1. Introduction
As the planet becomes increasingly connected, international trade has become an ever-growing part of the world’s economy, often outstripping growth in output [
1]. An array of literature examines the links between certification (organic and Fairtrade) and this expansion of trade, sustainable production, environmental services, and social benefits for producers [
2]. In addition to global trends, trade is encouraged in the Americas through agreements such as CAFTA—the Central America Free Trade Agreement—which promotes economically, environmentally, and socially responsible trade between the United States and Central America. Cocoa (
Theobroma cacao) is one of the more promising products that could benefit small landowners and producers in Central America and has a high market demand in the United States.
Two of the earliest market-based programs for increasing the environmental, social, and perhaps economic benefits of cocoa production are certified organic production and Fairtrade, as summarized in
Table 1. Considerable literature summarizes the expected and realized environmental and social benefits of organic and Fairtrade certification [
3]. As the general public has become ever more informed about not only the origin of their goods but also the conditions under which they are produced, value-added certification systems such as these have become more popular. As such, organic and Fairtrade certifications represent two possible ways to ensure that goods align with increasingly sensitive consumer values.
Table 1.
Selected Requirements for Organic and Fairtrade Certification Systems, 2009 [
4,
5].
Table 1.
Selected Requirements for Organic and Fairtrade Certification Systems, 2009 [4,5].
| | Eligibility | Conversion Period | Social Norms | Environmental Norms | Administrative/ Economic Norms |
|---|
| Organic | Open to all | Minimum of 2 years | None | Pests, diseases and weeds controlled without the use of agrochemicals; soil quality must be actively improved through a variety of non-agrochemical methods; buffer zones; GMO prohibited | Thorough recordkeeping; yearly audits |
| Fair-trade (specific to cocoa) | Open to small producer coopera-tives only | None | Workers are paid at least minimum wage; no child or forced labor; transparent, democratic, non-discriminative administrative system; workplace is safe and sanitary; Fairtrade premium to be used for social or environmental betterment of the community | Use of agrochemicals restricted; recycling of materials where possible; formal plan for the continual improvement of environmental/ agricultural practices; planting in virgin forest prohibited; buffer zones; GMO prohibited | Thorough recordkeeping; yearly audits |
Organic certification has seen considerable commercial success, having grown from approximately $6 billion in 2000 to an estimated $25 billion industry in 2010 in the United States [
6]. A purely environmentally focused program, organic certification varies from country to country. However, there are standards meant to link and serve internationally, such as the International Federation of Organic Movements (IFOAM) and the Codex Alimentarius organic standards. Most organic standards have common areas of focus, for example the prohibition of most chemical herbicides, pesticides and fertilizers; an emphasis on active building of soil structure and microbial activity; the effective use and incorporation of organic matter into the soil; and minimization of off-farm inputs.
Fairtrade, an emblem of socially conscious consumerism, expected double-digit growth in the years between 2008 and 2012 [
7]. A program designed to empower small producers, Fairtrade requires compliance with an array of social, environmental, and economic guidelines that vary depending on the product. In general, not all producers have been eligible; in the case of cocoa, only those who were not dependent on hired labor and who are organized into small producer cooperatives may participate.
Although these programs and others like them are not without challenges and drawbacks, they provide examples of success in ethical commerce, and therefore bear further consideration in the continuing push to expand the role of environmental sustainability and social equity in trade, including in the cocoa trade. As noted in the literature review, many studies have examined cocoa production, but few have examined the supply chain and how it can contribute to enhanced trade and mutual market benefits to producers in Central America and consumers in North America. Demonstration of social and environmental benefits is increasingly important to trade, including as components of the Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA).
We examine these issues with a qualitative evaluation of the cocoa supply chain in Costa Rica based on a series of semi-structured interviews with producers, buyers, manufacturers, exporters, and other experts in conventional as well as certified chains. Specifically, we employed: (1) an in-depth analysis of the cocoa supply chain; (2) field research and interviews; and (3) recent marketing concepts in order to develop a new theory about possible opportunities for an innovative approach to marketing cocoa. We provide context with a review of cocoa production and the chocolate industry; a summary of the cocoa supply chain; and details of the Costa Rican cocoa sector. Then we summarize our qualitative research on the opinions of the participants in the cocoa supply chain about commercial, organic, and Fairtrade production. Based on the interviews and related marketing literature, we propose a new approach to marketing cocoa that could enhance opportunities for small scale producers in the industry.
