Extraction of Alumina and Alumina-Based Cermets from Iron-Lean Red Muds Using Carbothermic Reduction of Silica and Iron Oxides
Abstract
1. Introduction
Aims of the Investigation
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Blend Compositions
2.2. Experimental
3. Results
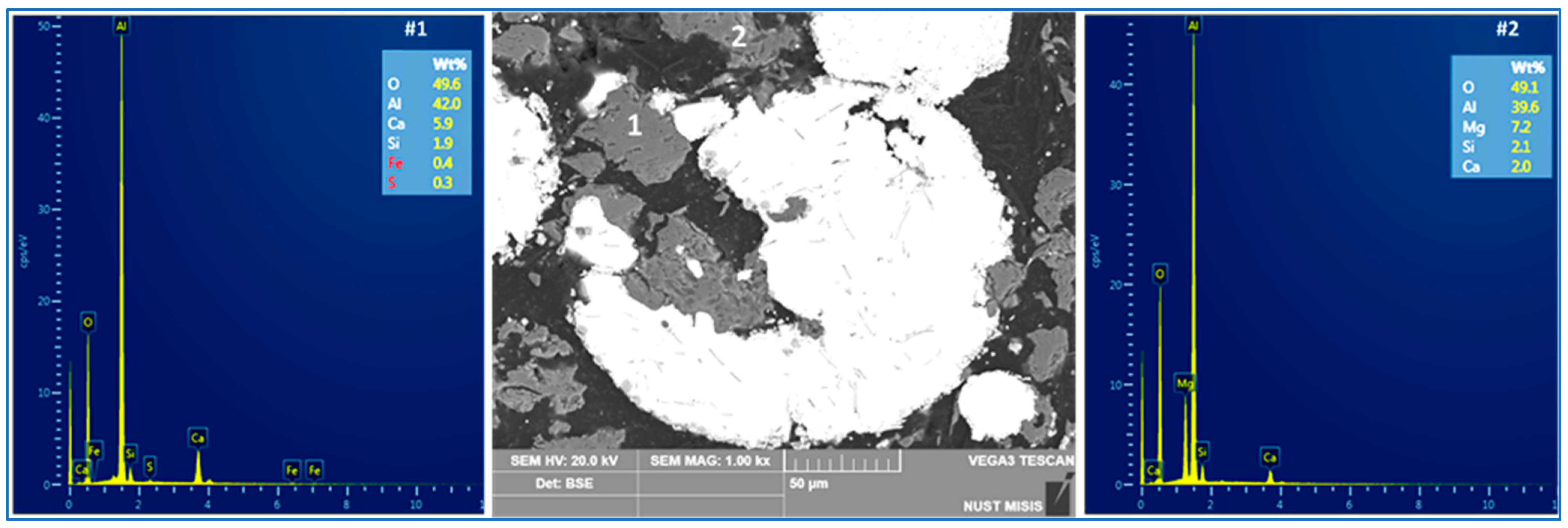
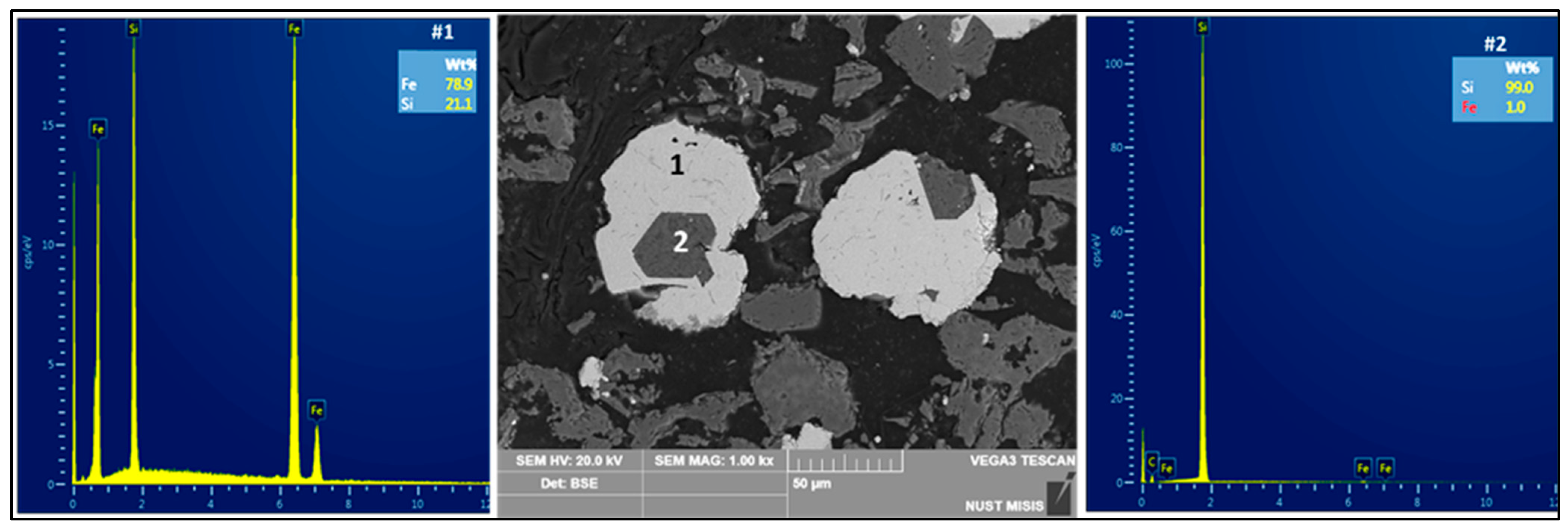
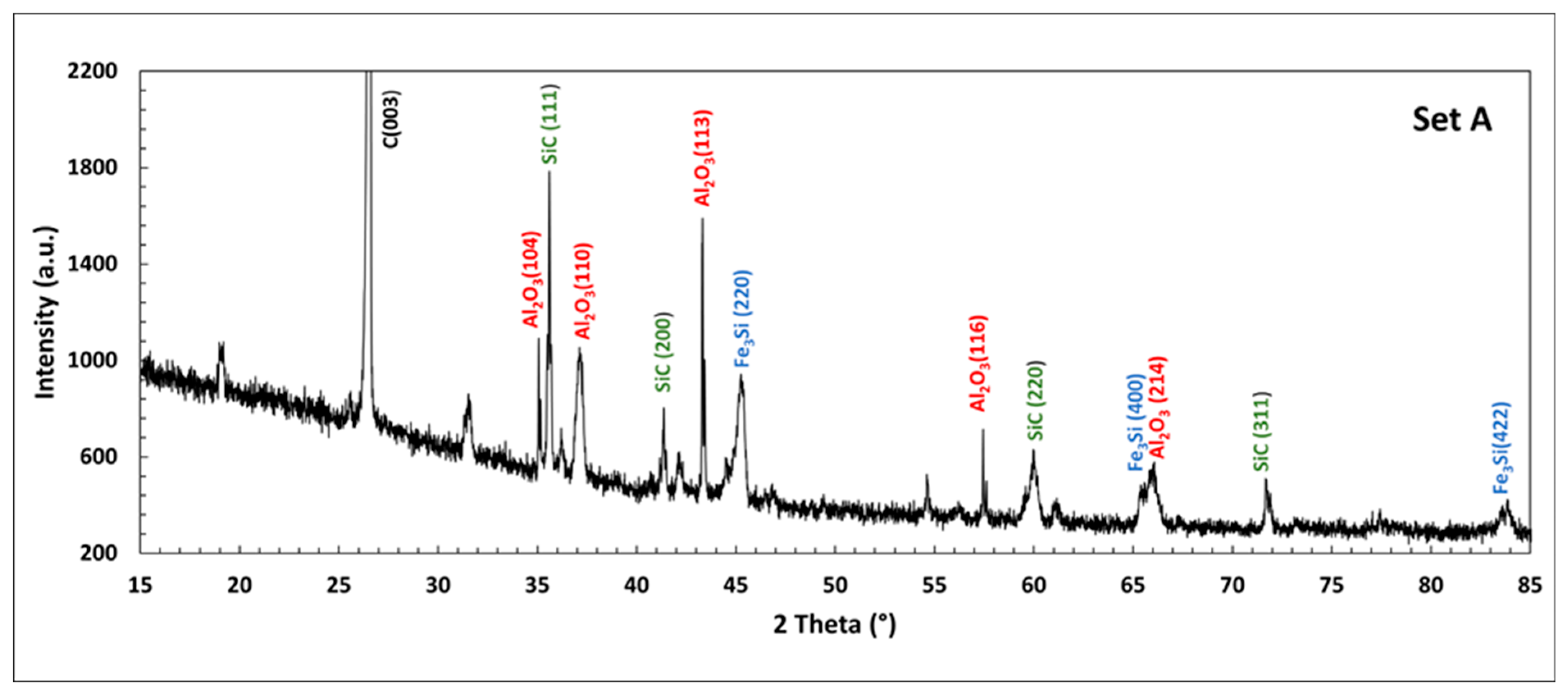
3.1. Set A: Carbothermic Reduction of Iron-Lean RM
3.2. Set B: Carbothermic Reduction of (20 g RM + 10 g Fe2O3) Blend
3.3. Set C: Carbothermic Reduction of (20 g RM + 10 g Red MS) Blend
4. Discussion
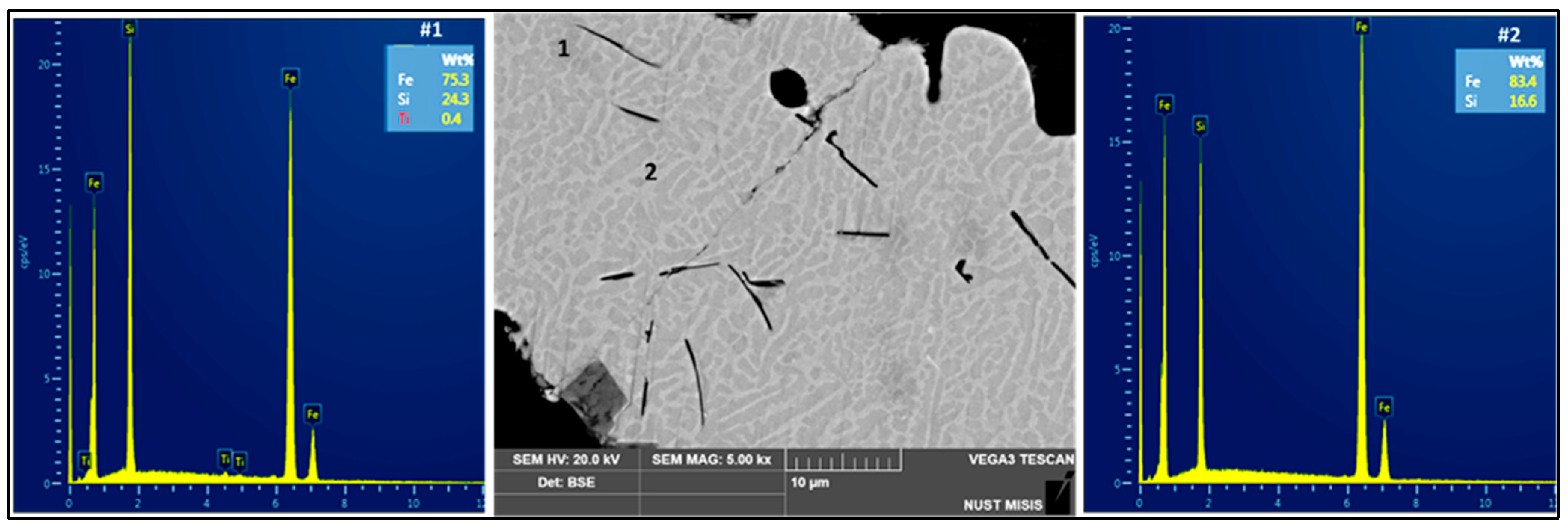
4.1. Resource Recovery: Fe–Si Alloys
4.2. Alumina Segregation
4.3. Formation of Cermets: RM/Red MS Blends
4.4. Industrial Implications
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Aluminium Cycle 2023. Available online: https://alucycle.international-aluminium.org/public-access/public-global-cycle/ (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Available online: https://international-aluminium.org/landing/aluminium-facts/ (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Haupin, W.E.; Frank, W.B. Electrometallurgy of Aluminum, Electrochemical Processing; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 2, pp. 301–325. [Google Scholar]
- Brough, D.; Jouhara, H. The aluminium industry: A review on state-of-the-art technologies, environmental impacts and possibilities for waste heat recovery. Int. J. Thermofluids 2020, 1–2, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/264963/global-alumina-production-by-country/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Zhang, R.; Zheng, S.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y. Recovery of alumina and alkali in Bayer red mud by the formation of andradite-grossular hydrogarnet in hydrothermal process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambo, M.; Kawatra, S.K. Red mud: Fundamentals and new avenues for utilization. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 42, 427–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Konyukhov, Y.; Zinoveev, D.; Li, K.; Maslennikov, N.; Burmistrov, I.; Kargin, J.; Kravchenko, M.; Mukherjee, P.S. Production of Soft Magnetic Materials Fe-Si and Fe-Si-Al from Blends of Red Muds and Several Additives: Resources for Advanced Electrical Devices. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatjana, S.; Jens, R.; Klaus, F. Research adsorption of aliphatic polyhydroxy carboxylic acids on gibbsite: pH dependency and importance of adsorbate structure. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P. The processing of high silica bauxites—Review of existing and potential processes. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremin, N.I.; Shmorgunenko, N.S. Some theoretical and practical questions of low-grade bauxite processing by the sinter process and the in-series combined Bayer-sinter process. Trav. ICSOBA 1974, 12, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Dong, K.; Zhang, W.; Bi, S. The Sintering and Leaching of Low-Grade Diasporic Bauxite by the Improved Lime-Sintering Process. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 616–618, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.M. Red mud-based catalysts for the catalytic removal of typical air pollutants: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alton, T.; Tabereaux, R.D.; Peterson, D. Aluminum Production. In Treatise on Process Metallurgy; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, D.Y. Physical and Chemical Properties of Sintering Red Mud and Bayer Red Mud and the Implications for Beneficial Utilization. Materials 2012, 5, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, C. Analysis on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Red Mud Materials and Stockpile Stability after Dilatation. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 8784232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.; Ray, A.K.; Bandopadhyay, S.A. Proposal for resources, utilization and processes of red mud in India—A review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 118, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K. The History, Challenges, and New Developments in the Management and Use of Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Met. 2016, 2, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Q.; Li, S.Q.; Guo, Z.J.; Kong, J.W. Application and prospect of superconducting high gradient magnetic separation in disposal of micro-fine tailings. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 275, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.B.; Niu, Z.P.; Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Q.J. A novel process for recovery of aluminum, iron, vanadium, scandium, titanium and silicon from red mud. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 8, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaussen, F.M.; Friedrich, B. Phase characterization and thermochemical simulation of (landfilled) bauxite residue (“red mud”) in different alkaline processes optimized for aluminum recovery. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 176, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeev, D.; Zinoveev, D.; Kondratiev, A.; Lubyanoi, D.; Pankratov, D. Reductive smelting of neutralized red mud for iron recovery and produced pig iron for heat-resistant castings. Metals 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Jin, H.X.; Deng, Y.; Xiao, Y.D. Comprehensive utilization status of red mud in China: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 289, 125136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lei, T.; Wang, B.; Ma, S.; Lin, Y.; Lu, X.; Ye, Z. An Eco-Friendly Acid Leaching Strategy for Dealkalization of Red Mud by Controlling Phase Transformation. Materials 2022, 15, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.Y.; Zhou, K.G.; Ning, L.F.; Peng, C.H.; He, D.W. Stepwise leaching of valuable metals from red mud using hydrochloric acid. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 12, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Mo, W.; Feng, J.P.; Ren, R.L.; He, C.Y.; Su, X.J. Differential leaching behavior of iron and aluminum from Bayer red mud in sulfuric acid/oxalic acid system. Nonferr. Met. (Miner. Process. Sect.) 2023, 2, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Rayapudi, V.; Dhawan, N. Microwave reduction of red mud for recovery of iron values. J. Sustain. Metall. 2018, 4, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Han, Y.X.; He, F.Y.; Gao, P.; Yuan, S. Characteristic, hazard and iron recovery technology of red mud—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasankar, K.; Ray, P.K.; Chaubey, A.K.; Padhi, A.; Satapathy, B.K.; Mukherjee, P.S. Production of pig iron from red mud waste fines using thermal plasma technology. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2012, 19, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Sun, S.Y.; Zhang, L.; Jahanshahi, S.; Yang, J.K. Experimental and simulative study on phase transformation in Bayer red mud soda-lime roasting system and recovery of Al, Na and Fe. Miner. Eng. 2012, 39, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Dhawan, N. Evaluation of red mud as a polymetallic source—A review. Min. Eng. 2021, 171, 107084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.M.A.; Sun, T.; Dai, M.; Xu, W.; Ye, Y.; Ali, I.; Gao, F.; Peng, C. Technologies for recovery of iron from red mud: Processes, challenges and opportunities. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 41, e01053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Konyukhov, Y.V.; Burmistrov, I.; Cayumil, R.; Belov, V.A.; Rogachev, S.O.; Leybo, D.V.; Mukherjee, P.S. An innovative route for valorising iron and aluminium oxide rich industrial wastes: Recovery of multiple metals. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 295, 113035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairul, M.A.; Zanganeh, J.; Moghtaderi, B. The composition, recycling and utilisation of Bayer red mud. Resour. Conserv. Recyc. 2019, 141, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; Li, J.; Cao, Y. Comprehensive utilization of red mud and blast furnace dust: Synergistic preparation of direct reduced iron and functional ceramsite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 345, 127436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Mao, R. Waste control by waste: Recovering iron from red mud with the effect of Phosphogypsum-included additive. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 206, 107641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, H.; Mishra, S.C.; Sahoo, S.K.; Chakraverty, A.P.; Maharana, H.S. Progress of Red Mud Utilization: An Overview. Am. Chem. Sci. J. 2014, 4, 255–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altundŏgan, H.S.; Altundŏgan, S.; Tümen, F.; Bildik, M. Arsenic adsorption from aqueous solutions by activated red mud. Waste Manage. 2002, 22, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçin, N.; Sevinç, V. Utilization of bauxite waste in ceramic glazes. Ceram. Int. 2000, 26, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, D.; Hou, J.; He, B.; Xiao, B. Preparation of glass-ceramics from red mud in the aluminium industries. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Yu, Y.; Yan, K. Environmental assessment, management and utilization of red mud in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 84, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Jun, B.R. Improvement of red mud polymer-matrix nanocomposites by red mud surface treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snars, K.; Gilkes, R.J. Evaluation of bauxite residues (red muds) of different origins for environmental applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, J.; Boumaza, R.; Ambroise, J. Development of a pozzolanic pigment from red mud. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, P.; Tyagi, R.D.; Auclair, J.C.; Wilkinson, K.J. Chemical and biological leaching of aluminum from red mud. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Boyjoo, Y.; Choueib, A.; Zhu, Z.H. Removal of dyes from aqueous solution using fly ash and red mud. Water Res. 2005, 39, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukiza, E.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, N. Utilization of red mud in road base and subgrade materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://international-aluminium.org/statistics/alumina-production/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Svobodova-Sedlackova, A.; Calderón, A.; Fernandez, A.I.; Chimenos, J.M.; Berlanga, C.; Yücel, O.; Barreneche, C.; Rodriguez, R. Mapping the research landscape of bauxite by-products (red mud): An evolutionary perspective from 1995 to 2022. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Borghi, A.; Moreschi, L.; Gallo, M. Circular economy approach to reduce water–energy–food nexus. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 13, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoveev, D.; Pasechnik, L.; Grudinsky, P.; Yurtaeva, A.; Dyubanov, V. Kinetics and Mechanism of Red Mud Carbothermic Reduction and Reduced Iron Grain Growth: An Influence of Sodium Sulfate. Crystals 2023, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudinsky, P.; Zinoveev, D.; Yurtaeva, A.; Kondratiev, A.; Dyubanov, V.; Petelin, A. Iron Recovery from Red Mud Using Carbothermic Roasting with Addition of Alkaline Salts. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudinsky, P.; Zinoveev, D.; Pankratov, D.; Semenov, A.; Panova, M.; Kondratiev, A.; Zakunov, A.; Dyubanov, V.; Petelin, A. Influence of Sodium Sulfate Addition on Iron Grain Growth during Carbothermic Roasting of Red Mud Samples with Different Basicity. Metals 2020, 10, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoveev, D.; Grudinsky, P.; Zakunov, A.; Semenov, A.; Panova, M.; Valeev, D.; Kondratiev, A.; Dyubanov, V.; Petelin, A. Influence of Na2CO3 and K2CO3 Addition on Iron Grain Growth during Carbothermic Reduction of Red Mud. Metals 2019, 9, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Singh, S.; Dunn, K.A.; Liang, Y. Optimizing Leaching of Rare Earth Elements from Red Mud and Spent Fluorescent Lamp Phosphors Using Levulinic Acid. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paswan, D.; Malathi, M.; Minj, R.K.; Bandopadhyay, D. Mill scale: A potential raw material for iron and steel making. Steel World 2015, 21, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, R.; Konyukhov, Y.; Li, K.; Jayasankar, K.; Maslennikov, N.; Zinoveev, D.; Kargin, J.; Burmistrov, I.; Leybo, D.; Kravchenko, M.; et al. Innovative Transformation and Valorisation of Red Mill Scale Waste into Ferroalloys: Carbothermic Reduction in the Presence of Alumina. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.speccement.ru/index.php?m_id=787&grp=cement (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Khanna, R.; Sahajwalla, V. An atomistic model for the graphite–alumina/liquid iron system: Monte-Carlo simulations on carbon dissolution. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Fruehan, R.J. Activity of silica in calcium-aluminate based slags. Metall. Trans. B 1987, 18, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram-ul-Haq, M.; Khanna, R.; Koshy, P.; Sahajwalla, V. High-temperature Interactions of Alumina–Carbon Refractories with Molten Iron. ISIJ Int. 2010, 50, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilkerson, R.P.; Gludovatz, B.; Watts, J.; Tomsia, A.P.; Hilmas, G.E.; Ritchie, R.O. A novel approach to developing biomimetic (“nacre-like”) metal-compliant-phase (nickel-alumina) ceramics through coextrusion. Adv. Mater. 2018, 28, 10061–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.B.; Leung, N.; Jargalsaikhan, U.; Ho, E.R.