Analysis of Spatial Changes in Urban Areas Due to Revitalization Investments Based on China and Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
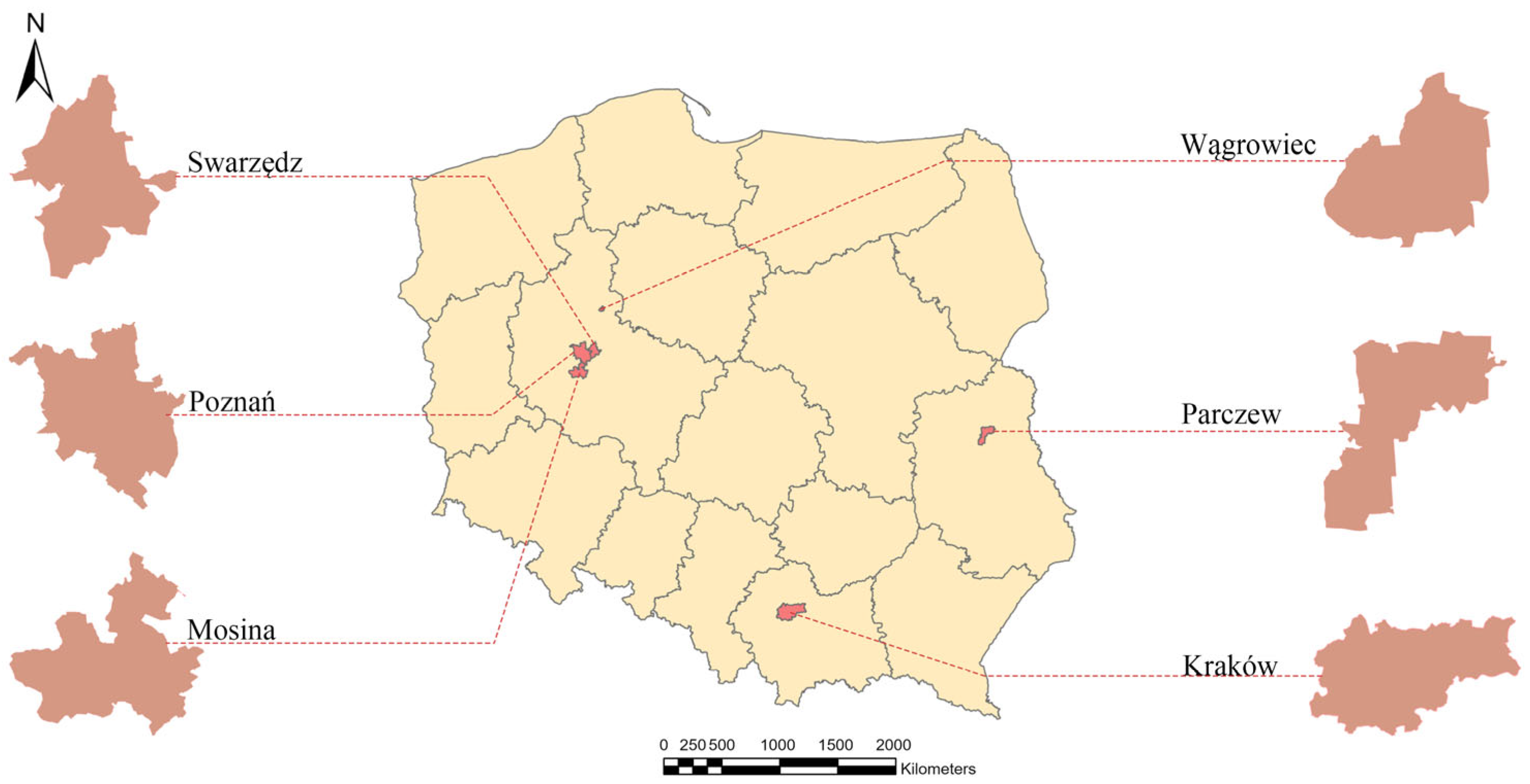
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
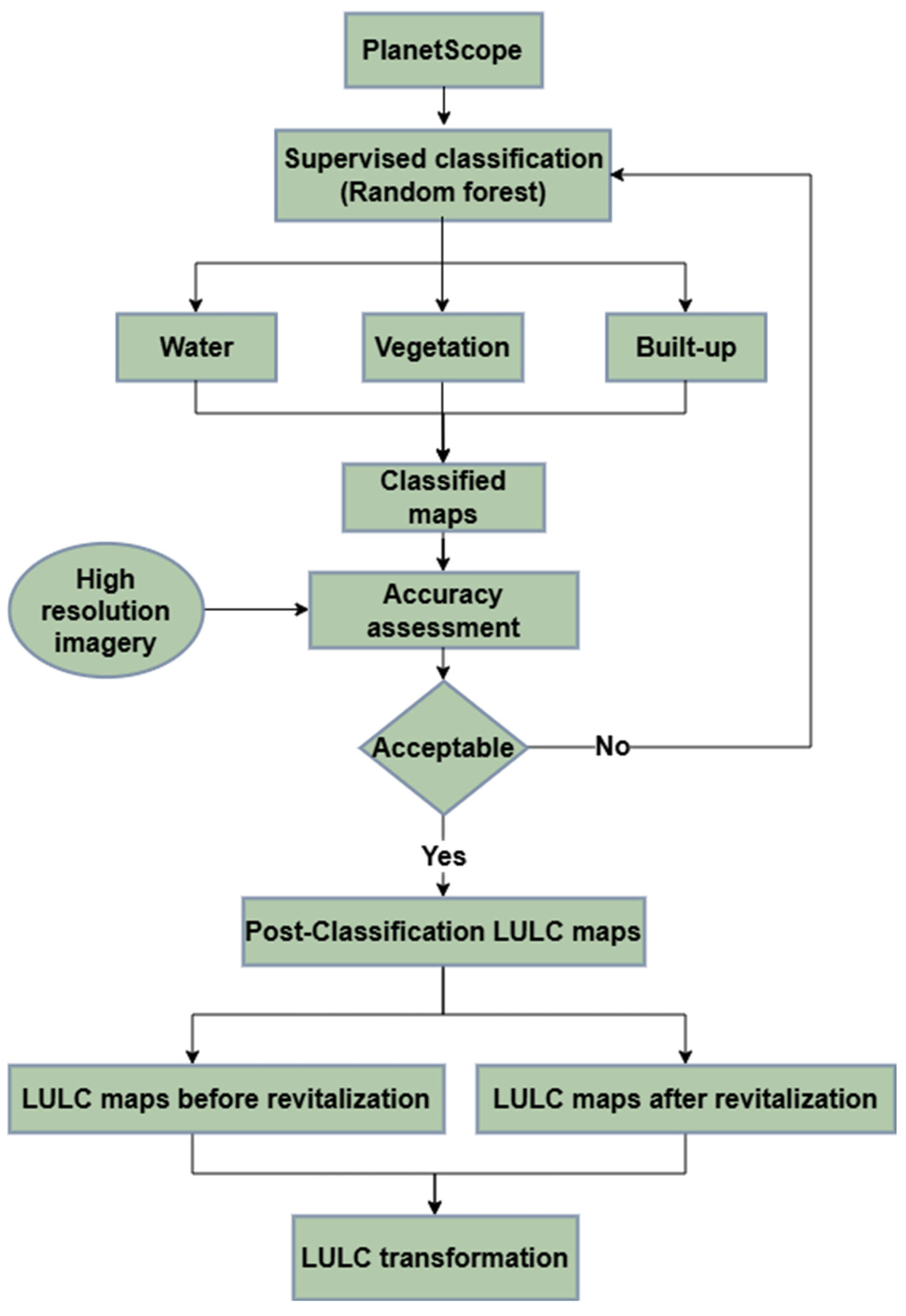
2.3. Research Methodology
3. Results
3.1. China
3.1.1. Beijing
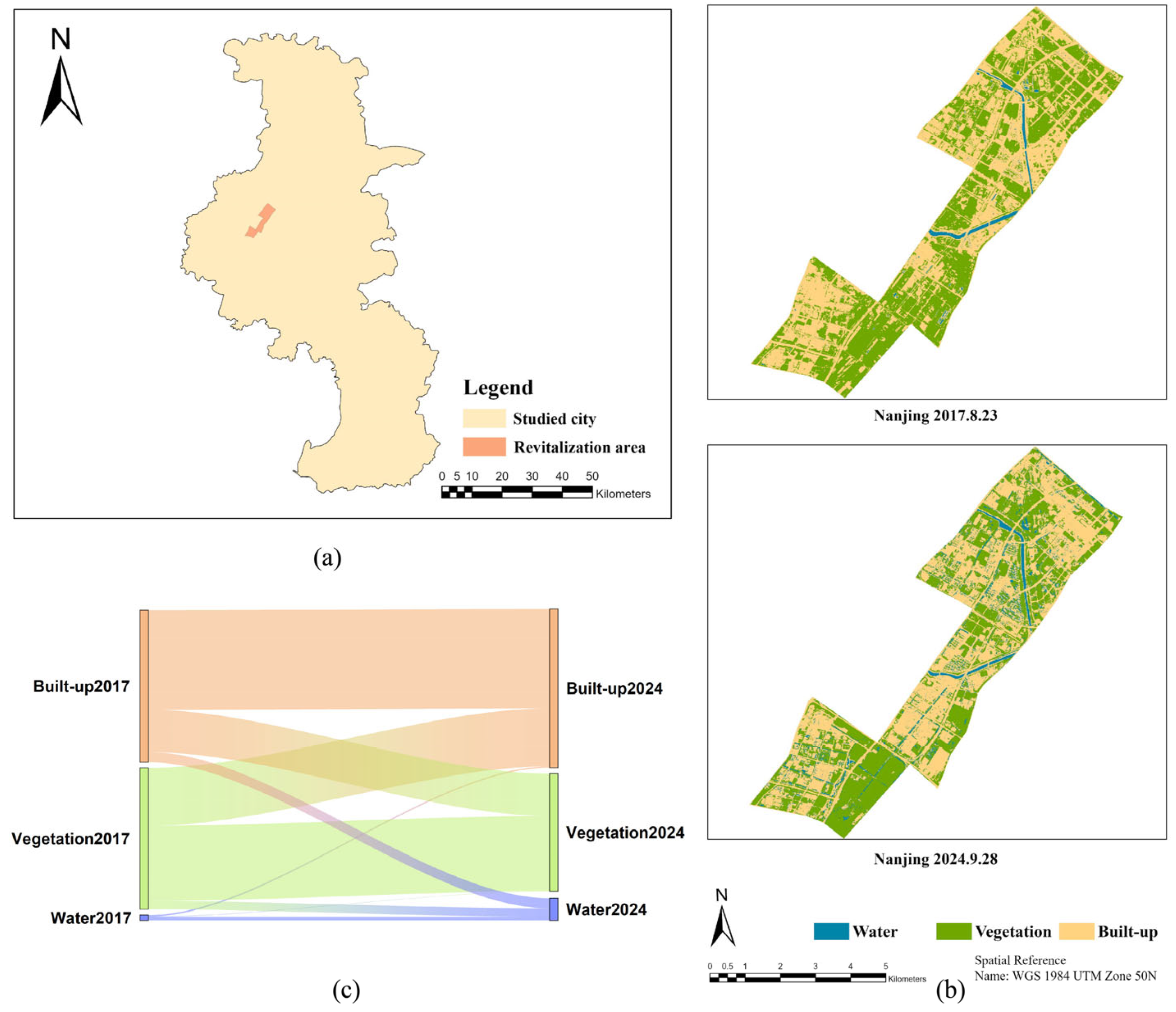
3.1.2. Nanjing
3.2. Poland
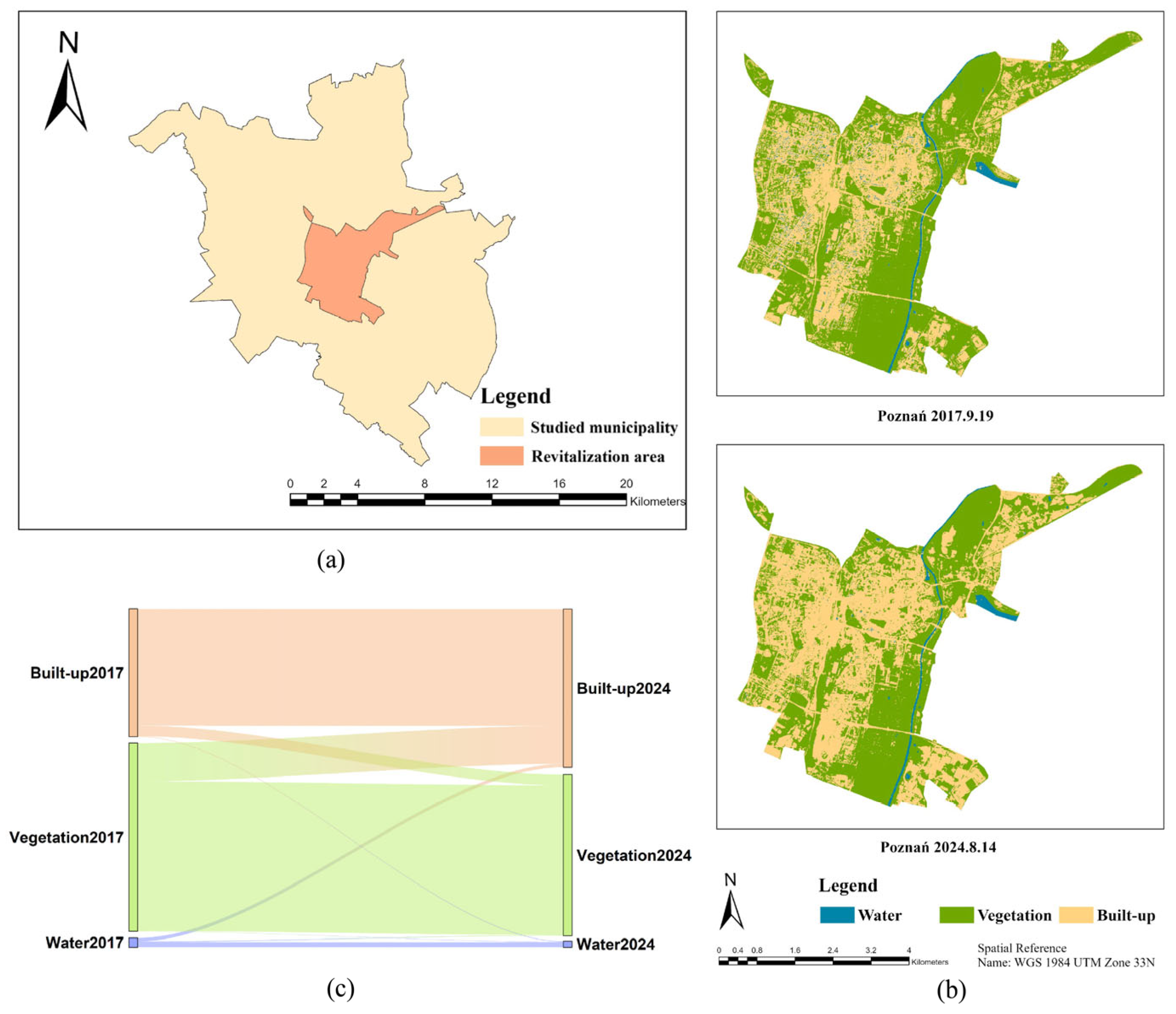
3.2.1. Poznań
3.2.2. Kraków
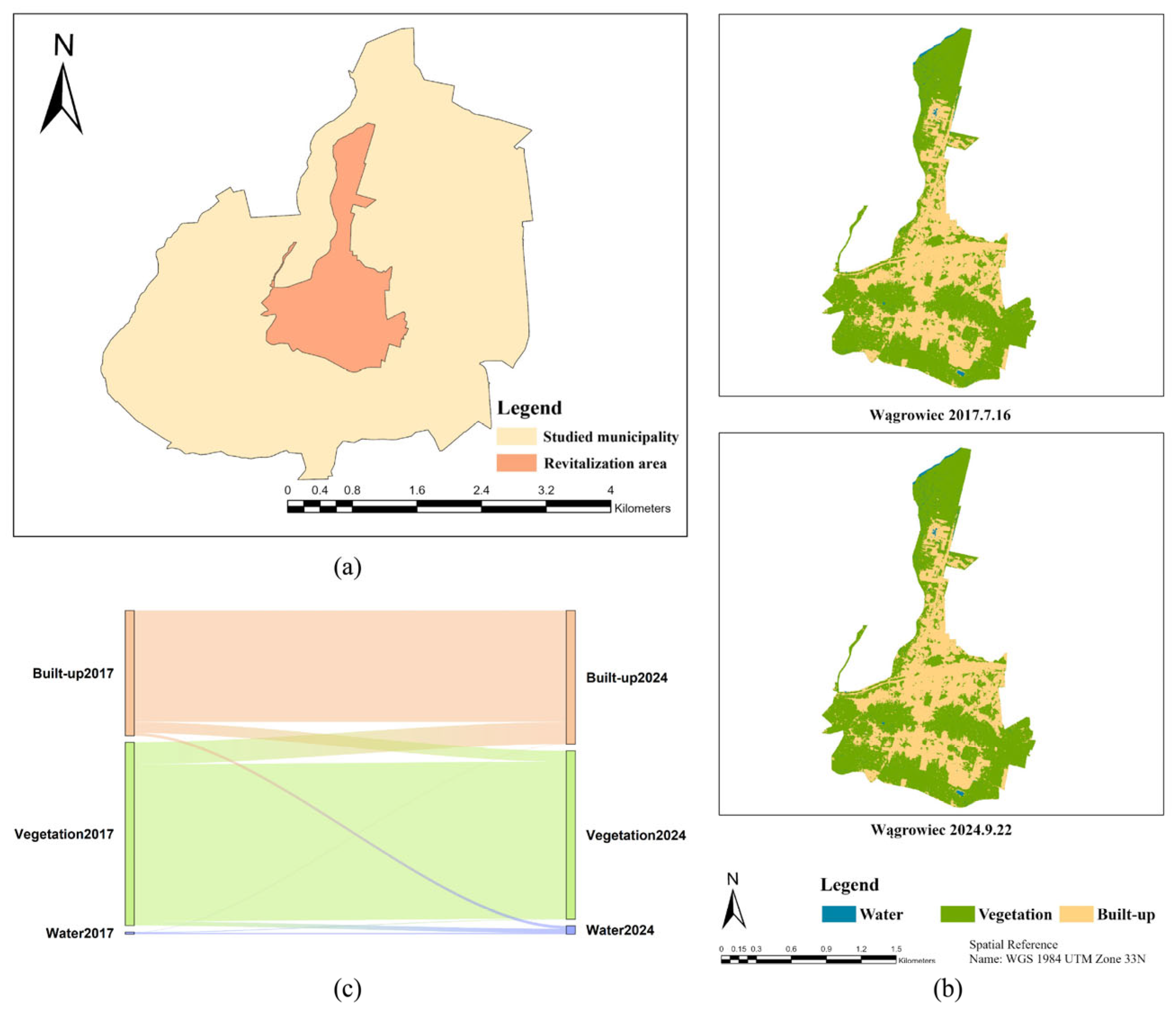
3.2.3. Wągrowiec
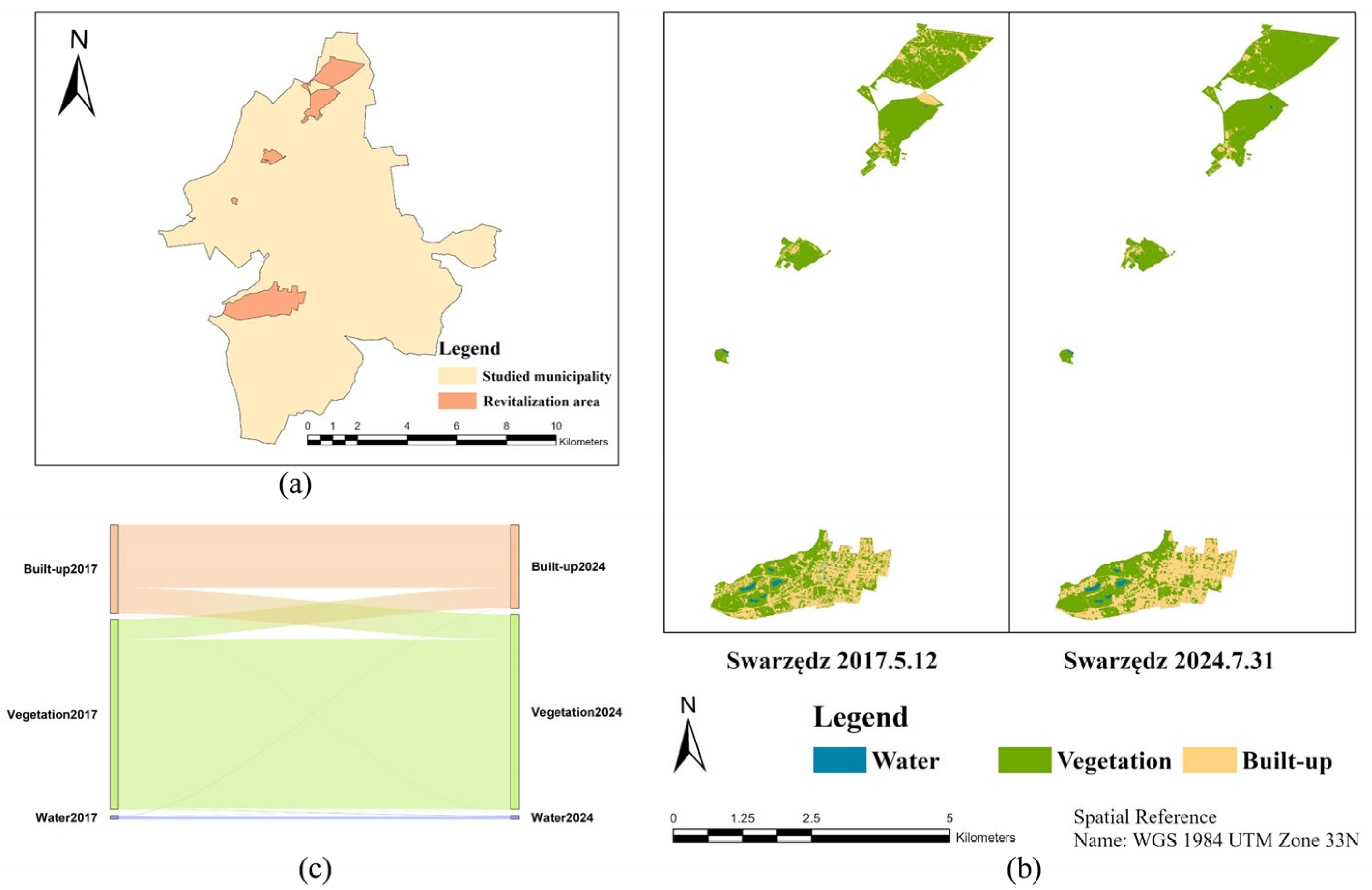
3.2.4. Swarzędz
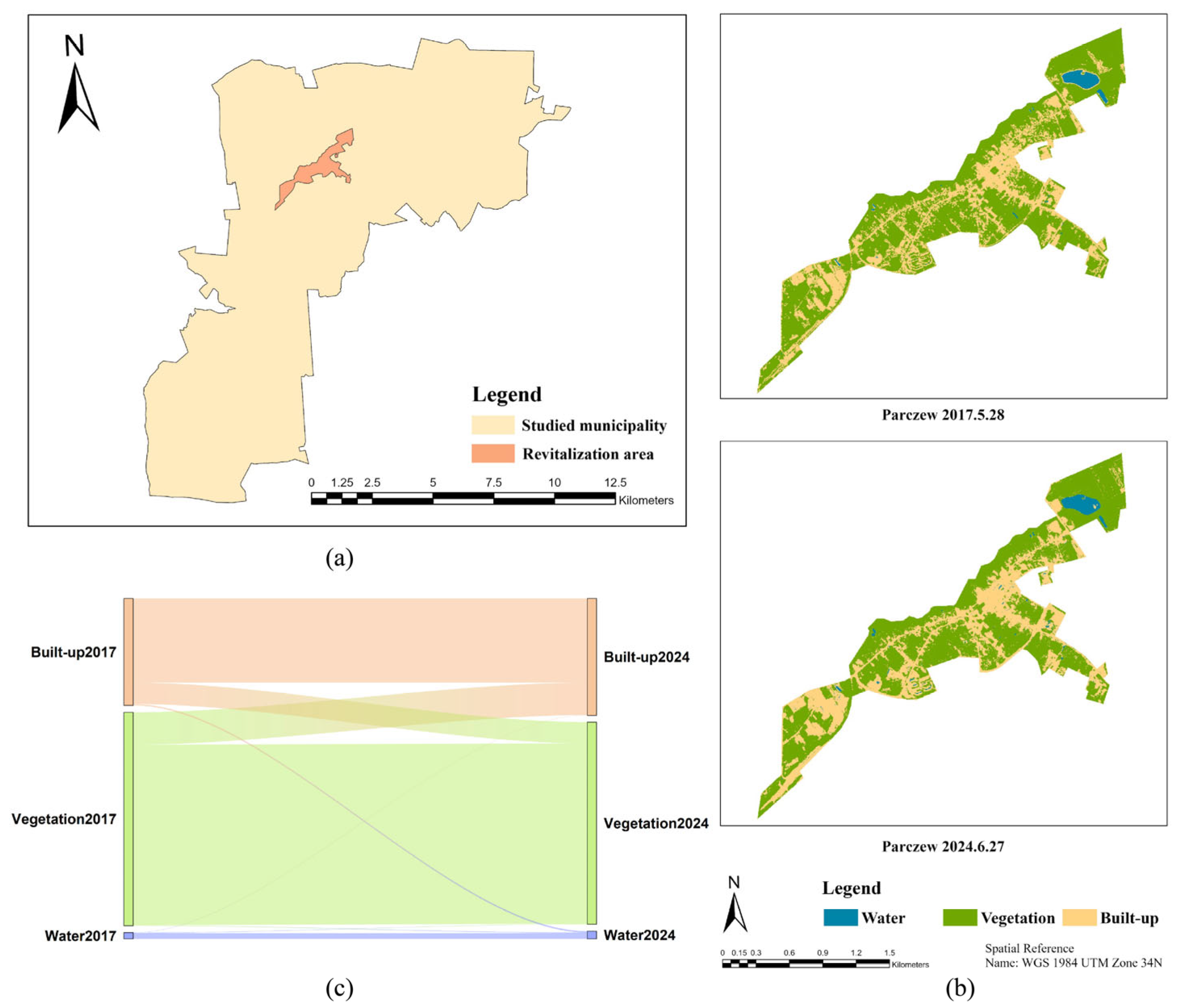
3.2.5. Parczew
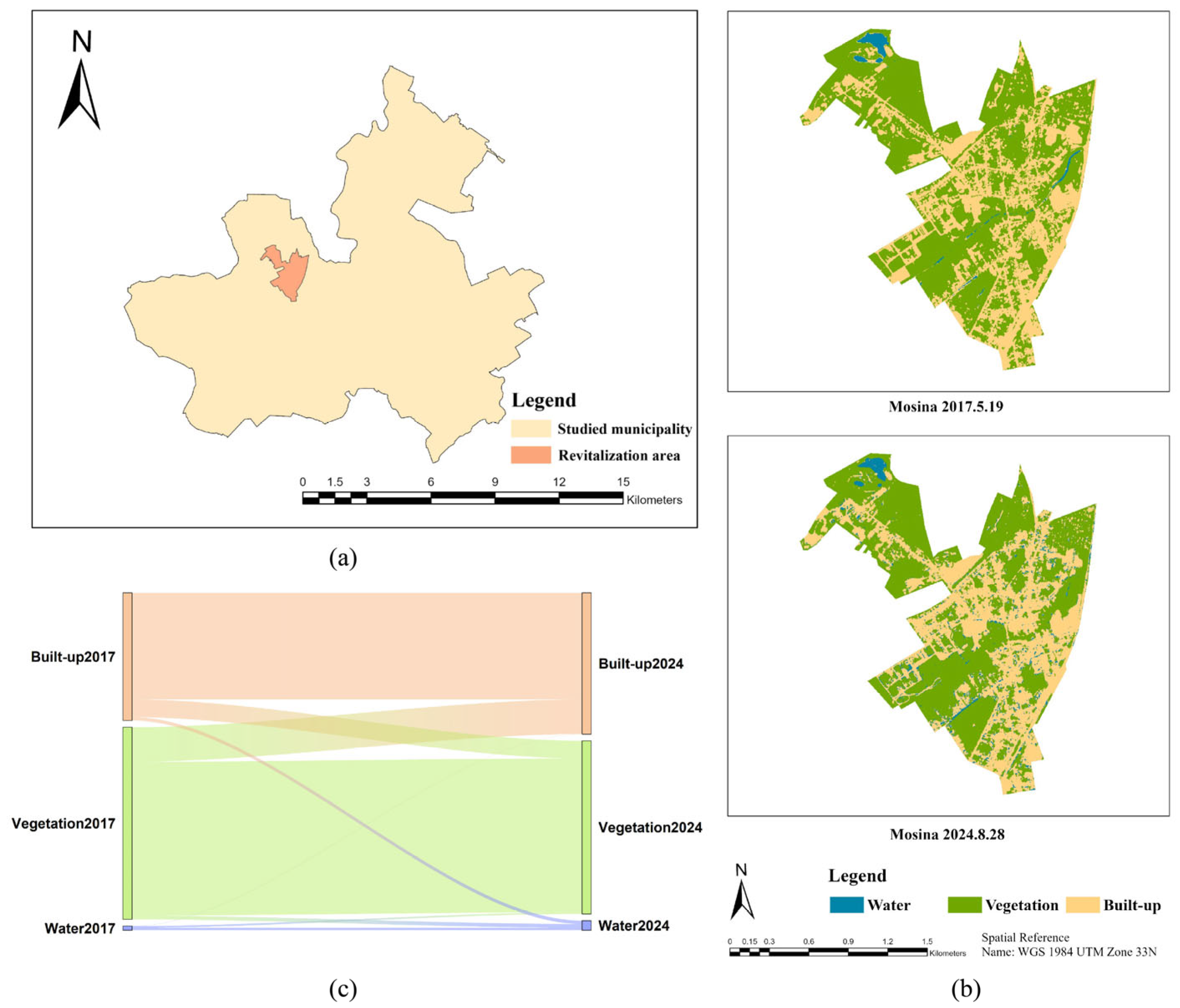
3.2.6. Mosina
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| LULC | Land Use and Land Cover |
| RF | Random Forest |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| MLC | Maximum Likelihood Classifier |
Appendix A
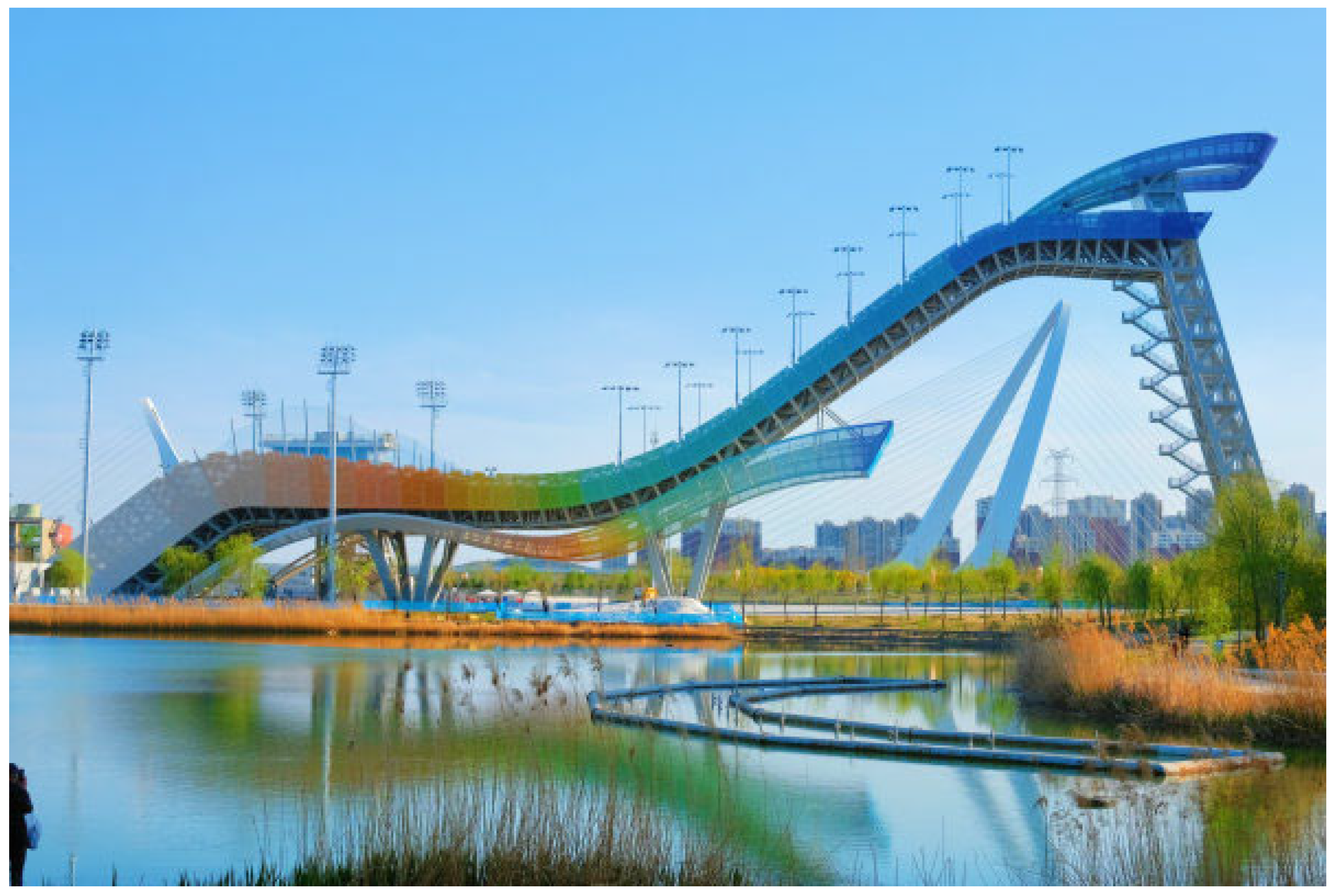
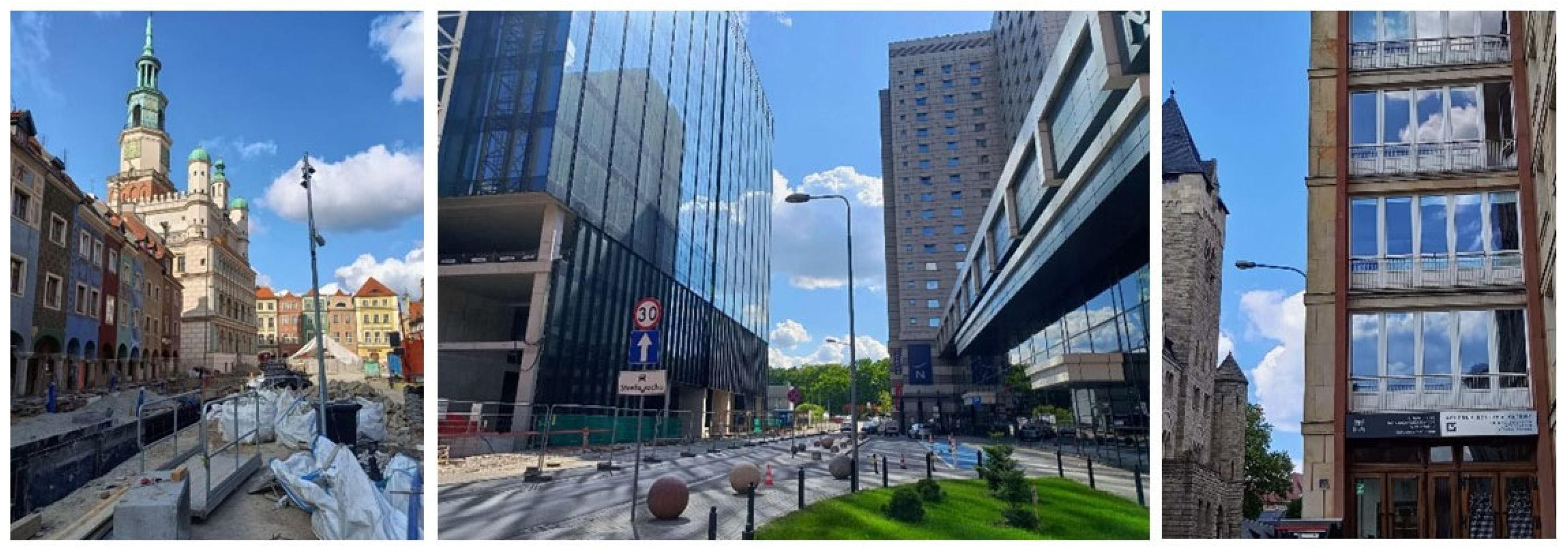
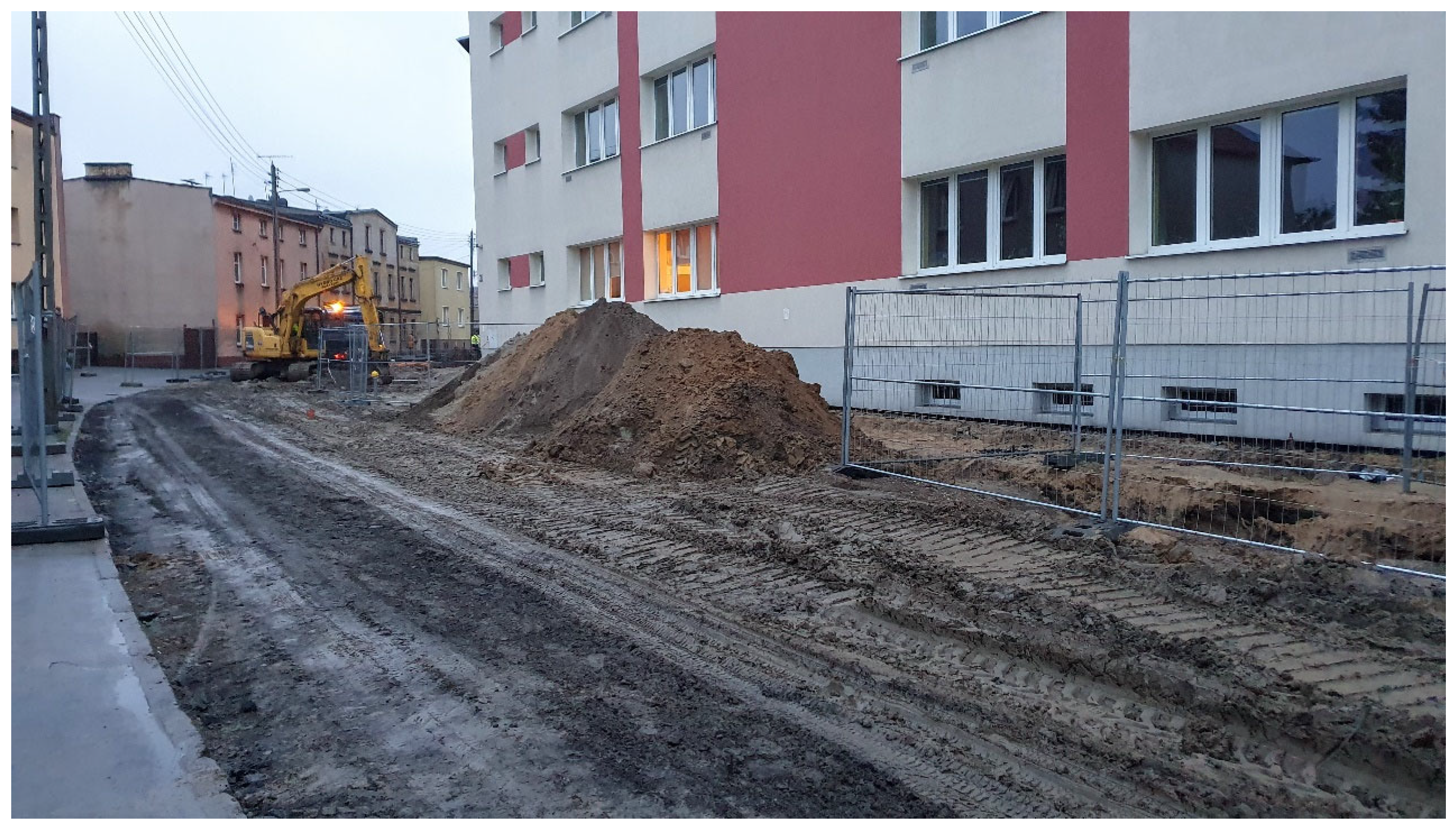
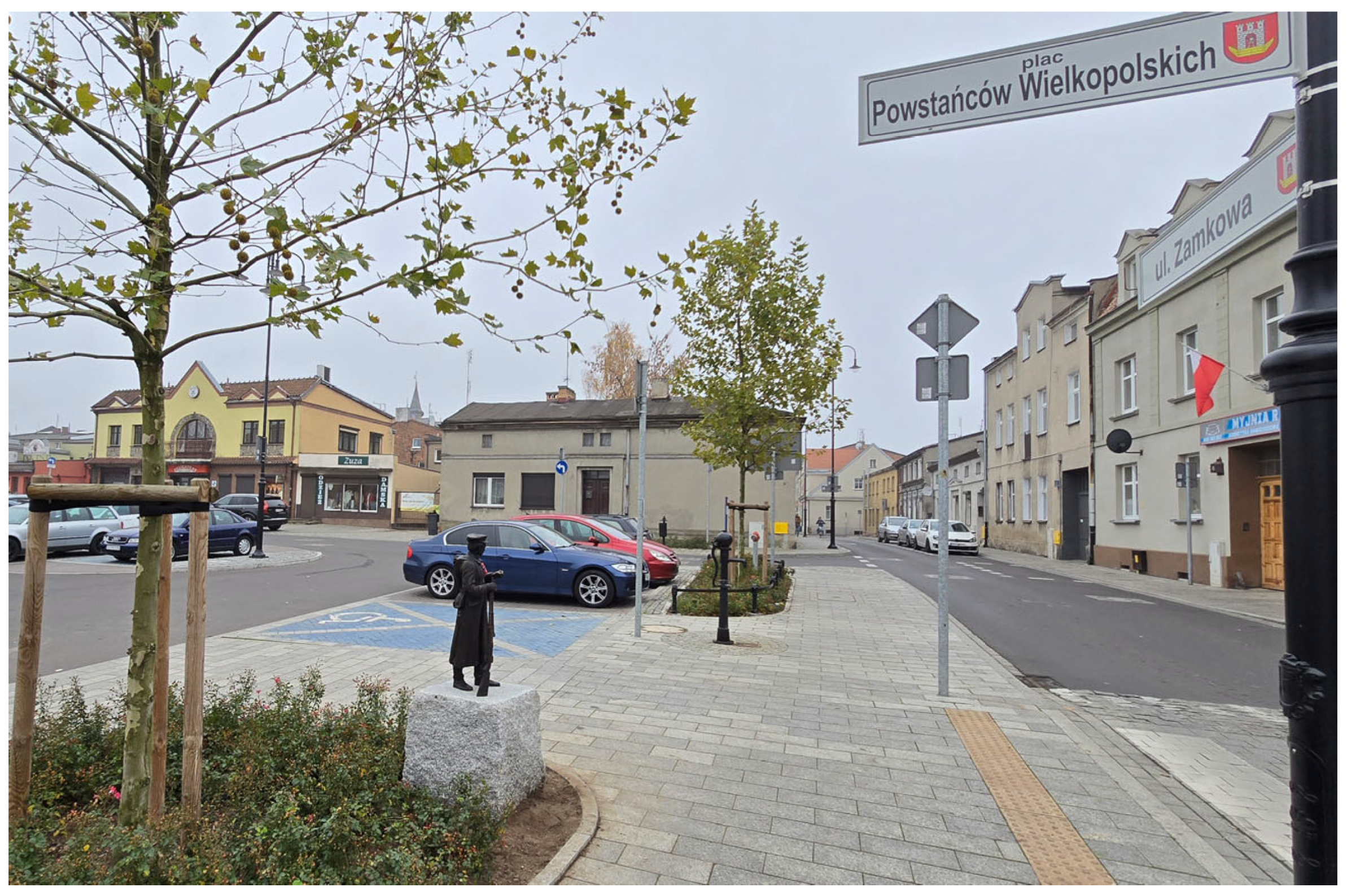





| Beijing | Nanjing | Poznań | Kraków | Wągrowiec | Swarzędz | Parczew | Mosina | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of inhabitants (thousand) | 21,858 | 9425 | 536.818 | 807.644 | 25.394 | 56.873 | 13.622 | 35.552 |
| Area/km2 | 16,410.54 | 6587.02 | 262 | 327 | 18 | 102 | 147 | 172 |
| Population density (person/km2) | 1332 | 1431 | 2055.8 | 2466.6 | 1425.30 | 556.6 | 93.3 | 207 |
| Type of municipality | urban | urban | urban | urban | urban | urban–rural | urban–rural | urban–rural |
| Yearly budget expenditure in USD (million) | 82,199.66 | 22,193.91 | 1536.14 | 2072.56 | 42.77 | 128.62 | 23.8 | 59.88 |
| Unemployment rate (registered) | 3.08% | 2.70% | 0.68% | 1.32% | 1.83% | 0.45% | 2.69% | 0.57% |
References
- Biegańska, J.; Środa-Murawska, S.; Rogatka, K.; Finc, D.; Cielicki, M.; Kuczmowski, W.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Werner, M.; Kopczyńska, L. Revitalization of urban space—Case study of Ghent, Belgium. Acta Sci. Pol. Adm. Locorum 2019, 18, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholz, S. Urban Centres in Asia and Latin America; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Lou, H.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y. Spatial and Temporal Evolution Assessment of Landscape Ecological Resilience Based on Adaptive Cycling in Changsha–Zhuzhou–Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration, China. Land 2025, 14, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Bai, X.; Wang, S.; Kang, L.; Cai, X. The Coupling Relationship and Driving Mechanism between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services in the Yellow River Basin from a Multi-Spatial Scale Perspective. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0293319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choryński, A.; Pińskwar, I.; Graczyk, D.; Krzyżaniak, M. The Emergence of Different Local Resilience Arrangements Regarding Extreme Weather Events in Small Municipalities—A Case Study from the Wielkopolska Region, Poland. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.S.; Singh, P.; Rai, S.C. Modelling LULC change dynamics and its impact on environment and water security: Geospatial technology based assessment. Ecol. Environ. Conserv. 2018, 24, S292–S298. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Rotich, B.; Czimber, K. Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of Conflict-Driven Internally Displaced Persons: A Sentinel-2 Satellite Based Analysis of Land Use/Cover Changes in the Kas Locality, Darfur, Sudan. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchan, A.; Nitivattananon, V.; Tripathi, N.K.; Winijkul, E.; Mandadi, R.R. A Spatio-Temporal Examination of Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Smart Cities of the Delhi–Mumbai Industrial Corridor. Land 2024, 13, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fu, D.; Zevenbergen, C.; Busker, T.; Yu, M. Assessing Sponge Cities Performance at City Scale Using Remotely Sensed LULC Changes: Case Study Nanjing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supiyandi, S.; Mailok, R. binti Advances in Spatial Analysis for Land Change Science: A Systematic Review of Geospatial Methodologies. J. Komput. Teknol. Inf. Sist. Inf. 2025, 4, 1085–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkowski, W.; Latocha-Wites, A.; Grochowska, A. Landscape Effects of Urbanisation in a Post-Socialist City. A Case Study of Wrocław (Poland). Cities 2024, 145, 104730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wei, L.; Liu, G.; Cui, W.; Xie, F.; Deng, X. “Inspiring” Policy Transfer: Analysis of Urban Renewal in Four First-Tier Chinese Cities. Land 2023, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Majumder, A.; Swain, S.; Gareema; Pateriya, B.; Al-Ansari, N. Analysis of Decadal Land Use Changes and Its Impacts on Urban Heat Island (UHI) Using Remote Sensing-Based Approach: A Smart City Perspective. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Mu, R.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, N. An Observational Analysis of Warm-Sector Rainfall Characteristics Associated with the 21 July 2012 Beijing Extreme Rainfall Event. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 3274–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pińskwar, I.; Choryński, A.; Graczyk, D. Risk of Flash Floods in Urban and Rural Municipalities Triggered by Intense Precipitation in Wielkopolska of Poland. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2023, 14, 440–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, T.; Qian, Q.K.; Visscher, H.J.; Elsinga, M.G.; Wu, W. The Role of Stakeholders and Their Participation Network in Decision-Making of Urban Renewal in China: The Case of Chongqing. Cities 2019, 92, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martone, A.; Sepe, M. Creativity, Urban Regeneration and Sustainability/The Bordeaux Case Study. J. Urban Regen. Renew. 2012, 5, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H. The Local Press and Urban Renewal: A South Wales Case Study. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 1994, 18, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DzU 2015 Poz. 1777, Ustawa z Dnia 9 Października 2015 r. o Rewitalizacji, 2015. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20150001777/T/D20151777L.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Tenah, B.; Chadli, M.; Badreddine, R.; Wail, D.A.; Saad, C. Urban Expension Analysis of New Cities in North Africa, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Betewen 2004–2024. Case Study of Sidi Abdellah, Algeria. J. Inf. Syst. Eng. Manag. 2025, 10, 1828–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.; Singh, R. A Comprehensive Review on Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) Change Modeling for Urban Development: Current Status and Future Prospects. Sustainability 2023, 15, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshari, E.A.; Abdulkareem, M.B.; Gawali, B.W. Classification of Land Use/Land Cover Using Artificial Intelligence (ANN-RF). Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, 964279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Yuan, X.; Ren, T.; Yu, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. Comparison and Assessment of Data Sources with Different Spatial and Temporal Resolution for Efficiency Orchard Mapping: Case Studies in Five Grape-Growing Regions. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?” Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Proceedings of the Demonstrations Session (NAACL-HLT 2016), San Diego, CA, USA, 12–17 June 2016; pp. 