3. The Cocoa Supply Chain
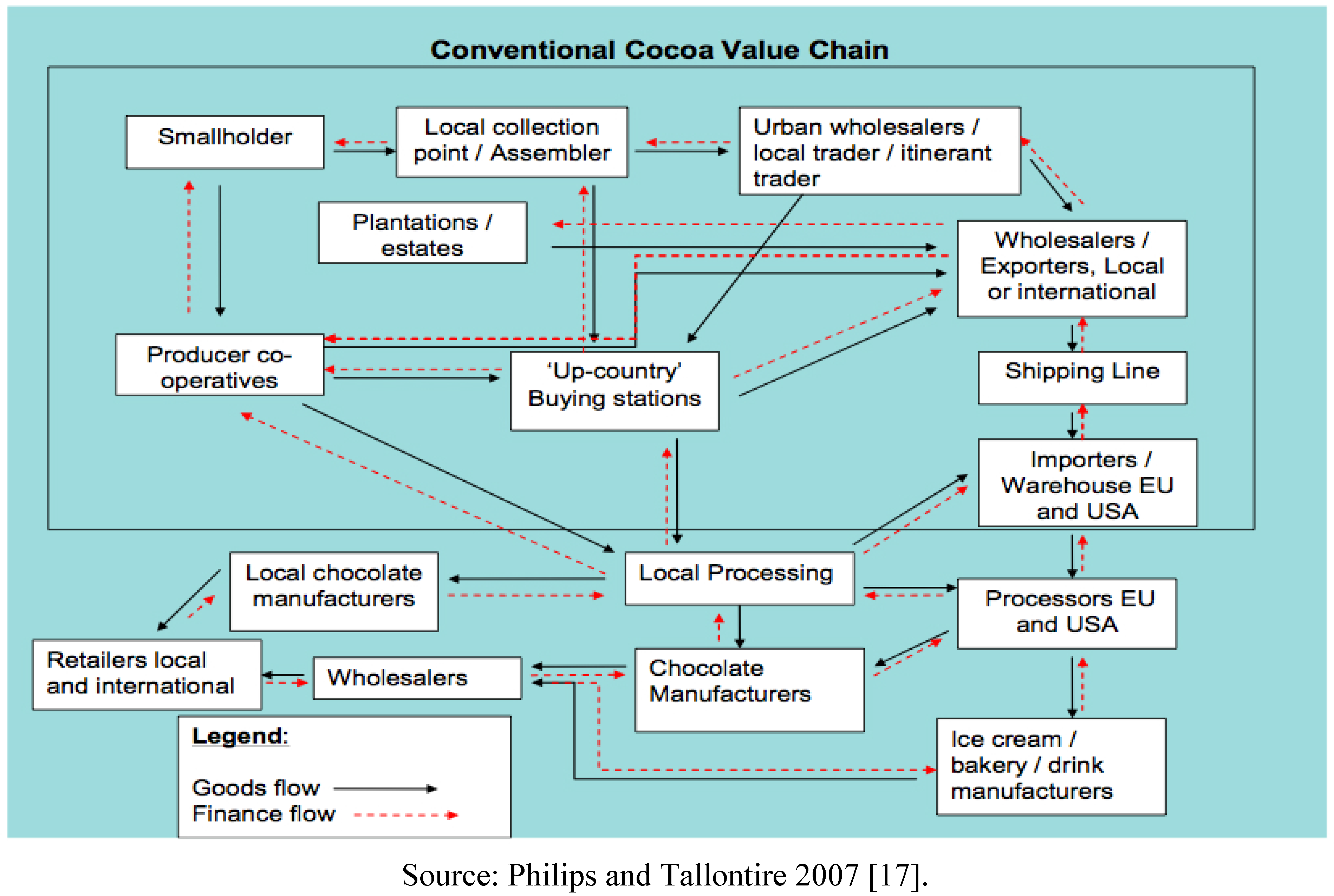
The cocoa supply chain is comprised of an elaborate network of actors, the majority of which are invisible to the casual consumer. Raw cocoa undergoes a variety of processes, usually changing hands many times before it becomes a chocolate bar (
Figure 1) [
17]. Two particular challenges affect the cocoa supply chain. First, it is complex, relying on many discrete actors before the finished product is complete. This makes communication up and down the length of the chain challenging; producers may be unaware of cocoa characteristics that buyers are willing to pay a premium for, while marketers often find it onerous to locate a source for the high value differentiated product demanded by consumers.
Second, the cocoa industry, for the most part, is geared toward large-scale production by multinational companies; 65% of the global chocolate market is dominated by just six multinational industry giants, including Mars, Cadbury, and Nestle [
22]. Although not uncommon, such uneven distribution of power within the supply chain has been criticized as neo-colonialism, based on perceived inequitable division of profits among actors in the supply chain [
17]. Smaller-scale operations attempting to innovate within this framework may find that they are at a disadvantage merely because of the scope of their operation. Small firms cannot afford expensive research and marketing programs, placing them at a market disadvantage.
Figure 1.
Conventional Cocoa Supply Chain.
Figure 1.
Conventional Cocoa Supply Chain.
3.1. Key Components
Because some companies play multiple roles in the elaborate process of chocolate manufacturing and others do not, it is difficult to predict the exact configuration of the supply chain for any particular final product. There are, however, similarities among the supply chains of most chocolate products. The supply chain from producer to consumer usually includes such discrete intermediate companies as dealers, processers, manufacturers, and retailers.
Fresh cocoa has an extremely short shelf life, so producers usually ferment and dry their own beans, which is critical to the taste of the final chocolate product. Producers range from independent small producers who sell directly to the next link in the chain, to small producers who form part of larger producers’ cooperatives, to large-scale producers who may have the capacity to export or even process their own beans. Producers are often located in remote areas, making transport one of their biggest obstacles to commercial success. Collection agents link producers with buyers by amassing small amounts of cocoa from hundreds of diverse sources into commercially efficient quantities. Dealers do not affect bean quality, but seek to meet buyers’ expectations. Dealers operate either within the country the beans are grown, or post-export at an international location. Good storage is critical in the collection process to avoid mold and other problems with cocoa beans; storage facilities with a regulated climate are expensive.
Cocoa processors roast and grind raw beans into such products as nibs, butter, powder, cake, and liquor, for subsequent manufacture. Chocolate manufacturers purchase these intermediate products and create the finished product that will eventually be sold on the shelf. The chocolate marketers who buy this “industrial” chocolate, the last in the supply chain except for the consumer, may use it for anything from a simple unaltered, repackaged bar of chocolate to the main ingredient in handmade artisan truffles. Because chocolate manufacturers specialize in creating specific recipes and flavor profiles, it is at this stage that significant choices about bean quality, origin, and other determining factors are made. The manufacturers, however, must convey their preferences back through several actors in the supply chain, which is difficult. A few manufacturers deal directly with producers, which improves communication.
