Reinforcement Learning-Based Adaptive Hierarchical Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy for Fuel Cell Hybrid Engineering Vehicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
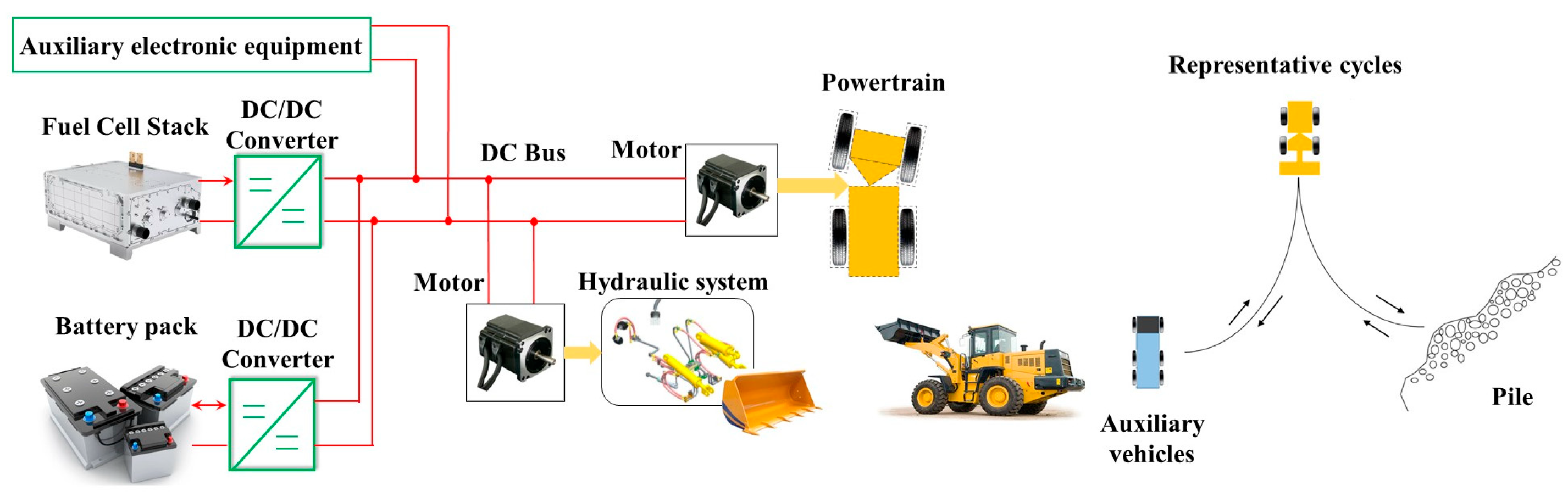
2. System Model
3. Energy Management Strategy Development
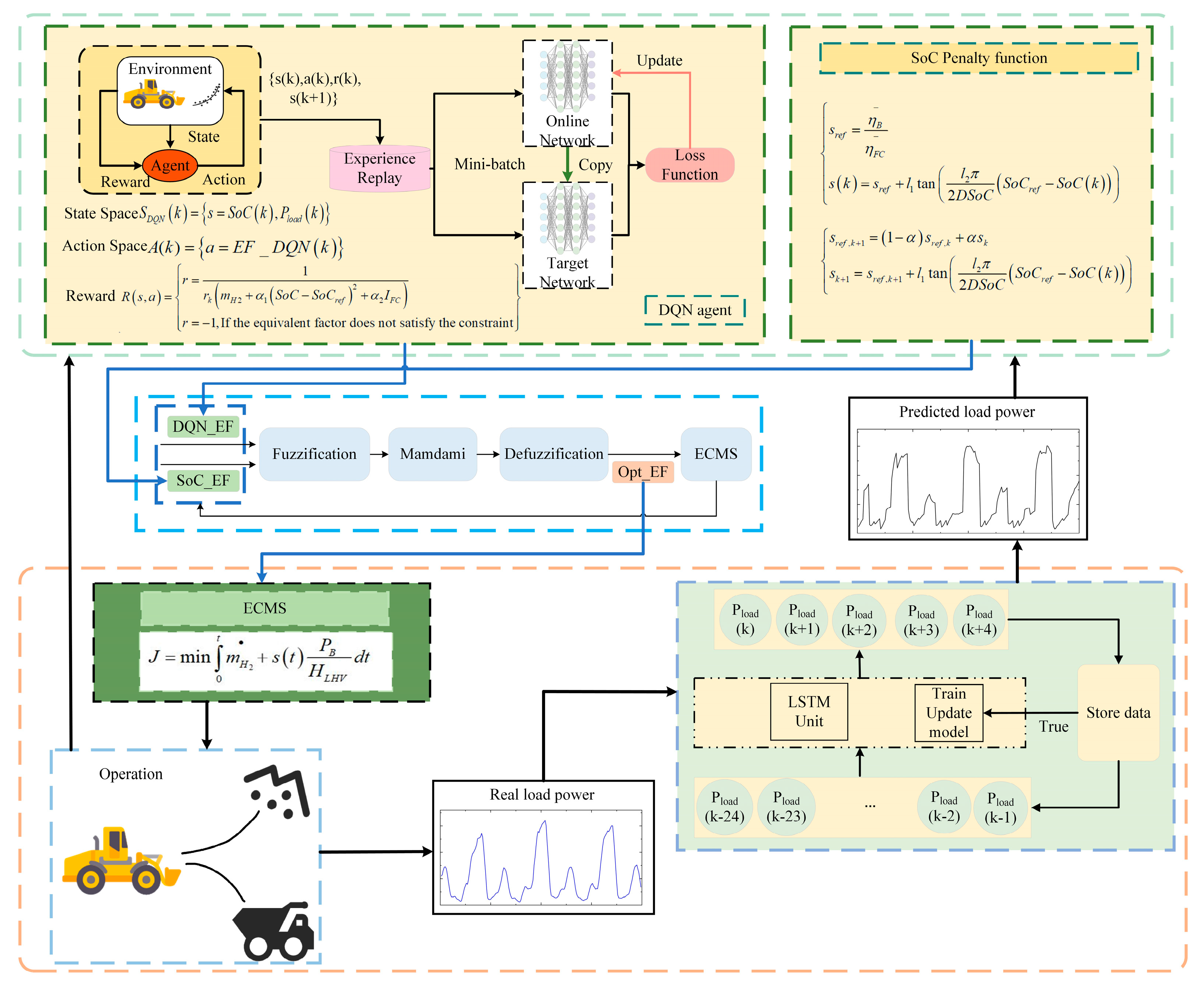
3.1. ECMS Energy Management Framework Based on Hierarchical Structure
| Algorithm 1 H-ECMS |
| 1: Initialize all variables and models NLSTM, QRE, QRT |
| 2: Import LSTM neural network training sample set |
| 3: Training NLSTM |
| 4: From historical environment data, retrieve training tuples Φ(st, a, r, st+1) and store them in the replay buffer R |
| 5: Perform the gradient descent step using QRE(s, a) |
| 6: Set QRT = QRE |
| 7: loop |
| 8: Forecast the demand power for the next five steps using NLSTM and obtain the known Ppred |
| 9: s (current row status from environment) |
| 10: Choose a(ε-greed(s, a)) |
| 11: Take a, reward r and st + 1 (select fuel cell output power through new equivalent factor a) |
| 12: Draw N oversamples (st, a, r, st+1) from R |
| 13: Perform gradient descent step using QRE |
| 14: Set QRT=QRE |
| 15: Based on the SoC penalty function, the SoC_EF at this time is obtained |
| 16: Taking action a, SoC_EF as fuzzy logic input, the output Opt_EF is obtained |
| 17: Use ECMS to output fuel cell output power through Ppred, Opt_EF, etc. |
| 18: And store the historical actual power into the LSTM memory bank |
| 19: if LSTM memory bank > 100 then |
| 20: Train NLSTM and update the model and LSTM memory library |
| 21: end if |
| 22: end loop |
3.2. Equivalence Factor Regulator Based on DQN Reinforcement Learning
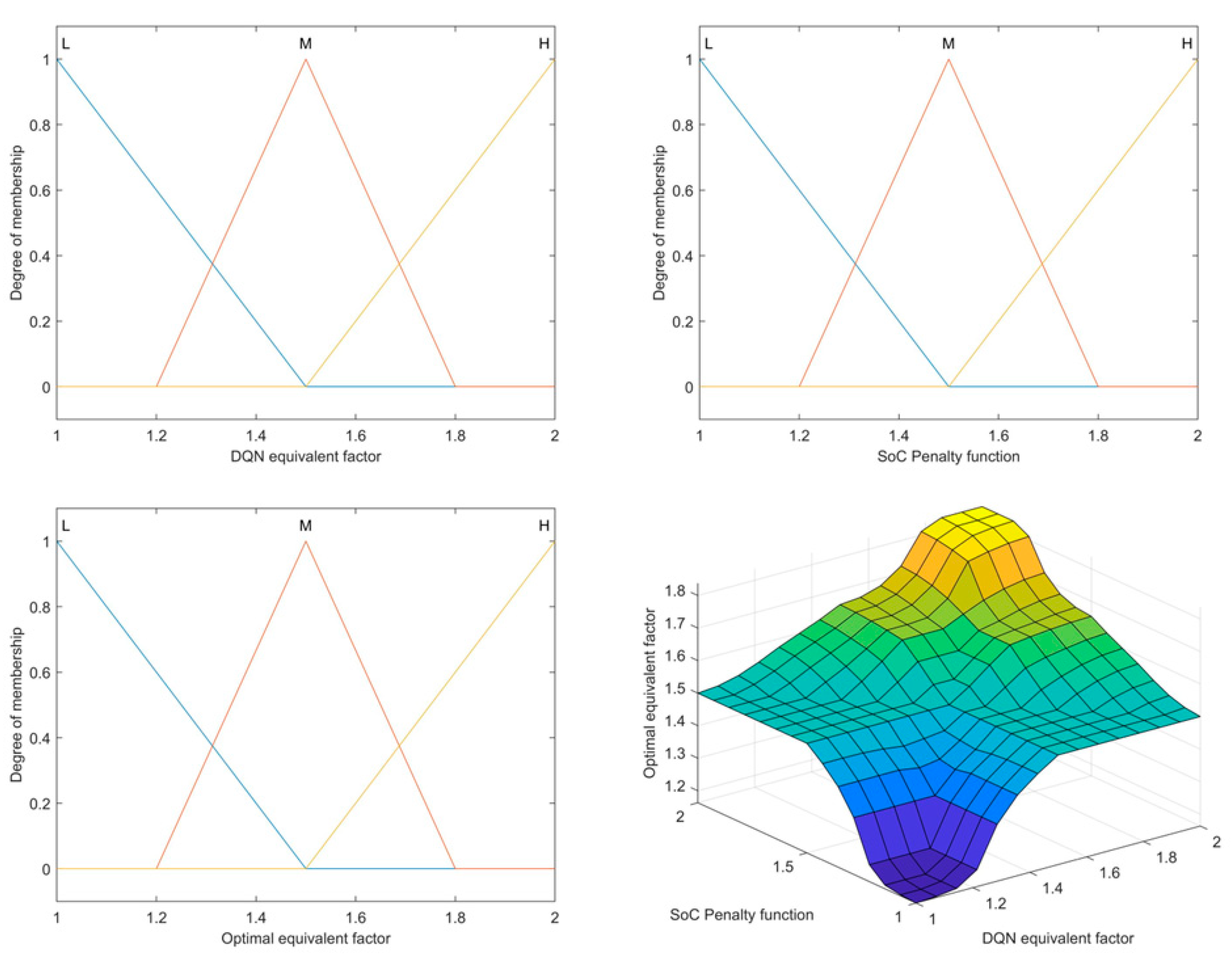
3.3. Fuzzy Logic-Based Fusion Coefficient Adjustment
3.4. Proof of Optimal Range of Equivalent Factors
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
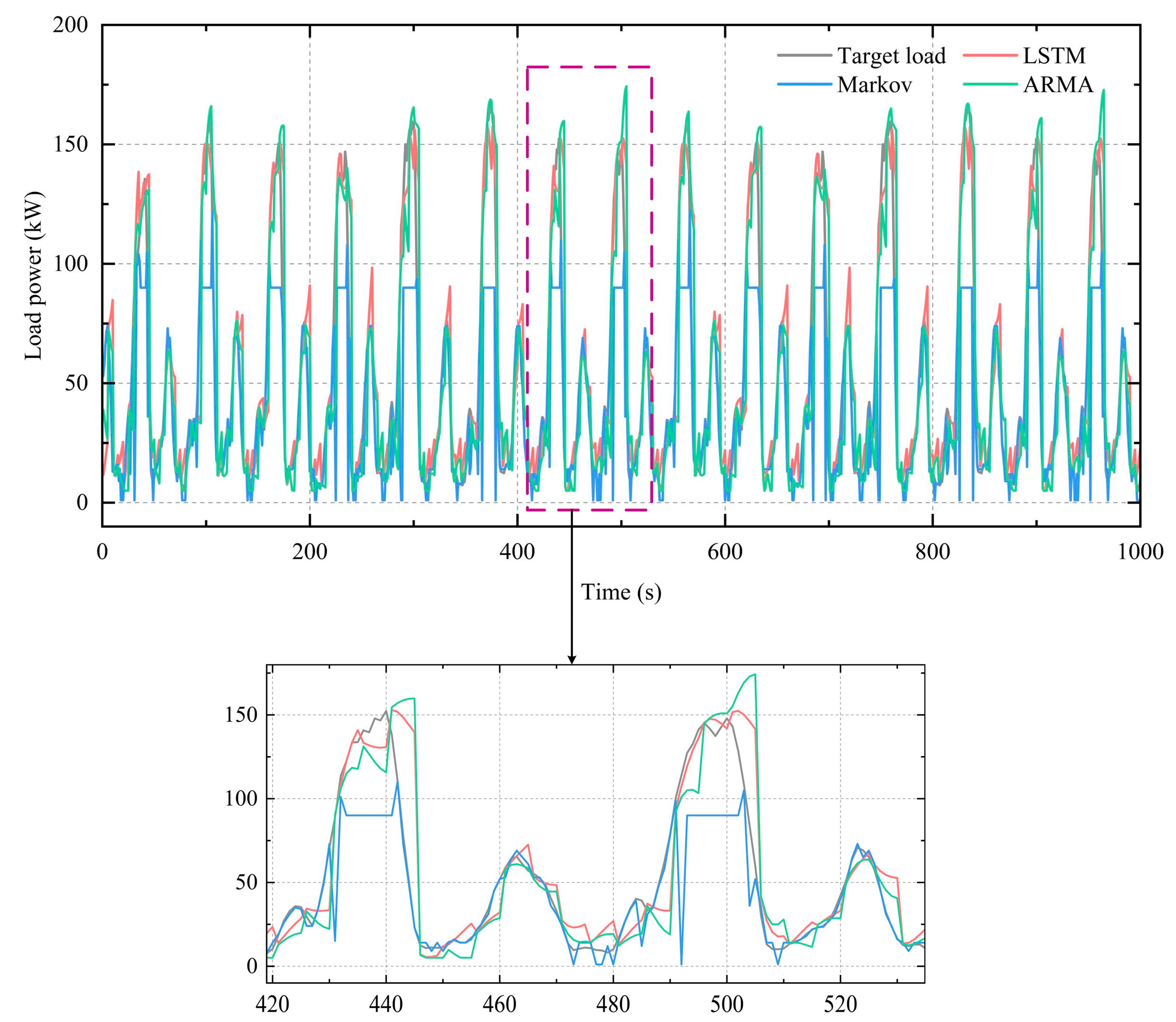
4.1. LSTM Neural Network Prediction Effect
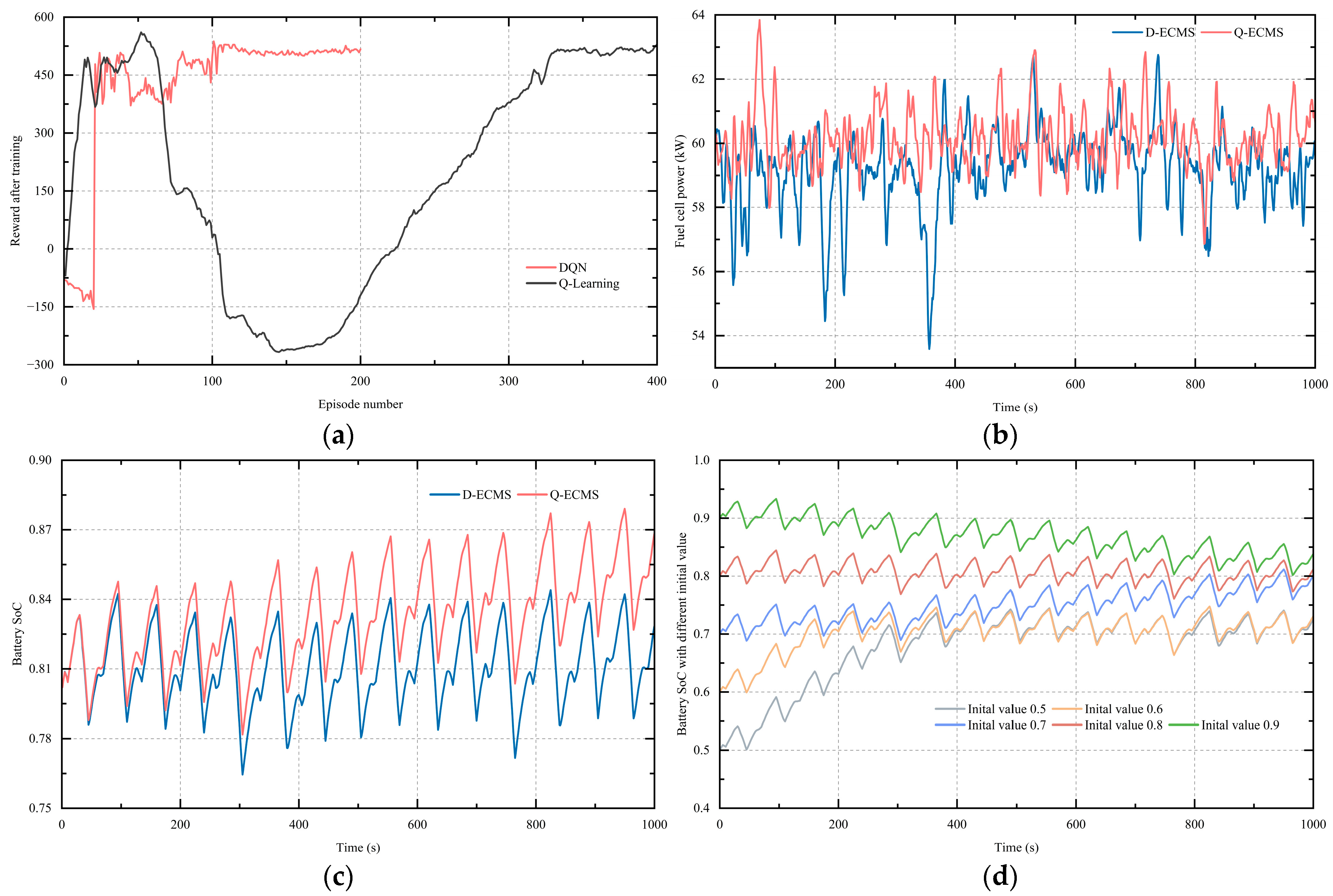
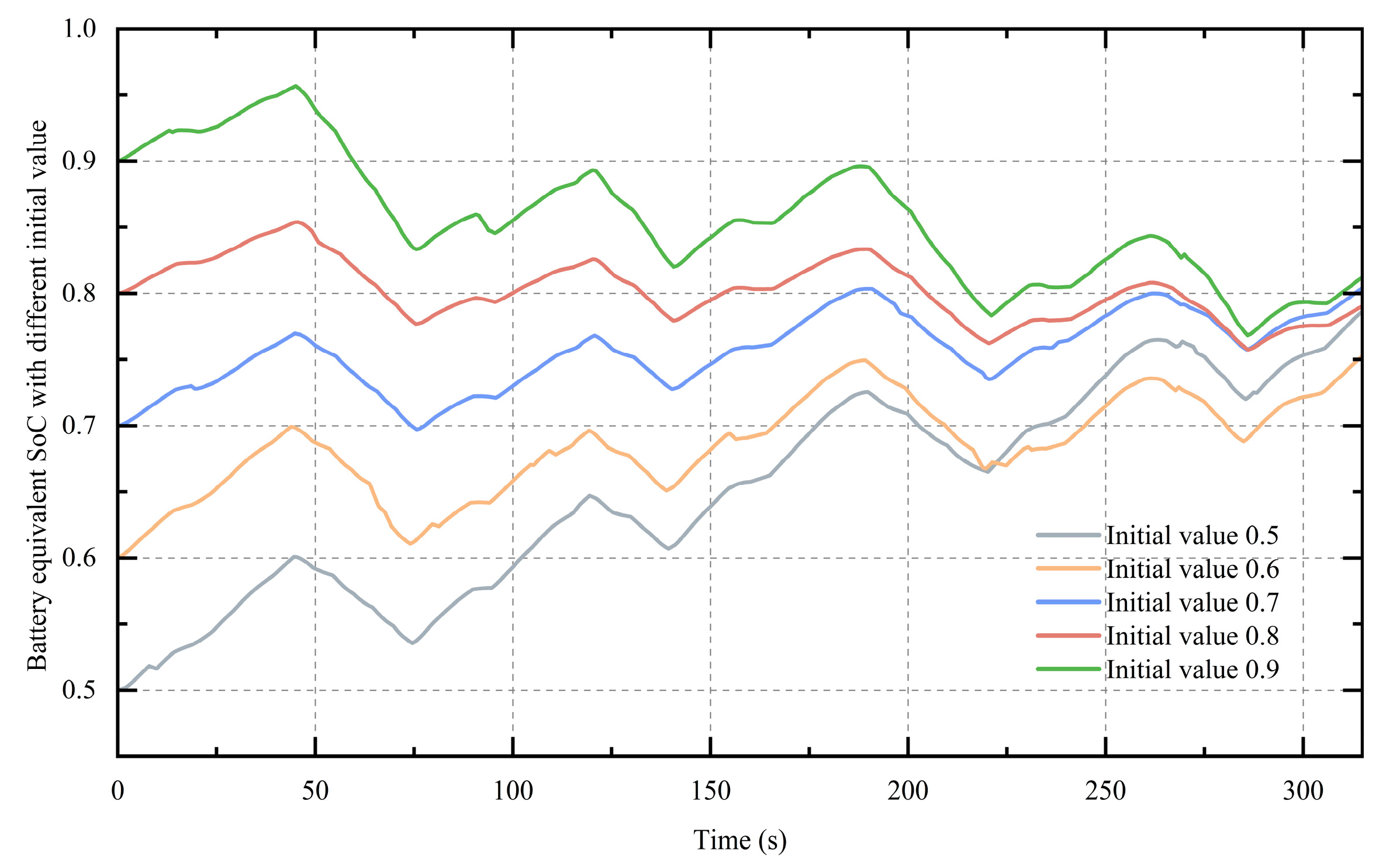
