What Role Does “Great Heritage Site” Conservation Play in Shaping Sustainable Urban Intensity Patterns? An Empirical Study from Luoyang
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. An Introduction of the Study Area
3. Data Sources and Research Methods
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Research Methods
3.2.1. Development Intensity Index Representation
- Floor Area Ratio (FAR)
- 2.
- Building height
3.2.2. Spatial Correlation Analysis
3.2.3. Kernel Density Analysis
3.2.4. Viewshed Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Land Use Types and Area Proportions for Planned Construction
4.2. Characterization of Planned Construction Development Intensity Indicators
4.3. The Spatial Distribution of Planned Development Intensity
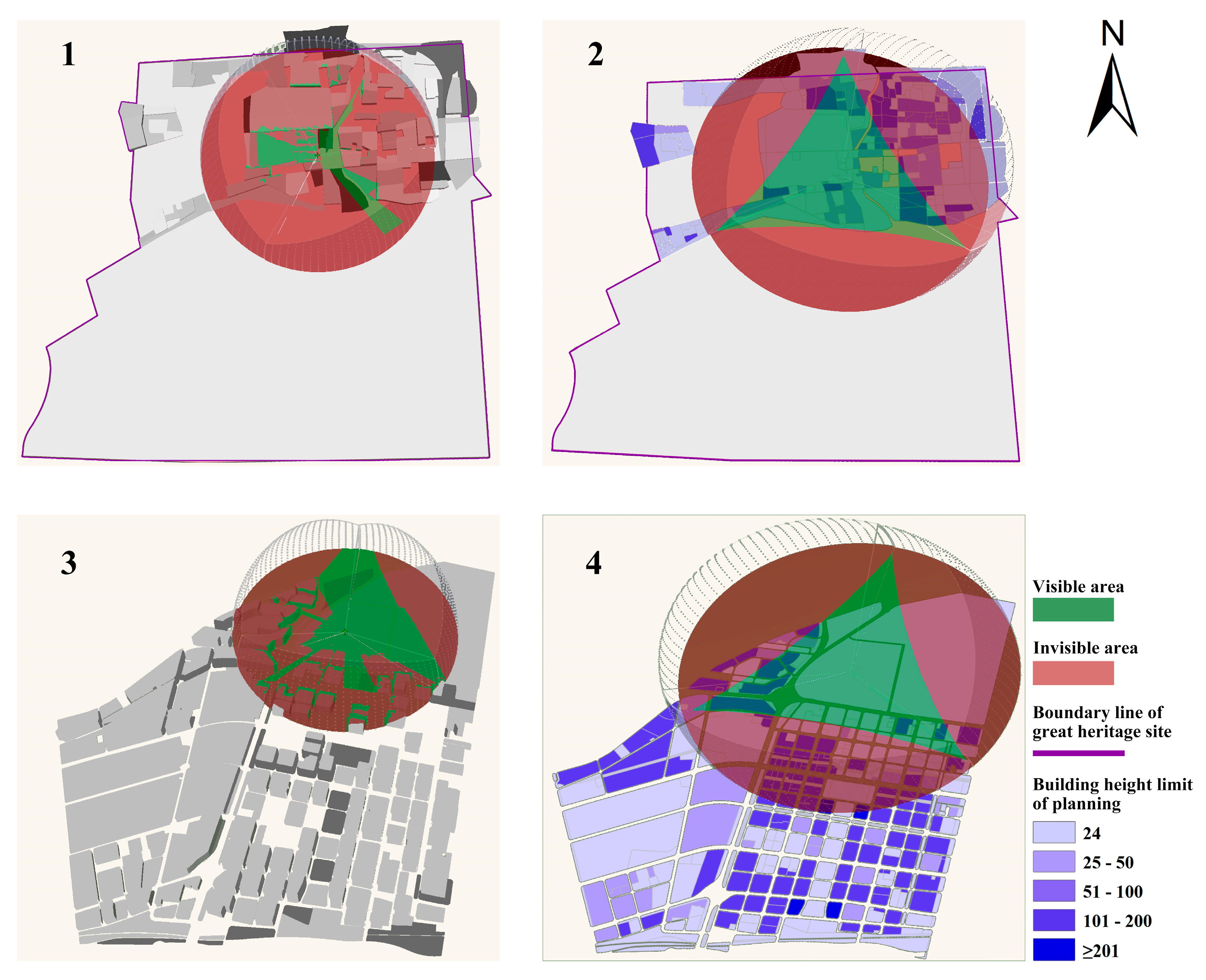
4.4. Viewshed Loss in Heritage Protection Planning
5. Discussion
5.1. Linking the Conservation of the Great Heritage Site with the Intensity of Urban Development
5.2. Cultural Heritage Tourism Overload Risks and Impacts on Urban Construction
5.3. Comparison with Other Studies
5.4. Policy Recommendations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Bank; International Monetary Fund. Global Monitoring Report 2013: Rural-Urban Dynamics and the Millennium Development Goals; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zeng, W.; Yang, X. Coupling coordination evaluation and sustainable development pattern of geo-ecological environment and urbanization in Chongqing municipality, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, L.; Wei, H.; Tan, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Qian, Y. Linking urbanization and air quality together: A review and a perspective on the future sustainable urban development. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 130988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A.I.; Cobbinah, P.B. Can rapid urbanization be sustainable? The case of Saudi Arabian cities. Habitat Int. 2023, 139, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Abbas, J.; He, C.; Pilař, L.; Shah, S.A.R. Tourism, urbanization and natural resources rents matter for environmental sustainability: The leading role of AI and ICT on sustainable development goals in the digital era. Resour. Policy 2023, 82, 103445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Gu, R. Spatial-temporal evolution pattern of multidimensional urban shrinkage in China and its impact on urban form. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 159, 103062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, D. History, modernity, and city branding in China: A multimodal critical discourse analysis of Xi’an’s promotional videos on social media. Soc. Semiot. 2023, 33, 402–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J. An Introduction to Urban Design; HarperCollins Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Brunn, S.D.; Williams, J.F.; Zeigler, D.J. Cities of the World: World Regional Urban Development; Rowman & Littlefield: Lanham, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pincetl, S. Nature, urban development and sustainability–what new elements are needed for a more comprehensive understanding? Cities 2012, 29, S32–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.E. Form and meaning in the earliest cities: A new approach to ancient urban planning. J. Plan. Hist. 2007, 6, 3–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Council of the People’s Republic of China, the National Cultural Heritage Administration, Notice on Issuing the “14th Five-Year Special Plan for the Protection and Utilization of Major Heritage Sites”. 