Chocolate marketers generally choose from a set of “standard”, readymade recipes available from manufacturers, which they then package and sell. Should a marketer wish to create and market a unique recipe, they are generally faced with minimum purchase requirements, or “minimum run” requirements, and are also charged the cost of cleaning the equipment before and after each unique recipe is manufactured. Unfortunately, this presents a problem for small companies who are least able to afford frequent production changes, but wish to distinguish their product as a means of competing with larger, mainstream companies.
3.2. Costa Rica
The cocoa supply chain in Costa Rica is in many ways typical of the industry. The heart of cocoa production in Costa Rica lies in the Talamanca region, located in the province of Limon in the southeast portion of the country. It is home to two indigenous reservations, a booming tourist industry, and rich but threatened levels of biodiversity, tangling sustainable land management in a knot of conflicting interests.
A significant proportion of the cocoa produced in Costa Rica is grown by the Cabecar and Bribri indigenous peoples. The typical farm is small (about 10 hectares, with only 1 ha of cocoa), run by a family characterized by a low level of income and little formal education compared to other Costa Ricans [
23]. They farm with traditional methods that require little purchased inputs, technology, and maintenance. Often these farms are remote and may not be accessible by road.
Many scholars, NGOs, and multinational organizations believe that improving the profitability of traditional cocoa-producing agroforestry systems in Talamanca is critical for improving community livelihoods and environmental services. In Talamanca, cocoa plantations connect and serve as high-quality buffer zones for a number of nearby protected areas that form part of the Mesoamerican Biological Corridor [
11]. This has global significance. Although the La Amistad-Talamanca region covers only 12% of Costa Rica’s total territory, it houses 80% of its total biodiversity, forming a UNESCO-recognized “hotspot”, or area that contains greater than 0.5% of the world’s biodiversity while having lost over 70% of its original habitat [
24].
A brief description of some principal players in the Costa Rican cocoa industry is shown in Box 1.
Box 1: Main Actors in the Costa Rica Cocoa Supply Chain.
The Association of Small Producers of Talamanca (APPTA), located in the town of Bribri, has about 1200 members, 80% of whom are indigenous and 38% of whom are women [
25]. Working primarily in certified organic and Fairtrade cocoa, this organization has enjoyed exemplary commercial success and continues to explore new avenues of expansion.
The Association Commission of Indigenous Women of Talamanca (ACOMUITA), located in the Bribri reservation in the town of Shiroles, strives to encourage the full participation of indigenous women in the life and politics of the region. In 2003 they began an organic, artisanal chocolate business called Tsirushka, with the aim of creating jobs and income for affiliated certified organic farmers. They sell cocoa at fairs.
Koproxa, located in the Brirbi reservation in the town of Suretka, is a private collection/exportation company linked to the Panamanian company Cocoa Del Istmo. Koproxz buys and exports organic and conventional cocoa to Panama, but does not separate or distinguish between them.
Collectors/Truckers, reach individual farms and buy cocoa and other products, as well as selling farm inputs and other goods to the farmers at the same time. These collectors supply municipal markets with cocoa beans.
Costa Rican Cocoa Products (CCP), located in San Jose, buys domestic beans from small producers and collectors, dividing them into distinct grades and processing them into industrial chocolate, or couverture. In the 1980s and 90s before crop disease struck and collapsed the cocoa industry, CCP routinely processed 170 tons of beans a month. Currently they process no more than 15 tons per month due to lack of product availability. Although they process organic beans upon request, most of their product is conventional. They sell primarily to Costa Rican buyers.
FINMAC, located in Guapiles, is a certified organic cocoa farm and processing plant, and considered by many to be one of the best run in the world. It processes conventional and organic beans into liquor blocks, and recently began experimenting with manufacturing its own chocolate bars.
Finca La Amistad is a larger, certified organic cocoa plantation similar in profile to FINMAC, whose owner is president of the National Board of Fine Cocoa (Camara Nacional de Cocoa Fino). Finca la Amistad both produces and buys organic cocoa from small local producers and does their own exporting.
4. Interview Methods
We conducted a series of semi-structured interviews in Costa Rica and the U.S. with producers, buyers, manufacturers, exporters, and other experts in the conventional as well as certified chains. Costa Rican contacts were identified with colleagues at the Centro Agronómico Tropical de Investigación y Enseñanza (CATIE). Drafts of an open-ended survey instrument were critiqued and pre-tested with colleagues at CATIE and others in the cocoa sector in Costa Rica. Thirteen qualitative interviews were carried out with eight participants in Costa Rica and five in the United States.
Twelve interviewees worked in the commercial cocoa supply chain; in addition, a small-scale coffee roaster in the U.S. whose business model shared many similarities with those involved in the cocoa supply chain, was also interviewed. Informants were selected based on cocoa or cocoa products being the primary or sole focus of their business, with the exception of the coffee roaster who was selected based on the fact that producing, sourcing, and marketing their product with a strong focus on sustainability shares great similarities to that of the cocoa supply chain. In total, these interviews covered all parts of cocoa supply chain from Costa Rica to the United States.
Although there were many instances of crossover or multiple functionality, Costa Rican respondents included two large commercial producers, two small producer organizations, one of which manufactures and markets their own brand of chocolate, a collector/exporter, and an industrial processor. U.S. respondents included managers of grocery-type retail outlets, and chocolate makers or marketers.
We used a qualitative research approach to assess the opportunities for actors in Costa Rica to capture more of the profits while employing more environmentally friendly production practices. The qualitative research was based on interviews with participants and an analysis of the cocoa supply chain in Costa Rica and the United States. We used a naturalistic qualitative approach [
26,
27], which collects information through interviews to obtain perspectives of each informant, allowing themes to surface from their experiences in order to identify meanings and the processes studied [
26]. The individual participants in the study were identified based on key initial contacts and subsequent follow ups.
