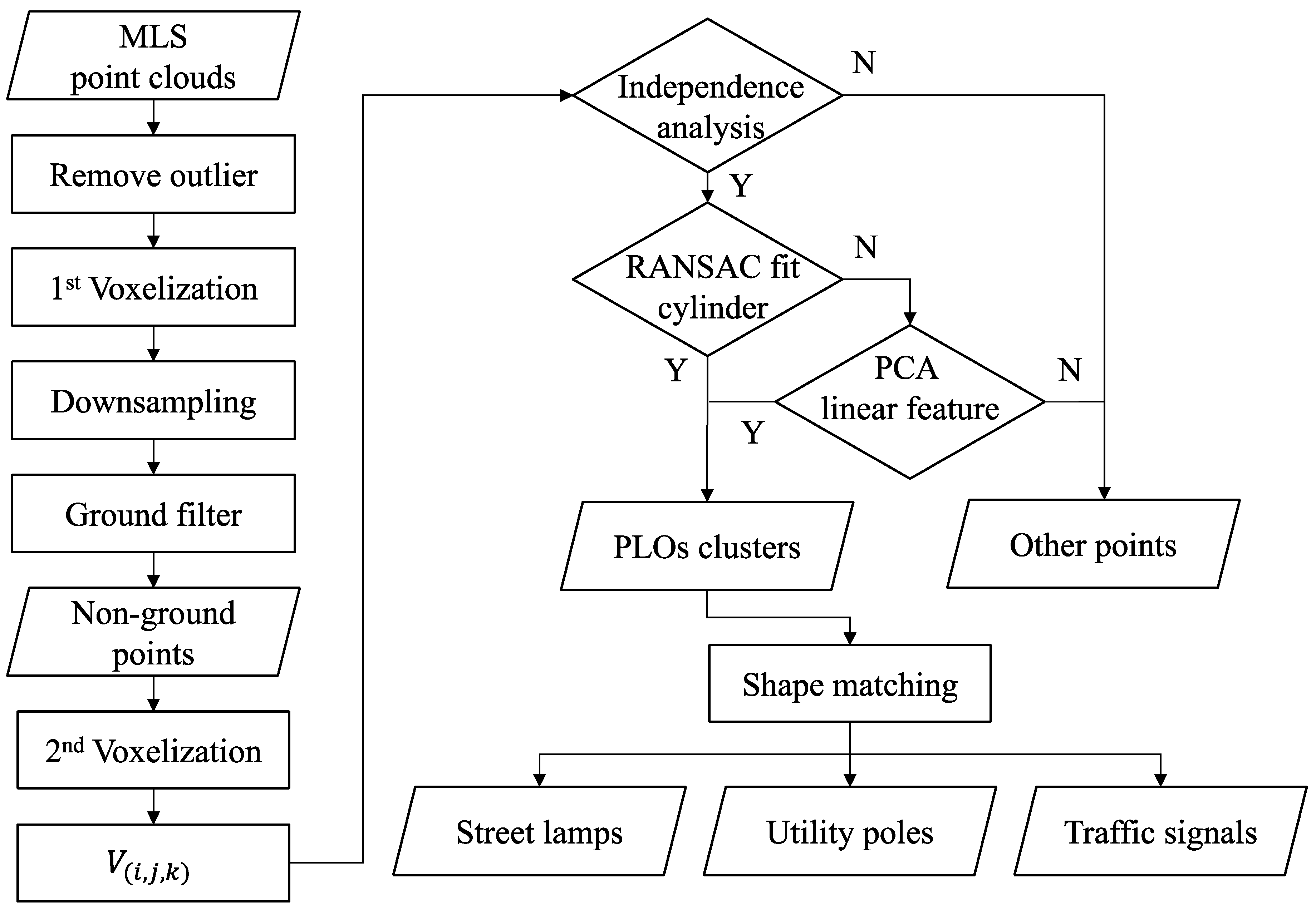
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mobile Laser Scanning Point Clouds
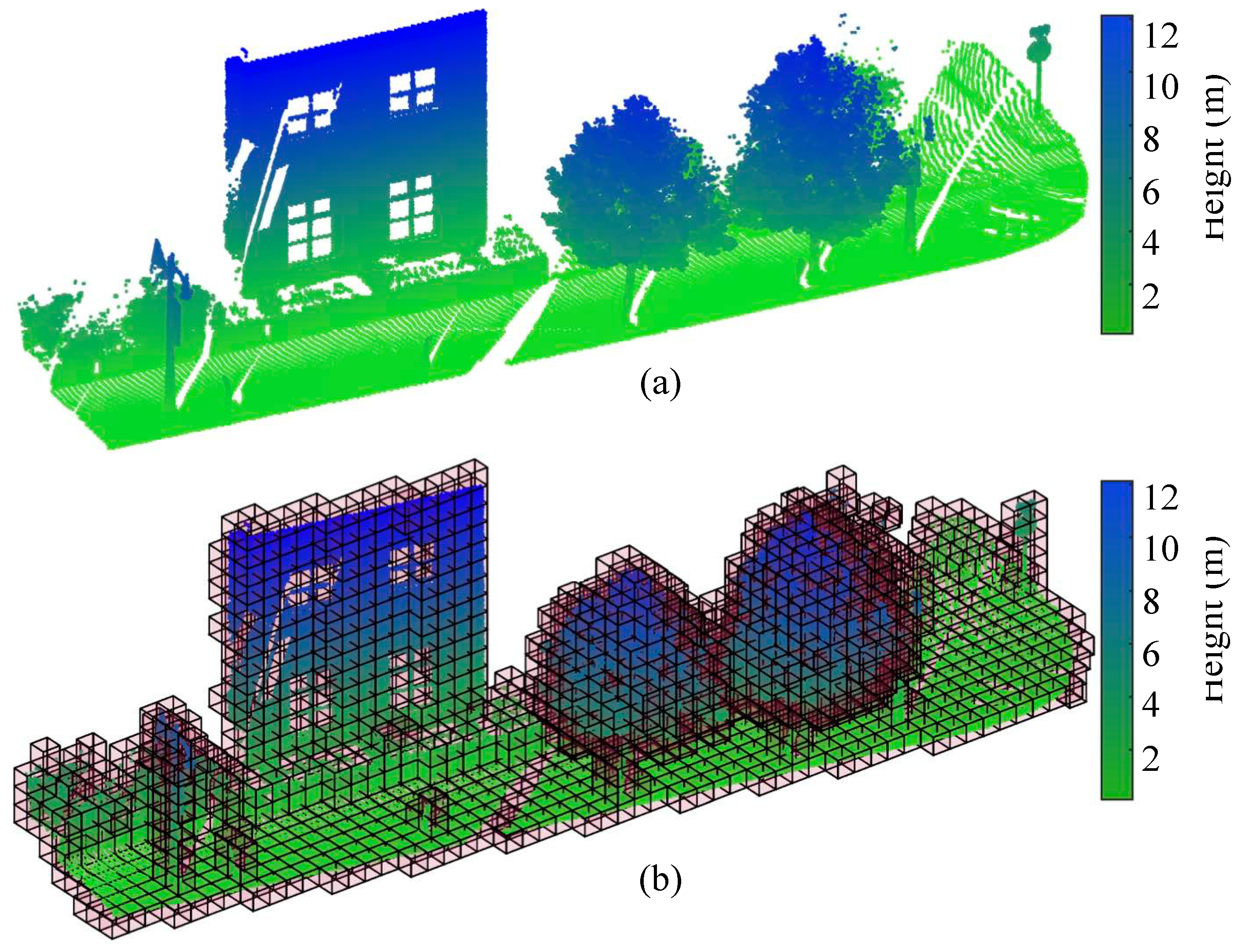
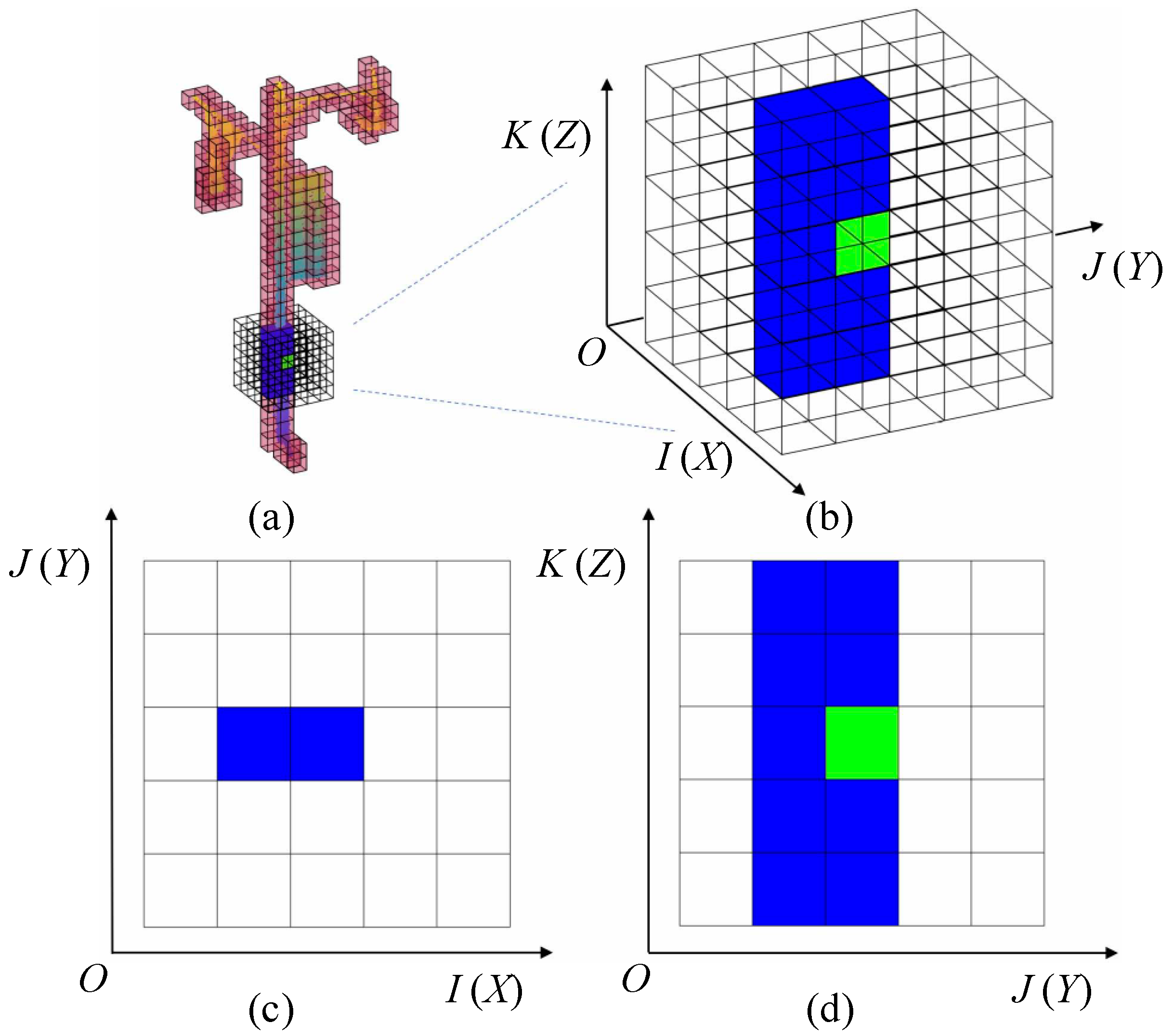
2.2. Voxelization
2.3. Preprocessing
2.3.1. Sparse Outlier Removal
2.3.2. Downsampling
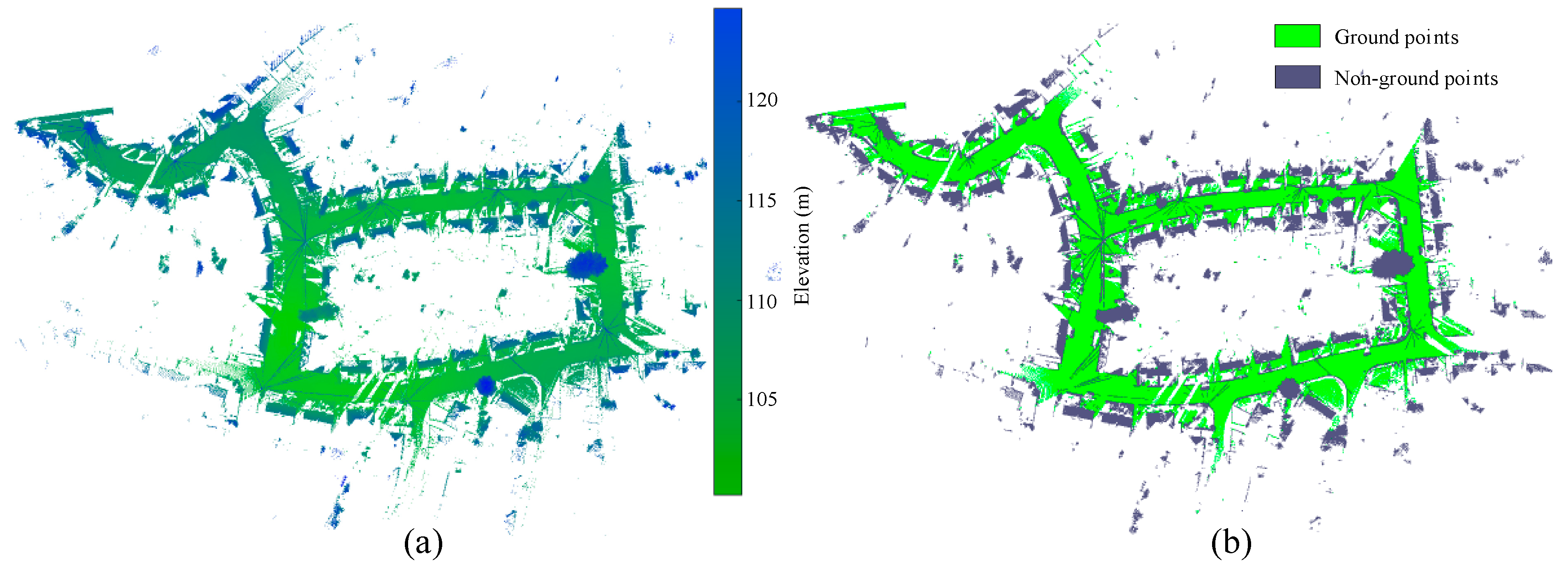
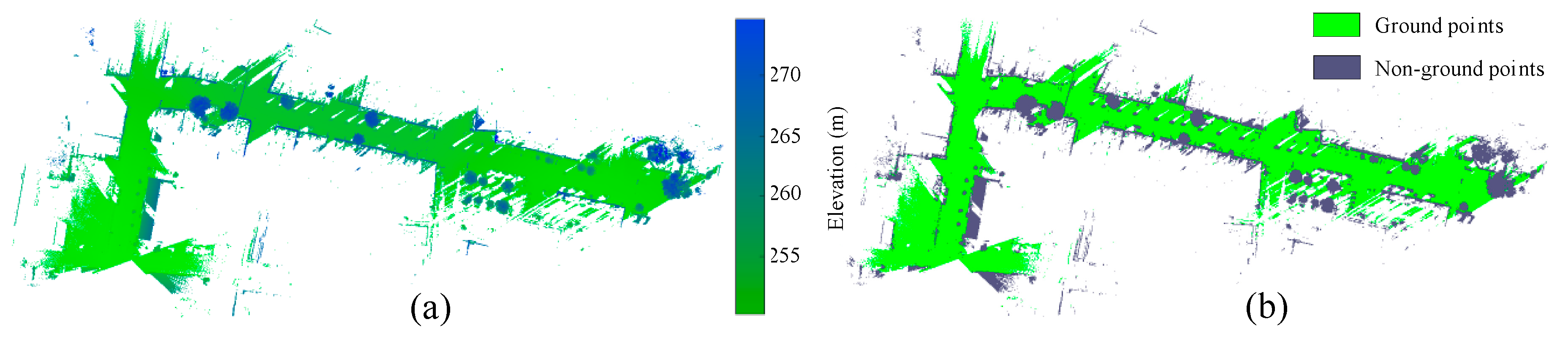
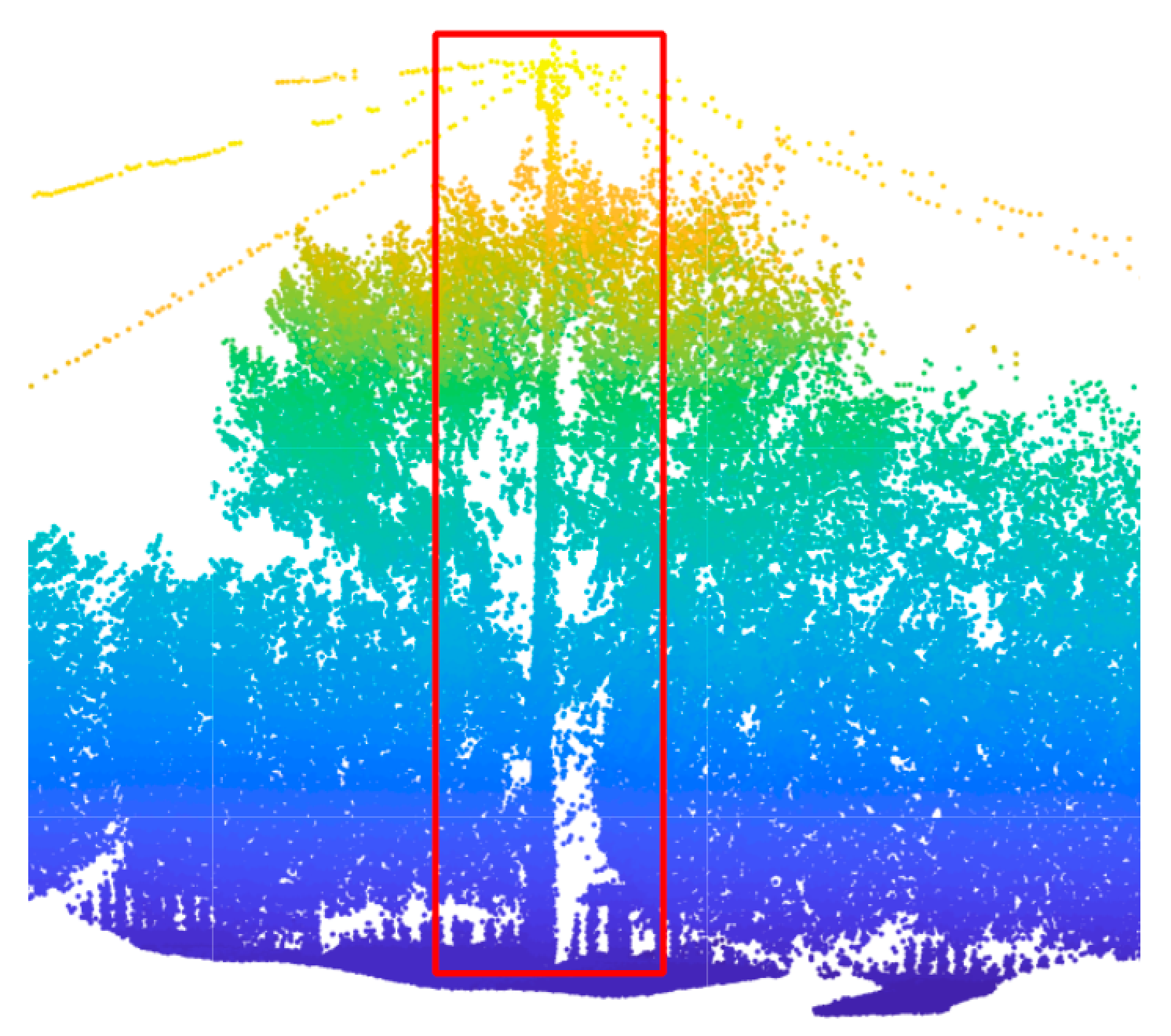
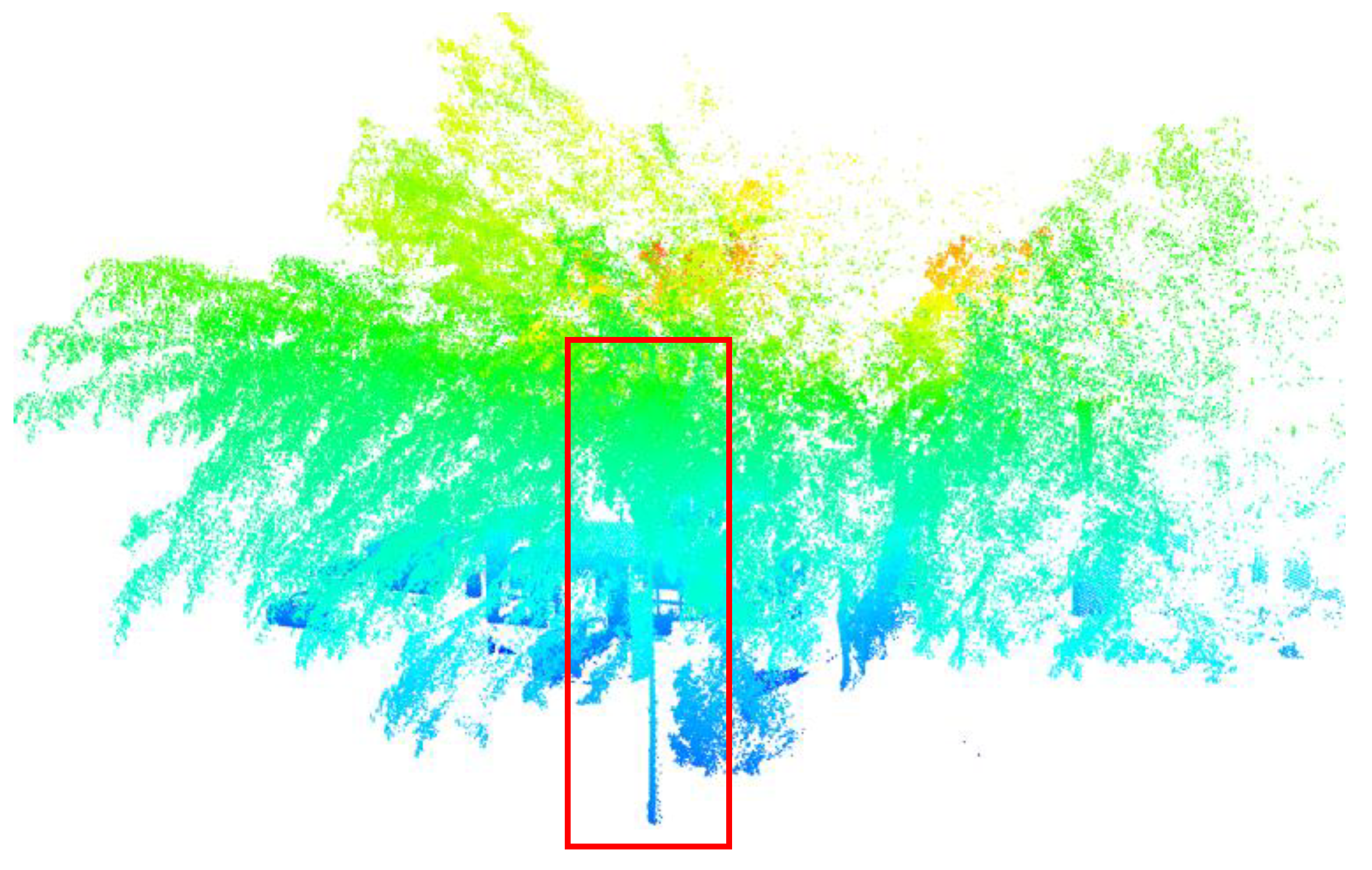
2.3.3. Ground Points Filtering
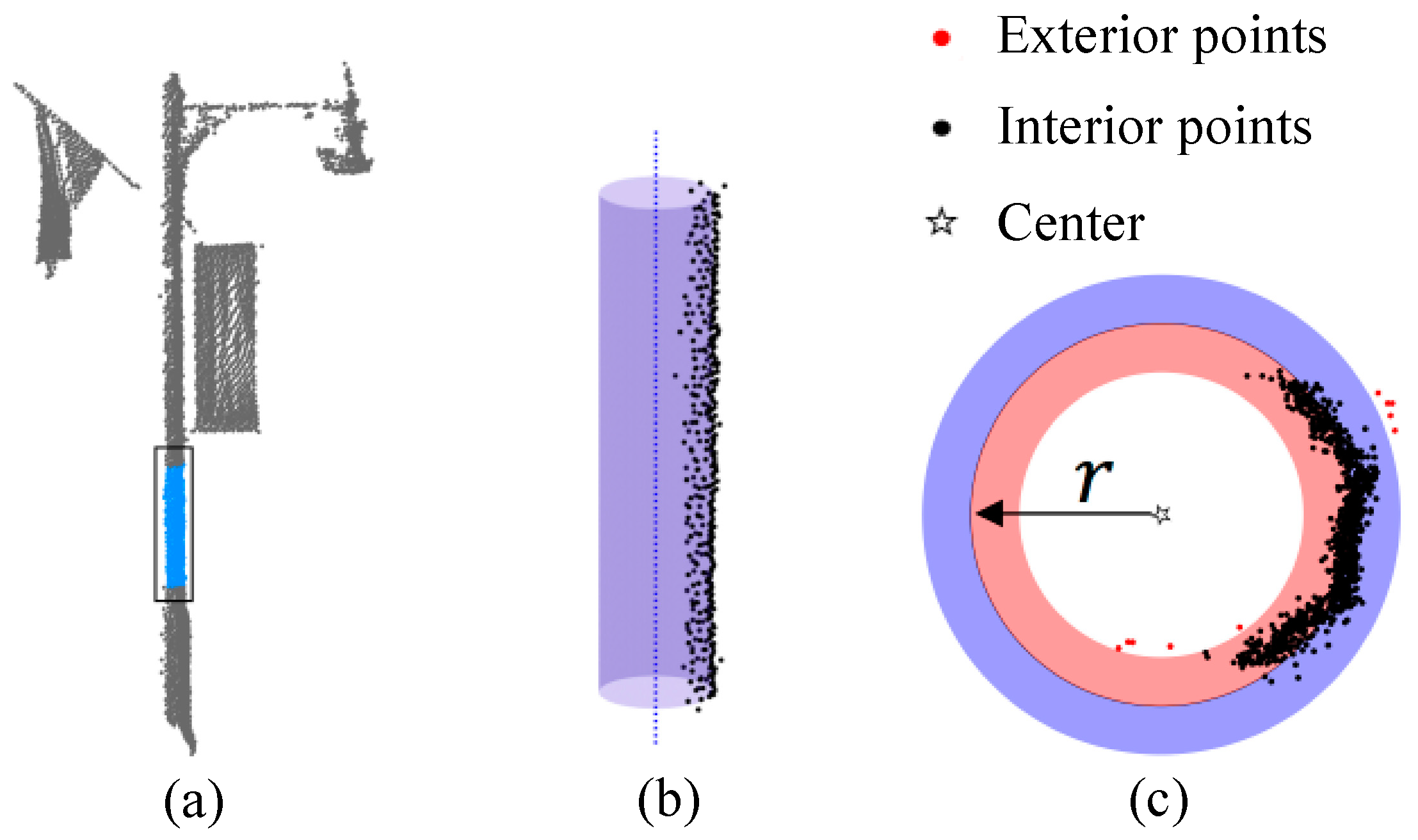
2.4. Extraction of Pole-Like Object
2.5. Classification
3. Results
3.1. Parameters Setting
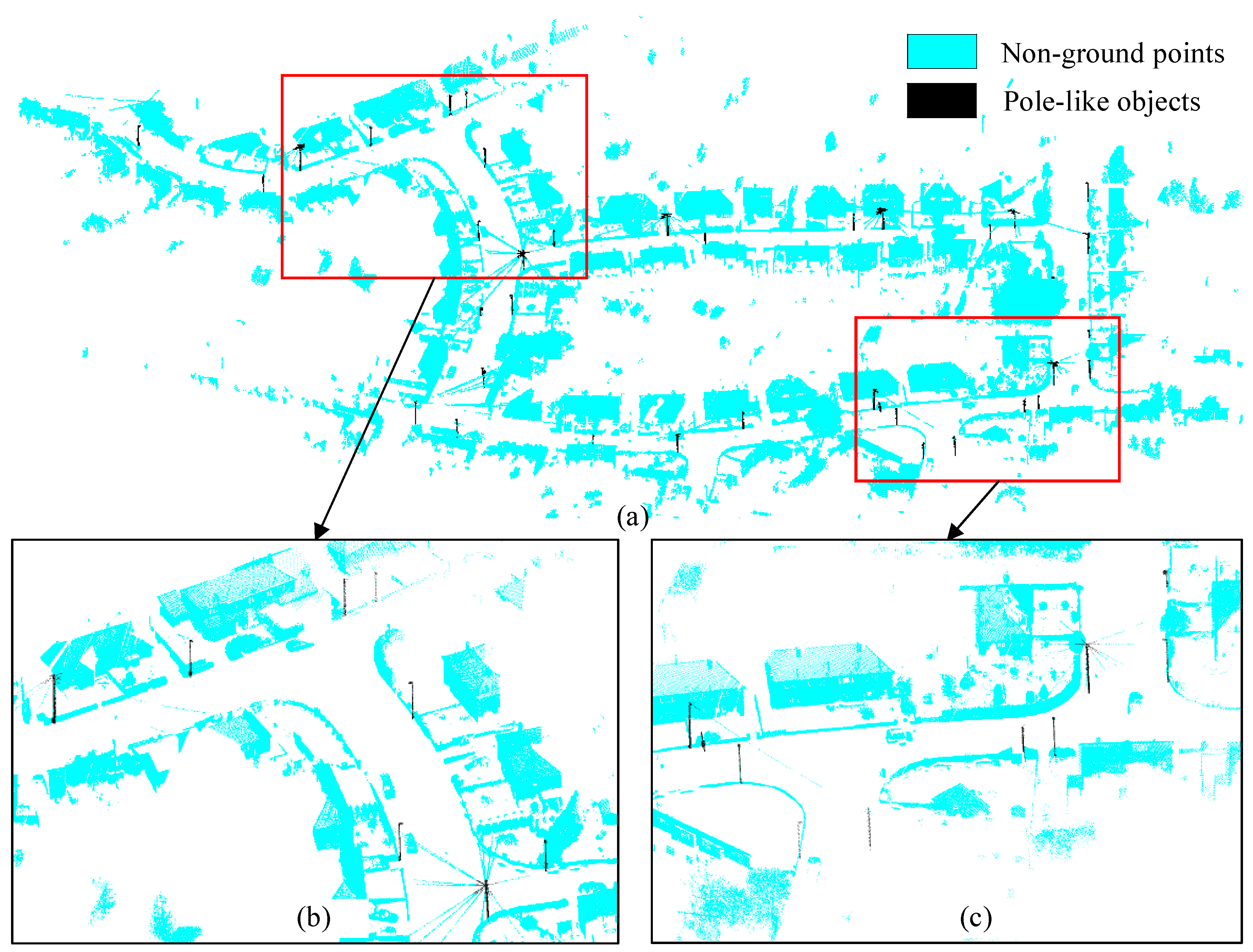
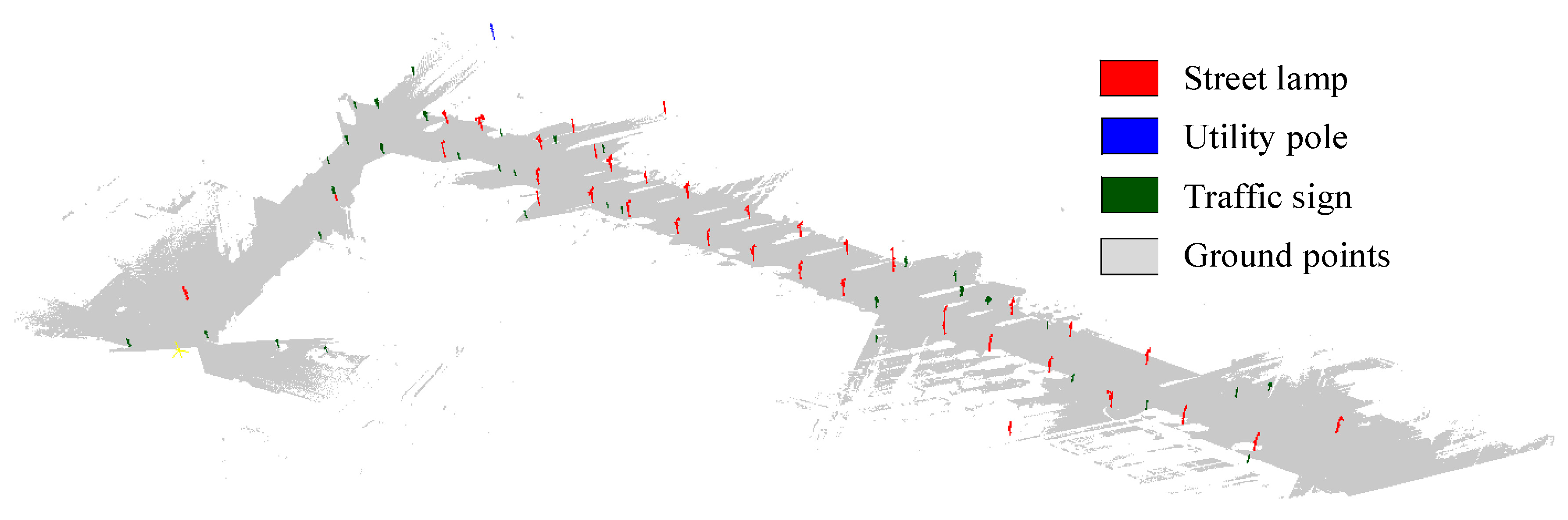
3.2. Recognition Result
3.3. Computational Complexity
4. Discussion
4.1. Sensitivity Analysis
4.2. Pole-Like Object Recognition
4.3. Comparison with Previous Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pu, S.; Rutzinger, M.; Vosselman, G.; Oude Elberink, S. Recognizing basic structures from mobile laser scanning data for road inventory studies. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, S28–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtomäki, M.; Jaakkola, A.; Hyyppä, J.; Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H. Detection of Vertical Pole-Like Objects in a Road Environment Using Vehicle-Based Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 641–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakkola, A.; Hyyppä, J.; Hyyppä, H.; Kukko, A. Retrieval Algorithms for Road Surface Modelling Using Laser-Based Mobile Mapping. Sensors 2008, 8, 5238–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Oude Elberink, S. Optimizing detection of road furniture (pole-like object) in Mobile Laser Scanner data. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, 1, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtomäki, M.; Jaakkola, A.; Hyyppä, J.; Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H. Performance Analysis of a Pole and Tree Trunk Detection Method for Mobile Laser Scanning Data. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Calgary 2011 Workshop, Calgary, AB, Canada, 29–31 August 2011; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Aijazi, A.; Checchin, P.; Trassoudaine, L. Segmentation Based Classification of 3D Urban Point Clouds: A Super-Voxel Based Approach with Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1624–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y. A Density-Based Clustering Method for Urban Scene Mobile Laser Scanning Data Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Halawany, S.I.; Lichti, D.D. Detecting road poles from mobile terrestrial laser scanning data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 704–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H.; Hyyppä, J.; Chen, Y. Multiplatform Mobile Laser Scanning: Usability and Performance. Sensors 2012, 12, 11712–11733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Li, D. A method based on an adaptive radius cylinder model for detecting pole-like objects in mobile laser scanning data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 7, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Tan, F.T.; Wang, R.S. Pole-Like Object Extraction from Mobile Lidar Data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Lohani, B.; Singh, A.K.; Husain, A. Identification of pole-like structures from mobile lidar data of complex road environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 4748–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Singh, A.K.; Lohani, B. Extraction of road surface from mobile LiDAR data of complex road environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 4655–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ji, R.; Wen, C.; Weng, S.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Road traffic sign detection and classification from mobile LiDAR point clouds. In Proceedings of the 2nd ISPRS International Conference on Computer Vision in Remote Sensing (CVRS 2015), Xiamen, China, 28–30 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.T.; Li, J.; Guan, H.Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, J. Semiautomated Extraction of Street Light Poles From Mobile LiDAR Point-Clouds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Husain, A.; Singh, A.K.; Lohani, B. Pole-Shaped Object Detection Using Mobile Lidar Data in Rural Road Environments. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 3, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabo, C.; Ordoñez, C.; García-Cortés, S.; Martínez, J. An algorithm for automatic detection of pole-like street furniture objects from Mobile Laser Scanner point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 87, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.H.; Suter, D. 3D terrestrial LIDAR classifications with super-voxels and multi-scale Conditional Random Fields. Comput. Aided Des. 2009, 41, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wen, C.L.; Guo, Y.L.; Wang, J.J.; Yu, Y.T.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Rapid Localization and Extraction of Street Light Poles in Mobile LiDAR Point Clouds: A Supervoxel-Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, T.; Van Den Heuvel, F. Efficient hough transform for automatic detection of cylinders in point clouds. In Proceedings of the Workshop “Laser Scanning 2005”, Enschede, The Netherlands, 12–14 September 2005; pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, J.; Kusevic, K.; Mrstik, P.; Harrap, R.; Greenspan, M. Urban Scene Extraction from Mobile Ground Based LiDAR Data. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on 3D Data Processing, Visualization and Transmission, Paris, France, 17–20 May 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, J.; Guo, L. A Novel Approach to Extracting Street Lamps from Vehicle-borne Laser Data. In Proceedings of the 2011 19th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Shanghai, China, 24–26 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Tan, J.