Surface Deformation Monitoring in Zhengzhou City from 2014 to 2016 Using Time-Series InSAR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Dataset
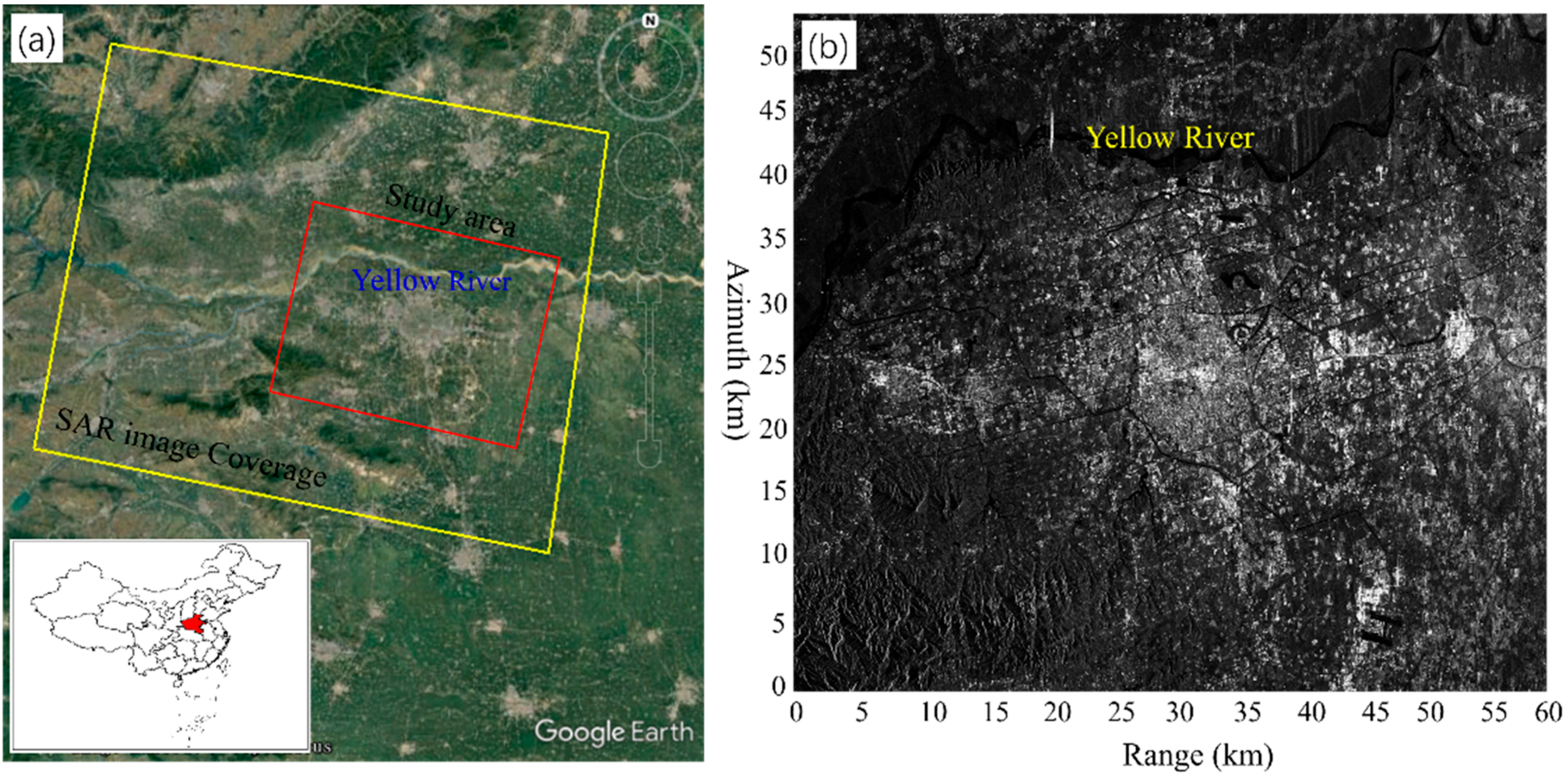
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
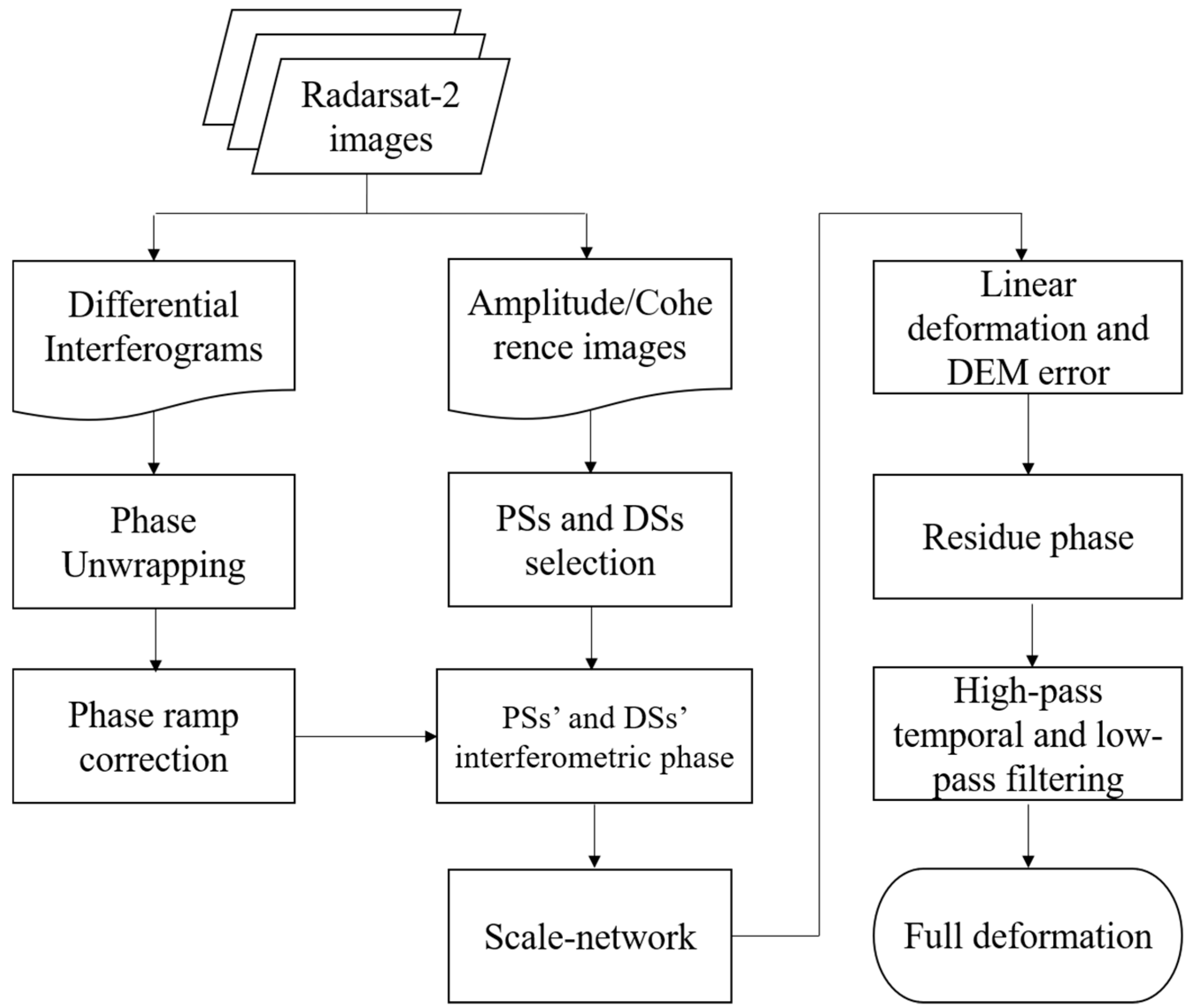
3. Methodology
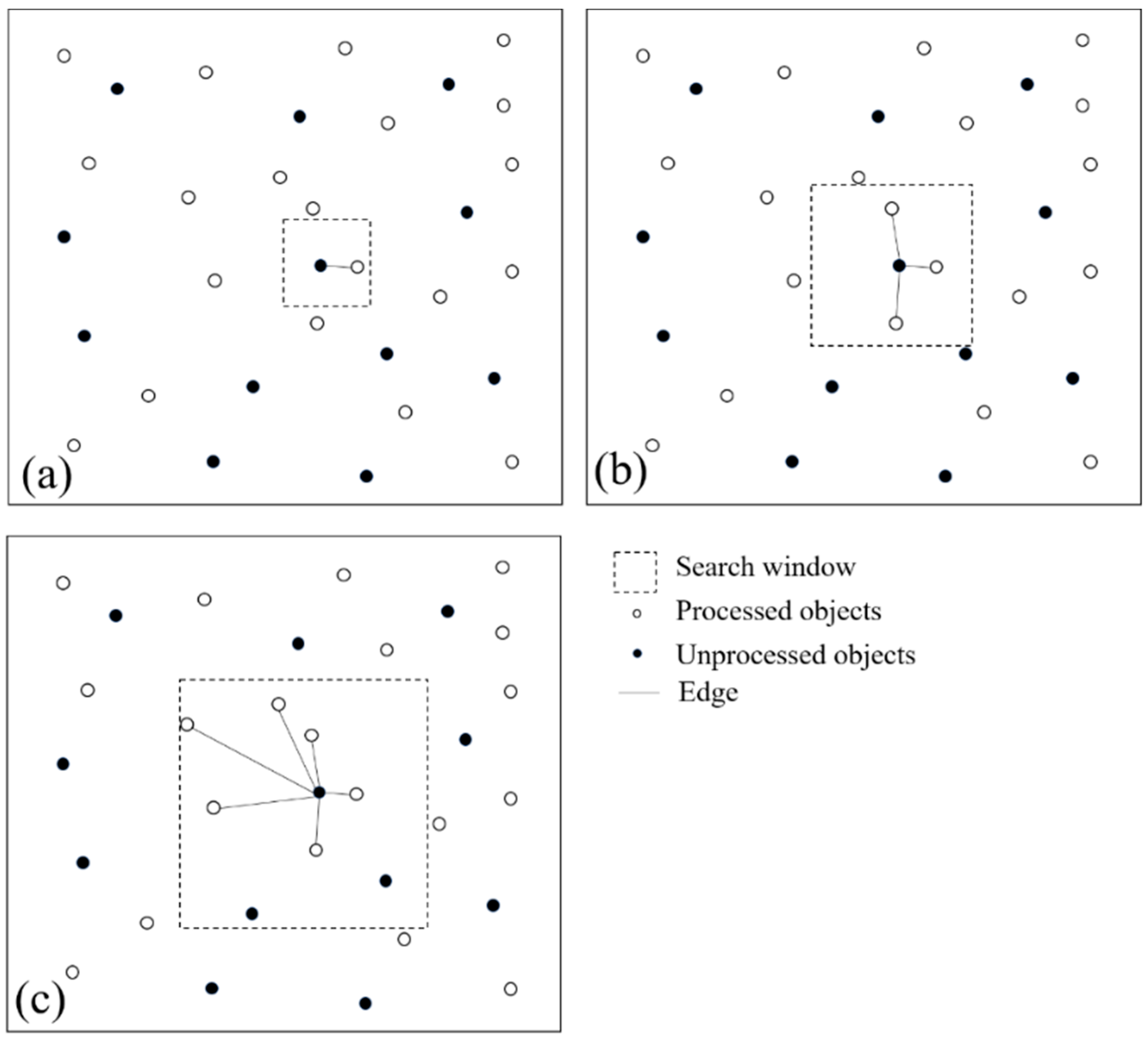
3.1. PSs and DSs Selections
3.2. Correction for Phase Ramps
3.3. Deformation Estimation on PSs and DSs
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Phase Ramps Correction
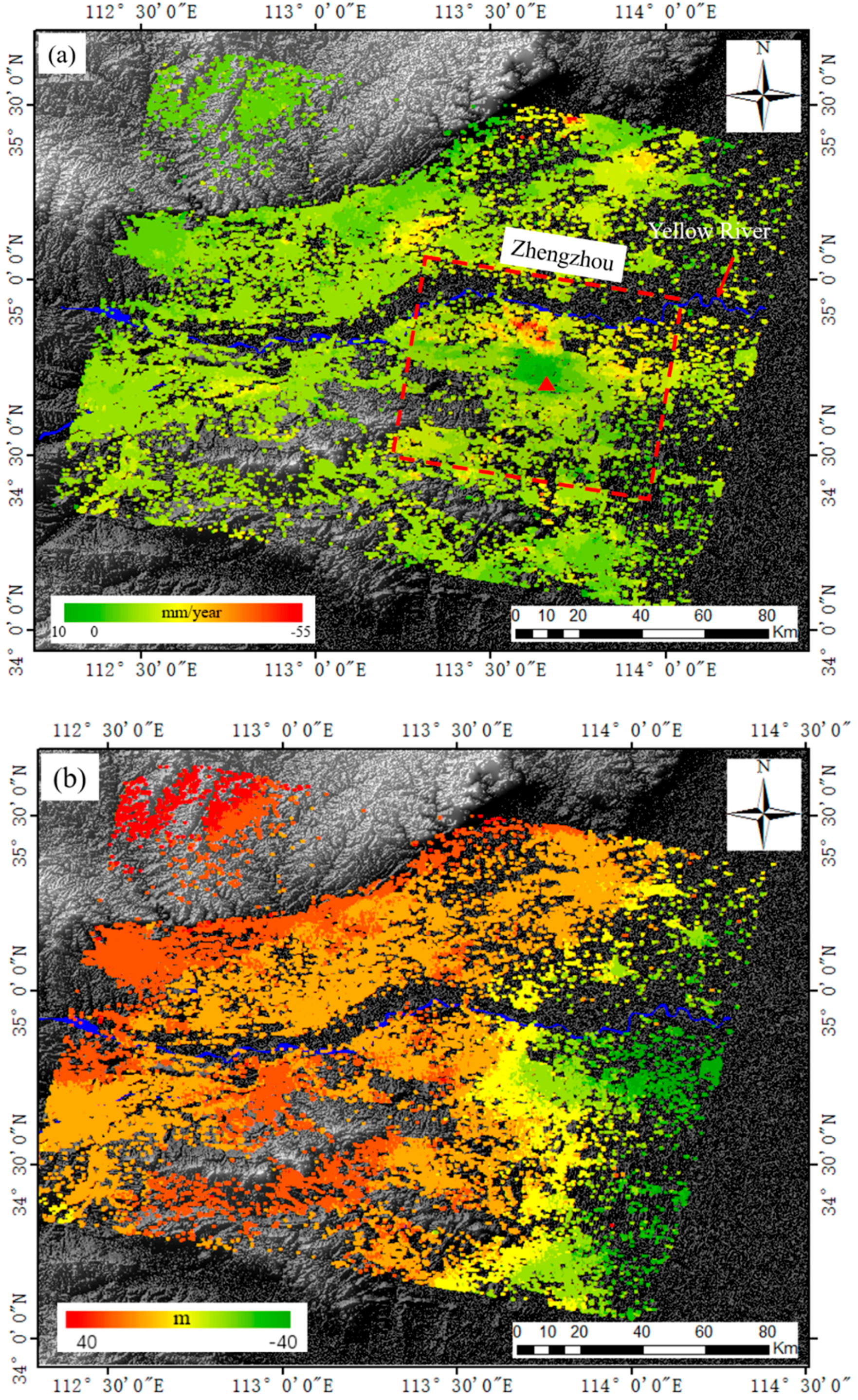
4.2. Time-Series InSAR Results
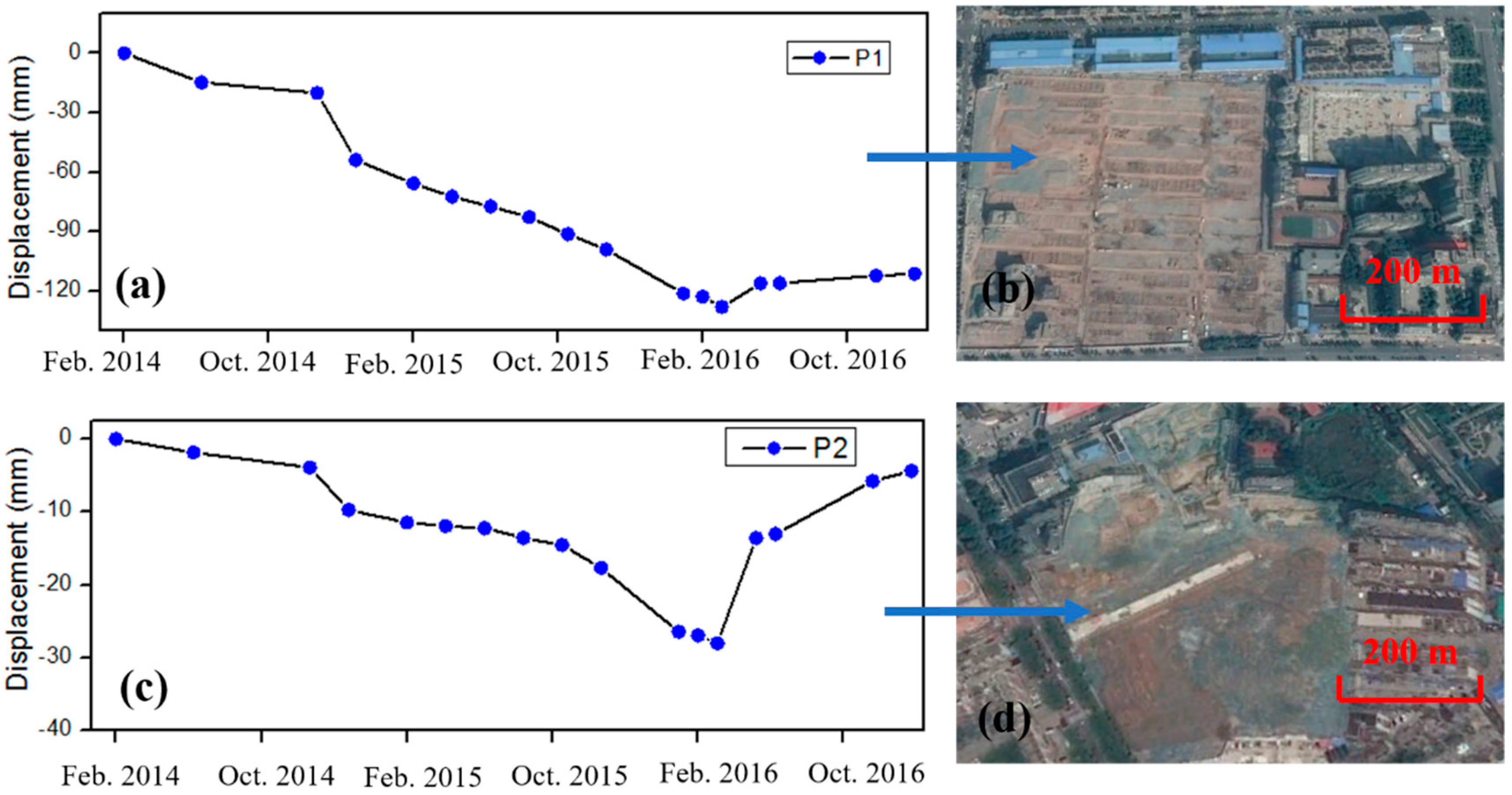
4.3. Validation
5. Discussion
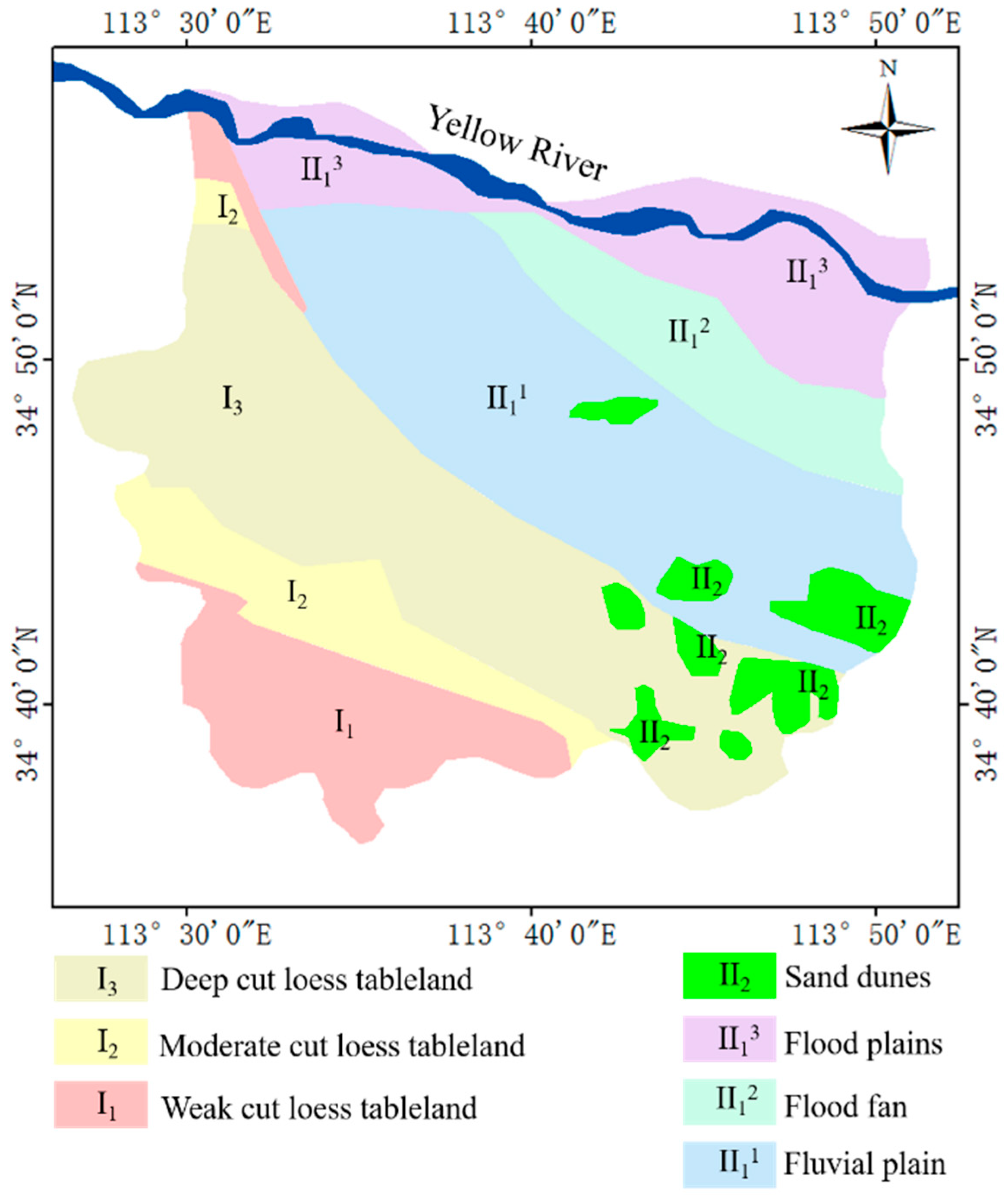
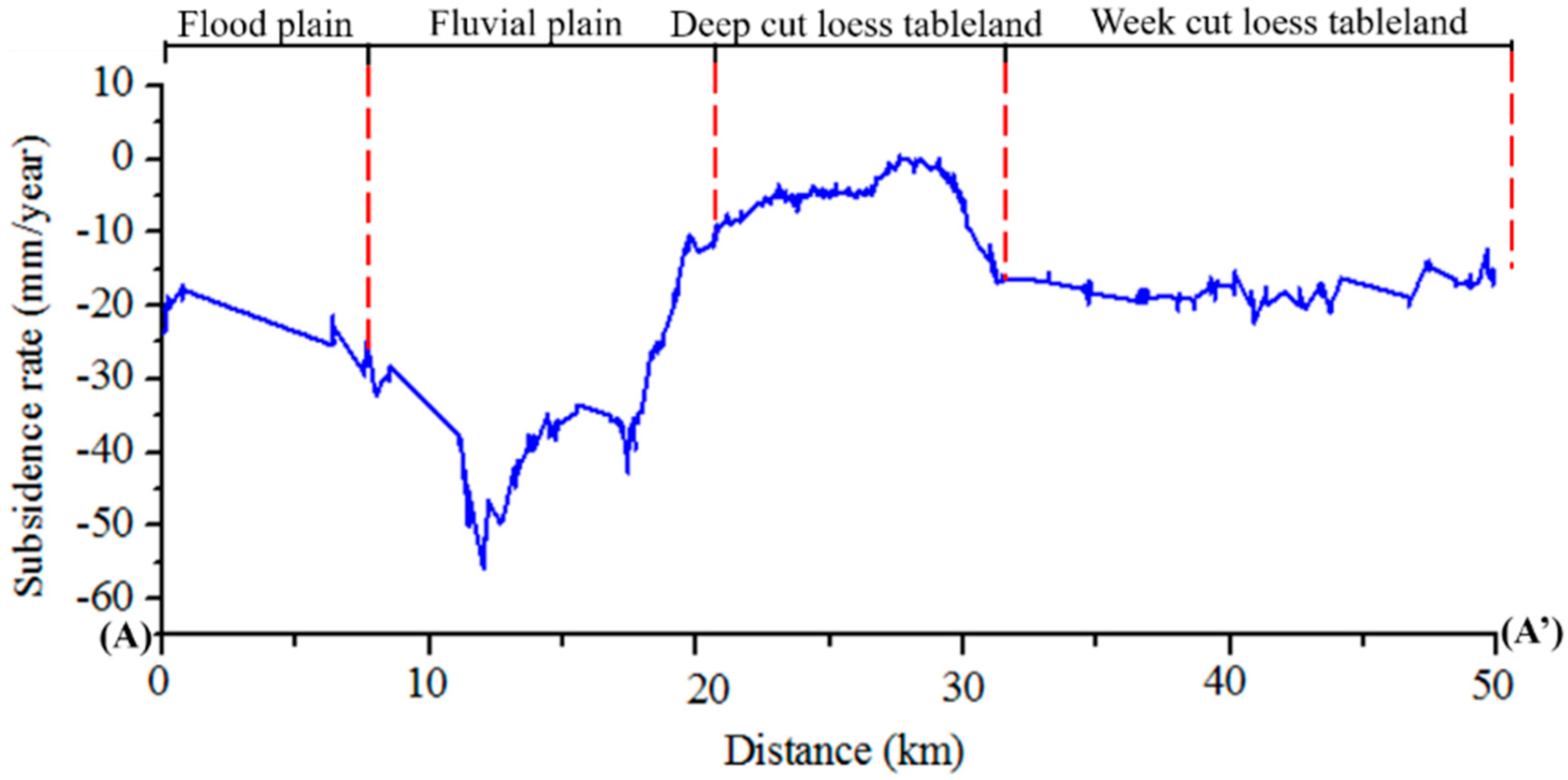
5.1. Geology and Subsidence
5.2. Urban Expansion and Subsidence
5.3. Ground Water and Subsidence
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The ground displacement in our study area could be retrieved by the proposed method combining PSs and DSs. A dense ground-surface deformation map of Zhengzhou city has been obtained, which could enhance the identification of the deformation area.
- (2)
- Clear ground subsidence has been detected in Zhengzhou city, with the maximum subsidence rate of −55 mm/year. Ground motion in Zhengzhou city is remarkable uneven, and two significant subsidence areas are detected in Zhengzhou. Most of the deforming areas are located in the north and northeast of Zhengzhou city.
