Significant Changes in Soil Properties in Arid Regions Due to Semicentennial Tillage—A Case Study of Tarim River Oasis, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
2.3. Analysis of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
2.4. Environmental Covariates
2.5. Modeling Approaches
2.6. Statistical and Validation Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
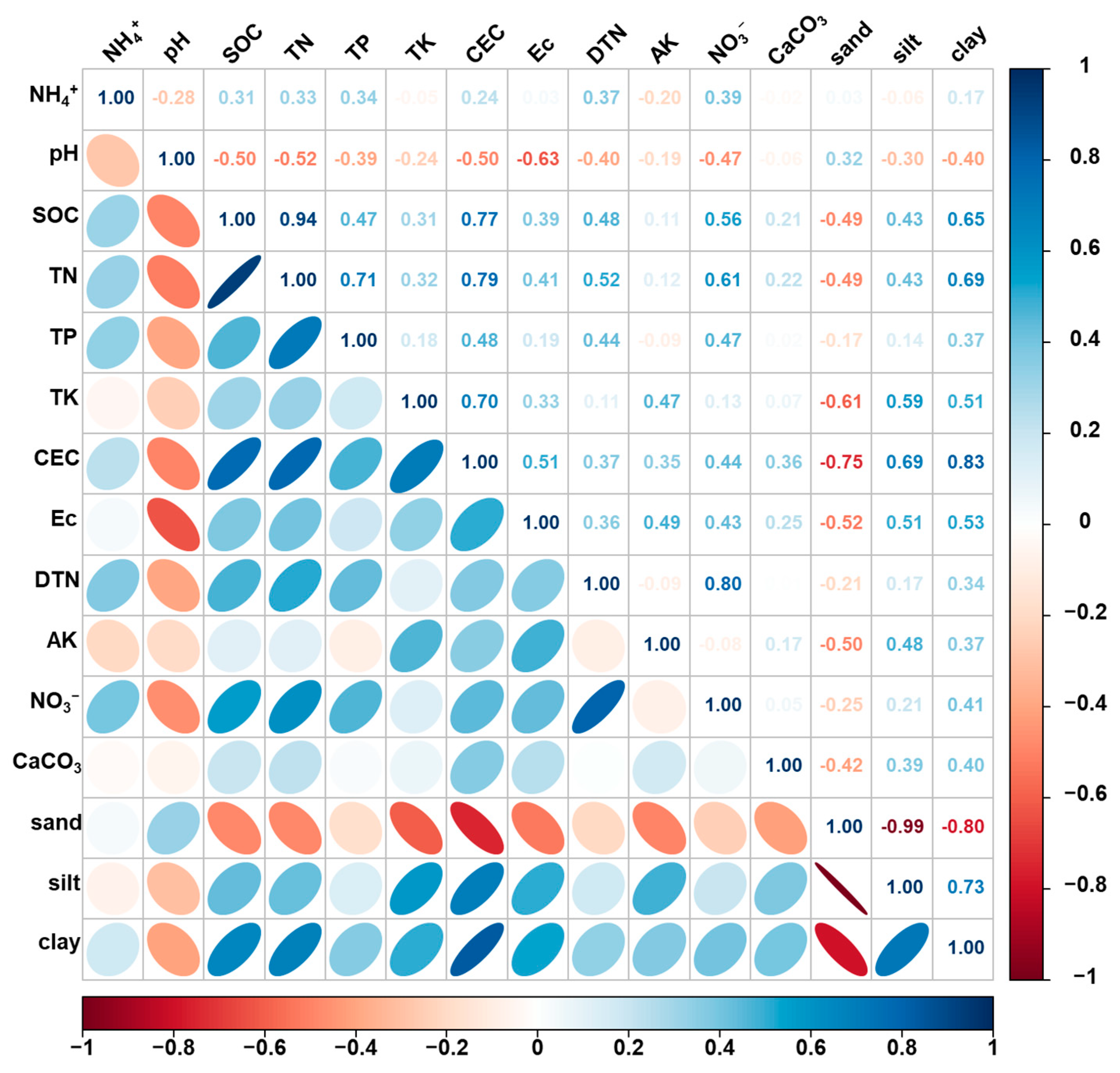
3.1. Correlation Analysis and Descriptive Statistics
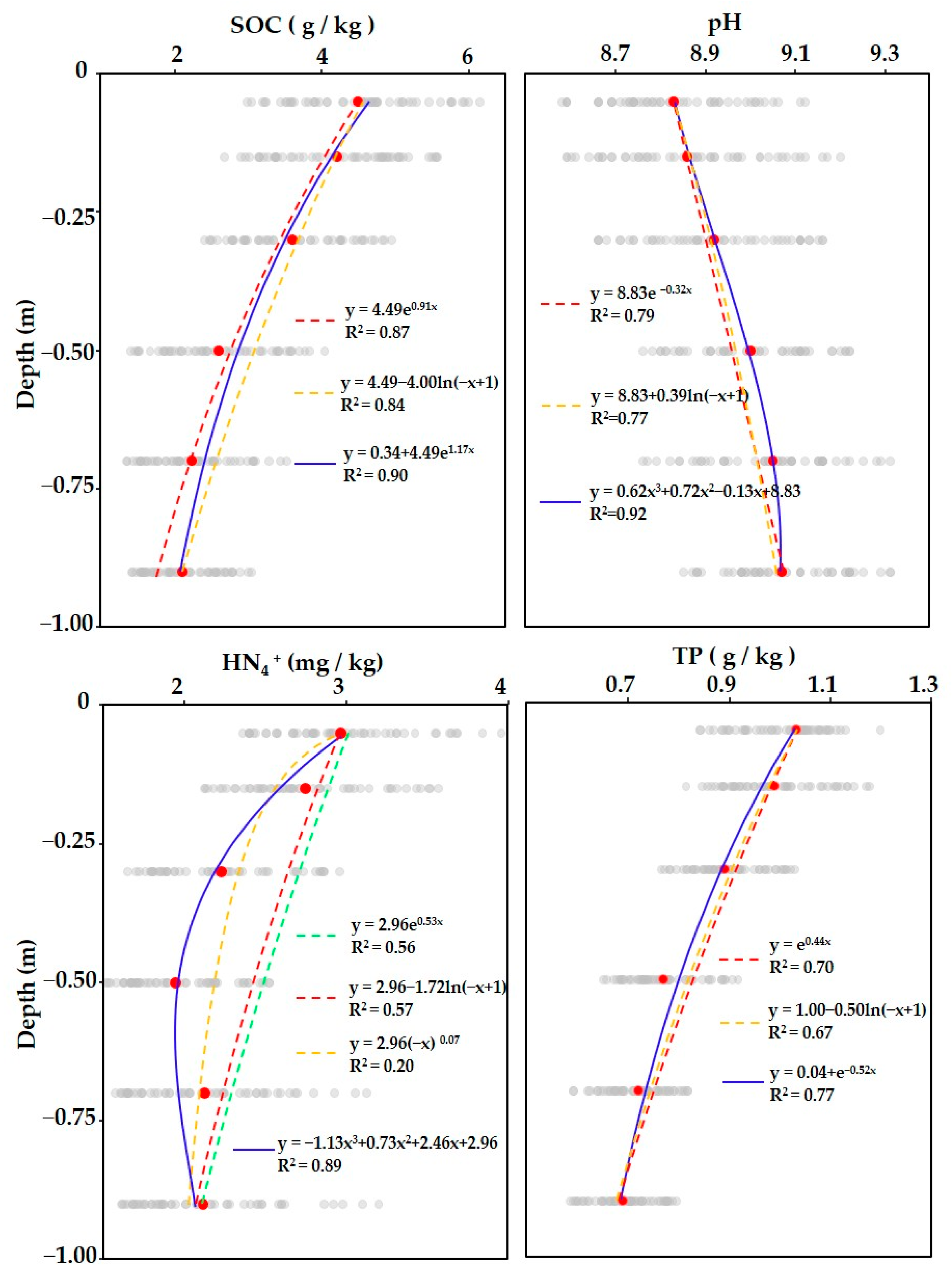
3.2. Optimal Depth Functions Selection
3.3. Model Performance
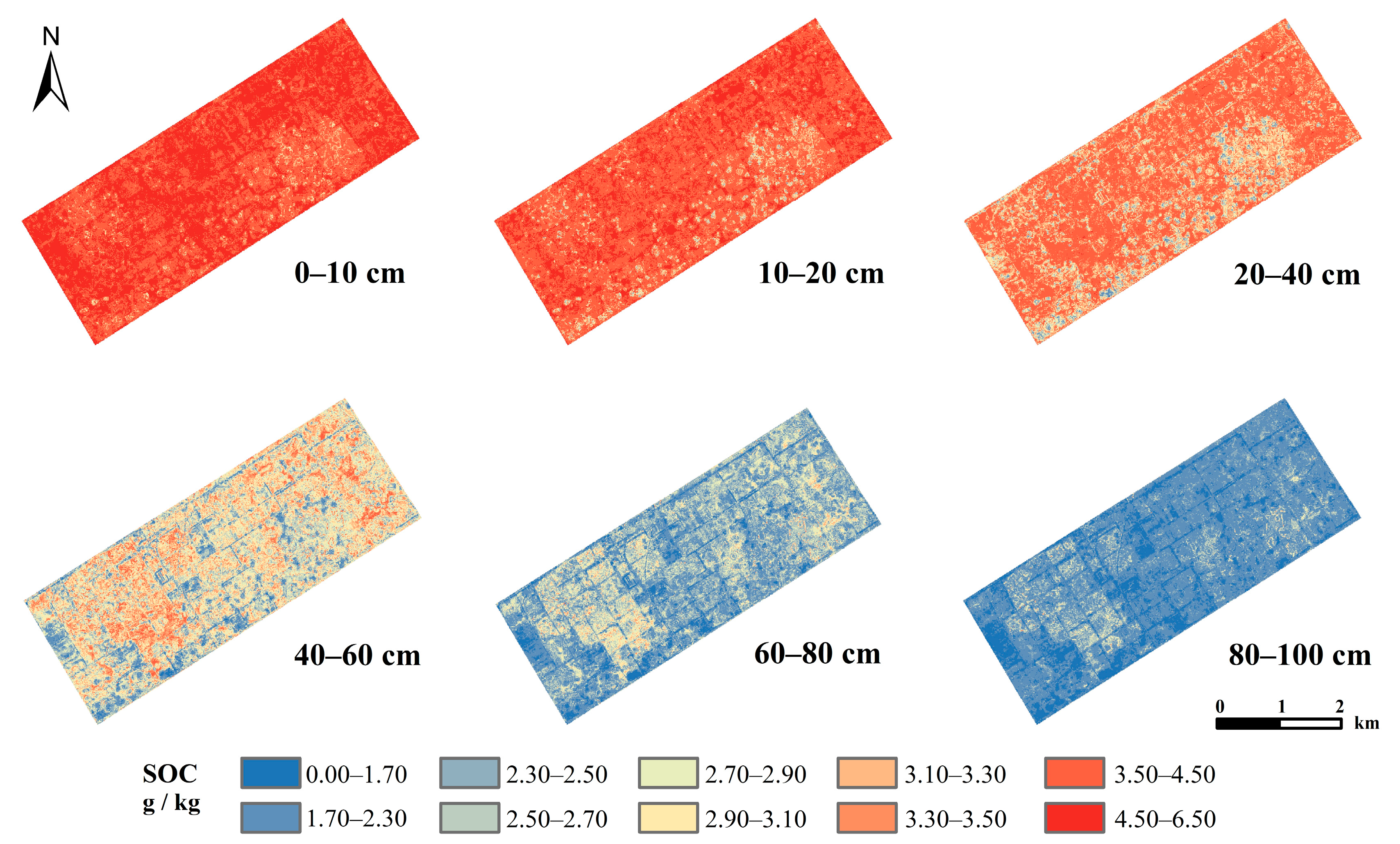
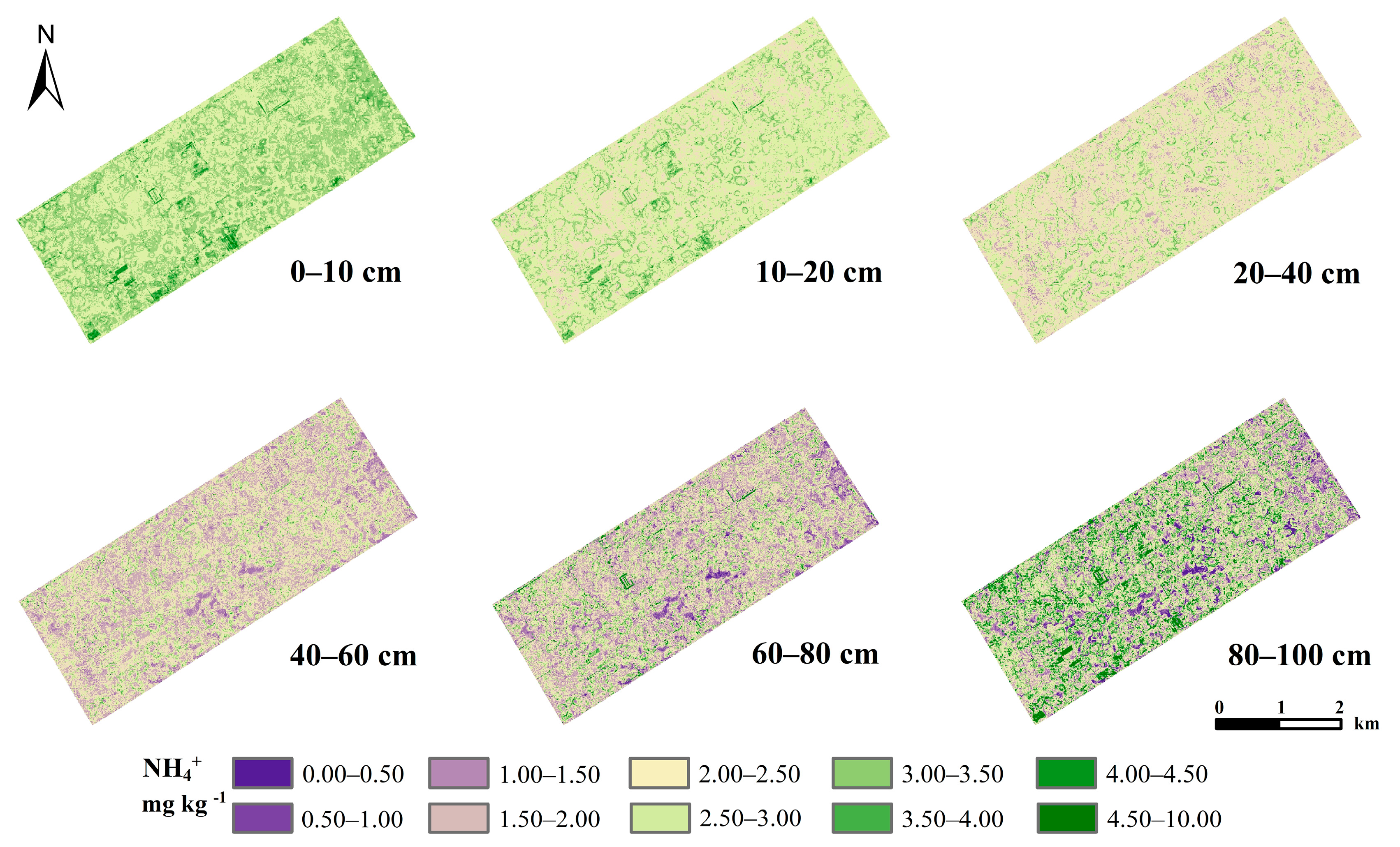
3.4. Confidence Interval of Prediction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lian, X.; Piao, S.; Chen, A.; Huntingford, C.; Fu, B.; Li, L.Z.X.; Huang, J.; Sheffield, J.; Berg, A.M.; Keenan, T.F.; et al. Multifaceted Characteristics of Dryland Aridity Changes in a Warming World. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wei, C.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Meng, C.; Cai, Y. The Dominant Influencing Factors of Desertification Changes in the Source Region of Yellow River: Climate Change or Human Activity? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Patterns and Driving Mechanisms of Land Desertification in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Guo, Z.; Shi, P.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Pang, S.; Xie, B. Spatiotemporal Changes of Land Desertification Sensitivity in Northwest China from 2000 to 2017. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, F.T.; Benito, B.M.; Berdugo, M.; Concostrina-Zubiri, L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Eldridge, D.J.; Guirado, E.; Gross, N.; Kéfi, S.; Le Bagousse-Pinguet, Y.; et al. Biogeography of Global Drylands. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 540–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachmi, A.; Andich, K.; Alaoui-Faris, F.E.E.; Mahyou, H. Amélioration de l’état de la végétation et de la fertilité des sols des parcours arides du Maroc par les techniques de restauration et de réhabilitation. Revue d’Écologie 2018, 73, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihi, A.; Tarai, N.; Chenchouni, H. Can Palm Date Plantations and Oasification Be Used as a Proxy to Fight Sustainably against Desertification and Sand Encroachment in Hot Drylands? Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.K.; Maixner, F.; Franklin, O.; Daims, H.; Richter, A.; Battin, T. Linking Microbial and Ecosystem Ecology Using Ecological Stoichiometry: A Synthesis of Conceptual and Empirical Approaches. Ecosystems 2011, 14, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry of Microbial Organic Nutrient Acquisition in Soil and Sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Law, R.M.; Pak, B. A Global Model of Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycles for the Terrestrial Biosphere. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 2261–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; He, Z.; Ju, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, P.; Wang, W.; Lin, P. Long-Term Conventional Cultivation after Desert Reclamation Is Not Conducive to the Improvement of Soil Carbon Pool and Nutrient Stocks, a Case Study from Northwest China. Geoderma 2024, 445, 116893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, S.; Sun, Z.; Wang, H.; Qu, S.; Lei, N.; He, J.; Dong, Q. Tillage Effects on Soil Properties and Crop Yield after Land Reclamation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, M.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; Dunfield, K.E.; Deen, B.; Simpson, M.J. Long-Term Crop Rotation and Different Tillage Practices Alter Soil Organic Matter Composition and Degradation. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahzade, J.; Karimi, A.; Naderi, M.; Shirani, H. Soil Mechanical Properties and Wind Erosion Following Conversion of Desert to Irrigated Croplands in Central Iran. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.H.; Cao, J.J.; Degen, A.A.; Zhang, D.W.; Long, R.J. A Four Year Study in a Desert Land Area on the Effect of Irrigated, Cultivated Land and Abandoned Cropland on Soil Biological, Chemical and Physical Properties. CATENA 2019, 175, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, D.; Xin, Z.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, K. On the Spatial Variability and Influencing Factors of Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen Stocks in a Desert Oasis Ecotone of Northwestern China. CATENA 2021, 206, 105533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, Z.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Wang, L. Soil Structure and Nutrient Supply Drive Changes in Soil Microbial Communities during Conversion of Virgin Desert Soil to Irrigated Cropland. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 71, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-R.; Liu, J.-L.; Ren, W.; Liu, L.-L. Land-Use Change Alters Patterns of Soil Biodiversity in Arid Lands of Northwestern China. Plant Soil 2018, 428, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, F. Evaluation of Soil Environment after Saline Soil Reclamation of Xinjiang Oasis, China. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, J.; Paul, B. Challenges in Arid Region Reclamation with Special Reference to Indian Thar Desert—Its Conservation and Remediation Techniques. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 12753–12774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Yang, R.