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, H.X.; Su, B.; Sui, T. Fabrication and characterization of alumina/aluminum composite materials with a nacre-like micro-layered architecture. Mater. Des. 2022, 223, 1111190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraskar, N.D.; Tiwari, G.; Goel, M.D. Impact response of ceramic structures—A review. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 27262–27279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Kumar, R.; Mitra, R.; Charalambous, H.; Chuang, A.C.; Biswas, K.; Jha, S.K. Novel processing route for design and manufacturing of metal toughened nanoceramics: Al-Al2O3 nanocermets. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 25168–25182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Lou, B.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Mingcui, C.; Zhang, S. In-situ preparation of alumina-based cermet after reduction of iron oxide in red mud with aluminum dross. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 21630–21637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Shen, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. In-situ preparation of porous metal-ceramic composite from secondary aluminum dross and red mud for adsorption of organic pollutant. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 986, 174135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Preveniou, A.; Kladis, A.; Pettersen, J.B. Circular economy and life cycle assessment of alumina production: Simulation-based comparison of Pedersen and Bayer processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.E.H.; Haynes, R.J. Bauxite processing residue: A critical review of its formation, properties, storage, and revegetation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 271–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
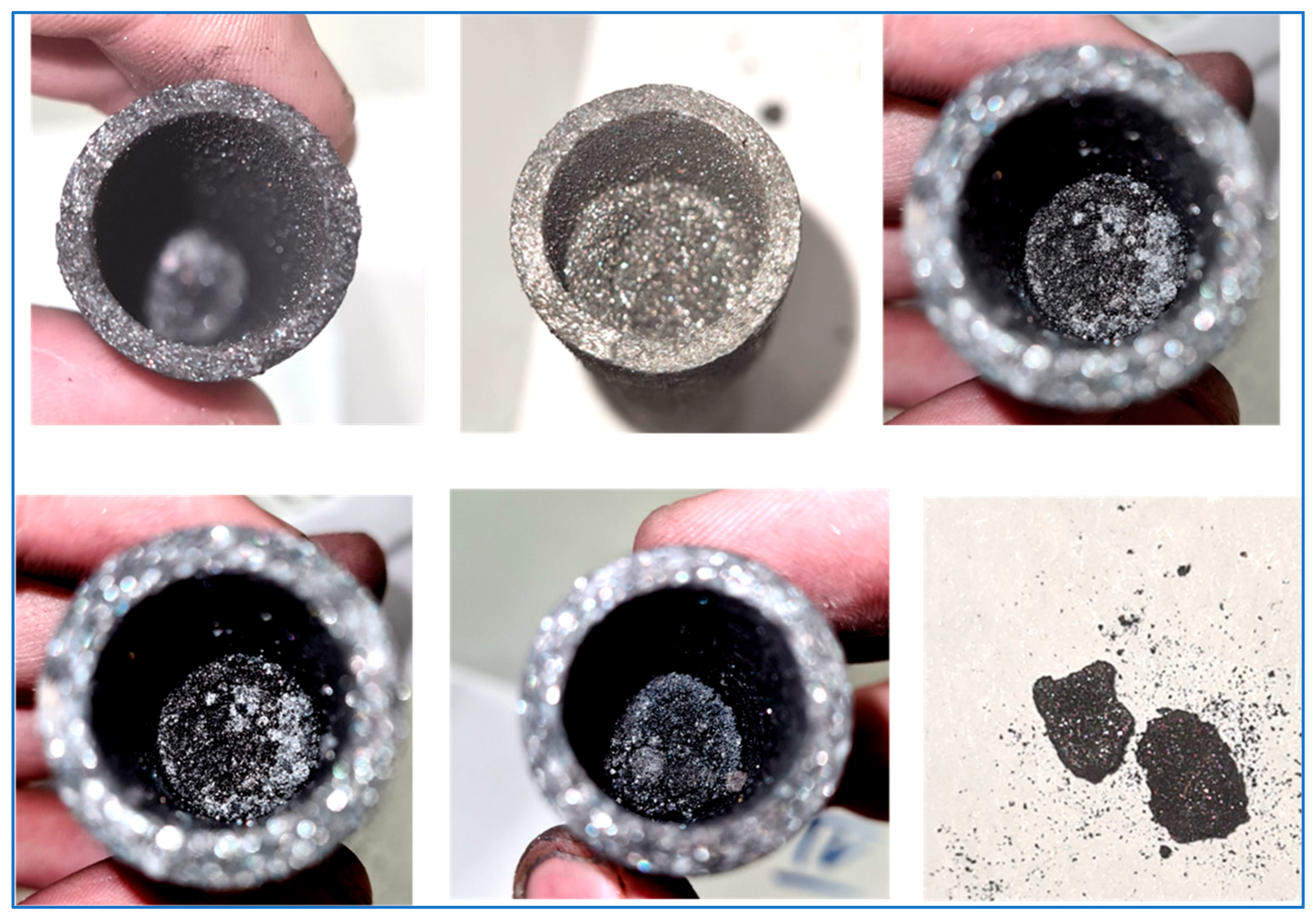


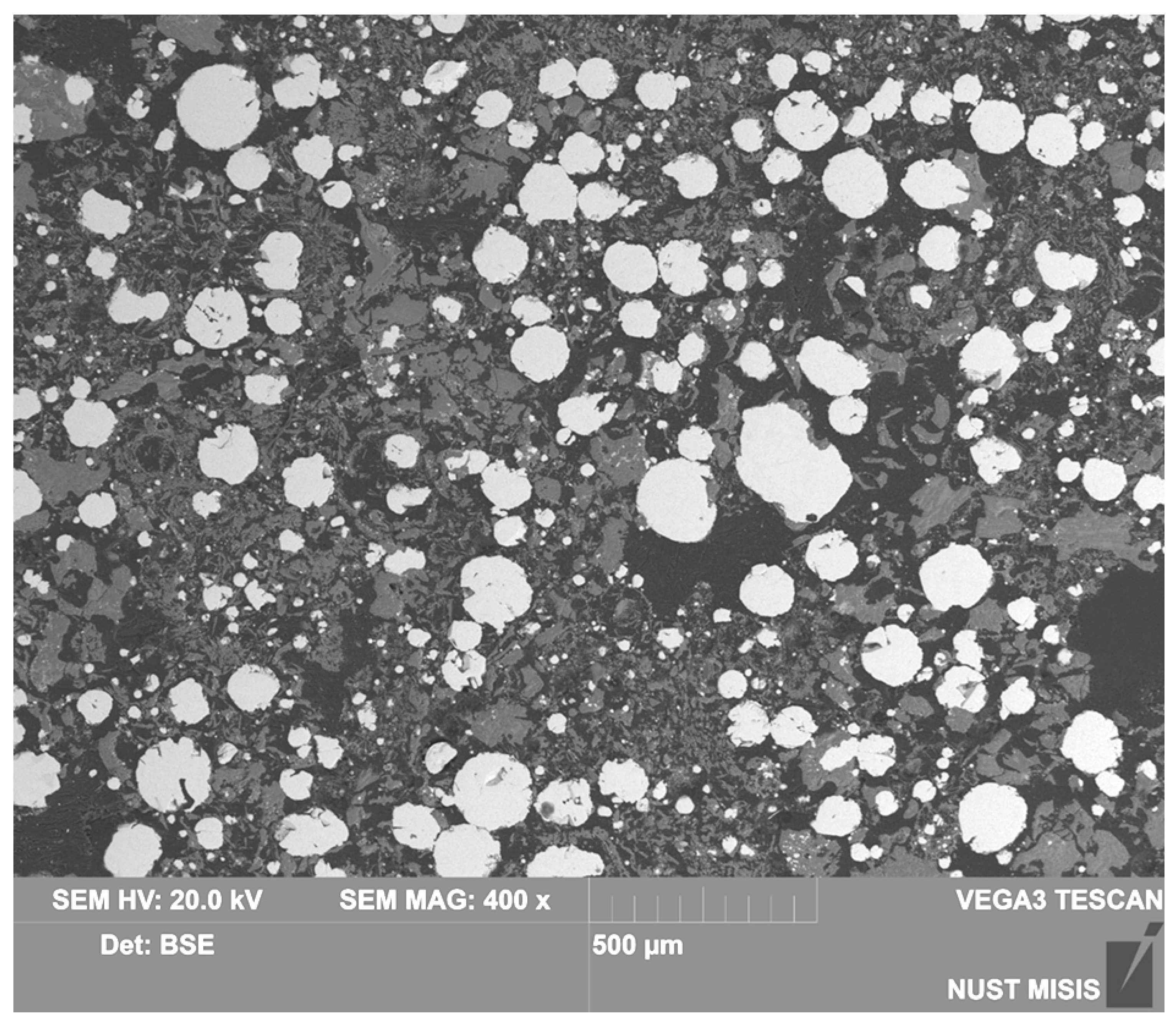
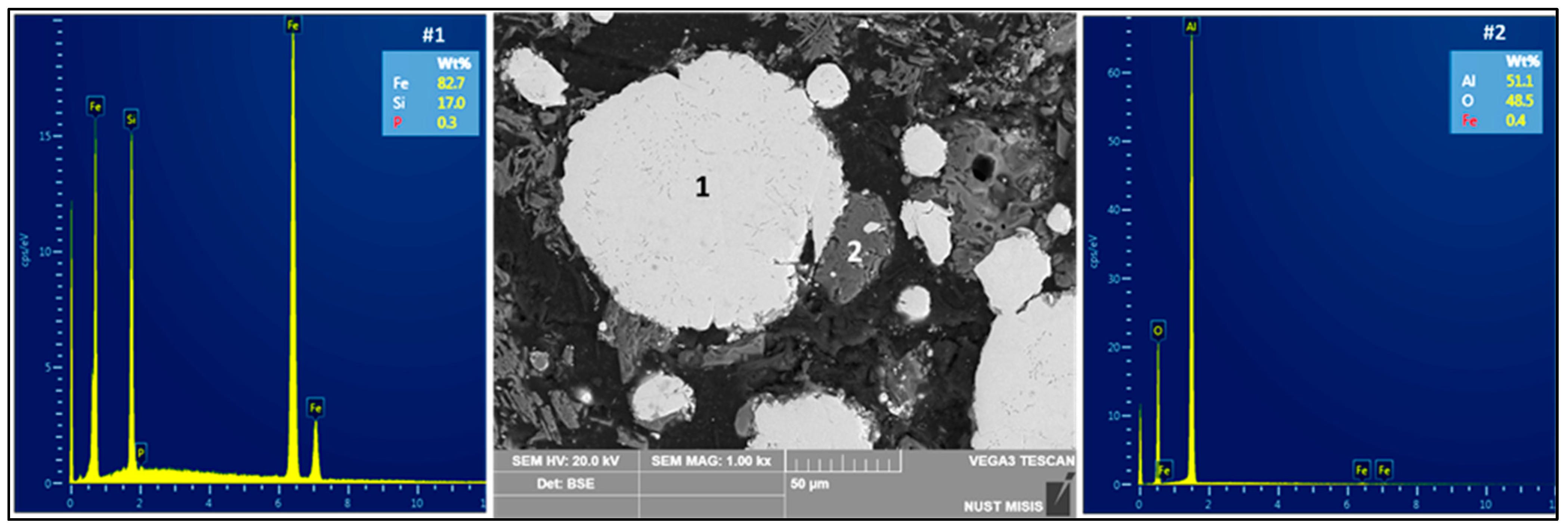
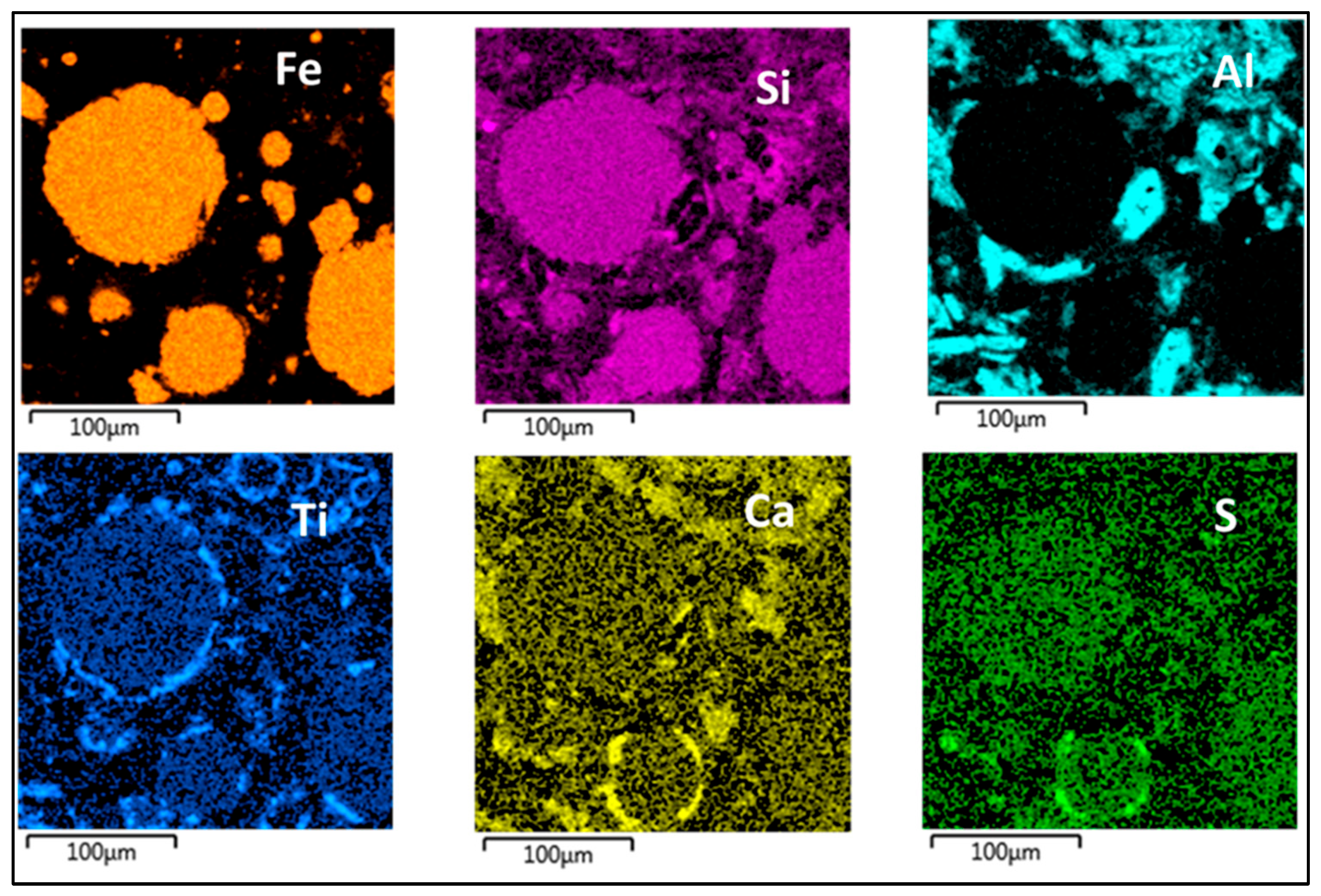
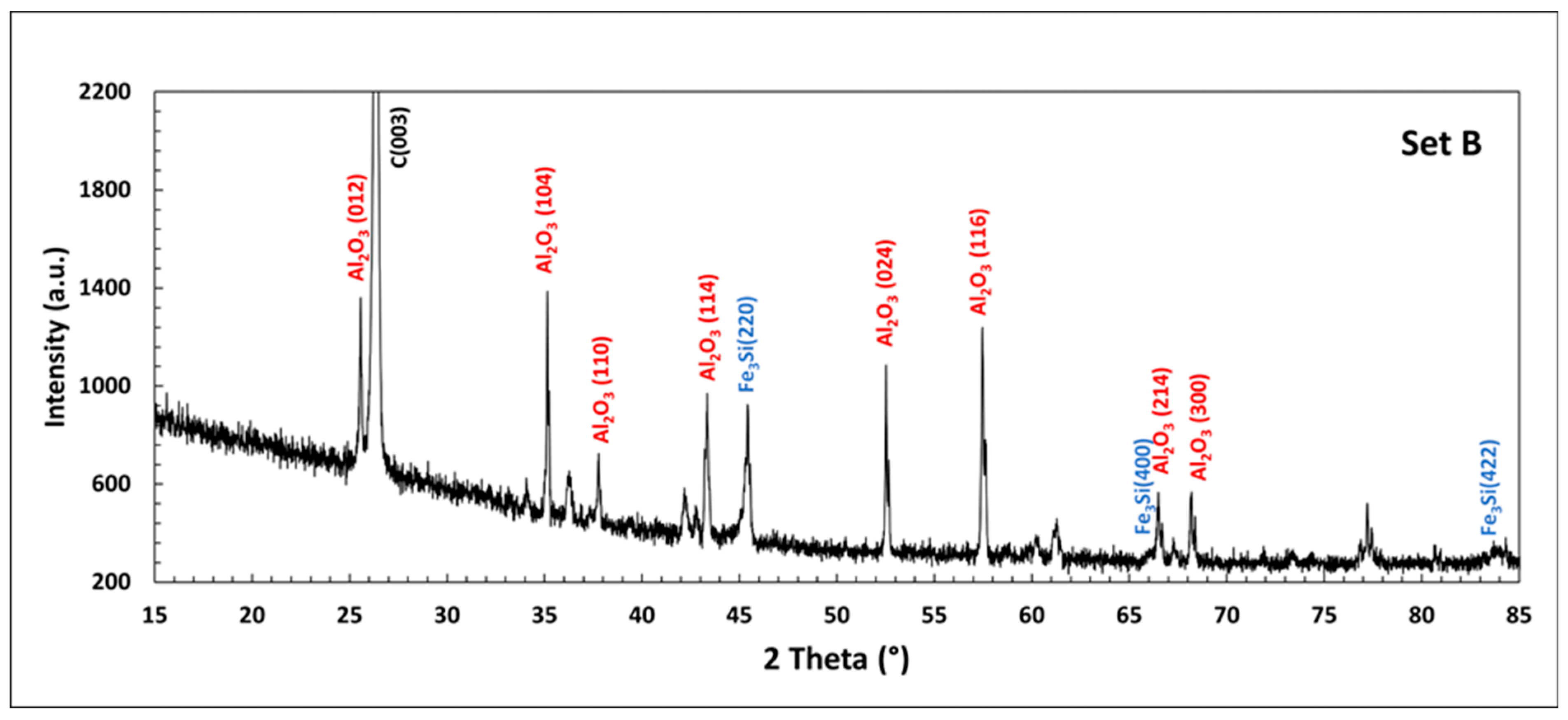
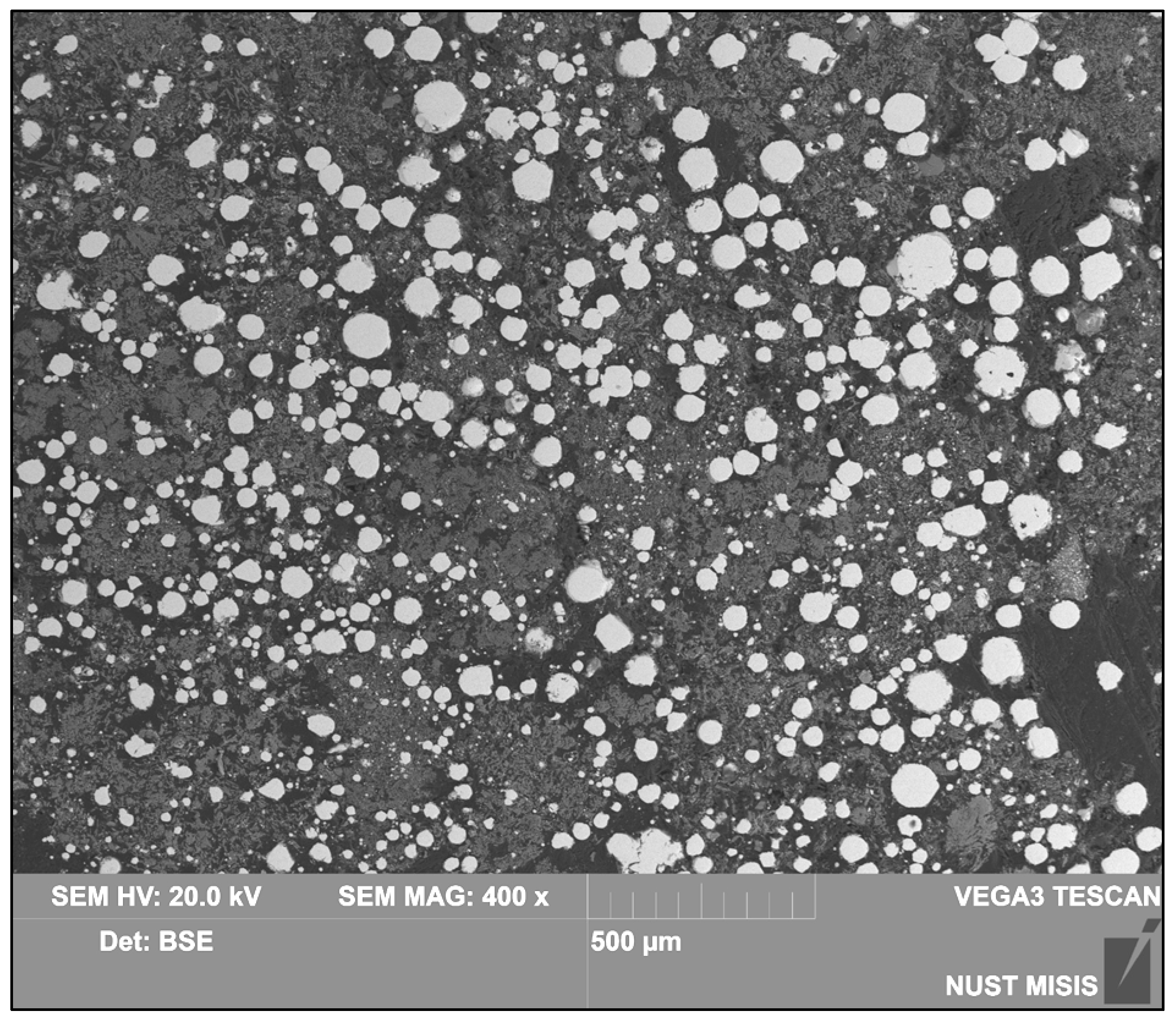
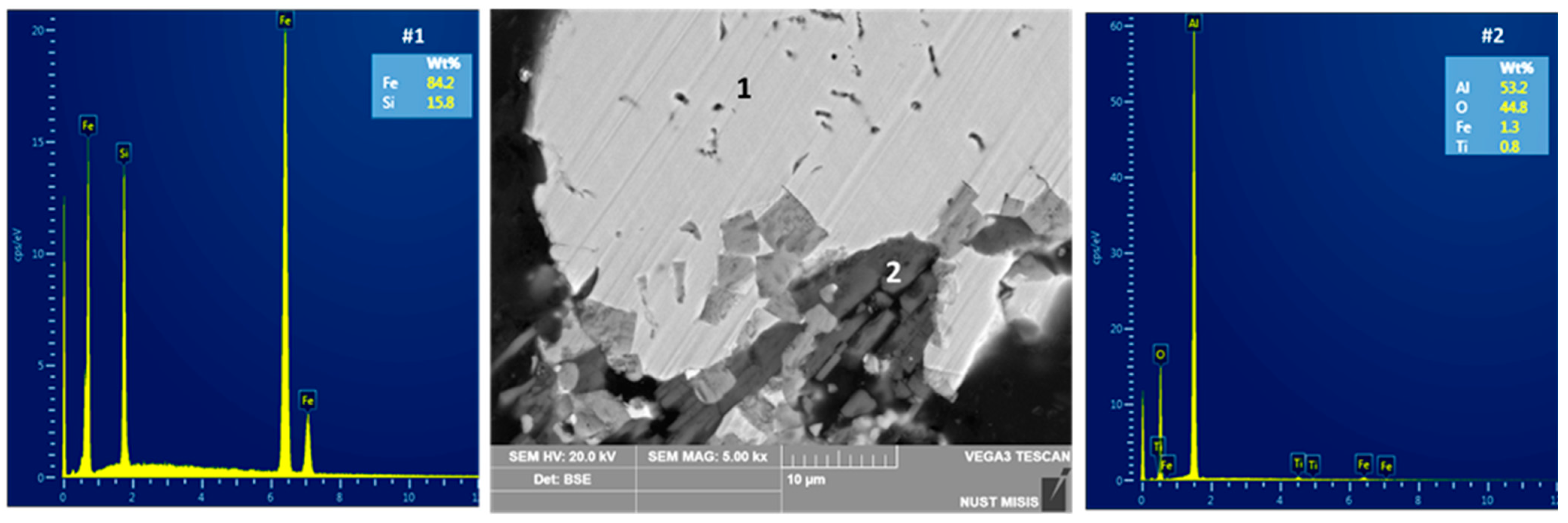
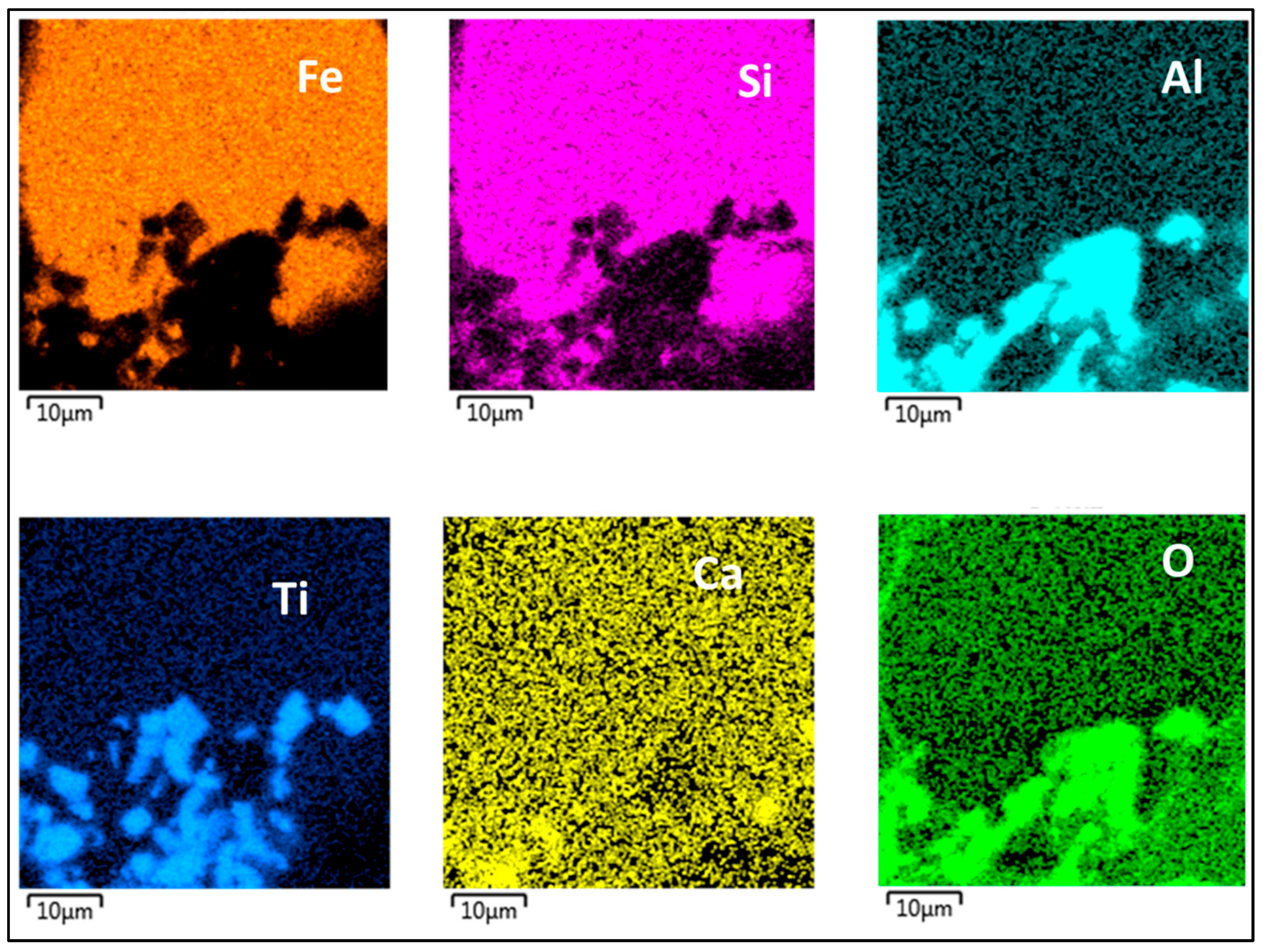
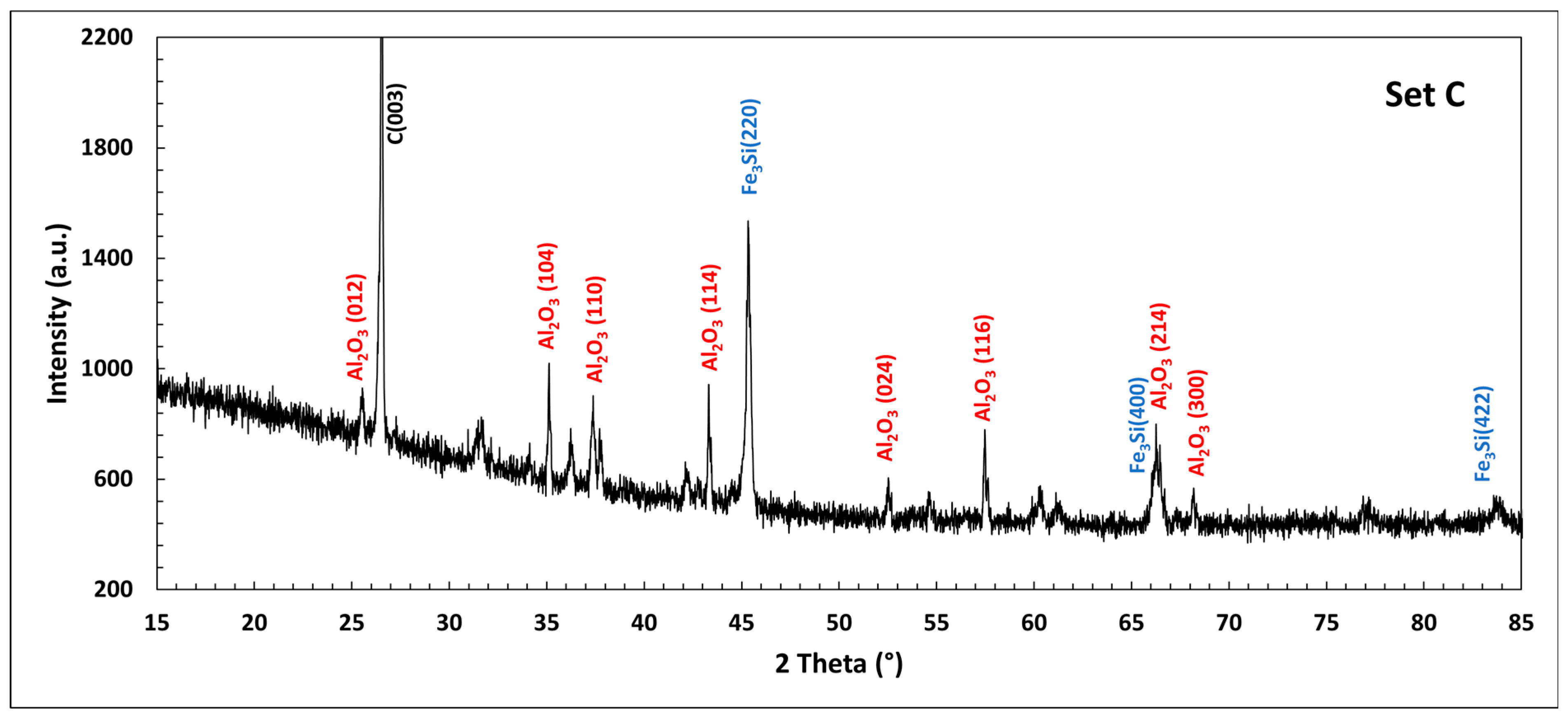
| Country | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| India | 28.1 | 21.9 | 7.5 | 10.2 | Hindalco Renukoot [37] |
| 27.9 | 19.4 | 7.3 | 11.8 | BALCO Korba [37] | |
| 24.5 | 24.3 | 6.2 | - | INDAL Muri [37] | |
| Turkey | 36.9 | 20.4 | 15.7 | 2.2 | SAP Konya [38] |