- (3)
- The distribution of deformation is highly consistent with the geomorphologic type in Zhengzhou city, with maximum subsidence detected in fluvial plain area. The ground subsidence of Zhengzhou city is also correlated to urban expansion and ground water exploitation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ao, M.; Wang, C.; Xie, R.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Du, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Kuang, C. Monitoring the land subsidence with persistent scatterer interferometry in Nansha District, Guangdong, China. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2947–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W. Monitoring land subsidence in the southern part of the lower Liaohe plain, China with a multi-track PS-InSAR technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, J. Subsidence prediction and susceptibility zonation for collapse above goaf with thick alluvial cover: A case study of the Yongcheng coalfield, Henan Province, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2016, 75, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Li, J.; Gao, M.; Zhu, F.; Chen, W.; Liang, Y. InSAR Time-Series Analysis of Land Subsidence under Different Land Use Types in the Eastern Beijing Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.L.; Liang, X.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, Q.Y. Experience of capturing flood water for artificial recharge of groundwater in North China. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Management of Aquifer Recharge, Berlin, Germany, 11–16 June 2005; IHP-VI, Series on Groundwater No. 13. Unesco: Paris, France, 2005; pp. 727–732. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Jin, M.; Giordano, M.; Villholth, K.G. Urban and rural groundwater use in Zhengzhou, China: Challenges in joint management. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Jiao, J.J. Groundwater-derived land subsidence in the North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Guo, G. Characterizing land displacement in complex hydrogeological and geological settings: A case study in the Beijing Plain, China. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Huang, H.J.; Bi, H.B. Land subsidence in the modern Yellow River Delta based on InSAR time series analysis. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xu, J.; Ma, R.; Wang, F. Characteristics and mechanism of the Longyao ground fissure on North China Plain, China. Eng. Geol. 2016, 214, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.L.; Lu, C.H. Evaluation and trend analysis of surface water quality in Zhengzhou in 1998–2008. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 10, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.C.; Li, F.F.; Fan, D. Application of PS-InSAR technique in land subsidence investigation of Zhengzhou. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2013, 38, 43–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Setan, H.; Singh, R. Deformation analysis of a geodetic monitoring network. Geomatica 2001, 55, 333–346. [Google Scholar]
- Taşçi, L. Dam deformation measurements with GPS. Geodezijair Kartografija 2008, 34, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, N.; LeBlanc, A.M.; Sladen, W.; Oldenborger, G.; Mathon-Dufour, V.; Brisco, B. RADARSAT-2 D-InSAR for ground displacement in permafrost terrain, validation from Iqaluit Airport, Baffin Island, Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Rosen, P.A.; Goldstein, R.M.; Gabriel, A.; Werner, C.L. On the derivation of coseismic displacement fields using differential radar interferometry: The Landers earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 19617–19634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Sanchez, P.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Duque, S.; Monells, D. The coherent pixels technique (CPT): An advanced DInSAR technique for nonlinear deformation monitoring. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2008, 165, 1167–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Broquetas, A. Linear and nonlinear terrain deformation maps from a reduced set of interferometric SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.M.; Li, X.; Abidin, H.Z.; Gumilar, I. Land subsidence characteristics of Bandung Basin as revealed by ENVISAT ASAR and ALOS PALSAR interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.J.; Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Qiu, G. InSAR reveals coastal subsidence in the Pearl River Delta, China. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Peng, J.H. Monitoring urban subsidence with multi-master radar interferometry based on coherent targets. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2015, 43, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Retrieval of phase history parameters from distributed scatterers in urban areas using very high resolution SAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Tang, Y.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, H. Subsidence monitoring in coal area using time-series InSAR combining persistent scatterers and distributed scatterers. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 39, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, T. Repeat-pass SAR interferometry with partially coherent targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Ding, X.; Jung, H.S.; Feng, G.; Lee, C.W. Mapping ground surface deformation using temporarily coherent point SAR interferometry: Application to Los Angeles Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Q.; Liu, W.B.; Li, Z.M. Land subsidence survey and monitoring in the North China Plain. Geol. J. China Univ. 2006, 12, 195–209. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-Filled Seamless SRTM Data V4. International Centre for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT). 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi. cgiar.org (accessed on 30 October 2018).
- Wu, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.X.; Tian, L. Deformation retrieval in large areas based on multibaseline DInSAR algorithm: A case study in Cangzhou, northern China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3633–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Fan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Jia, M.; Tong, L.; Lu, Y. Flat earth removal and baseline estimation based on orbit parameters using Radarsat-2 image. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS’2013, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X.L.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J. Slope deformation prior to Zhouqu, China landslide from InSAR time series analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.; England, P.C.; Fielding, E.J. InSAR observations of low slip rates on the major faults of western Tibet. Science 2004, 305, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Lu, Z.; Jung, H.S.; Hu, J.; Feng, G. A novel multitemporal InSAR model for joint estimation of deformation rates and orbital errors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3529–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Q. Analysis of ground subsidence at a coal-mining area in Huainan using time-series InSAR. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 5790–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Peng, J.H.; Wang, B.C.; Song, Y.Z.; Zhang, D.X.; Li, L. Ground deformation monitoring of Zhengzhou city from 2012 to 2013 using an improved IPTA. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.C.; Wu, G.X. Study on the spatial expansion and optimization of Zhengzhou City base on GIS. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Water Resource and Environmental Protection (ISWREP), Xi’an, China, 20–22 May 2011; Volume 4, pp. 2871–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z. Ground subsidence geo-hazards induced by rapid urbanization: Implications from InSAR observation and geological analysis. Nat. Hazard Earth Syst. 2012, 12, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. Typical Soil Body Deformation Characteristic and Land Subsidence Prediction in Zhengzhou Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
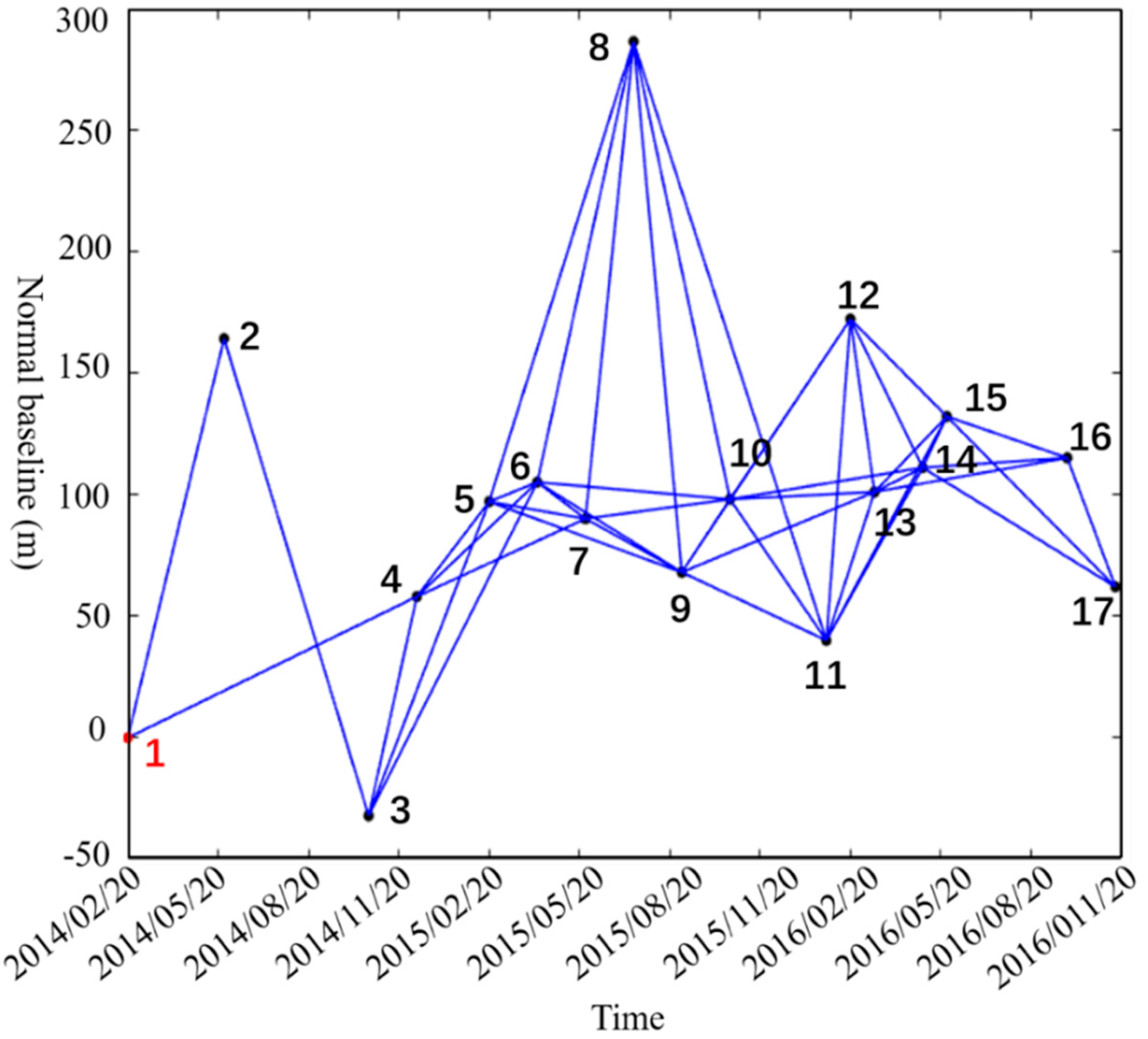






| ID | Acquisition Time | Normal Baseline (m) | Temporal Baseline (Day) | ID | Acquisition Time | Normal Baseline (m) | Temporal Baseline (Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 February 2014 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 13 October 2015 | 98 | 600 |
| 2 | 27 May 2014 | 164 | 96 | 11 | 17 January 2016 | 40 | 696 |
