A Review on the Impact of Condenser Technologies on Solar Still Productivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method of Review
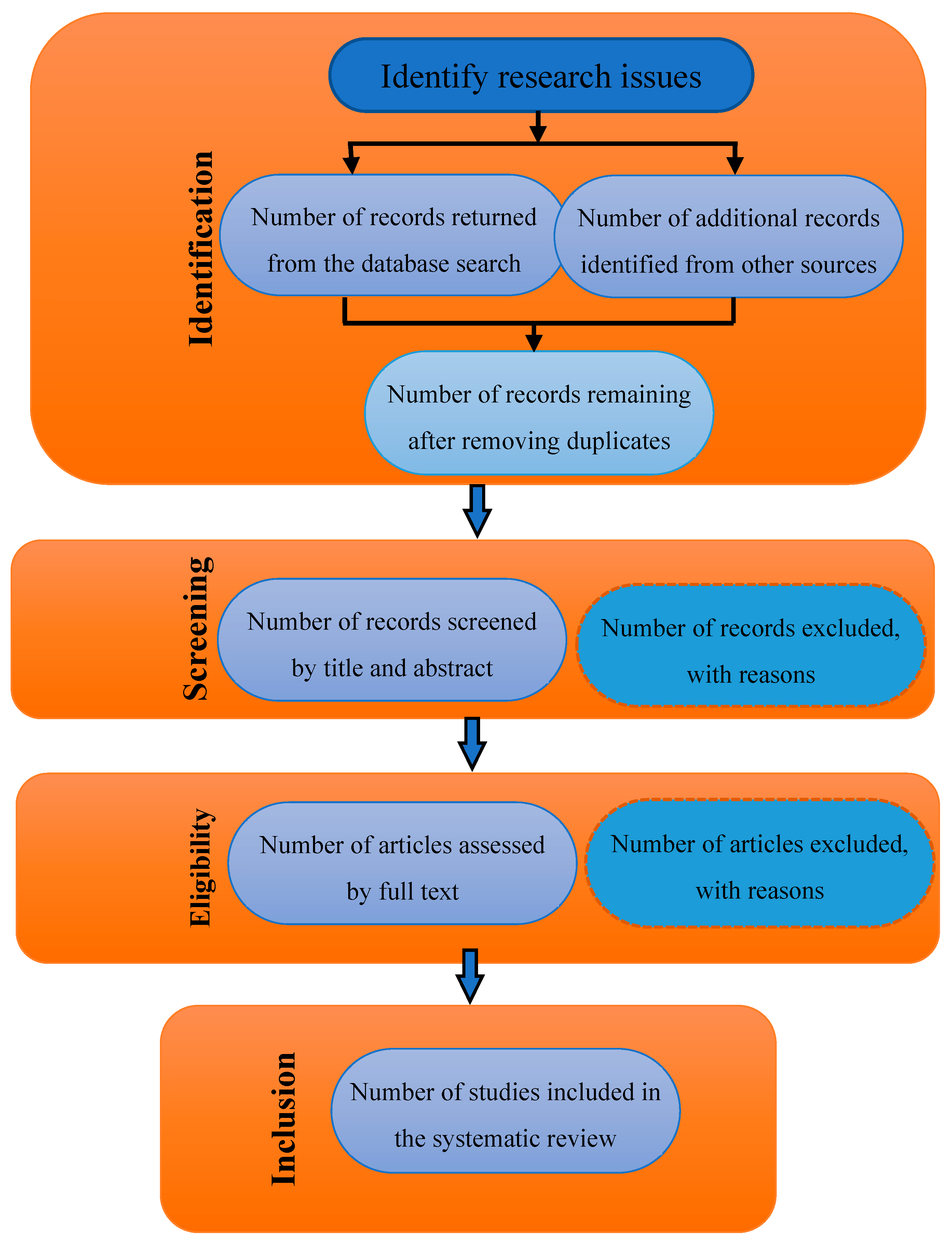
2.1. Systematic Review Protocol: PRISMA-Based Literature Review
2.2. Solar Stills with External Condensers
2.3. Solar Stills with Internal Condensers
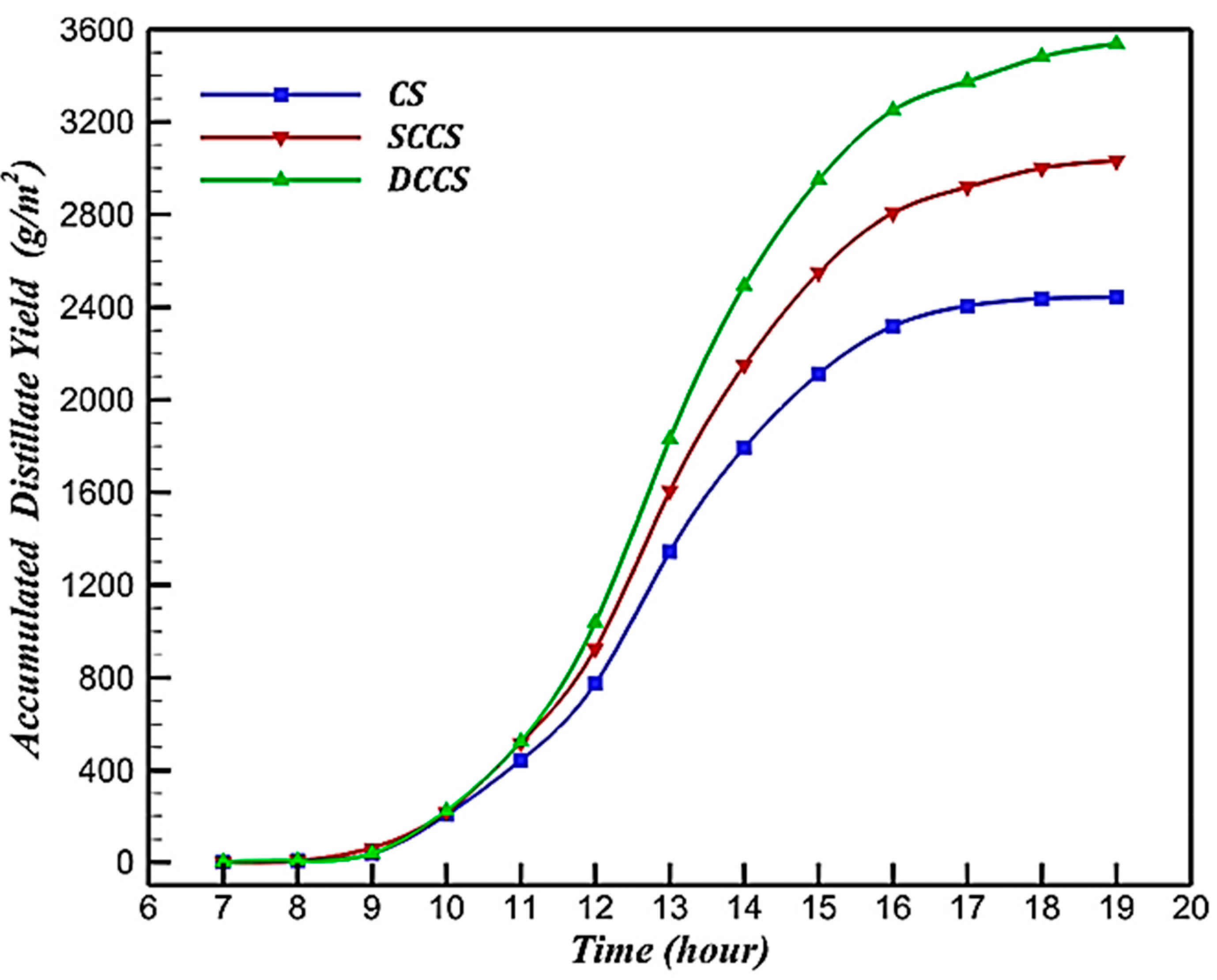
3. Critical Evaluation of Solar Stills with External and Internal Condensers
4. Further Enhancements and Accompanying Challenges
5. Conclusions
- Greater water production was achieved compared to traditional solar still systems by integrating external and internal condensers into solar stills. Statistically, an improvement of water production between 24% and 165% was reported for external condensers and between 30% and 150% for internal condensers.
- High-temperature gradients for condensation were ascertained using external condensers. However, they necessitate additional space, while consuming auxiliary energy and requiring frequent maintenance. However, internal condensers are more susceptible to ambient conditions and internal airflow dynamics as they passively operate, i.e., fail to efficiently operate in humid or low-sunlight environments.
- The integration of nanofluids and PCMs has augmented the evaporation and condensation rates, introducing an efficient improvement of more than 116%. Nonetheless, long-term stability and operational cost were demonstrated as being related issues to be resolved. In this regard, the integration of condensers with reflectors, wick materials, and solar tracking mechanisms can be introduced as a successful solution.
- Long-term reliability can be challenged by fouling, corrosion, and degradation of condenser surfaces, particularly in systems using nanofluids. There is a need for innovative anti-fouling coatings and durable materials.
- The high cost of advanced materials (e.g., graphene, thermoelectric modules) and components (e.g., solar trackers) limits scalability, especially in low-resource settings and developing countries.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Definition |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| COSS | Coiled solar still |
| CPSS | Conventional pyramid solar still |
| CSS | Conventional solar still |
| CTSS | Conventional tubular solar still |
| EC | External condenser |
| FAF | Floating aluminium fins |
| GOR | Gain output ratio (desalination efficiency metric) |
| HDH | Humidification–dehumidification (desalination process) |
| HSC | Heat sink condenser |
| MCEC | Multiple cylindrical external condensers |
| MCOSS | Modified coiled solar still |
| MED | Multi-effect distillation |
| MHSS | Modified hemispherical solar still |
| MOF | Metal–organic framework |
| MSS | Modified solar still |
| NCL | Natural circulation loop |
| NPCM | Nano-enhanced phase change material |
| PCM | Phase change material |
| PSDD | Passive single-basin double-slope distiller |
| PTC/PTSC | Parabolic trough (solar) collector |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| REC | Rectangular external condenser |
| RMSE | Root-mean-square error |
| SPV | Solar photovoltaic |
| SWH | Solar water heater |
| VWSS | Vertical wick solar still |
References
- Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Rasn, K.H.; Aladwani, S.H.; Kadhom, M.; Mujtaba, I.M. Flexible design and operation of multi-stage reverse osmosis desalination process for producing different grades of water with maintenance and cleaning opportunity. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 182, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, F.A.; Saleh, B.; Algethami, A.A.; Oyedepo, S.O.; Omara, Z.M.; El-Sebaey, M.S. Enhanced solar desalination via hemispheric distiller with thermal storage, heaters, and condensation: Exergoeconomic and environmental analysis. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2025, 285, 113529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.K.; Rashid, F.L.; Rasul, M.K.; Basem, A.; Younis, O.; Homod, R.Z.; Attia, M.E.H.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Hamida, M.B.B.; Ali, B.; et al. A review of the application of hybrid Nanofluids in solar still energy systems and guidelines for future prospects. Sol. Energy 2024, 272, 112485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.L.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Hussein, A.K.; Akkurt, N.; Ali, B.; Younis, O. Floating solar stills and floating solar-driven membranes: Recent advances and overview of designs, performance, and modern combinations. Sol. Energy 2022, 247, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkar, M.; Kanathala, Y.; Naik, B.K. Recent developments in solar-driven adsorption and humidification-dehumidification based hybrid desalination system: A state-of-the-art review. Sol. Compass 2025, 15, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Alsadaie, S.; Alsarayreh, A.; Sowgath, M.T.; Mujtaba, I.M. Integration of Renewable Energy Systems in Desalination. Processes 2024, 12, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luberti, M.; Capocelli, M. Enhanced humidification–dehumidification (HDH) systems for sustainable water desalination. Energies 2023, 16, 6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, B.; Bizhani, M.; Hakkaki-Fard, A.; Hannani, S.K. Performance evaluation of different configurations of solar humidification-dehumidification desalination system with subsurface condenser. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 269, 116186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amori, K.E.; Alsaady, S.M. Solar-Powered Humidifiers for Humidification–Dehumidification Desalination Systems: A Review. Heat Transfer 2025, 54, 2703–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharshir, S.W.; Abdo, M.R.; Yusuf, K.; El-Naggar, A.A.; Joseph, A.; Ismail, M.; Elsaid, A.M.; Abdelfatah, M.; El-Shaer, A.; Yuan, Z. Thermo-economic and environmental evaluation of thin film evaporation using novel metal-organic frameworks to enhance solar desalination performance. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 199, 107223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.L.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Dulaimi, A.; Bahlol, H.Y.; Hasan, A. A review of the current situation and prospects for nanofluids to improve solar still performance. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 149, 13511–13531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, P.; Goharrizi, A.S.; Ayatollahi, S.; Feilizadeh, M.; Dashti, H. Efficiency improvement of solar stills through wettability alteration of the condensation surface: An experimental study. Appl. Energy 2020, 268, 114923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamzawi, H.A.H.; Al Sailawi, A.S.A. Optimised multi-generation system for sustainable desalination and power production using solar-driven Multi-Effect Distillation (MED) in Basra, Iraq. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2025, 85, 101684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hotmani, O.M.A.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Li, J.P.; John, Y.M.; Patel, R.; Mujtaba, I.M. A multi-objective optimisation framework for MED-TVC seawater desalination process based on particle swarm optimisation. Desalination 2022, 525, 115504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilagan, K.; Advaith, S.; Mani, A. Simulation studies and experimental validation on solar multi-effect desalination system. Sol. Compass 2025, 13, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harby, M.; Hanafi, A.; Hamed, A. Exergetic investigation of solar powered multiple effect desalination with thermal vapor compression. Sol. Energy 2025, 298, 113636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, G.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Manenti, F.; Mujtaba, I.M. Design and economic evaluation of solar-powered hybrid multi effect and reverse osmosis system for seawater desalination. Desalination 2019, 465, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Kumar, A. Humidification-dehumidification desalination system based on solar air and water heaters. Sol. Energy 2025, 297, 113637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.L.; Kaood, A.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Mohammed, H.I.; Alsarayreh, A.A.; Al-Muhsen, N.F.; Abbas, A.S.; Zubo, R.H.; Mohammad, A.T.; Alsadaie, S.; et al. A review of the configurations, capabilities, and cutting-edge options for multistage solar stills in water desalination. Designs 2023, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gazar, E.F.; Yousef, M.S.; Elshaer, A.M.; Khattab, M.A.; Mouneer, T.A.; Hawwash, A.A. Enhancing solar still performance with hybrid nanofluid: A comprehensive assessment of energy, exergy, economics, and environmental impact using a novel fractional model. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 24, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, M.E.; Alawee, W.H.; Dhahad, H.A. Application of Advanced Techniques in Double Slope Solar Stills: An Experimental Study in Iraqi Climates. Heat Transf. 2025, 54, 3564–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.M.; El-Sharkawy, I.I.; Kabeel, A.E.; Uddin, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Saha, B.B. Characterization of silica gel-based composites for adsorption cooling applications. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 118, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.M.; El-Sharkawy, I.I.; Kabeel, A.E.; Saha, B.B. A review on adsorbent-adsorbate pairs for cooling applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 114, 394–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.E.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M. Techniques used to improve the performance of the stepped solar still—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 46, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.M.; Abdullah, A.S.; Essa, F.A.; Omara, Z.M. Half barrel and corrugated wick solar stills–Comprehensive study. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.M.; Abdullah, A.S.; Essa, F.A.; Omara, Z.M.; Amro, M.I. Enhancing the wick solar still performance using half barrel and corrugated absorbers. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 150, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Younes, M.M.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A. New design of trays solar still with enhanced evaporation methods–comprehensive study. Sol. Energy 2020, 203, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A.; Younes, M.M.; Shanmugan, S.; Abdelgaied, M.; Amro, M.I.; Kabeel, A.E.; Farouk, W.M. Improving the performance of trays solar still using wick corrugated absorber, nano-enhanced phase change material and photovoltaics-powered heaters. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J. A plastic solar water purifier with high output. Sol. Energy 2003, 75, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.E.; Khalil, A.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M. Theoretical and experimental parametric study of modified stepped solar still. Desalination 2012, 289, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, Z.M.; Kabeel, A.E.; Younes, M.M. Enhancing the stepped solar still performance using internal reflectors. Desalination 2013, 314, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, Z.M.; Kabeel, A.E.; Younes, M.M. Enhancing the stepped solar still performance using internal and external reflectors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 78, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, F.A.; Abdullah, A.S.