A Comparative Analysis of Circular Economy Practices in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
- Identify the initiatives and opportunities available to Saudi Arabia.
- Benchmark leading countries by examining their established policies and strategies.
- Develop a framework to compare circular economy practices across various countries.
- Analyse these policies using thematic analysis and provide recommendations to support Saudi Arabia’s successful adoption of CE practices.
- Databases and Academic Journals: Major databases like Scopus, ResearchGate, and Google Scholar were accessed to retrieve a wide array of academic papers.
- Governmental and Industry Websites: Official websites of government organisations, such as Eurostat and Vision 2030.
- Policies and Strategies
- Economic and Financial Opportunities
- Resource Management
- Innovation and Technology
- Social Aspects
- Monitoring Framework
- Sustainability Outcomes
- Future Planning
- Government Strategies, Policies, and Initiatives
- Economic Opportunities and Challenges
- Waste Management and Recycling
- Technological Integration and Innovation
- Social and Community Engagement Indicators
- Policy Outcomes
- Future Projects.
3. Comparison of Circular Economy Strategies
3.1. Saudi Arabia
3.1.1. KSA Initiatives
- A.
- Waste management
- Maximising resource efficiency that involves developing processes and facilities to handle various types of waste and convert them into reusable materials or energy.
- Infrastructure development where a focus on building advanced recycling and waste management plants for municipal solid waste, industrial waste, and construction and demolition waste
- Waste-to-energy projects to reduce landfill waste while generating renewable energy, aligning with Vision 2030’s goals to increase the share of renewable energy in the country’s energy mix.
- To secure commitments from institutions to implement waste reduction and recycling initiatives by applying circular models.
- To save the environment by following best practices to reduce waste and maximise its benefits.
- To ensures the adoption of a circular economy by developing a real plan to apply the 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle).
- To spread awareness and engage the community in preserving the environment through waste reduction practices.
- To promote corporate responsibility by transferring the knowledge of waste management concepts and correcting common societal behaviours.
- B.
- Energy
3.1.2. Opportunities
- Conducting thorough planning before implementing a CE strategy could create favourable conditions and attract investment for key CE activities [36].
- Policies that provide clear guidelines and support can encourage stakeholders to adopt CE practices, facilitating a smoother transition toward circularity [3].