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Choi, J. Fully Convolutional Networks with Multiscale 3D Filters and Transfer Learning for Change Detection in High Spatial Resolution Satellite Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwisch, M.; Saha, S.; Matzarakis, A. Spatial Neighborhood Analysis Linking Urban Morphology and Green Infrastructure to Atmospheric Conditions in Karlsruhe, Germany. Urban Clim. 2023, 51, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefulebe, B.E.; Van der Walt, A.; Xulu, S. Fine-Scale Classification of Urban Land Use and Land Cover with PlanetScope Imagery and Machine Learning Strategies in the City of Cape Town, South Africa. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, C.; Budak, M.; Yagmur, N.; Balcik, F.B. Comparison between Random Forest and Support Vector Machine Algorithms for LULC Classification. Int. J. Eng. Geosci. 2023, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices. In Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Administration of Sport of China. Framework Agreement on Preparing for the 2022 Winter Olympics and Establishing a National Sports Industry Demonstration Zone; General Administration of Sport of China: Beijing, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Nanjing Jiangbei New District Management Committee. Environmental Impact Assessment Brief of Core Area and Surrounding Regions Planning in Nanjing Jiangbei New District (2018–2030); Nanjing Jiangbei New District Management Committee: Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Posadzińska, I.; Sieg, P.; Jóźwiak, M. New Product Concept Development as an Effect of Revitalizing the Old Market in Bydgoszcz. In Scientific Papers of Silesian University of Technology Organization and Management Series; Silesian University of Technology Publishing House: Gliwice, Poland, 2022; Volume 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchwała Rady Miasta Poznania z Dnia 7 Listopada 2017 r. Nr LVI/1021/VII/2017, w Sprawie Przyjęcia Gminnego Programu Rewitalizacji Dla Miasta Poznania. Available online: https://bip.poznan.pl/bip/uchwaly/uchwala-nr-lvi-1021-vii-2017-z-dnia-2017-11-07,71611/ (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Uchwała Nr LXII/1373/17, Rady Miasta Krakowa z Dnia 11 Stycznia 2017 r. w Sprawie Przyjęcia z Aktualizacji Miejskiego Programu Rewitalizacji Krakowa. Available online: https://bip.krakow.pl/zarzadzenia/2017/3322/X19UUF9fNDQxMzY=/aMPRK_fin_16_11_2017.doc.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Uchwała Rady Miejskiej w Wągrowcu z Dnia 22 Czerwca 2017 r. Nr XXXIII/225/2017, w Sprawie Przyjęcia Lokalnego Programu Rewitalizacji Miasta Wągrowca Na Lata 2017–2025. Available online: https://www.wagrowiec.eu/assets/files/dzialy/dokumenty-strategiczne/uchwala-lpr_2017-2025.