Characteristics of the Water Environment and the Mechanism of Nitrogen Metabolism in the Xisha River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Water Quality Analysis
2.2.1. Methods of Analysis of Physical and Chemical Indicators
2.2.2. PCA Analysis and Seasonal Statistical Analysis
2.3. Macro-Genomic Analysis
2.4. Methods of Analysis
2.5. Correlation Heatmap Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Characteristics Analysis
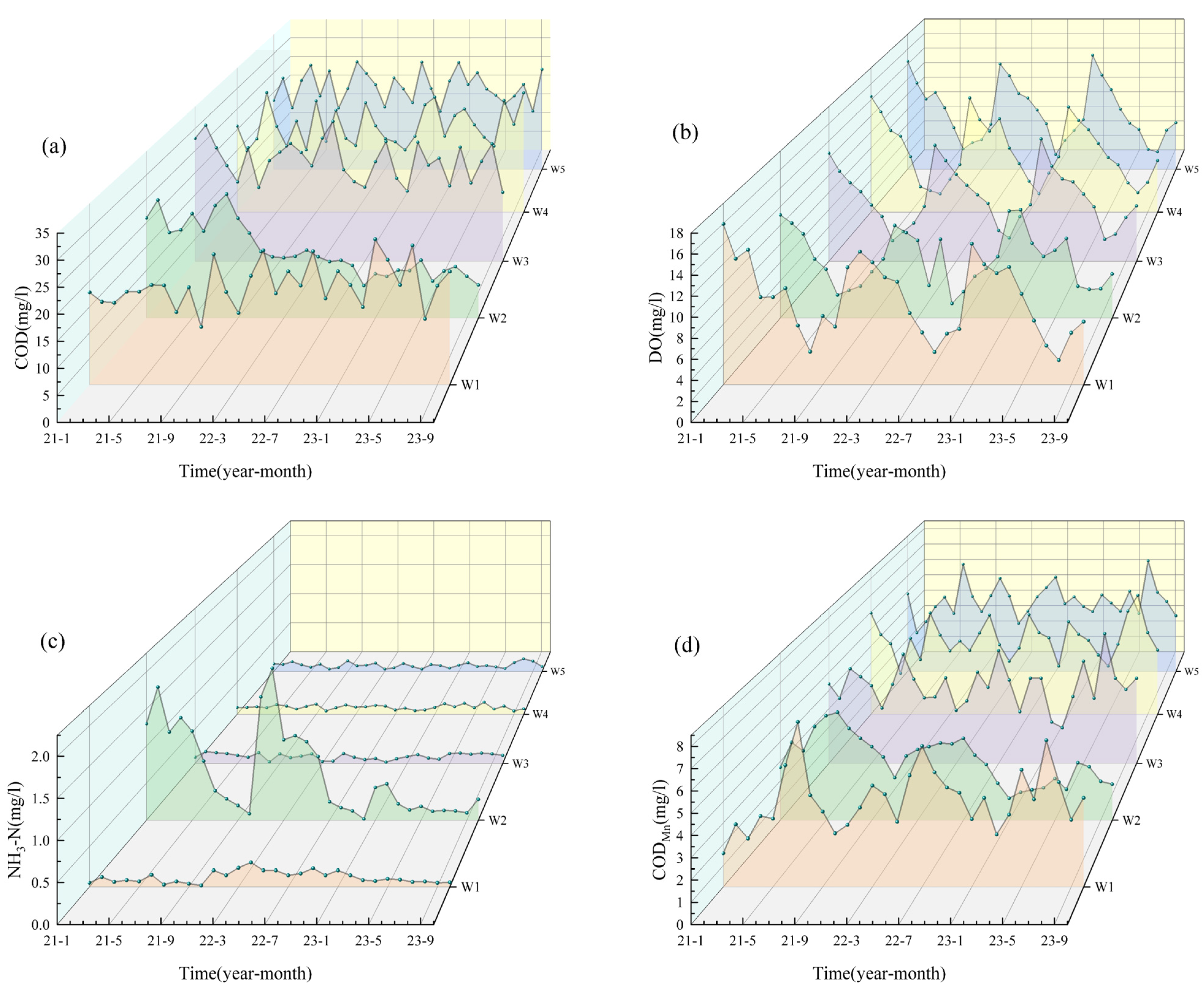
3.1.1. Water Quality Analysis from 2021 to 2023
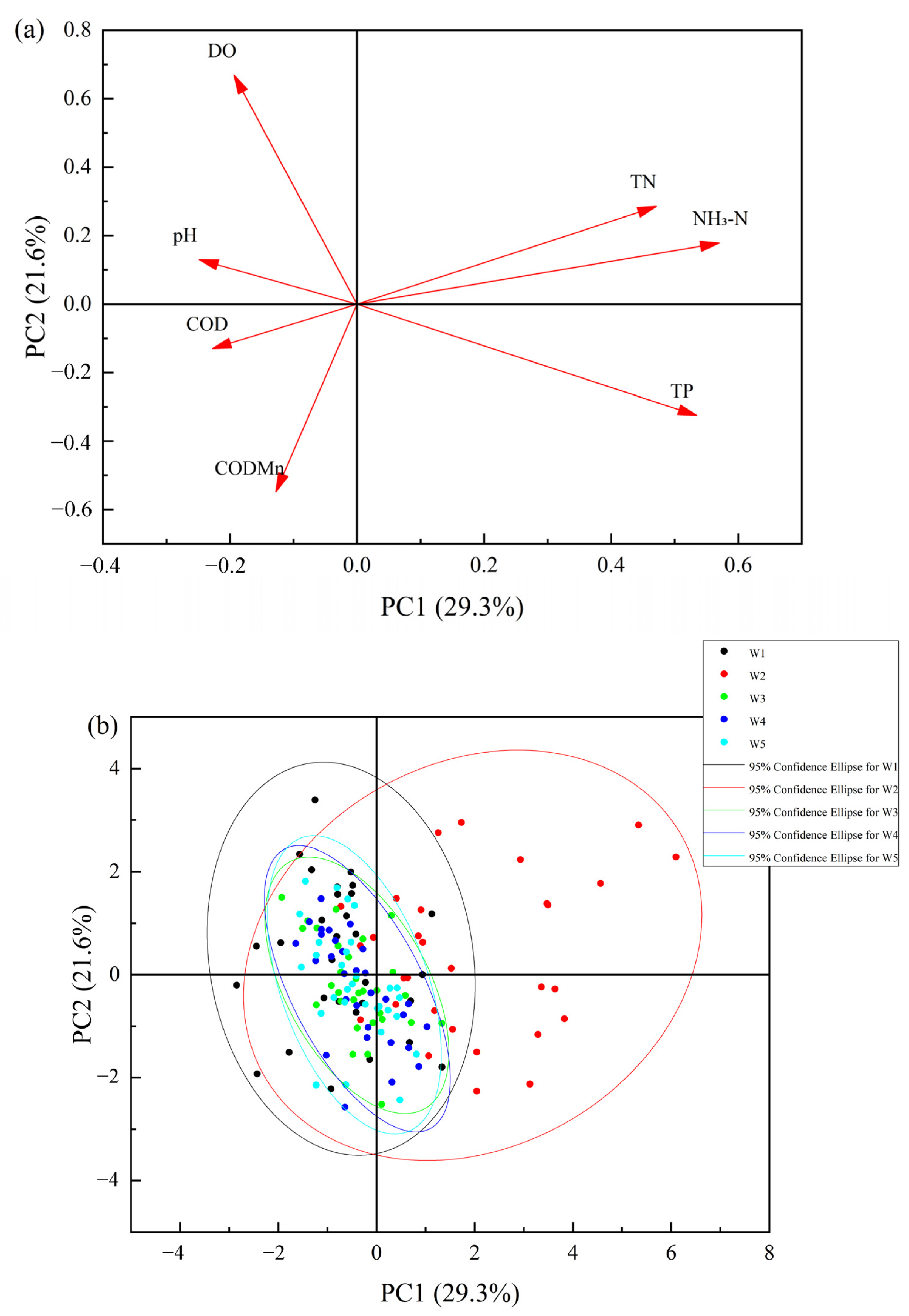
3.1.2. Analysis of the Main Factors of the Degree of Water Pollution
3.2. Analysis of Microbial Diversity in the Xisha River
3.2.1. The Analysis of Alpha Diversity
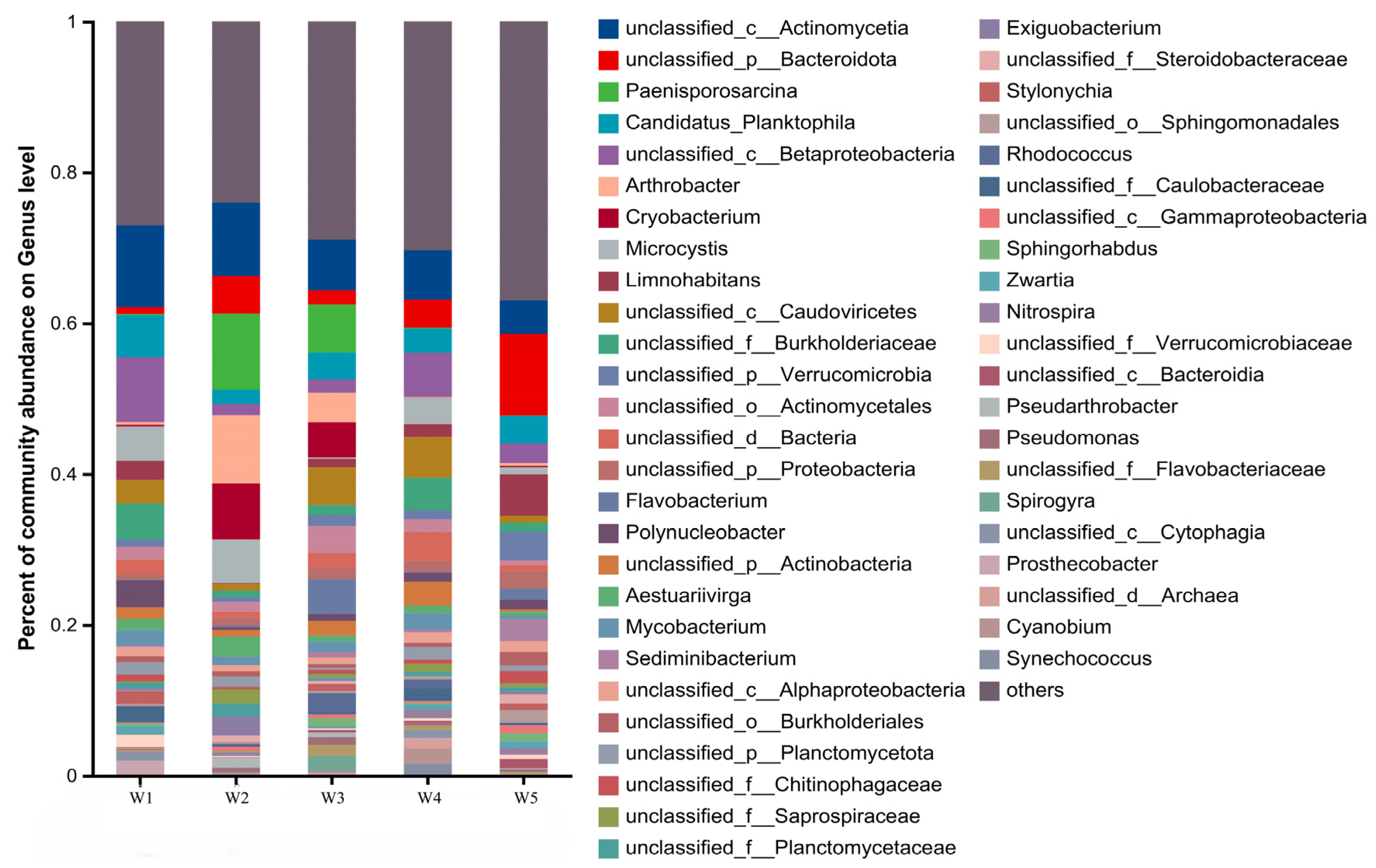
3.2.2. Analysis of Microbial Community Composition
3.3. Analysis of Key Control Factors of Nitrogen Pollution in Xisha River Water Body
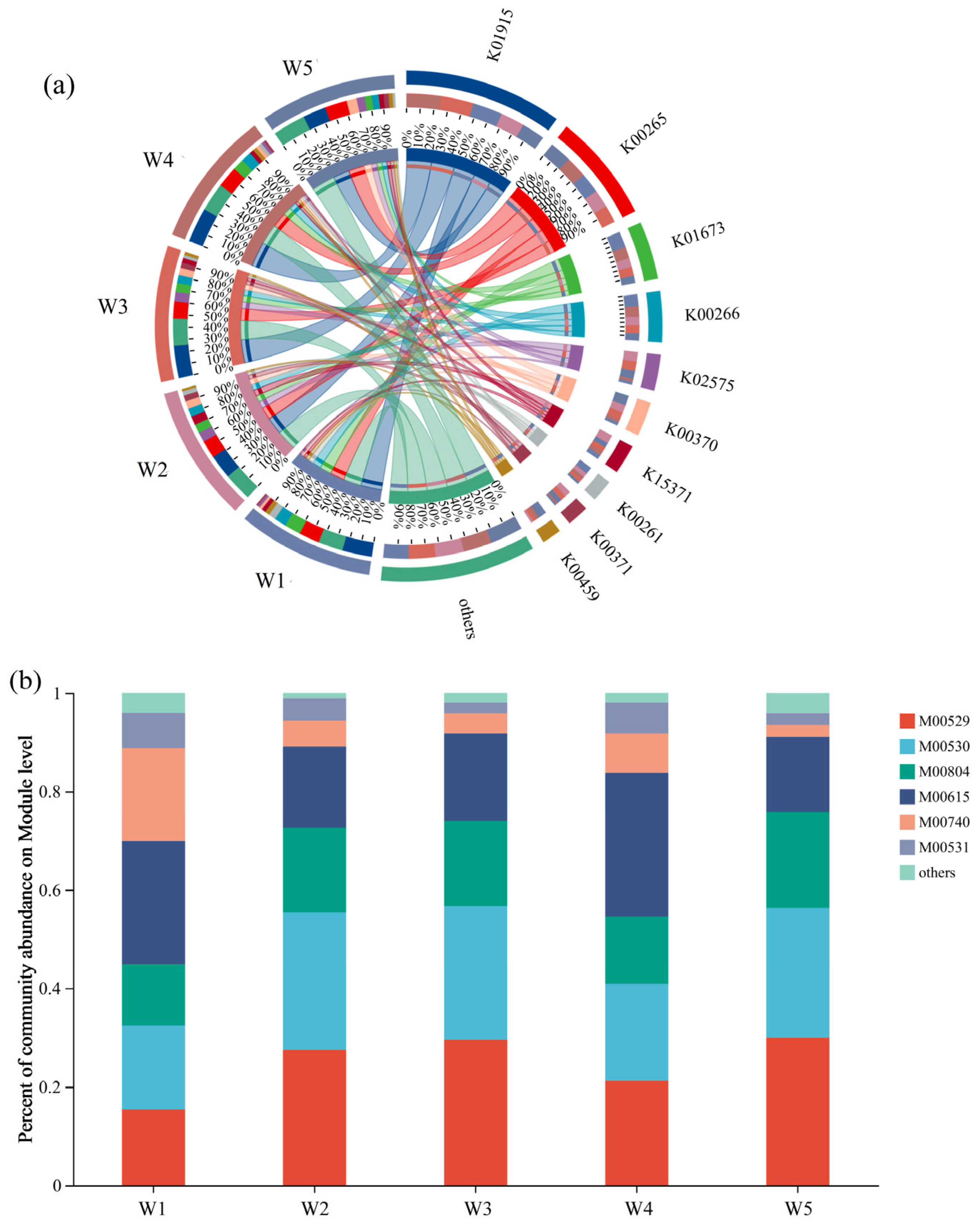
3.3.1. Analysis of Functional Genes and Pathways of Nitrogen Metabolism in the Xisha River
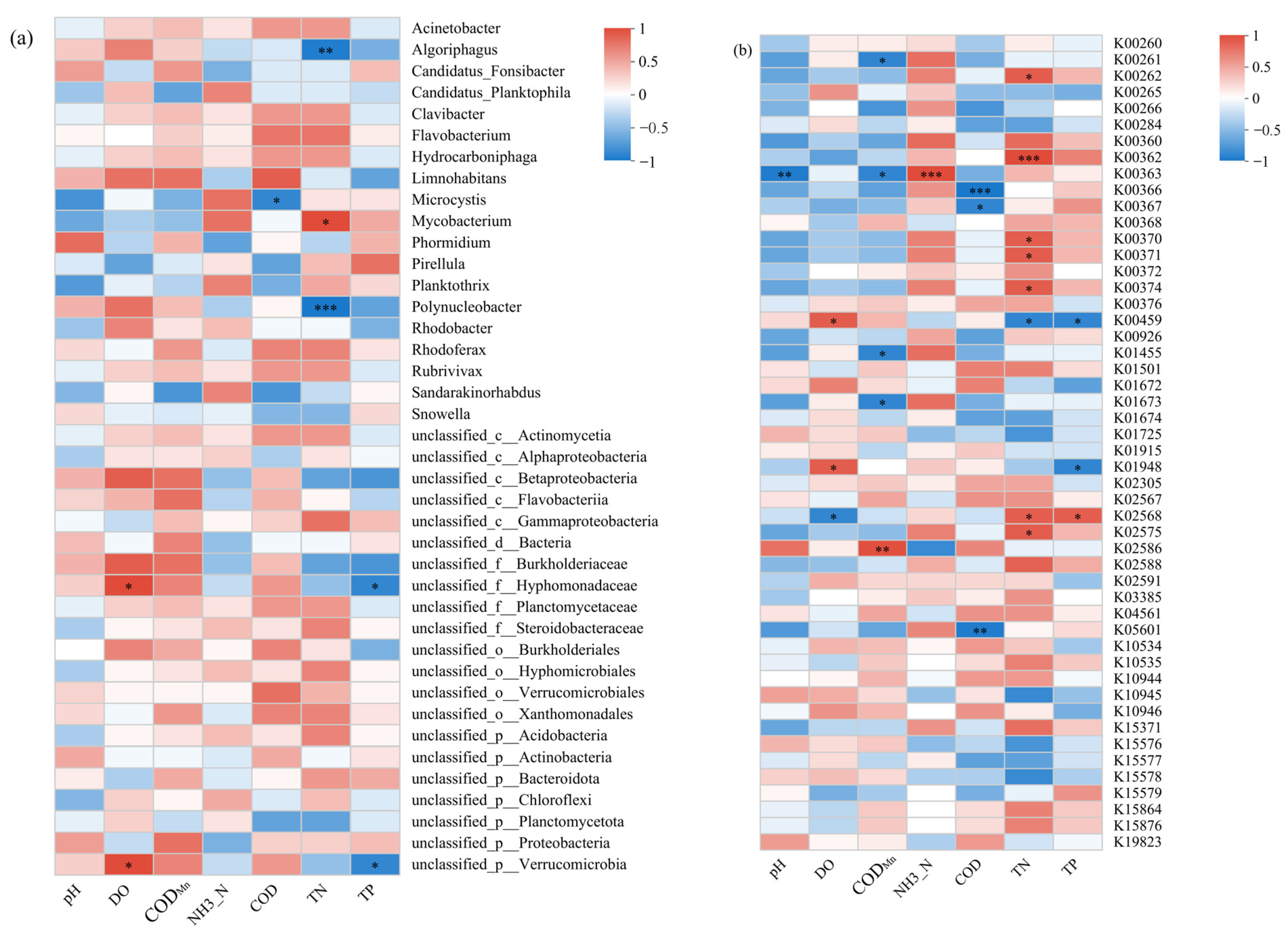
3.3.2. Correlations Between Physicochemical Factors, Bacterial Communities, and KEGG Metabolic Functions