- Engaging community leaders—such as public figures and experts in promoting sustainable living and resource efficiency could foster greater acceptance of the CE concept [36].
- Adopting a circular economy could help Saudi Arabia diversify its economy away from dependence on finite oil resources and reduce excessive waste levels [8].
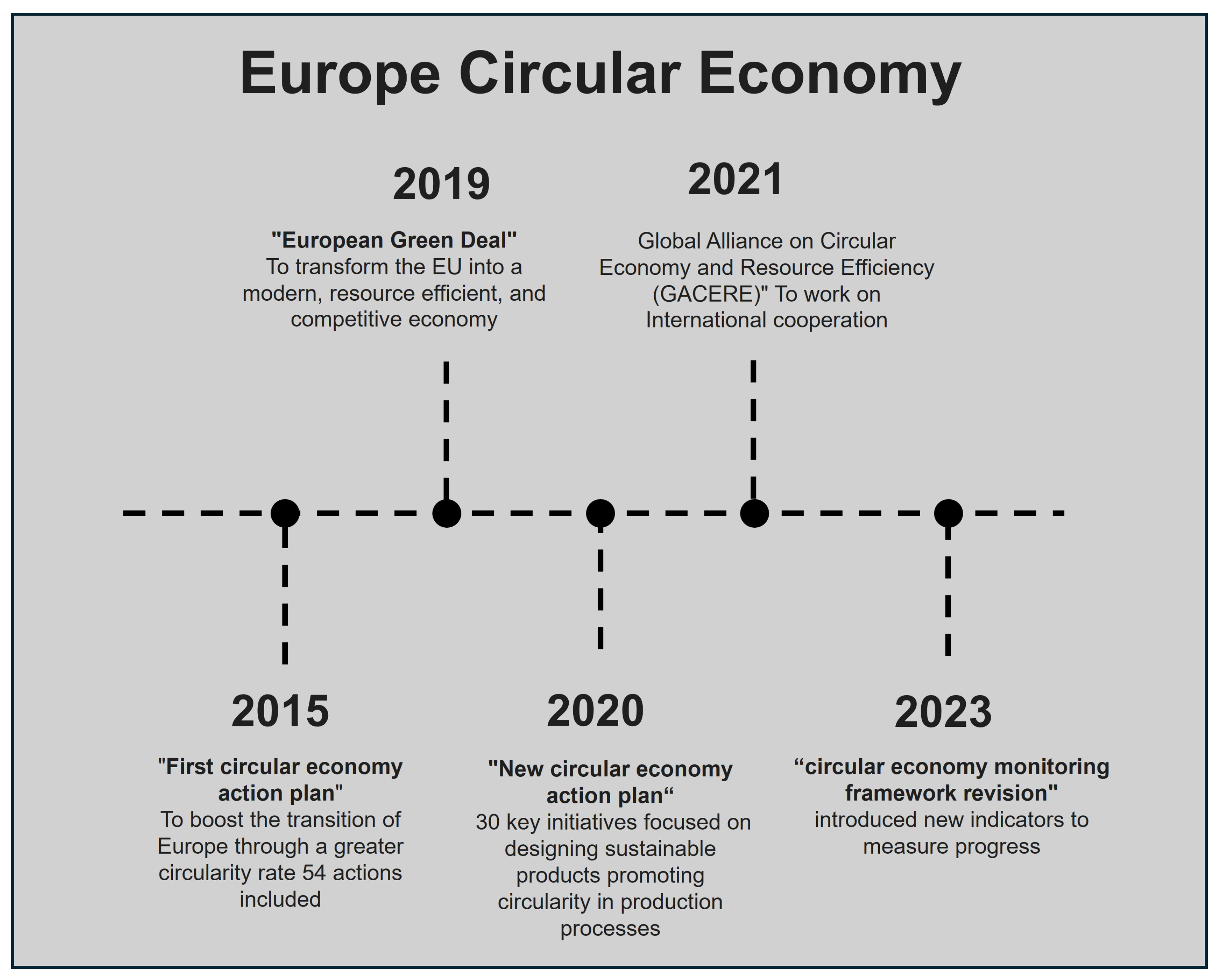
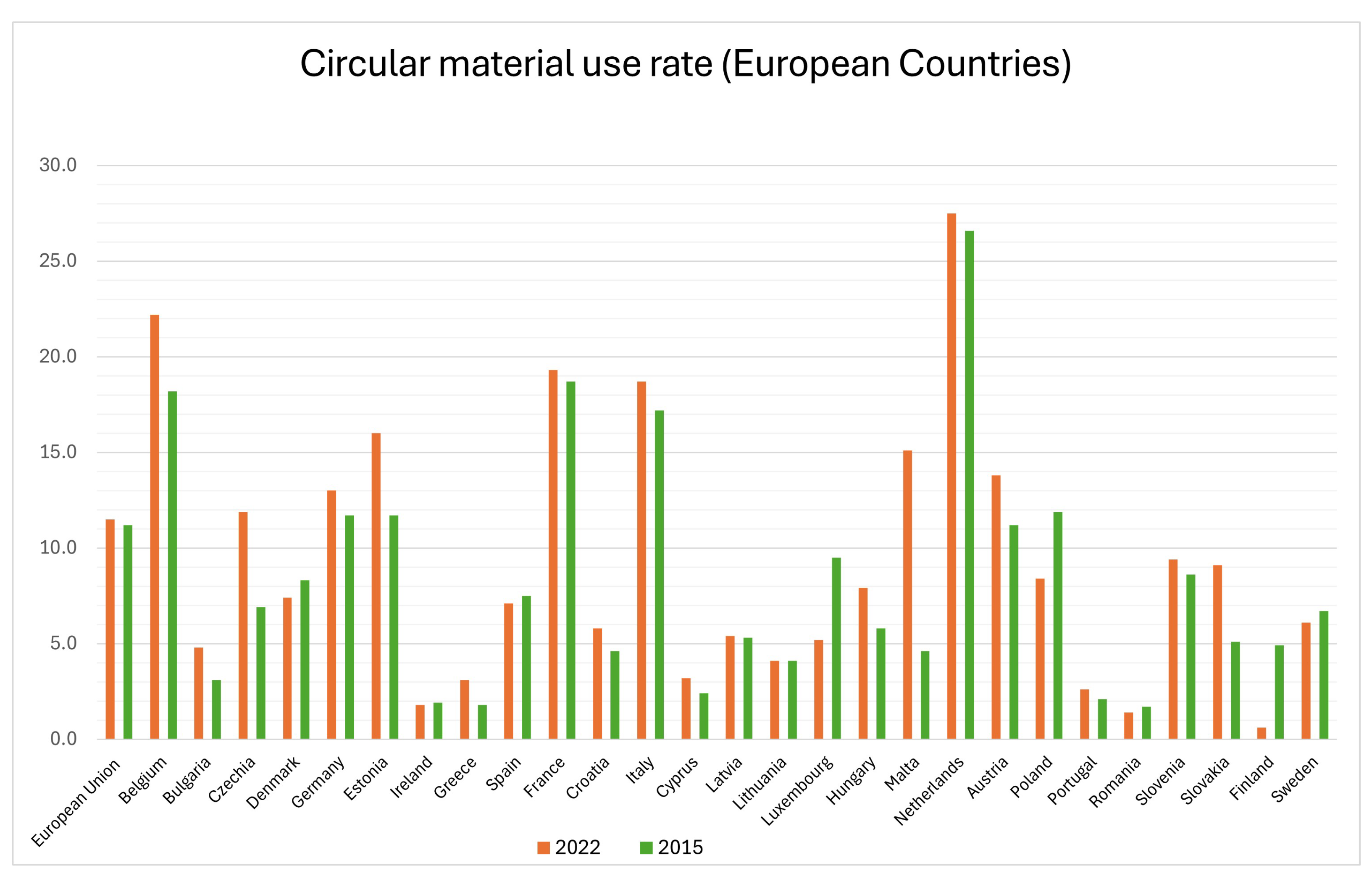
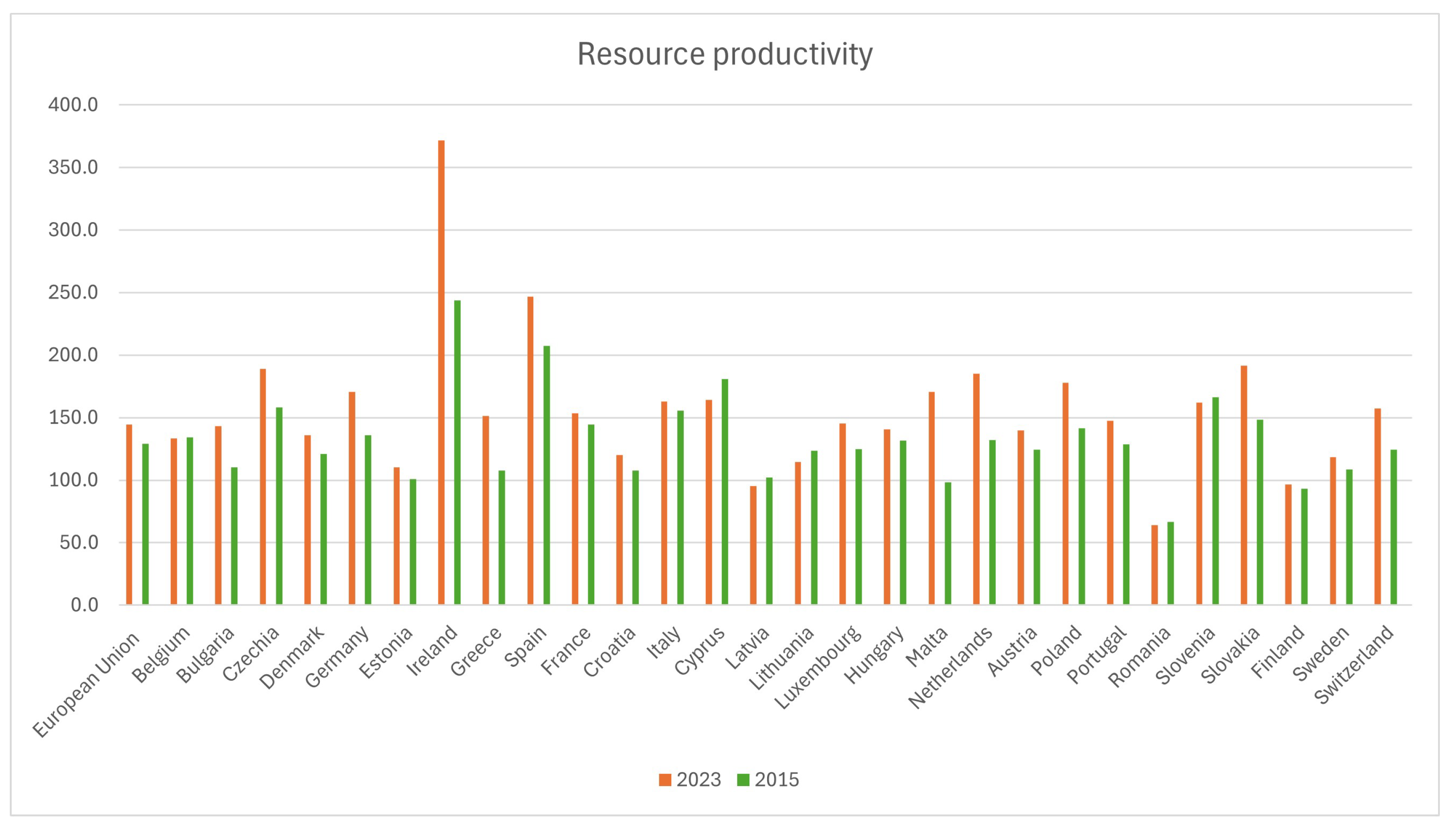
3.2. Europe
3.2.1. Strategies and Policies
3.2.2. Outcomes and Future Directions
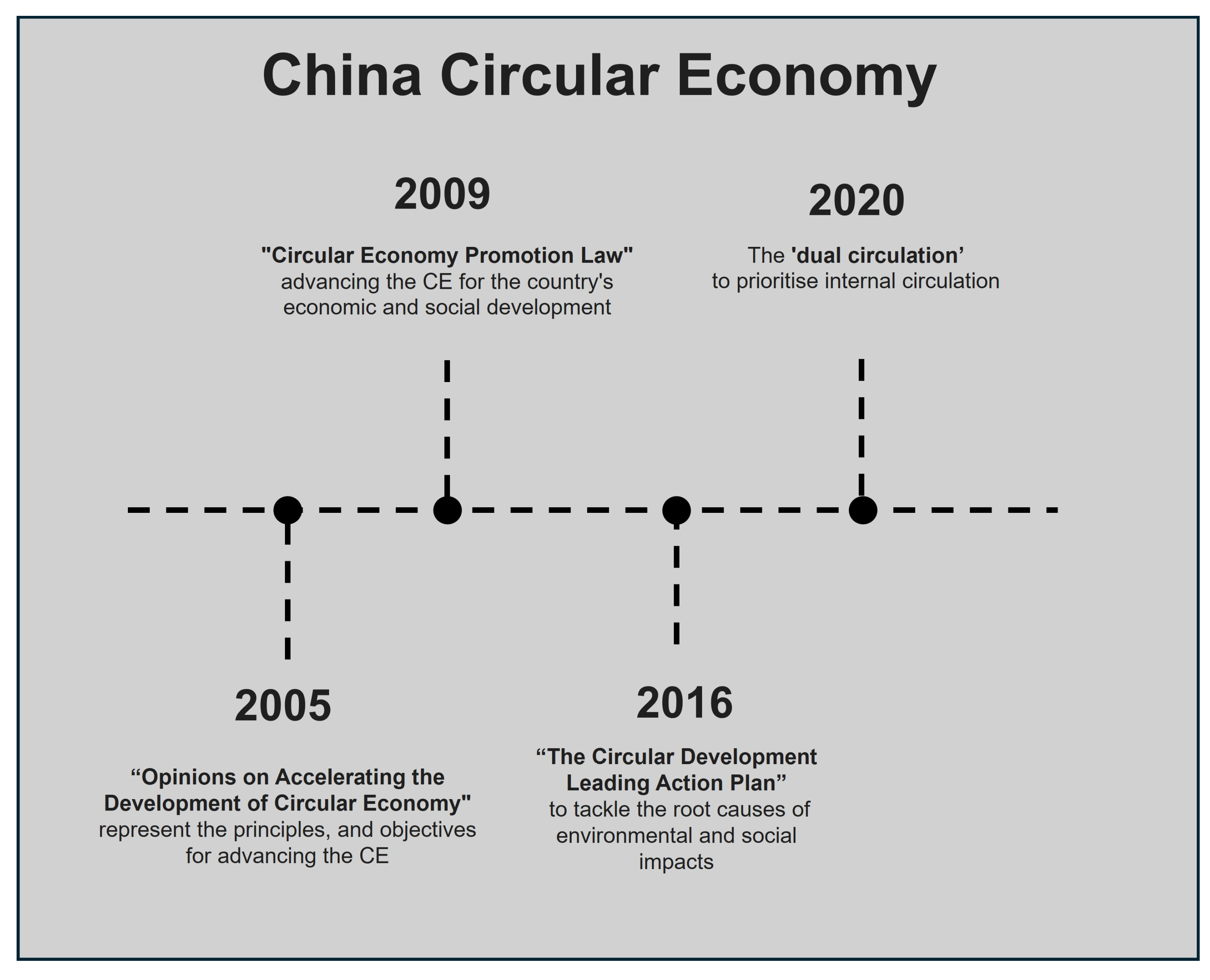
3.3. China
3.3.1. Strategies and Policies
- Achieving 20% more resource productivity than in 2020.
- Reducing the amount of energy and water used per GDP unit by 13.5% and 16%, respectively, in comparison to 2020 levels.
- To process 320 million tonnes of scrap steel and using 60 million tonnes of wastepaper.
3.3.2. Outcomes and Future Directions
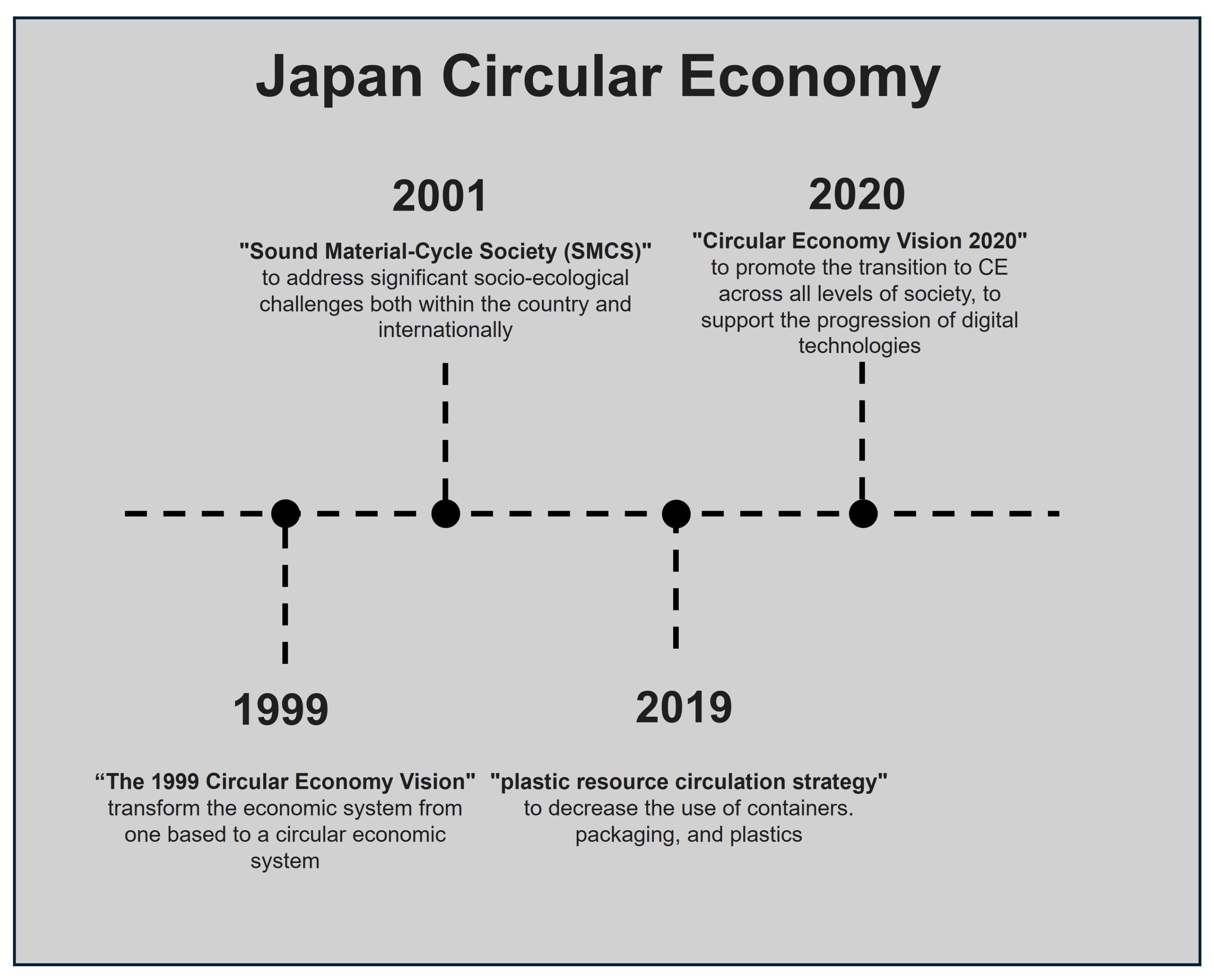
3.4. Japan
3.4.1. Strategies and Policies
- The Way Forward to a Circular Economy System,
- Reconstruction of Waste Management and Recycling Measures,
- Future Challenges and Policy Responses for Establishing CE,
- Current Status and Issues in Individual Areas [53].
- By 2025, recycle and reuse designs for plastic packaging and containers.
- By 2030, reduce single-use plastic waste generation by 25%, recycle and reuse 60% of plastic packaging, and double the amount of recycled plastic.
- By 2035, achieve full reuse of all plastics [21].
3.4.2. Outcomes and Future Directions
4. Discussion
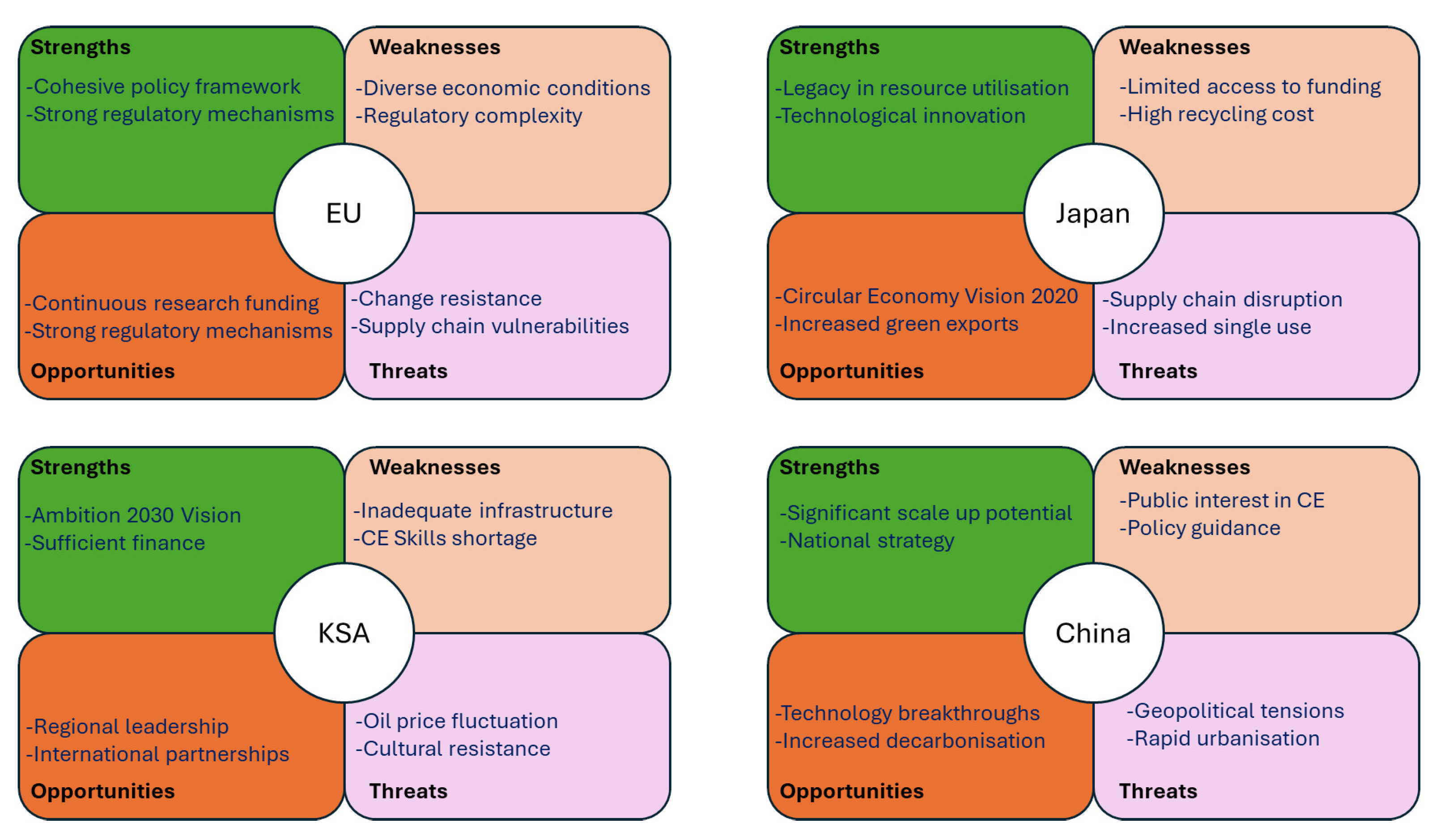
4.1. SWOT Analysis
4.2. Economic and Financial Opportunities
4.3. Outcomes and Achievements
4.4. Recommendations for Saudi Arabia
- Establish a centralised circular economy strategy that aligns efforts across all relevant entities and ensures stakeholder coordination to enhance efficiency and impact.
- Enhance the role of regulatory and legislative bodies in overseeing circular economy initiatives by providing strong institutional backing for effective implementation.
- Set specific, quantifiable goals within the circular economy strategy, such as the practice implemented by the leading countries.
- Offer incentives and support mechanisms to encourage private sector participation in adopting CE. Establish a digital transformation framework that institutionalises digital technologies (e.g., IoT and Big Data) to facilitate the execution of the circular economy strategy.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDW | construction and demolition waste |
| CE | Circular Economy |
| EC | European Commission |
| EIB | European Investment Bank |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| IEA | International Energy Agency |
| MoE | Ministry of Environment |
| MSW | municipal solid waste |
| NDRC | National Development and Reform Commission |
| NCWM | National Centre for Waste Management |
| OECD | Economic Co-operation and Development |
