Bridging LLMs, Education, and Sustainability: Guiding Students in Local Community Initiatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review: Leveraging LLMs for Sustainable Development
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. LLM Chatbots for Sustainable Development Projects
3.2. LLM Frameworks—Effective Communication Strategies for Interacting with LLM Chatbots
3.3. The Project Assignment—Students Engaging with Local Community Sustainability
3.4. Evaluation of LLM Effectiveness in Student Sustainability Projects
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. The Project Assignment with LLM Prompting Frameworks
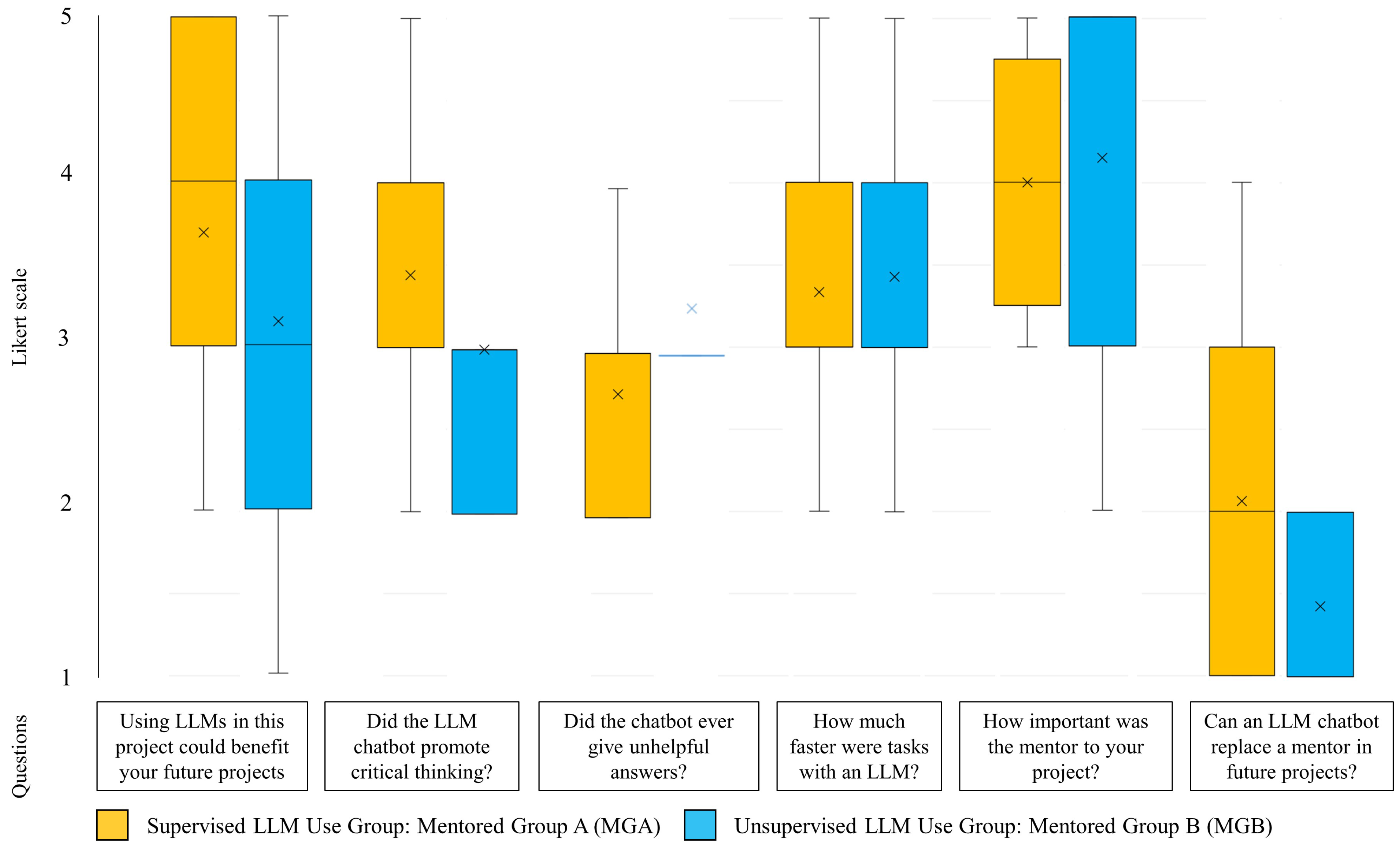
4.2. Descriptive Evaluation of Student Responses: A Pilot Study of Supervised and Unsupervised LLM Use
4.3. Inferential Evaluation of Student Responses: A Pilot Study of Supervised and Unsupervised LLM Use
5. Challenges and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations/Nomenclature
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| LLM | Large Language Models |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PF | Prompting Framework |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| R.A.C.E. | Role, Action, Context, Expectation |
| R.O.S.E.S. | Role, Objective, Scenario, Expected Solution, Steps |
References
- Shaya, N.; AbuKhait, R.; Madani, R.; Ahmed, V. Conceptualizing Blended Learning Models as a Sustainable and Inclusive Educational Approach: An Organizational Dynamics Perspective. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2025, 26, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.G.; Urbanowicz, R.J.; Martin, P.C.N.; O’Connor, K.; Li, R.; Peng, P.C.; Bright, T.J.; Tatonetti, N.; Won, K.J.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, G.; et al. ChatGPT and Large Language Models in Academia: Opportunities and Challenges. BioData Min. 2023, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontche Steve, M. Ethical Considerations for Companies Implementing LLMs in Education Software. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2024, 9, 1856–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- März, M.; Himmelbauer, M.; Boldt, K.; Oksche, A. Legal Aspects of Generative Artificial Intelligence and Large Language Models in Examinations and Theses. GMS J. Med. Educ. 2024, 41, Doc47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perković, G.; Drobnjak, A.; Botički, I. Hallucinations in LLMs: Understanding and Addressing Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2024 47th MIPRO ICT and Electronics Convention (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 20–24 May 2024; pp. 2084–2088. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, P.; Gogtay, N.J. Large Language Models and the Future of Academic Writing. J. Postgrad. Med. 2024, 70, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorin, V.; Brin, D.; Barash, Y.; Konen, E.; Charney, A.; Nadkarni, G.; Klang, E. Large Language Models and Empathy: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e52597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marche, S. Will ChatGPT Kill the Student Essay? The Atlantic. Available online: https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2022/12/chatgpt-ai-writing-college-student-essays/672371/ (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Ravi, A.; Neinstein, A.; Murray, S.G. Large Language Models and Medical Education: Preparing for a Rapid Transformation in How Trainees Will Learn to Be Doctors. ATS Sch. 2023, 4, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez-Sánchez, I.C.; Velarde-Camaqui, D.; Glasserman-Morales, L.D. The Impact of Large Language Models on Higher Education: Exploring the Connection between AI and Education 4.0. Front. Educ. 2024, 9, 1392091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab Idris, M.; Feng, X.; Dyo, V. Revolutionizing Higher Education: Unleashing the Potential of Large Language Models for Strategic Transformation. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 67738–67757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.L.; Ong, C.W.; Chen, C.L. Exploring the Use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Chemical Engineering Education: Building Core Course Problem Models with Chat-GPT. Educ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 44, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, E.; Lege, R.; Frazier, E. Large Language Model-Based Artificial Intelligence in the Language Classroom: Practical Ideas for Teaching. Teach. Engl. Technol. 2023, 2023, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrdoljak, J.; Boban, Z.; Vilović, M.; Kumrić, M.; Božić, J. A Review of Large Language Models in Medical Education, Clinical Decision Support, and Healthcare Administration. Healthcare 2025, 13, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siino, M.; Falco, M.; Croce, D.; Rosso, P. Exploring LLMs Applications in Law: A Literature Review on Current Legal NLP Approaches. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 18253–18276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.F.; Ferreira Mello, R. A Systematic Literature Review on Large Language Models Applications in Computer Programming Teaching Evaluation Process. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 113449–113460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, T.; Mazhar, T.; Tariq, M.U.; Ahmad, W.; Ouahada, K.; Hamam, H. A Comprehensive Review of Large Language Models: Issues and Solutions in Learning Environments; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; Volume 6, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Thurzo, A.; Strunga, M.; Urban, R.; Surovková, J.; Afrashtehfar, K.I. Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Dental Education: A Review and Guide for Curriculum Update. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, B. Future of Textile: Sustainable Manufacturing & Prediction via ChatGPT. Eduzone Int. Peer Rev. Acad. Multidiscip. J. 2023, 12, 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, B.C.; Freitas, L.A.d.; Aguiar, M.S.d. Chatbot as Support to Decision-Making in the Context of Natural Resource Management. In Proceedings of the Workshop de Computação Aplicada à Gestão do Meio Ambiente e Recursos Naturais, Maceió, Brazil, 20–24 July 2021; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Parović, M. Could Artificial Intelligence (AI) Contribute to a Just Energy Transition? Energ. Ekon. Ekol. 2024, 26, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, S.A.; Mengiste, E.T.; Soto, B.G. de Investigating the Use of ChatGPT for the Scheduling of Construction Projects. Buildings 2023, 13, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, D.B. Future of AI & Generation Alpha: ChatGPT beyond Boundaries. Eduzone Int. Peer Rev. Multidiscip. J. 2023, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jungwirth, D.; Haluza, D. Artificial Intelligence and Ten Societal Megatrends: An Exploratory Study Using GPT-3. Systems 2023, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungwirth, D.; Haluza, D. Artificial Intelligence and the Sustainable Development Goals: An Exploratory Study in the Context of the Society Domain. J. Softw. Eng. Appl. 2023, 16, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudici, M.; Abbo, G.A.; Belotti, O.; Braccini, A.; Dubini, F.; Izzo, R.A.; Crovari, P.; Garzotto, F. Assessing LLMs Responses in the Field of Domestic Sustainability: An Exploratory Study. In Proceedings of the 2023 Third International Conference on Digital Data Processing (DDP), London, UK, 27–29 November 2023; pp. 