The interviews took place between August 25, 2009 and December 22, 2009 on location at each place of business. They were recorded, with the written permission of the interviewee, transcribed and translated, if applicable. Interviewees were asked questions about their business models, their views on organic and Fairtrade certification, why they did or did not participate in such programs, and which factors they felt were most necessary for increased commercial success.
5. Results
The supply chain mapping and field interviews yielded a wide range of experiences and perspectives with regard to organic and Fairtrade certification. The challenges and rewards of existing business models, combined with our analysis of the supply chain interviews, led us to identify a new possible differentiation strategy based on the “integration of meaning” into cocoa as product, which we introduce and discuss below.
5.1. Participation in Fairtrade and Organic Certification
Eleven out of thirteen respondents were either currently or previously certified organic or selling organic products. The high incidence of involvement with organic certification documents its success in garnering large-scale recognition. However, this seemingly high proportion may be misleading and does not necessarily speak for the ease or desirability of participation in the program. Of the eleven experienced with organic certified products, only four (the two small producer organizations, a small independent chocolate marketer, and the coffee roaster) stated that they operated out of a conviction that organic certification was wholly the best choice for their business model.
Of the remaining seven interviews, two were retail outlets not required to be organic certified in order to sell the prepackaged organic product of others; organic chocolate only made up a portion of their total chocolate selection. Two were larger producers who both said that organic cocoa did not deliver the expected higher profit margin and that organic farming does not necessarily correlate with improved ecological benefits. One was an industrial chocolate processor who dealt mainly in conventional cocoa but occasionally processed organic beans for special orders, and another was an independent chocolate maker who buys certified organic beans not because they are organic but because he believes they offer the best flavor profile. The final participant was a specialty chocolate shop that began with organic certification and decided to drop it for a variety of reasons.
Fairtrade certification offered a slightly different story. Of the thirteen interviewees, five were either Fairtrade certified or worked with Fairtrade products, but only one, a small producers’ organization, chose to participate in the program as a key tenet of their business model. Of the remaining four, two were retailers whose product selection only contained a relatively small portion of Fairtrade certified chocolates, and another was an independent chocolate marketer whose preferred chocolate happened to be Fairtrade certified. The last was the coffee roaster who bought Fairtrade certified coffee but did not advertise it as such because it conflicts with the roaster’s own social justice-oriented marketing scheme.
5.2. Business Challenges
The most commonly cited challenges to success in the cocoa business included company size or product volume, product consistency, and financing. The first challenge, small product volume, stems from the fact that the chocolate industry is geared to large-scale, high-volume companies. An inability to compete in this respect can have direct, immediate financial repercussions. On the retail end of the chain, small company size or product volume can translate to less competitive supplier pricing, significantly higher freight costs, and poor customer service from the supplier due to the comparative insignificance of product volume.
On the production side, major buyers exhibit a high level of risk aversion to dealing with many small-scale growers [
17]. As a producer relations specialist observed, “small producers and small shops can find themselves in a similar place of not being able to make that direct connection. If you’re really, really small nobody wants to trade directly with you. You don’t have enough buying power”.
A candy buyer for an independent gourmet foods store sums up the problem of product volume in her comment, “I have to hit certain minimums, otherwise my price is higher and I pay the freight. And freight, even if it’s just UPS, is routinely very expensive. It can really mess up your pricing expectations. But how much can I sell? Say it’s an African chocolate. I probably can’t sell a pallet of that. And if you think of those big ships, a pallet is nothing. Those big containers probably hold twenty pallets each, at least. Well, if you can picture that—one twentieth of one container? And it’s way more than I even need.
A step or two down the supply chain, an independent chocolatier buys dried beans instead of finished bars. He expresses a similar sentiment: “We buy small. Last time we bought four tons, which is a lot to us, but four tons in the industry is nothing. We had to air freight that, but to make it economical, you need to sea freight it. And to do that, you need like twenty-four tons. So there’s this economy of scale…it costs us about a dollar a kilo to air freight it, and it costs about eighteen cents if you sea freight it”.
The second most often mentioned business challenge was product consistency, a concern throughout the entire supply chain. In a large-scale, standardized industry requiring cooperation among multiple players, buyers need to have confidence in the consistency of the cocoa product, both in terms of quality and of quantity. As an independent producer observes of his buyers’ requirements, “for them it’s important that it be the same. They don’t want it to be one day good tasting and then [not]…they just want it to be the same”. This undeviating uniformity can be difficult to deliver for small companies working with a variable agricultural product.
One American chocolate maker has just transitioned from making chocolate from purchased industrial couverture to creating their own chocolate directly from the bean, using somewhat less-than-reliable antique Spanish equipment. When he talks about the demand for his chocolate beginning to exceed his ability to dependably create it, he says, “It’s not exciting, it’s horrible. [The machinery broke] and we had gotten completely behind. Right now we like to say that we’re at about a two-week back order, but sometimes it’s worse than that. People don’t tolerate that too well. Especially chains like Whole Foods, it’s absolutely unacceptable”.
Like any agricultural product, achieving consistency in the quality of cocoa and chocolate products can also prove challenging. An independent chocolate maker in Costa Rica has experienced problems sourcing a consistent product. He explains why he no longer buys couverture from his original source: “One shipment would be good, and then another would be like they hadn’t even tempered it. The product has highs and lows”.
5.3. Limitations of the Two Certification Systems
Organic and Fairtrade certification systems have transformed public perceptions of the ability of international trade to contribute to social justice, environmental sustainability, and ethical trade. Nevertheless, some limitations were experienced and expressed by our sample from the industry.