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, X.F. Evolution of Soil Structure and Fertility After Conversion of Native Sandy Desert Soil to Irrigated Cropland in Arid Region, China. Soil Sci. 2010, 175, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacq-Labreuil, A.; Neal, A.L.; Crawford, J.; Mooney, S.J.; Akkari, E.; Zhang, X.; Clark, I.; Ritz, K. Significant Structural Evolution of a Long-term Fallow Soil in Response to Agricultural Management Practices Requires at Least 10 Years after Conversion. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBratney, A.B.; Mendonça Santos, M.L.; Minasny, B. On Digital Soil Mapping. Geoderma 2003, 117, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Digital Soil Mapping: A Brief History and Some Lessons. Geoderma 2016, 264, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, L.; de Sousa, L.M.; Batjes, N.H.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Kempen, B.; Ribeiro, E.; Rossiter, D. SoilGrids 2.0: Producing Soil Information for the Globe with Quantified Spatial Uncertainty. SOIL 2021, 7, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrouays, D.; McBratney, A.; Bouma, J.; Libohova, Z.; Richer-de-Forges, A.C.; Morgan, C.L.S.; Roudier, P.; Poggio, L.; Mulder, V.L. Impressions of Digital Soil Maps: The Good, the Not so Good, and Making Them Ever Better. Geoderma Reg. 2020, 20, e00255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Webster, R. Spatial Statistics and Soil Mapping: A Blossoming Partnership under Pressure. Spat. Stat. 2022, 50, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimer, F.; Ledin, S.; Abdelkadir, A. Soil Property Variations in Relation to Topographic Aspect and Vegetation Community in the South-Eastern Highlands of Ethiopia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 232, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, K.J.; McDonnell, J.J.; Weiler, M.; Kendall, C.; McGlynn, B.L.; Welker, J.M.; Seibert, J. The Role of Topography on Catchment-Scale Water Residence Time. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W05002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Barthold, F.; Blank, B.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Digital Mapping of Soil Organic Matter Stocks Using Random Forest Modeling in a Semi-Arid Steppe Ecosystem. Plant Soil 2011, 340, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Ayoubi, S.; Jafari, A.; Tajik, S.; Finke, P. Digital Mapping of Soil Properties Using Multiple Machine Learning in a Semi-Arid Region, Central Iran. Geoderma 2019, 338, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamat, S.; Ilgiz, A.; Ruslan, S.; Mirsayapov, R.; Ilyusya, G.; Tuktarova, I.; Belan, L. Assessing and Mapping of Soil Organic Carbon at Multiple Depths in the Semi-Arid Trans-Ural Steppe Zone. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 38, e00855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, L.; Gimona, A. National Scale 3D Modelling of Soil Organic Carbon Stocks with Uncertainty Propagation—An Example from Scotland. Geoderma 2014, 232–234, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, H. Factors of Soil Formation: A System of Quantitative Pedology; McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, T.F.A.; McBratney, A.B.; Laslett, G.M. Modelling Soil Attribute Depth Functions with Equal-Area Quadratic Smoothing Splines. Geoderma 1999, 91, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B. Prediction and Digital Mapping of Soil Carbon Storage in the Lower Namoi Valley. Available online: https://www.publish.csiro.au/sr/SR05136 (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Zhang, Y.; Biswas, A.; Adamchuk, V.I. Implementation of a Sigmoid Depth Function to Describe Change of Soil pH with Depth. Geoderma 2017, 289, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allory, V.; Séré, G.; Ouvrard, S. A Meta-Analysis of Carbon Content and Stocks in Technosols and Identification of the Main Governing Factors. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Clanton, C.; Demuth, K.M.; Goodman, V.; Griffith, L.; Khim-Young, M.; Maddalena, J.; LaMarca, K.; Wright, L.A.; Schurman, D.W.; et al. Accurate Quantification of 0–30 Cm Soil Organic Carbon in Croplands over the Continental United States Using Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.-Z.; Li, S.-S.; Latif Virk, A.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, X.-P.; Zhang, H.-L. Effects of Tillage and Residue Management on Soil Aggregates and Associated Carbon Storage in a Double Paddy Cropping System. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walk, J.; Schulte, P.; Bartz, M.; Binnie, A.; Kehl, M.; Mörchen, R.; Sun, X.; Stauch, G.; Tittmann, C.; Bol, R.; et al. Pedogenesis at the Coastal Arid-Hyperarid Transition Deduced from a Late Quaternary Chronosequence at Paposo, Atacama Desert. CATENA 2023, 228, 107171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global Predictions of Primary Soil Salinization under Changing Climate in the 21st Century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil Salinization Management for Sustainable Development: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASF Data Search. Available online: https://search.asf.alaska.edu/#/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Wang, F.; Shi, Z.; Biswas, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, J. Multi-Algorithm Comparison for Predicting Soil Salinity. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Minasny, B.; Sarmadian, F.; Malone, B.P. Digital Mapping of Soil Salinity in Ardakan Region, Central Iran. Geoderma 2014, 213, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Rastoskuev, V.V.; Sato, Y.; Shiozawa, S. Assessment of Hydrosaline Land Degradation by Using a Simple Approach of Remote Sensing Indicators. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 77, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrena-González, J.; Gabourel-Landaverde, V.A.; Mora, J.; Contador, J.F.L.; Fernández, M.P. Exploring Soil Property Spatial Patterns in a Small Grazed Catchment Using Machine Learning. Earth Sci. Inform. 2023, 16, 3811–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, A.J.; Feudale, R.N.; Liu, Y.; Woody, N.A.; Brown, S.D. An Introduction to Decision Tree Modeling. J. Chemom. 2004, 18, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinshausen, N. Quantile Regression Forests. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 983–999. [Google Scholar]
- Draper, N.R.; Smith, H. Applied Regression Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mbagwu, J.S.C.; Abeh, O.G. Prediction of engineering properties of tropical soils using intrinsic pedological parameters. Soil Sci. 1998, 163, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, F.; McBratney, A.B.; Mayr, T.; Montanarella, L. Digital soil assessments: Beyond DSM. Geoderma 2007, 142, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuer, R.; Poggi, J.-M.; Tuleau-Malot, C. Variable Selection Using Random Forests. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauman, T.W.; Thompson, J.A. Semi-Automated Disaggregation of Conventional Soil Maps Using Knowledge Driven Data Mining and Classification Trees. Geoderma 2014, 213, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The Interplay between Microbial Communities and Soil Properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhetaer, N.; Nurmemet, I.; Abulaiti, A.; Xiao, S.; Zhao, J. A Quantifying Approach to Soil Salinity Based on a Radar Feature Space Model Using ALOS PALSAR-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamalero, E.; Bona, E.; Todeschini, V.; Lingua, G. Saline and Arid Soils: Impact on Bacteria, Plants, and Their Interaction. Biology 2020, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Yao, S.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, B. Responses of Soil Mineral-Associated and Particulate Organic Carbon to Carbon Input: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lyu, M.; Xiong, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, T.; Yang, Y. Substrate Availability and Soil Microbes Drive Temperature Sensitivity of Soil Organic Carbon Mineralization to Warming along an Elevation Gradient in Subtropical Asia. Geoderma 2020, 364, 114198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Morrissey, E.M.; Mau, R.L.; Hayer, M.; Piñeiro, J.; Mack, M.C.; Marks, J.C.; Bell, S.L.; Miller, S.N.; Schwartz, E.; et al. The Temperature Sensitivity of Soil: Microbial Biodiversity, Growth, and Carbon Mineralization. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Sui, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bao, T.; Jiao, X. Soil Organic Carbon Mineralization and Its Temperature Sensitivity under Different Substrate Levels in the Mollisols of Northeast China. Life 2022, 12, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Ruis, S.J. No-Tillage and Soil Physical Environment. Geoderma 2018, 326, 164–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Xu, D.; Min, X. Effects of Land Reclamation on Soil Organic Carbon and Its Components in Reclaimed Coal Mining Subsidence Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wan, Y.-B.; Li, H.; Du, M.-D.; Shi, Q.-D. Influence of Surface Water and Groundwater Gradient on Spatial Distribution of Typical Vegetation in the Hinterland of Taklamakan Desert. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, X.; Wang, S.; Pu, X. Benefits of Organic Manure Combined with Biochar Amendments to Cotton Root Growth and Yield under Continuous Cropping Systems in Xinjiang, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, F.; Shen, C.; Wang, N.; Shao, L. Semantic Segmentation Model of Cotton Roots In-Situ Image Based on Attention Mechanism. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 189, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Wang, Q.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J. Distribution of Soil Available Nutrients and Their Response to Environmental Factors Based on Path Analysis Model in Arid and Semi-Arid Area of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Maharjan, B.; Yu, C.; Su, A.; Jin, V.; Ferguson, R.B. A Laboratory Evaluation of Ammonia Volatilization and Nitrate Leaching Following Nitrogen Fertilizer Application on a Coarse-Textured Soil. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinten, A.J.A.; Vivian, B.J.; Wright, F.; Howard, R.S. A Comparative Study of Nitrate Leaching from Soils of Differing Textures under Similar Climatic and Cropping Conditions. J. Hydrol. 1994, 159, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shareef, M.; Gui, D.; Zeng, F.; Waqas, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Zhang, B.; Iqbal, H.; Xue, J. Nitrogen Leaching, Recovery Efficiency, and Cotton Productivity Assessments on Desert-Sandy Soil under Various Application Methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 223, 105716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, J.; He, K.; Gao, H.; Li, Z.; Tian, D. Phosphorus Biogeochemistry Regulated by Carbonates in Soil. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wang, L.; Nan, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Kumar, T.V.; Wang, C. Phosphorus Adsorption by Functionalized Biochar: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 497–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, S.M.; Mahmud, A.A.; Abdullahi, M.; Haruna, A. Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium as Fertilizers in Soil: A Review. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.W.; Wilson, B.R.; Koen, T. Mathematical Functions to Model the Depth Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon in a Range of Soils from New South Wales, Australia under Different Land Uses. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiru, N.; Gebrekidan, H. Effect of Land Use Changes and Soil Depth on Soil Organic Matter, Total Nitrogen and Available Phosphorus Contents of Soils in Senbat Watershed, Western Ethiopia. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2013, 8, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D.; Niu, S. A Global Analysis of Soil Acidification Caused by Nitrogen Addition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 024019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Li, B.; Vogt, R.D.; Mulder, J.; Song, H.; Chen, J.; Guo, J. Straw Return Exacerbates Soil Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Tian, D.; Zeng, H.; Li, Z.; Yi, C.; Niu, S. Global Soil Acidification Impacts on Belowground Processes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Pourtaghi, Z.S.; Al-Katheeri, M.M. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Random Forest, Boosted Regression Tree, Classification and Regression Tree, and General Linear Models and Comparison of Their Performance at Wadi Tayyah Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Landslides 2016, 13, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.-M.; Zhang, G.-L.; Liu, F.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, F.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Li, D.-C. Comparison of Boosted Regression Tree and Random Forest Models for Mapping Topsoil Organic Carbon Concentration in an Alpine Ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavan-Rad, M.R.; Dahmardeh, K.; Hadizadeh, M.; Keykha, G.; Mohammadnia, N.; Gangali, M.; Keikha, M.; Davatgar, N.; Brungard, C. Prediction of Soil Water Infiltration Using Multiple Linear Regression and Random Forest in a Dry Flood Plain, Eastern Iran. CATENA 2020, 194, 104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Chagas, C.; de Carvalho Junior, W.; Bhering, S.B.; Calderano Filho, B. Spatial Prediction of Soil Surface Texture in a Semiarid Region Using Random Forest and Multiple Linear Regressions. CATENA 2016, 139, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Du, H.; Li, S.; Wang, T.; Fan, Y. Effects of Different Cropland Reclamation Periods on Soil Particle Size and Nutrients From the Perspective of Wind Erosion in the Mu Us Sandy Land. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 861273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Crop Type | Irrigation Method | Irrigation Volume | Water Source | Fertilizer Application | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m3/ha | kg/ha | kg/ha | |||
