Spatiotemporal Extraction of Aquaculture Ponds Under Complex Surface Conditions Based on Deep Learning and Remote Sensing Indices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
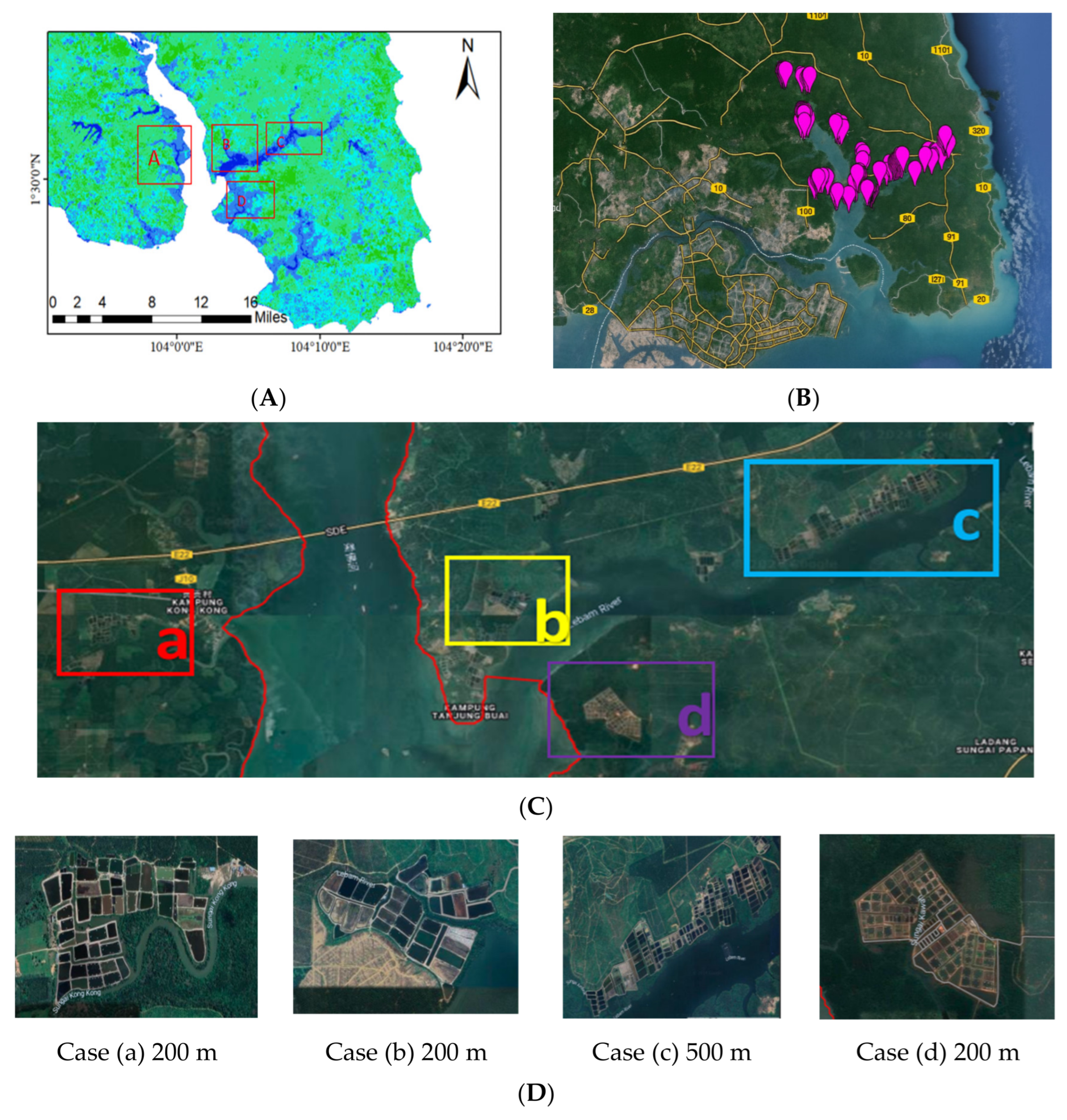
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. The Rivers in Johor
2.1.2. The Lakes in Johor
2.2. Satellite Imagery
3. Methods
3.1. Extraction Index of Aquaculture Ponds and Water Surface in the Study Area
- (1)
- Water Index (WI)
- (2)
- Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI)
- (3)
- The Automatic Water Extraction Index (AWEI)
3.2. The Composite Water Index (CWI)
4. Results
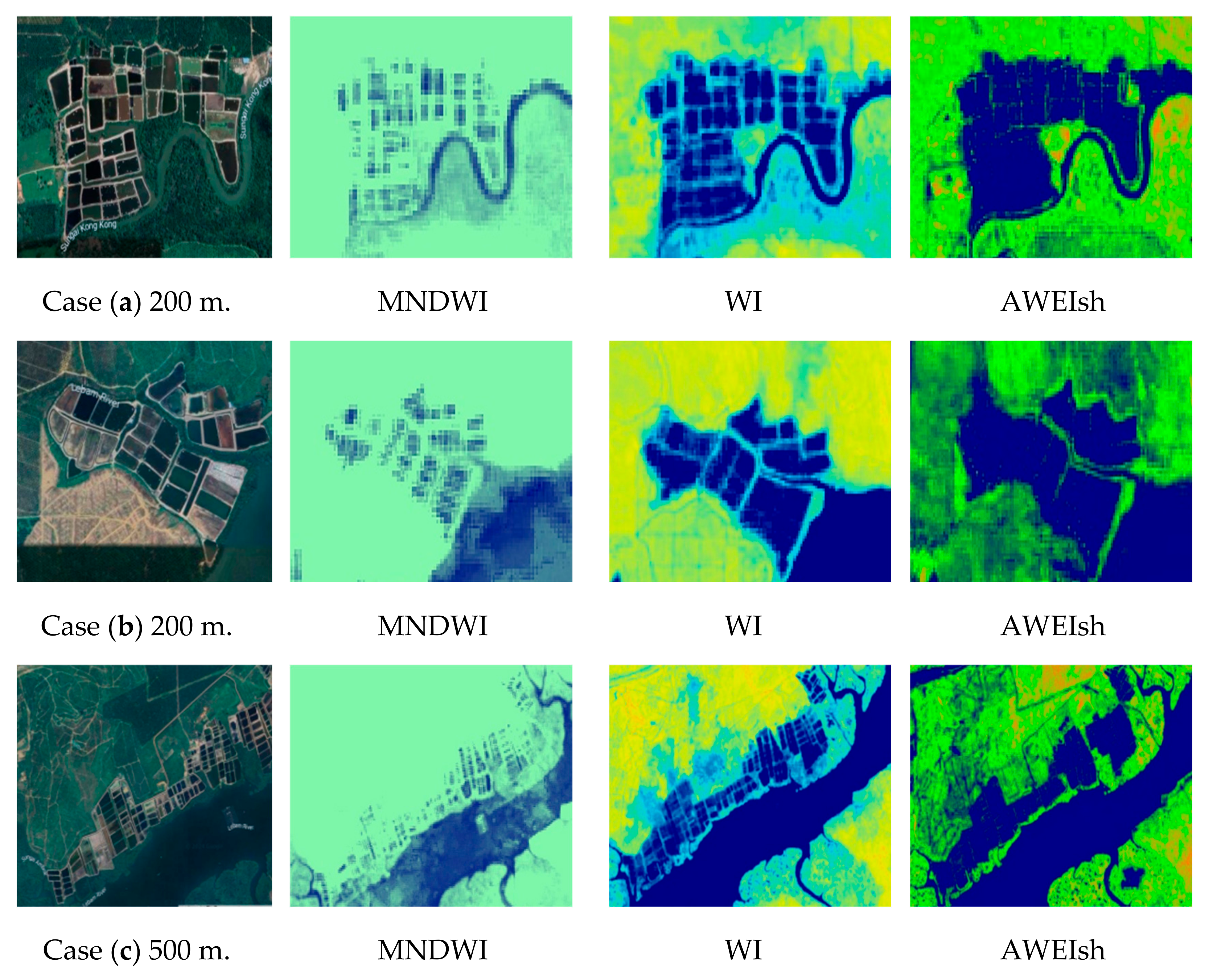
4.1. The Optimized WI, MNDWI, and AWEIsh for Surface Water Detection
4.2. The Computational Load for Composite Water Index (CWI)
4.3. The Analysis of the CWI Results
4.4. Extraction Results of Water Surface and Aquaculture Ponds
5. Discussion
5.1. Adaptability and Superiority of the CWI Method
5.2. Robustness and Applicability of the CWI Method
5.3. Scalability and Global Applicability of the CWI Method
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ottinger, M.; Clauss, K.; Leinenkugel, P.; Künzer, C. Earth Observation for the Assessment of Pond Aquaculture in Coastal Asia-Status and Future Potentials. In Proceedings of the 38th EARSeL Symposium, Chania, Greece, 9–13 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, D.; Ji, H. Detecting spatiotemporal changes of large-scale aquaculture ponds regions over 1988–2018 in Jiangsu Province, China using Google Earth Engine. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 188, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Luo, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Dynamics of coastal aquaculture ponds in Vietnam from 1990 to 2015 using Landsat data. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 502, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, S.H.; Ramlee, M.N.A.; Lola, M.S.; Ikhwanuddin, M.; Azra, M.; Abdullah, M.; Zakaria, S.; Ibrahim, Y. A system dynamics model for analysing the eco-aquaculture system of integrated aquaculture park in Malaysia with policy recommendations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 23, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Di, L.; Rahman, M.S.; Tang, J. Fishpond mapping by spectral and spatial-based filtering on google earth engine: A case study in singra upazila of Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.; Le, H.; Campos, R.; Yu, S.; Bhuiya, A. Quantifying spatial and temporal patterns of aquaculture in North Carolina using cloud computing. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2018, 52, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottinger, M.; Clauss, K.; Kuenzer, C. Aquaculture: Relevance, distribution, impacts and spatial assessments–A review. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 119, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Research on extracting water body information by using improved normalized Differential water body Index (MNDWI). J. Remote Sens. 2005, 9, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing Landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Kou, W. Automatic water surfaces extraction from Sentinel-2 remote sensing images using deep semantic segmentation model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 43454–43464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, A.M.; Kreitler, J.; Sadegh, M. Augmented Normalized Difference Water Index for improved surface water monitoring. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 140, 105030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Xiao, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zou, Z.; Qin, Y. Open surface water mapping algorithms: A comparison of water-related spectral indices and sensors. Water 2017, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Detecting, extracting, and monitoring surface water from space using optical sensors: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lin, N.; Liu, Z. Comparing water indices for Landsat data for automated surface water body extraction under complex ground background: A case study in Jilin Province. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenovský, Z.; Rott, H.; Cihlar, J.; Schaepman, M.E.; García-Santos, G.; Fernandes, R.; Berger, M. Sentinels for science: Potential of Sentinel-1, -2, and -3 missions for scientific observations of ocean, cryosphere, and land. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Hughes, L.H.; Qiu, C.; Zhu, X.X. Aggregating cloud-free sentinel-2 images with google earth engine. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 4, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Ma, M.; Song, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W. Water extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images based on deep learning semantic segmentation model. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2022, 34, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Feng, A.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Wu, X.; Liao, J.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X.; Pu, H. New deep learning method for efficient extraction of small water from remote sensing images. PLoS ONE 2022, 27, e0272317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billson, J.; Islam, M.S.; Sun, X.; Cheng, I. Water body extraction from sentinel-2 imagery with deep convolutional networks and pixelwise category transplantation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, W.; Fen, Q. A review of remote sensing image water extraction. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2018, 43, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, V.S.; Kaleita, A.L.; Gelder, B.K.; da Silveira, H.L.; Abe, C.A. Exploring multiscale object-based convolutional neural network (multi-OCNN) for remote sensing image classification at high spatial resolution. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 168, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 18Abdelal, Q.; Assaf, M.N.; Al-Rawabdeh, A.; Arabasi, S.; Rawashdeh, N.A. Assessment of Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 OLI for Small-Scale Inland Water Quality Modeling and Monitoring Based on Handheld Hyperspectral Ground Truthing. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 4643924. [Google Scholar]