| 3 | 10 October 2014 | −32 | 240 | 12 | 10 February 2016 | 172 | 720 |
| 4 | 5 December 2014 | 58 | 288 | 13 | 5 March 2016 | 101 | 744 |
| 5 | 15 February 2015 | 97 | 360 | 14 | 22 April 2016 | 111 | 792 |
| 6 | 4 April 2015 | 105 | 408 | 15 | 16 May 2016 | 132 | 816 |
| 7 | 22 May 2015 | 90 | 456 | 16 | 13 September 2016 | 115 | 936 |
| 8 | 9 July 2015 | 286 | 504 | 17 | 31 October 2016 | 62 | 984 |
| 9 | 26 August 2015 | 68 | 552 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Surface Deformation Monitoring in Zhengzhou City from 2014 to 2016 Using Time-Series InSAR. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111731
Zhang Z, Wang C, Wang M, Wang Z, Zhang H. Surface Deformation Monitoring in Zhengzhou City from 2014 to 2016 Using Time-Series InSAR. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(11):1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111731
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhengjia, Chao Wang, Mengmeng Wang, Ziwei Wang, and Hong Zhang. 2018. "Surface Deformation Monitoring in Zhengzhou City from 2014 to 2016 Using Time-Series InSAR" Remote Sensing 10, no. 11: 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111731
APA StyleZhang, Z., Wang, C., Wang, M., Wang, Z., & Zhang, H. (2018). Surface Deformation Monitoring in Zhengzhou City from 2014 to 2016 Using Time-Series InSAR. Remote Sensing, 10(11), 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111731







