Effects of Specific Land-Use Categories on Heavy-Metal Pollution in Mangrove Sediments—A Case Study of Bamen Bay Reserve in Hainan, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
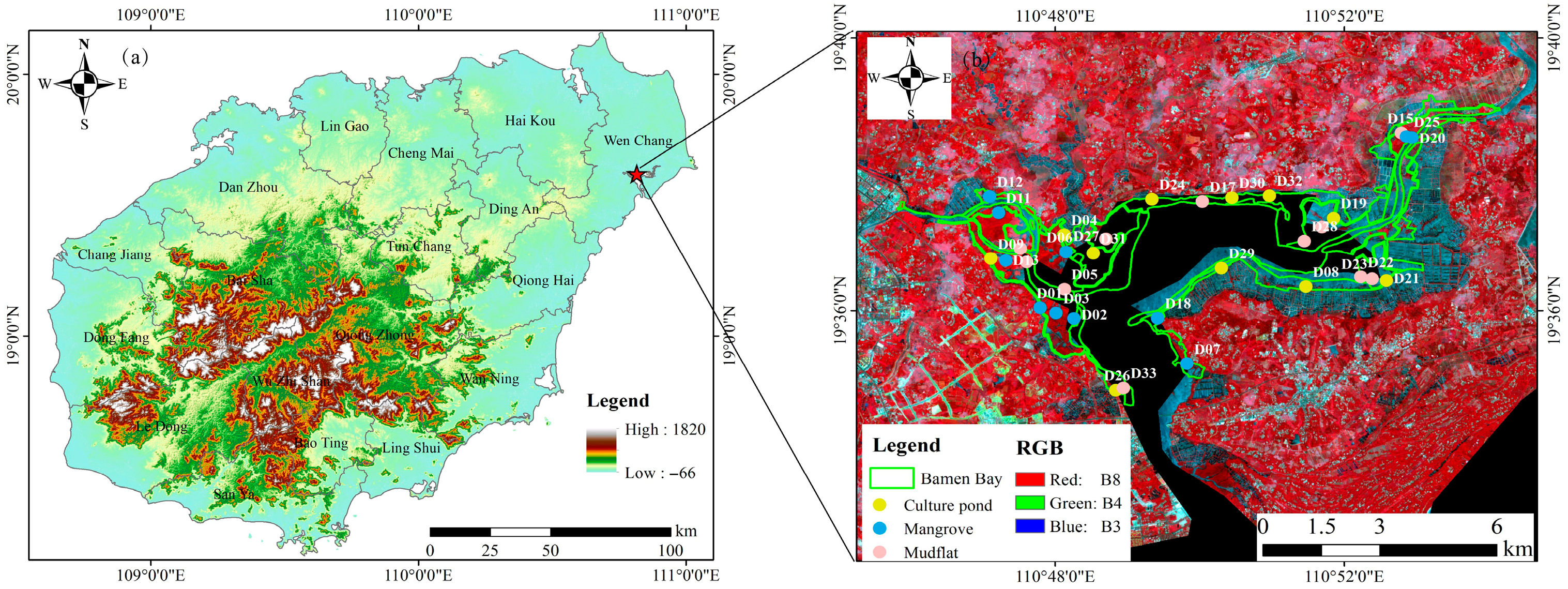
2.1. Study Area and Soil Sampling
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analytical Procedures
2.3. Contamination Assessment
2.4. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
2.5. Geo-Accumulation of Metals
2.6. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metal Concentrations
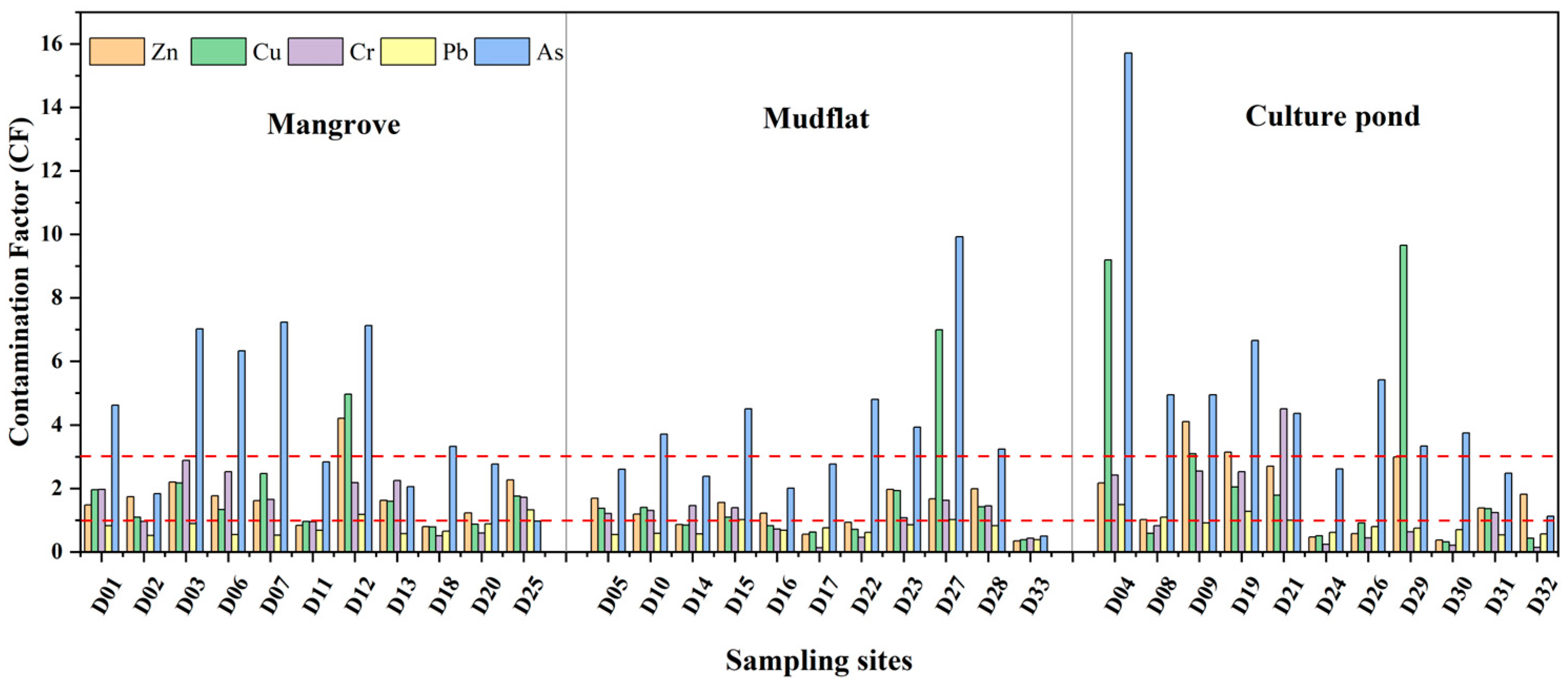
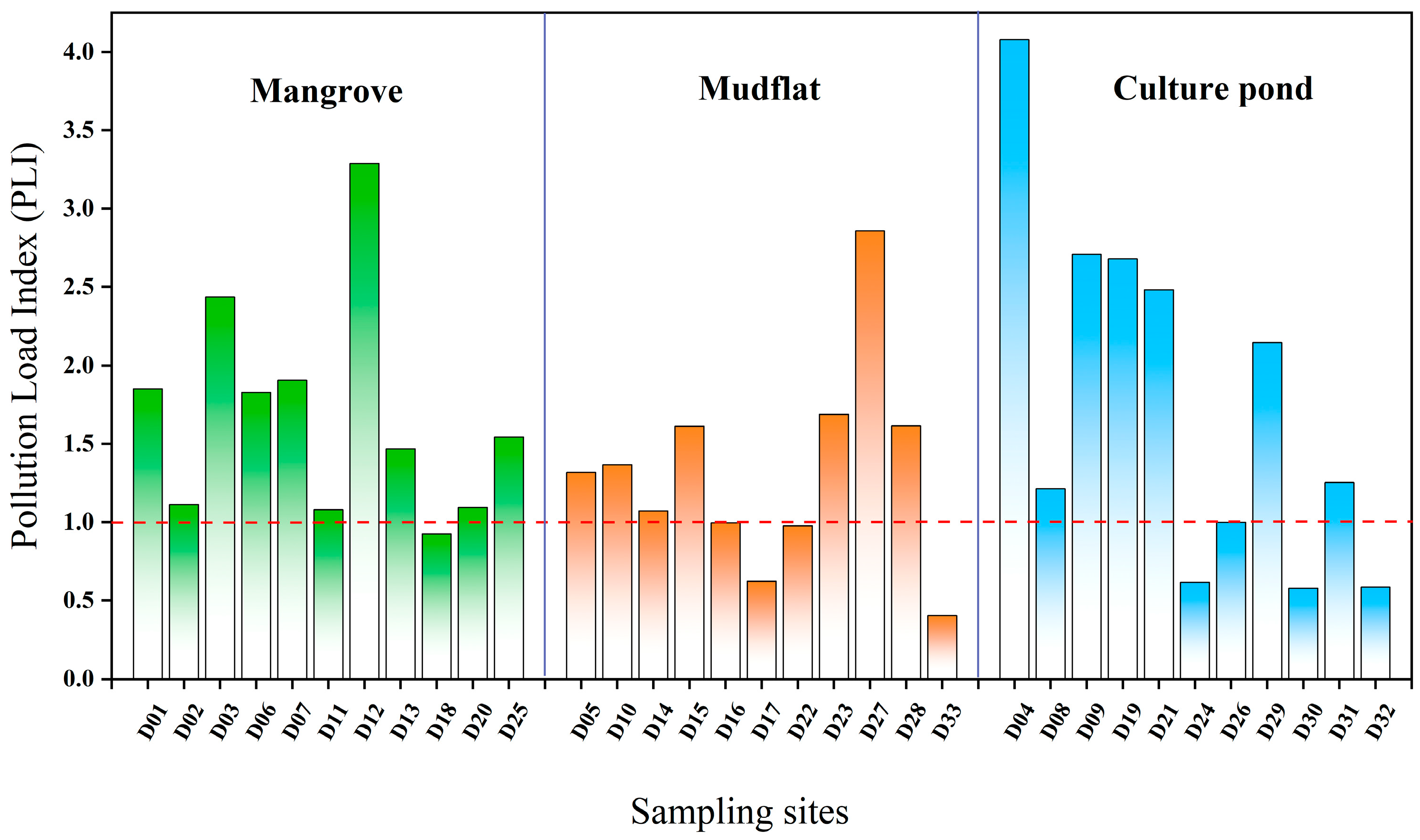
3.2. Heavy Metal Pollution Risks
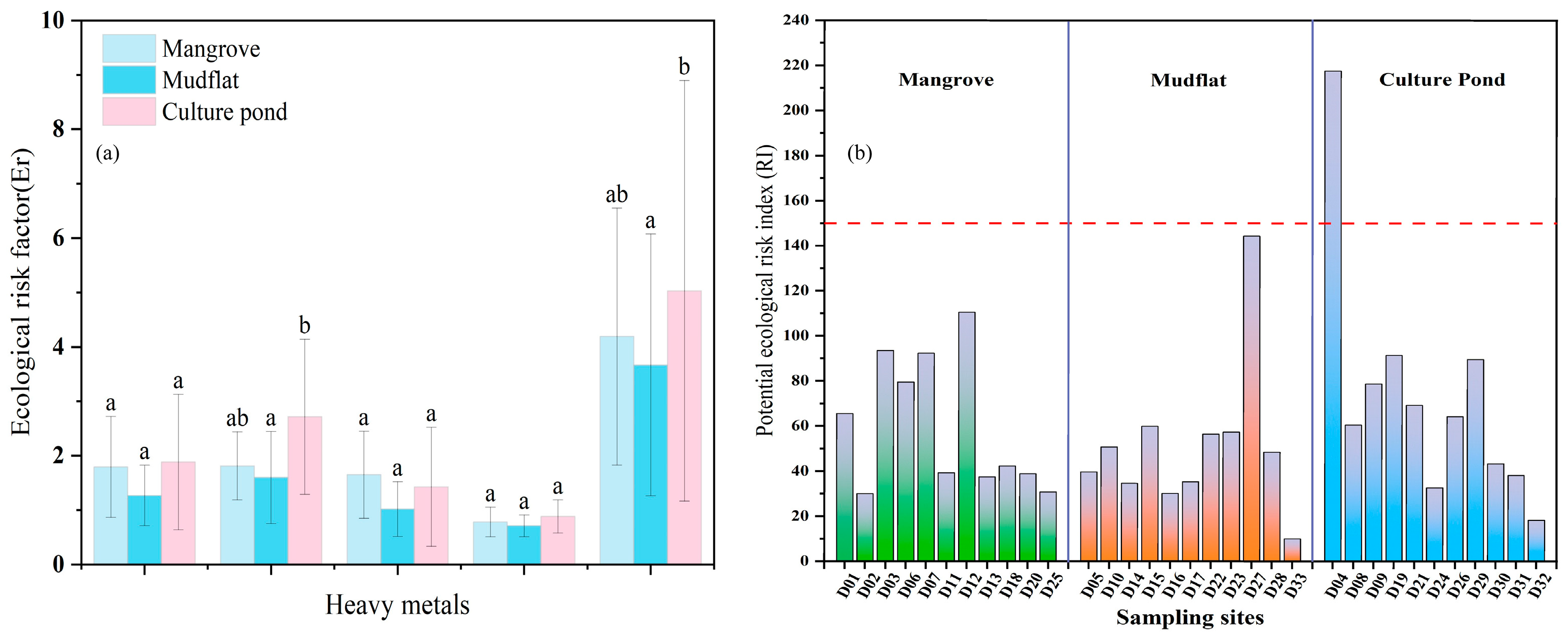
3.3. Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation
3.4. Geo-Accumulation of Heavy Metals
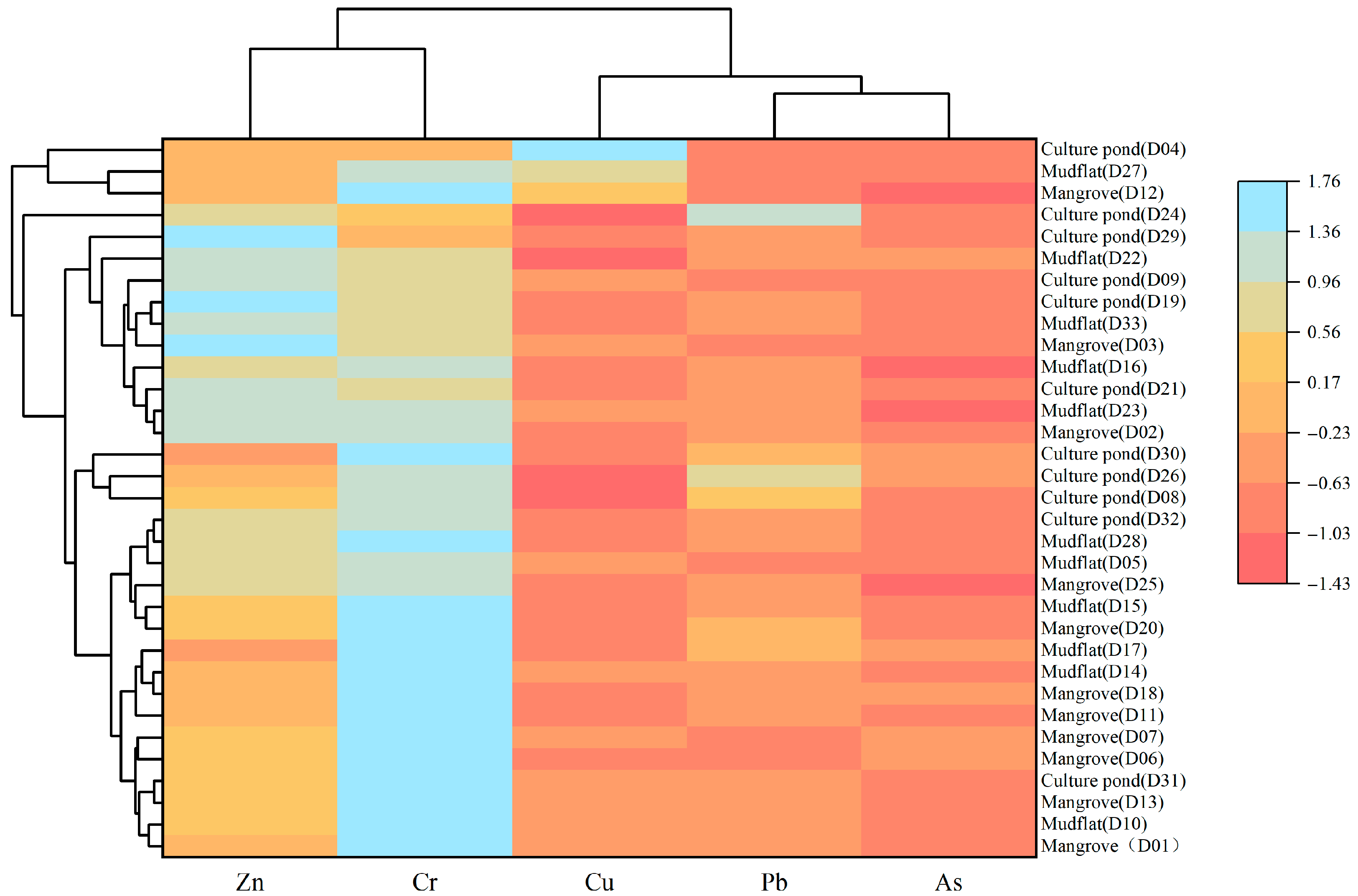
3.5. Differences and Source Distribution of Heavy Metals Under Different Land-Use Types
4. Discussion
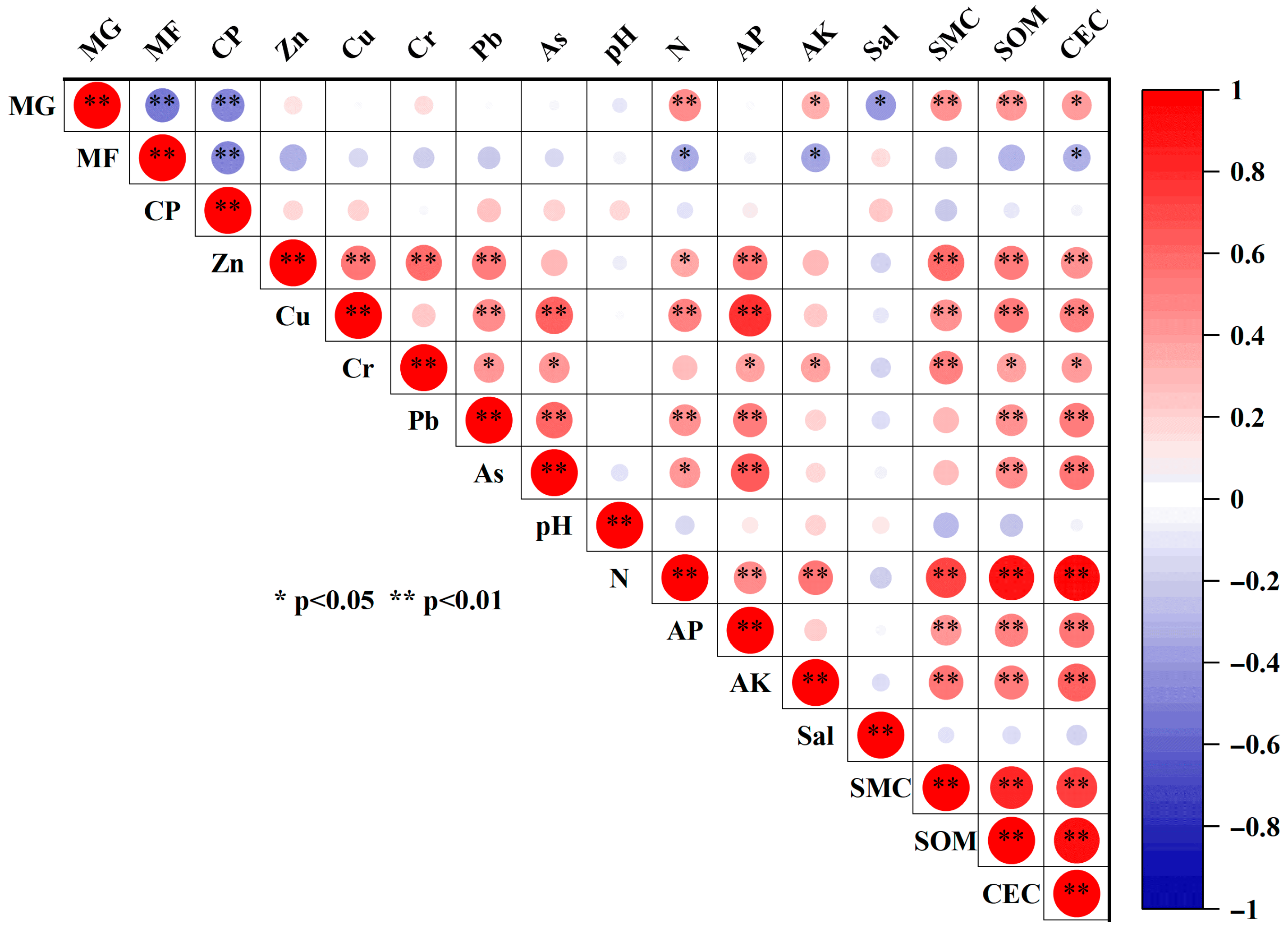
4.1. Influence of Land-Use-Driven Changes in Sediment Physicochemical Properties on Heavy-Metal Accumulation
4.2. Influencing Factors and Source of Heavy Metal Concentration for Mangrove Wetlands
4.3. Management Strategies for Heavy-Metal Pollution in Mangrove Forests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Li, X.; Bai, J.; Meng, Y.; Diao, X.; Pan, K.; Zhu, X.; Lin, G. Effects of land use on the heavy metal pollution in mangrove sediments: Study on a whole island scale in Hainan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Long, R.; Ma, B.; Chang, Y.; Mao, C. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of a Tropical Mangrove Wetlands in Hainan, China, and Their Biological Effectiveness. Minerals 2023, 13, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, K.; Huang, X.; Hu, J.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Arndt, S.K. Land use change impacts on heavy metal sedimentation in mangrove wetlands—A case study in Dongzhai Harbor of Hainan, China. Wetlands 2014, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D.M. Mangrove forests: Resilience, protection from tsunamis, and responses to global climate change. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D.M. Carbon cycling and storage in mangrove forests. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.; Deobagkar, D.; Zinjarde, S. Metals in mangrove ecosystems and associated biota: A global perspective. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chai, M.; Qiu, G.Y. Distribution, fraction, and ecological assessment of heavy metals in sediment-plant system in mangrove forest, South China Sea. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrooz, R.D.; Khammar, S.; Poma, G.; Rajaei, F. Occurrence and patterns of metals in mangrove forests from the Oman Sea, Iran. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 198, 115866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, L.; Chunxiang, L.; Jin, L.; HU, W.; Danyi, W.; Yongze, X.; Xiang, S. Heavy Metals Fate in Mangrove Wetlands: Integrated Insights into Sediment-Microbe-Plant Interactions and Fraction Control. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 499, 140191. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, N.F.; Wong, Y.S. Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 110, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, S.R.; Santos, I.R.; Brown, D.R.; Sanders, L.M.; van Santen, M.L.; Sanders, C.J. Mangrove sediments reveal records of development during the previous century (Coffs Creek estuary, Australia). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, S.; Aich, A.; Sengupta, P.; Chakraborty, A.; Sudarshan, M. Assessment of trace metal contamination of wetland sediments from eastern and western coastal region of India dominated with mangrove forest. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, C.; Lallier-Vergès, E.; Baltzer, F.; Albéric, P.; Cossa, D.; Baillif, P. Heavy metals distribution in mangrove sediments along the mobile coastline of French Guiana. Mar. Chem. 2006, 98, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluturhan, E.; Kucuksezgin, F. Heavy metal contaminants in Red Pandora (Pagellus erythrinus) tissues from the eastern Aegean Sea, Turkey. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.; Pryor, R.; Wilking, L. Fate and effects of anthropogenic chemicals in mangrove ecosystems: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2328–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lin, C.; Qiu, P.; Song, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, G.; Feng, X.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Niu, A. Tungsten-and cobalt-dominated heavy metal contamination of mangrove sediments in Shenzhen, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, G.; Burchett, M. Toxicity, growth and accumulation relationships of copper, lead and zinc in the grey mangrove Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 54, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cen, D.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Fu, S.; Cai, R.; Wu, X.; Tang, M.; Sun, Y. Detection and analysis of 12 heavy metals in blood and hair sample from a general population of Pearl River Delta area. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 70, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Ding, H.; Zan, Q.; Li, R. Spatial variation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in mangrove sediments across China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 143, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, P.; Han, J.; Li, W. Aquaculture exacerbates the accumulation and ecological risk of heavy metal from anthropogenic and natural sources, a case study in Hung-tse Lake, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; You, W.; Hu, H.; Hong, W.; Liao, X.; Xiao, S.; Wang, R.; Cai, J.; Fan, X.; Tan, Y. Spatial distribution of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cd) in sediments of a coastal wetlands in eastern Fujian, China. J. For. Res. 2015, 26, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Composition and degradation of lipid biomarkers in mangrove forest sediments of Hainan Island, China. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2011, 30, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, G.; Ma, M. Characteristics of surface water quality and stable isotopes in Bamen Bay watershed, Hainan Province, China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wang, J. The Spatial Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediments of Bamenwan mangrove wetland, Hainan Island. J. Hainan Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2015, 28, 432–437. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Guo, J.; Wu, G.; Lü, L.; Li, W. Mangrove Landscape Changes Process and Land Use and Coverage Change in Its Surrounding Area: A Case Study of Qinglangang Bay in Hainan Province. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2013, 49, 169–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Kang, X.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Song, J.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, Y. Heavy metals in surface sediments along the Weihai coast, China: Distribution, sources and contamination assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.; Jeffrey, D. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, K.; Gong, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, K.; Hu, S.; Fu, Y. Differentiating environmental scenarios to establish geochemical baseline values for heavy metals in soil: A case study of Hainan Island, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, L.; Xie, Z.; Du, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, C.; Long, T. Contaminations of Heavy Metals in Surface Soils of Various Lands and Their Health Risks in Tianjin Qilihai Ancient Lagoon Wetlands, China. Wetl. Sci. 2016, 14, 700–709. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Ren, F.; Xiong, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Leng, P.; Li, Z.; Bai, Y. Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metal pollution of sediments in coastal reclamation areas: A case study in Shenzhen Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Peng, R.; Yang, Y.; He, L.; Wang, W.; Zheng, T.; Lin, G. Mariculture pond influence on mangrove areas in south China: Significantly larger nitrogen and phosphorus loadings from sediment wash-out than from tidal water exchange. Aquaculture 2014, 426, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y. Soil aggregate-associated heavy metals subjected to different types of land use in subtropical China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branoff, B.L. Quantifying the influence of urban land use on mangrove biology and ecology: A meta-analysis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 1339–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Laing, G.; Rinklebe, J.; Vandecasteele, B.; Meers, E.; Tack, F.M. Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3972–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, N.F.; Wong, Y.-S. Accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in a simulated mangrove system treated with sewage. Hydrobiologia 1997, 352, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.K.; Chowdhury, A. Effects of anthropogenic pollution on mangrove biodiversity: A review. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.-G.; Zeng, G.-M.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.-Y.; Shen, L.-Q.; Hu, L. Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, D.E.; Akinci, G. Effect of sediment size on bioleaching of heavy metals from contaminated sediments of Izmir Inner Bay. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.-W.; Gunn, J.M.; Dixit, S.S. Sediment trace metal profiles in lakes of Killarney Park, Canada: From regional to continental influence. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 130, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobi, E.; Dilipan, E.; Thangaradjou, T.; Sivakumar, K.; Kannan, L. Geochemical and geo-statistical assessment of heavy metal concentration in the sediments of different coastal ecosystems of Andaman Islands, India. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 87, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, Z.; Liu, G.; Kalla, P.; Scheidt, D.; Cai, Y. Evaluation of the possible sources and controlling factors of toxic metals/metalloids in the Florida Everglades and their potential risk of exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9714–9723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.-G.; Lin, Q.; Yu, Z.-L.; Wang, X.-N.; Ke, C.-L.; Ning, J.-J. Speciation and risk of heavy metals in sediments and human health implications of heavy metals in edible nekton in Beibu Gulf, China: A case study of Qinzhou Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanesch, M.; Scholger, R.; Dekkers, M.J. The application of fuzzy c-means cluster analysis and non-linear mapping to a soil data set for the detection of polluted sites. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A Solid Earth Geod. 2001, 26, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micó, C.; Recatalá, L.; Peris, M.; Sánchez, J. Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Bao, K.; Yan, Y.; Neupane, B.; Gao, C. Spatial distribution of potentially harmful trace elements and ecological risk assessment in Zhanjiang mangrove wetland, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 114033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, T.; Petersen, S.; Levings, C.; Martin, A. Distinguishing between natural and aquaculture-derived sediment concentrations of heavy metals in the Broughton Archipelago, British Columbia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavhane, S.; Sapkale, J.; Susware, N.; Sapkale, S. Impact of heavy metals in riverine and estuarine environment: A review. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2021, 25, 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Manceau, A. The mechanism of anion adsorption on iron oxides: Evidence for the bonding of arsenate tetrahedra on free Fe (O, OH) 6 edges. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 3647–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.M.; Randall, S.R. Surface complexation of arsenic (V) to iron (III)(hydr) oxides: Structural mechanism from ab initio molecular geometries and EXAFS spectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 4223–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Chen, K.-C.; Li, K.-B.; Nie, X.-P.; Wu, S.C.; Wong, C.K.-C.; Wong, M.-H. Arsenic contamination in the freshwater fish ponds of Pearl River Delta: Bioaccumulation and health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4484–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yan, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wu, T.; Luan, C.; Shao, Y. Arsenic distribution characteristics and release mechanisms in aquaculture lake sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, R.