12 October 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-11/19/content_5651816.htm (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Xue, L. Research on management and control of the complex site space in territorial space planning. Urban Dev. Studies 2022, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X. Dream glory: Construction of our large site protection display system and park—Discussion on the protection ideas of large sites in china. Southeast Cult. 2001, 1, 6–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J. The big cultural sites in china: Protection cases, existing problems and suggestions. Fudan J. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2005, 6, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Quan, D. The channel of the great relics protection and the region economic harmony development: To develop the great relics cultural industrial cluster. Econ. Geogr. 2007, 27, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tian, R. Study on the construction of theoretical approaches and research frameworks for the protection of complex site. J. Northwest Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 51, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Chen, L. An innovative study on urban large sites under perspective of TEEB. Environ. Prot. 2016, 44, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M. Discussion on the Conservation and Utilization Mode of Earthen Sites: A Case Study of Xi’an Area. Southeast Cult. 2011, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, P. Research Progress and Trend of Archaeological Site Park. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2019, 35, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K. Interpretation of the overall planning for Daming Palace National Relics Protection and Demonstration Park and Relics Park. China Cult. Herit. 2009, 4, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Bi, J.; Lv, Z. A sustainable development research based on the overall protection of city big site area—Taking Xi’an Daming palace ruins for example. Archit. Cult. 2014, 8, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J. Protection and Display of Large Urban Sites: A Case Study of the Practice in Sui-Tang Luoyang City. Archit. J. 2012, 6, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Analysis and Reflection on the Status Quo of the Studies on Conservation and Use of Largescale Sites:Based on Knowledge Mapping Based on CSSCI Literature. China Cult. Herit. 2022, 4, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Xiao, J.; Kuang, X.; Zhang, S. The “Nature-based Solutions” of Linking City Development with the Preservation of Great Sites Urban Planning Forum. Urban Plan. Forum 2021, 1, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, S. Multi-Value Paths of Urban Heritage Site Conservation and Utilization: A Case Study of Xi’an City. Mod. Urban Res. 2022, 7, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. A Research on Heritage Preservation Strategies Based on City Planning. J. Chifeng Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Chin. Ed.) 2022, 43, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, D.; Qin, M.; Jing, W. Spatial heterogeneity analysis and driving forces exploring of built-up land development intensity in Chinese prefecture-level cities and implications for future Urban Land intensive use. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C.; Ramankutty, N. Putting people in the map: Anthropogenic biomes of the world. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yan, H.; Liu, J.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y. Spatial pattern of land use intensity in China in 2000. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1130–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Erb, K.-H.; Haberl, H.; Jepsen, M.R.; Kuemmerle, T.; Lindner, M.; Müller, D.; Verburg, P.H.; Reenberg, A. A conceptual framework for analysing and measuring land-use intensity. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. The intensity change of urban development land: Implications for the city master plan of Guangzhou, China. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, U.; Stein, C. Indicators of hemeroby for the monitoring of landscapes in Germany. J. Nat. Conserv. 2014, 22, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellmann, T.; Haase, D.; Knapp, S.; Salbach, C.; Selsam, P.; Lausch, A. Urban land use intensity assessment: The potential of spatio-temporal spectral traits with remote sensing. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainstein, S.S. Planning theory and the city. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2005, 25, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, M.B.; Haupt, P.A. Spacematrix. Space, Density and Urban Form; NAi Publishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, W.; Rijs, J.V.; Koek, R. Farmax: Excursions on Density; 010 Uitgeverij Publishers: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Song, W. Evolution of rural settlements in the Tongzhou District of Beijing under the new-type urbanization policies. Habitat Int. 2020, 101, 102198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Resource and Environmental Science Information Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Available online: https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Geospatial Data Cloud Platform. Available online: https://www.gscloud.cn/ (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Tan, S.; Liu, Q.; Han, S. Spatial-temporal evolution of coupling relationship between land development intensity and resources environment carrying capacity in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Gao, H.; Song, X.; Xu, H. Convergence or divergence between small towns and villages: A perspective from changes in built-up land development intensity. Habitat Int. 2023, 138, 102874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50137-2011; Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, Code for Classification of Urban Land Use and Planning Standards of Development Land. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GBT50280-98; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Standard of Basic Urban Planning Terminology. Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Anselin, L. An Introduction to Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis with GeoDa Spatial Analysis Laboratory; University of Illinois: Champagne-Urbana, IL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dormann, C.F.; McPherson, J.M.; Araújo, M.B.; Bivand, R.; Bolliger, J.; Carl, G.; Davies, R.G.; Hirzel, A.; Jetz, W.; Daniel Kissling, W. Methods to account for spatial autocorrelation in the analysis of species distributional data: A review. Ecography 2007, 30, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, B.; Tiefelsdorf, M. Global and local spatial autocorrelation in bounded regular tessellations. J. Geogr. Syst. 2000, 2, 319–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Testing for local spatial autocorrelation in the presence of global autocorrelation. J. Reg. Sci. 2001, 41, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambom, A.Z.; Ronaldo, D. A review of kernel density estimation with applications to econometrics. Int. Econom. Rev. 2013, 5, 20–42. [Google Scholar]
- De Smith, M.; Goodchild, M.; Longley, P. Geospatial Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Principles, Techniques and Software Tools; Troubador: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Throsby, D. Economics and Culture; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Xin, Z.; Sun, D. Urban land use effects of high-speed railway network in China: A spatial spillover perspective. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Long, F.; Chang, Z.; Ye, J. Ghost town or city of hope? The spatial spillover effects of high-speed railway stations in China. Transp. Policy 2019, 81, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinahan, K.L. Historic preservation as a community development tool in legacy city neighbourhoods. Community Dev. J. 2019, 54, 581–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecemis Kilic, S. Preservation plan applications for the historical city centre, Kemeralti (Izmir, Turkey). Eur. Plan. Stud. 2008, 16, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, I. Planning for change, conserving the past: Towards sustainable development policy in historic cities? Cities 1997, 14, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L. Research on Conservation and Construction to the Surrounding Spatial Setting of Xi’an Great Heritage Sites; Tsinghua University Press: Bejing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
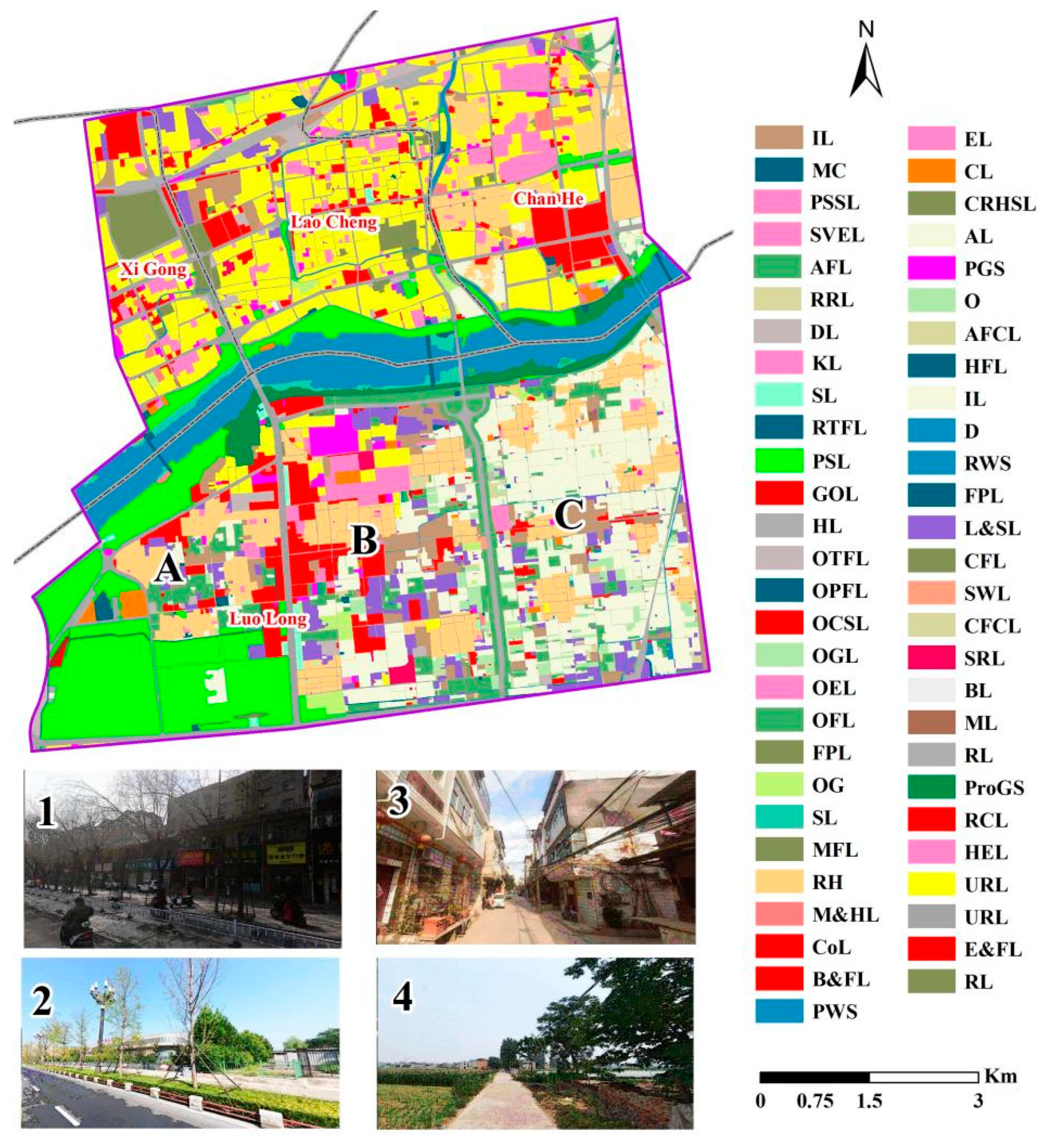
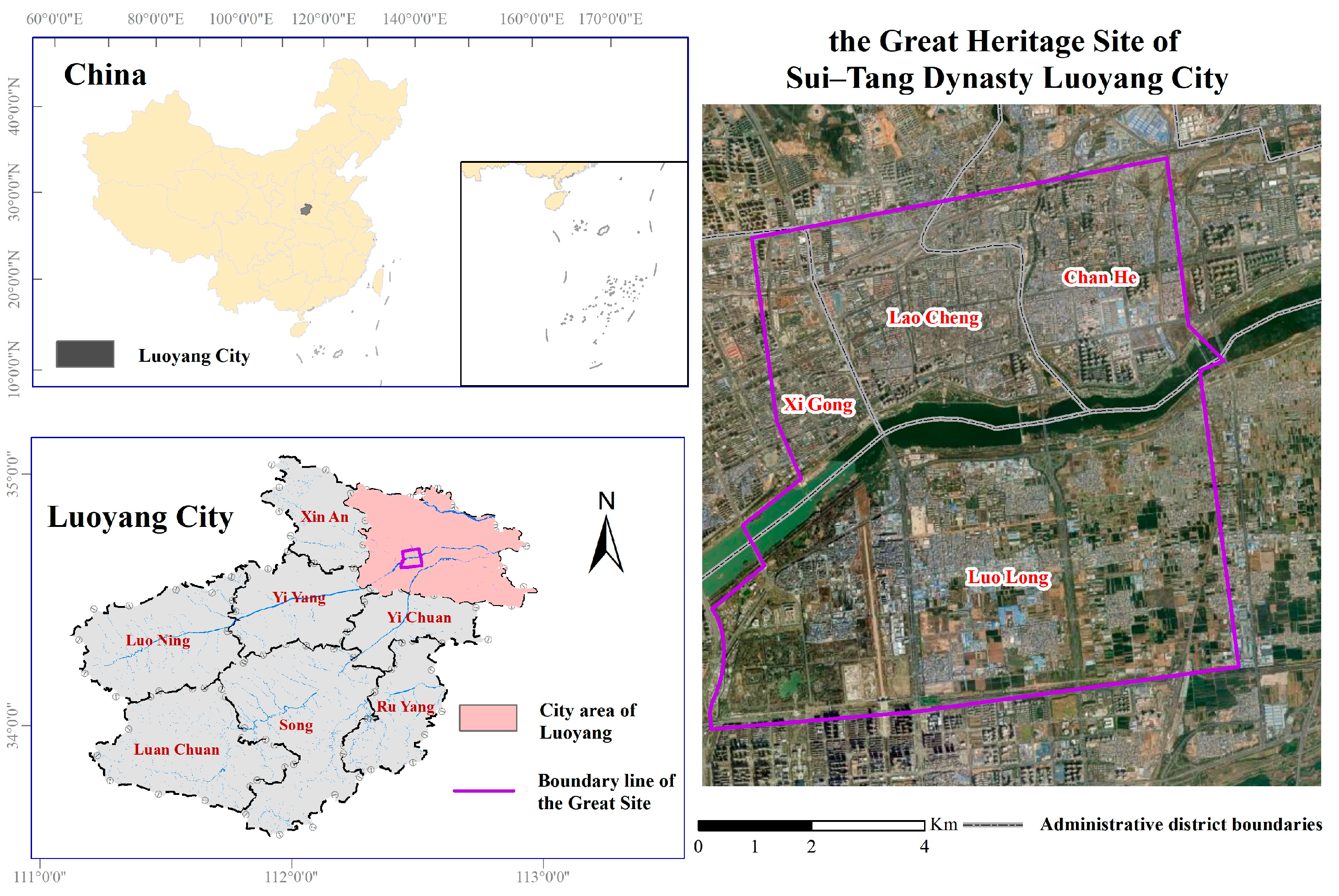
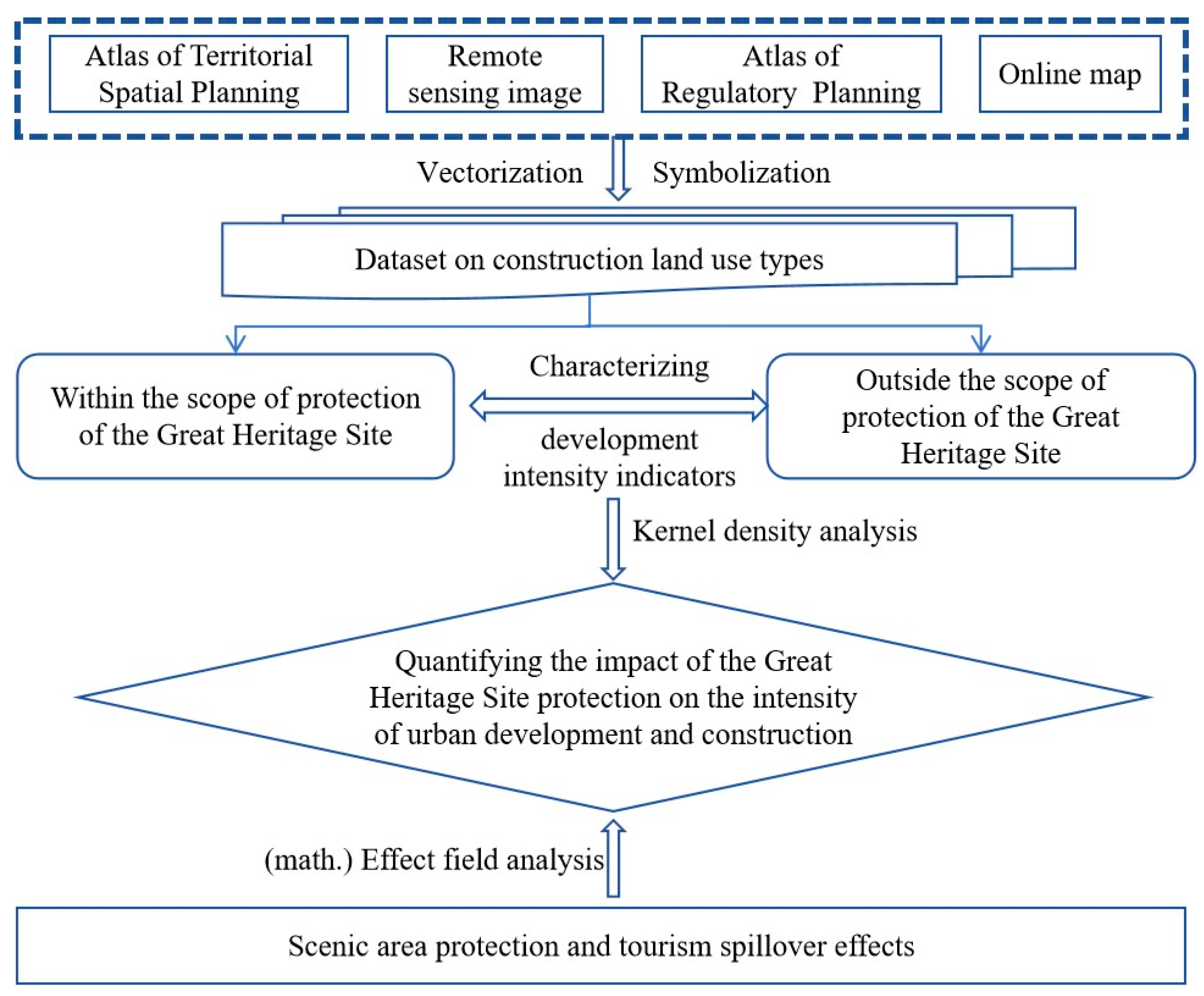

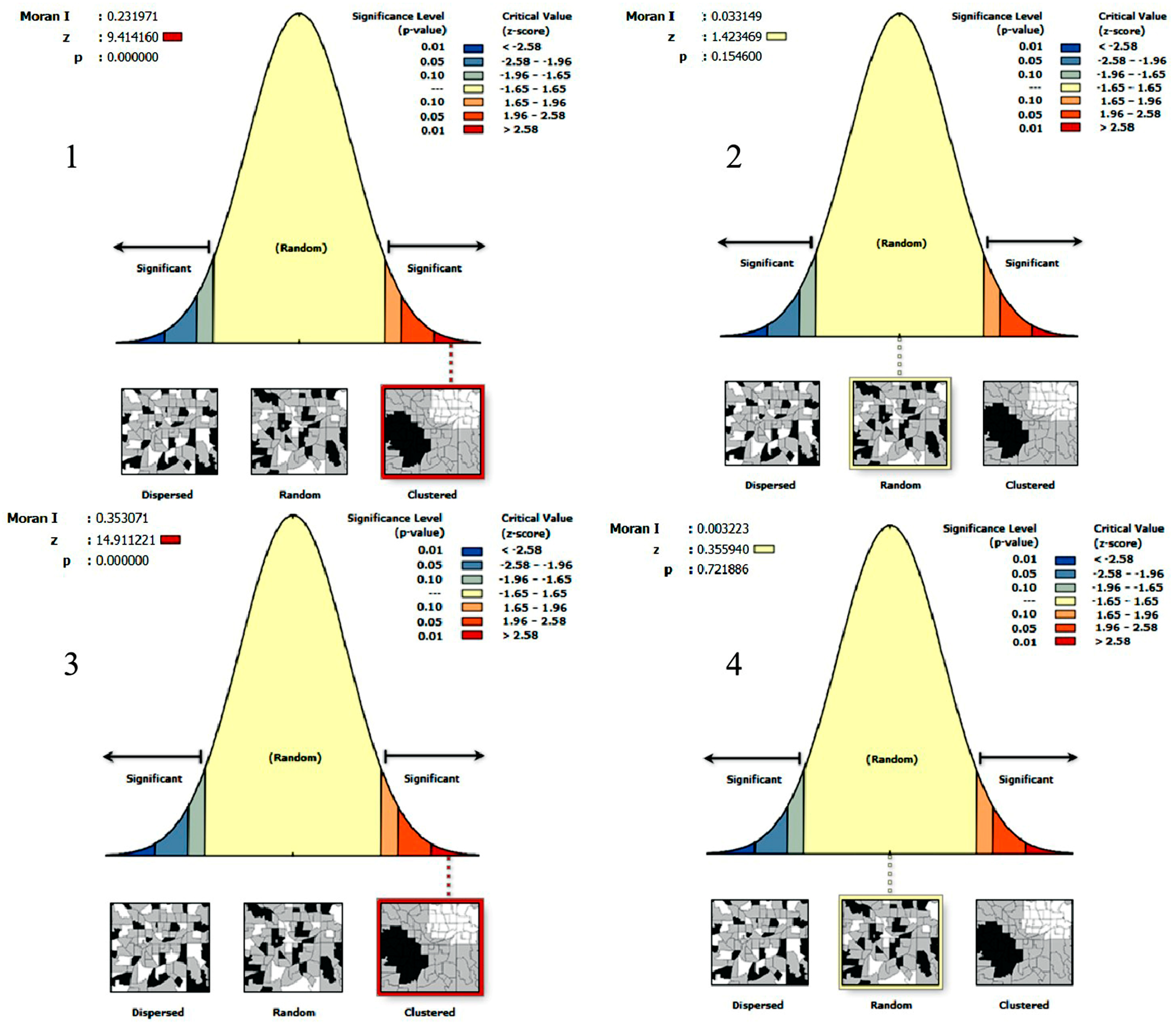
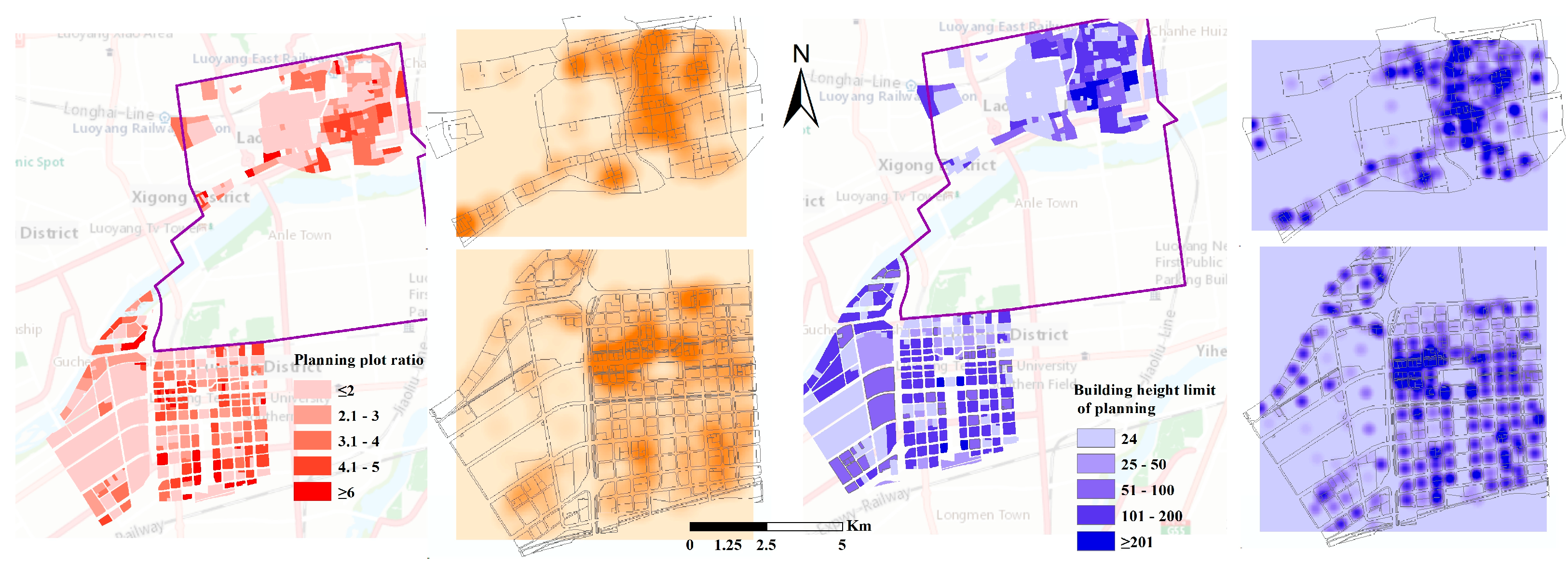
| Land Use Type | Within the Scope of the Great Heritage Site | Outside the Scope of the Great Heritage Site | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (Hectares) | Percentage | Area (Hectares) | Percentage | |
| Residential | 657.89 | 35.96% | 772.66 | 27.91% |
| Administration and public services | 172.91 | 9.45% | 608.88 | 21.99% |
| Commercial and business facilities | 169.5 | 9.26% | 146.06 | 5.28% |
| Industrial and manufacturing | 0 | 0.00% | 0 | 0.00% |
| Logistics and warehouse | 4.01 | 0.22% | 0 | 0.00% |
| Road, street, and transportation | 427.21 | 23.35% | 650.69 | 23.50% |
| Municipal utilities | 44.71 | 2.44% | 15.91 | 0.57% |
| Green space and square | 339.21 | 18.54% | 486.44 | 17.57% |
| Water and other land | 14.11 | 0.77% | 87.73 | 3.17% |