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Uchwała Rady Miejskiej w Swarzędzu z Dnia 28 Listopada 2017 r. Nr XLIV/422/2017, w Sprawie Przyjęcia Lokalnego Programu Rewitalizacji Swarzędza Na Lata 2017–2023. Available online: https://bip.swarzedz.pl/fileadmin/BIP/Prawo/Uchwaly/2017/422_2017.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Uchwała Rady Miejskiej w Parczewie z Dnia 29 Maja 2017 r. Nr XXXV/256/2017 w Sprawie Przyjęcia Aktualizacji Lokalnego Programu Rewitalizacji Miasta Parczew Na Lata 2017–2023. Available online: https://www.parczew.com/images/2024/ZIT_MOF/Projekt%20GPR%20Parczew.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Uchwała Rady Miejskiej w Mosinie z Dnia 26 Października 2017 r. Nr LVII/645/17 w Sprawie Przyjęcia Gminnego Programu Rewitalizacji Dla Gminy Mosina Na Lata 2017–2027. Available online: http://bip.mosina.pl/um/prawo/uchwaly-rady/kadencja-2014-20181/lvii-sesja-rady-miejskiej-w-mosinie-26.10.2017-r.html?pid=12535 (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- de Souza, J.M.; Morgado, P.; da Costa, E.M.; de Novaes Vianna, L.F. Modeling of Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) Change Based on Artificial Neural Networks for the Chapecó River Ecological Corridor, Santa Catarina/Brazil. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Du, H.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C. Influence of Meteorological Conditions on the Air Quality during the 2022 Winter Olympics in Beijing. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 987272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Zhang, L.; Pang, J. The Spatial–Temporal Evolution of the Trade-Offs and Synergy between the Suburban Rural Landscape’s Production–Living–Ecological Functions: A Case Study of Jiashan in the Yangtze River Delta Eco-Green Integrated Development Demonstration Zone, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xia, H.; Zhang, X. How to Promote the Coordinated Development of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Under the Background of Digitalization? In Digitalization and Management Innovation III; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Xin, Y.; Baoquan, J.; Xiaoting, L.; Xianwen, L.; Chengyang, X.; Kaicun, W. Long-term characteristics and driving factors of vegetation cover changes in 328 Chinese cities. SSTe 2024, 54, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żuber, P.; Szmigiel-Rawska, K.; Krukowska, J. Boosting National Urban Policies by European Integration. The Case of