4.2. Adaptability of Equivalence Factor Regulator Based on DQN
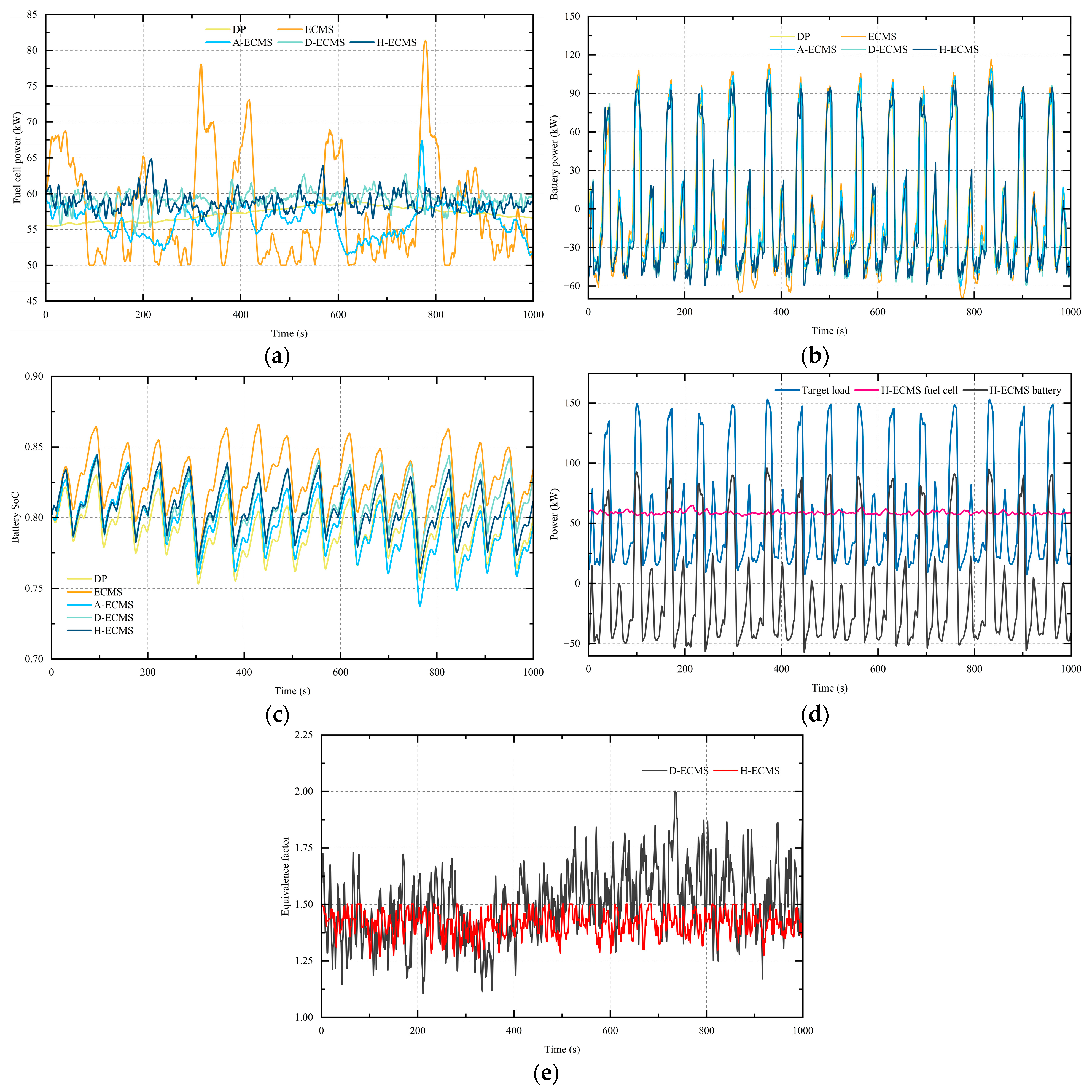
4.3. Comparison of EMSs
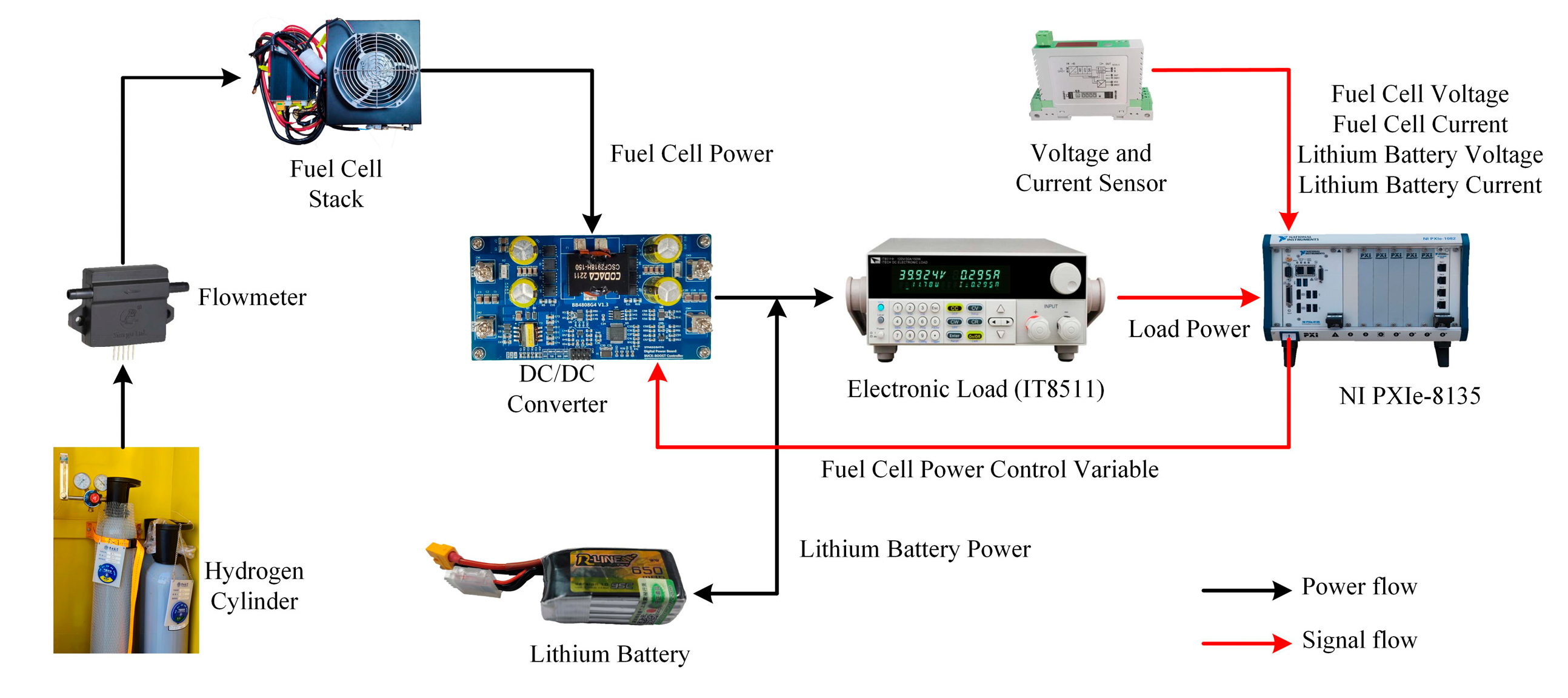
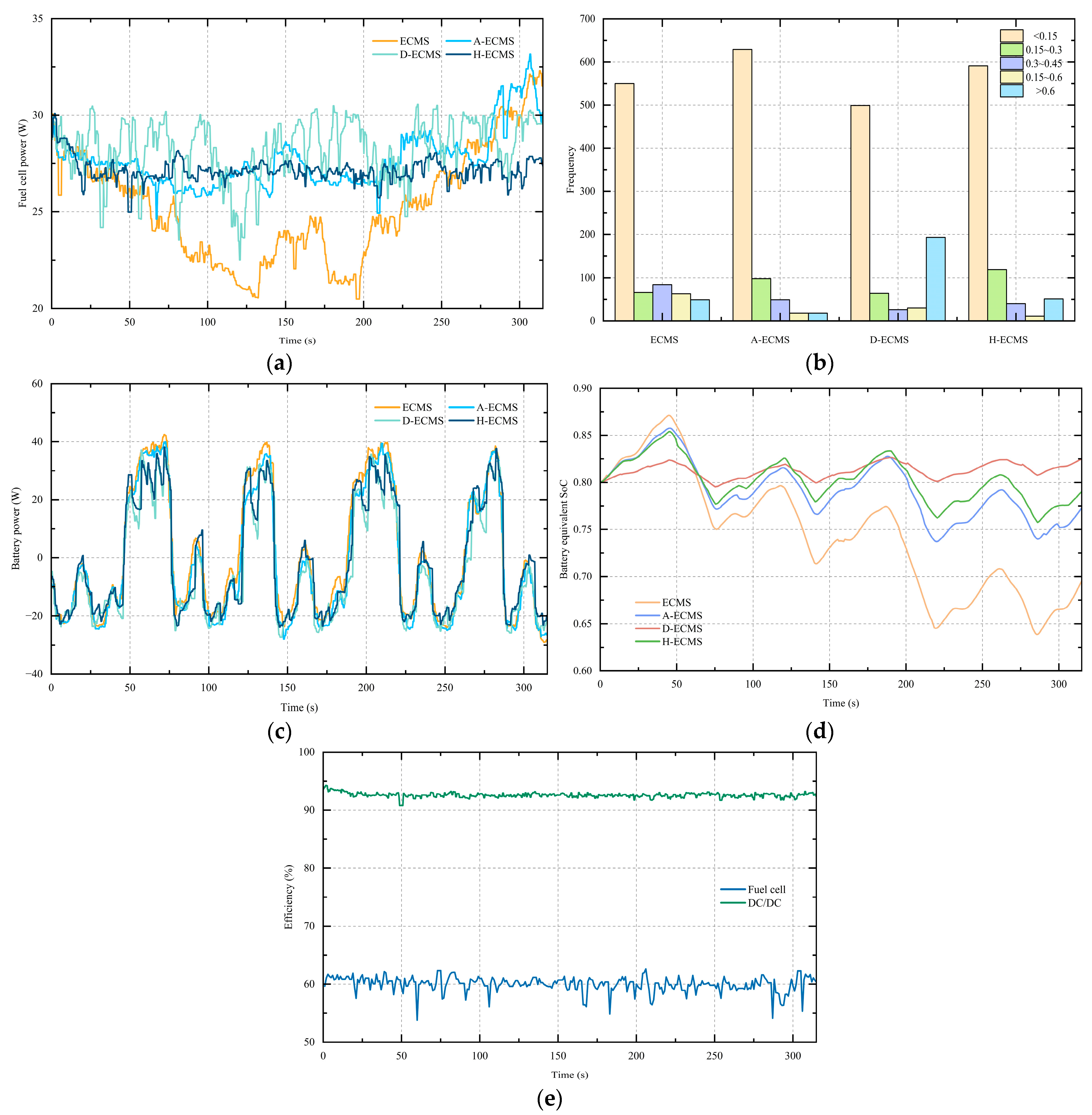
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sabri, M.F.M.; Danapalasingam, K.A.; Rahmat, M.F. A review on hybrid electric vehicles architecture and energy management strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Lin, M.; Lin, T.E.; Lan, T.; Liao, X.; Maréchal, F.; Van Herle, J.; Yang, Y.P.; Dong, C.Q.; Wang, L.G. Fuel cell-battery hybrid systems for mobility and off-grid applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali, Y.; Stegen, S. Review of energy storage systems for vehicles based on technology, environmental impacts, and costs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, B.G.; Kocha, S.S.; Staffell, I. Current status of automotive fuel cells for sustainable transport. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sen, S.; Ajayan, J. A comprehensive techno-economic analysis for hydrogen fuel-cell supported HEVs using predictive control approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 83, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hames, Y.; Kaya, K.; Baltacioglu, E.; Turksoy, A. Analysis of the control strategies for fuel saving in the hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 10810–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Chau, K.T. Deep reinforcement learning-based energy management strategy for fuel cell buses integrating future road information and cabin comfort control. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 321, 119032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motapon, S.N.; Dessaint, L.A.; Al-Haddad, K. A Comparative Study of Energy Management Schemes for a Fuel-Cell Hybrid Emergency Power System of More-Electric Aircraft. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Hofmann, H.; Li, J.; Hou, J.; Han, X.; Ouyang, M. Energy management strategies comparison for electric vehicles with hybrid energy storage system. Appl. Energy 2014, 134, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, M.; Payman, A.; Martin, J.P.; Pierfederici, S.; Davat, B.; Meibody-Tabar, F. Energy Management of a Fuel Cell/Supercapacitor/Battery Power Source for Electric Vehicular Applications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.; Liu, Y.; Ding, F.; Chen, Z.; Hao, W. A novel strategy for power sources management in connected plug-in hybrid electric vehicles based on mobile edge computation framework. J. Power Sources 2020, 477, 228650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; He, H.; Xiong, R. Rule based energy management strategy for a series–parallel plug-in hybrid electric bus optimized by dynamic programming. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G.; Sharkh, S.M.; Walsh, F.C.; Zhang, C.N. Energy and Battery Management of a Plug-In Series Hybrid Electric Vehicle Using Fuzzy Logic. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 3571–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.M.; Hu, X.; Cao, D.; Velenis, E.; Gao, B.; Wellers, M. Energy Management in Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Recent Progress and a Connected Vehicles Perspective. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 4534–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, J.H. Development of equivalent fuel consumption minimization strategy for hybrid electric vehicles. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2012, 13, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Song, J. Correctional DP-Based Energy Management Strategy of Plug-In Hybrid Electric Bus for City-Bus Route. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 2792–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tarsitano, D.; Hu, X.; Cheli, F. Real time energy management strategy for a fast charging electric urban bus powered by hybrid energy storage system. Energy 2016, 112, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Görges, D. Ecological Adaptive Cruise Control and Energy Management Strategy for Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Heuristic Dynamic Programming. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 3526–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wei, Q. Policy Iteration Adaptive Dynamic Programming Algorithm for Discrete-Time Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 25, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yi, F.; Hu, D.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J. Online optimization of energy management strategy for FCV control parameters considering dual power source lifespan decay synergy. Appl. Energy 2023, 348, 121516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Khajepour, A.; He, H.; Ji, J. Model predictive control power management strategies for HEVs: A review. J. Power Sources 2017, 341, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, A.; Torchio, M.; Braatz, R.D.; Raimondo, D.M. Optimal charging of an electric vehicle battery pack: A real-time sensitivity-based model predictive control approach. J. Power Sources 2020, 461, 228133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mi, C.C.; Xu, J.; Gong, X.; You, C. Energy Management for a Power-Split Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Based on Dynamic Programming and Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 1567–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Shang, F.; Zhan, J. Hybrid-Trip-Model-Based Energy Management of a PHEV With Computation-Optimized Dynamic Programming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, R.; Ashok, B. Intelligent energy management through neuro-fuzzy based adaptive ECMS approach for an optimal battery utilization in plugin parallel hybrid electric vehicle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 280, 116792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinoquet, D.; Rousseau, G.; Milhau, Y. Design optimization and optimal control for hybrid vehicles. Optim. Eng. 2011, 12, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, R.; Wei, X.; Huang, W. PMP method with a cooperative