Developing the Urban Diversity Index (UDI): A Global Comparison of Urban Qualitative Aspect and Its Implications for Sustainable Urban Planning Using POI Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background: Significance and Challenges in Capturing Urban Diversity
1.1.1. The Value and Role of Diversity in Urban Contexts
1.1.2. Limitations of Conventional Urban Indicators and Cross-City Comparison Challenges
1.1.3. Difficulties in Acquiring Qualitative Data and Capturing Urban Dynamics
1.2. Literature Review
1.2.1. Attempts to Quantify Urban Qualitative Characteristics and Their Limitations
1.2.2. Barriers to Global Comparative Research: Inconsistent Statistical Frameworks, Spatial Resolution, and Update Frequency
1.2.3. Challenges in Data Infrastructure in Developing and Peripheral Urban Areas
1.2.4. Limitations of Researcher-Initiated Urban Data Collection: Cost, Scalability, and Sustainability
1.3. A New Opportunity: A Turning Point Enabled by Global-Scale POI Data
1.4. Rationale for Emphasizing the Restaurant Category in Evaluating Urban Diversity
1.5. Research Objective and Paper Outline
1.5.1. Research Objective
1.5.2. Paper Outline
2. Methods
2.1. Data
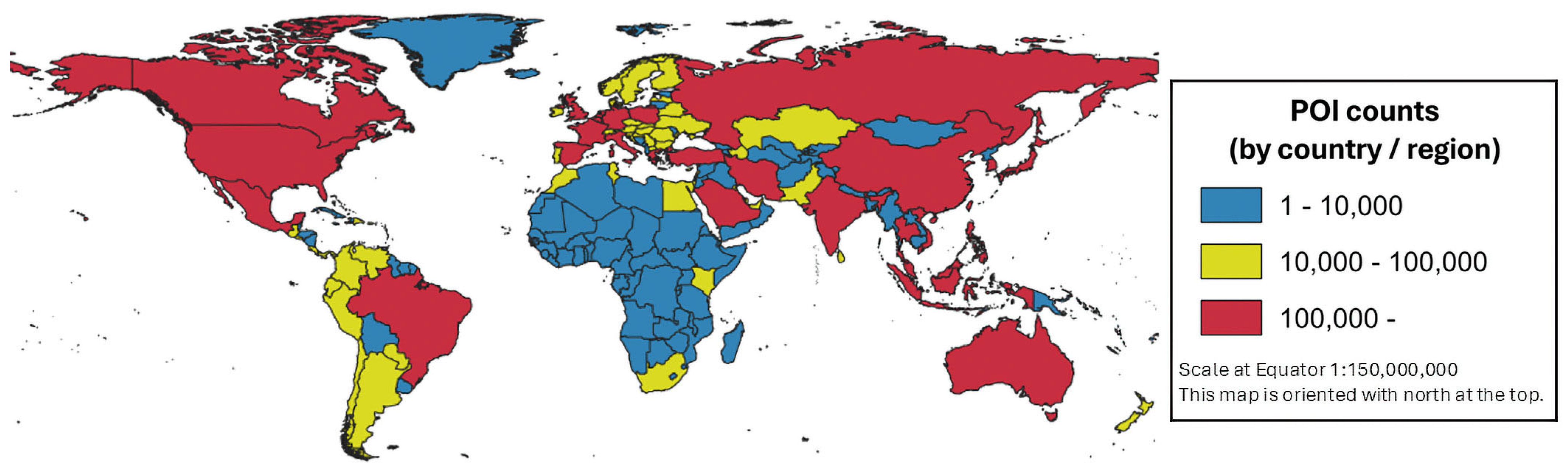
2.1.1. Foursquare Places OS Data
2.1.2. Metropolitan Population Data
2.1.3. Marine Area Data
2.2. Development of Evaluation Indicators
2.2.1. Unit of Analysis
2.2.2. Definitions of the Indicators Constituting the UDI
- (1)
- Shannon–Wiener Index (H) and Pielou’s Evenness Index (J)
- (2)