| Total | 1829.55 | 100.00% | 2768.37 | 100.00% |
| Development Intensity Indicators | Within the Great Heritage Site Area | Luolong District (Outside the Great Heritage Site Area) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plot Size (Hectares) | Proportions | Plot Size (Hectares) | Proportions | ||
| FAR | ≤2 | 803.5 | 43.92% | 1264.46 | 45.68% |
| 2.1–3 | 202.69 | 11.08% | 359.03 | 12.97% | |
| 3.1–4 | 301.96 | 16.50% | 339.18 | 12.25% | |
| 4.1–5 | 163.14 | 8.92% | 243.94 | 8.81% | |
| ≥6 | 89.55 | 4.89% | 120.66 | 4.36% | |
| Building height | 24 | 781 | 42.69% | 782.49 | 28.27% |
| 25–50 | 292.06 | 15.96% | 273.25 | 9.87% | |
| 51–100 | 454.72 | 24.85% | 415.1 | 14.99% | |
| 101–200 | 77.99 | 4.26% | 928.73 | 33.55% | |
| ≥201 | 0 | 0.00% | 30.79 | 1.11% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, D.; Cheng, J.; Yin, J.; Li, H. What Role Does “Great Heritage Site” Conservation Play in Shaping Sustainable Urban Intensity Patterns? An Empirical Study from Luoyang. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093882
Kang D, Cheng J, Yin J, Li H. What Role Does “Great Heritage Site” Conservation Play in Shaping Sustainable Urban Intensity Patterns? An Empirical Study from Luoyang. Sustainability. 2025; 17(9):3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093882
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Daxi, Jinlong Cheng, Jie Yin, and Huanhuan Li. 2025. "What Role Does “Great Heritage Site” Conservation Play in Shaping Sustainable Urban Intensity Patterns? An Empirical Study from Luoyang" Sustainability 17, no. 9: 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093882
APA StyleKang, D., Cheng, J., Yin, J., & Li, H. (2025). What Role Does “Great Heritage Site” Conservation Play in Shaping Sustainable Urban Intensity Patterns? An Empirical Study from Luoyang. Sustainability, 17(9), 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093882