- Balha, A.; Mallick, J.; Pandey, S.; Gupta, S.; Singh, C.K. A comparative analysis of different pixel and object-based classification algorithms using multi-source high spatial resolution satellite data for LULC mapping. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 14, 2231–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdağ, A.; Ünal, Z.; Karkınlı, A.E.; Soomro, A.B.; Mir, M.S.; Gulzar, Y. An Integrated Approach for Groundwater Potential Prediction Using Multi-Criteria and Heuristic Methods. Water 2025, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Guo, X.; Chen, R. Automatic extraction of aquaculture ponds based on Google Earth Engine. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2020, 198, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B. Multitemporal Water Extraction of Dongting Lake and Poyang Lake Based on an Automatic Water Extraction and Dynamic Monitoring Framework. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Huang, H.; He, F.; Luo, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, L.; Guo, R.; Tang, S. Unsupervised stepwise extraction of offshore aquaculture ponds using super-resolution hyperspectral images. J. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 119, 103326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Hu, Y. Surface Water body Extraction using a Progressive Enhancement Model from remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2016 4th International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Guangzhou, China, 4–6 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Bujang, J.S.; Zakaria, M.H.; Hashim, M. The application of remote sensing to seagrass ecosystems: An overview and progress in Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2015, 6, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shao, W.; Sun, J. Extraction of offshore aquaculture areas from medium-resolution remote sensing images based on deep learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Xia, J.; Ha, N.T.; Bui, D.T.; Le, N.N.; Takeuchi, W. A review of remote sensing approaches for monitoring blue carbon ecosystems: Mangroves, seagrasses and salt marshes during 2010–2018. Sensors 2019, 19, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. NASA Spec. Publ. 1974, 351, 309. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S.; Mesev, V. Change vector analysis, tasseled cap, and NDVI-NDMI for measuring land use/cover changes caused by a sudden short-term severe drought: 2011 Texas event. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijith, H.; Dodge-Wan, D. Applicability of MODIS land cover and Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) for the assessment of spatial and temporal changes in strength of vegetation in tropical rainforest region of Borneo. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 18, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Chen, S.; Yin, T.; Chavanon, E.; Lauret, N.; Guilleux, J.; Henke, M.; Qin, W.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; et al. Using the negative soil adjustment factor of soil adjusted vegetation index (SAVI) to resist saturation effects and estimate leaf area index (LAI) in dense vegetation areas. Sensors 2021, 21, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; He, G.; Wang, G.; Yang, G. WE-NDBI-A new index for mapping urban built-up areas from GF-1 WFV images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 11, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, S.; Salehi, B.; Granger, J.; Amani, M.; Brisco, B.; Huang, W. Remote sensing for wetland classification: A comprehensive review. GIScience Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 623–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A new index for delineating built-up land features in satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 4699–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikdogan, F.; Bovik, A.; Passalacqua, P. Surface water mapping by deep learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4909–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjir, U.; Greidanus, H.; Oštir, K. Vessel detection and classification from spaceborne optical images: A literature survey. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 207, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Feng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Sun, J.; Shi, C.; Hu, W. Urban water extraction with UAV high-resolution remote sensing data based on an improved U-Net model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaohui, F.; Qin, L.; Liusheng, H.; Guochao, X.; Hongying, Z. Remote sensing image water body extraction based on improved watershed. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2019, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, D.; Shi, D.; Luan, Z. Automatic Extraction of Open Water Using Imagery of Landsat Series. Water 2020, 12, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, P.; Guo, F.; Tao, C. Comparative study of water-body extraction methods based on Landsat8 remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Computer Science and Communication Technology, Beijing, China, 30–31 July 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegen, M.V.; Huvenne, V.; Kasamatsu, C.; Völker, D.; Davies, J.S. Coastal bathymetry mapping by fusing optical and synthetic aperture radar data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Qi, J.; Wang, X.; Yao, J.; Feng, L. Water–land classification using time series of optical and SAR remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, G.; Wang, Y. OCNet-Based Water Body Extraction from Remote Sensing Images. Water 2023, 15, 3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, M.; Breuer, L. Performance of Water Indices for Water Resources Monitoring Using Large-Scale