- Coverage ratio (C)
- (3)
- Dining and Restaurant Density ()
2.2.3. Definitions of the UDI
2.2.4. Peak Distance (d)
2.2.5. Defining Metropolitan Coverage Distances
3. Results
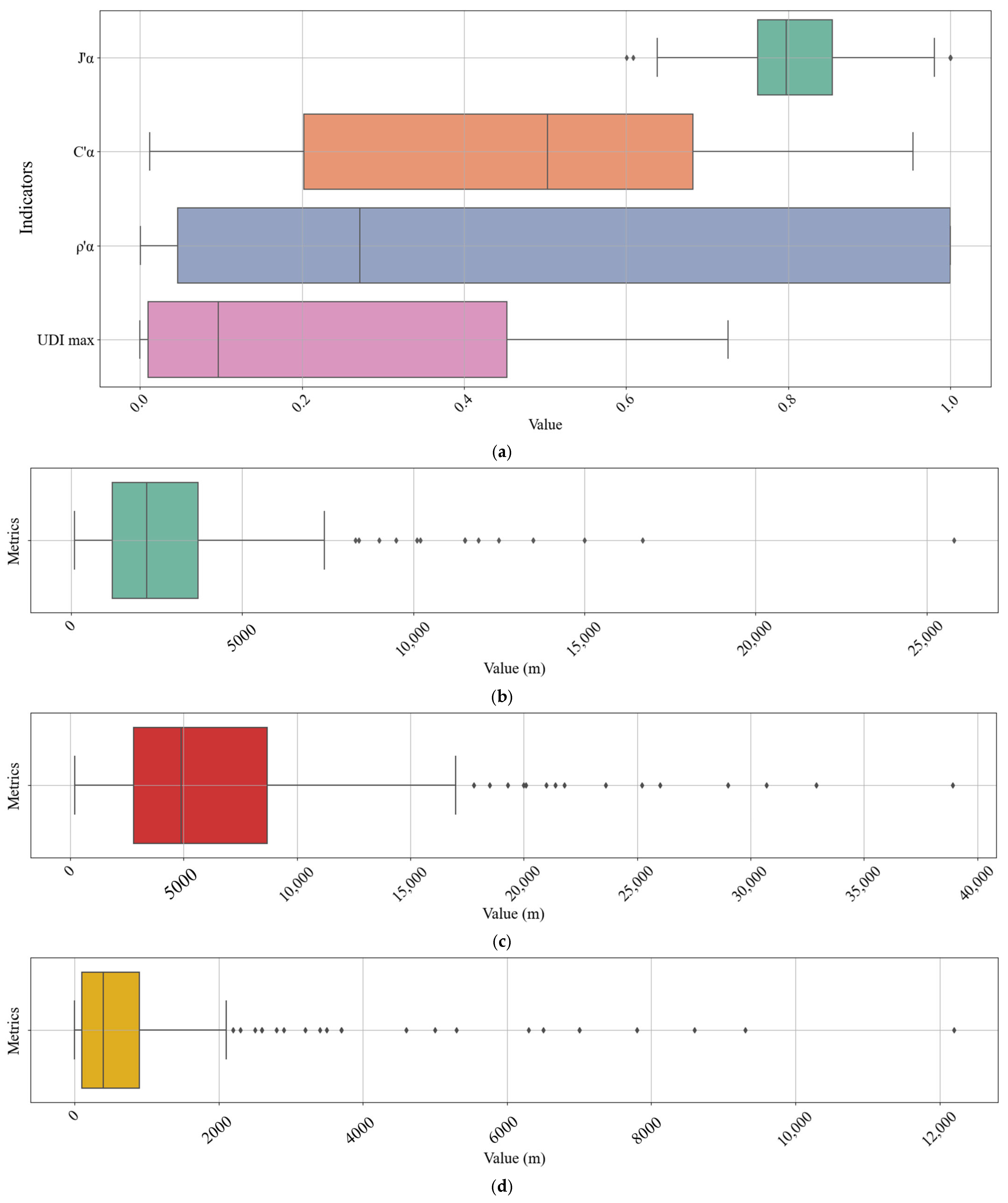
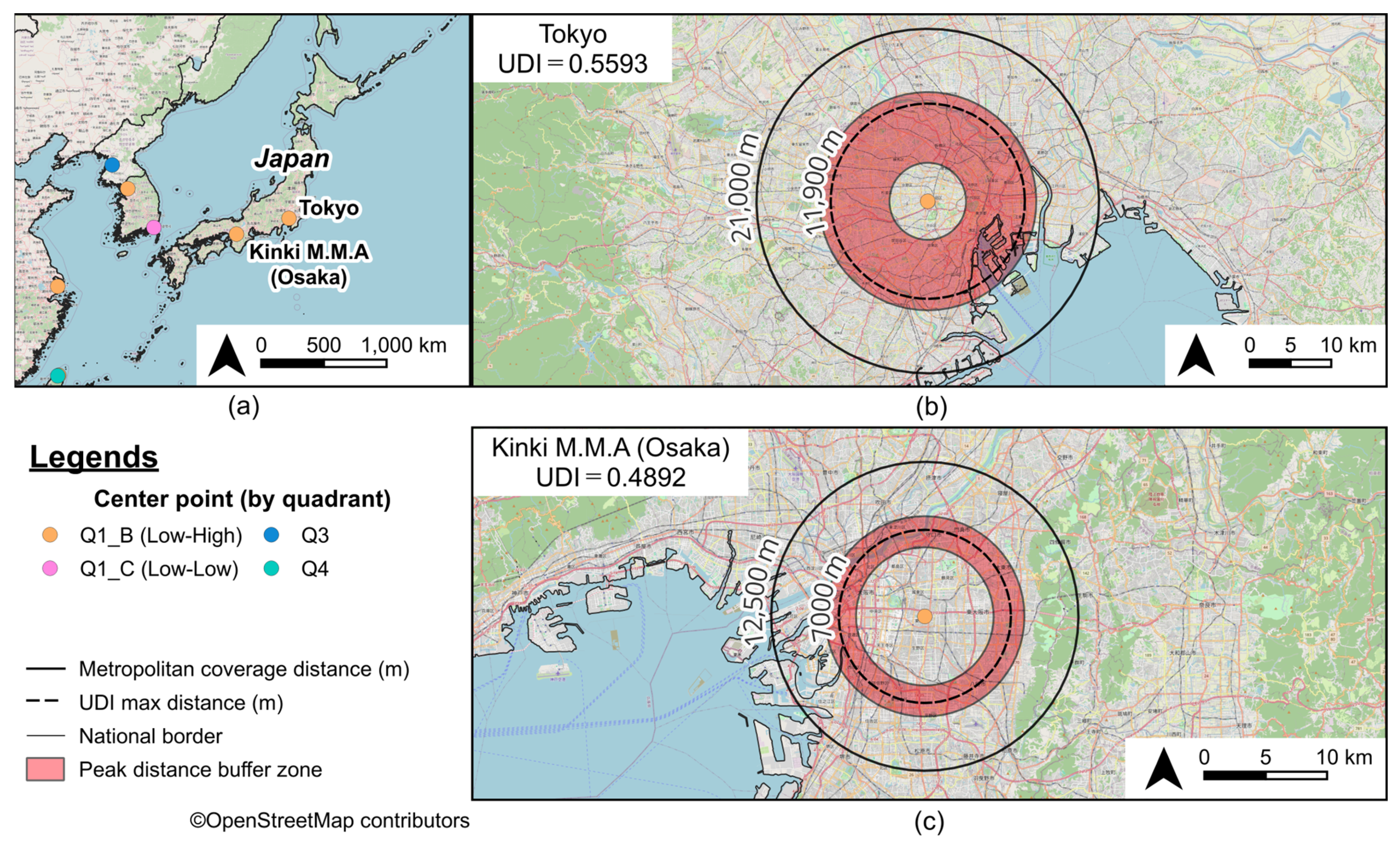
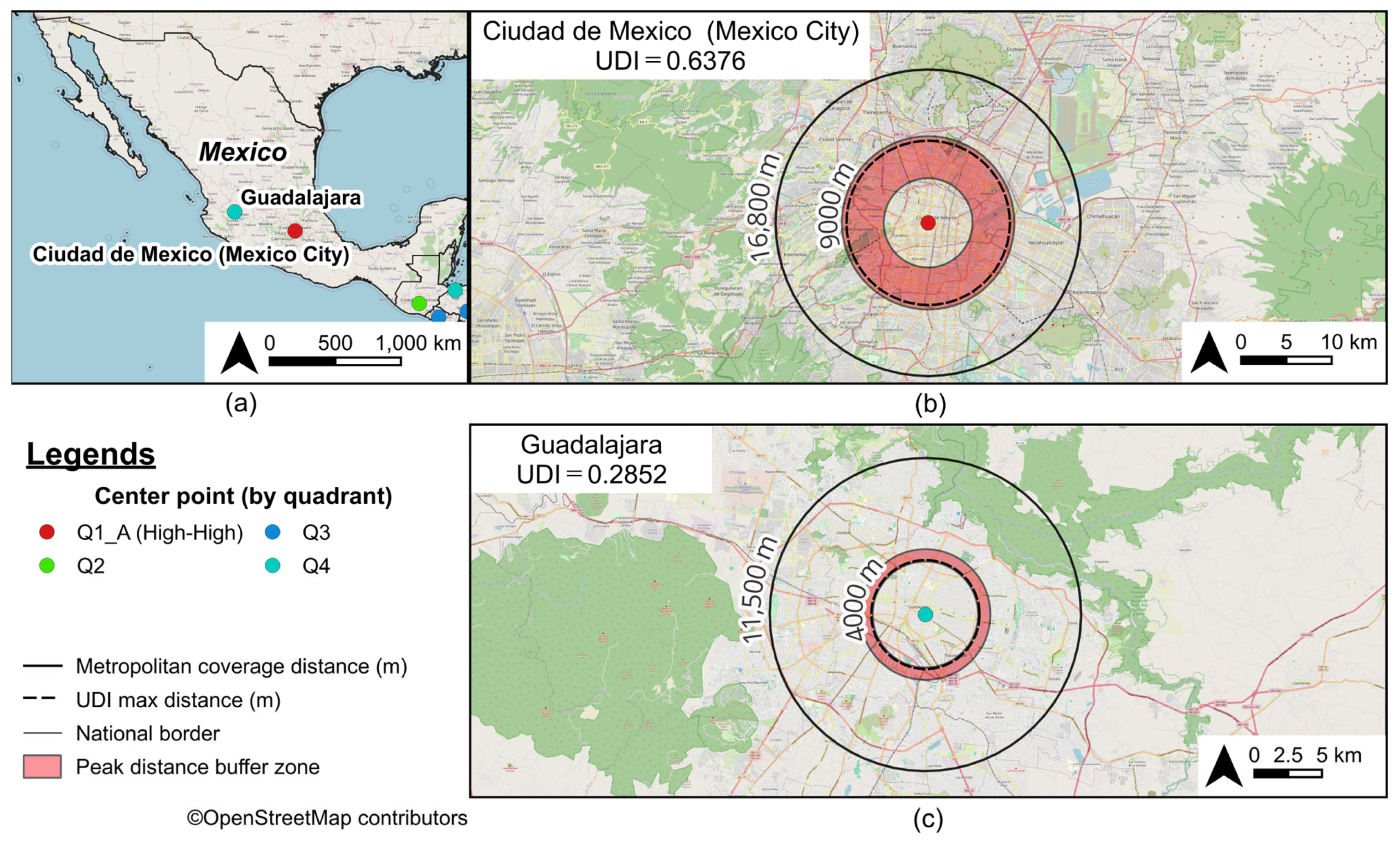
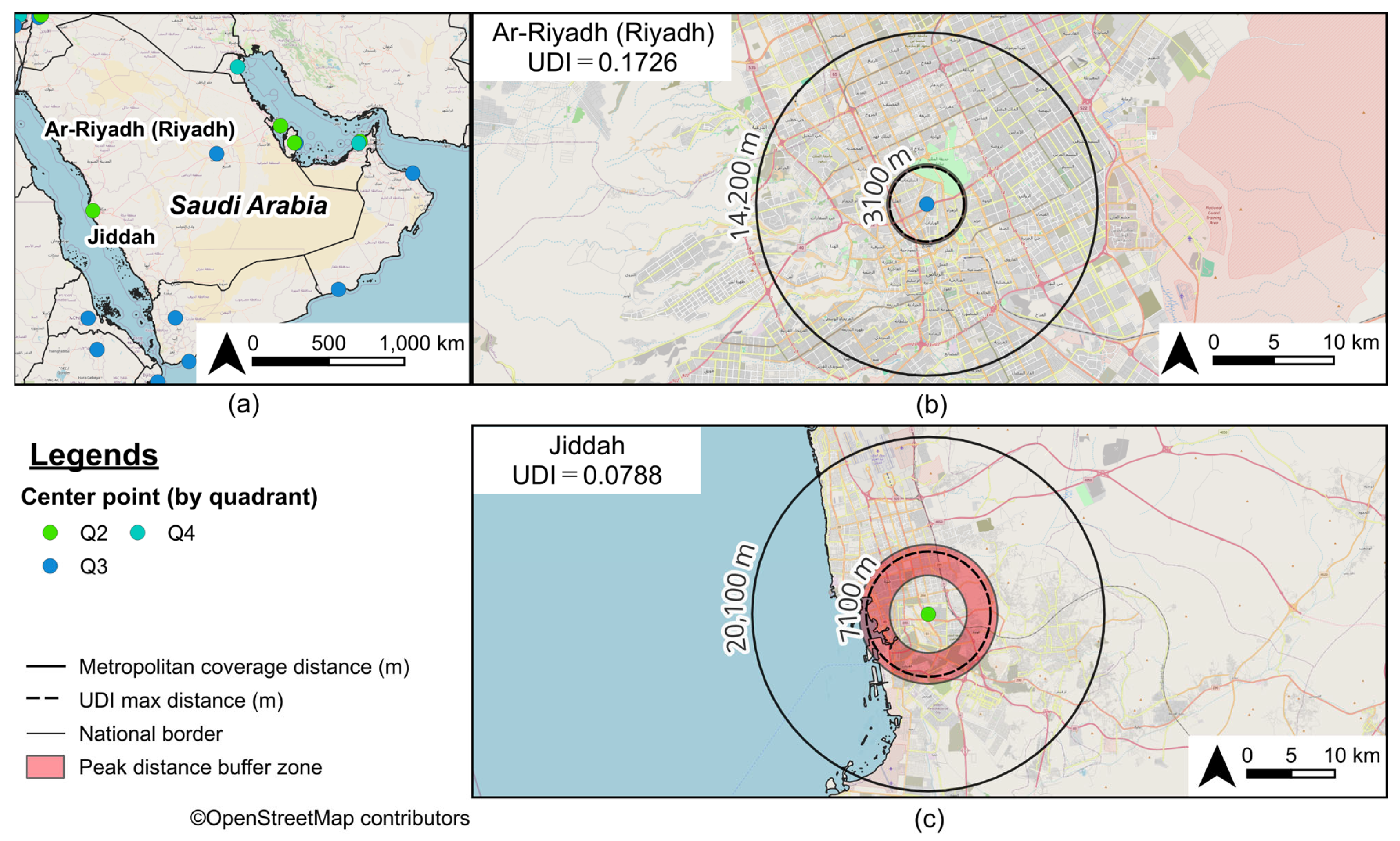
3.1. Diversity Index of Food-Related Establishments in Urban Areas
3.1.1. Pielou’s Evenness Index ()
3.1.2. Coverage Ratio ()
3.1.3. Dining and Restaurant Density ()
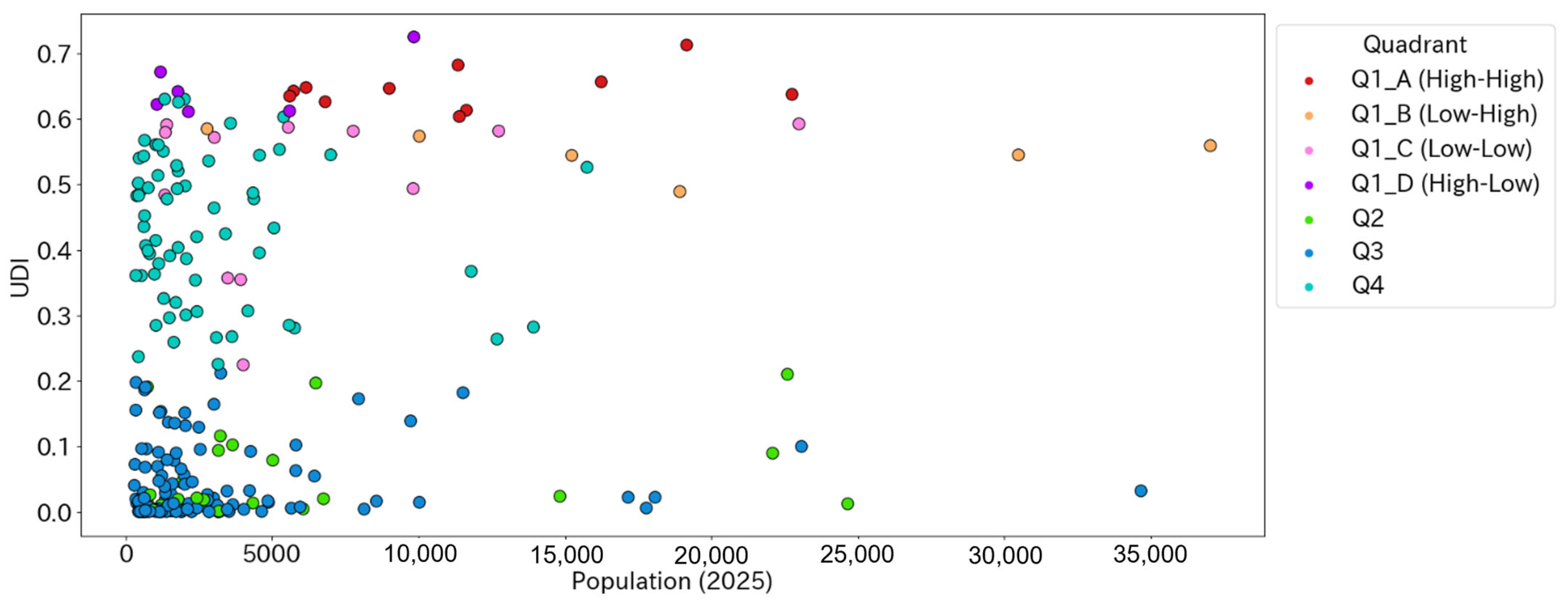
3.2. UDI (Urban Diversity Index)
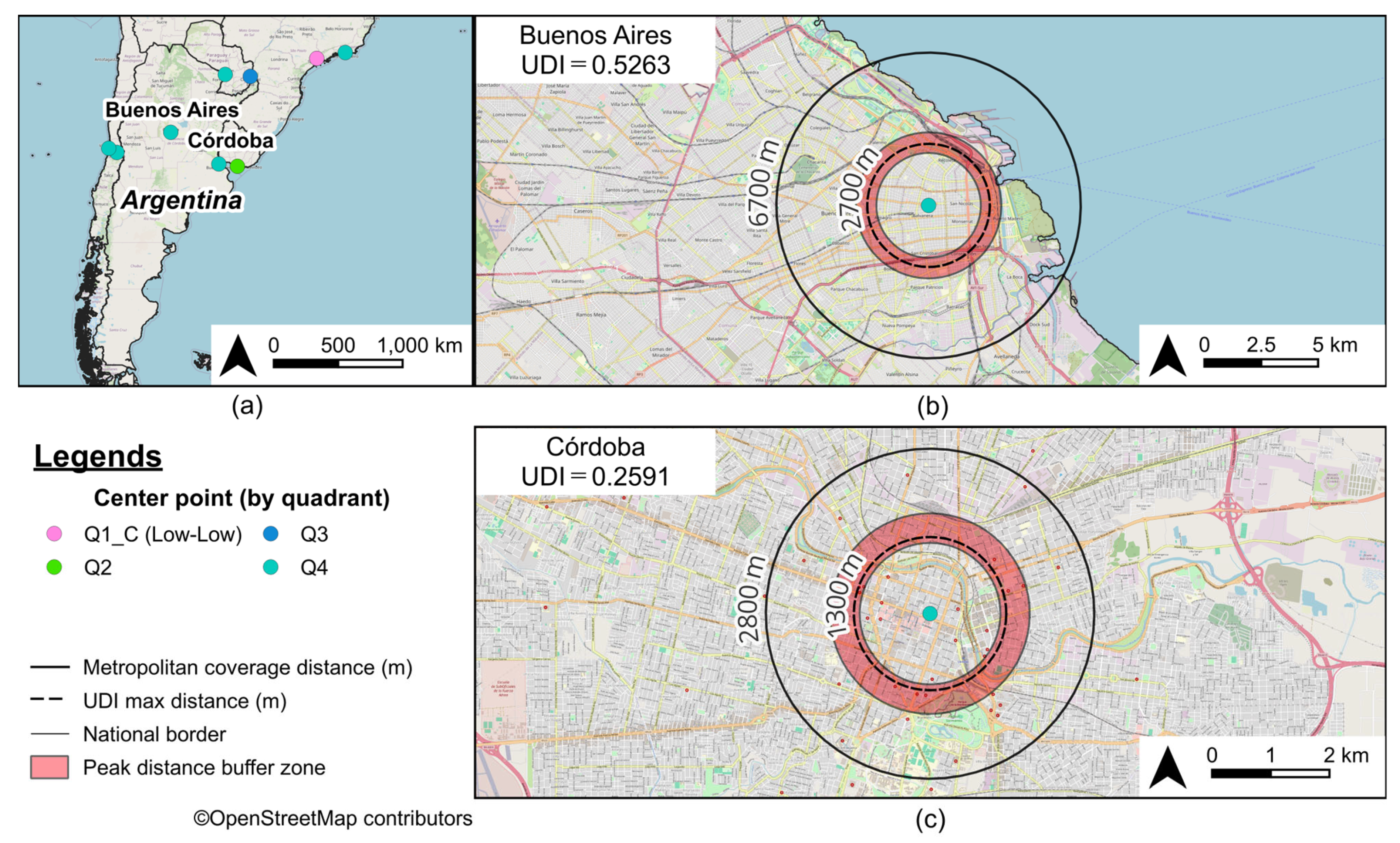
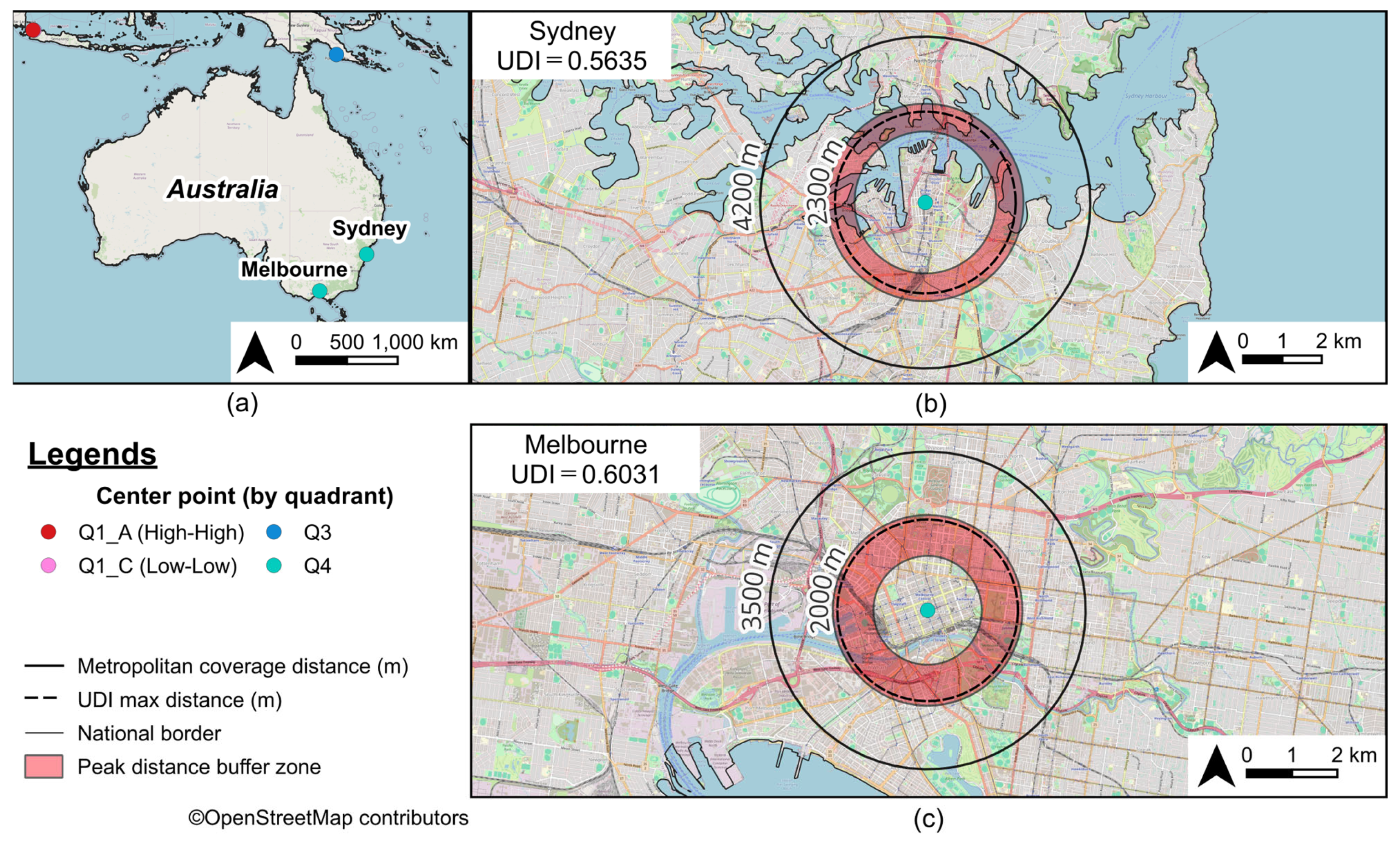
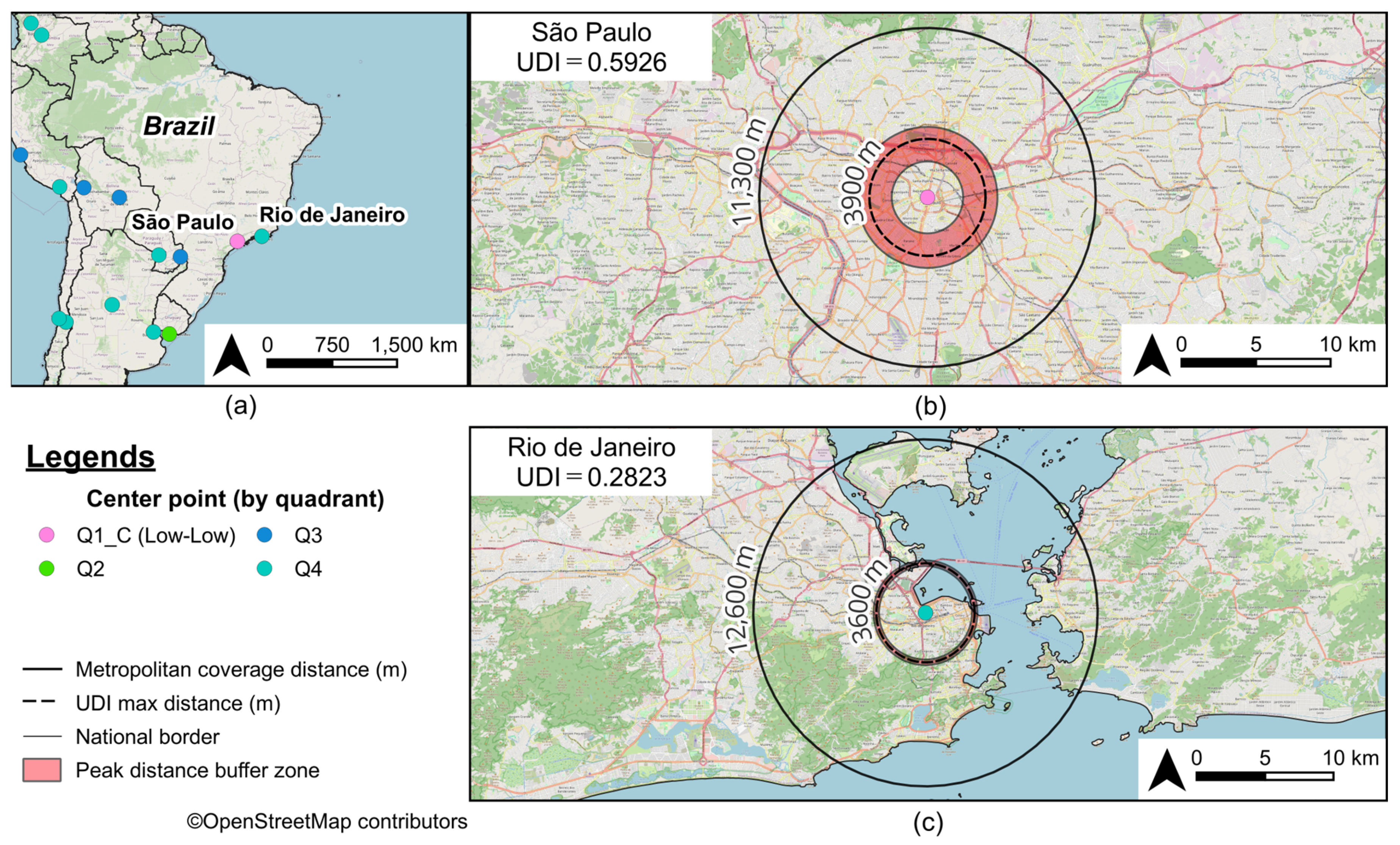
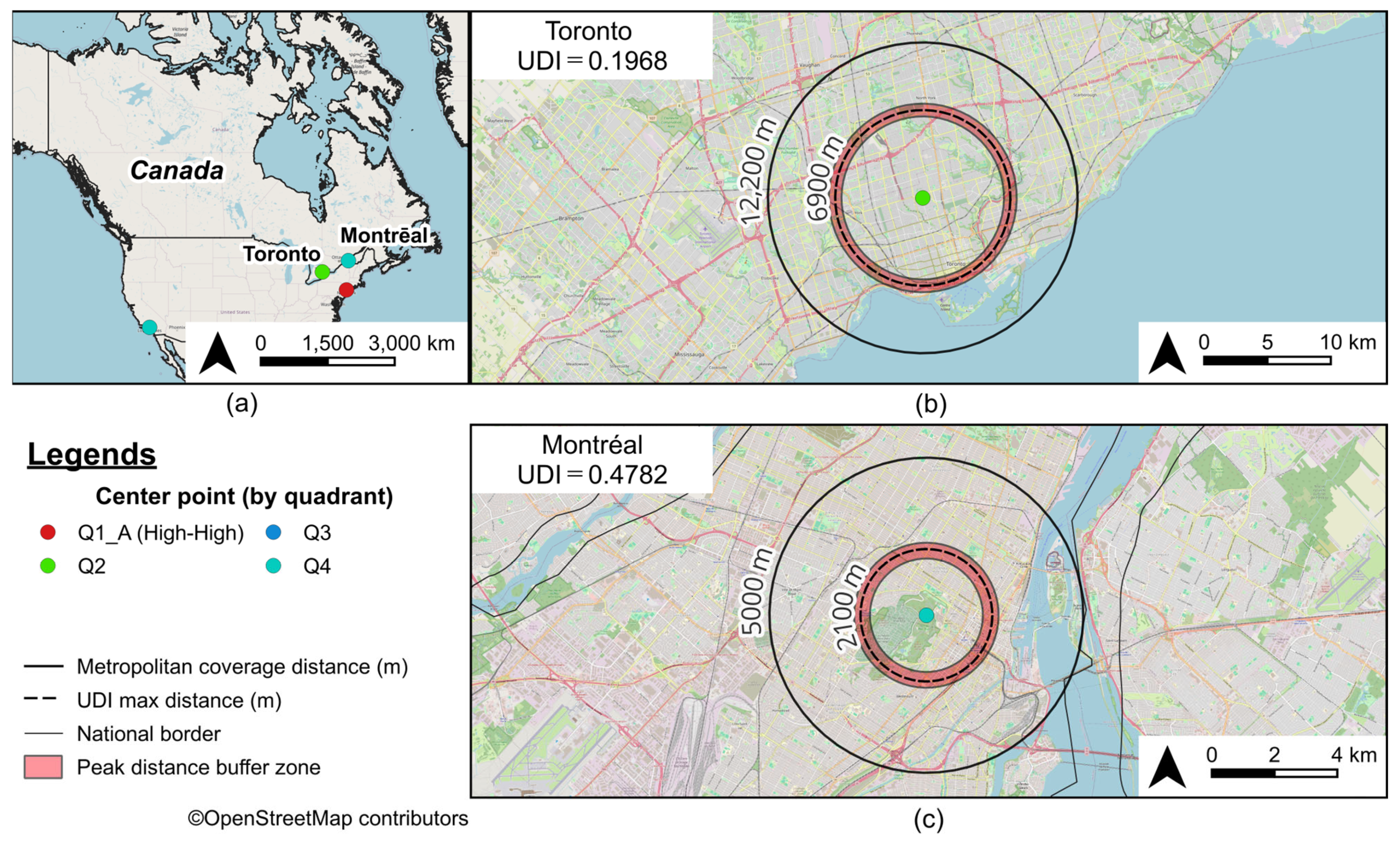
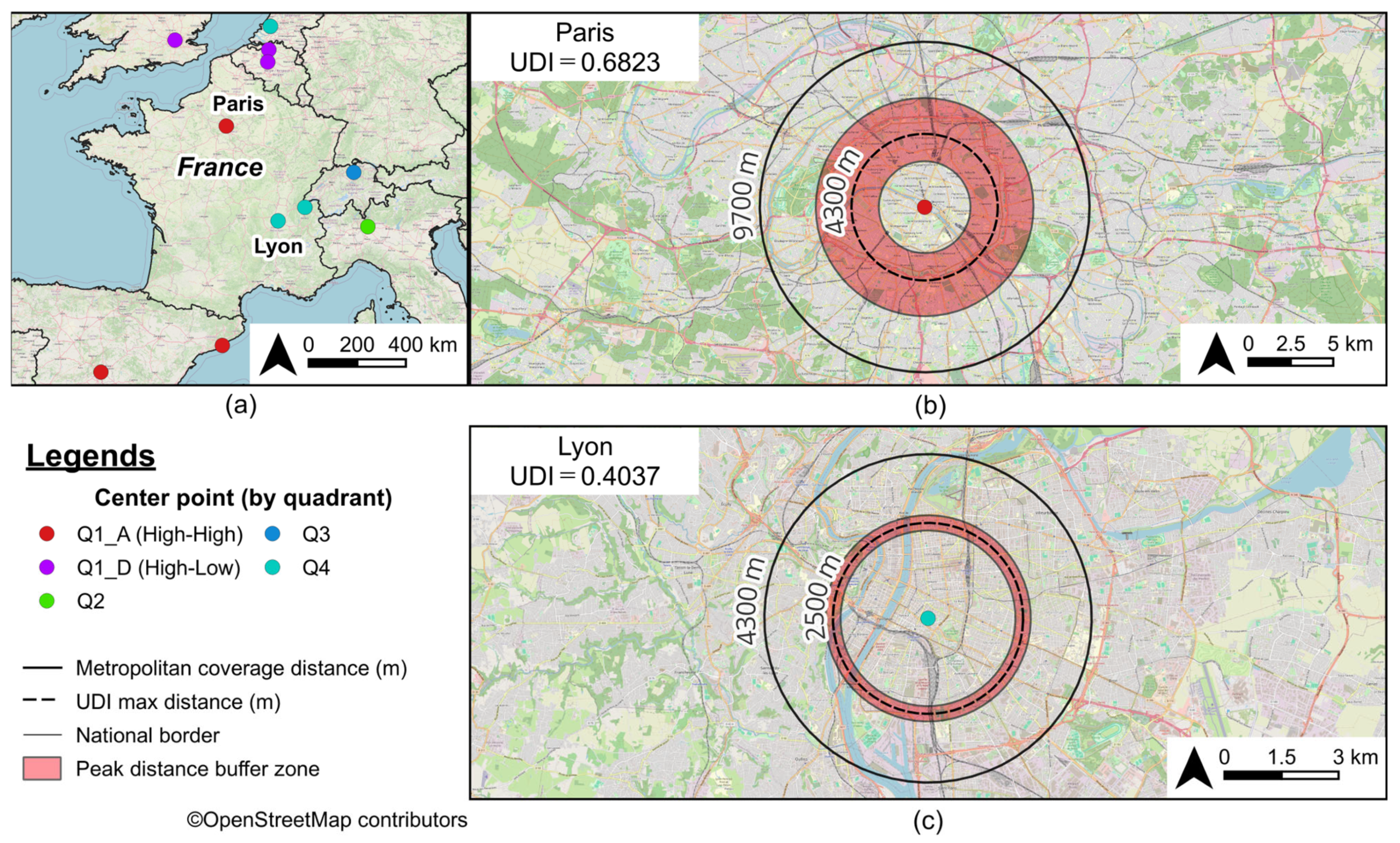