5.3.1. Organic Certification
Despite the large share of respondents who produced or traded organic cocoa products, many expressed some dissatisfaction with organic cocoa. Their concerns were that organic certification is more time-consuming, more complicated, less profitable, and less environmentally sustainable than anticipated.
Some interviewees doubted that production meeting organic standards is truly more sustainable than conventional production practices. The owner of a medium-sized independent cocoa farm and member the National Board of Fine Cocoa in Costa Rica reflected on the impracticality of operating a larger farm organically. “I question whether organic is sustainable. We thought that being organic was the way to express sustainable development, and that was important for us”, he said. “Maybe it was a mistake to think that organic was the way to do that”. Another of the larger organically certified independent producers expressed doubts about the effectiveness of the certification standards: “I have to start a program for reducing water consumption on the farm. But we get 4500 mm of water a year. You make a hole a meter deep and there is the groundwater. So why should we save groundwater? It doesn’t make sense”.
In the traditional cocoa-producing agroforestry systems of Talamanca, organic certification from the standpoint of sustainability may truly be a moot point. In 2009, there were approximately 1440 small cocoa producers in the region, 76% of which do not use of synthetic pesticides or herbicides [
25]. They are popularly referred to as organic although most lack certification. Because their systems use few off-farm inputs, cultivate diversified crops, and thrive off natural rainfall, it is possible that compliance with organic regulations would do little to improve their existing systems of cultivation from an environmental standpoint.
The organic cocoa profit margin is often not as high as expected at the production level, where it is most critical. Observed an independent cocoa farmer, “With organic, production costs are higher. But quality is much more important [to the buyer], so the markup isn’t so much, and it’s gone down with time”. He is echoed by another medium-sized independent producer, who said, “We thought there was a bigger price difference between organic and non-organic when we decided to certify”. He maintains that his buyers would continue to buy his product whether it was certified organic or not.
This lack of enthusiasm permeated higher levels of the supply chain as well. A chocolatier who makes his own chocolate from certified organic beans, says “My first priority is the flavor of the chocolate. If I had the choice between something that was organic but of lower quality, which in the past has often been the case, or something that is grown in a responsible way but not certified, I’m going to take the best bean that I can get”.
Consumer allegiance to the program may be flagging due to the multitude of actors cashing in on the organic boom, who have until recently exhibited little interest in the values that drove early organic practitioners [
28]. As the buyer at a small chain of earth-friendly grocery stores noted, “There is a big conversation about organic not being what it used to be, which is true”.
Indeed, Time Magazine, a barometer of popular sentiment, published an article called
Eating Better Than Organic in March 2007, asserting, “Many chefs, food writers and politically minded eaters are outraged that “Big Organic” firms now use the same industrial-size farming and long-distance-shipping methods as conventional agribusiness”. “In addition, some consumers may remain indifferent”. In a study examining consumers’ interest in organic and Fairtrade labels on chocolate, Siriex and Tagbata [
29] found that almost half their sample was “insensitive to the label’s presence”.
Finally, organic certification may be at a particular disadvantage in the confectionary industry where quality and taste are given highest priority; many in the industry have reported disappointment with the quality of organic products. As one candy buyer observed, “there is a receptivity to [organic chocolate] but…they don’t want to get pigeonholed into the ‘healthy’ area. Because in candy that has a lot less appeal than taste”.
5.3.2. Fairtrade
Having achieved widespread name recognition due to its success in the coffee and tea industries, Fairtrade began certifying chocolate in 2002. Conner and Mabaya [
16] observed that the Fairtrade movement is “where organic was 10–15 years ago: confined to niche markets, below the radar of the mainstream food system”, perhaps partially explaining why comparatively few interviewees participated in Fairtrade.
One candy buyer, in a unique position to provide a bird’s eye view of the market, observes, “Fairtrade seems to be a huge issue in the coffee and tea department, but I don’t get too many requests for it [in chocolate] and I’m not sure why. There are not a huge number of vendors in that as far as I can tell”.
The interviews suggested two specific factors that likely prevented many cocoa producers from certifying in Fairtrade: lack of familiarity with the Fairtrade program and restrictions on participation. First, actors throughout the supply chain had low levels of familiarity with the program, ranging from a lack of awareness of its existence to varying levels of confusion about standards for participation in the program. As the producer relations manager of the small coffee roaster observes, “The producers, who are often rural poor, marginalized, don’t really have a strong sense even of what they’re signing up for when they sign up for these value-added certifications”.
This proved true not only for producers in the sample but other participants in the supply chain. When asked if he participated in the Fairtrade program, a Costa Rican chocolate maker simply replied, “No. What’s that?” The administrator of the indigenous women’s chocolate company admitted, “…we are in the process of figuring out what [Fairtrade] is because we don’t have much information about it”. The chief of logistics at a Costa Rican processing plant expresses his frustration at what he perceives to be arbitrary and illogical restrictions: “We’re trying to figure out how to [get certified], but it’s very difficult. The regulations are very strict so we don’t really fit. It’s something I don’t really understand”.
This appears to be one of the main drawbacks of the program even at the consumer level. A United States-based chocolate maker comments, “People will ask me whether I’m Fairtrade, and I’ll engage in a whole conversation about it, but then I’ll realize that they have absolutely no idea what it really means”. The coffee roaster continues, “There’s a disconnect between what the producer knows and feels is important about Fairtrade Certification and what the consumer knows. Most consumers have no idea that co-ops are part of this whole thing, they only know it has to do with a fair price to farmers and then they’ll say something like, ‘and healthcare’, something that’s totally random and not associated at all”.
Achieving greater awareness and understanding may largely be a matter of time. As noted, Fairtrade has achieved popular recognition already in the coffee and tea industries, and despite the fact that its acclaim lags in the cocoa sector, its popularity there is rapidly growing.
