Interconnections Between Environmental Awareness and Green Technology Adoption: Empirical Evidence from Informal Business Enterprises
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
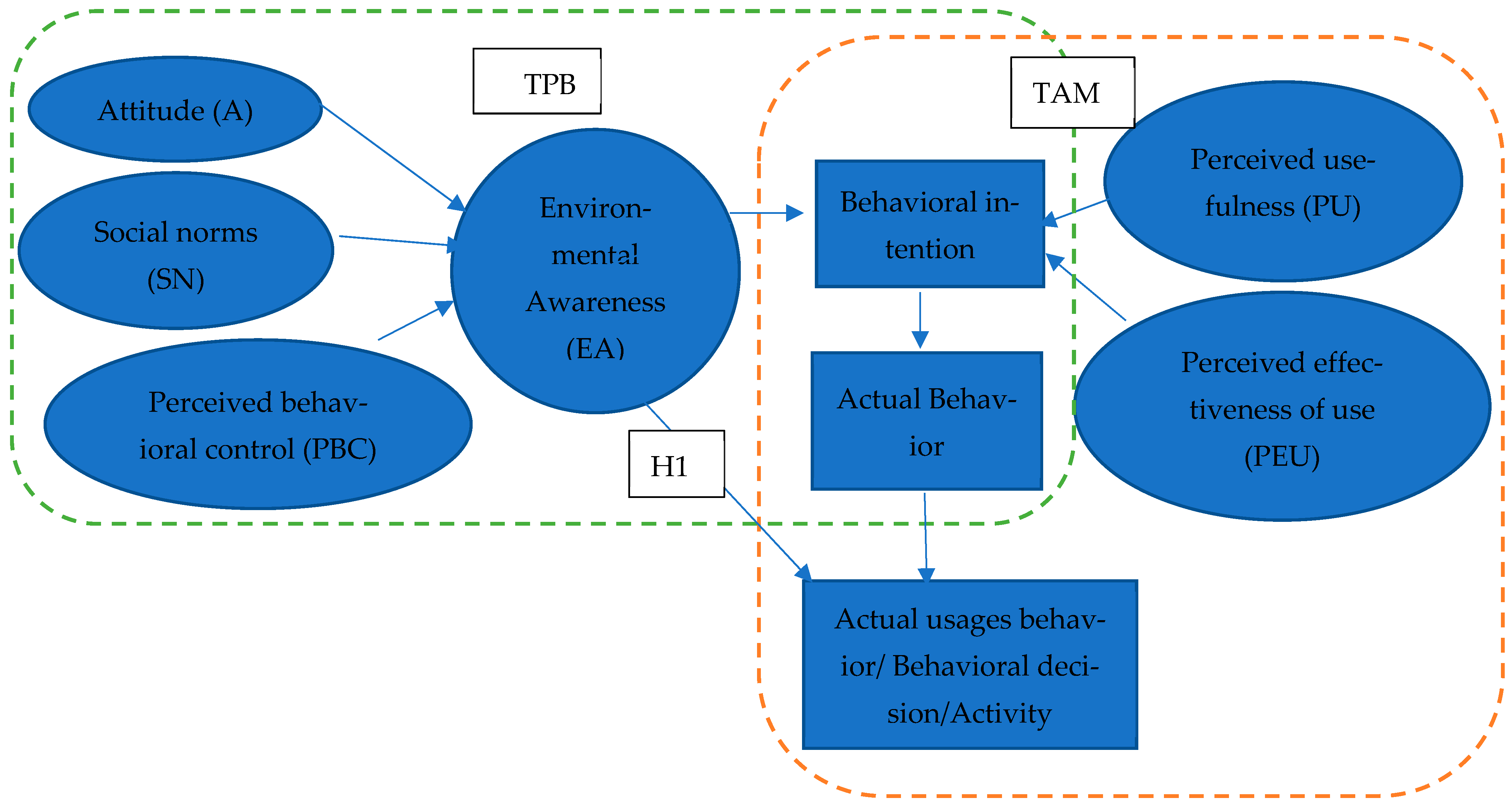
3. Theoretical Background and Hypothesis
4. Research Methodology
4.1. Survey and Data Collection
4.2. Methods
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Results
5.2. Discussions
6. Limitations and Future Research
7. Conclusions and Policy Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, L.; Sun, Z.; Zha, L.; Liu, F.; He, L.; Sun, X.; Jing, X. Environmental awareness and pro-environmental behavior within China’s road freight transportation industry: Moderating role of perceived policy effectiveness. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakimova, D.; Lösch, S.; Wende, D.; Wiesmeth, H.; Okhrin, O. Index of environmental awareness through the MIMIC approach. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2019, 98, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, M.K.; Kari, F.B.; Ali, M.A. Linkage between Public Policy, Green Technology and Green Products on Environmental Awareness in the Urban Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2017, 4, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coertjens, L.; Pauw, J.B.; Maeyer, S.D.; Petegem, P.V. Do schools make a difference in their students’ environmental attitudes and awareness? Evidence from PISA 2006. Int. J. Sci. Math. Educ. 2010, 8, 497–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saricam, H.; Sahin, S.H. The Relationship between the Environmental Awareness, Environmental Attitude, Curiosity and Exploration in Highly Gifted Students: Structural Equation Modelling. Educ. Process Int. J. 2015, 4, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruga, K. Is environmental awareness a good predictor of an individual’s altruism level? Sustainability 2020, 12, 7929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; Santos, F.C.A.; Fonseca, S.A.; Nagano, M.S. Green teams: Understanding their roles in the environmental management of companies located in Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 46, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittneben, B.B.F.; Kiyar, D. Climate change basics for managers. Manag. Decis. 2009, 47, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonn, B. The intergovernmental panel on climate change: A global scale transformation initiative. Futures 2007, 39, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolk, A.; Pinkse, J. Business responses to climate change:idenyifying emergent strategies. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2005, 47, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kencanasari, R.A.V.; Surahman, U.; Permana, A.Y. The Instrumental Framework to Measuring Environmental Awareness. Innov. Vocat. Technol. Educ. 2019, 15, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincbas, T.; Ergeneli, A.; Yigitbasioglu, H. Clean technology adoption in the context of climate change: Application in the mineral products industry. Technol. Soc. 2021, 64, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manika, D.; Antonetti, P.; Papagiannidis, S.; Guo, X. How Pride Triggered by Pro-environmental Technology Adoption Spills Over into Conservation Behaviours: A Social Business Application. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 172, 121005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.B.; Rice, R.E.; Gustafson, A.; Goldberg, M.H. Relationships Among Environmental Attitudes, Environmental Efficacy, and Pro-Environmental Behaviors Across and Within 11 Countries. Environ. Behav. 2022, 54, 1063–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baksi, S.; Bose, P. Informal sector, regulatory compliance, and leakage. J. Dev. Econ. 2016, 121, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, A.; Meyer, R. Environmental attitudes in cross-national perspective: A multilevel analysis of the ISSP 1993 and 2000. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 2010, 26, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.R.; Barman, T.R. Environmental Pollution, Informal sector, Public Expenditure and Economic Growth. Hitotsubashi J. Econ. 2015, 56, 73–91. [Google Scholar]
- Blackman, A.; Shih, J.S.; Evan, D.; Batz, M.; Newbold, S.; Cook, J. The benefits and costs of informal sector pollution control: Mexican brick kilns. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2006, 11, 603–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, A.; Bannister, G.J. Community pressure and clean technology in the informal sector: An econometric analysis of the adoption of propane by traditional Mexican brickmakers. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1998, 35, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbahnasawy, N.G.; Ellis, M.A.; Adom, A.D. Political Instability and the Informal Economy. World Dev. 2016, 85, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, A. Informal sector pollution control: What policy options do we have? World Dev. 2000, 28, 2067–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hao, Y.; Feng, C. A race between economic growth and carbon emissions: What play important roles towards global low-carbon development? Energy Econ. 2021, 100, 105327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgin, C.; Oztunali, O. Pollution and informal economy. Econ. Syst. 2014, 38, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M. The close relationship between informal economic growth and carbon emissions in Tunisia since 1980: The (ir)relevance of structural breaks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 15, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, A.; Bannister, G.J. Pollution control in the informal sector: The Ciudad Juárez Brickmakers’ Project. Nat. Resour. J. 1998, 37, 829–854. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.K.; Farzanegan, M.R.; Thum, M. Pollution, shadow economy and corruption: Theory and evidence. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 75, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; Linde, C.V.D. Green and competitive: Breaking the stalemate. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1995, 73, 120–133. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, S.; Han, G.; An, D.; Hunter, W.C.; Li, H. The impact of green credit policy on technological innovation of firms in pollution-intensive industries: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Tong, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. How top management’s environmental awareness affect corporate green competitive advantage: Evidence from China. Kybernetes 2022, 51, 1250–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, P. A cognitive map of sustainable decision-making in entrepreneurship: A configurational approach. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2017, 24, 787–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploum, L.; Blok, V.; Lans, T.; Omta, O. Exploring the relation between individual moral antecedents and entrepreneurial opportunity recognition for sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintimehin, O.O.; Eniola, A.A.; Alabi, O.J.; Eluyela, D.F.; Okere, W.; Ozordi, E. Social capital and its effect on business performance in the Nigeria informal sector. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.X.; Tang, X.; Cheung, M.L.; Zhang, Y. An institutional perspective on consumers environmental awareness and pro-environmental. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 30, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuiii, S. Environmental concern, attitude toward frugality, and ease of behavior as determinants of pro-environmental behavior intentions. J. Environ. Psychol. 2006, 26, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M. Selected Readings on the Strategies for Inclusive Development in Bangladesh; Academic Press and Publishers Library: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Kashem, M.A. Carbon emissions, energy consumption and industrial growth in Bangladesh: Empirical evidence from ARDL cointegration and Granger causality analysis. Energy Policy 2017, 110, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baul, T.K.; Sarker, A.; Nath, T.K. Restaurants’ waste in Chittagong city, Bangladesh: Current management, awareness on environmental hazard and perception towards potential uses. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferronato, N.; Torretta, V. Waste mismanagement in developing countries: A review of global issues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadenne, D.L.; Kennedy, J.; McKeiver, C. An empirical study of environmental awareness and practices in SMEs. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 84, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, J.; Nilsson, J.; Modig, F.; Val, G.H. Commitment to Sustainability in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises: The Influence of Strategic Orientations and Management Value. Bus. Strategy Dev. 2017, 26, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.P. Sustainability Management and Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Managers Awareness and Implementation of Innovative Tools. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2013, 22, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harju-autti, P.; Kokkinen, E. Open Access Research Article A Novel Environmental Awareness Index Measured Cross-Nationally for Fifty Seven Countries Abstract: Motivation Environmental awareness Knowledge Skills. Univers. J. Environ. Res. Technol. 2014, 4, 178–198. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A. A preliminary investigation into the environmental awareness of the Omani public and their willingness to protect the environment. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 4, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Fujii, M.; Wang, P. Study on comparison of Citizens’ environmental awareness among four cities in China and Japan. Manag. Sci. Eng. 2011, 5, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaper, M. Small Firms and Environmental Management: Predictors of Green Purchasing in Western Australian Pharmacies. Int. Small Bus. J. 2002, 20, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Schaefer, A. Small and medium-sized enterprises and sustainability: Managers’ values and engagement with environmental and climate change issues. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2013, 22, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, G.M.; Côté, R.P.; Duffy, J.F. Improving environmental awareness training in business. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.I.; Jamadar, Y.; Islam, M.F.; Rashed, M.; Akter, T. Environmental sustainability practices in SMEs: Insights from integrated PLS-SEM and fsQCA approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 503, 145185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Jin, S.; Wang, H.; Ye, C. Estimating Effects of Cooperative Membership on Farmers’ Safe Production Behaviors: Evidence from Pig Sector in China. Food Policy 2019, 83, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Han, J. Understanding Ecological Agricultural Technology Adoption in China Using an Integrated Technological Acceptance Model–Theory of Planned Behavior Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 927668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clubbs, B.H.; Gray, N.; Madlock, P. Using the theory of planned behavior and the technology acceptance model to analyze a university employee fitness tracker program with financial incentive. J. Commun. Healthc. 2021, 14, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Cao, X. Research on designers’ behavioral intention toward Artificial Intelligence-Aided Design: Integrating the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Technology Acceptance Model. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1450717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chao, W. Habitual or reasoned? Using the theory of planned behavior technology acceptance model, and habit to examine switching intentions toward public transit. Transp. Res. Part F 2011, 14, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentosa, I.; Nik Mat, N.K. Examining a theory of planned behavior (TPB) and technology acceptance model (TAM) in internet purchasing using structural equation modeling. Int. Ref. Res. J. 2012, 3, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, S.; Gaughran, W.F. Developing a framework for sustainability management in engineering SMEs. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2007, 23, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassells, S.; Lewis, K. SMEs and environmental responsibility: Do actions reflect attitudes? Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2011, 18, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearins, K.; Collins, E.; Tregidga, H. Beyond corporate environmental management to a consideration of nature in visionary small enterprise. Bus. Soc. 2010, 49, 512–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, S. Going green:the evolution of micro-business environmental practices. Bus. Ethics Eur. Rev. 2012, 21, 220–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, S. Drivers of proactive environmental strategy in family firms. Bus. Ethics Q. 2011, 21, 309–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ILO. Women and Men in the Infromal Economy: A Statistical Picture, 3rd ed.; ILO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://www.ilo.org/global/publications/books/WCMS_626831/lang--en/index.htm (accessed on 15 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Roger, P.; Jalal, K.; Boyd, J. Challanges of Sustainable Development. In An Introduction to Sustainable Development; Glen Education Foundation, Inc.: Glen Cove, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 42–79. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A. Effect of asian-origin ethnicity on pork consumption evidence from the family food expenditure survey (Statistics Canada). Crossing Boundaries 2002, 1, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Uzunoz, M.; Akcay, Y. A Case Study of Probit Model Analysis of Factors Affecting Consumption of Packed and Unpacked Milk in Turkey. Econ. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.F. Interpreting Probability Models: Logit, Probit, and Other Generalized Linear Models; Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1994; Volume 101. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Xue, D.; Wang, B. Integrating Theories on Informal Economies: An Examination of Causes of Urban Informal Economies in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, W.H. Econometric Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Boateng, E.Y.; Abaye, D.A. A Review of the Logistic Regression Model with Emphasis on Medical Research. J. Data Anal. Inf. Process. 2019, 7, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klieštik, T.; Kočišová, K.; Mišanková, M. Logit and Probit Model used for Prediction of Financial Health of Company. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 23, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arı, E.; Yılmaz, V. Effects of environmental illiteracy and environmental awareness among middle school students on environmental behavior. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 19, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y. Consumer’s intention to purchase green furniture: Do health consciousness and environmental awareness matter? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieson, K. Predicting user intentions: Comparing the technology acceptance model with the theory of planned behavior. Inf. Syst. Res. 1991, 2, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/downloads/report/IPCC_AR6_WGI_SPM_final.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2025).