Poland. In A Modern Guide to National Urban Policies in Europe; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, M.; Szopińska, K.; Siemińska, E.; Kostov, I. Revitalization as an Action in Space-Case Study of Large Cities in Poland and Bulgaria. GIS Odyssey J. 2022, 2, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churski, P. Cohesion Policy in Poland Assumptions and Implementation. In Proceedings of the 11th Slovak-Czech-Polish Seminar “Flows, Spaces and Societies in Central Europe”, Trenčianske Teplice, Slovakia, 14–16 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Czupich, M. Level of Social Participation in the Creation of Urban Regeneration Programmes-The Case Study of Small Towns in Poland. Eur. Spat. Res. Policy 2018, 25, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darem, A.A.; Alhashmi, A.A.; Almadani, A.M.; Alanazi, A.K.; Sutantra, G.A. Development of a Map for Land Use and Land Cover Classification of the Northern Border Region Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2023, 26, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.I.; Ameen, S.A. Predicting Land Use and Land Cover Spatiotemporal Changes Utilizing CA-Markov Model in Duhok District between 1999 and 2033. Acad. J. Nawroz Univ. 2020, 9, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Lu, D. A 30 m Resolution Dataset of China’s Urban Impervious Surface Area and Green Space, 2000–2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Qi, Z.; Liu, X.; Niu, N.; Zhang, H. Urban Land Use and Land Cover Classification Using Multisource Remote Sensing Images and Social Media Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, T.; Pathania, S.S. Land Use-Land Cover Changes and Associated Drivers: A Case of Salooni Block of Chamba. Curr. World Environ. 2024, 19, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Cuesta, J.M.; Minacapilli, M.; Motisi, A.; Consoli, S.; Intrigliolo, D.S.; Vanella, D. Characterization of the Main Land Processes Occurring in Europe (2000–2018) through a MODIS NDVI Seasonal Parameter-Based Procedure. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengan, S.; Karn, A.L.; Pustokhin, D.A.; Pustokhina, I.V.; Alharbi, M. A Hybrid Learning Model for Efficient Classification of Land Use and Land Change from Satellite Images. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 128, 103284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasu, D. Remote Sensing-Based Urban Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection and Monitoring. J. Remote Sens. GIS 2017, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Before Revitalization | After Revitalization | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PlanetScope | World Imagery Wayback | PlanetScope | World Imagery Wayback | |