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C. Detection and classification of pole-like road objects from mobile LiDAR data in motorway environment. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 97, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Cuenca, B.; García-Cortés, S.; Ordóñez, C.; Alonso, M. Automatic Detection and Classification of Pole-Like Objects in Urban Point Cloud Data Using an Anomaly Detection Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12680–12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, I.S.; Yu, X. Adaptive multiple-band CFAR detection of an optical pattern with unknown spectral distribution. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1990, 38, 1760–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, P. Pole-Like Road Object Detection in Mobile LiDAR Data via Supervoxel and Bag-of-Contextual-Visual-Words Representation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, R.S.; Xu, S. Recognizing Street Lighting Poles From Mobile LiDAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, F.; Omasa, K. Voxel-Based 3-D Modeling of Individual Trees for Estimating Leaf Area Density Using High-Resolution Portable Scanning Lidar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3610–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yu, B.; Yue, W.; Shu, S.; Tan, W.; Hu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, H. A Voxel-Based Method for Automated Identification and Morphological Parameters Estimation of Individual Street Trees from Mobile Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 584–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lindenbergh, R.; Menenti, M. SigVox—A 3D feature matching algorithm for automatic street object recognition in mobile laser scanning point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, H.-Y. Effects of scanning orientation on outlier formation in 3D laser scanning of reflective surfaces. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 81, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoodeh, S. Outlier detection in laser scanner point clouds. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2006, 36, 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero-Huerta, M.; Lindenbergh, R.; Rodriguez-Gonzalvez, P. Automatic tree parameter extraction by a Mobile LiDAR System in an urban context. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0196004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, R.B.; Marton, Z.C.; Blodow, N.; Dolha, M.; Beetz, M. Towards 3D Point cloud based object maps for household environments. Robot. Autom. Syst. 2008, 56, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackel, T.; Wegner, J.D.; Schindler, K. Fast Semantic Segmentation of 3d Point Clouds with Strongly Varying Density. In Proceedings of the 2016 ISPRS Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–19 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, T.A.; Chiu, C.M. Pole-Like Road Object Detection From Mobile Lidar System Using a Coarse-to-Fine Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4805–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zai, D.W.; Zhang, S.X.; Li, J. Exploiting Location Information to Detect Light Pole in Mobile Lidar Point Clouds. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Q.; Chen, S.C.; Whitman, D.; Shyu, M.L.; Yan, J.H.; Zhang, C.C. A progressive morphological filter for removing nonground measurements from airborne LIDAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosselman, G. Slope based filtering of laser altimetry data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2000, 33, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.M.; Qi, J.B.; Wan, P.; Wang, H.T.; Xie, D.