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, N.; Alshehri, A.S.; You, F. Large Language Models for Life Cycle Assessments: Opportunities, Challenges, and Risks. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 466, 142824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, D.; Picasso, F. Large Language Models for Sustainable Assessment and Feedback in Higher Education. Intell. Artif. 2024, 18, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, K.I.; Tselikas, N.D.; Nasiopoulos, D.K. Unveiling Sustainability in Ecommerce: GPT-Powered Software for Identifying Sustainable Product Features. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.V.Y.; Tan, S.C.; Teo, C.L. Designs and Practices Using Generative AI for Sustainable Student Discourse and Knowledge Creation. Smart Learn. Environ. 2023, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.A.G.d.; Ramos, F.N.; de Moraes, R.V.; Santos, E.L. dos ChatGPT: Challenges and Benefits in Software Programming for Higher Education. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulibdeh, A.; Zaidan, E.; Abulibdeh, R. Navigating the Confluence of Artificial Intelligence and Education for Sustainable Development in the Era of Industry 4.0: Challenges, Opportunities, and Ethical Dimensions. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 437, 140527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, C.; Dimes, R.; Molinari, M. How Will AI Text Generation and Processing Impact Sustainability Reporting? Critical Analysis, a Conceptual Framework and Avenues for Future Research. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2024, 15, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalov, F.; Santandreu Calonge, D.; Gurrib, I. New Era of Artificial Intelligence in Education: Towards a Sustainable Multifaceted Revolution. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, W.; Porayska-Pomsta, K.; Holstein, K.; Sutherland, E.; Baker, T.; Shum, S.B.; Santos, O.C.; Rodrigo, M.T.; Cukurova, M.; Bittencourt, I.I.; et al. Ethics of AI in Education: Towards a Community-Wide Framework. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2022, 32, 504–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelaert, J.; Coavoux, S.; Ollion, É.; Petev, I.; Präg, P. Machine Bias. How Do Generative Language Models Answer Opinion Polls? Sociol. Methods Res. 2025, 54, 1156–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaveerapandiyan, A.; Vinoth, A.; Neelam, T. Netizens, Academicians, and Information Professionals’ Opinions About AI with Special Reference to ChatGPT. Libr. Philos. Pract. 2023, 1–15. Available online: https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/libphilprac/7596 (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Wangsa, K.; Karim, S.; Gide, E.; Elkhodr, M. A Systematic Review and Comprehensive Analysis of Pioneering AI Chatbot Models from Education to Healthcare: ChatGPT, Bard, Llama, Ernie and Grok. Future Internet 2024, 16, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaraju, D. Zero-Shot Learning: Teaching AI to Understand the Unknown. Int. J. Res. Rev. 2021, 8, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Schuurmans, D.; Bosma, M.; Ichter, B.; Xia, F.; Chi, E.H.; Le, Q.V.; Zhou, D. Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November 2022; Volume 35, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kanika, B.K. 9 Frameworks to Master ChatGPT Prompt Engineering. Medium. Available online: https://medium.com/@KanikaBK/9-frameworks-to-master-chatgpt-prompt-engineering-e2fac983bc61 (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Lange, R.T. Inter-Rater Reliability. In Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-387-79948-3. [Google Scholar]