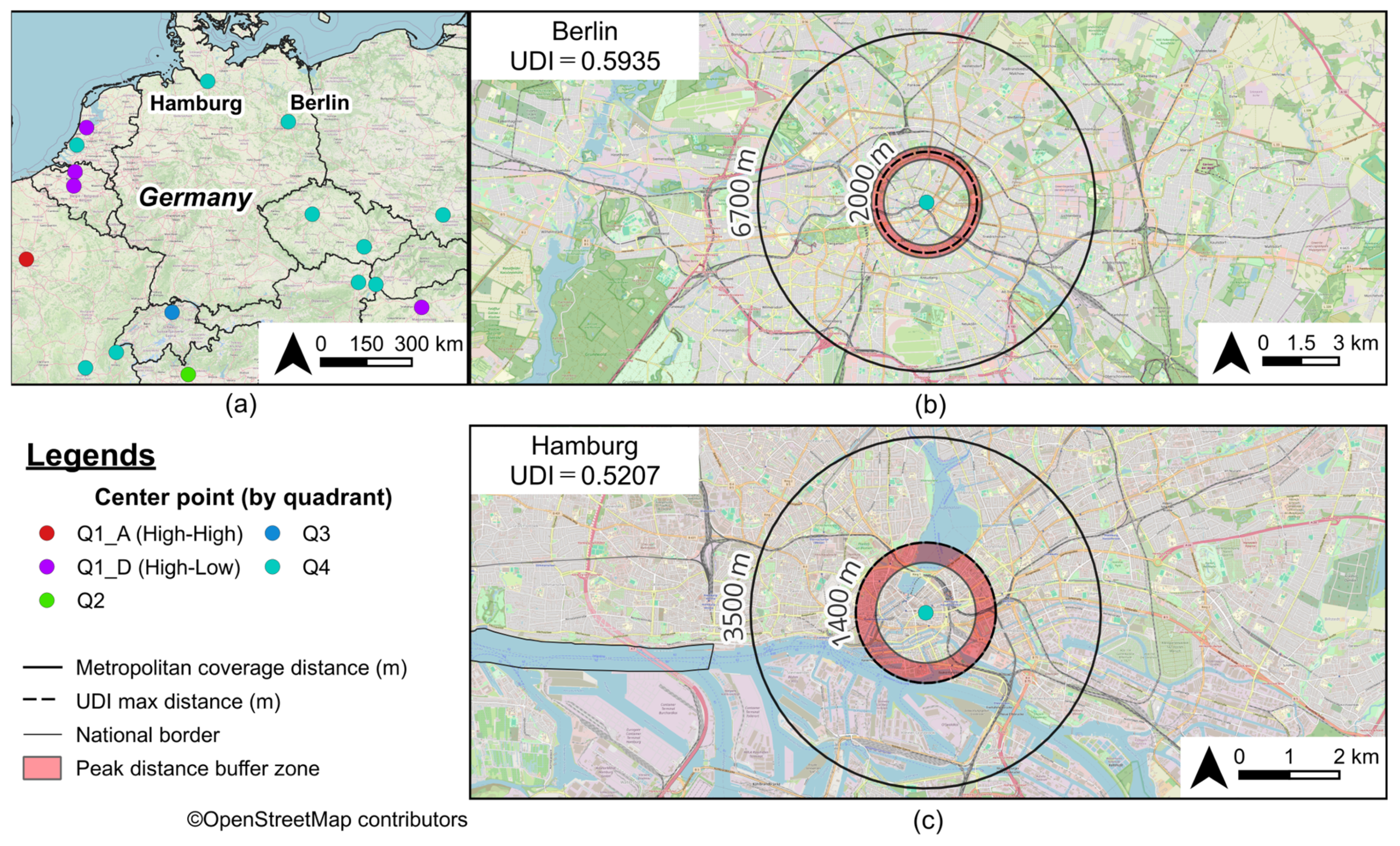
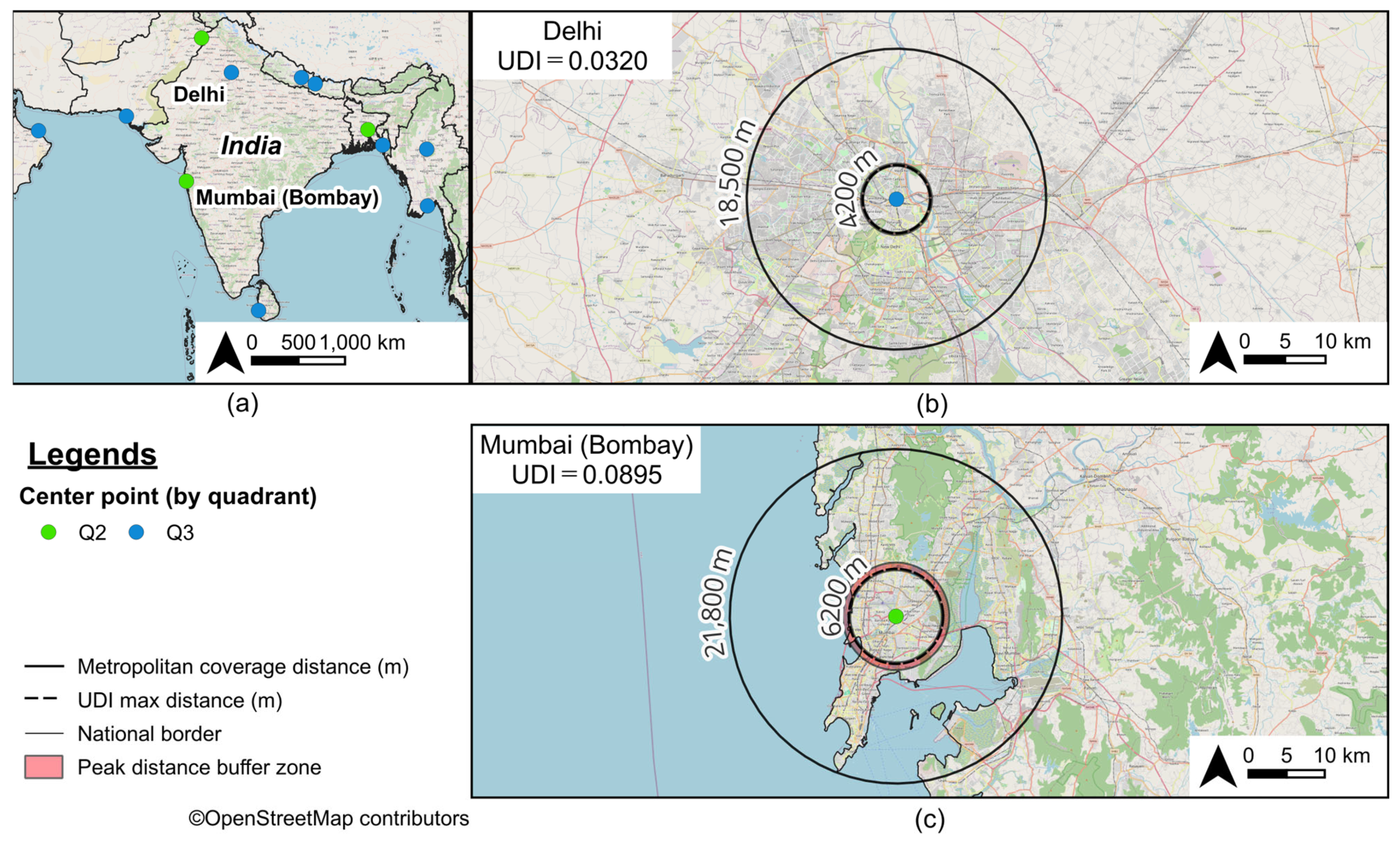
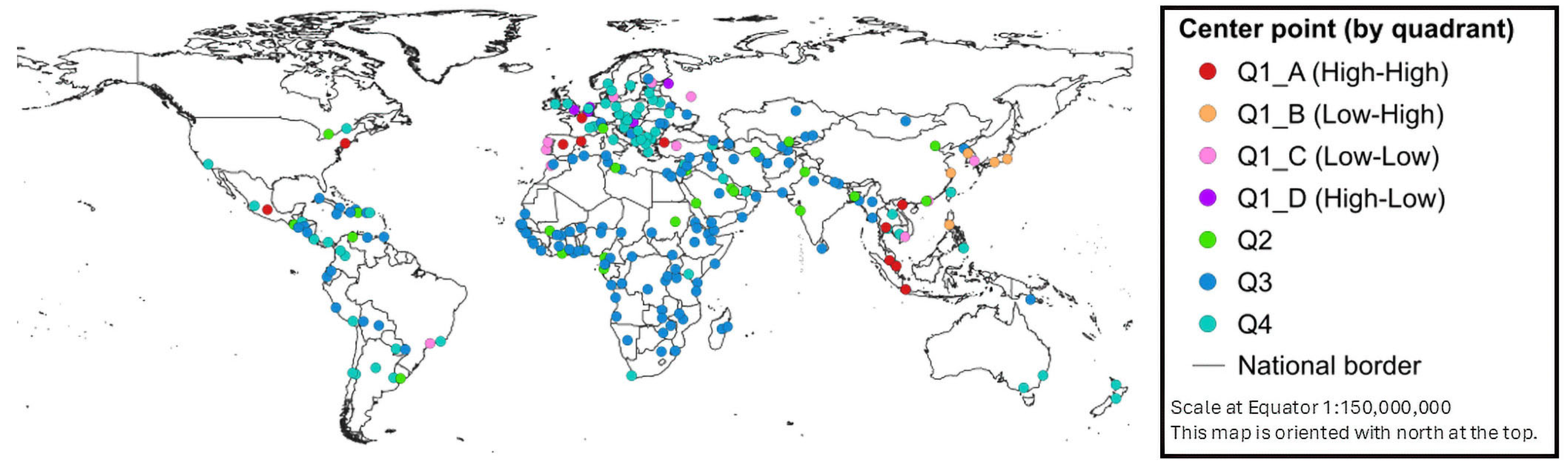
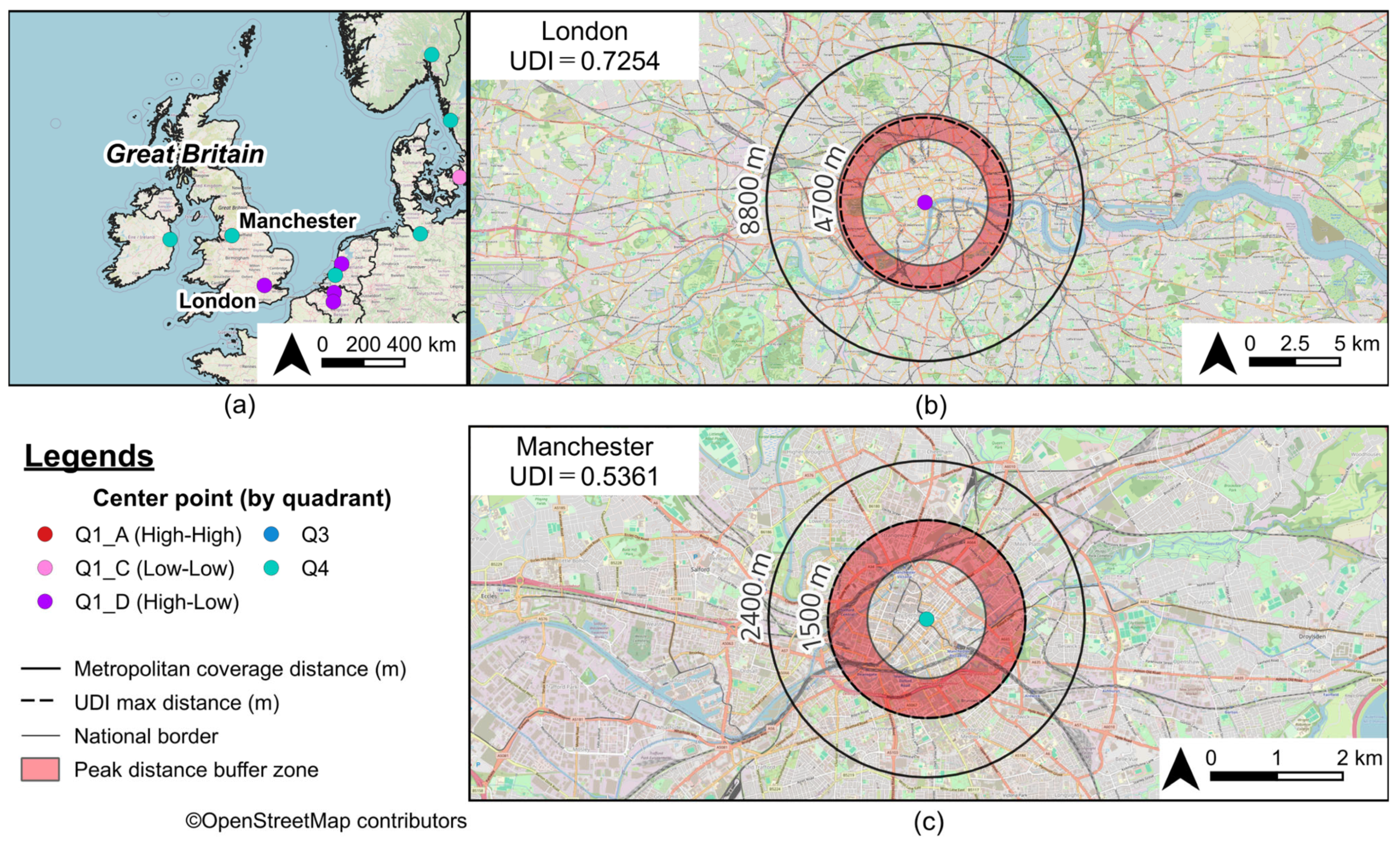
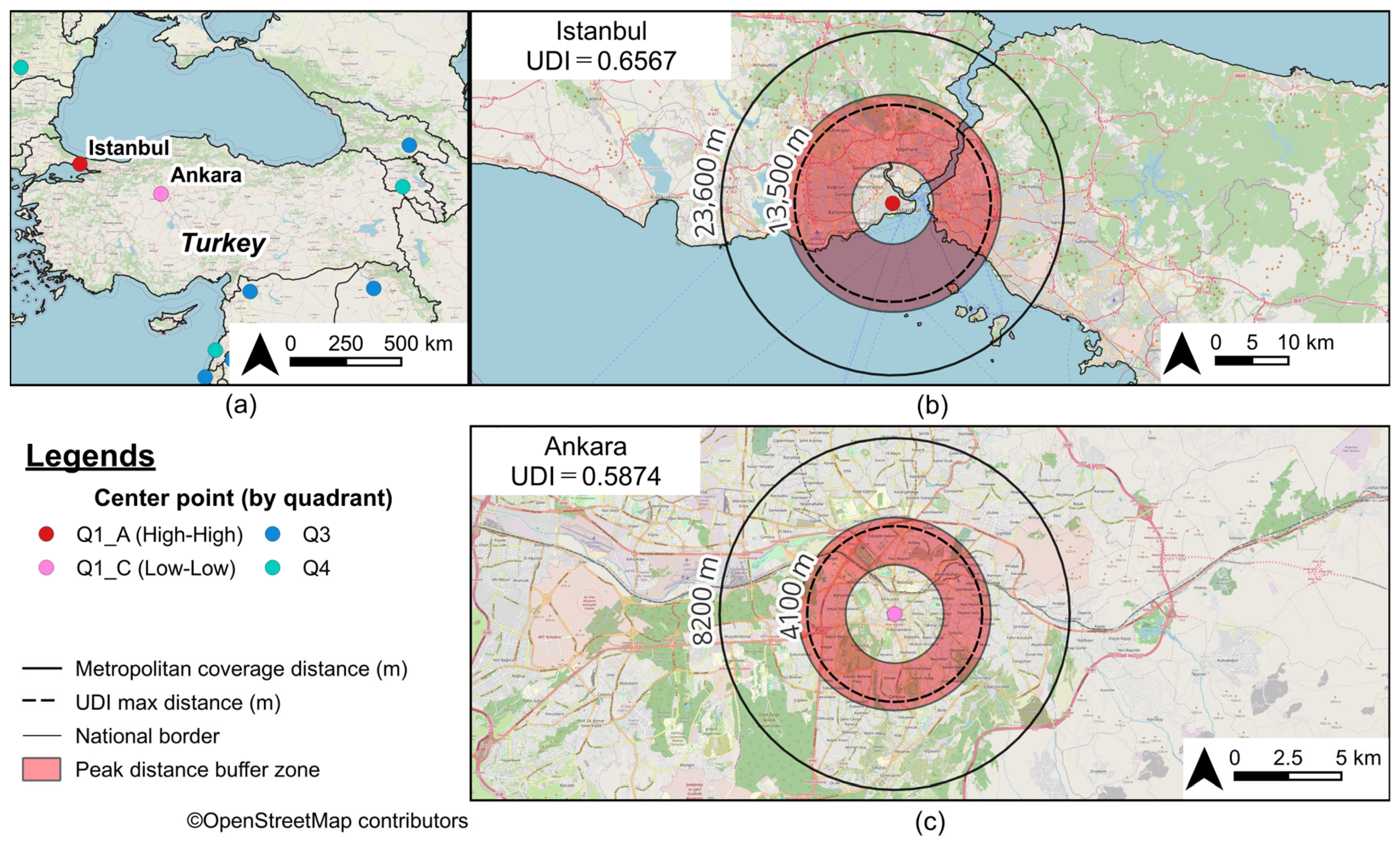
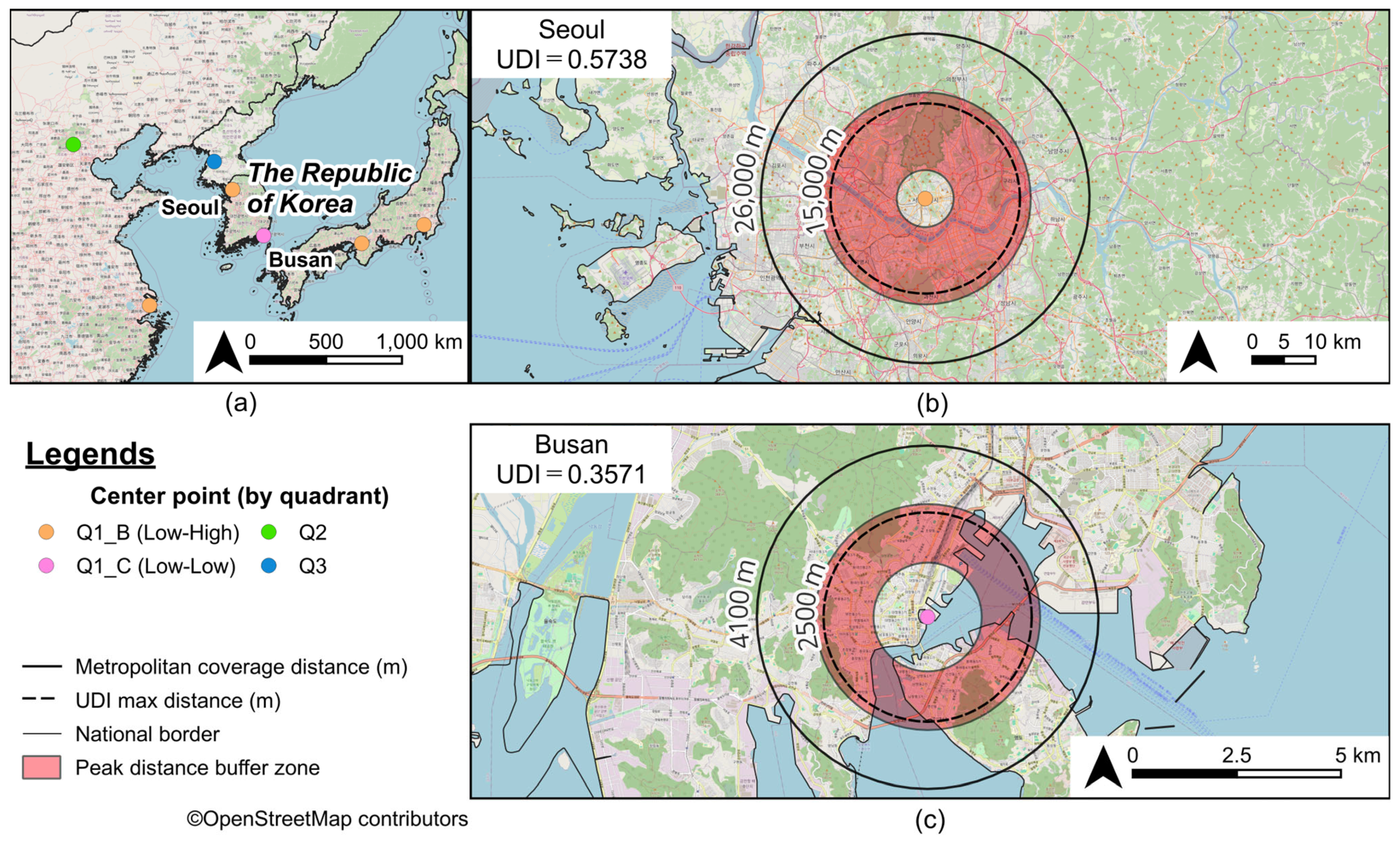
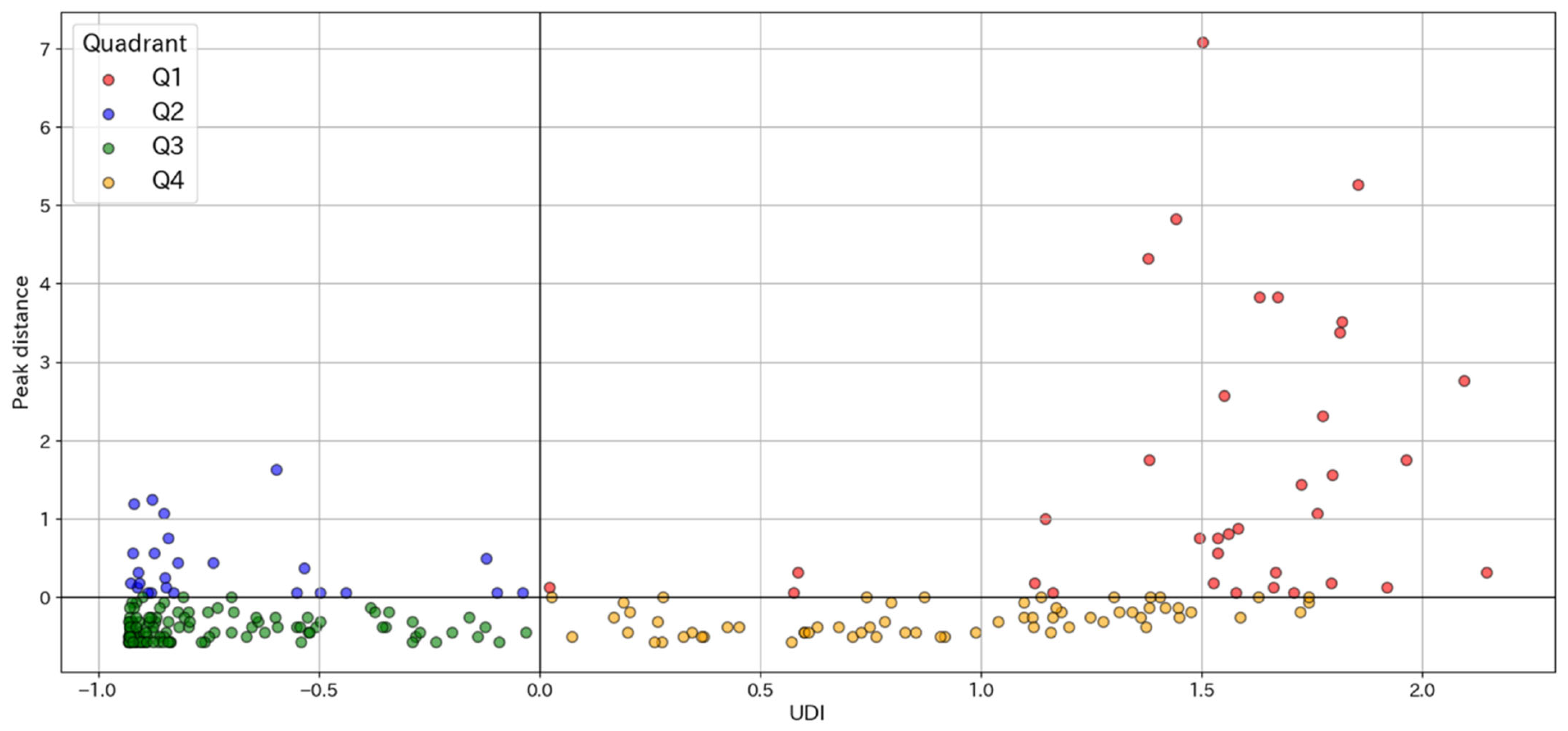
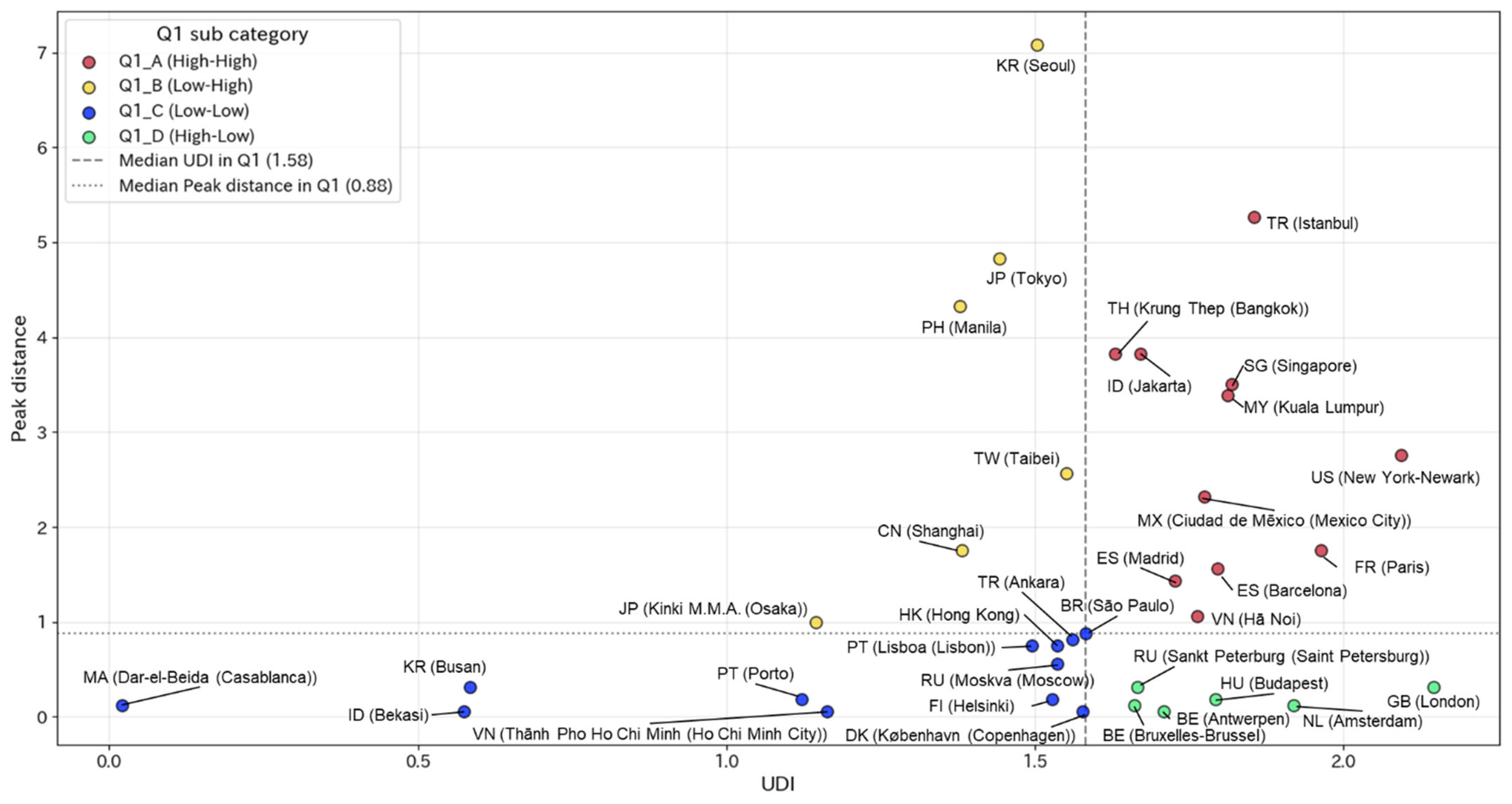
3.3. Urban Diversity as Revealed by Peak Distance
4. Discussion
4.1. Significance of the UDI
4.2. Practical Applicability of the UDI in Society
4.3. Role and Potential of the UDI in Assessing Urban Sustainability
5. Conclusions
5.1. Summary of Key Findings and Contributions
- (1)
- There are clear regional differences in the categorical composition and spatial distribution of food-related facilities across the globe.