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Bioaccumulation characteristics of heavy metal in intertidal zone sediments from northern Hainan Island. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 842–846. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Saenger, P.; McConchie, D. Heavy metals in mangroves: Methodology, monitoring and management. Envis For. Bull. 2004, 4, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Zhu, G.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Yi, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, M.; Wang, Z. Risk assessment of heavy metals in a typical mangrove ecosystem—A case study of Shankou Mangrove National Natural Reserve, southern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Luo, S.; Deng, S.; Huang, R.; Chen, B.; Deng, Z. Heavy metal pollution status and deposition history of mangrove sediments in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 989584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Analysis of the Development Path of Mangrove Ecotourism. J. Humanit. Arts Soc. Sci. 2023, 7, 2256–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.U.; Han, J.-C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Farman, A.; Zhao, X.; Riaz, L.; Yasin, G.; Ullah, S. Eco-resilience of China’s mangrove wetlands: The impact of heavy metal pollution and dynamics. Environ. Res. 2025, 277, 121552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Land Use | Sample ID |
|---|---|
| Mangrove | D01 D02 D03 D06 D07 D11 D12 D13 D18 D20 D25 |
| Culture pond | D05 D10 D14 D15 D16 D17 D22 D23 D27 D28 D33 |
| Mudflat | D04 D08 D09 D19 D21 D24 D26 D29 D30 D31 D32 |
| Cr | Zn | Pb | Cu | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bn | 8.50 | 8.10 | 11.8 | 2.10 | 1.41 |
| Index | Classification | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Potential ecological risk factor (Er) | Er < 40 | Low risk |
| 40 ≤ Er < 80 | Moderate risk | |
| 80 ≤ Er < 160 | Considerable risk | |
| 160 ≤ Er < 320 | High risk | |
| Er > 320 | Extremely high risk | |
| Potential ecological risk index (RI) | RI < 150 | Low risk |
| 150 ≤ RI < 300 | Moderate risk | |