optimization algorithm considering speed planning and energy management for fuel cell vehicles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 79, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Z.; Huang, W.F.; Niu, T.; Liu, Z.T.; Li, G.F.; Cao, D.P. Review of Clustering Technology and Its Application in Coordinating Vehicle Subsystems. Automot. Innov. 2023, 6, 89–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Lin, X. Longevity-conscious energy management strategy of fuel cell hybrid electric Vehicle Based on deep reinforcement learning. Energy 2022, 238, 121593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Chau, K.T. Health-conscious energy management for fuel cell vehicles: An integrated thermal management strategy for cabin and energy source systems. Energy 2025, 333, 137330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zou, Y.; Liu, D.; Sun, F. Reinforcement Learning of Adaptive Energy Management With Transition Probability for a Hybrid Electric Tracked Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7837–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; He, H.; Wei, Z.; Yang, Q.; Igic, P. Battery Optimal Sizing Under a Synergistic Framework With DQN-Based Power Managements for the Fuel Cell Hybrid Powertrain. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Chau, K.T. Superior energy management for fuel cell vehicles guided by improved DDPG algorithm: Integrating driving intention speed prediction and health-aware control. Appl. Energy 2025, 394, 126195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhou, J.; Jia, C.; Yi, F.; Zhang, C. Energy sources durability energy management for fuel cell hybrid electric bus based on deep reinforcement learning considering future terrain information. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; He, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, K.; Li, M. A novel deep reinforcement learning-based predictive energy management for fuel cell buses integrating speed and passenger prediction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 100, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Huang, R.; Meng, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. A novel hierarchical predictive energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric bus combined with deep deterministic policy gradient. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Fu, Z.; Tao, F.; Zhu, L.; Si, P. Data-driven reinforcement-learning-based hierarchical energy management strategy for fuel cell/battery/ultracapacitor hybrid electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2020, 455, 227964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, J. An Adaptive Hierarchical Energy Management Strategy for Hybrid Electric Vehicles Combining Heuristic Domain Knowledge and Data-Driven Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 3275–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tao, F.; Fu, Z.; Gao, A.; Jiao, L. Driving-Behavior-Aware Optimal Energy Management Strategy for Multi-Source Fuel Cell Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Adaptive Soft Deep-Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 4127–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chu, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Z. DRL-ECMS: An Adaptive Hierarchical Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Aachen, Germany, 4–9 June 2022; pp. 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Li, W. Reinforcement learning-based energy management strategies of fuel cell hybrid vehicles with multi-objective control. J. Power Sources 2022, 543, 231841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Fu, J.; Yang, H.; Xie, M.; Liu, J. An energy management strategy for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles based on deep learning and improved model predictive control. Energy 2023, 269, 126772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Jia, T.; Hu, X.; Huang, Y.; Deng, Z.; Pu, H. Naturalistic Data-Driven Predictive Energy Management for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, D.; Xiang, C. A multi-objective optimization energy management strategy for power split HEV based on velocity prediction. Energy 2022, 238, 121714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Li, Z. Equivalent consumption minimization strategy based on a variable equivalent factor. In Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Jinan, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 4215–4219. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Chen, L.; Yin, C. Deep reinforcement learning based adaptive energy management for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle with double deep Q-network. Energy 2024, 305, 132402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Burl, J.B.; Zhou, B. Estimation of the ECMS Equivalent Factor Bounds for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 26, 2198–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.; Guo, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Chang, Y. A real-time energy management strategy for fuel cell vehicle based on Pontryagin’s minimum principle. iScience 2024, 27, 109473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Tao, Y.; Liu, Q.; He, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, L. Grey wolf fuzzy optimal energy management for electric vehicles based on driving condition prediction. J. Energy Storage 2021, 44, 103398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | Value |
|---|---|
| Fuel cell rated power | 100 kW |
| Battery capacity | 5.92 kWh |
| Standard bucket capacity | 3 m3 |
| Maximum vehicle speed | 37 km/h |
| Vehicle mass | 16,800 kg |
| Rated load | 5000 kg |
| Maximum bucket digging force | 128 kN |
| Maximum traction force | 160 kN |
| Maximum gradient | 30° |
| Bucket operation sum time | ≤12 s |
| Motor average efficiency | 0.92 |
| Hydraulic average efficiency | 0.9 |
| Converter average efficiency | 0.95 |
| LSTM Neural Network | Markov Model | ARMA Model | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 18.18 | 31.44 | 25.58 |
| MAE | 12.06 | 22.31 | 14.31 |
| MSE | 330.54 | 988.76 | 654.20 |