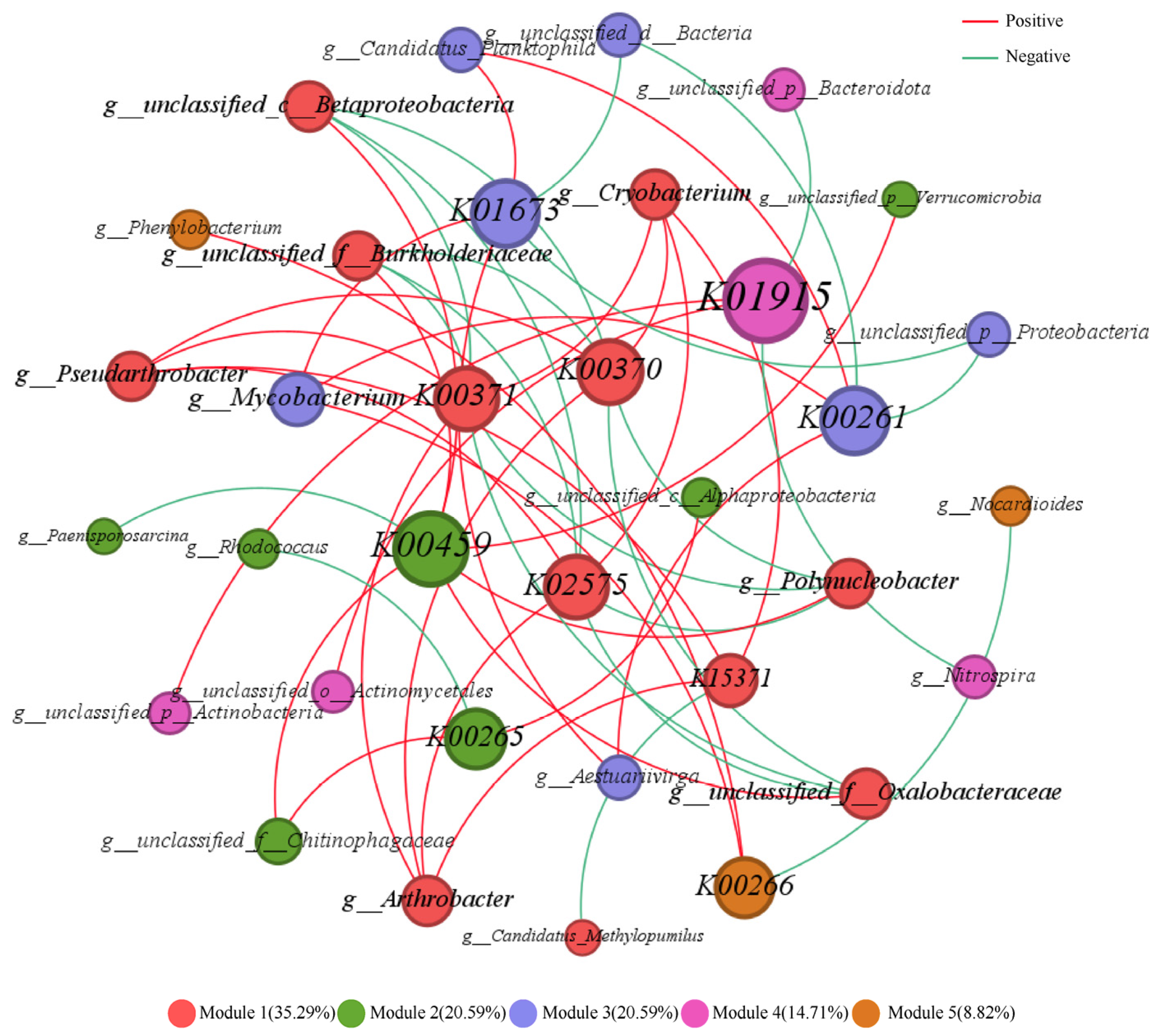
3.3.3. Analysis of Co-Occurrence Networks Between Microorganisms and Nitrogen Metabolism Functional Genes
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Quality Analysis of the Xisha River
4.2. Microbiological Diversity of the Xisha River
4.3. Microbial Community Composition of the Xisha River
4.4. Analysis of Nitrogen Metabolism in the Xisha River
4.5. Correlation Analysis of Environmental Factors with Microbial Communities and Nitrogen Metabolism Genes in Xisha River
4.6. Co-Occurrence of Bacterial Communities with Nitrogen Metabolism Genes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; He, G. Rivers: Linking nature, life, and civilization. River 2022, 1, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strokal, M.; Bai, Z.; Franssen, W.; Hofstra, N.; Koelmans, A.A.; Ludwig, F.; Ma, L.; van Puijenbroek, P.; Spanier, J.E.; Vermeulen, L.C.; et al. Urbanization: An increasing source of multiple pollutants to rivers in the 21st century. Npj Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Water pollution during China’s industrial