| Cotton | Subsurface drip irrigation | 3900–4800 | Reservoir (glacial meltwater) | 750–1200 (N: 46.4%) | 6000–7800 |
| Winter–Spring flooding | 2250–3000 | Groundwater | 450–600 (K2O: 34.2%) | ||
| Jujube | Drip tape irrigation | 4800–6000 | Reservoir (glacial meltwater) | 384 (N: 46.4%) | 27,000–33,000 |
| Winter–Spring flooding | 1050–1350 | Groundwater | 704 (P2O5: 60.5%) |
| Soil Property | Type of Depth Function | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC (g/kg) | A x ek x depth | 0.87 | 0.54 | 0.45 |
| B + A x ek x depth | 0.90 | 0.46 | 0.39 | |
| A + k x ln(-depth + 1) | 0.84 | 0.55 | 0.46 | |
| pH | A + B x depth3 + C x depth2 + D x depth | 0.92 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| A x ek x depth | 0.79 | 0.10 | 0.07 | |
| A + k x ln(-depth + 1) | 0.77 | 0.10 | 0.08 | |
| NH4+ (mg/kg) | A x (-depth)k | 0.20 | 1.12 | 0.82 |
| A + k x ln(-depth + 1) | 0.57 | 0.77 | 0.45 | |
| B + A x ek x depth | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.40 | |
| A x ek x depth | 0.56 | 0.78 | 0.45 | |
| A + B x depth3 + C x depth2 + D x depth | 0.89 | 0.38 | 0.25 | |
| TP (g/kg) | A + k x ln(-depth + 1) | 0.67 | 0.15 | 0.09 |
| B + A x ek x depth | 0.77 | 0.12 | 0.08 | |
| A x ek x depth | 0.70 | 0.14 | 0.08 |
| Soil Property | Type of Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC (g/kg) | QRF | 0.78 | 0.62 | 0.51 |
| BRT | 0.72 | 0.61 | 0.47 | |
| MLR | 0.13 | 1.36 | 1.04 | |
| pH | QRF | 0.79 | 0.10 | 0.07 |
| BRT | 0.76 | 0.10 | 0.07 | |
| MLR | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.17 | |
| NH4+ (mg/kg) | QRF | 0.78 | 0.38 | 0.28 |
| BRT | 0.73 | 0.40 | 0.29 | |
| MLR | 0.19 | 0.80 | 0.64 | |
| TP (g/kg) | QRF | 0.71 | 0.12 | 0.08 |
| BRT | 0.62 | 0.14 | 0.09 | |
| MLR | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Song, X. Significant Changes in Soil Properties in Arid Regions Due to Semicentennial Tillage—A Case Study of Tarim River Oasis, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094194
Xiao Y, Ye M, Zhang J, Chen Y, Sun X, Li X, Song X. Significant Changes in Soil Properties in Arid Regions Due to Semicentennial Tillage—A Case Study of Tarim River Oasis, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094194
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Ying, Mingliang Ye, Jing Zhang, Yamin Chen, Xinxin Sun, Xiaoyan Li, and Xiaodong Song. 2025. "Significant Changes in Soil Properties in Arid Regions Due to Semicentennial Tillage—A Case Study of Tarim River Oasis, China" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094194
APA StyleXiao, Y., Ye, M., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., Sun, X., Li, X., & Song, X. (2025). Significant Changes in Soil Properties in Arid Regions Due to Semicentennial Tillage—A Case Study of Tarim River Oasis, China. Sustainability, 17(9), 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094194