| Beijing | 4 August 2017 | 10 August 2017 | 10 August 2022 | 10 August 2022 |
| Nanjing | 23 August 2017 | 30 August 2017 | 28 September 2024 | 19 September 2024 |
| Poznań | 19 September 2017 | 13 September 2017 | 14 August 2024 | 15 August 2024 |
| Kraków | 30 September 2016 | 12 October 2016 | 24 September 2024 | 19 September 2024 |
| Wągrowiec | 16 July 2017 | 14 July 2017 | 22 September 2024 | 19 September 2024 |
| Swarzędz | 12 May 2017 | 17 May 2017 | 31 July 2024 | 15 August 2024 |
| Parczew | 28 May 2017 | 31 May 2017 | 27 June 2024 | 27 June 2024 |
| Mosina | 19 May 2017 | 17 May 2017 | 28 August 2024 | 15 August 2024 |
| LULC Category | Definition |
|---|---|
| Vegetation | Areas where the land surface is covered by various plants, whether naturally grown or artificially planted. |
| Water | Areas where the land surface is covered by water, both flowing and stagnant, naturally formed and artificially constructed. |
| Built-up | Areas predominantly covered by impermeable artificial constructions (e.g., buildings, roads, pavement, squares) that seal the natural ground, primarily used for human habitation, commerce, transportation, and recreation. |
| Accuracy Assessment | Kappa Coefficient | Overall Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Revitalization | After Revitalization | Before Revitalization | After Revitalization | |
| Beijing | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.94 |
| Nanjing | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.90 |
| Poznań | 0.80 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.95 |
| Kraków | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| Wągrowiec | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| Swarzędz | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.91 | 0.90 |
| Parczew | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| Mosina | 0.79 | 0.80 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| City/Municipality | Land Cover Categories | Area (Before Revitalization/km2) | Area (After Revitalization/km2) | Persistence (Area/km2) | Net Change Rate/% | Gain Rate/% | Loss Rate/% | Swap Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | Water | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.14 | −12.98 | 38.32 | 51.30 | 76.64 |
| Vegetation | 2.56 | 2.75 | 1.46 | 7.36 | 50.35 | 42.99 | 85.97 | |
| Built-up | 5.78 | 5.63 | 4.44 | −2.62 | 20.57 | 23.19 | 41.14 | |
| Nanjing | Water | 0.62 | 2.50 | 0.42 | 302.31 | 334.52 | 32.21 | 64.42 |