- (2)
- Cities with high UDI values are primarily concentrated in Europe, North America, and East and Southeast Asia, with results suggesting that high urban diversity is closely associated with the structural characteristics of each city.
- (3)
- Analyzing the spatial decay of UDI values from the city center enabled measurement of the geographical extent of urban diversity.
5.2. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Fs POI dataset | The POI dataset was created by reorganizing the Foursquare Places OS data into categories in Table A1 in Appendix A for this study. |
| OSM | OpenStreetMap |
| POI | Point-of-interest |
| UDI | Urban Diversity Index |
Appendix A
| No. | The Restructured Categories | No. | The Restructured Categories | No. | The Restructured Categories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Snack Place | 33 | Seafood Restaurant | 65 | Food Truck |
| 2 | Restaurant | 34 | Beer Garden | 66 | Irish Pub |
| 3 | Diner | 35 | Distillery | 67 | Speakeasy |
| 4 | Spanish Restaurant | 36 | Italian Restaurant | 68 | Hookah Bar |
| 5 | Sports Bar | 37 | Lounge | 69 | Hot Dog Joint |
| 6 | Burger Joint | 38 | Steakhouse | 70 | Empanada Restaurant |
| 7 | Bar | 39 | Japanese Restaurant | 71 | Modern European Restaurant |
| 8 | Chinese Restaurant | 40 | Breakfast Spot | 72 | Belgian Restaurant |
| 9 | Gastropub | 41 | Mexican Restaurant | 73 | Karaoke Bar |
| 10 | Cafeteria | 42 | Creperie | 74 | Thai Restaurant |
| 11 | Café | 43 | Wings Joint | 75 | Rooftop Bar |
| 12 | Pizzeria | 44 | Asian Restaurant | 76 | Indian Restaurant |
| 13 | Piano Bar | 45 | Brewery | 77 | Pastry Shop |
| 14 | South American Restaurant | 46 | French Restaurant | 78 | Latin American Restaurant |
| 15 | Cocktail Bar | 47 | Molecular Gastronomy Restaurant | 79 | Swiss Restaurant |
| 16 | Hotel Bar | 48 | Filipino Restaurant | 80 | Frozen Yogurt Shop |
| 17 | Gay Bar | 49 | Eastern European Restaurant | 81 | Apres Ski Bar |
| 18 | Coffee Shop | 50 | Buffet | 82 | Moroccan Restaurant |
| 19 | Mediterranean Restaurant | 51 | Dive Bar | 83 | Bagel Shop |
| 20 | Fast Food Restaurant | 52 | Vegan and Vegetarian Restaurant | 84 | Ukrainian Restaurant |
| 21 | Pub | 53 | Ice Cream Parlor | 85 | Cafe, Coffee, and Tea House |
| 22 | Beer Bar | 54 | Bubble Tea Shop | 86 | Fondue Restaurant |
| 23 | Comfort Food Restaurant | 55 | Falafel Restaurant | 87 | Noodle Restaurant |
| 24 | Winery | 56 | Fried Chicken Joint | 88 | Kebab Restaurant |
| 25 | Bakery | 57 | Sandwich Spot | 89 | Gluten-Free Restaurant |
| 26 | Dutch Restaurant | 58 | Cupcake Shop | 90 | Arepa Restaurant |
| 27 | American Restaurant | 59 | German Restaurant | 91 | Korean Restaurant |
| 28 | Bistro | 60 | Theme Restaurant | 92 | Food Court |
| 29 | Wine Bar | 61 | Turkish Restaurant | 93 | African Restaurant |
| 30 | Portuguese Restaurant | 62 | Dessert Shop | 94 | Vineyard |
| 31 | BBQ Joint | 63 | Tea Room | 95 | Whisky Bar |
| 32 | Deli | 64 | Russian Restaurant | 96 | Middle Eastern Restaurant |
| No. | The Restructured Categories | No. | The Restructured Categories | No. | The Restructured Categories |
| 97 | Lebanese Restaurant | 123 | Egyptian Restaurant | 149 | Waffle Shop |
| 98 | Pakistani Restaurant | 124 | Hawaiian Restaurant | 150 | Champagne Bar |
| 99 | Shawarma Restaurant | 125 | Caucasian Restaurant | 151 | Austrian Restaurant |
| 100 | Afghan Restaurant | 126 | Indian Chinese Restaurant | 152 | Burmese Restaurant |
| 101 | Juice Bar | 127 | Sri Lankan Restaurant | 153 | Singaporean Restaurant |
| 102 | Greek Restaurant | 128 | Dumpling Restaurant | 154 | Mac and Cheese Joint |
| 103 | English Restaurant | 129 | Bosnian Restaurant | 155 | Jewish Restaurant |
| 104 | Persian Restaurant | 130 | Indonesian Restaurant | 156 | Slovak Restaurant |
| 105 | Caribbean Restaurant | 131 | Scandinavian Restaurant | 157 | Polish Restaurant |
| 106 | Australian Restaurant | 132 | Ethiopian Restaurant | 158 | Poutine Restaurant |
| 107 | Vietnamese Restaurant | 133 | Mongolian Restaurant | 159 | Dining and Drinking |
| 108 | Beach Bar | 134 | Night Market | 160 | Scottish Restaurant |
| 109 | Tiki Bar | 135 | Pie Shop | 161 | Cambodian Restaurant |
| 110 | Yemeni Restaurant | 136 | Pet Café | 162 | Cidery |
| 111 | Donut Shop | 137 | Hungarian Restaurant | 163 | Czech Restaurant |
| 112 | New American Restaurant | 138 | Soup Spot | 164 | Meadery |
| 113 | Smoothie Shop | 139 | Southern Food Restaurant | 165 | Israeli Restaurant |
| 114 | Ice Bar | 140 | Food Stand | 166 | Friterie |
| 115 | Fish and Chips Shop | 141 | Himalayan Restaurant | 167 | Bulgarian Restaurant |
| 116 | Malay Restaurant | 142 | Bangladeshi Restaurant | 168 | Mauritian Restaurant |
| 117 | Syrian Restaurant | 143 | Romanian Restaurant | 169 | Satay Restaurant |
| 118 | Salad Restaurant | 144 | Armenian Restaurant | 170 | Tatar Restaurant |
| 119 | Hotpot Restaurant | 145 | Sake Bar | 171 | Salvadoran Restaurant |
| 120 | Cajun and Creole Restaurant | 146 | Gelato Shop | 172 | Belarusian Restaurant |
| 121 | Iraqi Restaurant | 147 | Kurdish Restaurant | 173 | Honduran Restaurant |
| 122 | Halal Restaurant | 148 | Tibetan Restaurant |
Appendix B
| UDI Rank | Peak Distance Rank | City | Country /Region | J′α | C′α | ρ′α | UDI Max | UDI Max Distance (m) | Metropolitan Coverage Distance (m) | Peak Distance Buffer Zone (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34 | London | GB | 0.7746 | 0.9364 | 1.0000 | 0.7254 | 4700 | 8800 | 1400 |
| 2 | 9 | New York–Newark | US | 0.7709 | 0.9249 | 1.0000 | 0.7130 | 7200 | 12,500 | 5300 |
| 3 | 12 | Paris | FR | 0.7424 | 0.9191 | 1.0000 | 0.6823 | 4300 | 9700 | 3700 |
| 4 | 44 | Amsterdam | NL | 0.7961 | 0.8439 | 1.0000 | 0.6719 | 2800 | 4800 | 1100 |
| 5 | 2 | Istanbul | TR | 0.7013 | 0.9364 | 1.0000 | 0.6567 | 13,500 | 23,600 | 9300 |
| 6 | 7 | Singapore | SG | 0.7475 | 0.8671 | 1.0000 | 0.6481 | 7300 | 16,200 | 6500 |
| 7 | 8 | Kuala Lumpur | MY | 0.7510 | 0.8613 | 1.0000 | 0.6468 | 5100 | 16,700 | 6300 |
| 8 | 15 | Barcelona | ES | 0.7412 | 0.8671 | 1.0000 | 0.6427 | 5400 | 8900 | 3400 |
| 9 | 39 | Budapest | HU | 0.7713 | 0.8324 | 1.0000 | 0.6420 | 2900 | 5200 | 1200 |
| 10 | 11 | Ciudad de Mexico (Mexico City) | MX | 0.6852 | 0.9306 | 1.0000 | 0.6376 | 9000 | 16,800 | 4600 |
| 11 | 19 | Hanoi | VN | 0.6658 | 0.9538 | 1.0000 | 0.6350 | 4100 | 6800 | 2600 |
| 12 | 61 | Praha (Prague) | CZ | 0.7680 | 0.8208 | 1.0000 | 0.6304 | 2600 | 4800 | 900 |
| 13 | 74 | Wien (Vienna) | AT | 0.7572 | 0.8324 | 1.0000 | 0.6303 | 2800 | 5000 | 800 |
| 14 | 16 | Madrid | ES | 0.7272 | 0.8613 | 1.0000 | 0.6264 | 4400 | 7200 | 3200 |
| 15 | 90 | Warszawa (Warsaw) | PL | 0.7845 | 0.7977 | 1.0000 | 0.6258 | 2200 | 4200 | 600 |
| 16 | 49 | Antwerpen | BE | 0.8034 | 0.7746 | 1.0000 | 0.6223 | 2000 | 3400 | 1000 |
| 17 | 5 | Jakarta | ID | 0.6846 | 0.8960 | 1.0000 | 0.6134 | 10,100 | 25,200 | 7000 |
| 18 | 34 | Sankt Peterburg (Saint Petersburg) | RU | 0.7566 | 0.8092 | 1.0000 | 0.6123 | 3000 | 5400 | 1400 |
| 19 | 44 | Bruxelles-Brussel | BE | 0.7950 | 0.7688 | 1.0000 | 0.6112 | 2500 | 4900 | 1100 |
| 20 | 5 | Krung Thep (Bangkok) | TH | 0.6783 | 0.8902 | 1.0000 | 0.6038 | 8300 | 20,000 | 7000 |
| 21 | 61 | Melbourne | AU | 0.7822 | 0.7746 | 0.9955 | 0.6031 | 2000 | 3500 | 900 |
| 22 | 102 | Berlin | DE | 0.7959 | 0.7457 | 1.0000 | 0.5935 | 2000 | 6700 | 500 |
| 23 | 22 | São Paulo | BR | 0.7375 | 0.8035 | 1.0000 | 0.5926 | 3900 | 11,300 | 2300 |
| 24 | 49 | København (Copenhagen) | DK | 0.7929 | 0.7457 | 1.0000 | 0.5913 | 2500 | 4600 | 1000 |
| 25 | 23 | Ankara | TR | 0.7156 | 0.8208 | 1.0000 | 0.5874 | 4100 | 8200 | 2200 |
| 26 | 10 | Taibei | CN/TW | 0.7029 | 0.8324 | 1.0000 | 0.5851 | 5700 | 12,000 | 5000 |
| 27 | 27 | Moskva (Moscow) | RUI | 0.7624 | 0.7630 | 1.0000 | 0.5817 | 3100 | 6700 | 1800 |
| 28 | 24 | Hong Kong | CN/HK | 0.6890 | 0.8439 | 1.0000 | 0.5815 | 5500 | 9900 | 2100 |
| 29 | 39 | Helsinki | FI | 0.8021 | 0.7225 | 1.0000 | 0.5795 | 1900 | 4400 | 1200 |
| 30 | 1 | Seoul | KR | 0.6446 | 0.8902 | 1.0000 | 0.5738 | 15,000 | 26,000 | 12,200 |
| 31 | 24 | Lisboa (Lisbon) | PT | 0.7117 | 0.8035 | 1.0000 | 0.5718 | 3800 | 6500 | 2100 |
| 32 | 90 | Genève | CH | 0.7982 | 0.7110 | 1.0000 | 0.5675 | 1600 | 2700 | 600 |
| 33 | 102 | Rotterdam | NL | 0.8437 | 0.6647 | 1.0000 | 0.5609 | 1300 | 2500 | 500 |
| 34 | 81 | Oslo | NO | 0.7949 | 0.7052 | 1.0000 | 0.5605 | 2000 | 3300 | 700 |
| 35 | 3 | Tokyo | JP | 0.6086 | 0.9191 | 1.0000 | 0.5593 | 11,900 | 21,000 | 8600 |
| 36 | 81 | Sydney | AU | 0.7723 | 0.7168 | 1.0000 | 0.5535 | 2300 | 4200 | 700 |
| 37 | 61 | Sofia | BG | 0.7746 | 0.7110 | 1.0000 | 0.5508 | 1800 | 3400 | 900 |
| 38 | 61 | Santiago | CL | 0.7862 | 0.6936 | 1.0000 | 0.5453 | 3000 | 5900 | 900 |
| 39 | 12 | Shanghai | CN | 0.6736 | 0.8092 | 1.0000 | 0.5451 | 4100 | 8800 | 3700 |
| 40 | 81 | Tel Aviv-Yafo (Tel Aviv-Jaffa) | IL | 0.7926 | 0.6879 | 0.9991 | 0.5447 | 2400 | 4700 | 700 |
| 41 | 4 | Manila | PH | 0.7785 | 0.6994 | 1.0000 | 0.5445 | 2600 | 16,300 | 7800 |
| 42 | 137 | Riga | LV | 0.7901 | 0.6879 | 1.0000 | 0.5435 | 1500 | 3300 | 300 |
| 43 | 102 | Tallinn | EE | 0.7920 | 0.6821 | 1.0000 | 0.5402 | 1500 | 2700 | 500 |
| 44 | 90 | Manchester | GB | 0.7995 | 0.6705 | 1.0000 | 0.5361 | 1500 | 2400 | 600 |
| 45 | 90 | Stockholm | SE | 0.7206 | 0.7341 | 1.0000 | 0.5290 | 2600 | 4200 | 600 |
| 46 | 61 | Buenos Aires | AR | 0.7418 | 0.7225 | 0.9820 | 0.5263 | 2700 | 6700 | 900 |
| 47 | 120 | Hamburg | DE | 0.8189 | 0.6358 | 1.0000 | 0.5207 | 1400 | 3500 | 400 |
| 48 | 102 | Yerevan | AM | 0.7936 | 0.6474 | 1.0000 | 0.5138 | 1300 | 2000 | 500 |
| 49 | 137 | Wellington | NZ | 0.7970 | 0.6301 | 1.0000 | 0.5022 | 1200 | 1900 | 300 |
| 50 | 90 | Davao City | PH | 0.8050 | 0.6185 | 1.0000 | 0.4979 | 1700 | 3500 | 600 |
| 51 | 81 | Kraków (Cracow) | PL | 0.7646 | 0.6474 | 1.0000 | 0.4950 | 1500 | 3100 | 700 |
| 52 | 49 | Thành Pho Ho Chí Minh (Ho Chi Minh City) | VN | 0.6761 | 0.8382 | 0.8713 | 0.4938 | 5500 | 9600 | 1000 |
| 53 | 102 | Bucuresti (Bucharest) | RO | 0.7979 | 0.6185 | 1.0000 | 0.4935 | 1300 | 3500 | 500 |
| 54 | 161 | Vilnius | LT | 0.8381 | 0.5896 | 0.9965 | 0.4924 | 1000 | 2400 | 200 |
| 55 | 21 | Kinki M.M.A. (Osaka) | JP | 0.6003 | 0.8150 | 1.0000 | 0.4892 | 7000 | 12,500 | 2500 |
| 56 | 61 | Roma (Rome) | IT | 0.6484 | 0.7514 | 1.0000 | 0.4872 | 3200 | 6000 | 900 |
| 57 | 39 | Porto | PT | 0.7250 | 0.6705 | 0.9957 | 0.4840 | 1900 | 3100 | 1200 |
| 58 | 137 | Bratislava | SK | 0.7813 | 0.6185 | 1.0000 | 0.4832 | 1300 | 2500 | 300 |
| 59 | 102 | Brno | CZ | 0.7806 | 0.6185 | 1.0000 | 0.4828 | 1200 | 2300 | 500 |
| 60 | 102 | Montréal | CA | 0.8151 | 0.7168 | 0.8184 | 0.4782 | 2100 | 5000 | 500 |
| 61 | 74 | Beograd (Belgrade) | RS | 0.7383 | 0.6474 | 1.0000 | 0.4780 | 1800 | 3300 | 800 |
| 62 | 120 | Kyiv (Kiev) | UA | 0.7485 | 0.6243 | 0.9936 | 0.4643 | 1300 | 3200 | 400 |
| 63 | 161 | Göteborg | SE | 0.7525 | 0.6012 | 1.0000 | 0.4524 | 1300 | 2500 | 200 |
| 64 | 186 | Skopje | MK | 0.7850 | 0.5549 | 1.0000 | 0.4356 | 1000 | 2800 | 100 |
| 65 | 186 | Cape Town | ZA | 0.7896 | 0.5491 | 1.0000 | 0.4336 | 900 | 1900 | 100 |
| 66 | 61 | Al Kuwayt (Kuwait City) | KW | 0.7133 | 0.5954 | 1.0000 | 0.4247 | 1500 | 7600 | 900 |
| 67 | 161 | Phnum Pénh (Phnom Penh) | KH | 0.7825 | 0.6763 | 0.7941 | 0.4203 | 1900 | 3500 | 200 |
| 68 | 161 | Valparaíso | CL | 0.8059 | 0.5145 | 1.0000 | 0.4146 | 1200 | 2100 | 200 |
| 69 | 74 | Zagreb | HR | 0.7040 | 0.5780 | 1.0000 | 0.4069 | 1300 | 2800 | 800 |
| 70 | 120 | Lyon | FR | 0.7403 | 0.7110 | 0.7670 | 0.4037 | 2500 | 4300 | 400 |
| 71 | 186 | Vientiane | LA | 0.7962 | 0.5029 | 0.9966 | 0.3990 | 900 | 1600 | 100 |
| 72 | 137 | Xinbei | CN/TW | 0.7522 | 0.5260 | 1.0000 | 0.3957 | 1900 | 4300 | 300 |
| 73 | 61 | Thessaloniki | GR | 0.6753 | 0.5838 | 1.0000 | 0.3943 | 1900 | 3400 | 900 |
| 74 | 161 | San José | CR | 0.8152 | 0.4798 | 1.0000 | 0.3911 | 1000 | 3100 | 200 |
| 75 | 186 | Minsk | BY | 0.7959 | 0.6763 | 0.7186 | 0.3868 | 1400 | 3000 | 100 |
| 76 | 137 | Johor Bahru | MY | 0.7905 | 0.5838 | 0.8214 | 0.3791 | 1200 | 4400 | 300 |
| 77 | 137 | Bogotá | CO | 0.7765 | 0.6243 | 0.7579 | 0.3674 | 2000 | 4900 | 300 |
| 78 | 161 | Arequipa | PE | 0.8157 | 0.4451 | 1.0000 | 0.3631 | 700 | 1200 | 200 |
| 79 | 161 | Plovdiv | BG | 0.8329 | 0.4335 | 1.0000 | 0.3611 | 700 | 1700 | 200 |
| 80 | 161 | Tiranë (Tirana) | AL | 0.7434 | 0.4855 | 1.0000 | 0.3609 | 1100 | 2000 | 200 |
| 81 | 34 | Busan | KR | 0.6643 | 0.5376 | 1.0000 | 0.3571 | 2500 | 4100 | 1400 |
| 82 | 49 | Bekasi | ID | 0.7051 | 0.7052 | 0.7136 | 0.3548 | 3300 | 30,700 | 1000 |
| 83 | 213 | Bayrut (Beirut) | LB | 0.8274 | 0.4277 | 1.0000 | 0.3539 | 1100 | 6300 | 0 |
| 84 | 137 | Dublin | IE | 0.7868 | 0.6069 | 0.6825 | 0.3259 | 1900 | 3800 | 300 |
| 85 | 137 | Auckland | NZ | 0.7635 | 0.7052 | 0.5939 | 0.3198 | 2300 | 4600 | 300 |
| 86 | 186 | Medellín | CO | 0.7964 | 0.4162 | 0.9263 | 0.3070 | 800 | 1600 | 100 |
| 87 | 186 | San Juan | PR | 0.7900 | 0.4393 | 0.8816 | 0.3060 | 1400 | 4300 | 100 |
| 88 | 161 | Ciudad de Panamá (Panama City) | PA | 0.8409 | 0.6127 | 0.5836 | 0.3007 | 1700 | 4000 | 200 |
| 89 | 186 | Chon Buri | TH | 0.7551 | 0.3988 | 0.9843 | 0.2964 | 1000 | 2500 | 100 |
| 90 | 61 | Guadalajara | MX | 0.7188 | 0.6532 | 0.6074 | 0.2852 | 4000 | 11,500 | 900 |
| 91 | 213 | San Pedro Sula | HN | 0.8737 | 0.4335 | 0.7521 | 0.2849 | 800 | 2000 | 0 |