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Yan, G.J. An Easy-to-Use Airborne LiDAR Data Filtering Method Based on Cloth Simulation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random Sample Consensus—A Paradigm for Model-Fitting with Applications to Image-Analysis and Automated Cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Wang, B.Q.; Li, Z.; Jia, F.M. An Optimized BaySAC Algorithm for Efficient Fitting of Primitives in Point Clouds. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Zhong, R.; Wu, A.; Shi, Z.; Luo, Z. An Efficient Planar Feature Fitting Method Using Point Cloud Simplification and Threshold-Independent BaySAC. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1842–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; Thoennessen, U. Extraction of Lines From Laser Point Clouds. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2006, 36, 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, H.; Date, H.; Kanai, S.; Takeda, H. Pole-Like Objects Recognition from Mobile Laser Scanning Data Using Smoothing and Principal Component Analysis. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2011, 38, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wu, G.; Ye, X.; Huang, L.; Lei, J. A Novel Method to Reconstruct Overhead High-Voltage Power Lines Using Cable Inspection Robot LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hyyppa, J.; Jaakkola, A. Mini-UAV-Borne LIDAR for Fine-Scale Mapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, D.; Ichim, A.E.; Tombari, F.; Rusu, R.B.; Behnke, S. Registration with the Point Cloud Library a Modular Framework for Aligning in 3-D. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2015, 22, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. A Method for Registration of 3-D Shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.Y.; Morsy, S.; Shaker, A.; Tulloch, M. Automatic extraction of highway light poles and towers from mobile LiDAR data. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 77, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