| Vegetation | 15.79 | 13.14 | 8.38 | −16.79 | 30.09 | 46.89 | 60.19 | |
| Built-up | 16.96 | 17.73 | 11.10 | 4.54 | 39.11 | 34.57 | 69.14 | |
| Poznań | Water | 0.71 | 0.46 | 0.39 | −35.30 | 10.34 | 45.63 | 20.67 |
| Vegetation | 14.36 | 12.28 | 11.42 | −14.48 | 6.05 | 20.52 | 12.09 | |
| Built-up | 9.72 | 12.05 | 8.86 | 23.98 | 32.75 | 8.77 | 17.53 | |
| Kraków | Water | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.0006 | −1.72 | 91.36 | 93.09 | 182.73 |
| Vegetation | 4.29 | 3.80 | 3.36 | −11.33 | 10.20 | 21.52 | 20.39 | |
| Built-up | 4.19 | 4.68 | 3.75 | 11.58 | 22.03 | 10.45 | 20.90 | |
| Wągrowiec | Water | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 288.51 | 332.81 | 44.29 | 88.59 |
| Vegetation | 1.31 | 1.20 | 1.12 | −8.02 | 6.34 | 14.36 | 12.69 | |
| Built-up | 0.90 | 0.96 | 0.80 | 6.79 | 17.77 | 10.98 | 21.97 | |
| Swarzędz | Water | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 1.18 | 23.59 | 22.42 | 44.83 |
| Vegetation | 3.70 | 3.80 | 3.30 | 2.57 | 13.52 | 10.94 | 21.89 | |
| Built-up | 1.72 | 1.62 | 1.23 | −5.59 | 23.20 | 28.79 | 46.40 | |
| Parczew | Water | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 21.63 | 32.43 | 10.79 | 21.59 |
| Vegetation | 1.53 | 1.45 | 1.29 | −5.28 | 10.21 | 15.49 | 20.43 | |
| Built-up | 0.77 | 0.84 | 0.60 | 9.24 | 30.53 | 21.30 | 42.59 | |
| Mosina | Water | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 128.41 | 168.77 | 40.36 | 80.71 |
| Vegetation | 1.27 | 1.15 | 1.02 | −9.90 | 10.08 | 19.98 | 20.16 | |
| Built-up | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.71 | 10.62 | 27.13 | 16.51 | 33.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Choryński, A. Analysis of Spatial Changes in Urban Areas Due to Revitalization Investments Based on China and Poland. Sustainability 2025, 17, 10126. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210126
Wang Y, Choryński A. Analysis of Spatial Changes in Urban Areas Due to Revitalization Investments Based on China and Poland. Sustainability. 2025; 17(22):10126. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210126
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yingxin, and Adam Choryński. 2025. "Analysis of Spatial Changes in Urban Areas Due to Revitalization Investments Based on China and Poland" Sustainability 17, no. 22: 10126. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210126
APA StyleWang, Y., & Choryński, A. (2025). Analysis of Spatial Changes in Urban Areas Due to Revitalization Investments Based on China and Poland. Sustainability, 17(22), 10126. https://doi.org/10.3390/su172210126