| 92 | 120 | Rio de Janeiro | BR | 0.7362 | 0.6358 | 0.6031 | 0.2823 | 3600 | 12,600 | 400 |
| 93 | 213 | Nairobi | KE | 0.7563 | 0.3757 | 0.9881 | 0.2808 | 700 | 1700 | 0 |
| 94 | 90 | Asunción | PY | 0.8036 | 0.6647 | 0.5011 | 0.2677 | 2400 | 5000 | 600 |
| 95 | 161 | Dubayy (Dubai) | AE | 0.8023 | 0.5145 | 0.6452 | 0.2663 | 1200 | 5900 | 200 |
| 96 | 74 | Los Angeles–Long Beach–Santa Ana | US | 0.7667 | 0.6590 | 0.5224 | 0.2639 | 2600 | 5900 | 800 |
| 97 | 102 | Córdoba | AR | 0.7862 | 0.4624 | 0.7126 | 0.2591 | 1300 | 2800 | 500 |
| 98 | 186 | Alajuela | CR | 0.8541 | 0.2775 | 1.0000 | 0.2370 | 500 | 1800 | 100 |
| 99 | 61 | Athínai (Athens) | GR | 0.6432 | 0.6763 | 0.5185 | 0.2255 | 3900 | 9800 | 900 |
| 100 | 44 | Dar-el-Beida (Casablanca) | MA | 0.7630 | 0.5318 | 0.5534 | 0.2245 | 1500 | 3900 | 1100 |
| 101 | 161 | Guayaquil | EC | 0.8388 | 0.5145 | 0.4910 | 0.2119 | 1300 | 4000 | 200 |
| 102 | 49 | Beijing | CN | 0.6384 | 0.7688 | 0.4282 | 0.2101 | 5400 | 12,600 | 1000 |
| 103 | 213 | Tampere | FI | 0.8173 | 0.5549 | 0.4357 | 0.1976 | 1200 | 2600 | 0 |
| 104 | 49 | Toronto | CA | 0.8038 | 0.8844 | 0.2768 | 0.1968 | 6900 | 12,200 | 1000 |
| 105 | 30 | Al-Manamah (Manama) | BH | 0.8074 | 0.6590 | 0.3585 | 0.1908 | 2600 | 7700 | 1700 |
| 106 | 137 | Ad-Dawhah (Doha) | QA | 0.8043 | 0.5954 | 0.3974 | 0.1903 | 1900 | 4600 | 300 |
| 107 | 186 | Colombo | LK | 0.8915 | 0.3295 | 0.6347 | 0.1864 | 600 | 4500 | 100 |
| 108 | 102 | Lima | PE | 0.8049 | 0.3410 | 0.6629 | 0.1820 | 800 | 13,800 | 500 |
| 109 | 161 | Ar-Riyadh (Riyadh) | SA | 0.7664 | 0.7110 | 0.3168 | 0.1726 | 3100 | 14,200 | 200 |
| 110 | 213 | Caracas | VE | 0.8945 | 0.3526 | 0.5209 | 0.1643 | 800 | 5100 | 0 |
| 111 | 161 | Ciudad del Este | PY | 0.8759 | 0.4451 | 0.3986 | 0.1554 | 1100 | 2300 | 200 |
| 112 | 186 | Hefa (Haifa) | IL | 0.8179 | 0.4451 | 0.4210 | 0.1533 | 1100 | 1900 | 100 |
| 113 | 120 | Bishkek | KG | 0.8354 | 0.3757 | 0.4829 | 0.1516 | 800 | 3100 | 400 |
| 114 | 213 | Rabat | MA | 0.8475 | 0.3237 | 0.5515 | 0.1513 | 600 | 2200 | 0 |
| 115 | 90 | Tehran | IR | 0.6475 | 0.5491 | 0.3903 | 0.1388 | 3000 | 11,800 | 600 |
| 116 | 137 | Zürich (Zurich) | CH | 0.7742 | 0.7457 | 0.2371 | 0.1369 | 3800 | 6200 | 300 |
| 117 | 137 | Kathmandu | NP | 0.7382 | 0.4971 | 0.3692 | 0.1355 | 2000 | 4200 | 300 |
| 118 | 90 | Almaty | KZ | 0.7974 | 0.6474 | 0.2549 | 0.1316 | 3100 | 6300 | 600 |
| 119 | 81 | Baku | AZ | 0.7288 | 0.7630 | 0.2324 | 0.1292 | 5600 | 9300 | 700 |
| 120 | 49 | Ciudad de Guatemala (Guatemala City) | GT | 0.8243 | 0.6069 | 0.2318 | 0.1160 | 3700 | 7000 | 1000 |
| 121 | 49 | Santo Domingo | DO | 0.8324 | 0.6358 | 0.1933 | 0.1023 | 4700 | 9800 | 1000 |
| 122 | 120 | Yangon | MM | 0.8009 | 0.5780 | 0.2205 | 0.1021 | 3700 | 6000 | 400 |
| 123 | 137 | Al-Qahirah (Cairo) | EG | 0.7767 | 0.3642 | 0.3530 | 0.0998 | 1300 | 6500 | 300 |
| 124 | 161 | Port of Spain | TT | 0.8612 | 0.3815 | 0.2937 | 0.0965 | 1300 | 3300 | 200 |
| 125 | 161 | Santiago | DO | 0.8612 | 0.3757 | 0.2972 | 0.0962 | 1200 | 3200 | 200 |
| 126 | 102 | Tunis | TN | 0.6756 | 0.5202 | 0.2714 | 0.0954 | 2700 | 6300 | 500 |
| 127 | 33 | Milano (Milan) | IT | 0.6725 | 0.8208 | 0.1699 | 0.0938 | 11,500 | 19,300 | 1500 |
| 128 | 213 | Kampala | UG | 0.7903 | 0.2890 | 0.4039 | 0.0922 | 800 | 2400 | 0 |
| 129 | 137 | Managua | NI | 0.8244 | 0.5029 | 0.2198 | 0.0911 | 2500 | 5300 | 300 |
| 130 | 137 | Ulaanbaatar | MN | 0.7936 | 0.5202 | 0.2177 | 0.0899 | 2400 | 5400 | 300 |
| 131 | 49 | Mumbai (Bombay) | IN | 0.7301 | 0.7110 | 0.1726 | 0.0896 | 6200 | 21,800 | 1000 |
| 132 | 137 | Kharkiv | UA | 0.7648 | 0.6127 | 0.1695 | 0.0794 | 3100 | 7100 | 300 |
| 133 | 14 | Jiddah | SA | 0.7735 | 0.7572 | 0.1346 | 0.0788 | 7100 | 20,100 | 3500 |
| 134 | 102 | Tegucigalpa | HN | 0.8253 | 0.5491 | 0.1730 | 0.0784 | 3100 | 5500 | 500 |
| 135 | 161 | Iasi | RO | 0.8382 | 0.4624 | 0.1870 | 0.0725 | 1700 | 3000 | 200 |
| 136 | 120 | Tbilisi | GE | 0.7651 | 0.6358 | 0.1426 | 0.0694 | 3100 | 7500 | 400 |
| 137 | 102 | Safaqis | TN | 0.7740 | 0.3642 | 0.2418 | 0.0682 | 1400 | 3600 | 500 |
| 138 | 137 | Santa Cruz | BO | 0.8327 | 0.4913 | 0.1605 | 0.0657 | 2400 | 7400 | 300 |
| 139 | 186 | Al-Iskandariyah (Alexandria) | EG | 0.7716 | 0.3353 | 0.2430 | 0.0629 | 1200 | 2500 | 100 |
| 140 | 90 | La Paz | BO | 0.8142 | 0.5376 | 0.1283 | 0.0562 | 3200 | 4900 | 600 |
| 141 | 161 | Maputo | MZ | 0.8179 | 0.4624 | 0.1453 | 0.0549 | 2000 | 4000 | 200 |
| 142 | 61 | Johannesburg | ZA | 0.8399 | 0.1908 | 0.3408 | 0.0546 | 600 | 3300 | 900 |
| 143 | 81 | San Salvador | SV | 0.8230 | 0.5896 | 0.0972 | 0.0472 | 6200 | 11,400 | 700 |
| 144 | 161 | Amman | JO | 0.7669 | 0.4335 | 0.1376 | 0.0457 | 2200 | 11,500 | 200 |
| 145 | 31 | Ash-Shariqah (Sharjah) | AE | 0.7225 | 0.8382 | 0.0743 | 0.0450 | 16,700 | 32,900 | 1600 |
| 146 | 186 | Mandalay | MM | 0.9321 | 0.2023 | 0.2274 | 0.0429 | 700 | 2200 | 100 |
| 147 | 90 | Quito | EC | 0.8051 | 0.6358 | 0.0823 | 0.0421 | 6200 | 14,400 | 600 |
| 148 | 213 | Aguadilla-Isabela-San Sebastian | PR | 0.9452 | 0.1965 | 0.2175 | 0.0404 | 700 | 1500 | 0 |
| 149 | 213 | Kigali | RW | 0.8941 | 0.1561 | 0.2772 | 0.0387 | 500 | 900 | 0 |
| 150 | 120 | Antananarivo | MG | 0.8181 | 0.3468 | 0.1142 | 0.0324 | 1800 | 3700 | 400 |
| 151 | 137 | Delhi | IN | 0.7232 | 0.5029 | 0.0881 | 0.0320 | 4200 | 18,500 | 300 |
| 152 | 90 | Mashhad | IR | 0.8055 | 0.3988 | 0.0989 | 0.0318 | 2200 | 4900 | 600 |
| 153 | 102 | Kingston | JM | 0.7840 | 0.4220 | 0.0889 | 0.0294 | 2400 | 7100 | 500 |
| 154 | 61 | Astana | KZ | 0.8161 | 0.4509 | 0.0783 | 0.0288 | 3100 | 9200 | 900 |
| 155 | 137 | Mombasa | KE | 0.8426 | 0.2486 | 0.1269 | 0.0266 | 1100 | 2800 | 300 |
| 156 | 90 | Accra | GH | 0.7566 | 0.3873 | 0.0903 | 0.0265 | 2400 | 8100 | 600 |
| 157 | 31 | Ar-Rayyan | QA | 0.7624 | 0.8150 | 0.0419 | 0.0260 | 12,500 | 21,400 | 1600 |
| 158 | 49 | Lahore | PK | 0.7890 | 0.5607 | 0.0536 | 0.0237 | 4400 | 8700 | 1000 |
| 159 | 213 | Karachi | PK | 0.9755 | 0.0347 | 0.6556 | 0.0222 | 100 | 600 | 0 |
| 160 | 213 | Lagos | NG | 0.9755 | 0.0347 | 0.6556 | 0.0222 | 100 | 200 | 0 |
| 161 | 24 | Maracaibo | VE | 0.8323 | 0.5145 | 0.0497 | 0.0213 | 6200 | 13,100 | 2100 |
| 162 | 120 | El Djazaïr (Algiers) | DZ | 0.8540 | 0.3410 | 0.0718 | 0.0209 | 2100 | 4100 | 400 |
| 163 | 213 | Samarkand | UZ | 0.8345 | 0.1965 | 0.1273 | 0.0209 | 800 | 3000 | 0 |
| 164 | 44 | Al-Khartum (Khartoum) | SD | 0.7460 | 0.5145 | 0.0518 | 0.0199 | 5400 | 10,900 | 1100 |
| 165 | 161 | Sarajevo | BA | 0.7117 | 0.5723 | 0.0485 | 0.0198 | 6200 | 9100 | 200 |
| 166 | 38 | Montevideo | UY | 0.7870 | 0.6416 | 0.0381 | 0.0193 | 9500 | 17,000 | 1300 |
| 167 | 186 | Bujumbura | BI | 0.9376 | 0.0809 | 0.2497 | 0.0189 | 300 | 700 | 100 |
| 168 | 74 | Chişinău | MD | 0.7931 | 0.3815 | 0.0614 | 0.0186 | 3200 | 6200 | 800 |
| 169 | 19 | Tashkent | UZ | 0.7720 | 0.6301 | 0.0381 | 0.0185 | 7400 | 15,400 | 2600 |
| 170 | 213 | Dimashq (Damascus) | SY | 0.7981 | 0.1387 | 0.1625 | 0.0180 | 700 | 4000 | 0 |
| 171 | 186 | Yaoundé | CM | 0.9655 | 0.0751 | 0.2289 | 0.0166 | 300 | 1700 | 100 |
| 172 | 81 | Dar es Salaam | TZ | 0.8210 | 0.4104 | 0.0482 | 0.0163 | 2600 | 10,300 | 700 |
| 173 | 213 | Port Moresby | PG | 0.9168 | 0.1676 | 0.1051 | 0.0162 | 700 | 1300 | 0 |
| 174 | 102 | Luanda | AO | 0.8166 | 0.3815 | 0.0467 | 0.0146 | 2700 | 5600 | 500 |
| 175 | 120 | Kabul | AF | 0.7849 | 0.1965 | 0.0937 | 0.0144 | 1100 | 2200 | 400 |
| 176 | 27 | Douala | CM | 0.7291 | 0.2139 | 0.0860 | 0.0134 | 1400 | 4500 | 1800 |
| 177 | 161 | Sumquayit | AZ | 0.8716 | 0.1734 | 0.0880 | 0.0133 | 1000 | 2200 | 200 |
| 178 | 213 | Harare | ZW | 0.9654 | 0.0751 | 0.1769 | 0.0128 | 300 | 1600 | 0 |
| 179 | 137 | La Habana (Havana) | CU | 0.6955 | 0.4046 | 0.0454 | 0.0128 | 3700 | 6900 | 300 |
| 180 | 17 | Dhaka | BD | 0.7806 | 0.7110 | 0.0221 | 0.0123 | 11,500 | 17,800 | 2900 |
| 181 | 102 | Masqat (Muscat) | OM | 0.7794 | 0.3699 | 0.0413 | 0.0119 | 5900 | 29,000 | 500 |
| 182 | 49 | Cotonou | BJ | 0.8354 | 0.3873 | 0.0362 | 0.0117 | 2700 | 5700 | 1000 |
| 183 | 102 | Dakar | SN | 0.8524 | 0.3931 | 0.0324 | 0.0109 | 3500 | 14,100 | 500 |
| 184 | 120 | Windhoek | NA | 0.8636 | 0.1965 | 0.0637 | 0.0108 | 1300 | 3200 | 400 |
| 185 | 49 | Tarabulus (Tripoli) | LY | 0.7467 | 0.2659 | 0.0502 | 0.0100 | 2600 | 6700 | 1000 |
| 186 | 186 | Port-au-Prince | HT | 0.9015 | 0.1387 | 0.0790 | 0.0099 | 800 | 2200 | 100 |
| 187 | 213 | Mwanza | TZ | 0.9258 | 0.0636 | 0.1665 | 0.0098 | 300 | 1200 | 0 |
| 188 | 161 | Pokhara | NP | 0.7526 | 0.3873 | 0.0318 | 0.0093 | 3800 | 5900 | 200 |
| 189 | 213 | Salahah (Salalah) | OM | 0.9121 | 0.1561 | 0.0647 | 0.0092 | 900 | 5000 | 0 |
| 190 | 137 | Gomel | BY | 0.8099 | 0.3064 | 0.0354 | 0.0088 | 2900 | 4800 | 300 |
| 191 | 213 | Bata | GQ | 0.9410 | 0.0405 | 0.2107 | 0.0080 | 200 | 300 | 0 |
| 192 | 61 | Addis Ababa | ET | 0.7756 | 0.4220 | 0.0226 | 0.0074 | 5600 | 9300 | 900 |
| 193 | 213 | Gaza (incl. Ash Shati Camp) | PS | 0.8177 | 0.2601 | 0.0317 | 0.0067 | 2300 | 4700 | 0 |
| 194 | 213 | Abomey-Calavi | BJ | 0.8842 | 0.3699 | 0.0189 | 0.0062 | 3300 | 4800 | 0 |
| 195 | 213 | Halab (Aleppo) | SY | 0.9025 | 0.0867 | 0.0754 | 0.0059 | 600 | 1100 | 0 |
| 196 | 120 | Kinshasa | CD | 0.8087 | 0.3064 | 0.0234 | 0.0058 | 3400 | 6200 | 400 |
| 197 | 161 | Chittagong | BD | 0.8167 | 0.2775 | 0.0246 | 0.0056 | 3200 | 6000 | 200 |
| 198 | 39 | Macao | CN/MO | 0.7966 | 0.3699 | 0.0186 | 0.0055 | 5400 | 9600 | 1200 |
| 199 | 186 | Blantyre-Limbe | MW | 0.9494 | 0.0925 | 0.0554 | 0.0049 | 700 | 1500 | 100 |
| 200 | 34 | Zarqa | JO | 0.7154 | 0.7803 | 0.0085 | 0.0048 | 25,800 | 38,900 | 1400 |
| 201 | 44 | Abidjan | CI | 0.7510 | 0.4855 | 0.0123 | 0.0045 | 8400 | 13,700 | 1100 |
| 202 | 74 | Baghdad | IQ | 0.7676 | 0.3642 | 0.0149 | 0.0042 | 6700 | 10,600 | 800 |
| 203 | 102 | Lomé | TG | 0.9002 | 0.1676 | 0.0271 | 0.0041 | 1500 | 4900 | 500 |
| 204 | 213 | Lubango | AO | 1.0000 | 0.0462 | 0.0832 | 0.0039 | 300 | 500 | 0 |
| 205 | 137 | Lusaka | ZM | 0.8930 | 0.1098 | 0.0387 | 0.0038 | 1100 | 9300 | 300 |
| 206 | 213 | Kumasi | GH | 0.8983 | 0.0405 | 0.1041 | 0.0038 | 300 | 1200 | 0 |
| 207 | 186 | Brazzaville | CG | 0.9483 | 0.1214 | 0.0312 | 0.0036 | 1200 | 2200 | 100 |
| 208 | 213 | Misratah | LY | 0.8000 | 0.0809 | 0.0468 | 0.0030 | 800 | 1300 | 0 |
| 209 | 161 | Wahran (Oran) | DZ | 0.8254 | 0.1503 | 0.0244 | 0.0030 | 1900 | 5800 | 200 |
| 210 | 81 | Dushanbe | TJ | 0.8274 | 0.3353 | 0.0102 | 0.0028 | 5400 | 8800 | 700 |
| 211 | 18 | Ashgabat | TM | 0.8450 | 0.1329 | 0.0249 | 0.0028 | 1300 | 8400 | 2800 |
| 212 | 186 | Matola | MZ | 0.9278 | 0.0867 | 0.0322 | 0.0026 | 800 | 1400 | 100 |
| 213 | 213 | Lilongwe | MW | 0.8056 | 0.2312 | 0.0128 | 0.0024 | 3500 | 5700 | 0 |
| 214 | 213 | Bulawayo | ZW | 0.9200 | 0.0925 | 0.0255 | 0.0022 | 1100 | 2200 | 0 |
| 215 | 186 | Djibouti | DJ | 0.9805 | 0.0925 | 0.0231 | 0.0021 | 900 | 6400 | 100 |
| 216 | 161 | Monrovia | LR | 0.9261 | 0.1503 | 0.0145 | 0.0020 | 2600 | 5400 | 200 |
| 217 | 186 | Asmara | ER | 0.9579 | 0.0578 | 0.0364 | 0.0020 | 600 | 1000 | 100 |
| 218 | 27 | Libreville | GA | 0.9039 | 0.2254 | 0.0094 | 0.0019 | 3300 | 6000 | 1800 |
| 219 | 120 | Nouakchott | MR | 0.8437 | 0.1965 | 0.0109 | 0.0018 | 2900 | 4500 | 400 |
| 220 | 120 | Banjul | GM | 0.7578 | 0.2370 | 0.0091 | 0.0016 | 4900 | 9000 | 400 |
| 221 | 120 | Ouagadougou | BF | 0.8904 | 0.1965 | 0.0083 | 0.0015 | 3000 | 7100 | 400 |
| 222 | 74 | Niamey | NE | 0.9006 | 0.1214 | 0.0127 | 0.0014 | 1900 | 3500 | 800 |
| 223 | 186 | Bissau | GW | 0.8937 | 0.1272 | 0.0120 | 0.0014 | 1700 | 3100 | 100 |
| 224 | 213 | Pointe-Noire | CG | 0.9338 | 0.1503 | 0.0077 | 0.0011 | 2900 | 6600 | 0 |
| 225 | 39 | Bamako | ML | 0.9175 | 0.2197 | 0.0053 | 0.0011 | 3800 | 6800 | 1200 |
| 226 | 186 | Hargeysa | SO | 0.8695 | 0.0462 | 0.0234 | 0.0009 | 800 | 1200 | 100 |
| 227 | 213 | Santiago de Cuba | CU | 0.8597 | 0.0809 | 0.0127 | 0.0009 | 1300 | 2400 | 0 |
| 228 | 213 | Mekele | ET | 0.9005 | 0.0636 | 0.0144 | 0.0008 | 1300 | 2000 | 0 |
| 229 | 186 | Kitwe | ZM | 0.9085 | 0.1214 | 0.0061 | 0.0007 | 2600 | 5000 | 100 |
| 230 | 137 | Juba | SS | 0.8811 | 0.1387 | 0.0052 | 0.0006 | 3400 | 5500 | 300 |
| 231 | 120 | Kano | NG | 0.8830 | 0.1792 | 0.0039 | 0.0006 | 5200 | 9400 | 400 |
| 232 | 186 | P’yongyang | KP | 1.0000 | 0.0173 | 0.0312 | 0.0005 | 300 | 600 | 100 |
| 233 | 213 | Bobo-Dioulasso | BF | 1.0000 | 0.0173 | 0.0312 | 0.0005 | 300 | 800 | 0 |
| 234 | 213 | Bangui | CF | 1.0000 | 0.0116 | 0.0468 | 0.0005 | 200 | 300 | 0 |
| 235 | 137 | Toamasina | MG | 0.8587 | 0.1329 | 0.0046 | 0.0005 | 4000 | 7200 | 300 |
| 236 | 81 | Sana’a’ | YE | 0.7817 | 0.1965 | 0.0032 | 0.0005 | 6400 | 9700 | 700 |
| 237 | 102 | Freetown | SL | 0.8191 | 0.1676 | 0.0034 | 0.0005 | 7300 | 11,700 | 500 |
| 238 | 213 | N’Djaména | TD | 0.9346 | 0.0751 | 0.0054 | 0.0004 | 1900 | 3400 | 0 |
| 239 | 213 | Herat | AF | 0.7395 | 0.0462 | 0.0110 | 0.0004 | 1400 | 2800 | 0 |
| 240 | 161 | Thies | SN | 0.9359 | 0.0347 | 0.0104 | 0.0003 | 900 | 1600 | 200 |
| 241 | 137 | Conakry | GN | 0.9322 | 0.1734 | 0.0018 | 0.0003 | 10,200 | 14,900 | 300 |
| 242 | 213 | Nyala | SD | 1.0000 | 0.0289 | 0.0073 | 0.0002 | 800 | 1700 | 0 |
| 243 | 186 | Bouake | CI | 0.9222 | 0.0520 | 0.0039 | 0.0002 | 1900 | 3400 | 100 |
| 244 | 213 | Al-Mawsil (Mosul) | IQ | 0.9740 | 0.0462 | 0.0029 | 0.0001 | 1800 | 2600 | 0 |
| 245 | 120 | Muqdisho (Mogadishu) | SO | 0.9381 | 0.0751 | 0.0011 | 0.0001 | 4900 | 8800 | 400 |