| 300 ≤ RI < 600 | Considerable risk | |
| RI ≥ 600 | High risk |
| Land Use | Zn | Cu | Cr | Pb | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mangrove | Average | 0.11 | 0.06 | −0.06 | −1.01 | 1.23 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.67 | 0.78 | 0.86 | 0.47 | 0.96 | |
| Mudflat | Average | −0.41 | −0.38 | −0.84 | −1.13 | 1.00 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.80 | 1.09 | 1.11 | 0.43 | 1.06 | |
| Culture pond | Average | −0.05 | −0.07 | −0.84 | −0.84 | 1.45 |
| Standard Deviation | 1.20 | 1.69 | 1.69 | 0.48 | 0.96 | |
| ≤0 | Unpolluted | 3–4 | Strongly polluted | |||
| 0–1 | Unpolluted to moderately polluted | 4–5 | Strongly to extremely polluted | |||
| 1–2 | Moderately polluted | ≥5 | Extremely polluted | |||
| 2–3 | Moderately to strongly polluted | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Hou, Y.; Li, F.; Yu, R.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, X. Effects of Specific Land-Use Categories on Heavy-Metal Pollution in Mangrove Sediments—A Case Study of Bamen Bay Reserve in Hainan, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 11246. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411246
Liu J, Hou Y, Li F, Yu R, Zheng B, Zhang X. Effects of Specific Land-Use Categories on Heavy-Metal Pollution in Mangrove Sediments—A Case Study of Bamen Bay Reserve in Hainan, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(24):11246. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411246
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiahui, Yaoqi Hou, Fangyi Li, Rui Yu, Binbin Zheng, and Xiaohai Zhang. 2025. "Effects of Specific Land-Use Categories on Heavy-Metal Pollution in Mangrove Sediments—A Case Study of Bamen Bay Reserve in Hainan, China" Sustainability 17, no. 24: 11246. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411246
APA StyleLiu, J., Hou, Y., Li, F., Yu, R., Zheng, B., & Zhang, X. (2025). Effects of Specific Land-Use Categories on Heavy-Metal Pollution in Mangrove Sediments—A Case Study of Bamen Bay Reserve in Hainan, China. Sustainability, 17(24), 11246. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172411246