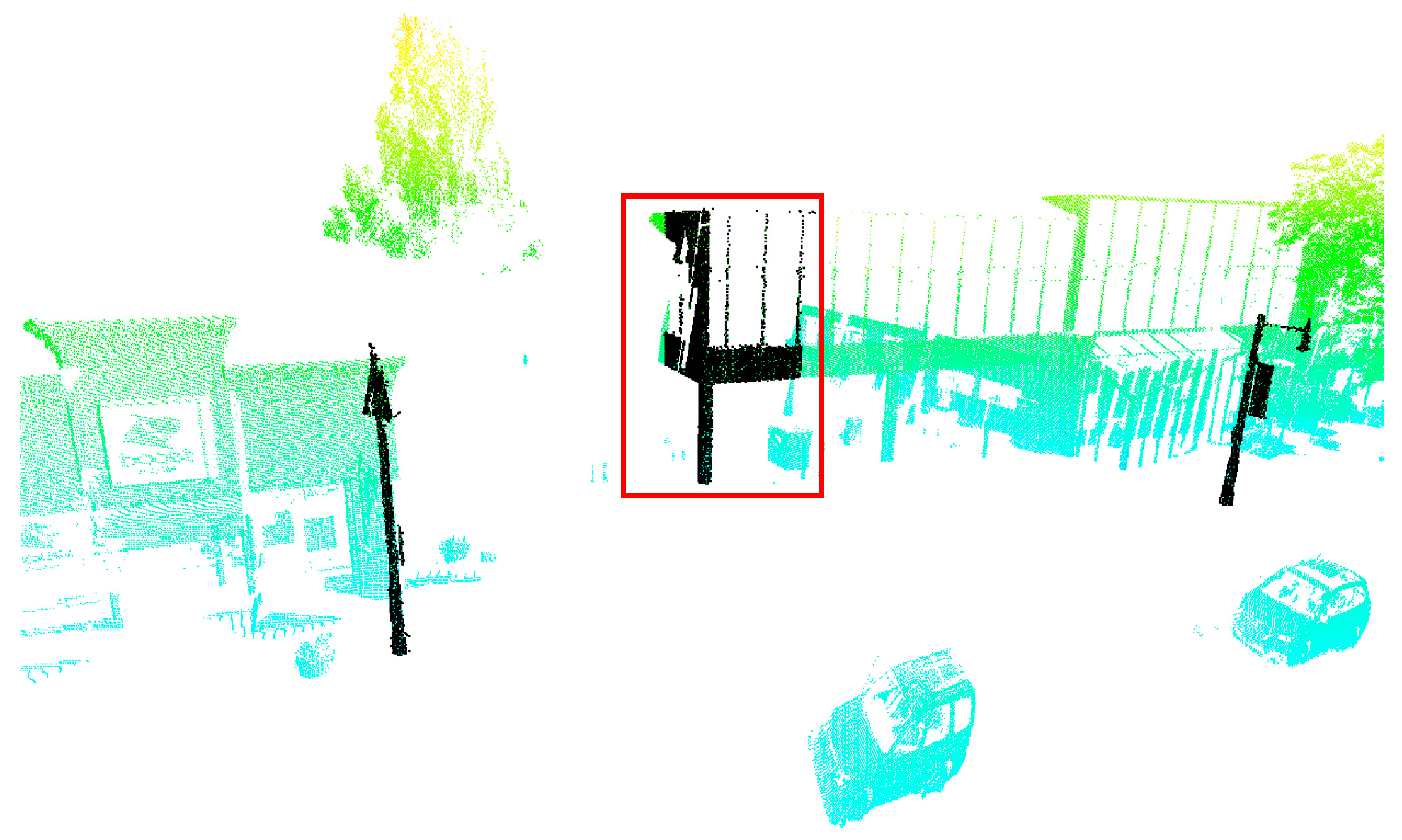

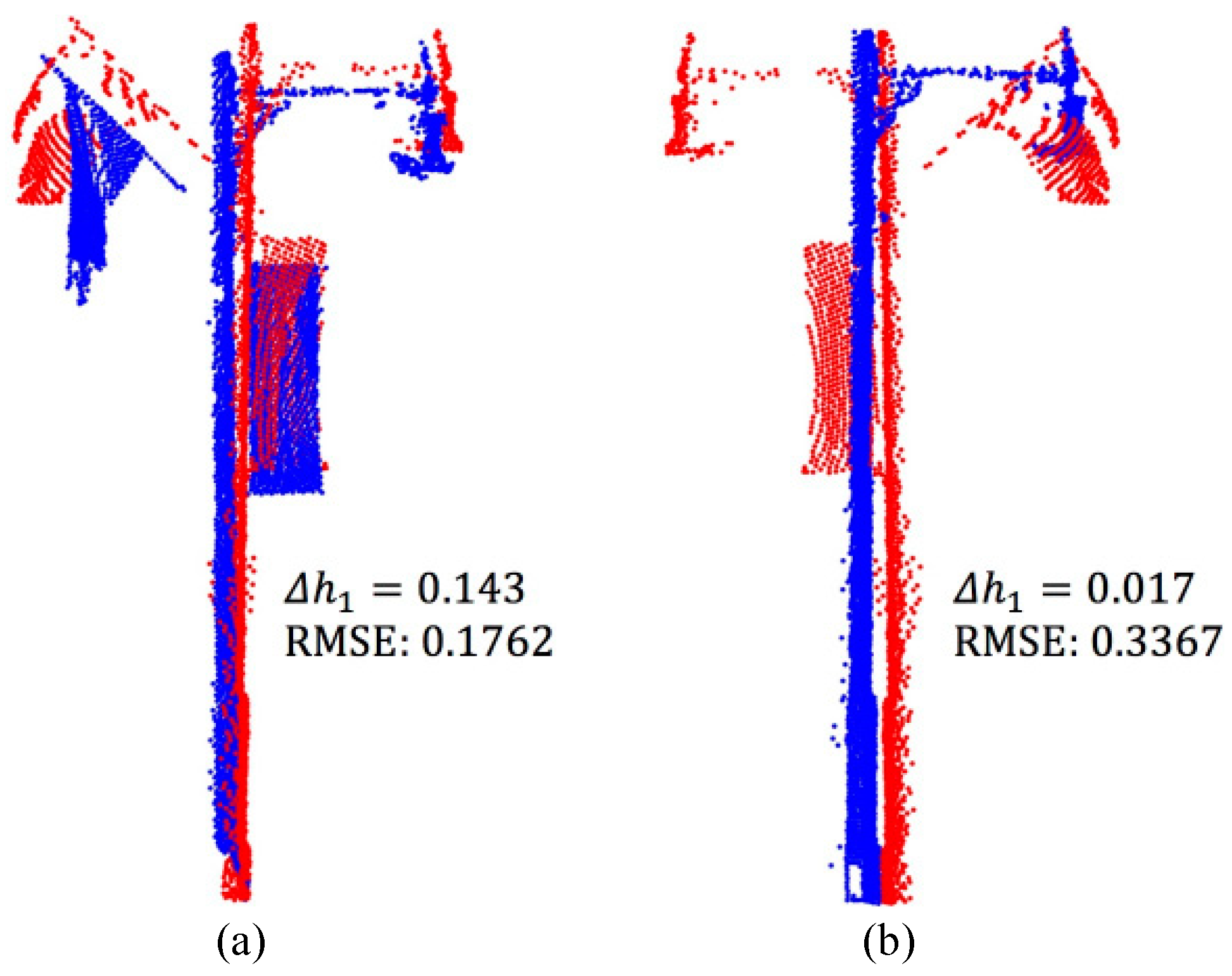
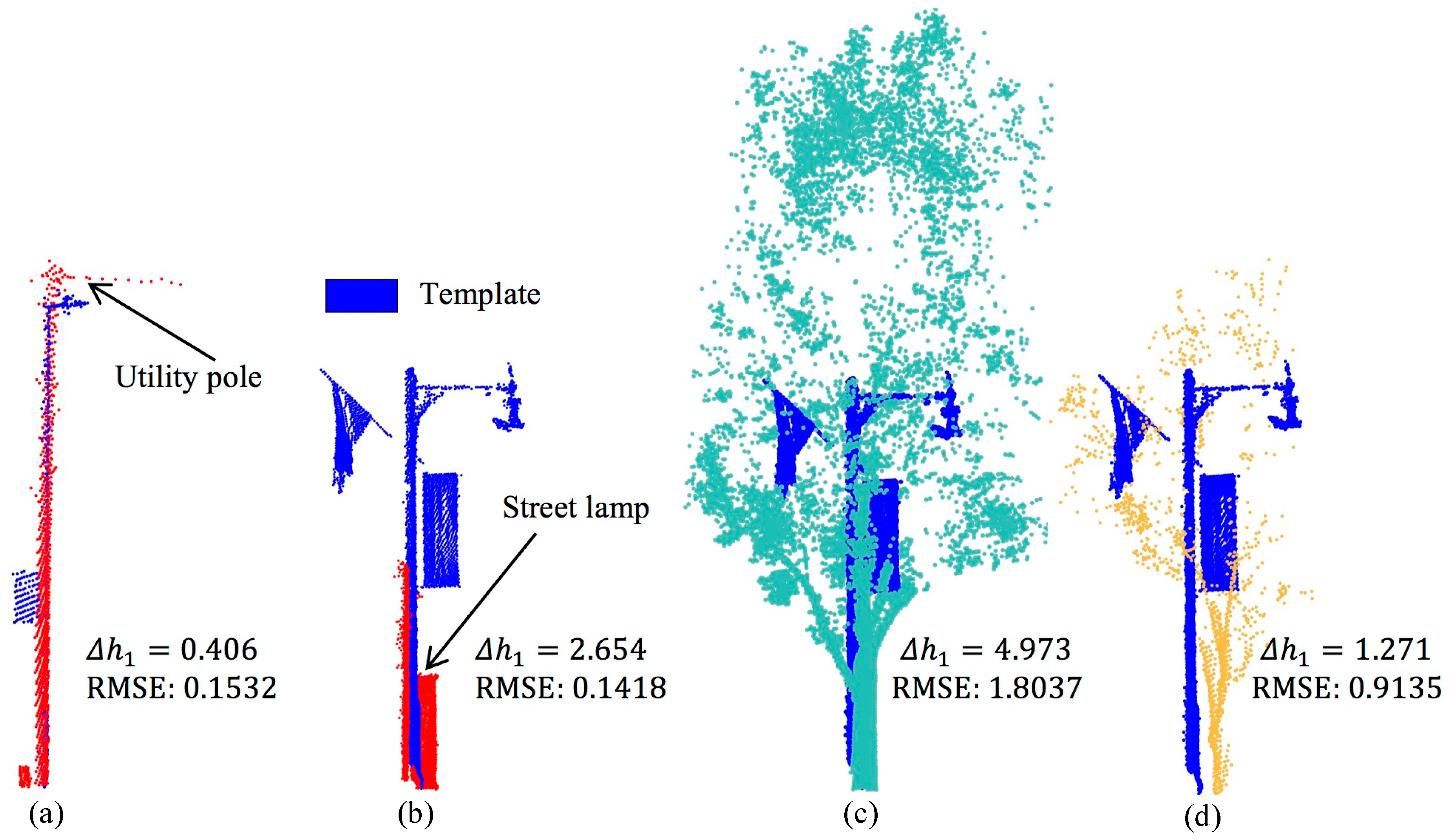
| Data | Original Points | Removed Points | Non-Ground Points | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data I | 8,139,726 | 733 | 1,703,153 (20.9%) | 2,202,120 (27%) |
| Data II | 35,527,813 | 4183 | 11,112,865 (31.3%) | 7,795,873 (21.9%) |
| Classification Features | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | The street lamp with high point density and clear shape in the raw point cloud. | |
| The unclassified poles are used as input data for the classification process. | ||
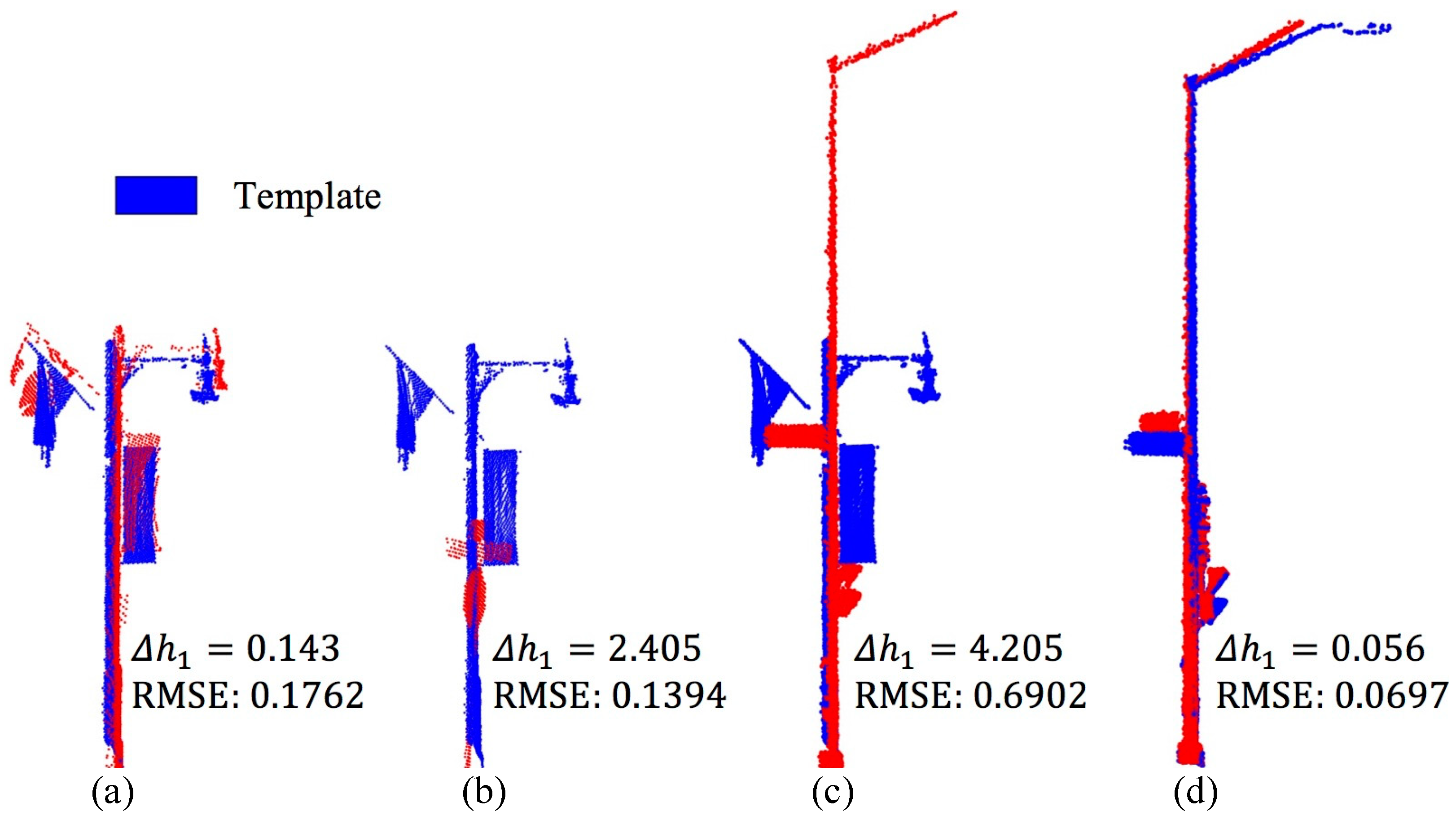
| RMSE | RMSE is used to judge whether the 3D shape matching is successful. If RMSE is greater than , will be classified as others. | |
| If the RMSE value is between and , falls in the utility pole category. If the RMSE is less than or equal to , the category of needs to be further judged based on the height feature. | ||
| Height | If is less than or equal to , belongs to the category street lamp. | |
| If is greater than , then can be classified to be category traffic signal, otherwise it is a utility pole. and denote different levels of height difference between and , . | ||
| Data | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data I | 0.80 | 0.15 | 1.5 | 3.00 | 3.6 |
| Data II | 0.80 | 0.20 | 1.0 | 1.50 | 3.6 |
| Data | TP | FP | FN | Completeness | Correctness | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data I | 38 | 1 | 3 | 92.7% | 97.4% | 90.5% |
| Data II | 67 | 2 | 7 | 90.5% | 97.1% | 88.2% |
| Data | Street Lamp | Utility Pole | Traffic Sign | Others | Precision (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data I | Street lamp | 22 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 91.7 |
| Utility pole | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 100.0 | |