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M. Improving the performance of tubular solar still using rotating drum–experimental and theoretical investigation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.E.; Abdelgaied, M.; Harby, K.; Eisa, A. Augmentation of diurnal and nocturnal distillate of modified tubular solar still having copper tubes filled with PCM in the basin. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.L.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Dulaimi, A.; Bahlol, H.Y.; Hasan, A. Recent advances, development, and impact of using phase change materials as thermal energy storage in different solar energy systems: A review. Designs 2023, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihnayyish, I.L.; Ahmed, A.Q.; Mohammad, A.T.; Al-Syyab, A.K.S. Numerical study to investigate the performance of U-shaped flat plate solar collector using phase change materials (PCMs). J. Tech. 2023, 5, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalib, M.M.; Manokar, A.M.; Essa, F.A.; Vasimalai, N.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Garcia Marquez, F.P. Comparative study of tubular solar stills with phase change material and nano-enhanced phase change material. Energies 2020, 13, 3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.K.; Rashid, F.L.; Abed, A.M.; Sultan, H.S.; Togun, H.; Attia, M.E.H.; Manokar, A.M.; Hamida, M.B.B.; Ali, B.; Younis, O.; et al. Review of recent designs, performance, and configurations for the pyramid solar still. Int. J. Energy Water Res. 2024, 9, 1145–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Alawee, W.H.; Mohammed, S.A.; Alqsair, U.F.; Dhahad, H.A.; Essa, F.A.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M. Performance improvement of tubular solar still via tilting glass cylinder, nano-coating, and nano-PCM: Experimental approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 65088–65099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.E.; Teamah, M.A.; Abdelgaied, M.; Aziz, G.B.A. Modified pyramid solar still with v-corrugated absorber plate and PCM as a thermal storage medium. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Murugan, M. Performance evaluation of square pyramid solar still with various vertical wick materials–an experimental approach. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 19, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawee, W.H.; Essa, F.A.; Mohammed, S.A.; Dhahad, H.A.; Abdullah, A.S.; Omara, Z.M.; Gamiel, Y. Improving the performance of pyramid solar distiller using dangled cords of various wick materials: Novel working mechanism of wick. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 28, 101550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawee, W.H.; Mohammed, S.A.; Dhahad, H.A.; Abdullah, A.S.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A. Improving the performance of pyramid solar still using rotating four cylinders and three electric heaters. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabchi, F.; Gorjian, S.; Sabzehparvar, S.; Shadram, Z.; Ghoreishi, M.S.; Rahimzadeh, H. Experimental performance evaluation of a modified solar still integrated with a cooling system and external flat-plate reflectors. Sol. Energy 2019, 187, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azm Najjar, M.N.; AlMallahi, M.N.; Elgendi, M. Evaluating the effect of external and internal condensers on the productivity of solar stills: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2024, 24, 100763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monowe, P.; Masale, M.; Nijegorodov, N.; Vasilenko, V. A portable single-basin solar still with an external reflecting booster and an outside condenser. Desalination 2011, 280, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeroual, M.; Bouguettaia, H.; Bechki, D.; Boughali, S.; Bouchekima, B.; Mahcene, H.J.E.P. Experimental investigation on a double-slope solar still with partially cooled condenser in the region of Ouargla (Algeria). Energy Procedia 2011, 6, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.E.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A. Enhancement of modified solar still integrated with external condenser using Nanofluids: An experimental approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 78, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samadony, Y.A.F.; Abdullah, A.S.; Omara, Z.M. Experimental Study of Stepped Solar Still Integrated with Reflectors and External Condenser. Exp. Heat Transfer 2014, 28, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refalo, P.; Ghirlando, R.; Abela, S. The use of a solar chimney and condensers to enhance the productivity of a solar still. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 23024–23037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Ten Kortenaar, M.V.; Mudde, R.F. Inflatable plastic solar still with passive condenser for single family use. Desalination 2016, 398, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.A.; Esakkimuthu, G.; Murugavel, K.K. Performance enhancement of a single basin single slope solar still using agitation effect and external condenser. Desalination 2016, 399, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.; Boutriaa, A. Numerical and experimental study of a passive solar still integrated with an external condenser. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 29047–29055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabhi, K.; Nciri, R.; Nasri, F.; Ali, C.; Bacha, H.B. Experimental performance analysis of a modified single-basin single-slope solar still with pin fins absorber and condenser. Desalination 2017, 416, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Abo-Elfadl, S. Effect of the condenser type and the medium of the saline water on the performance of the solar still in hot climate conditions. Desalination 2017, 417, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.E.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A. Numerical investigation of modified solar still using Nanofluids and external condenser. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 75, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Nehar, L.; Sarker, M.R.I.; Tuly, S.S.; Beg, R.A. Performance test of a solar still for different surface to volume ratio absorber plate with an external condenser. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2121, 130003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Ahmed, M.S.; Fathy, M.; Yousef, M.S. Impact of salty water medium and condenser on the performance of single acting solar still incorporated with parabolic trough collector. Desalination 2020, 480, 114324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Yousef, M.S.; Fathy, M.; Ahmed, M.S. Impact of condenser heat transfer on energy and exergy performance of active single slope solar still under hot climate conditions. Sol. Energy 2020, 204, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.M.; Rahbar, A.; Koleini, M.H.; Aberoumand, S.; Afrand, M.; Amidpour, M. A renewable energy-driven thermoelectric-utilized solar still with external condenser loaded by silver/nanofluid for simultaneously water disinfection and desalination. Desalination 2020, 480, 114354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toosi, S.S.A.; Goshayeshi, H.R.; Heris, S.Z. Experimental investigation of stepped solar still with phase change material and external condenser. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevada, D.; Panchal, H.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Investigation on evacuated tubes coupled solar still with condenser and fins: Experimental, exergo-economic and exergo-environment analysis. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 27, 101217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Singh, D.; Devnani, G.L.; Sinha, S.; Singh, D. Potable water production via desalination technique using solar still integrated with partial cooling coil condenser. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 43, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.; Khemmar, F.; Saadi, Z. Experimental investigation on the negative effect of the external condenser on the conventional solar still performance. Desalination 2021, 501, 114914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuly, S.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Sarker, M.R.I.; Beg, R.A. Combined influence of fin, phase change material, wick, and external condenser on the thermal performance of a double slope solar still. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgaied, M.; Harby, K.; Eisa, A. Performance improvement of modified tubular solar still by employing vertical and inclined pin fins and external condenser: An experimental study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 13504–13514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaram, P.M.; Dinesh Kumar, S.; Premalatha, M.; Sivasankar, T.; Arunagiri, A. Experimental and numerical study of stepped solar still integrated with a passive external condenser and its application. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 2143–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawee, W.H.; Abdullah, A.S.; Mohammed, S.A.; Majdi, A.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M. Testing a single slope solar still with copper heating coil, external condenser, and phase change material. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.; Samimi, M. Effect of condenser geometrical feature on evacuated tube collector basin solar still performance: Productivity optimisation using a Box-Behnken design model. Desalination 2022, 542, 116092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.A.; Jassim, N.A. Experimental investigation of solar still with separate condenser coupled. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 60, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharshir, S.W.; Kandeal, A.W.; Algazzar, A.M.; Eldesoukey, A.; El-Samadony, M.O.A.; Hussien, A.A. 4-E analysis of pyramid solar still augmented with external condenser, evacuated tubes, nanofluid and ultrasonic foggers: A comprehensive study. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 164, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, M.A.; Pasha, G.; Ebrahimpour, B.; Guodarzi, A.M.; Morshedsolouk, F.; Roshan, H.H.; Shafaghat, R. Experimental investigation of a novel single-slope tilted wick solar still with an affordable channeled absorber sheet, an external condenser, and a reflector. Sol. Energy 2022, 241, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehar, L.; Rahman, T.; Tuly, S.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Sarker, M.R.I.; Beg, M.R.A. Thermal performance analysis of a solar still with different absorber plates and external copper condenser. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 17, 100763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuly, S.S.; Hassan, R.; Das, B.K.; Sarker, M.R.I. Investigating the energetic, exergetic, and sustainability aspects of a solar still integrating fins, wick, phase change materials, and external condenser. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, F.A.; Alawee, W.H.; Mohammed, S.A.; Dhahad, H.A.; Abdullah, A.S.; Alqsair, U.F.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M. Improving the pyramid solar distiller performance by using pyramidal absorber, mirrors, condenser, and thermal storing material. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 40, 102515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveenkumar, R.; Shanmugam, S.; Veerappan, A. Performance and exergy analysis of solar-operated vacuum fan and external condenser integrated double-slope solar still using various nanofluids. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 12883–12902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevada, D.; Panchal, H.; Nayyar, A.; Sharma, K.; Manokar, A.M.; El-Sebaey, M.S.; Hussien, A.G. Experimental performance evaluation of solar still with zig-zag shape air-cooled condenser: An energy–exergy analysis approach. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Alawee, W.H.; Mohammed, S.A.; Majdi, A.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M. Utilizing a single slope solar still with copper heating coil, external condenser, phase change material, along with internal and external reflectors—Experimental study. J. Energy Storage 2023, 63, 106899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, B.; Ahmed, M.H.; Shanmugan, S.; Elsheikh, A.H.; El-Sebaey, M.S.; Stephen, M.T.; Oyedepo, S.O.; Raja, V.; Essa, F.A. Enhancing desalination performance of a stepped solar still using nano-enhanced phase change material and condenser integration. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2024, 277, 113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamy, M.I.; Mohammed, S.A.; Basem, A.; Alawee, W.H.; Abdullah, A.S.; Aldabesh, A.; Majdi, H.S.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A. Enhancing coiled solar still performance with vertical wick distiller, reflectors, nanomaterial-infused PCM, and condenser integration. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 61, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarra, S.; Sokhna, S.M.; Faye, S.; Byrne, P.; Sow, O. Data on the experimental characterization of a mobile wick solar still with external condenser tested under the climatic conditions of Rennes, France. Data Brief 2024, 54, 110395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqsair, U.F.; Abdullah, A.S.; Younes, M.M.; Omara, Z.M.; Essa, F.A. Augmenting hemispherical solar still performance: A multifaceted approach with reflectors, external condenser, advanced wick materials, and nano-PCM integration. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 61, 104890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabil, H.A.N.; Hameed, H.G.; Al-Manaa, A.; Alahmer, A. Enhancing solar still productivity and efficiency using external condensers and a copper pipe solar collector. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2025, 103652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Nehar, L.; Prodhan, Y.; Shahed, S.; Al Hasib, S.; Rahman, M.S.; Tuly, S.S. Enhancing solar still performance using external condensers and floating fins: A comparative study. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2025, 11, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, F.A.; Basem, A.; Gadallah, H.Y.; El-Sebaey, M.S.; Alawee, W.H.; Majdi, H.S.; Omara, Z.M. Experimental multi-faceted approach for enhance pyramidal solar still productivity: Tracking, corrugated absorber, reflectors, external condenser, and phase change material integration. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 197, 107061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Umar, H.; Rizal, T.A.; Amir, F.; Abdullah, N.A.; Ginting, S.F.; Mahlia, T.I. Thermal performance improvement of a solar distillation system using a spiral coil condenser with a parabolic dish. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 71, 107353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanaat, S.; Safarzadeh, S.; Eidgah, E.E.F.; Ghafurian, M.M.; Passandideh-Fard, M.; Niazmand, H. Improving multi-stage solar desalination efficiency through vibration-induced frequencies and grooved condenser technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 490, 144623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nimr, M.A.; Dahdolan, M.E. Modeling of a novel concentrated solar still enhanced with a porous evaporator and an internal condenser. Sol. Energy 2015, 114, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadj, M.M.; Bouguettaia, H.; Marif, Y.; Zerrouki, M. Numerical study of a double-slope solar still coupled with capillary film condenser in south Algeria. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 94, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilizadeh, M.; Estahbanati, M.K.; Khorram, M.; Rahimpour, M.R. Experimental investigation of an active thermosyphon solar still with enhanced condenser. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, V.; Sahota, L.; Jain, V.K.; Tiwari, G.N. Performance and cost analysis of a modified built-in-passive condenser and semitransparent photovoltaic module integrated passive solar distillation system. J. Energy Storage 2019, 24, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaisen, H.S.; Esfahani, J.A.; Ayani, M.B. Improvement in the performance and cost of passive solar stills using a finned-wall/built-in condenser: An experimental study. Renew. Energy 2021, 168, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Elfadl, S.; Yousef, M.S.; Hassan, H. Energy, exergy, economic and environmental assessment of using different passive condenser designs of solar distiller. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, H. Enhancing the stepped solar still performance using a built-in passive condenser. Sol. Energy 2022, 248, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emran, N.Y.; Ahsan, A.; Al-Qadami, E.H.; El-Sergany, M.M.; Shafiquzzaman, M.; Imteaz, M.; Ng, A.W.M.; Tariq, M.A.U.R.; Idrus, S.; Mustaffa, Z.; et al. Efficiency of a triangular solar still integrated with external PVC pipe solar heater and internal separated condenser. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeal, A.W.; Xu, Z.; Peng, G.; Hamed, M.H.; Kabeel, A.E.; Yang, N.; Sharshir, S.W. Thermo-economic performance enhancement of a solar desalination unit using external condenser, nanofluid, and ultrasonic foggers. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, A.K.; Murugavel Kulandaivelu, K. Performance comparison of solar still with inbuilt condenser and agitator over conventional solar still with energy and exergy analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 83378–83388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, A.K.; Kulandiavelu, K.M. Performance study on solar still with agitator, inbuilt condenser and fans using energy, exergy and economic analysis. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 306, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, B.; Hakkaki-Fard, A.; Hannani, S.K. On the performance of solar humidification-dehumidification desalination system with subsurface condenser. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 220, 119721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, M.M.; Esmaili, Q.; Ramiar, A. Improved performance of vertical solar still by bio-inspired hybrid wettability condenser surface. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 2024, 64, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, H. Development and application of a thermal model for the improved stepped solar still with a built-in passive condenser. Sol. Energy 2024, 270, 112378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazy, A. Mathematical study of a double-slope passive solar distiller with water heater condenser. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaisen, H.S.; Alhusseny, A. Enhancing productivity and cost-effectiveness of single-slope solar stills using a multi-cavity built-in condenser: Experimental and performance analysis. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2025, 26, 100970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozza, M.A.; Sharaby, M.R.; Abdullah, A.S.; Elashmawy, M.; Abdelaziz, G.B.; Abd EL-Gawaad, N.S.; Sharshir, S.W. A study of different gap spaces and polycarbonate condenser cover on a novel trapezoidal solar still performance. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2025, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
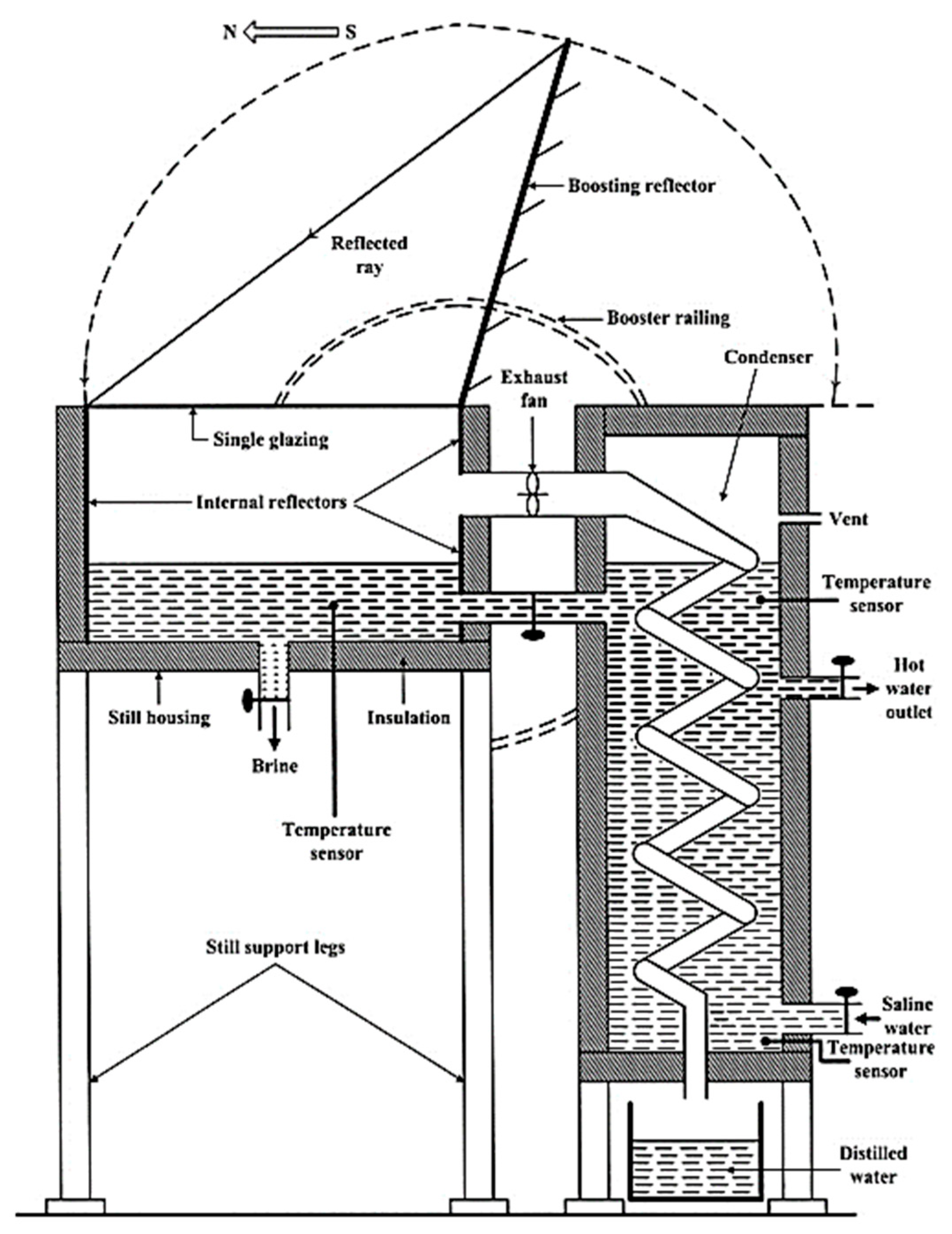
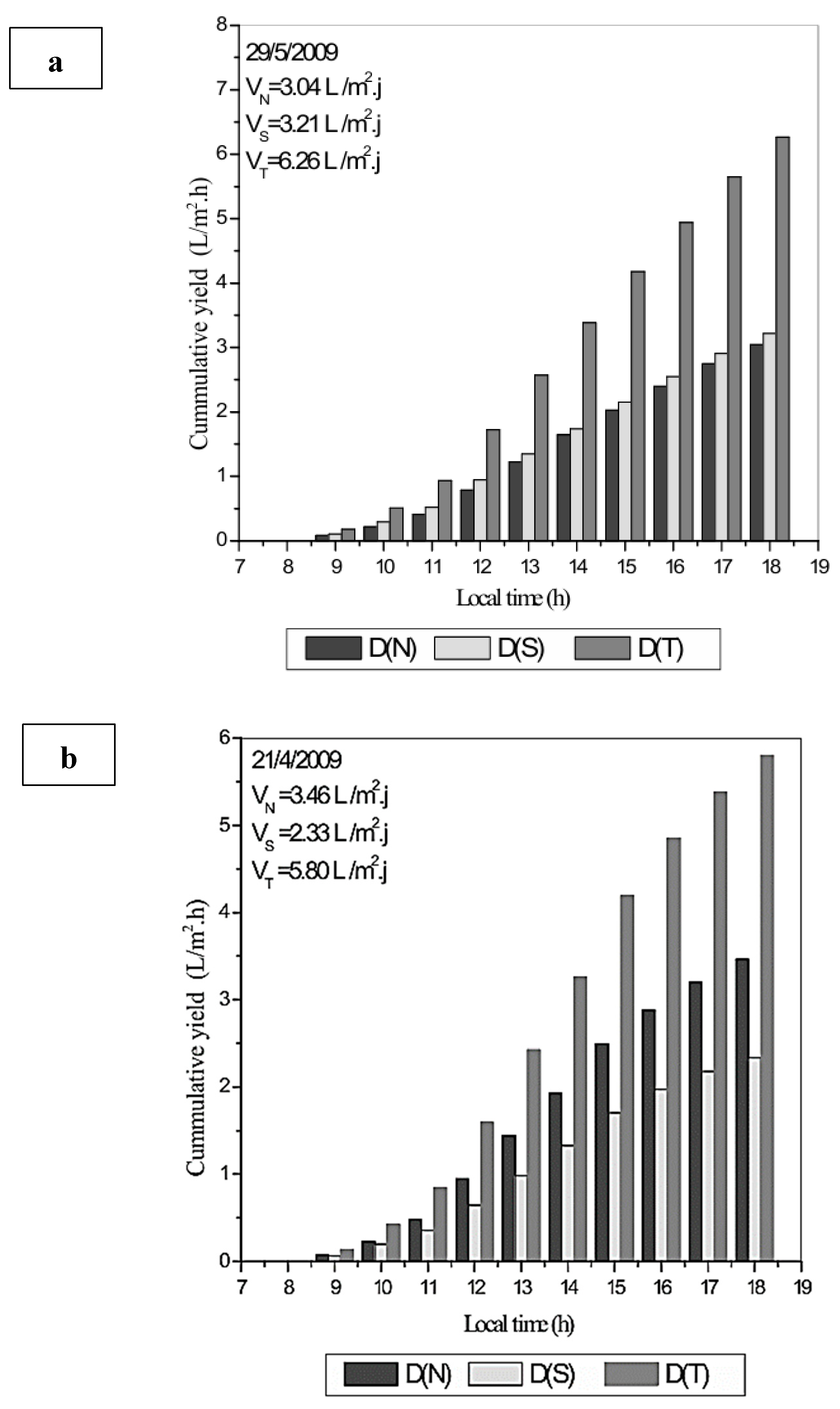
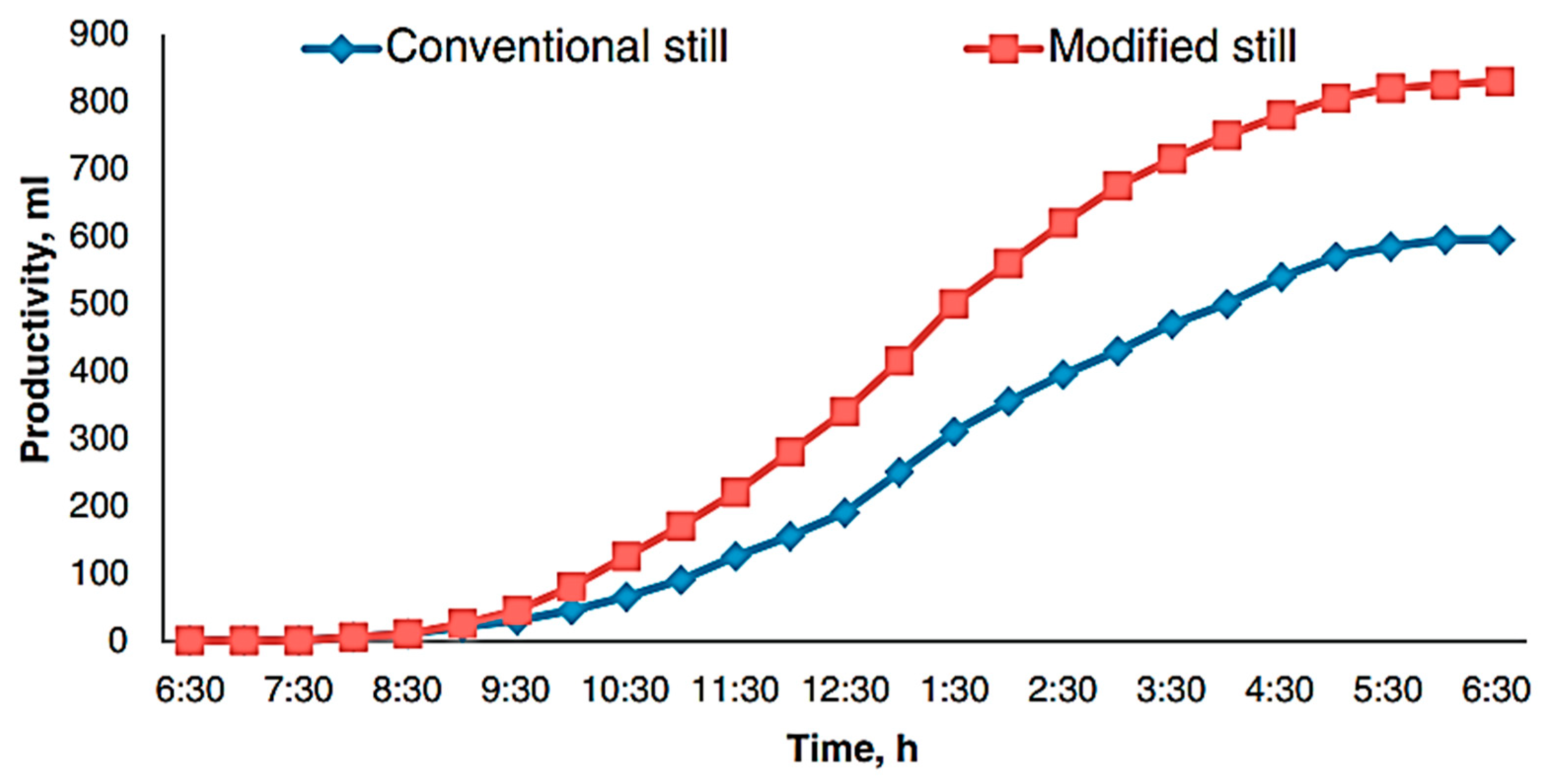

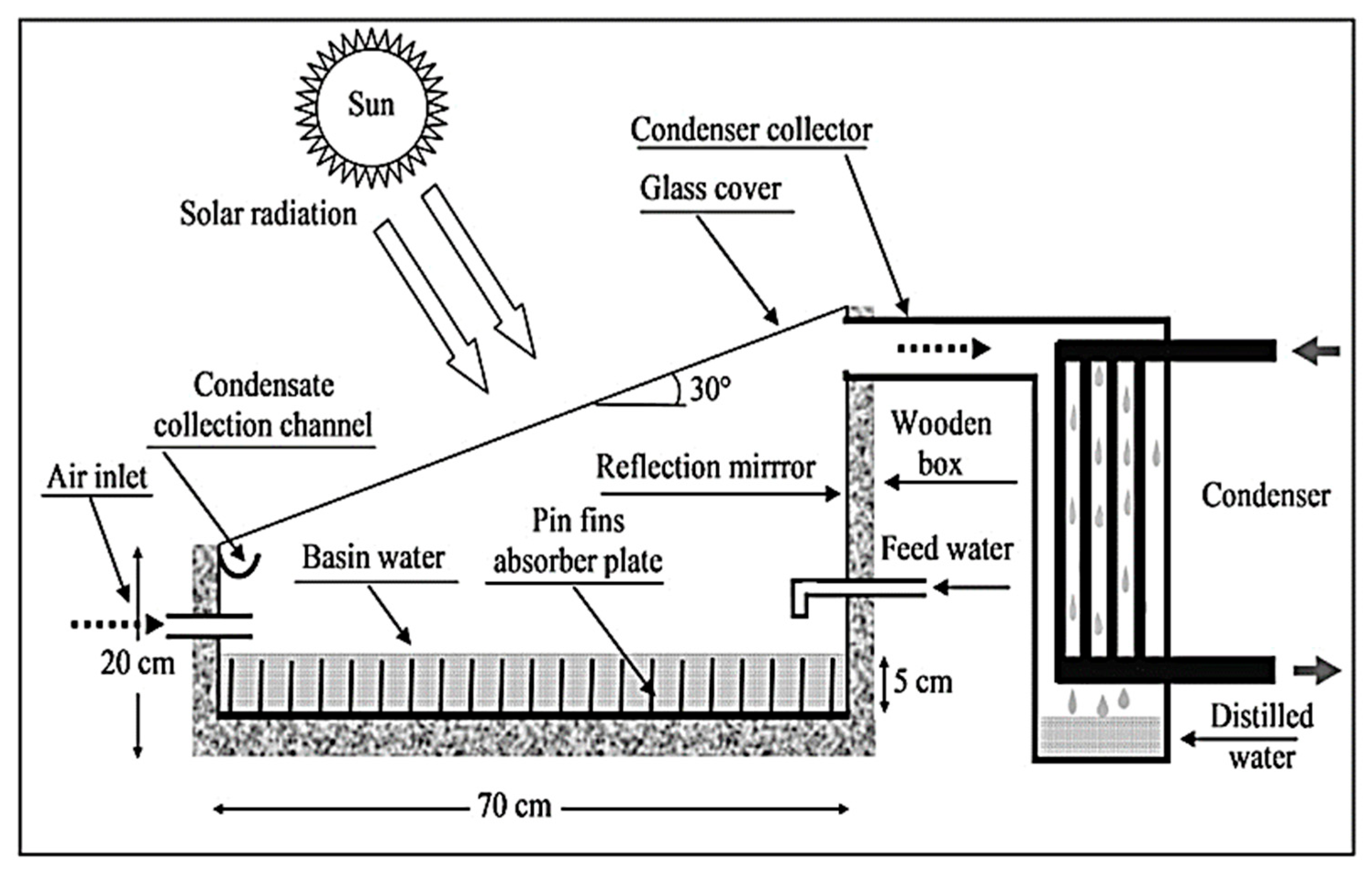
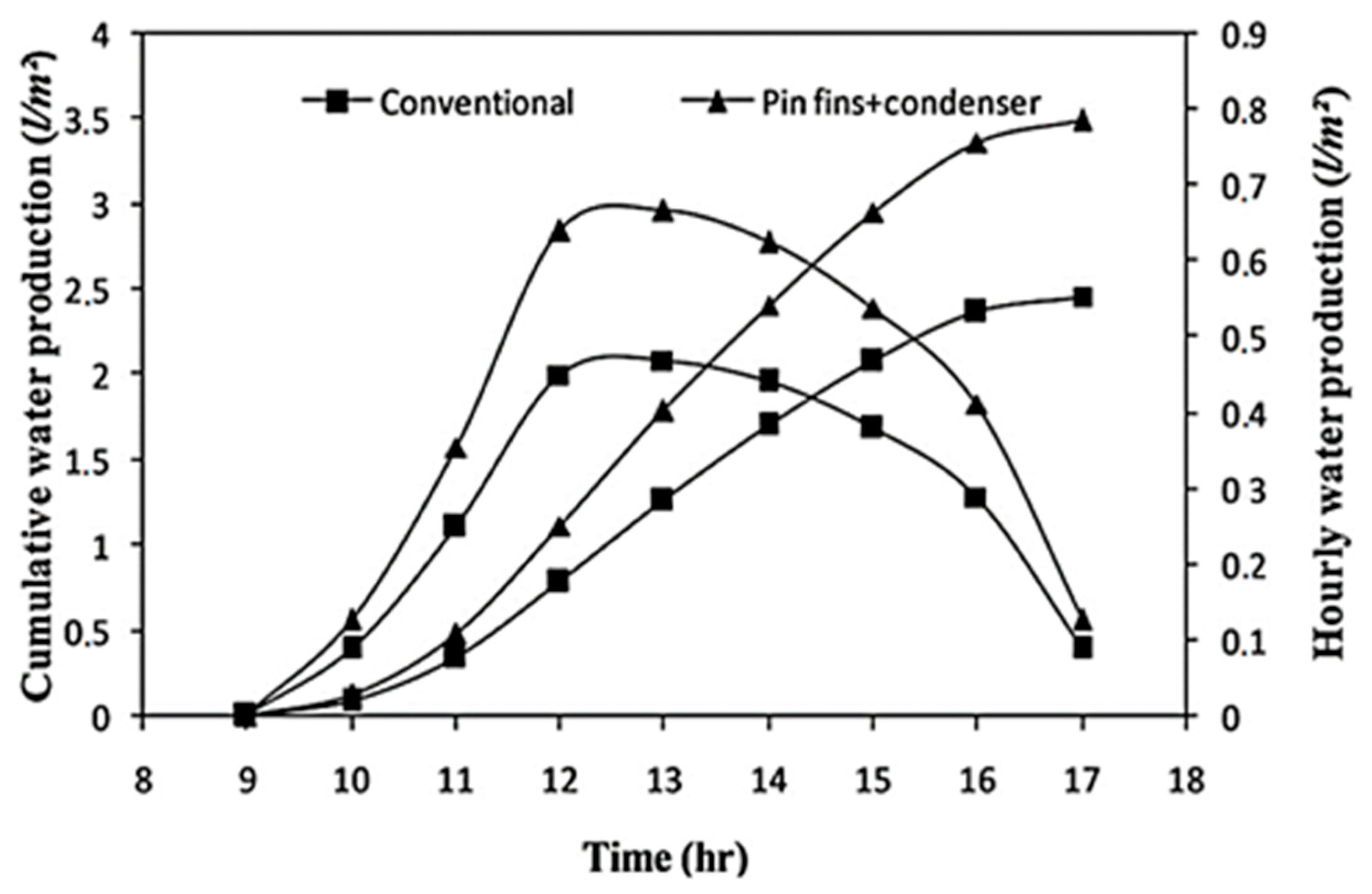
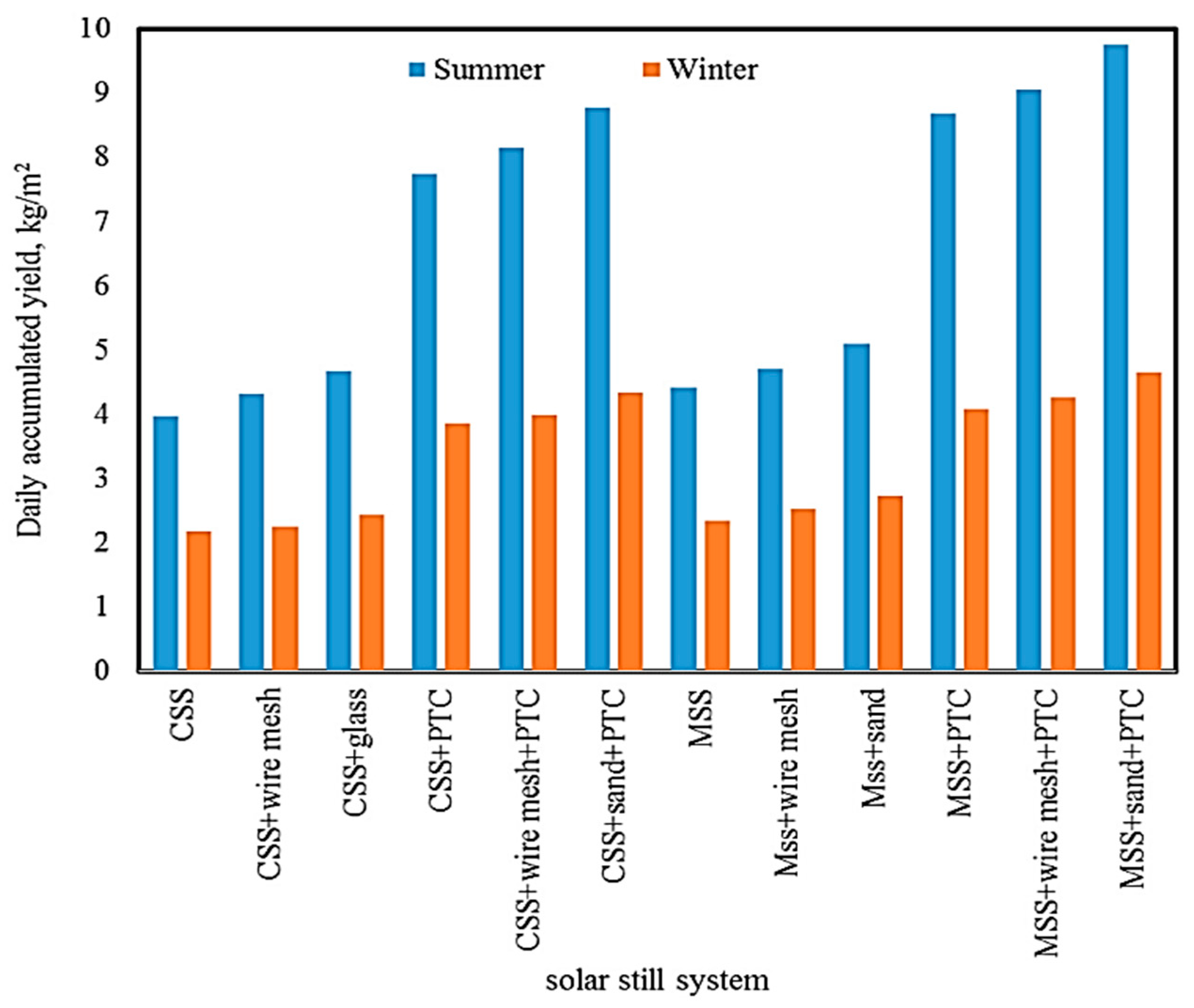
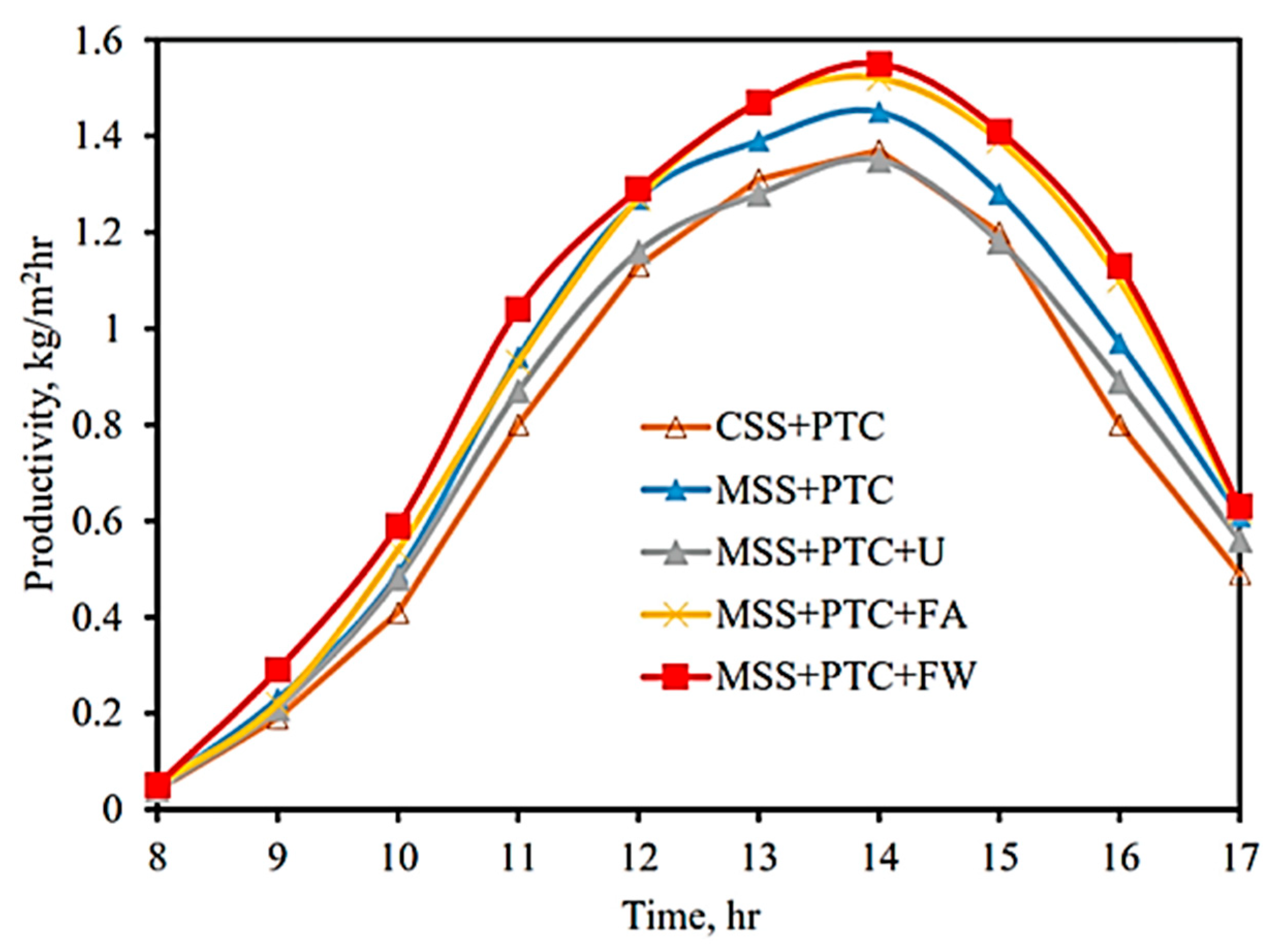

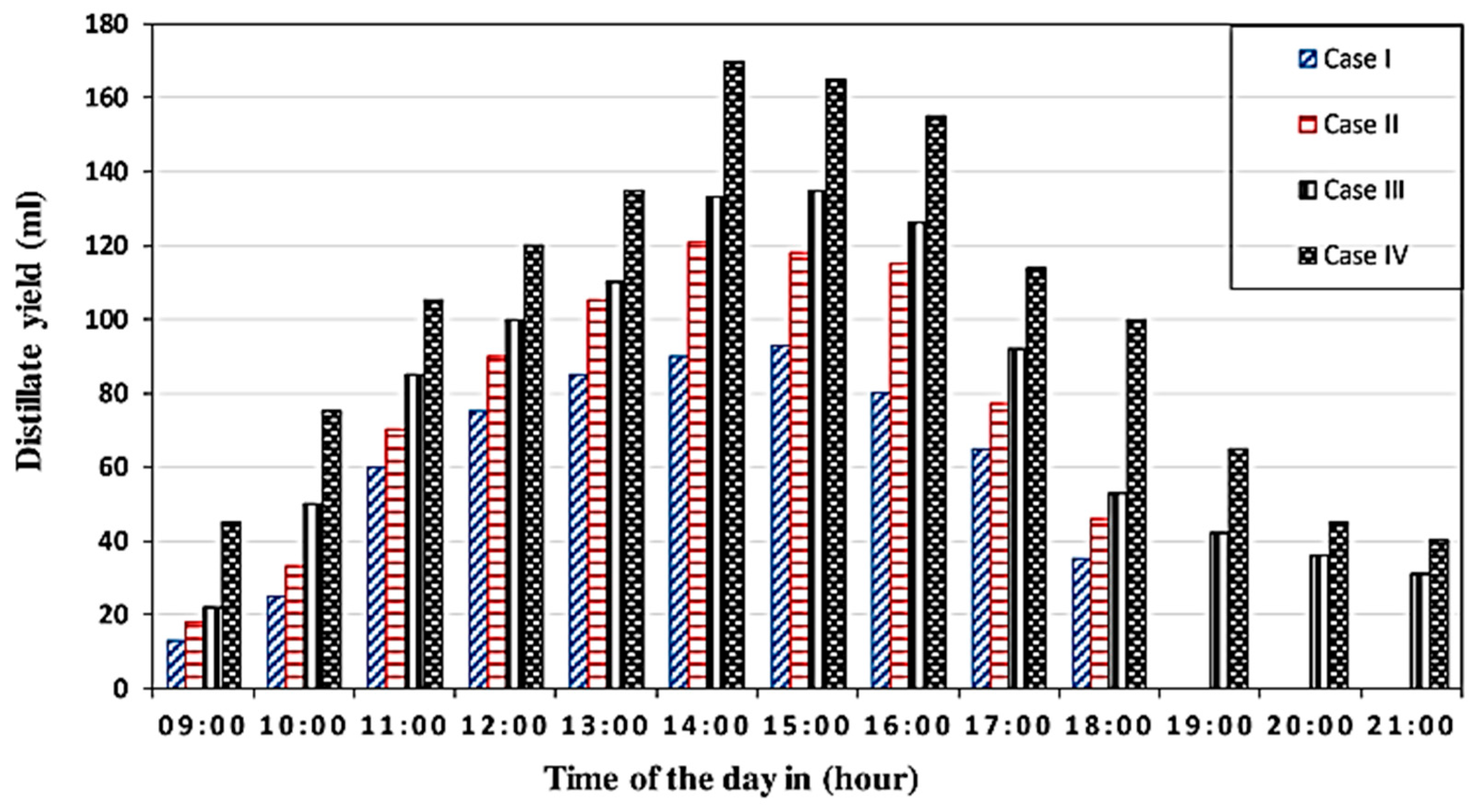
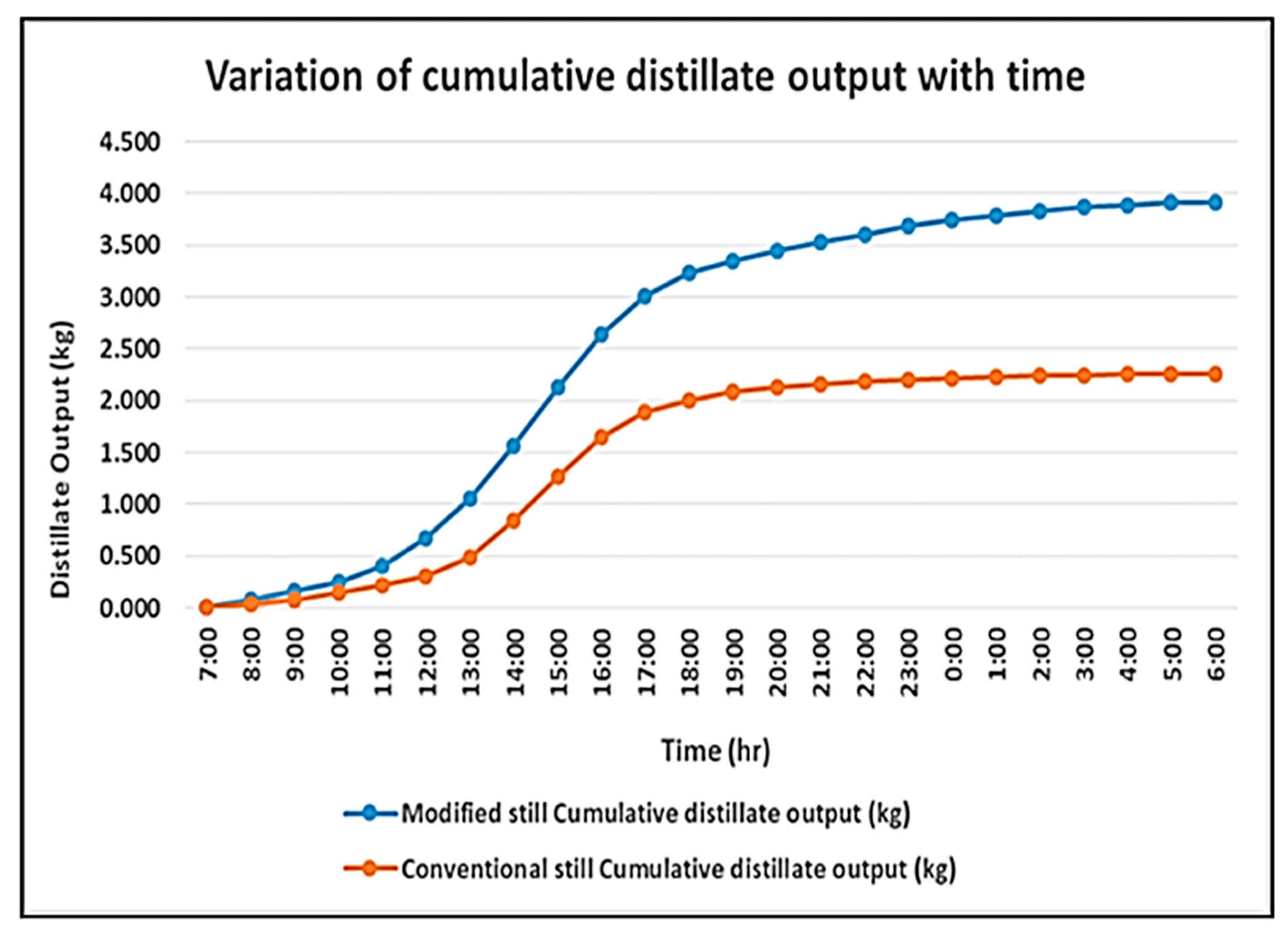
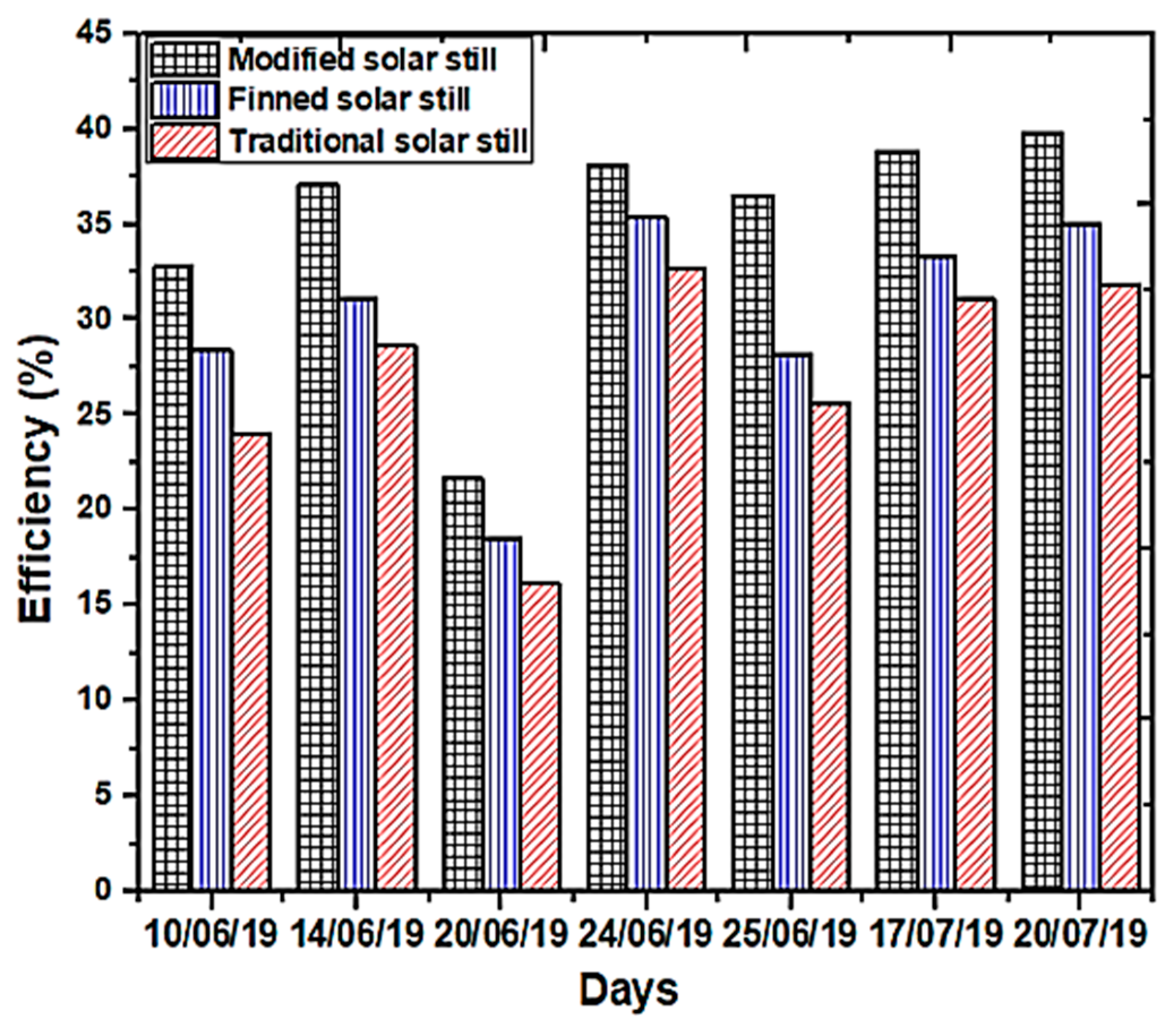

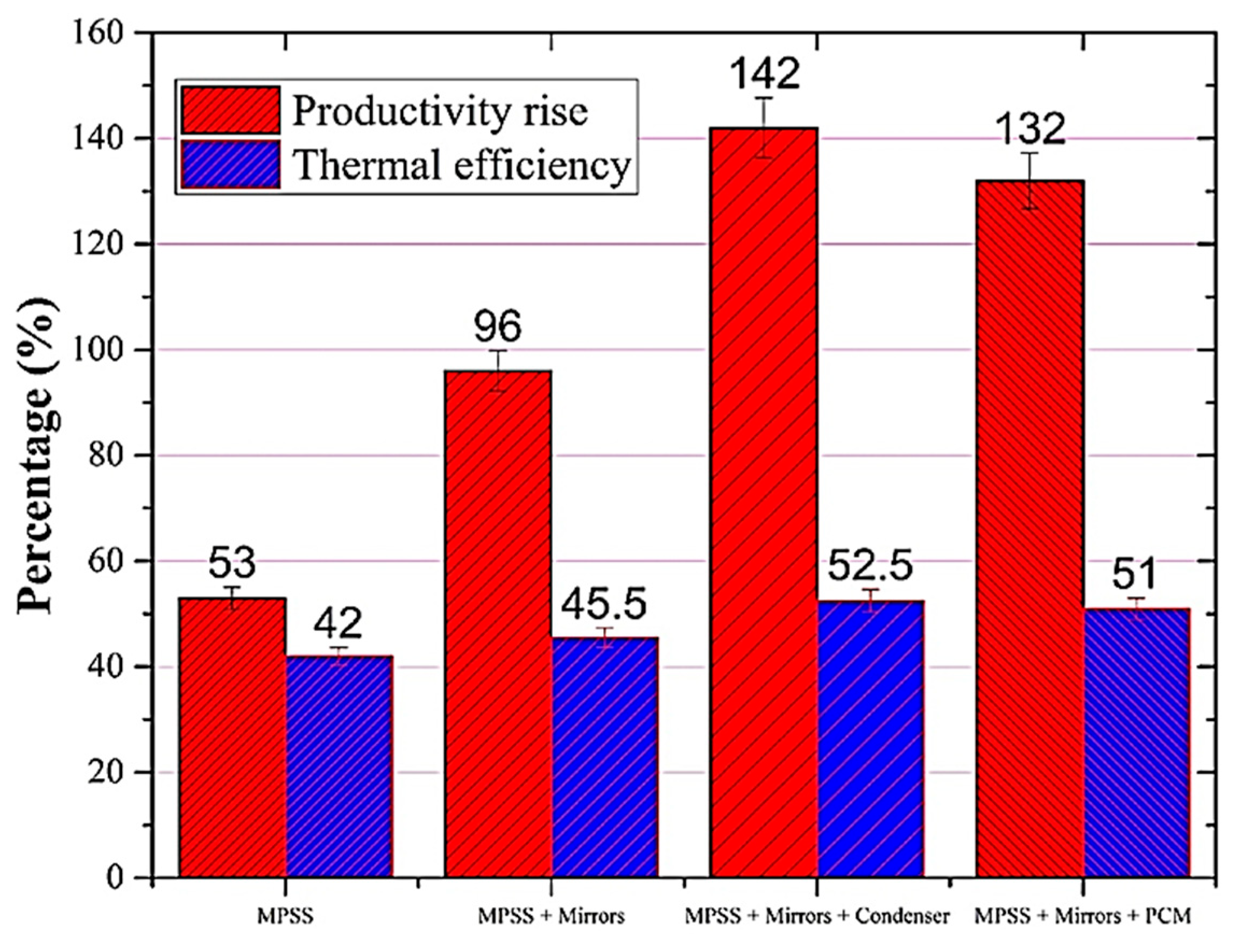
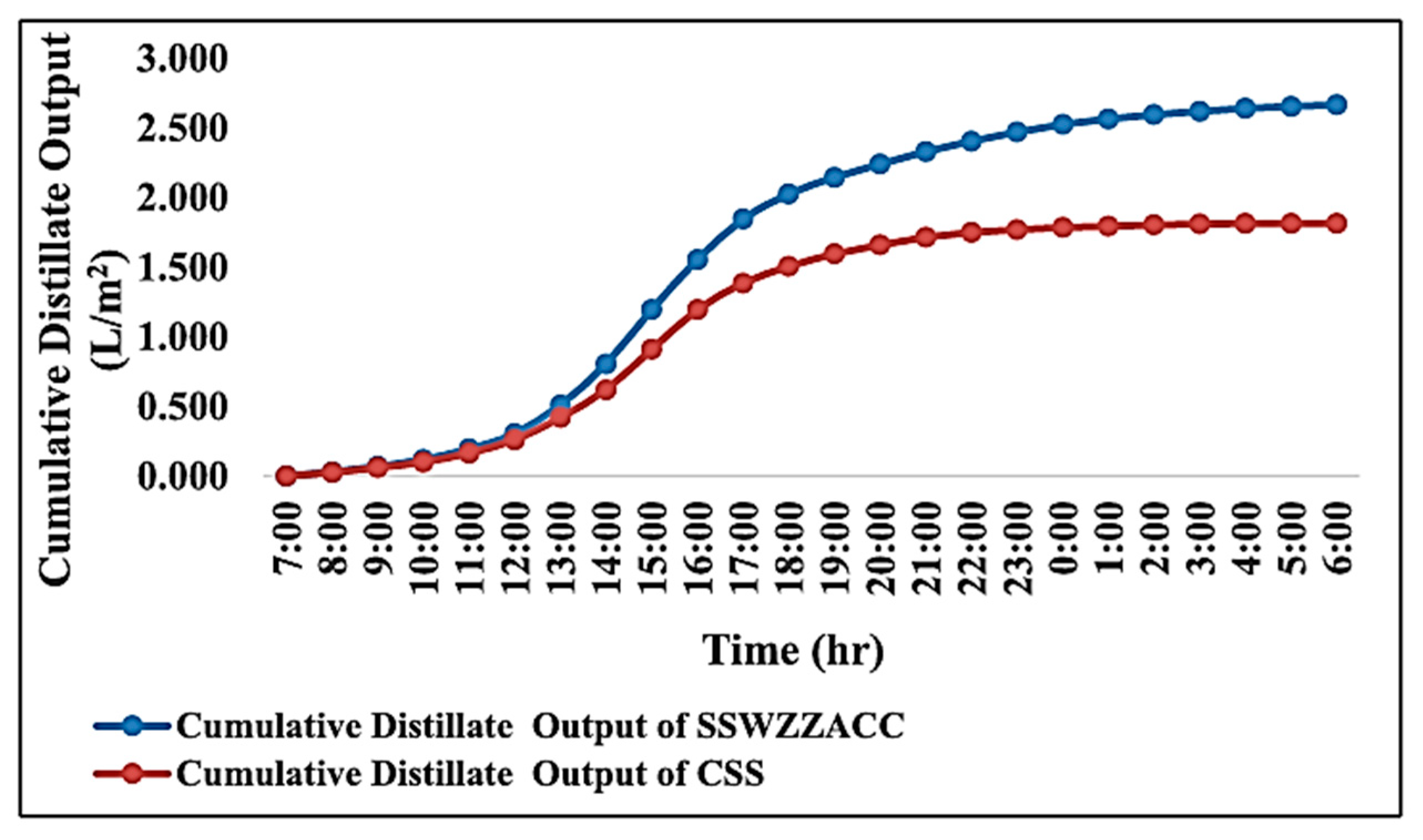
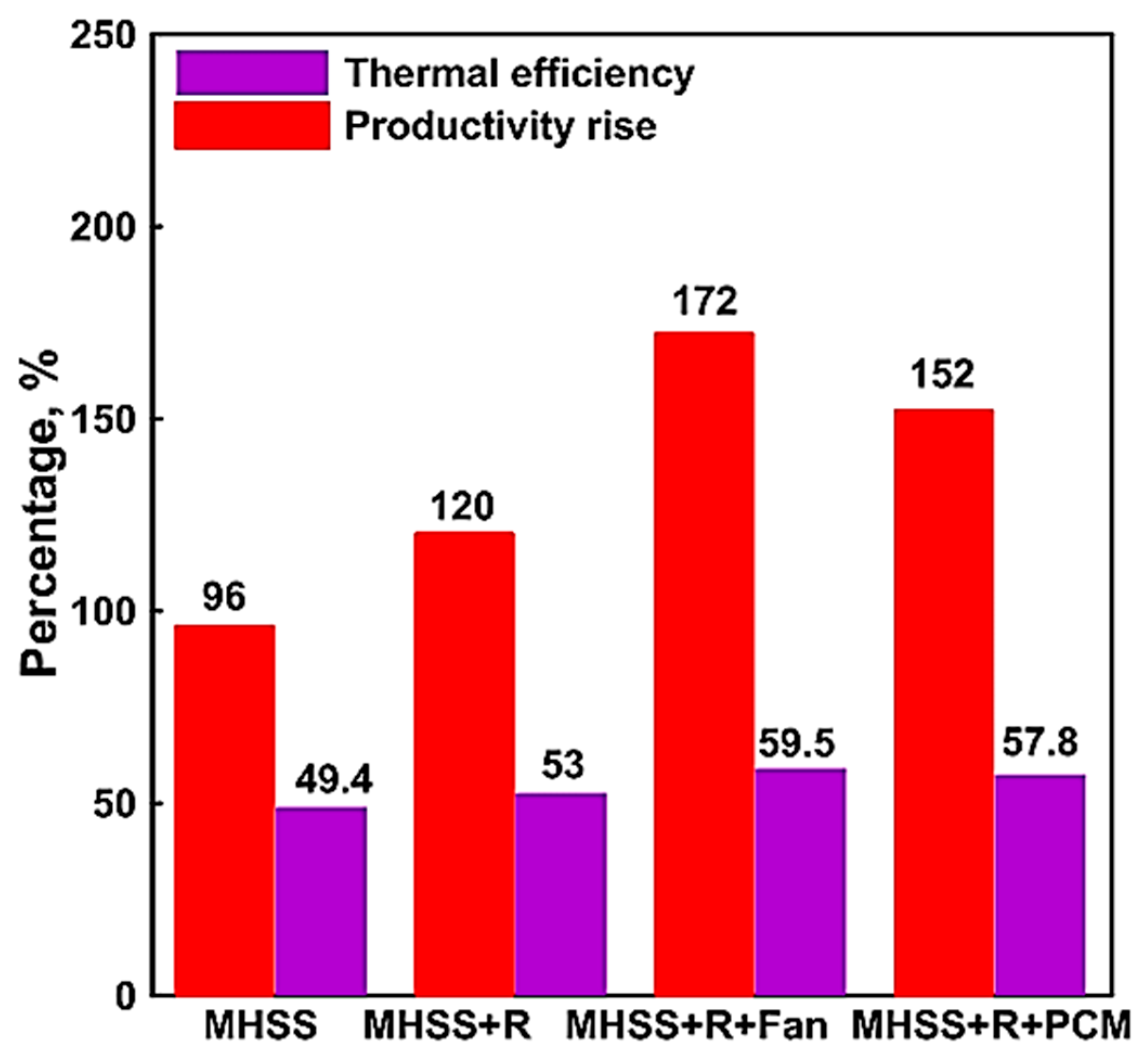
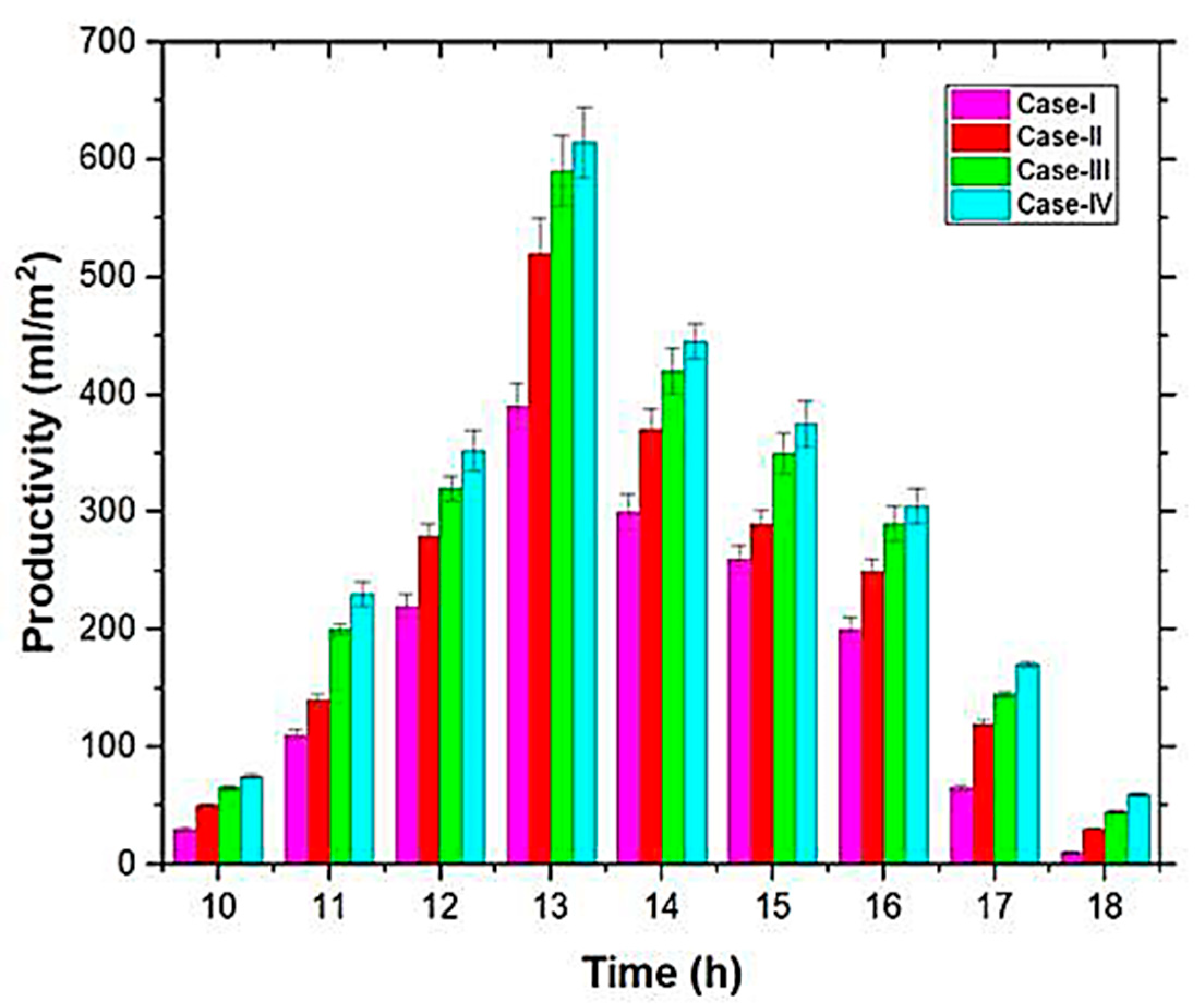
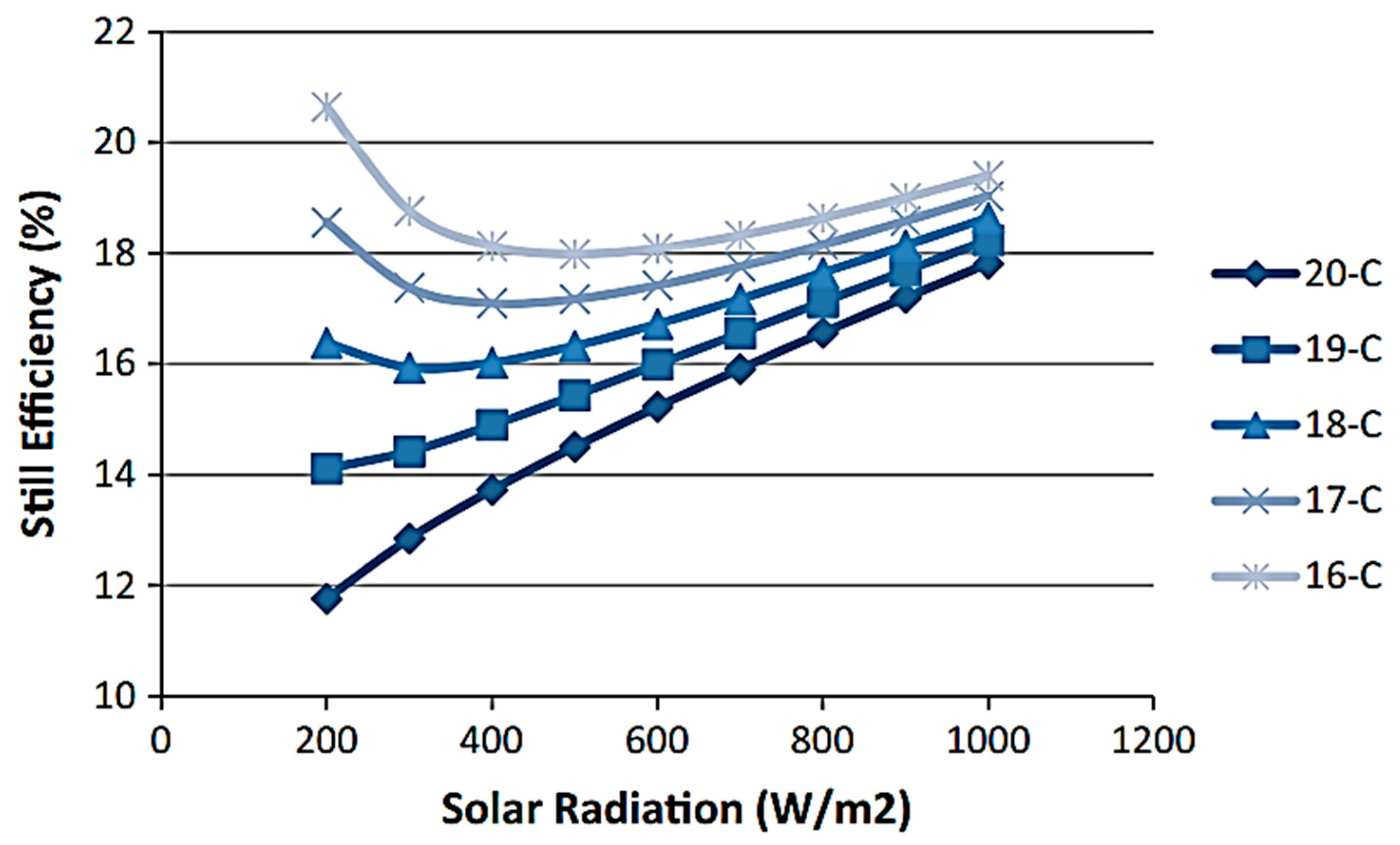
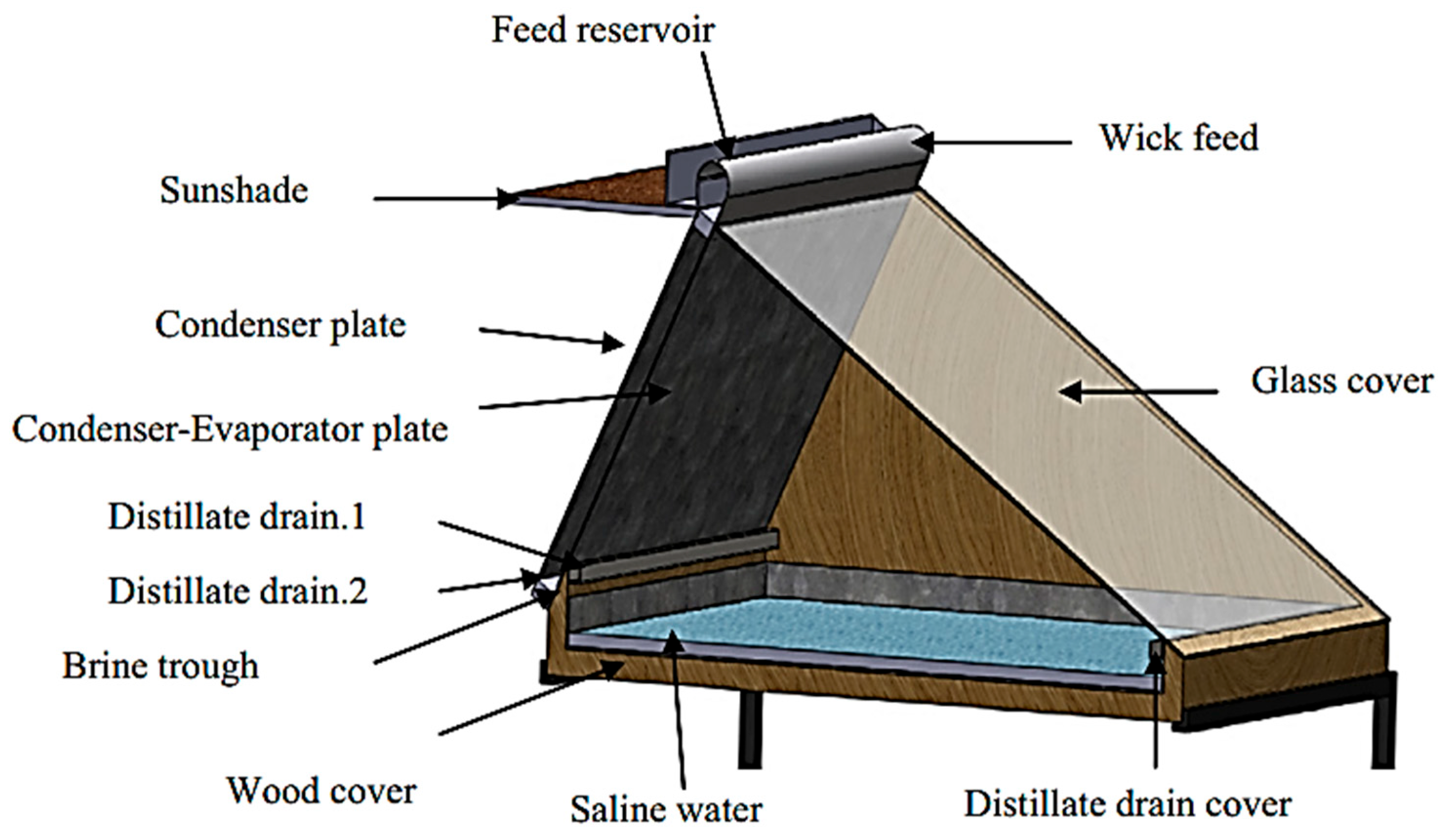

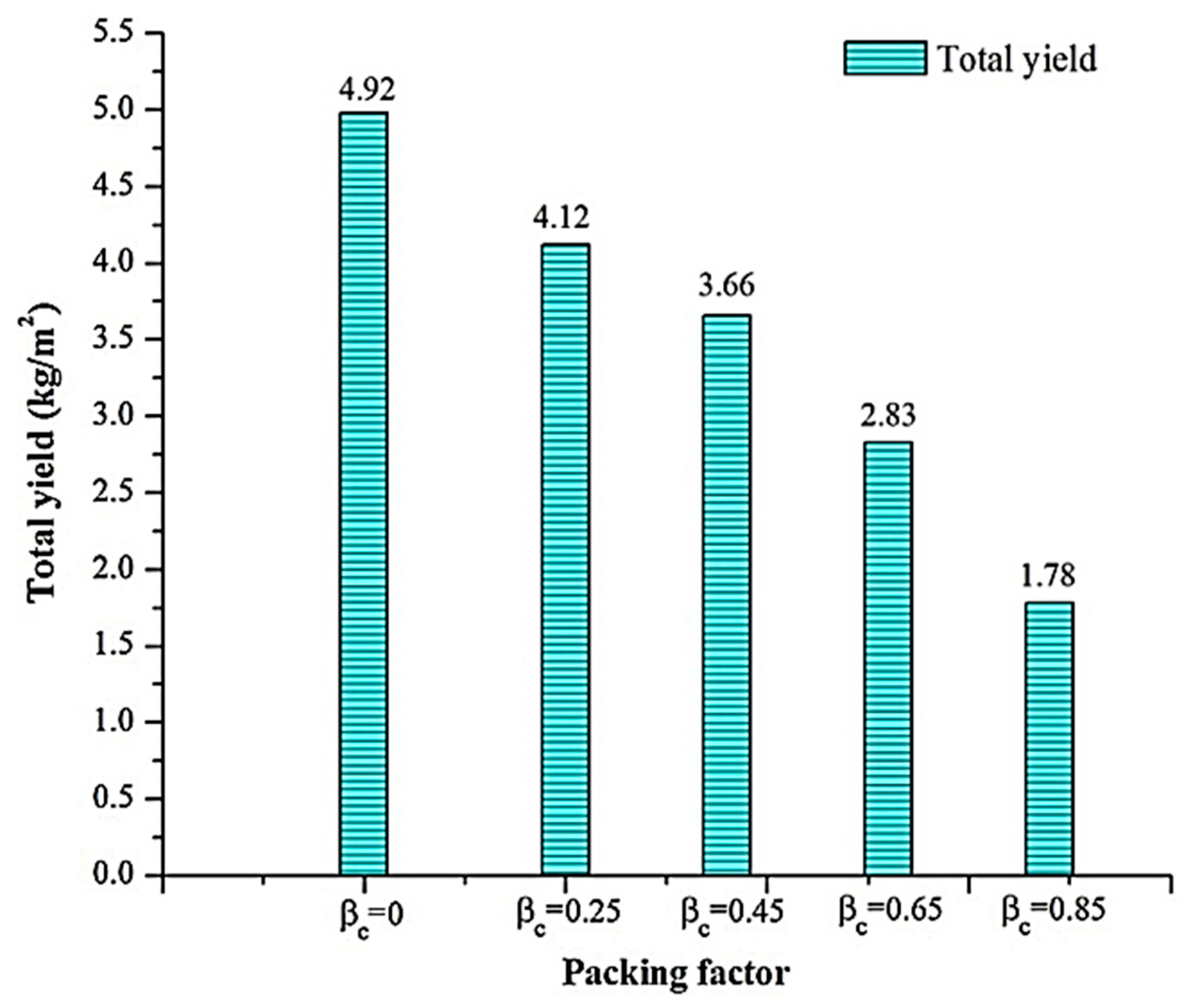
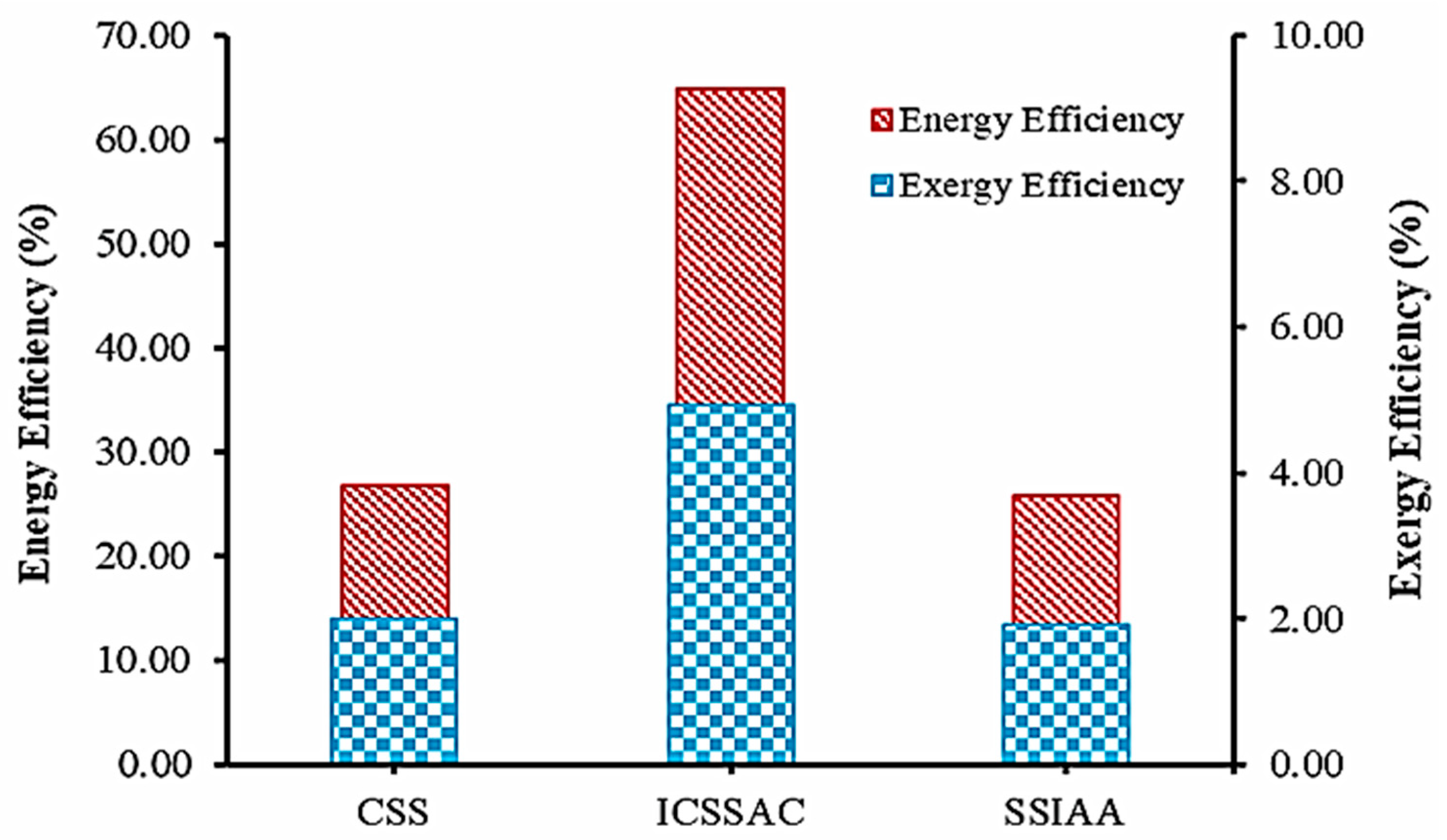
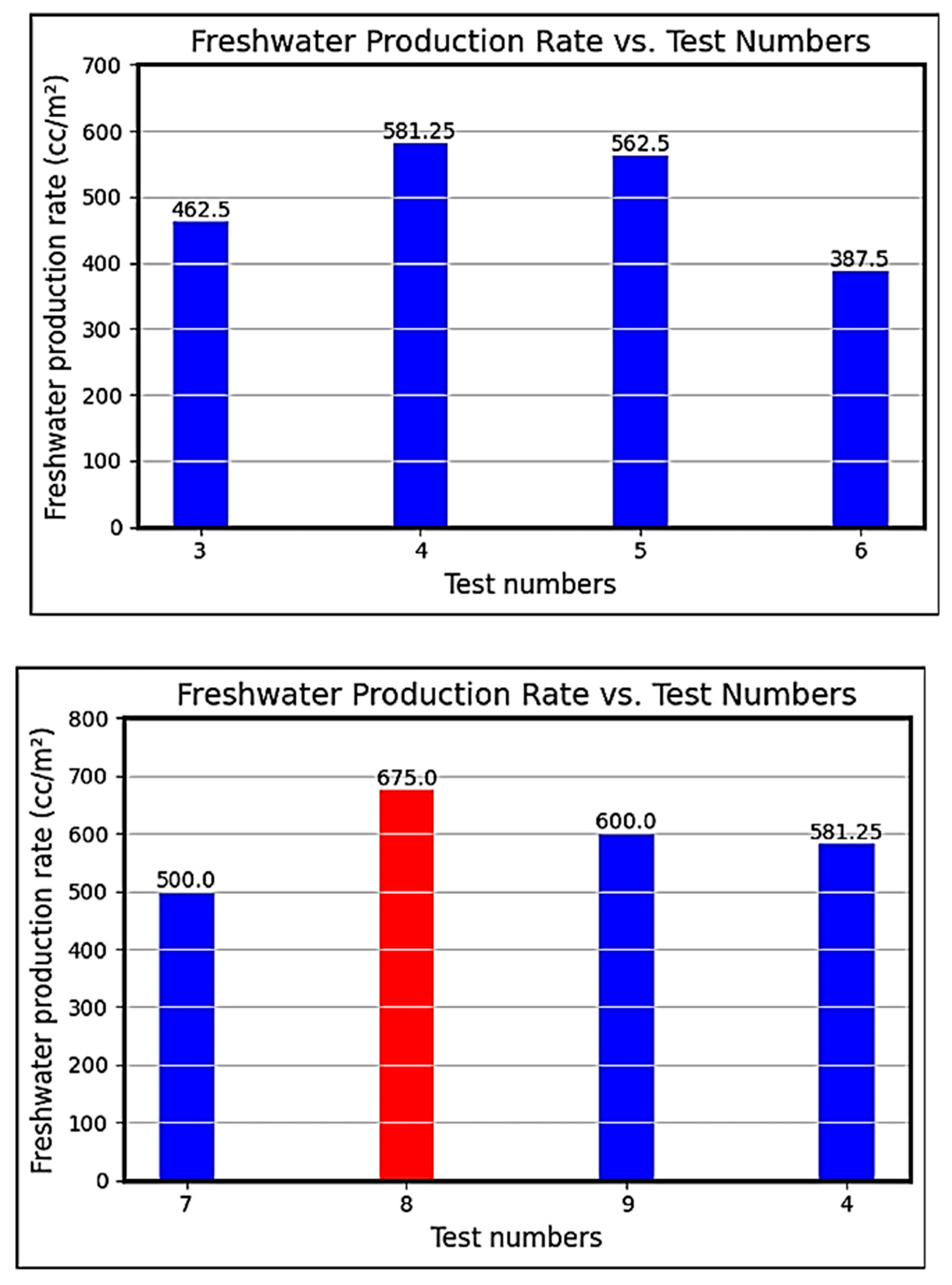
| Authors (Year) [Reference] | Type of Solar Still | Modification | Key Performance Metrics | Results and Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monowe et al. (2011) [46] | Portable single-basin | External reflecting booster and outside condenser | Efficiency, distillate rate | Efficiency up to 77–85% with preheated saline water. |
| Zeroual et al. (2011) [47] | Double-slope | Cooling by flowing water or shading on the north glass cover | Daily yield, productivity | Cooling by water improved yield by 11.82%. |
| Kabeel et al. (2014) [48] | Single basin | Nanofluids (Al2O3) and external condenser | Productivity, efficiency | Nanofluids improved productivity by 116%. |
| El-Samadony et al. (2014) [49] | Stepped | Internal and external reflectors with external condenser | Daily productivity | Productivity increased by 165% with reflectors and condenser. |
| Refalo et al. (2016) [50] | Solar still with solar chimney | Solar chimney and condensers with seawater-cooled tubes | Efficiency, yield | 8.8% better efficiency with condenser. |
| Bhardwaj et al. (2016) [51] | Inflatable | Plastic channels as passive condenser | Production rate | 0.95 L/h with air flow over condenser. |
| Kumar et al. (2016) [52] | Single basin single slope | Agitation effect and external condenser with exhaust fan | Productivity | 39.49% higher productivity with condenser. |
| Rahmani and Boutriaa (2017) [53] | Natural Circulation Loop (NCL) | External condenser with varying area and wind velocity | Daily yield | Productivity increased with condenser area. |
| Rabhi et al. (2017) [54] | Modified single basin | Pin fins absorber and external condenser | Hourly water production | Pin fins and condenser increased yield. |
| Hassan and Abo-Elfadl (2017) [55] | Single slope | Heat sink condenser and saline water mediums (steel fibres, sand) | Daily productivity | Heat sink condenser increased yield by 52%. |
| Kabeel et al. (2017) [56] | Single basin | Nanofluids (Cu2O, Al2O3) and external condenser with low-pressure fan | Daily efficiency | 84.16% efficiency with Cu2O Nanoparticles. |
| Rahman et al. (2019) [57] | Modified with absorber plate | Absorber plate with triangular/rectangular channels and external condenser | Average yield | 24–30% increase with external condenser. |
| Hassan et al. (2020) [58] | Single slope with PTC | PTC, heat sink condenser, and porous media | Daily yield, efficiency | 67% yield increase in summer with PTC. |