Sentinel-2 Data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 196, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.A.H.; Wee, S.Y.; Haron, D.E.M.; Kamarulzaman, N.H.; Aris, A.Z. Occurrence of endocrine disrupting compounds in mariculture sediment of Pulau Kukup, Johor, Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus. Sentinel-2 Overview. Available online: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/copernicus/sentinel-2 (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Sabjan, A.; Lee, L.K.; See, K.F.; Wee, S.T. Comparison of three water indices for tropical aquaculture ponds extraction using google earth engine. Sains Malays. 2022, 51, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Foster, J.L.; Kumar, S.V. Development and evaluation of a cloud-gap-filled MODIS daily snow-cover product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Hu, F.; Meng, L. Multiscale features supported DeepLabV3+ optimization scheme for accurate water semantic segmentation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 155787–155804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, I.; Ahmed, M.; Gulzar, Y.; Baba, S.H.; Mir, M.S.; Soomro, A.B.; Sultan, A.; Elwasila, O. Estimation of the extent of the vulnerability of agriculture to climate change using analytical and deep-learning methods: A case study in Jammu, Kashmir, and Ladakh. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, Y. Fruit image classification model based on MobileNetV2 with deep transfer learning technique. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, Y.; Ünal, Z.; Kızıldeniz, T.; Umar, U.M. Deep learning-based classification of alfalfa varieties: A comparative study using a custom leaf image dataset. MethodsX 2024, 13, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Index | Modeling Formula | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| NDVI | NDVI = (NIR − RED)/(NIR + RED) | Rouse et al., 1974 [36] |
| NDWI | NDWI = (GREEN − NIR)/(GREEN + NIR) | McFeeters, 1996 [9] |
| MNDWI | MNDWI = (GREEN − SWIR)/(GREEN + SWIR) | Xia et al., 2022 [29] |
| NDMI | NDMI = (NIR − SWIR)/(NIR + SWIR) | Rahman and Mesev 2019 [37] |
| EVI | Vijith and Dodge-Wan, 2020 [38] | |
| SAVI | SAVI = (NIR − RED)/(NIR + RED + L) × (1 + L) | Zhen et al., 2021 [39] |
| WI | WI = (GREEN+RED)/(NIR + SWIR) | Rad et al., 2021 [14] |
| BAI | Bai et al., 2020 [40] | |
| AWEI | Feyisa et al., 2014 [10] |
| Satellite | The Time Frame of The Image | Accuracy (m) | Number of Images Cloud < 20% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-2 | 2016–2023 | 10 | 66 × 8 = 528 |
| Water | JRC/GSW1_1/MonthlyHistory | mask | |
| JRC/GSW1_3/GlobalSurfaceWater | essential data statistics |
| Band Name | Description | Spatial Resolution (m) | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B2 | BLUE | 10 | 496.6 (S2A)/492.1 (S2B) |
| B3 | GREEN | 10 | 560 (S2A)/559 (S2B) |
| B4 | RED | 10 | 664.5 (S2A)/665 (S2B) |
| B8 | NIR 1 | 10 | 835.1 (S2A)/833 (S2B) |
| B8A | Red Edge 4 | 20 | 864.8 nm (S2A)/864 nm (S2B) |