transition. Environ. Dev. 2013, 8, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Sanaullah, M.; Ullah, A.; Li, S.; Farooq, M. Nitrogen Pollution Originating from Wastewater and Agriculture: Advances in Treatment and Management. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 260, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xue, H.; Xu, T.; Liu, K.; Xian, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Spatio-temporal evolution mechanism and dynamic simulation of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution of the Yangtze River economic Belt in China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 357, 124402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijay, S.; Craswell, E. Fertilizers and nitrate pollution of surface and ground water: An increasingly pervasive global problem. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Bi, Z.; Shan, Z.; Ren, L. The deep challenge of nitrate pollution in river water of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Bae, H.-S.; Reddy, K.R.; Ogram, A. Distributions, abundances and activities of microbes associated with the nitrogen cycle in riparian and stream sediments of a river tributary. Water Res. 2016, 106, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Niu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Nitrogen cycling processes and the role of multi-trophic microbiota in dam-induced river-reservoir systems. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; et al. Response of nitrogen pollution in surface water to land use and social-economic factors in the Weihe River watershed, northwest China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Xiong, L.; Wang, F. The spatial spillover effect and impact paths of agricultural industry agglomeration on agricultural non-point source pollution: A case study in Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 401, 136600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoo, R.; Suman, B.M. Microbial roles in the terrestrial and aquatic nitrogen cycle—Implications in climate change. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2023, 370, fnad061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Su, C.; Geng, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, W.; Pan, H.; Xie, X.; Feng, G. Novel insights into the DOM-driven processes affecting nitrogen cycling in shallow aquifers of the West Liao River Plain: Evidence from FT-ICR MS and isotope analyses. J. Hydrol. 