The second possible reason for the low participation rate is that, unlike organic certification that is open to anyone willing to comply with the guidelines, Fairtrade certification is not. In seeking to eliminate middlemen, promote direct trade, and empower small producers, Fairtrade regulations restrict who is eligible for participation. Only small producer cooperatives are permitted to participate; the somewhat larger independent producers interviewed were ineligible under certification requirements at the time of the interviews.
This is limiting not only for producers but also all along the supply chain. For example, the coffee roaster interviewed stopped using the Fairtrade logo because they felt the system was too restrictive to adequately express the range of social values that were important to them. The producer relations manager explained, “If [Fairtrade] included farms that are not organized into co-ops, or if it had a provision for farms larger than five hectares who are structurally dependent on hired labor, then we might be able to use it to describe everything we do. But because of its limitations we felt like…we might as well just come up with [our own] way to describe what we do well”.
6. The Integration of Meaning as an Alternative Differentiation Method
Despite their growing popularity and significant contribution to improved trade, organic and Fairtrade certification systems have limitations and may not provide the best approach to product differentiation for some businesses.
In their frank comments regarding the effectiveness of their cocoa business, the interviews conducted in this study suggest the possibility of a new differentiation method. We drew on the underlying themes that emerged from the interviews and insights promoted by Daniel Pink [
30], who suggests that intuitive, artistic, “right-brain” approaches to business and commerce will succeed best in this century. Psychology and popular literature posits that the right side of your brain is responsible for creativity, while the left side handles the details and implementation. The left side is analytical while the right side is artistic.
According to Pink, society has reached an era where various advances in technology have created a level of abundance that satisfies and even oversatisfies many people’s material needs, resulting in the newly important role of meaning in a commercial context. Chocolate, and even high-quality luxury chocolate, is not only within financial reach of many consumers, but they have access to a wider selection than ever before in history. Products of all kinds are no longer adequate in themselves to stand out from the crowd; what does stand out, however, is meaning.
Drawing on Pink and similar concepts—e.g., see an interview of Pink with Oprah [
31]—and our interviews—we posit a new perspective on cocoa production, supply chain management, and marketing, which we adapt from Pink [
30] who referred to the principle as the “
integration of meaning”. This approach would involve linking holistic cocoa production processes, consumer desires for ethically sourced products, and novel marketing approaches that convey these linkages. Such an approach is particularly well suited to smaller companies that face disadvantages in the chocolate industry because of their size. Using the integration of meaning as a differentiation and marketing strategy may secure some of the positive features of certification systems while bypassing many of the drawbacks, as described below.
A potentially harmonious counterpoint to large-scale certification systems that by necessity must employ a somewhat bureaucratic approach, the integration of meaning draws on unique personal expression and presence as a means of product differentiation. It is a distinctly right-brain marketing technique: subjective, intuitive, and big-picture oriented. It is precisely this quality that sells in an automated, standardized, and mass-produced avalanche of consumer goods.
We employ three key components of the integration of meaning—story, shared values, and committed personal interaction, any one of which can be an effective marketing tool. Moreover, combining all three may create an effective alternative to certification in situations when the drawbacks or challenges seem greater than the rewards.
6.1. Story
Long after abstract facts become foggy and drop out of our memories altogether, stories remain. Perhaps even more importantly, Pink argues that facts alone have lost much of their value. Thanks to a variety of advances in technology, a staggering wealth of virtually instant and often free information is available to the average person. Facts can conveniently be found to support or counter almost any argument, and in this data-rich environment, Pink advocates for the heightened comparative value of “context enriched by emotion, a deeper understanding of how we fit in and why that matters”. In other words, consumers are interested in a colorful telling of the origin of a product, who produced it, and how they did it.
Retail is fiercely competitive and products must vie for shelf space even before they can court the eye of the consumer. A contextual backdrop can allow a product to stand out from the meaningless packaging of its competitors. If this is true in general, it is particularly applicable in the realm of environmentally and socially enhanced trade certifications. Facts, studies, and figures are used to bolster the certification’s credibility and justification, but in the words of a producer relations specialist, “It is true that most people don’t want to hear the complex truth, they want a simple answer”. And though facts are an important means of understanding the world around us, the very reason these facts are compelling in the context of certification derives from a sense of empathy of how our actions fit into a larger context—factors that lend themselves perfectly to the differentiation technique of story.
The producer relations manager of the small coffee roasting company has built her company’s success in part on this precept. “We wanted to tell the story of the producer, of the coffee, of what makes this thing special and different”, she explains. “So a regular feature of our demos is to hand out coffee and say, ‘this comes from a farm in El Salvador called “Finca Idealismo”. We’ve been working with this grower for six years. She’s super quality-driven, she just got her organic certification after this really tough four-year transition, she was really nervous about it but she did it and we supported her, and we’re really excited about her and her coffee has never tasted better’. So it’s like telling the story as people drink the coffee”.
A buyer for a specialty foods store confirms the popular appeal of this approach, asserting, “When [chocolate] is bean to bar, or it’s made in a specific locale, we’re always looking for things like that because it helps to make us different. That will have more customer impact than if it just says organic”.
An independent farmer’s wife in Costa Rica, situated as far as possible from the marketing end of the supply chain, intuitively grasps the commercial appeal of storytelling. She shrugs when asked why their farm has been successful. “We have the cute and cuddly image”, she said, motioning to her five children clamoring noisily about the cozy dinner table where we are talking.
Of course, finding ways to convey such meaning and story will be difficult, as will getting “shelf space” for the story and the product in already crowded stores. But the personal appeal to both producers and to consumers is motivation to overcome this challenge. There are limits on the number of stories that can be told, especially in larger stores, so this niche is apt to work best in small stores and for artisan chocolates.