| EMS | Equivalent Hydrogen Consumption (g) |
|---|---|
| D-ECMS | 720.24 |
| Q-ECMS | 733.17 |
| EMS | Equivalent Hydrogen Consumption (g) |
|---|---|
| DP | 693.90 |
| H-ECMS | 712.14 |
| D-ECMS | 720.24 |
| A-ECMS | 746.28 |
| ECMS | 756.66 |
| Experimental Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Fuel cell power | 60 W |
| Battery storage capacity | 650 mAh |
| Battery voltage | 14.8 V |
| DC link voltage | 14.8 V |
| Different Strategy | Experimental (g) | Simulation (g) | Experimental Equivalence to Simulation (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H-ECMS | 0.0976 | 712.14 | 773.48 |
| D-ECMS | 0.1009 | 720.24 | 799.63 |
| A-ECMS | 0.1065 | 746.28 | 844.01 |
| ECMS | 0.1136 | 756.66 | 900.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; He, B.; Lei, Y. Reinforcement Learning-Based Adaptive Hierarchical Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy for Fuel Cell Hybrid Engineering Vehicles. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10167. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210167
Liu H, Xu H, Li H, He B, Lei Y. Reinforcement Learning-Based Adaptive Hierarchical Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy for Fuel Cell Hybrid Engineering Vehicles. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10167. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210167
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huiying, Hai Xu, Haofa Li, Binggao He, and Yanmin Lei. 2025. "Reinforcement Learning-Based Adaptive Hierarchical Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy for Fuel Cell Hybrid Engineering Vehicles" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10167. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210167
APA StyleLiu, H., Xu, H., Li, H., He, B., & Lei, Y. (2025). Reinforcement Learning-Based Adaptive Hierarchical Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy for Fuel Cell Hybrid Engineering Vehicles. Sustainability, 17(22), 10167. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210167