| 246 | 213 | Zinder | NE | 1.0000 | 0.0116 | 0.0029 | 0.0000 | 800 | 1200 | 0 |
| 247 | 213 | Adan (Aden) | YE | 0.9610 | 0.0231 | 0.0013 | 0.0000 | 2500 | 3800 | 0 |
| 248 | 186 | Mbuji-Mayi | CD | 0.9165 | 0.0289 | 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 4000 | 5700 | 100 |
| 249 | 186 | Sikasso | ML | 1.0000 | 0.0116 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 5600 | 8000 | 100 |
Appendix C
| J′α | C′α | ρ′α | UDI Max | UDI Max Distance (m) | Metropolitan Coverage Distance (m) | Peak Distance Buffer Zone (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 0.8092 | 0.4674 | 0.4549 | 0.2195 | 3024.4980 | 6634.5382 | 903.6145 |
| Std | 0.0822 | 0.2674 | 0.4199 | 0.2357 | 3038.4768 | 5972.3094 | 1595.0614 |
| Min | 0.6003 | 0.0116 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 100.0000 | 200.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Median | 0.7974 | 0.5029 | 0.2714 | 0.0962 | 2200.0000 | 4900.0000 | 400.0000 |
| Max | 1.0000 | 0.9538 | 1.0000 | 0.7254 | 25,800.0000 | 38,900.0000 | 12,200.0000 |
Appendix D






References
- Sassen, S. The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo; REV-Revised; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780691070636. [Google Scholar]
- Moulaert, F.; Rodríguez, A.; Swyngedouw, E. The Globalized City: Economic Restructuring and Social Polarization in European Cities; Oxford Geographical and Environmental Studies; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 9780199260409. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, M.J. The Urbanism of Exception: The Dynamics of Global City Building in the Twenty-First Century; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 9781107169241. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, M. Globalization and Cities. In Sustainable Cities and Communities; Leal Filho, W., Marisa Azul, A., Brandli, L., Gökçin Özuyar, P., Wall, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 204–215. ISBN 978-3-319-95717-3. [Google Scholar]
- Grodach, C. Urban Cultural Policy and Creative City Making. Cities 2017, 68, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duconseille, F.; Saner, R. Creative Placemaking for Inclusive Urban Landscapes. J. Arts Manag. Law Soc. 2020, 50, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J. The Death and Life of Great American Cities; Random House: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Florida, R.L. The Rise of the Creative Class: And How It’s Transforming Work, Leisure, Community and Everyday Life; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 9780465024766. [Google Scholar]
- Bettencourt, L.M.A.; Samaniego, H.; Youn, H. Professional Diversity and the Productivity of Cities. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desrochers, P.; Leppälä, S.; Szurmak, J. Urban Diversity and Innovation. In The Elgar Companion to Innovation and Knowledge Creation; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Manaugh, K.; Kreider, T. What Is Mixed Use? Presenting an Interaction Method for Measuring Land Use Mix. J. Transp. Land Use 2013, 6, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbata, R. Urban Revitalization: Enhancing Quality of Life through Mixed-Use Developments. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2024, 11, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Su, T.; Sun, M.; Noyman, A.; Zhang, F.; Pentland, A.; Moro, E. Diversity beyond Density: Experienced Social Mixing of Urban Streets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Nexus 2023, 2, pgad077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannillo, A.; Fasolino, I. Land-Use Mix and Urban Sustainability: Benefits and Indicators Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebuhr, A. Migration and Innovation: Does Cultural Diversity Matter for Regional R&D Activity? Pap. Reg. Sci. 2010, 89, 563–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, G.; Carruthers, J. Amenities, Quality of Life, and Regional Development. In Investigating Quality of Urban Life; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 45, pp. 107–133. ISBN 978-94-007-1741-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrowolska, E.; Kopczewska, K. Mapping Urban Well-Being with Quality Of Life Index (QOLI) at the Fine-Scale of Grid Data. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-saedi, A.Z.M.; Rasul, H.Q. New Roadmap toward Social Sustainability, from Physical Structures to Perceived Spaces. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglitz, J.; Sen, A.; Fitoussi, J. Report by the Commission on the Measurement of Economic Performance and Social Progress (CMEPSP). 2009. Available online: https://www.economie.gouv.fr/files/finances/presse/dossiers_de_presse/090914mesure_perf_eco_progres_social/synthese_ang.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Giannetti, B.F.; Agostinho, F.; Almeida, C.M.V.B.; Huisingh, D. A Review of Limitations of GDP and Alternative Indices to Monitor Human Wellbeing and to Manage Eco-System Functionality. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumain, D.; Swerts, E.; Cottineau, C.; Vacchiani-Marcuzzo, C.; Ignazzi, C.A.; Bretagnolle, A.; Delisle, F.; Cura, R.; Lizzi, L.; Baffi, S. Multilevel Comparison of Large Urban Systems. Cybergeo Eur. J. Geogr. 2015, 706, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csomós, G. On the Challenges Ahead of Spatial Scientometrics Focusing on the City Level. Aslib J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 72, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, E.; Dennett, A. New Forms of Data for Understanding Urban Activity in Developing Countries. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2019, 12, 45–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalan, T.P.; Du, B.; Kumarage, A.S.; Wickramasuriya, R.; Perez, P. High Frequency Data in Land Use and Transport Integrated Model: A Review of Sources and Application. Asian Transp. Stud. 2023, 9, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evance, S.M. Examining Data Limitations and Technical Infrastructure in Urban Planning and Land Use: A Case of Kabwe Council Zambia. PM World J. 2025, 14, 2330–4480. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, G.; Wang, J.; Gross, T.; Kwan, M.-P.; Peng, X.; Liu, Y. Mobility Census for Monitoring Rapid Urban Development. J. R. Soc. Interface 2024, 21, 20230495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earth Observation: Sustainable Urban Planning. Available online: https://initiatives.weforum.org/earth-observation/case-study-details/sustainable-urban-planning/aJYTG0000000P9h4AE (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Kuffer, M.; Wang, J.; Thomson, D.R.; Georganos, S.; Abascal, A.; Owusu, M.; Vanhuysse, S. Spatial Information Gaps on Deprived Urban Areas (Slums) in Low-and-Middle-Income-Countries: A User-Centered Approach. Urban. Sci. 2021, 5, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneepong, K.; Yamanotera, R.; Akiyama, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Miyazawa, S.; Akiyama, C.M. Towards High-Resolution Population Mapping: Leveraging Open Data, Remote Sensing, and AI for Geospatial Analysis in Developing Country Cities—A Case Study of Bangkok. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Shu, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, R. Exploring the Spatiotemporal Patterns and Correlates of Urban Vitality: Temporal and Spatial Heterogeneity. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Li, S.; Sun, M.; Zhao, X.; Liu, D. Exploring the Relationship between Urban Vibrancy and Built Environment Using Multi-Source Data: Case Study in Munich. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, G.; Angkawisittpan, N.; Fu, X.; Sonasang, S. Investigating the Relationship between Built Environment and Urban Vitality Using Big Data. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolevsky, S.; Bojic, I.; Belyi, A.; Sitko, I.; Hawelka, B.; Arias, J.M.; Ratti, C. Scaling of City Attractiveness for Foreign Visitors through Big Data of Human Economical and Social Media Activity. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Congress on Big Data, New York, NY, USA, 27 June–2 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 600–607. [Google Scholar]
- Pavković, V.; Karabašević, D.; Jević, J.; Jević, G. The Relationship between Cities’ Cultural Strength, Reputation, and Tourism Intensity: Empirical Evidence on a Sample of the Best-Reputable European Cities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozeid, A.S.M.; AboElatta, T.A. Polycentric vs Monocentric Urban Structure Contribution to National Development. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2021, 68, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Polycentric Urban Development and Urban Amenities: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Environ. Plan. B Urban. Anal. City Sci. 2020, 48, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psyllidis, A.; Gao, S.; Hu, Y.; Kim, E.-K.; McKenzie, G.; Purves, R.; Yuan, M.; Andris, C. Points of Interest (POI): A Commentary on the State of the Art, Challenges, and Prospects for the Future. Comput. Urban. Sci. 2022, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Han, Y. Identification of Urban Functional Areas Based on POI Data: A Case Study of the Guangzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Ye, J.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y. Urban Functional Zone Classification Based on POI Data and Machine Learning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesz, J.G.B.; Miron, L.I.G.; Delsante, I.; Tzortzopoulos, P. Urban Quality of Life: A Systematic Literature Review. Urban. Sci. 2023, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Fang, C. Urban Remote Sensing with Spatial Big Data: A Review and Renewed Perspective of Urban Studies in Recent Decades. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-L. Urban Vitality Measurement Through Big Data and Internet of Things Technologies. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, E.L.; Kominers, S.D.; Luca, M.; Naik, N. Big Data and Big Cities: The Promises and Limitations of Improved Measures of Urban Life. Econ. Inq. 2018, 56, 114–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, J. Big Spatial Data for Urban and Environmental Sustainability. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 23, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F.; Oliver, R.; Buehler, R.; Lee, J.; Crawford, T.; Kim, J. Impacts of Point of Interest (POI) Data Selection on 15-Minute City (15-MC) Accessibility Scores and Inequality Assessments. Transp. Res. Part. A Policy Pract. 2025, 195, 104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Silva, E.A. Delineating Urban Functional Use from Points of Interest Data with Neural Network Embedding: A Case Study in Greater London. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2021, 88, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, X. Towards More Reliable Measures for “Perceived Urban Diversity” Using Point of Interest (POI) and Geo-Tagged Photos. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2025, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.H.; Xu, S.C.; Li, L.S. Reducing Vacant Houses Is More Important than the Implementation of Green Buildings. Adv. Mat. Res. 2011, 280, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcaute, E.; Hatna, E.; Ferguson, P.; Youn, H.; Johansson, A.; Batty, M. Constructing Cities, Deconstructing Scaling Laws. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20140745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottineau, C.; Hatna, E.; Arcaute, E.; Batty, M. Diverse Cities or the Systematic Paradox of Urban Scaling Laws. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2017, 63, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patacchini, E.; Zenou, Y.; Henderson, J.V.; Epple, D. Urban Sprawl in Europe. Brook.-Whart. Pap. Urban. Aff. 2009, 2009, 125–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission: Directorate-General for Regional and Urban Policy; De Dominicis, L.; Berlingieri, F.; d’Hombres, B.; Gentile, C.; Mauri, C.; Stepanova, E.; Pontarollo, N. Report on the Quality of Life in European Cities, 2023; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg City, Luxembourg, 2023; ISBN 978-92-68-07783-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, I.D.; Escobar, F.J.; Karuppannan, S.; Williamson, I.P.; Yates, P.M.; Suwarnarat, K.; Yaqub, H.W. Spatial Data Infrastructures for Cities in Developing Countries: Lessons from the Bangkok Experience. Cities 2000, 17, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Ritzert, O.S.E.; Vogeler, J.C.; Shah Heydari, S.; Fekety, P.A.; Laituri, M.; McHale, M.R. Effects of Land Use Data Spatial Resolution on SDG Indicator 11.3.1 (Urban Expansion) Assessments: A Case Study Across Ethiopia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneepong, K.; Yamanotera, R.; Akiyama, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Miyazawa, S.; Akiyama, C.M. Open Data-Driven 3D Building Models for Micro-Population Mapping in a Data-Limited Setting. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nengroo, Z.A.; Bhat, M.S.; Za, N.; Ah, S.; Ms, B. Dynamics of Land Use Change in Rural-Urban Fringe: A Case Study of Srinagar City. Environ. Sci. Indian J. 2017, 13, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Weldegebriel, A.; Assefa, E.; Janusz, K.; Tekalign, M.; Van Rompaey, A. Spatial Analysis of Intra-Urban Land Use Dynamics in Sub-Saharan Africa: The Case of Addis Ababa (Ethiopia). Urban. Sci. 2021, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshri, B.; Hu, A.; Adelson, P.; Chen, X.; Dupas, P.; Weinstein, J.; Burke, M.; Lobell, D.; Ermon, S. Infrastructure Quality Assessment in Africa Using Satellite Imagery and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 616–625. [Google Scholar]