2025, 655, 132969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bouwman, A.F.; Vilmin, L.; Beusen, A.H.W.; van Hoek, W.J.; Liu, X.; Middelburg, J.J. Global inland-water nitrogen cycling has accelerated in the Anthropocene. Nat. Water 2024, 2, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ruan, X.; Le, F.; Chen, S.; Chen, T. Multi-element coupling effect of nitrogen cycling in an intensively dam-controlled river system. J. Hydrol. 2025, 651, 132648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.H.; Zhang, S.B.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, L.W.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.F.; Li, Z.H. The cycle of nitrogen in river systems: Sources, transformation, and flux. Environ. Sci.-Process. IMPACTS 2018, 20, 863–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Fang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, H.; Zhang, S. Impact of different types of anthropogenic pollution on bacterial community and metabolic genes in urban river sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.E.; Wu, S.; Bhattacharjee, A.S.; Hamilton, J.J.; McMahon, K.D.; Goel, R.; Noguera, D.R. Metabolic network analysis reveals microbial community interactions in anammox granules. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wan, W.; Liu, W.; Xiong, X. Metagenomic insights into nitrogen-cycling microbial communities and their relationships with nitrogen removal potential in the Yangtze River. Water Res. 2024, 265, 122229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 1147-2020; Water Quality—Determination of pH Value—Electrode Method. China Environmental Publishing Group Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB 11893-89; Water Quality—Determination of Dissolved Oxygen—Iodometric Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- HJ 636-2012; Water Quality—Determination of Petroleum Hydrocarbons—Infrared Absorption Method. China Environmental Publishing Group Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GB 7489-87; Water Quality—Determination of Fluoride—Ion Selective Electrode Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1987.