6.2. Shared Values
For most consumers, actual organic and Fairtrade certification are less important than the values they are perceived to espouse. Lockie
et al. [
28] attest that consumers’ “individualized concerns regarding personal safety or enjoyment, relative to ecological or altruistic concerns regarding environmental or social health” will have a major bearing on the development of alternative foods schemes within a conventional framework. Theoretically, finding a way to satisfy these consumer value requirements without certification would be an effective marketing technique.
A merchandising manager for a small chain of natural foods stores in the U.S. considers herself responsible for addressing consumer value requirements in just such a way. Passionate about taking time to select environmentally and socially conscious products that will satisfy her customers’ often high requirements in terms of both ethics and quality, she asserts, “It’s not about a label. It’s about what’s behind [the label]. We don’t need the organic certification when we know how it is produced”.
A U.S. chocolate shop owner concurs, stating, “De facto organic is just as good as certified”. She continues, “we used to be a certified organic confectioner, but we were so disillusioned by the system that we stopped, and now we feel like we have more flexibility in getting good quality ingredients, especially with regard to local farmers, by dropping the certification”.
Fairtrade is no exception. A U.S.-based chocolatier was asked whether the idea of Fairtrade certification interested him, he replied, “If you’re buying a premium product, Fairtrade certification doesn’t seem to apply. I mean, you’re already paying more than a Fairtrade price. …We’re buying directly from the farm, which is a farm I visited, and there are no abuses there. Everybody seems to be happy, it’s clean, it’s safe. So to me it just doesn’t fit”.
While many consumers may be willing to accept a sense of shared values in lieu of certification, the approach carries a substantial hurdle: the matter of credibly conveying this to the potential customer. For many large companies, this can be problematic, and for this reason, certification may indeed be the best option for them.
One former organic-certified chocolate confectioner in the U.S. also feels this way. Preferring to select suppliers primarily through a sense of shared values, she nevertheless purchases Fairtrade and Organic certified industrial chocolate from a large company. She explains, “They’re bottom line driven; we doubt that they really care about the rest of the supply chain. So we see the third party certifications, both Fairtrade and organic, as an added assurance when we don’t necessarily trust their motivations”. She adds, “When we’re dealing with big companies, we’ve got to rely on the certification. When we’re dealing with smaller companies, we get to ask those important questions and get to a level of comfort”.
The relative accessibility of smaller companies can translate into unique opportunities to communicate shared values. Though large companies have equal and perhaps even greater capacity to pursue the differentiation strategy of shared values, their very size and anonymity may limit their ability to accomplish this, resulting in the need for certification to accomplish similar ends.
6.3. Committed Personal Interaction
In an age of self-checkout lines, internet shopping, and automated customer service, the presence of an actual human being can be powerful. The marketing industry has used this to its advantage since Morgan and Hunt [
32] defined the emerging field of Relationship Marketing as “all marketing activities directed towards establishing, developing, and maintaining successful relational exchanges”. The concept has met with great success, having “experienced explosive growth” in the past decade [
33].
The component of committed personal interaction builds on this recognition of the power of relationship. But what distinguishes it from Relationship Marketing is precisely that it is not merely a marketing scheme; committed personal interaction derives its unique power from the expression of genuine conviction and personal investment.
This quality is compelling and universally accessible no matter what the product or company mission. When asked what she looked for in choosing products to feature, one candy buyer paused. She looked over the widely varied selection of chocolate products available in her store, ranging from cut-to-order fudge priced at $50 per pound to comically oversized slices of chocolate pizza. Finally, she declared, “I want them to be good at what they do. It doesn’t matter if it’s expensive or cheap, because I have different expectations for those two categories. But they’ve got to be committed. And particularly the small companies, believe me, they are committed, they are diehard. They are entrepreneurs that believe in their product”.
The producer relations specialist has also discovered the power of personal emotional investment. According to her, one of the most persuasive elements of the product demos they do is the fact that the demonstrator, “is someone who obviously cares, and not just cares enough to be there on a Saturday with coffee but also cares enough to get excited and engage, use that moment as an opportunity to talk about the person behind the coffee and educate the consumer”.
Even in the absence of the other two components, shared values and story, committed personal interaction can make a substantial difference in commercial success. An independent chocolatier with a passion for dark chocolate recalls how when he first opened, customers would tell him that they didn’t like dark chocolate, requesting milk or white chocolate instead. But as he interacted with them on a daily basis and explained his preferences, there was a shift. “Now that I’ve been open for two years, they trust me. I don’t sell much milk chocolate and hardly any white chocolate”.
Committed personal interaction, while it appeals to many consumers simply for its own sake, is the vehicle that effectively delivers the appeal of story and shared values. Through interpersonal interaction, a trust is built between the vendor and the consumer that may even be viewed in some cases as superior to certification schemes shrouded in anonymity. One confectioner finds this to be the case, explaining, “We value direct relationships, because as we practice them with our farmers around western North Carolina, we can look them in the eyes and trust them. When we’re dealing with [the company we buy chocolate from], we’re talking to a customer service rep who’s in a building with lots of other customer service reps who have probably never been to a cocoa farm…”
6.4. Integration
When all three elements—story, shared values, and interpersonal interaction—are combined, consumers may be willing to accept them in lieu of certification, making them a powerful tool with which to compete with big business. One confectioner, having made the decision to drop their organic certification, discovered the power of this synthesis of all three components, observing, “Organic rings bells and makes people feel like they’re making the right decision. But if I’m standing at the truffle case and I can explain, no, it’s not organic, but the raspberries are from an hour away and we’ve been to the farm, they don’t spray. They’re de facto organic. If we can speak to the purity of the ingredients that we use, then a customer is willing to overlook certification just as we are”.