- European School Education Platform 4 C’s: Communication, Collaboration, Creativity and Critical Thinking|European School Education Platform. Available online: https://school-education.ec.europa.eu/en/learn/courses/4-cs-communication-collaboration-creativity-and-critical-thinking (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Pant, A.B. (Ed.) Odds Ratio BT. In Dictionary of Toxicology; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 737–738. ISBN 978-981-99-9283-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1988; ISBN 0805802835. [Google Scholar]
- Stojiljković, Z. Blockades and Strikes in Serbia. SEER 2024, 27, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ref. | Country | LLM | Aim | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [26] | Italy, Belgium | ChatGPT, BingAI, Bard, LLaMA | to compare the generative capabilities of four large language models in ecological sustainability | ChatGPT is a promising LLM for embedding into home assistants to foster sustainable behaviors in domestic environments. |
| [27] | USA, S. Arabia | Gemini, GPT-4 | to explore the opportunities, challenges, and risks associated with using LLMs in various life cycle assessment tasks | LLMs can enhance efficiency and accessibility but pose challenges such as hallucinations, data reliability issues, and the need for responsible oversight |
| [28] | Italy | GPT-3.5, GPT-4, Claude 1, Claude 2, Bard, LLaMA, LLaMA 2 | to propose a pedagogical and technological framework for using LLMs to address sustainability issues in assessment and feedback in higher education | LLMs enhance assessment in higher education by automating evaluation, providing personalized feedback, reducing workload, improving objectivity, and enabling continuous learning. |
| [29] | Greece | GPT-3.5, GPT-4 | to automate the identification of sustainable product attributes from product descriptions, titles, and product specifications. | GPT effectively identifies sustainable product features, supports eco-friendly purchasing, but requires improved response formatting and consistency |
| [30] | Singapore | ChatGPT /GPT-3.5 | to explore how GPT can be utilized in designs that support sustainable student discourse and knowledge creation. | Generative AI enhances student discourse but requires oversight due to potential inaccuracies, biases, and ethical concerns in educational use |
| [31] | Brazil | GPT-3.5 | to examine how the integration of ChatGPT in coding and programming courses impacts student perceptions of educational support, sustainability, and individual learning experiences. | The study finds that over 90% of students value ChatGPT in programming courses, 70% emphasize teacher interaction, and 29.7% worry about generative AI overuse in assessments |
| [32] | Qatar, Canada | ChatGPT /GPT-4 | to examine the integration of generative AI tools in education in the context of education for sustainable development (ESD). | Generative AI enhances personalized learning and collaboration in ESD but raises ethical concerns, digital divide issues, and risks of overreliance |
| [33] | S. Africa, N. Zealand, UK | ChatGPT | to analyze the benefits and risks of using generative AI tools for sustainability reporting. | Generative AI improves sustainability reporting efficiency but risks greenwashing, reliability issues, and transparency concerns, requiring governance, assurance, and ethical oversight |
| [34] | UAE | ChatGPT | to discuss the potential impact of generative AI on education and the need for a sustainable approach to its implementation. | Generative AI enhances personalized learning, tutoring, and assessment but raises concerns about privacy, bias, academic integrity, and teacher–student dynamics. |
| Criteria | ChatGPT | Gemini |
|---|---|---|
| Strengths and Opportunities | Multiple choice questions, academic text, advanced in academic and practical tasks | Non-original problems online, interactive feedback, real-time internet access |