| Hassan et al. (2020) [59] | Solar still with PTSC | PTSC with heat sink condenser and forced air/water cooling | Freshwater yield | 14.8% improvement with HSC and FW cooling. |
| Parsa et al. (2020) [60] | Stepped with thermoelectric | Thermoelectric heating, Nano fluid (Ag), and double-slope external condenser | Daily yield | 100.5% improvement with Nano fluid/condenser. |
| Toosi et al. (2021) [61] | Stepped with PCM | PCM and external condenser | Productivity rate | 104% improvement with PCM and condenser. |
| Mevada et al. (2021) [62] | Modified with fins and condenser | Fins, evacuated tubes, and zig-zag air-cooled condenser | Distillate output | 73.45% higher productivity. |
| Patel et al. (2021) [63] | Ultra-modified double slope | External partial cooling coil condenser | Daily yield, efficiency | 76.66% efficiency in summer. |
| Rahmani et al. (2021) [64] | Single-slope basin | New external condenser design (weather-dependent performance) | Productivity | 29% improvement in moderate weather. |
| Tuly et al. (2021) [65] | Double slope with modifications | Rectangular fins, paraffin wax, wick material, and external condenser | Daily efficiency | 39.74% efficiency with condenser. |
| Abdelgaied et al. (2021) [66] | Tubular | Pin fins (inclined/vertical) and external condenser | Accumulative yield | 27.6% improvement with inclined fins and condenser. |
| Sivaram et al. (2021) [67] | Stepped with condenser | Stepped evaporator with passive external condenser | Efficiency | 12.2% improvement in winter. |
| Alawee et al. (2022) [68] | Modified with PCM and condenser | Copper heating coil, external condenser, and Nano-PCM (Ag) | Productivity, efficiency | 120% productivity increase. |
| Moghadam and Samimi (2022) [69] | Evacuated tube collector | Evacuated tube collector with cube-shaped glass condenser | Water production | 7.231 kg.m−2.day−1 with optimal condenser. |
| Hussein and Jassim (2022) [70] | Solar still with separate condenser | Separate condenser with dividers and D.C. fan | Productivity | 39.329% higher yield. |
| Sharshir et al. (2022) [71] | Pyramid with modifications | Evacuated tubes, external condenser, Nanoparticles, and ultrasonic foggers | Freshwater output, efficiency | 91.09% higher output with condenser. |
| Darabi et al. (2022) [72] | Tilted wick with reflector | Channelled twin-wall plastic absorber, external condenser, and reflector | Daily efficiency | 46.13% efficiency with reflector. |
| Nehar et al. (2022) [73] | Double slope with absorber plates | Triangular/rectangular channelled absorber plates and external copper condenser | Productivity, efficiency | 17.86% overall efficiency. |
| Tuly et al. (2022) [74] | Double slope with fins, PCM, etc. | Fins, PCM, external condenser, and wick materials | Energy, exergy, economic metrics | 32.46% improvement in productivity. |
| Essa et al. (2022) [75] | Pyramid with modifications | Pyramidal absorber, jute/cotton wick, external condenser, and reflectors | Productivity, efficiency | 142% improvement with mirrors and condenser. |
| Naveenkumar et al. (2023) [76] | Double-slope with vacuum fan | Solar-operated vacuum fan, external condenser, and Nanofluids (CuO, Al2O3, ZnO) | Energy, exergy efficiency | 64.29% higher production. |
| Mevada et al. (2023) [77] | Solar still with zig-zag condenser | Zig-zag air-cooled condenser and CuO Nanoparticles | Distillate output, efficiency | 46.83% higher productivity. |
| Abdullah et al. (2023) [78] | Single slope with modifications | Copper heating coil, internal/external reflectors, Nano-PCM, and external condenser | Productivity, efficiency | 191% productivity increase with condenser. |
| Saleh et al. (2024) [79] | Stepped with NPCM and condenser | NPCM and condenser | Desalination yield | 110% improvement with NPCM and condenser. |
| Elamy et al. (2024) [80] | Coiled with vertical wick | Vertical wick distiller, reflectors, nanomaterial-infused PCM, and condenser | Distillate output | 269% increase with condenser and fan. |
| Diarra et al. (2024) [81] | Mobile wick | Mobile wick solar still with passive external condenser | Hourly production | Tested under sub-oceanic climate. |
| Alqsair et al. (2024) [82] | Hemispherical with modifications | Hemispherical absorber, jute wick, reflectors, fan, and Nano-PCM | Productivity, efficiency | 172% productivity increase with fan. |
| Diabil et al. (2025) [83] | Solar still with modifications | Multiple external condensers and copper pipe solar collector | Productivity, efficiency | 128.6% higher yield with three condensers. |
| Rahman et al. (2025) [84] | Modified with fins and condenser | Floating aluminium fins and multiple cylindrical external condensers | Daily yield, efficiency | 80.36% higher yield with multiple cylindrical external condensers. |
| Essa et al. (2025) [85] | Pyramid with modifications | Triangular-shaped absorber, tracking, reflectors, external condenser, and PCM | Productivity, efficiency | 166% increase with PCM. |
| Amin et al. (2025) [86] | Solar distillation with spiral coil | Spiral coil condenser with parabolic dish concentrator and coolant fluid | Water production rate | 12.59% higher yield with coolant. |
| Ghanaat et al. (2025) [87] | Multi-stage with PV panels | Water-collecting grooves in condenser and vibration frequencies | Freshwater production | 31% improvement with grooves. |
| Case Number | Contact Angle in Hydrophilic Regions (Degree) | Contact Angle in Hydrophobic Regions (Degree) | Thickness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrophilic Regions (mm) | Hydrophobic Regions (mm) | |||
| 3 | 5 ± 5 | 125 ± 5 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 5 ± 5 | 125 ± 5 | 1.5 | 2 |
| 5 | 5 ± 5 | 125 ± 5 | 2 | 2 |
| 6 | 5 ± 5 | 125 ± 5 | 2.5 | 2 |
| 7 | 5 ± 5 | 125 ± 5 | 1.5 | 1 |