- GB 11892-89; Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus—Molybdenum Blue Colorimetric Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- HJ 536-2009; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen—Nessler Reagent Spectrophotometric Method. China Environmental Publishing Group Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 32208-2015; Water Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Persulfate Digestion-UV Spectrophotometric Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; Locascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP: Short oligonucleotide alignment program. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality—Standard for Surface Water. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Wang, D.; Zheng, Q.C.; Lv, Q.; Cai, Y.Q.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.D.; Zhang, W.M. Analysis of Community Composition of Bacterioplankton in Changle Seawater in China by Illumina Sequencing Combined with Bacteria Culture. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Li, P.; Luo, Y.; Yan, H.; Liu, J.; Pan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Insights of microalgal municipal wastewater treatment at low temperatures: Performance, microbiota patterns, and cold-adaptation of tubular and aeration column photobioreactors. Chemosphere 2023, 340, 139910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Zhang, Z.; Mo, S.; Li, J.; He, S.; Kashif, M.; Liang, Z.; Shen, P.; Yan, B.; Jiang, C. Desulfobacterales stimulates nitrate reduction in the mangrove ecosystem of a subtropical gulf. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, Y.; Xie, T.; Song, Z.; Bai, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Seasonal Variations and Drivers of Total Nitrogen and Phosphorus in China’s Surface Waters. Water 2025, 17, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liang, M.; Qin, Z.; Qian, Y.; Li, M.; Cao, Y. A novel assessment considering spatial and temporal variations of water quality to identify pollution sources in urban rivers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, Q.; Ma, S.; Sun, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Dou, H.; Zhang, H. Factors affecting seasonal variation of microbial community structure in Hulun Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, V.; Cheng, L.; Hussain, A.; Ormeci, B. Nitrogen removal from wastewater: A comprehensive review of biological nitrogen removal processes, critical operation parameters and bioreactor design. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, Z.; Qu, X.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, W. Microbial community structure and functional properties in permanently and seasonally flooded areas in Poyang Lake. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J. Microbial interspecific interaction and nitrogen metabolism pathway for the treatment of municipal wastewater by iron carbon based constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Narihiro, T.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.-X.; Ren, H.; Ye, L. Diverse aromatic-degrading bacteria present in a highly enriched autotrophic nitrifying sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. Tracking composition and dynamics of nitrification and denitrification microbial community in a biofilm reactor by PCR-DGGE and combining FISH with flow cytometry. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 49, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, G.; Li, R. Genotypes of ITS region of rRNA in Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) populations in Erhai Lake (China) and their correlation with eutrophication level. J. Basic Microbiol. 2015, 55, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Carrión, V.J. Importance of Bacteroidetes in host–microbe interactions and ecosystem functioning. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Xing, Y.; Ding, A.; Sun, S.; Cheng, H.; Bian, Z.; Yang, K.; Wang, S.; Zhu, G. Brownification of freshwater promotes nitrogen-cycling microorganism growth following terrestrial material increase and ultraviolet radiation reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaresan, M.; Manoharan, M.; Sugumar, M.; Sistla, S. Species distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of Burkholderia cepacia complex isolates in clinical infections: Experience from a tertiary care hospital, Southern India. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2024, 49, 100613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Xie, X.; Feng, F.; Huang, S.; Sun, Y. Impact of acyl-homoserine lactones on the response of nitrogen cycling in sediment to florfenicol stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, G.