| Weaknesses and Challenges | Inaccurate information, consistency issues, academic concerns, lack of contextual awareness, safety concerns | Generates different answers, consistency issues, original scientific contribution |
| Performance Metrics 1 | High | Medium |
| Scope of Knowledge 2 | High | High (Real-time) |
| Use Cases Excelling In | Academic research, trivia, education | Education, real-time queries |
| Use Cases Limited By | Scientific contributions | Detailed scientific writing, complex reasoning tasks |
| Knowledge Update Frequency | High (Quarterly updates) | High (Real-time) |
| PFs | Meaning | Activity |
|---|---|---|
| R.A.C.E. | Role | Specify the role of the LLM chatbot. |
| Action | Detail what action is needed. | |
| Context | Provide relevant details of the situation. | |
| Expectation | Describe the expected outcome. | |
| R.O.S.E.S. | Role | Specify the role of the LLM chatbot. |
| Objective | State the goal or aim. | |
| Scenario | Describe the situation. | |
| Expected Solution | Define the desired outcome. | |
| Steps | Ask for the actions needed to reach the solution. |
| Task | LLM | PF |
|---|---|---|
| #1 INTRODUCTION | ||
| Original work | Original work |
| ChatGPT | R.A.C.E. |
| Gemini | R.A.C.E. |
| #2 RESEARCH OBJECT | ||
| Original work | Original work |
| Original work | Original work |
| Original work | Original work |
| Gemini | R.O.S.E.S. |
| Gemini | R.A.C.E. |
| #3 LONG-TERM EFFECTS | ||
| ChatGPT | R.A.C.E./Original work |
| #4 IMPACT OF THE PROBLEM ON SDGs | ||
| ChatGPT | R.O.S.E.S. |
| #5 EXAMPLES OF GOOD PRACTICES | ||
| Gemini | R.O.S.E.S. |
| #6 PROPOSED SOLUTION | ||
| ChatGPT | R.A.C.E. |
| ChatGPT | R.O.S.E.S. |
| ChatGPT | R.A.C.E. |
| Gemini | R.O.S.E.S. |
| ChatGPT | R.A.C.E. |
| #7ASSESSMENT OF IMPROVEMENT | ||
| ChatGPT | R.O.S.E.S. |
| ChatGPT | R.A.C.E. |
| ChatGPT | R.A.C.E. |
| ChatGPT | R.A.C.E. |
| Gemini | R.A.C.E. |
| Variable | Questions | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95%CI | p-Value | OR | 95%CI | p-Value | ||
| Q1 | Using LLMs in this project could benefit your future projects? | 0.670 | 0.199–2.251 | 0.517 | |||
| Q2 | Did the LLM chatbot promote critical thinking? | 0.137 | 0.022–0.862 | 0.034 | 0.224 | 0.058–0.860 | 0.029 |
| Q3 | Did the chatbot ever give unhelpful answers? | 3.657 | 0.627–21.548 | 0.149 | |||
| Q4 | How much faster were tasks with an LLM? | 14.440 | 1.180–176.630 | 0.037 | 3.876 | 0.881–17.057 | 0.073 |
| Q5 | How important was the mentor to your project? | 0.301 | 0.056–1.616 | 0.161 | |||
| Q6 | Can an LLM chatbot replace a mentor in future projects? | 0.155 | 0.025–0.984 | 0.048 | 0.278 | 0.072–1.020 | 0.054 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jurišević, N.; Nikolić, N.; Nemś, A.; Gordić, D.; Rakić, N.; Končalović, D.; Kocsis, D. Bridging LLMs, Education, and Sustainability: Guiding Students in Local Community Initiatives. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10148. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210148
Jurišević N, Nikolić N, Nemś A, Gordić D, Rakić N, Končalović D, Kocsis D. Bridging LLMs, Education, and Sustainability: Guiding Students in Local Community Initiatives. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10148. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210148
Chicago/Turabian StyleJurišević, Nebojša, Novak Nikolić, Artur Nemś, Dušan Gordić, Nikola Rakić, Davor Končalović, and Dénes Kocsis. 2025. "Bridging LLMs, Education, and Sustainability: Guiding Students in Local Community Initiatives" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10148. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210148
APA StyleJurišević, N., Nikolić, N., Nemś, A., Gordić, D., Rakić, N., Končalović, D., & Kocsis, D. (2025). Bridging LLMs, Education, and Sustainability: Guiding Students in Local Community Initiatives. Sustainability, 17(22), 10148. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210148