| SIRC | Saudi Investment Recycling Company |
| SMCS | Sound Material-Cycle Society |
| SMEs | Small and Medium Enterprises |
References
- Galli, A.; Kitzes, J.; Niccolucci, V.; Wackernagel, M.; Wada, Y.; Marchettini, N. Assessing the global environmental consequences of economic growth through the Ecological Footprint: A focus on China and India. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 17, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, J.M.D. Sustainability and Competition Law in Brazil. In Sustainability Objectives in Competition and Intellectual Property Law; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlJaber, A.; Martinez-Vazquez, P.; Baniotopoulos, C. Circular Economy in the Building Sector: Investigating Awareness, Attitudes, Barriers, and Enablers through a Case Study in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WorldData.info. Saudi Arabia: Country Data and Statistics. Available online: https://www.worlddata.info/asia/saudi-arabia/index.php (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- General Authority for Statistics. Today’s Information Is the Development of Tomorrow. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.sa/en/ (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Hadidi, L.A.; Ghaithan, A.; Mohammed, A.; Al-Ofi, K. Deploying municipal solid waste management 3R-WTE framework in Saudi Arabia: Challenges and future. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A.I. Toward a Greener Future: Applying Circular Economy Principles to Saudi Arabia’s Food Sector for Environmental Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdwell, J.E.A. Fixing Food 2021: An Opportunity for G20 Countries to Lead the Way. Available online: https://impact.economist.com/projects/foodsustainability/files/Fixing_Food_2021.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Mahmood, H.; Alkhateeb, T.T.Y.; Al-Qahtani, M.M.Z.; Allam, Z.; Ahmad, N.; Furqan, M. Energy consumption, economic growth and pollution in Saudi Arabia. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2020, 10, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadhi, A.; Abdelhadi, A.; Alyamani, R. Moving from Linear to Circular Economy in Saudi Arabia: Life-Cycle Assessment on Plastic Waste Management. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.B.; Al-Zahrani, K.H.; Schneider, F.; Straquadine, G.S.; Mourad, M. Food waste posing a serious threat to sustainability in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia—A systematic review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, H.; Almarshod, S.Y.; Alsaleem, S.S.; Ali, A.A.M.M.; Alinizzi, M.; Alresheedi, M.T.; Shafiquzzaman, M. Life Cycle Assessment of Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaisi, N.I. Construction and demolition waste management in Saudi Arabia: Current practice and roadmap for sustainable management. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Wierzbicka, E. Towards circular economy—A comparative analysis of the countries of the European Union. Resources 2021, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariatli, F. Linear Economy Versus Circular Economy: A Comparative and Analyzer Study for Optimization of Economy for Sustainability. Visegr. J. Bioeconomy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 6, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Schandl, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, F.; Yue, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, R. Measuring progress of China’s circular economy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieder, M.; Rashid, A. Towards circular economy implementation: A comprehensive review in context of manufacturing industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrador, M.; Van, M.L. Circular economy strategies in the ASEAN region: A comparative study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchherr, J.; Reike, D.; Hekkert, M. Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudio-Quiroga, G.; Poza, C. Measuring the circular economy in Europe: Big differences among countries, great opportunities to converge. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 4707–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrador, M.; de Jong, W.; Nasu, K.; Granrath, L. Circular economy and zero-carbon strategies between Japan and South Korea: A comparative study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.T.T.; Nguyen Thi Phuong, A.; Hang Nguyen, T. Advancing the Circular Business Models in Developing Countries: Lessons from China. Green Low-Carbon Econ. 2022, 2, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D. Circular economy and municipal solid waste management in China. J. Educ. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2023, 8, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Wierzbicka, E. Circular economy: Advancement of European Union countries. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranjanac, Ž.; Rađenović, Ž. EU countries hierarchical clustering towards circular economy performance indicators. Facta Univ. Ser. Work. Living Environ. Prot. 2022, 149, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, G. An Analysis on Japan’s Circular Economy and Its effects on Japan’s Economic Development. Int. Bus. Manag. 2016, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudi Government. Saudi Arabia’s Vision for 2030. Available online: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/media/rc0b5oy1/saudi_vision203.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Castleberry, A.; Nolen, A. Thematic analysis of qualitative research data: Is it as easy as it sounds? Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2018, 10, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Towards Saudi Arabia’s Sustainable Tomorrow: First Voluntary National Review 2018–1439. Available online: https://saudiarabia.un.org/sites/default/files/2020-02/VNR_Report972018_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Saudi Green Initiatives. His Royal Highness the Crown Prince and Prime Minister Announces the Saudi Green Initiative and the Middle East Green Initiative. Available online: https://www.sgi.gov.sa/knowledge-hub/his-royal-highness-the-crown-prince-and-prime-minister-announces-the-saudi-green-initiative-and-the-middle-east-green-initiative/ (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Aldhafeeri, Z.M.; Alhazmi, H. Sustainability Assessment of Municipal Solid Waste in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, in the Framework of Circular Economy Transition. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Investment Fund. The Public Investment Fund to Establish Recycling Sector Company. Available online: https://www.pif.gov.sa/en/news-and-insights/press-releases/2017/fund-to-establish-recycling/ (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Saudi Investment Recycling Company. About Us. Available online: https://sirc.sa/about.html (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- MWAN. National Centre for Waste Management. Available online: https://mwan.gov.sa/en (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Vincent, J. SIRC Plans to Build Recycling, Sorting Facilities in Riyadh. Available online: https://saudigazette.com.sa/article/573980 (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Almulhim, A.I.; Al-Saidi, M. Circular economy and the resource nexus: Realignment and progress towards sustainable development in Saudi Arabia. Environ. Dev. 2023, 46, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deulgaonkar, P. SIRC Seeks to Build Recycling Facilities to Boost Circular Economy in Riyadh. Available online: https://www.argaam.com/en/article/articledetail/id/1303850 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Roscoe, A. Saudi Arabia Sets New 58.7GW Renewable Energy Target for 2030. Available online: https://www.meed.com/saudi-arabia-renewable-energy-target (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Smol, M. Inventory and Comparison of Performance Indicators in Circular Economy Roadmaps of the European Countries. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2023, 3, 557–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. First Circular Economy Action Plan. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/circular-economy/first-circular-economy-action-plan_en (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- European Commission. Delivering the European Green Deal. Available online: https://commission.europa.eu/strategy-and-policy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal/delivering-european-green-deal_en (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Council of the European Union. European Green Deal. Available online: https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/policies/green-deal/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- European Commission. Monitoring Framework for the Circular Economy. Available online: https://commission.europa.eu/publications/monitoring-framework-circular-economy_en (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Eurostat. Monitoring Framework. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/circular-economy/monitoring-framework (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C. Circular economy development in China-current situation, evaluation and policy implications. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 84, 106441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Lee, J.C.K.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, H. Evaluation of Urban circular economy development: An empirical research of 40 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Vlieger De Oliveira, S.; Mahut, C. China’s Circular Economy Policies: Review and Reflection a Circular Economy Vision. Available online: https://www.circularinnovationlab.com/post/china-s-circular-economy-policies-review-and-reflection (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Bleischwitz, R.; Yang, M.; Huang, B.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.; McDowall, W.; Andrews-Speed, P.; Liu, Z.; Yong, G. The circular economy in China: Achievements, challenges and potential implications for decarbonisation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 183, 106350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Role of Circular Economy in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A Case Study of China. In Proceedings of the Seventh Regional 3R Forum in Asia and the Pacific, Adelaide, South Australia, 2–4 November 2016; pp. 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, A.; Hacking, N.; Xie, L. Governance of the circular economy: A comparative examination of the use of standards by China and the United Kingdom. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transitions 2019, 33, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Heshmati, A.; Geng, Y.; Yu, X. A review of the circular economy in China: Moving from rhetoric to implementation. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 42, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunmakinde, O.E. A review of circular economy development models in China, Germany and Japan. Recycling 2019, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- METI. Circular Economy Vision 2020. Available online: https://www.meti.go.jp/shingikai/energy_environment/junkai_keizai/pdf/20200522_03.