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Tan, W.; Bao, S.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Hu, X.; Xi, B. Macrogenomic analysis of the effects of aqueous-phase from hydrothermal carbonation of sewage sludge on nitrogen metabolism pathways and associated bacterial communities during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 389, 129811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, C.; Cai, J.; Hu, Y.; Shao, K.; Tang, X.; Gong, Y.; Yao, X.; Xu, Q.; Gao, G. Relationships between environmental factors and N-cycling microbes reveal the indirect effect of further eutrophication on denitrification and DNRA in shallow lakes. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, H.K.; Holtappels, M.; Lavik, G.; Ahmerkamp, S.; Winter, C.; Kuypers, M.M.M. Coupled nitrification–denitrification leads to extensive N loss in subtidal permeable sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, B.; Li, P.; Chen, A.; Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Organic management promotes nitrogen transformation in tea plantations soil: A case study from southwestern China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 206, 105878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.-C.; He, Y.-H.; Li, J. Functional Genes and Metabolic Pathways of Nitrogen Metabolism Microorganisms in Lake Sediments:A Case Study of Hongfeng Lake, Guizhou Province. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 45, 6086–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.-R.; Rohde, M. The Family Hyphomonadaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Alphaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 283–299. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Stevens, S.L.R.; Chan, L.K.; Bertilsson, S.; Glavina Del Rio, T.; Tringe, S.G.; Malmstrom, R.R.; McMahon, K.D. Ecophysiology of Freshwater Verrucomicrobia Inferred from Metagenome-Assembled Genomes. Msphere 2017, 2, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerst, J.A. Phylum Verrucomicrobia. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 4th ed.; Schmidt, T.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 551–563. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Yang, Y.-L.; Liu, Y.-W.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.-B. Quantitative ecology associations between heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification, nitrogen-metabolism genes, and key bacteria in a tidal flow constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ping, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Insight into using multi-omics analysis to elucidate nitrogen removal mechanisms in a novel improved constructed rapid infiltration system: Functional gene and metabolite signatures. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Du, S.; Guo, H.; Min, W. Long-term saline water drip irrigation alters soil physicochemical properties, bacterial community structure, and nitrogen transformations in cotton. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
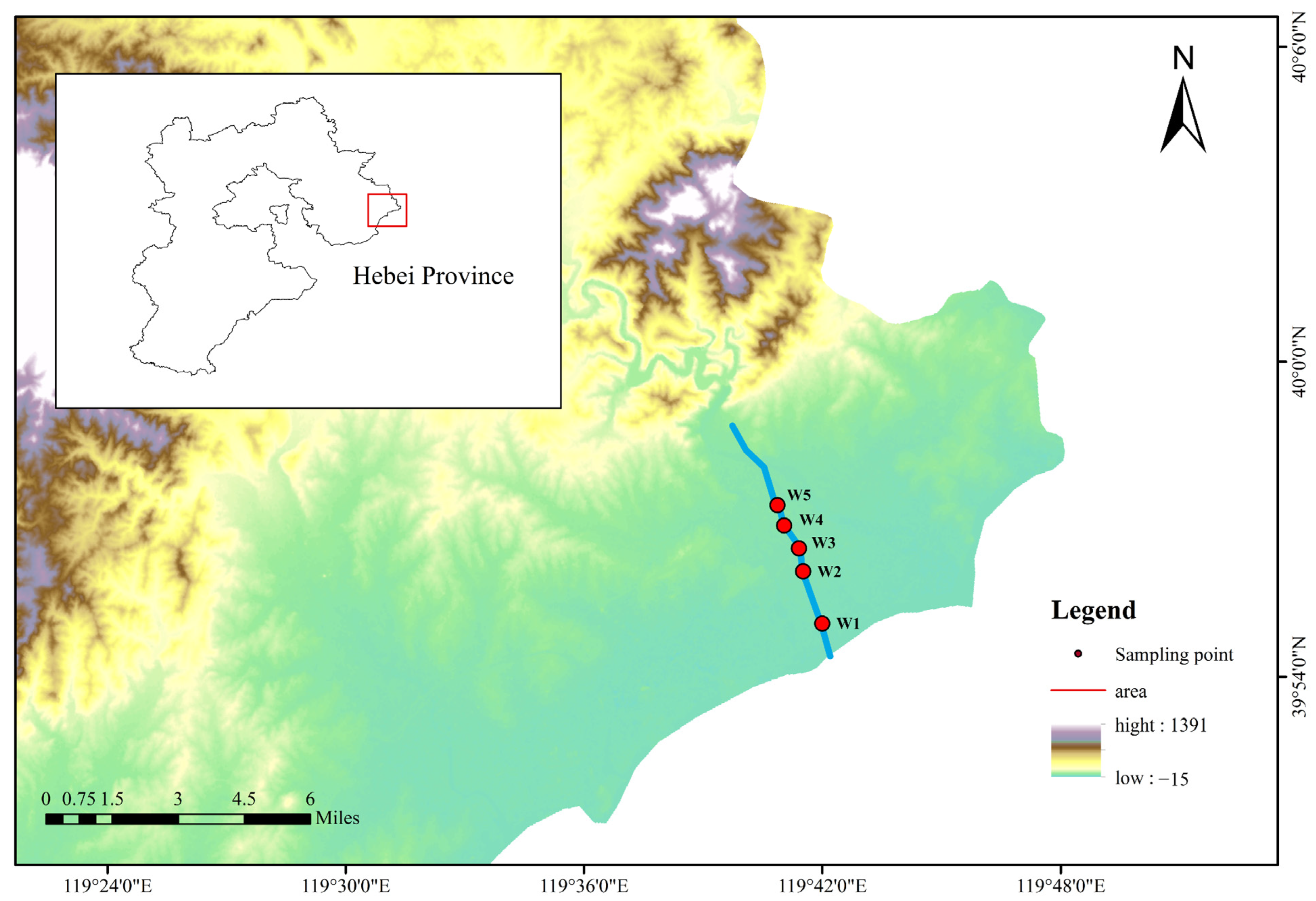

| Sampling Position | Sample Number | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| XSH-1 | W1 | 119°43′22.468″ | 39°57′9.652″ |
| XSH-2 | W2 | 119°43′11.683″ | 39°58′14.829″ |
| XSH-3 | W3 | 119°43′13.429″ | 39°58′42.198″ |
| XSH-4 | W4 | 119°42′59.135″ | 39°59′12.550″ |
| XSH-5 | W5 | 119°42′56.160″ | 39°59′37.625″ |
| Sample | Ace | Chao | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 307 | 307 | 3.807541 | 0.053817 |
| W2 | 427 | 427 | 3.813537 | 0.062374 |
| W3 | 442 | 442 | 4.1318 | 0.047394 |
| W4 | 321 | 321 | 4.321787 | 0.028587 |
| W5 | 496 | 496 | 4.659883 | 0.024094 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Wang, R.; Zhao, W. Characteristics of the Water Environment and the Mechanism of Nitrogen Metabolism in the Xisha River. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094060
Yang S, Wang R, Zhao W. Characteristics of the Water Environment and the Mechanism of Nitrogen Metabolism in the Xisha River. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094060
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shang, Ran Wang, and Wei Zhao. 2025. "Characteristics of the Water Environment and the Mechanism of Nitrogen Metabolism in the Xisha River" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094060
APA StyleYang, S., Wang, R., & Zhao, W. (2025). Characteristics of the Water Environment and the Mechanism of Nitrogen Metabolism in the Xisha River. Sustainability, 17(9), 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17094060