This application of integration of meaning—story, shared values, and committed personal interaction—to the cocoa supply chain offers promise to achieve the broader economic, social, and environmental benefits that are the objectives of organic and Fairtrade certification. But it would do so in a unique manner, which is less formulaic and generic and therefore harder to scale up, but perhaps more powerful and useful for small chocolatiers, retailers, producers and rural communities.
7. Conclusions
Through our qualitative examination of the cocoa supply chain, we confirmed that Fairtrade and organic certification are widely recognized. Organic certification has focused attention on safe environmental and worker practices, and provided a platform that aligns relatively well with existing traditional shade grown cocoa production systems in Costa Rica. It may be most appropriate, however, for larger growers, and therefore its most important functions may be to ensure that large growers maintain environmentally friendly cocoa systems and to provide them and their customers with standardized quality assurance. Fairtrade is relatively new in the cocoa trade in Costa Rica and has proved challenging for many growers (especially with limited resources or education) to understand let alone adopt.
Other marketing approaches may be required to secure increased environmental sustainability and social equity in cocoa production and trade by small-scale actors. Organic and Fairtrade have increased value-added trade over the past several decades and continue to do so, but they also have limitations that make certification challenging or less advantageous for some actors, particularly small operations. Furthermore, the standards may subtly or overtly favor large scale producers [
21].
As consumer awareness and therefore the market for ethically traded goods evolves, it is important to remain attuned to emerging, innovative differentiation strategies that build upon the successes of past endeavors. Because the chocolate industry, and to a large extent much of modern trade, is structured to favor high-volume players, it is critical to focus particularly on methods that assist smaller companies to viably compete.
In interview after interview, as we talked about the beneficial aspects of the cocoa business, a discussion originally aimed at the evaluation of Fairtrade and organic certification gave way to the piecing together of an entirely new strategy. The concept of the integration of meaning emerged as those surveyed pointed singly and en masse to the idea that small businesses can capitalize on their ability to thoughtfully produce an item in accordance with their own values (as distinguished from the mass production of industry giants driven by the bottom-line), then creatively tell their story through committed personal interaction to deliver a holistically appealing package to the consumer in a compelling way. This concept articulated by our respondents has been described in the popular literature by Daniel Pink, but has not previously appeared in the scientific literature on ethical or environmental trade.
We believe that the integration of meaning may provide a promising new strategy to achieve the ephemeral economic, environmental, and social benefits of sustainable development and trade. The integration of meaning in the cocoa and chocolate supply chain would involve integrating the story of producers’ commitment and dedication; shared producer and consumer values of social and environmental responsibility; and personal relationships between producers and consumers. As product abundance increasingly contributes to the thirst for meaning and context, and as consumer awareness of the social and environmental consequences of their buying patterns grows, the integration of meaning invites further study as one possible solution not just for the chocolate industry in Costa Rica, but for small-scale actors to gain a foothold in trade in general.
Various caveats and impediments of course limit our suggestions to adopt the integration of meaning as a marketing tool and business philosophy. Establishing a clear linkage, story, shared values, and personal interaction is difficult and more likely to be successful at small scales and with the artisan chocolate supply chain. At a large scale, conveying the story and getting shelf space seems daunting, even in natural and organic food store chains. In addition, the integration of meaning must be applied through all the players in the supply chain, not just at the consumer level. Thus the merits of the integration of meaning perhaps can only be realized through exceptionally creative practitioners and producers who can capitalize on such concepts. But marketing firms and modern success stories, such as Facebook, have built success on right brain approaches, at least validating the approach for some products and services.
Other trends in the global cocoa market also represent challenges. The rapid expansion of sustainable cocoa organizations and government programs may constrain the individualistic integration of meaning approach. As noted, the volume of Organic (IFOAM), Fairtrade, UTZ Certified, or Rainforest Alliance sustainable cocoa certifications grew by 248% from 2004 to 2009 [
14]. The Netherlands, which is the largest user and importer of cocoa beans in the EU [
34], has committed to importing only sustainable cocoa. This would create a barrier to growers relying on “integration of meaning” rather than certification or require some other exception to allow small growers demonstrate unique proof of sustainability. Further, many countries allow import only of cocoa, and not of chocolate, which can limit cocoa producers’ ability to capture the benefits of increased quality. Finally, world prices for cocoa have increased markedly in recent years, which reduces the possibilities and the importance of obtaining a premium on chocolate through either certification or integration of meaning.
Small-scale cocoa producers and other participants in the value chain can respond to many of the preceding concerns by focusing on differentiating their story and emphasizing values shared by consumers and producers. However, each link in the value chain must cooperate to track and promote the integration of meaning. Thus, limiting the number of links in the chain is important both for communicating the message and ensuring transference of quality and values up and down the chain. Another approach would be to develop an information system with product codes that can be looked up on a website that conveys the story of the producer and other participants in the value chain, without depending on retailers’ scarce time and shelf space.
Further research—and practice—could assess if the integration of meaning as a new approach improves cocoa producer incomes while promoting environmentally friendly farm practices. Would it also benefit collectors, buyers, processors, wholesalers, manufacturers, and retailers? Could it operate at a scale that is appropriate for small producers and businesses? Can it improve trade, social welfare, and environmental benefits sought under international trade agreements such as the CAFTA agreement? Is it particularly appropriate for cocoa and chocolate, where the future opportunities for small producers and players will be in more profitable and tasty niche markets? Further research and discussion certainly should consider the merits of our findings and conclusions regarding opportunities to integrate consumer desires for meaningful, holistic chocolate products, and cocoa producer and supply chain participants’ desires for sustainable incomes and farms.