| 8 | 5 ± 5 | 125 ± 5 | 1.5 | 1.25 |
| 9 | 5 ± 5 | 125 ± 5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Authors (Year) [Reference] | Type of Solar Still | Modification | Key Performance Metrics | Results and Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Nimr and Dahdolan (2015) [88] | Novel design with porous evaporator | Internal condenser and thermo-sephonic circulation | Efficiency, distillate rate | Efficiency increased with lower condenser temperature. |
| Belhadj et al. (2015) [89] | Double-slope with capillary film | Condensation cell attached to the still | Daily yield | 60% higher productivity than CSS. |
| Feilizadeh et al. (2019) [90] | Thermo-syphon active | Enhanced condenser and basin/condenser filling options | Distillate production | 66% increase with filled basin and condenser. |
| Saini et al. (2019) [91] | Passive with solar photovoltaic module | Built-in passive condenser and semi-transparent PV module | Energy efficiency | 57.5% efficiency with high packing factor. |
| Mohaisen et al. (2021) [92] | Passive single-slope | Incorporated condenser with external fins | Daily productivity | 92.3% increase with fins. |
| Abo-Elfadl et al. (2021) [93] | Solar distiller | Various condenser designs (e.g., pin fins, corrugated sheets) | Energy, exergy, economic metrics | 54% yield increase with PHS condenser. |
| Amiri (2022) [94] | Improved stepped | Built-in passive condenser and divided evaporation/condensation chambers | Daily yield, efficiency | 30–150% higher yield than standard still. |
| Emran et al. (2022) [95] | Triangular with PVC heater | Internal separated condenser | Daily water production | 24% higher yield in active still. |
| Kandeal et al. (2022) [96] | Solar still with modifications | Active/passive condensers and Nano fluid | Yield, energy efficiency | 31% yield increase with type-B condenser. |
| Rajasekaran and Kulandaivelu (2022) [97] | Modified with inbuilt condenser | Agitator and extended condensing area | Productivity | 98.69% more productivity than conventional. |
| Rajasekaran and Kulandiavelu (2023) [98] | Inbuilt condenser with agitator | Solar PV-powered agitator and condensing fans | Energy, exergy efficiency | 38.10% higher efficiency than conventional. |
| Asgari et al. (2023) [99] | Solar humidification–dehumidification | Subsurface condenser | Daily water yield, GOR | 1120% higher GOR in optimum system. |
| Bakhshi et al. (2024) [100] | Vertical solar still | Hybrid hydrophilic/hydrophobic condenser surfaces | Freshwater production rate | 17% improvement with hybrid surface. |
| Amiri (2024) [101] | Improved stepped | Theoretical model validation for built-in condenser | Daily yield, RMSE | 3.7% relative error in yield estimation. |
| Ghazy (2024) [102] | Double-slope passive | Condensation losses recovered to heat water in solar water heater | Thermal efficiency | 18–83% efficiency increase. |
| Mohaisen et al. (2025) [103] | Passive single-slope | Multi-cavity built-in condenser | Net daytime productivity | 44.8% improvement with double-cavity. |
| Rozza et al. (2025) [104] | Trapezoidal with jute wick | Adjustable gap between absorber and condenser cover | Productivity, cost | 34.2% lower cost at 5 cm gap. |
| Parameter | External Condenser | References | Internal Condenser | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Productivity Increase | 24–165% | [49,95] | 30–150% | [94] |
| Design Complexity | Higher design complexity as it requires additional components | - | Lower design complexity as it integrates within the still | - |
| Energy Dependency | May need active cooling (e.g., fans) | [43] | Mostly passive | [51] |
| Space Requirement | Larger footprint | - | Compact | - |
| Climate change | Less affected by ambient conditions | [64] | More sensitive to internal airflow | [94] |
| Cost Implications | Higher initial cost due to added components | [52] | More economical in basic configurations | [91] |
| Enhancement | Potential Benefit | Major Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Hybrid nanomaterials | Higher thermal conductivity, faster evaporation | Nanoparticle settling, high cost |
| Multi-stage condensation | Increased freshwater recovery | Complex design, space requirements |
| Solar tracking systems | Optimised solar absorption | Mechanical wear, energy consumption |
| Machine learning controls | Adaptive performance optimisation | High technical expertise needed |
| Biomimetic condenser surfaces | Improved droplet shedding | Fabrication difficulty, durability concerns |
| Nano-enhanced PCMs | Extended operational hours | Phase segregation, thermal degradation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Rashid, F.L.; Hashim, A.J.; Al-Musawi, S.S.; Almaamari, Q.; Mujtaba, I.M. A Review on the Impact of Condenser Technologies on Solar Still Productivity. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310786
Al-Obaidi MA, Rashid FL, Hashim AJ, Al-Musawi SS, Almaamari Q, Mujtaba IM. A Review on the Impact of Condenser Technologies on Solar Still Productivity. Sustainability. 2025; 17(23):10786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310786
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Obaidi, Mudhar A., Farhan Lafta Rashid, Ahmed Jasim Hashim, Sura S. Al-Musawi, Qais Almaamari, and Iqbal M. Mujtaba. 2025. "A Review on the Impact of Condenser Technologies on Solar Still Productivity" Sustainability 17, no. 23: 10786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310786
APA StyleAl-Obaidi, M. A., Rashid, F. L., Hashim, A. J., Al-Musawi, S. S., Almaamari, Q., & Mujtaba, I. M. (2025). A Review on the Impact of Condenser Technologies on Solar Still Productivity. Sustainability, 17(23), 10786. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172310786