- Panman, A. Surveys and the City: Three Challenges to Quality Data Collection in Urban Areas. Available online: https://www.oxfordurbanists.com/magazine/2019/4/17/surveys-and-the-city-three-challenges-to-quality-data-collection-in-urban-areas (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Farrell, K. The Rapid Urban Growth Triad: A New Conceptual Framework for Examining the Urban Transition in Developing Countries. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, D. Missing the Millennium Development Goal Targets for Water and Sanitation in Urban Areas. Environ. Urban. 2016, 28, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, D.; Cloutier, S. Planning for Happy Neighborhoods. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2016, 82, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, S.; Singer, M.M.; Van Cott, D.L. Field Research in Developing Countries: Hitting the Road Running. PS—Political Sci. Politics 2009, 42, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, A.R.; Abid, M.; Khan, F.A. Challenges of Research in Rural Poverty: Lessons from Large Field Surveys. Dev. Pract. 2018, 28, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Segura, D.; Schueler, B.E. Assessors Influence Results: Evidence on Enumerator Effects and Educational Impact Evaluations. J. Dev. Econ. 2023, 163, 103057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daggitt, M.L.; Noulas, A.; Shaw, B.; Mascolo, C. Tracking Urban Activity Growth Globally with Big Location Data. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 150688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeow, L.W.; Low, R.; Tan, Y.X.; Cheah, L. Point-of-Interest (POI) Data Validation Methods: An Urban Case Study. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.D.; Ullman, E.L. The Nature of Cities. Ann. Am. Acad. Political Soc. Sci. 1945, 242, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.L.; Lieber, S.R.; Rushton, G. Clustering of Services in Central Places. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1974, 64, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.L.J. Location Patterns of Urban Restaurants. Ann. Tour. Res. 1985, 12, 581–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, U.; Müller, D.K.; Långvall, A. The Spatial Distribution of Gourmet Restaurants. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour. 2022, 22, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.; Moretti, E. The Agglomeration of Urban Amenities: Evidence from Milan Restaurants. Am. Econ. Rev. Insights 2023, 5, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y. Exploring the Spatial Distribution Mechanisms of Restaurants Across Different Urban Morphologies: A Macau Case Study Using Space Syntax and Big Data. Land 2025, 14, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, H.; Bettencourt, L.M.A.; Lobo, J.; Strumsky, D.; Samaniego, H.; West, G.B. Scaling and Universality in Urban Economic Diversification. J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20150937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foursquare. Places Categories. Available online: https://docs.foursquare.com/data-products/docs/categories (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Yu, B.; Cui, X.; Li, H.; Luo, P.; Liu, R.; Yang, T. TOD and Vibrancy: The Spatio-Temporal Impacts of the Built Environment on Vibrancy. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1009094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Population of Urban Agglomerations with 300,000 Inhabitants or More in 2018, by Country, 1950–2035. Available online: https://population.un.org/wup/downloads?tab=Urban%20Agglomerations (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Borchert, J.R. American Metropolitan Evolution. Geogr. Rev. 1967, 57, 301–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, C. Port Cities and Urban Waterfronts: How Localized Planning Ignores Water as a Connector. WIREs Water 2016, 3, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.R.; Mallik, A.U. Species Diversity and Functional Diversity Relationship Varies with Disturbance Intensity. Ecosphere 2011, 2, art52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, N.J.; Halpern, D.; Nitoslawski, S.; Duarte, F.; Ratti, C.; Pilla, F. Mapping the Diversity of Street Tree Inventories across Eight Cities Internationally Using Open Data. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 61, 127099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. The Measurement of Diversity in Different Types of Biological Collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.J.; Baetens, J.M.; De Baets, B. Ecological Diversity: Measuring the Unmeasurable. Mathematics 2018, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurlbert, S.H. The Nonconcept of Species Diversity: A Critique and Alternative Parameters. Ecology 1971, 52, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopczewska, K.; Kubara, M.; Kopyt, M. Population Density as the Attractor of Business to the Place. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkind, N.J. Winsorize. In Encyclopedia of Research Design; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P.J.; Hubert, M. Anomaly Detection by Robust Statistics. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2018, 8, e1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C. Urban Population Densities. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 1951, 114, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, H.W. Studies in the Structure of the Urban Economy. Econ. J. 1973, 83, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Qu, S.; Qin, J.; Yi, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. A Method to Identify Urban Fringe Area Based on the Industry Density of POI. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, X.; Luo, L.; Li, R. Urban–Rural Boundary Delineation Based on Population Spatialization: A Case Study of Guizhou Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani-Murage, E.W.; Schofield, L.; Wekesah, F.; Mohamed, S.; Mberu, B.; Ettarh, R.; Egondi, T.; Kyobutungi, C.; Ezeh, A. Vulnerability to Food Insecurity in Urban Slums: Experiences from Nairobi, Kenya. J. Urban. Health 2014, 91, 1098–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahasranaman, A.; Bettencourt, L.M.A. Life between the City and the Village: Scaling Analysis of Service Access in Indian Urban Slums. World Dev. 2021, 142, 105435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chege, C.G.K.; Wanyama, R.; Lundy, M.; Nguru, W.; Jäger, M. Does Retail Food Diversity in Urban Food Environments Influence Consumer Diets? Sustainability 2021, 13, 7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, N.; Bramley, G.; Power, S.; Brown, C. The Social Dimension of Sustainable Development: Defining Urban Social Sustainability. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 19, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoev, T.; Tull, K.I.; Winn, N.; Mir, G.; King, N.V.; Wright, J.M.; Gong, Y.Y. Systematic Review of the Role of Social Inclusion within Sustainable Urban Developments. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2022, 29, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Xian, Y. Evaluating Inequality Divides in Urban Development Intensity between the Global North and South. Land Use Policy 2024, 145, 107291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudas, D.; Wnęk, A.; Hudecová, L’.; Fencik, R. Spatial Diversity Changes in Land Use and Land Cover Mix in Central European Capitals and Their Commuting Zones from 2006 to 2018. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Barbosa, H.; Youn, H.; Holme, P.; Ghoshal, G. Morphology of Travel Routes and the Organization of Cities. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, B.J.L. Recent studies concerning the role of transportation in the space economy. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1959, 49, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| City | Country/Region | UDI | UDI Rank | Peak Distance Buffer Zone (m) | Peak Distance Buffer Zone Rank | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P’yongyang | KP | 1.0000 | 0.0005 | 232 | 100 | 186 |
| Lubango | AO | 1.0000 | 0.0039 | 204 | 0 | 213 |
| Bobo-Dioulasso | BF | 1.0000 | 0.0005 | 233 | 0 | 213 |
| Bangui | CF | 1.0000 | 0.0005 | 234 | 0 | 213 |
| Nyala | SD | 1.0000 | 0.0002 | 242 | 0 | 213 |
| Zinder | NE | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 246 | 0 | 213 |
| Sikasso | ML | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 249 | 100 | 186 |
| City | Country/Region | UDI | UDI Rank | Peak Distance Buffer Zone (m) | Peak Distance Buffer Zone Rank | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hanoi | VN | 0.9538 | 0.6350 | 11 | 2600 | 19 |
| London | GB | 0.9364 | 0.7254 | 1 | 1400 | 34 |
| Istanbul | TR | 0.9364 | 0.6567 | 5 | 9300 | 2 |
| Ciudad de Mexico (Mexico City) | MX | 0.9306 | 0.6376 | 10 | 4600 | 11 |
| New York–Newark | US | 0.9249 | 0.7130 | 2 | 5300 | 9 |
| Paris | FR | 0.9191 | 0.6823 | 3 | 3700 | 12 |
| Tokyo | JP | 0.9191 | 0.5593 | 35 | 8600 | 3 |
| Jakarta | ID | 0.8960 | 0.6134 | 17 | 7000 | 5 |
| Krung Thep (Bangkok) | TH | 0.8902 | 0.6038 | 20 | 7000 | 5 |
| Seoul | KR | 0.8902 | 0.5738 | 30 | 12,200 | 1 |
| UDI Rank | City | Country/Region | UDI Max | UDI Max Distance (m) | Peak Distance Rank | Peak Distance Buffer Zone (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | London | GB | 0.7254 | 4700 | 0.7746 | 0.9364 | 1.0000 | 34 | 1400 |
| 2 | New York–Newark | US | 0.7130 | 7200 | 0.7709 | 0.9249 | 1.0000 | 9 | 5300 |
| 3 | Paris | FR | 0.6823 | 4300 | 0.7424 | 0.9191 | 1.0000 | 12 | 3700 |
| 4 | Amsterdam | NL | 0.6719 | 2800 | 0.7961 | 0.8439 | 1.0000 | 44 | 1100 |
| 5 | Istanbul | TR | 0.6567 | 13,500 | 0.7013 | 0.9364 | 1.0000 | 2 | 9300 |
| Average | 0.6899 | 6500 | 0.7571 | 0.9121 | 1.0000 | - | 4160 | ||
| Median | 0.6823 | 4700 | 0.7709 | 0.9249 | 1 | - | 3700 | ||
| Std | 0.0286 | 4221 | 0.0366 | 0.0389 | 0.0000 | - | 3351 | ||
| Peak Distance Buffer Zone Rank | Peak Distance Buffer Zone (m) | City | Country/Region | UDI Rank | UDI Max | UDI Max Distance (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12,200 | Seoul | KR | 30 | 0.5738 | 0.6446 | 0.8902 | 1.0000 | 15,000 |
| 2 | 9300 | Istanbul | TR | 5 | 0.6567 | 0.7013 | 0.9364 | 1.0000 | 13,500 |
| 3 | 8600 | Tokyo | JP | 35 | 0.5593 | 0.6086 | 0.9191 | 1.0000 | 11,900 |
| 4 | 7800 | Manila | PH | 41 | 0.5445 | 0.7785 | 0.6994 | 1.0000 | 2600 |
| 5 | 7000 | Jakarta | ID | 17 | 0.6134 | 0.6846 | 0.8960 | 1.0000 | 10,100 |
| 5 | 7000 | Krung Thep (Bangkok) | TH | 20 | 0.6038 | 0.6783 | 0.8902 | 1.0000 | 8300 |
| 7 | 6500 | Singapore | SG | 6 | 0.6481 | 0.7475 | 0.8671 | 1.0000 | 7300 |
| 8 | 6300 | Kuala Lumpur | MY | 7 | 0.6468 | 0.7510 | 0.8613 | 1.0000 | 5100 |
| 9 | 5300 | New York–Newark | US | 2 | 0.7130 | 0.7709 | 0.9249 | 1.0000 | 7200 |
| 10 | 5000 | Taibei | TW | 26 | 0.5851 | 0.7029 | 0.8324 | 1.0000 | 5700 |
| City | Country/Region | Maximum UDI | 95% Thresholds of Maximum UDI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seoul | Republic of Korea (KR) | 0.6446 | 0.8902 | 1.0000 | 0.5738 | 0.5738 |
| London | Great Britain (GR) | 0.7746 | 0.9364 | 1.0000 | 0.7254 | 0.6891 |
| Istanbul | Türkiye (TR) | 0.7013 | 0.9364 | 1.0000 | 0.6567 | 0.6239 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akiyama, Y.; Akiyama, C.M.; Mizutani, K.; Shimizu, T. Developing the Urban Diversity Index (UDI): A Global Comparison of Urban Qualitative Aspect and Its Implications for Sustainable Urban Planning Using POI Data. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7286. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167286
Akiyama Y, Akiyama CM, Mizutani K, Shimizu T. Developing the Urban Diversity Index (UDI): A Global Comparison of Urban Qualitative Aspect and Its Implications for Sustainable Urban Planning Using POI Data. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7286. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167286
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkiyama, Yuki, Chiaki Mizutani Akiyama, Kotaro Mizutani, and Takahito Shimizu. 2025. "Developing the Urban Diversity Index (UDI): A Global Comparison of Urban Qualitative Aspect and Its Implications for Sustainable Urban Planning Using POI Data" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7286. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167286
APA StyleAkiyama, Y., Akiyama, C. M., Mizutani, K., & Shimizu, T. (2025). Developing the Urban Diversity Index (UDI): A Global Comparison of Urban Qualitative Aspect and Its Implications for Sustainable Urban Planning Using POI Data. Sustainability, 17(16), 7286. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167286