| B11 | SWIR 1 | 20 | 1613.7 (S2A)/1610.4 (S2B) |
| B12 | SWIR 2 | 20 | 2202.4 (S2A)/2185.7 (S2B) |
| QA60 3 | Cloud mask | 60 | Cloud mask from polygons. Empty after Feb 2022. |
| Index | Total (km2) | Water (km2) | Non-Water (km2) | Overall Accuracy | Kappa Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNDWI (water ∈ (−0.2,0.5)) | 18,984 | 1866.66 | 17,117.34 | 0.930 | 0.919 |
| WI (water ∈ (0.75, 2)) | 18,984 | 1914.45 | 17,069.55 | 0.931 | 0.932 |
| AWEIsh (water ∈ (0, 0.224)) | 18,984 | 2062.39 | 16,921.61 | 0.922 | 0.916 |
| Random Points | β0 | β1WI | β2MNDWI | β3AWEIsh | MSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | −0.5517 | 0.5811 | 0.0103 | −0.2072 | 0.0001 | 0.982 |
| 800 | −0.5638 | 0.5867 | 0.0038 | −0.1976 | 0.0002 | 0.978 |
| 600 | −0.5625 | 0.5954 | 0.0004 | −0.2046 | 0.0001 | 0.984 |
| 400 | −0.5710 | 0.6071 | 0.0002 | −0.2014 | 0.0001 | 0.980 |
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| User Accuracy (Water) | 96.7% |
| Producer Accuracy (Water) | 97.2% |
| F1-Score (Water) | 97.0% |
| Overall Accuracy | 96.9% |
| Kappa Coefficient | 93.9% |
| Land Use Category | 2016 | 2019 | 2023 | 2016–2019 | 2019–2023 | 2016–2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | Change (km2) | |||||
| Mangrove | 266.32 | 249.56 | 238.11 | −16.76 | −11.45 | −28.21 |
| Pond Aquaculture | 19.91 | 33.12 | 43.18 | 13.21 | 10.06 | 23.27 |
| Water Surface | 8120.71 | 8124.01 | 8087.47 | 3.3 | −36.54 | −33.24 |
| Others | 5997.86 | 5998.11 | 6036.04 | 0.25 | 37.93 | 38.18 |
| Model | Mean mIoU | 95% CI (mIoU) | Mean oPA | 95% CI (oPA) | p-Value (vs. CWI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WI | 0.79 | [0.76, 0.82] | 0.92 | [0.91, 0.93] | <0.01 |
| MNDWI | 0.75 | [0.72, 0.78] | 0.91 | [0.90, 0.92] | <0.01 |
| AWEIsh | 0.77 | [0.73, 0.80] | 0.91 | [0.90, 0.92] | <0.01 |
| CWI | 0.84 | [0.82, 0.86] | 0.94 | [0.93, 0.95] | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, W.; Ismail, M.H.; Ramli, M.F.; Deng, J.; Wu, N. Spatiotemporal Extraction of Aquaculture Ponds Under Complex Surface Conditions Based on Deep Learning and Remote Sensing Indices. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167201
Qin W, Ismail MH, Ramli MF, Deng J, Wu N. Spatiotemporal Extraction of Aquaculture Ponds Under Complex Surface Conditions Based on Deep Learning and Remote Sensing Indices. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167201
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Weirong, Mohd Hasmadi Ismail, Mohammad Firuz Ramli, Junlin Deng, and Ning Wu. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Extraction of Aquaculture Ponds Under Complex Surface Conditions Based on Deep Learning and Remote Sensing Indices" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167201
APA StyleQin, W., Ismail, M. H., Ramli, M. F., Deng, J., & Wu, N. (2025). Spatiotemporal Extraction of Aquaculture Ponds Under Complex Surface Conditions Based on Deep Learning and Remote Sensing Indices. Sustainability, 17(16), 7201. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167201