| Traffic sign | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 80.0 | |
| OA: 36/39 = 92.3% | ||||||
| Data II | Street lamp | 35 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 92.1 |
| Utility pole | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 50.0 | |
| Traffic sign | 0 | 0 | 27 | 2 | 93.1 | |
| OA: 63/69 = 91.3% | ||||||
| Data | Preprocessing | 2nd Voxelization | Independence Analysis | Features Detection | PLOs Classification | Total Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data I | 126.3 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 41.6 | 139.5 | 309.6 |
| Data II | 381.4 | 1.1 | 15.7 | 237.5 | 813.6 | 1449.3 |
| Data | Objects | Poles | Topography | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (m) | Height (m) | Maximum Gradient | ||
| Data I | Houses, poles, trees, lawn, people, vehicles | 0.23, 0.27,0.13 | 6.32, 7.42, 2.70 | 2.2% |
| Data II | Buildings, poles, trees, people, vehicles | 0.21, 0.35, 0.08 | 5.75, 11.83, 3.07 | 3.0% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Kang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W. Automatic Recognition of Pole-Like Objects from Mobile Laser Scanning Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121891
Shi Z, Kang Z, Lin Y, Liu Y, Chen W. Automatic Recognition of Pole-Like Objects from Mobile Laser Scanning Point Clouds. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(12):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121891
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhenwei, Zhizhong Kang, Yi Lin, Yu Liu, and Wei Chen. 2018. "Automatic Recognition of Pole-Like Objects from Mobile Laser Scanning Point Clouds" Remote Sensing 10, no. 12: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121891
APA StyleShi, Z., Kang, Z., Lin, Y., Liu, Y., & Chen, W. (2018). Automatic Recognition of Pole-Like Objects from Mobile Laser Scanning Point Clouds. Remote Sensing, 10(12), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121891