A Sustainable Management-Oriented Model for Hydrodynamics and Pollutant Transport in Vegetated Seepage River Channels Using LBM-RDM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
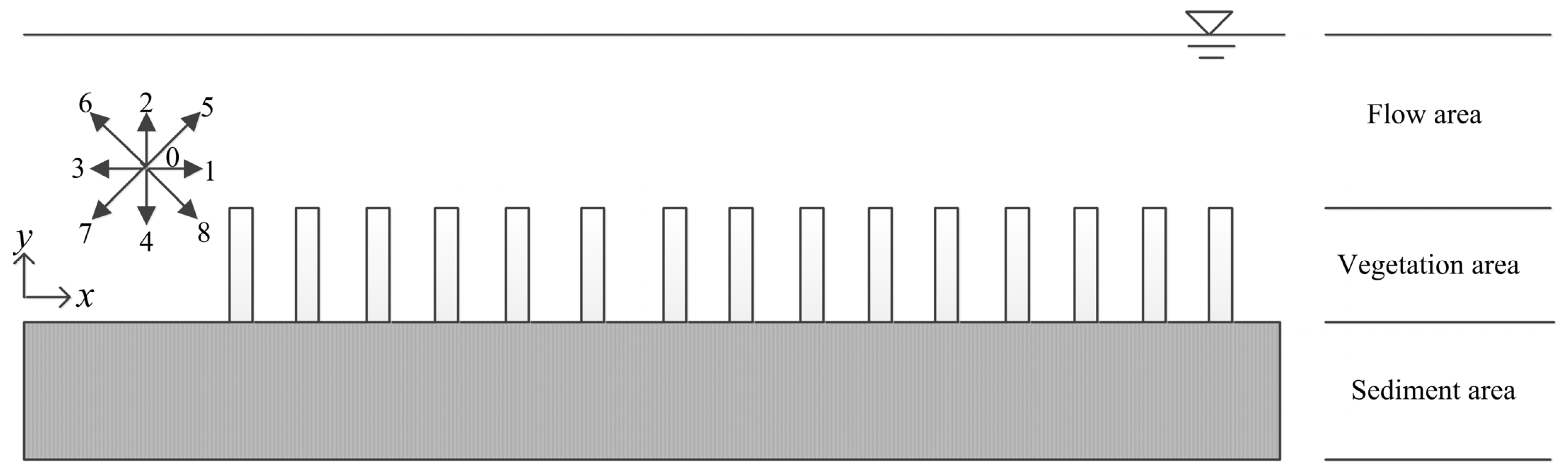
2.1. Numerical Model Framework
2.1.1. Hydraulic Model
2.1.2. Pollution Transport Model
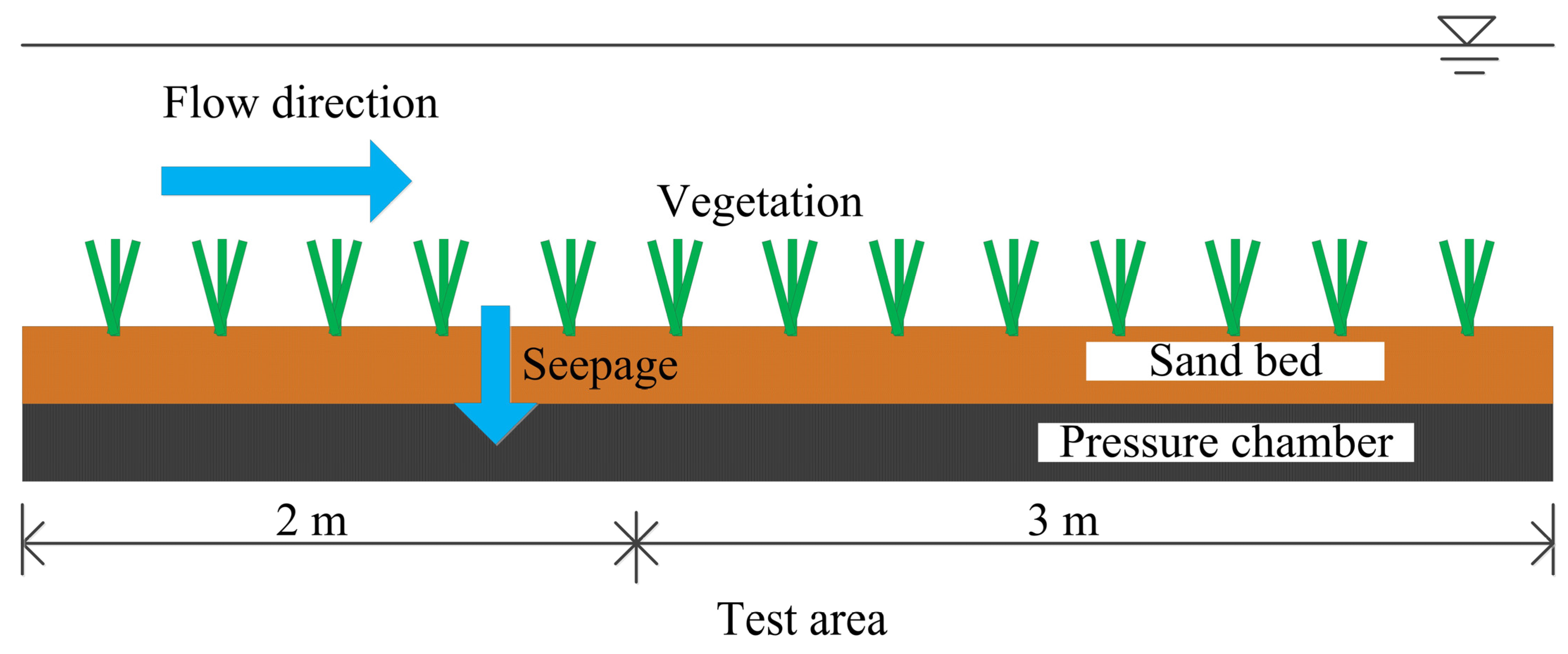
2.2. Validation Data
2.3. The Simulation Experiment of Pollution Retention
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Conclusions of This Study
4.2. Comparison with Other Studies
4.3. Advantages and Limitations
4.4. Further Direction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wijesiri, B.; Liu, A.; He, B.; Yang, B.; Zhao, X.; Ayoko, G.; Goonetilleke, A. Behaviour of Metals in an Urban River and the Pollution of Estuarine Environment. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, C.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, C. Microplastic Pollution in the Yangtze River Basin: Heterogeneity of Abundances and Characteristics in Different Environments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Hu, H. A Saturated–Unsaturated Coupling Model for Groundwater Flowing into Seepage Wells: A Modeling Study for Groundwater Development in River Basins. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, A.S.; Paiva, R.C.D.; Collischonn, W.; Siqueira, V.A.; Paris, A.; Moreira, D.M.; Garambois, P.A. Trade-offs between 1-D and 2-D Regional River Hydrodynamic Models. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Tsubaki, R. The Role of Riparian Vegetation Flexibility in a Bio-hydro-morphodynamic Simulation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2022, 47, 3481–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Y. Drag in Vegetation Canopy: Considering Sheltering and Blockage Effects. In Proceedings of the European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2024 (EGU24), Vienna, Austria, 14–19 April 2024; Volume EGU24-2069. [Google Scholar]
- Nosrati, K.; Afzalimehr, H.; Sui, J. Drag Coefficient of Submerged Flexible Vegetation Patches in Gravel Bed Rivers. Water 2022, 14, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defina, A.; Peruzzo, P. Floating Particle Trapping and Diffusion in Vegetated Open Channel Flow. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W11522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepf, H.M.; Sullivan, J.A.; Zavistoski, R.A. A Model for Diffusion within Emergent Vegetation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dai, H.C. Numerical Modeling of Pollution Transport in Flexible Vegetation. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 64, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Sun, G. Numerical Simulation of Velocity Distribution and Pollution Transport in a Two-Stage Channel with Vegetation on a Floodplain. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Deshpande, V.; Kumar, B. Turbulent Characteristics and Evolution of Sheet Flow in an Alluvial Channel with Downward Seepage. Geomorphology 2015, 248, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, A.; Al Faruque, M.A.; Balachandar, R. Vortices and Large-scale Structures in a Rough Open-channel Flow Subjected to Bed Suction and Injection. J. Eng. Mech. 2012, 138, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghysels, G.; Mutua, S.; Veliz, G.B.; Huysmans, M. A Modified Approach for Modelling River–Aquifer Interaction of Gaining Rivers in MODFLOW, Including Riverbed Heterogeneity and River Bank Seepage. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, T.B.; Kumar, B. Turbulent Flow Statistics of Vegetative Channel with Seepage. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 123, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Shen, D.; Sun, G. Numerical Simulation of Velocity Distribution and Pollution Retention in Flexible Submerged Vegetated Channel. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberle, J.; Järvelä, J. Flow Resistance of Emergent Rigid and Flexible Floodplain Vegetation. J. Hydraul. Res. 2013, 51, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvelä, J. Determination of Flow Resistance Caused by Non-submerged Woody Vegetation. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2004, 2, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvelä, J. Vegetative Flow Resistance: Characterization of Woody Plants for Modeling Applications. In World Environmental and Water Resource Congress 2006: Examining the Confluence of Environmental and Water Concerns, Omaha, NE, USA, 21–25 May 2006; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kubrak, E.; Kubrak, J.; Rowinski, P.M. Vertical Velocity Distributions Through and Above Submerged, Flexible Vegetation. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Shen, H.W.; Chou, Y.J. Variation of Roughness Coefficients for Unsubmerged and Submerged Vegetation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1999, 125, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, A.A. Lattice Boltzmann Method: Fundamentals and Engineering Applications with Computer Codes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Huai, W.; Li, D. Numerical Modeling of Open Channel Flow with Suspended Canopy. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 105, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Feng, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of Pre-Darcy Flow in Porous Media. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2025, 250, 213852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wu, X. A Random Walk Simulation of Scalar Mixing in Flows Through Submerged Vegetations. J. Hydrodyn. 2014, 26, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, W.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Cheng, Y.G. Predicting the Vertical Low Suspended Sediment Concentration in Vegetated Flow Using a Random Displacement Model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Park, I.; Shin, J. An Investigation of Contaminant Transport and Retention from Storage Zone in Meandering Channels. Water 2024, 16, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, L.E.; Rehmann, C.R. Importance of Turbulent Diffusion in Transverse Mixing in Rivers. J. Hydraul. Res. 2023, 61, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepf, H.M. Drag, Turbulence, and Diffusion in Flow Through Emergent Vegetation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, W.J.; Aller, R.C. Diffusion Coefficients in Nearshore Marine Sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1982, 27, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Shen, D.; Huang, D. Vertical Heterogeneity and Flexible Root Dynamics in Pollutant Transport: A Hybrid Lattice Boltzmann Method-Random Displacement Model Approach for Optimizing Artificial Floating Bed Design. Water Res. 2025, 280, 123536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, T.B.; Kumar, B. Experimentation on Submerged Flow over Flexible Vegetation Patches with Downward Seepage. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, A.G.; Willetts, B.B. Measurement of Boundary Shear Stress in Non-uniform Open Channel Flow. J. Hydraul. Res. 1986, 24, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chiew, Y.M. Velocity Distribution of Turbulent Open-Channel Flow with Bed Suction. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Chiew, Y.M. Suction Effects on Sediment Transport in Closed-Conduit Flows. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzuto, J.E. A Numerical Model for Calculating the Distributions of Velocity and Boundary Shear Stress Across Irregular Straight Open Channels. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammetoğlu, H.; Muhammetoğlu, A.; Soyupak, S. Vulnerability of Groundwater to Pollution from Agricultural Diffuse Sources: A Case Study. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zeng, Y. Lateral Distribution of Sediment and Phosphorus in a Two-Stage Ditch with Partial Emergent Vegetation on the Floodplain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29351–29365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Q. Retaining Performance of Four Types of Drainage Ditch on Phosphorus: Field Work. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashino, M.; Stefan, H.G. Non-linear Effects on Solute Transfer Between Flowing Water and a Sediment Bed. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6074–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Nie, B.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X. Hydrodynamic Disturbance on Phosphorus Release Across the Sediment–Water Interface in Xuanwu Lake, China. Water Supply 2019, 19, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Study of the Impact of Vegetation Direction and Slope on Drag Coefficient. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2018, 42, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xia, Y.; Geng, N.; Qi, Y.; Huang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Hua, E. Research on Oxygen Transfer in an Aerated Flow with Emergent Vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Treatment | Run 1 | Run 2 | Run 3 | Run 4 | Run 5 | Run 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pollution seepage rate (%) | 0 | 4.85 | 7.79 | 0 | 13.53 | 15.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xuan, W.; Bai, Y.; Tang, W. A Sustainable Management-Oriented Model for Hydrodynamics and Pollutant Transport in Vegetated Seepage River Channels Using LBM-RDM. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10138. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210138
Xuan W, Bai Y, Tang W. A Sustainable Management-Oriented Model for Hydrodynamics and Pollutant Transport in Vegetated Seepage River Channels Using LBM-RDM. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10138. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210138
Chicago/Turabian StyleXuan, Weidong, Yu Bai, and Wenlong Tang. 2025. "A Sustainable Management-Oriented Model for Hydrodynamics and Pollutant Transport in Vegetated Seepage River Channels Using LBM-RDM" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10138. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210138
APA StyleXuan, W., Bai, Y., & Tang, W. (2025). A Sustainable Management-Oriented Model for Hydrodynamics and Pollutant Transport in Vegetated Seepage River Channels Using LBM-RDM. Sustainability, 17(22), 10138. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210138