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Cheng, I. Why Asia matters: Circular economy in Japan, China and Taiwan. In Designing for the Circular Economy; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, R.; Calisto Friant, M.; Vermeulen, W.J.V. The Japanese Circular Economy and Sound Material-Cycle Society Policies: Discourse and Policy Analysis. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2024, 4, 619–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baziene, K.; Gargasas, J.; Rajendran, S.; Solomon, J.N. Towards Circular Economy Through Novel Waste Recycling Technologies. J. Entrep. Sustain. Issues 2024, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Fujii, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Murakami, S.; Daigo, I.; Pan, W.; Li, Z. Institutional, technology, and policies of end-of-life vehicle recycling industry and its indication on the circular economy-comparative analysis between China and Japan. Front. Sustain. 2021, 2, 645843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, R.L.; de Souza, E.B.; Mattos, C.A. Enhancing circular economy practices through the adoption of digital technologies. Bus. Strategy Dev. 2024, 7, e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wong, S.K.; Lu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. The Role of Technologies in Facilitating Circular Economy of China’s E-Commerce Section. In AI Strategies for Social Entrepreneurship and Sustainable Economic Development; IGI Global Scientific Publishing: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimova, V. Advancing Circular Economy Models: The Synergistic Role of Service Design and Blockchain Technology in Enhancing Sustainability and Consumer Engagement. Sci. Pap. Univ. Pardubic. Ser. D Fac. Econ. Adm. 2024, 32, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, M. The Role of Digital Technologies in a Data-driven Circular Business Model: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Bus. Model. 2023, 11, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivot, E. Enhancing Europe’s sustainability through innovation and technology. Eur. View 2023, 22, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Financing the Circular Economy. Available online: https://circulareconomy.europa.eu/platform/en/financing-circular-economy (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- IEA. 14th Five Year Plan on Circular Economy. Available online: https://www.iea.org/policies/24989-14th-five-year-plan-on-circular-economy (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- METI. Green Growth Strategy Through Achieving Carbon Neutrality in 2050. Available online: https://www.meti.go.jp/english/policy/energy_environment/global_warming/ggs2050/index.html (accessed on 16 January 2025).

| Outcome | Achievement | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Resource productivity | 26% increase from 2015 to 2020 | [47] |
| Circularity rate | Circularity rose from 2.7% to 5.8% from 1995 to 2015 | [16] |