| Question Grouping | Concept | Category | Covered Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge about environmental pollution [1,2,3,4,5] | The respondent’s familiarity with various types of pollution and their causes. | SN |
|
| Attitude to environmental concerns [1,2,3,4,5] | How do respondents rank different types of pollution in terms of their negative impact? | A | Level of concern with the environmental problems mentioned below:
|
| Practice on environmental conservation [1,2,3,4,5] | How do the firms control environmental activities? | PBC |
|
| General perception of environmental management [1,2,3,4,5] | To what extent the respondents are familiar with environmental management and its importance. | Cognitive |
|
| Variables | Model-1 | Model-2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Std. Error | Z-Statistic | Marginal Effects | Coefficient | Std. Error | Z-Statistic | Marginal Effects | |
| Environmental awareness (EA) | 0.723 *** (0.004) | 0.252 | 2.86 | 0.285 | 0.767 *** (0.005) | 0.270 | 2.84 | 0.301 |
| Perception of environmental management | 2.163 (0.130) | 1.429 | 1.51 | 0.852 | 2.145 (0.148) | 1.481 | 1.45 | 0.842 |
| Age | 0.067 * (0.067) | 0.016 | 1.83 | 0.012 | ||||
| Subcontract arrangements | 0.225 (0.481) | 0.319 | 0.70 | 0.087 | ||||
| Constant | −1.817 (0.104) | 1.118 | −1.63 | −3.293 ** (0.017) | 1.374 | −2.40 | ||
| Log-Likelihood LR Chi2(2) Prob>chi2 Pseudo R2 Predicted percentage correctly | −45.270 14.61 0.001 0.139 61.84 | −43.207 18.73 0.001 0.178 60.53 | ||||||
| Variables | Model-1 | Model-2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Std. Error | Z-Statistic | Marginal Effect | Coefficient | Std. Error | Z-Statistic | Marginal Effect | |
| Environmental awareness | 1.241 ** (0.012) | 0.492 | 2.52 | 0.304 | 1.278 ** (0.011) | 0.500 | 2.55 | 0.312 |
| General perception of environmental management | 3.348 (0.142) | 2.282 | 1.47 | 0.819 | 3.381 (0.161) | 2.410 | 1.40 | 0.827 |
| Age | 0.049 * (0.074) | 0.027 | 1.79 | 0.012 | ||||
| Subcontract arrangements | 0.357 (0.498) | 0.526 | 0.68 | 0.087 | ||||
| Constant | −2.855 (0.111) | 1.791 | −1.59 | −5.263 ** (0.021) | 2.284 | −2.30 | ||
| Log-Likelihood LR Chi2(2) Prob>chi2 Pseudo R2 Predicted percentage correctly | −45.318 14.51 0.001 0.138 61.84 | −40.215 24.07 0.000 0.229 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sultana, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Khanam, R. Interconnections Between Environmental Awareness and Green Technology Adoption: Empirical Evidence from Informal Business Enterprises. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9595. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219595
Sultana N, Rahman MM, Khanam R. Interconnections Between Environmental Awareness and Green Technology Adoption: Empirical Evidence from Informal Business Enterprises. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9595. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219595
Chicago/Turabian StyleSultana, Nahid, Mohammad Mafizur Rahman, and Rasheda Khanam. 2025. "Interconnections Between Environmental Awareness and Green Technology Adoption: Empirical Evidence from Informal Business Enterprises" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9595. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219595
APA StyleSultana, N., Rahman, M. M., & Khanam, R. (2025). Interconnections Between Environmental Awareness and Green Technology Adoption: Empirical Evidence from Informal Business Enterprises. Sustainability, 17(21), 9595. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219595