| Recycling of end-of-life waste | Increased from 7.2% to 17% | [16] |
| Decoupling of GDP from resource use | Relative decoupling of GDP achieved | [48] |
| Resource intensity | Drop from 4.3 kg of materials per unit GDP in 1990 to 2.5 kg in 2011 | [46] |
| Outcome | Achievement | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Recycling rate of metals | 98% recycled | [54] |
| Recycling rate of materials | Between 74% and 89% recycled | [54] |
| Cyclical use rate | Rose from 10% to 15,4% from 2000 to 2016 | [53] |
| Waste generated | significant reduction | [53] |
| CE technology patents | Japan holds the highest share, accounting for 28% | [54] |
| Decouple the use of non-renewable resources | Enabled by high technology and expertise | [52] |
| Framework Element | Themes | Saudi Arabia | Europe | China | Japan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policies and Strategies | Government Strategies, Policies and Initiatives |
|
|
|
|
| Economic Financial Opportunities | Economic Opportunities and Challenges |
|
|
| Not Implemented. |
| Resource Management | Waste Management and Recycling |
|
|
|
|
| Innovation and Technology | Technological Integration and Innovation | Plans to locally develop technology to expand the capacity of recycling within Saudi Arabia | Not Implemented |
| The new Circular Economy Vision supports the progression of digital technologies. |
| Social Aspects | Social Community Engagement |
|
|
|
|
| Monitoring Framework | Indicators | No monitoring framework and indicators were implemented. | Created a monitoring framework to measure progress towards a circular economy, it consists of 10 indicators. | China has developed a set of comprehensive Circular Economy indicators at various macro, meso, and micro levels. | SMCS framework includes 151 indicators for monitoring progress until 2025. |
| Sustainability Outcomes | Outcomes of the policies | No outcomes since Saudi is newly emerging in CE. |
|
|
|
| Future Planning | Future projects |
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsaud, K.; Assad, F.; Patsavellas, J.; Salonitis, K. A Comparative Analysis of Circular Economy Practices in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083281
Alsaud K, Assad F, Patsavellas J, Salonitis K. A Comparative Analysis of Circular Economy Practices in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083281
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsaud, Khalid, Fadi Assad, John Patsavellas, and Konstantinos Salonitis. 2025. "A Comparative Analysis of Circular Economy Practices in Saudi Arabia" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083281
APA StyleAlsaud, K., Assad, F., Patsavellas, J., & Salonitis, K. (2025). A Comparative Analysis of Circular Economy Practices in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 17(8), 3281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083281