| 35.0 | 20.2 | 13.5 | 5.3 | SAP Konya [39] | |
| China | 13.7 | 7.0 | 18.1 | 42.2 | Shandong [40] |
| 11.8 | 25.5 | 20.6 | 14.0 | Henan [41] | |
| 6.8 | 10.1 | 22.2 | 42.3 | Shanxi [41] | |
| Korea | 16.6 | 23.7 | 22.9 | 6.7 | Korea Chemical [42] |
| Italy | 15.2 | 24.7 | 18.6 | 4.2 | Eurallumina [43] |
| France | 26.6 | 15.0 | 5.0 | 22.2 | [44] |
| Canada | 31.6 | 20.6 | 8.8 | 1.6 | ALCAN [45] |
| Australia | 29.6 | 17.3 | 30.0 | 3.6 | ALCOA [46] |
| 28.5 | 24.0 | 18.8 | 5.3 | ALCOA [46] |
| Blends | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | Na2O | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM | 29.3 | 22.2 | 20.0 | 1.2 | 12.2 | 3.4 |
| 20 g RM + 10 g Fe2O3 | 53.0 | 14.9 | 13.4 | 0.8 | 8.2 | 2.3 |
| 20 g RM + 10 g red MS | 64.6 | 11.1 | 10.0 | 0.6 | 6.1 | 1.7 |
| Blends | 100% RM | RM/Fe2O3 | RM/Red MS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic droplets | |||
| Size range | 10–100 μm | 100–300 μm | 25–125 μm |
| Composition | Si (16.6–24.3 wt.%), balance Fe | Si (17 wt.%), balance Fe | Si (15.8 wt.%), balance Fe |
| Number density | Low | High | High |
| Slag Composition | Al2O3, CaO, MgO, SiO2 etc. | Primarily Al2O3, Fe2O3, TiO2 | Primarily Al2O3, Fe2O3, TiO2 |
| Alumina segregation | Limited extent | Extensive | Extensive |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khanna, R.; Zinoveev, D.; Konyukhov, Y.; Li, K.; Maslennikov, N.; Burmistrov, I.; Kargin, J.; Kravchenko, M.; Mukherjee, P.S. Extraction of Alumina and Alumina-Based Cermets from Iron-Lean Red Muds Using Carbothermic Reduction of Silica and Iron Oxides. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156802
Khanna R, Zinoveev D, Konyukhov Y, Li K, Maslennikov N, Burmistrov I, Kargin J, Kravchenko M, Mukherjee PS. Extraction of Alumina and Alumina-Based Cermets from Iron-Lean Red Muds Using Carbothermic Reduction of Silica and Iron Oxides. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156802
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhanna, Rita, Dmitry Zinoveev, Yuri Konyukhov, Kejiang Li, Nikita Maslennikov, Igor Burmistrov, Jumat Kargin, Maksim Kravchenko, and Partha Sarathy Mukherjee. 2025. "Extraction of Alumina and Alumina-Based Cermets from Iron-Lean Red Muds Using Carbothermic Reduction of Silica and Iron Oxides" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156802
APA StyleKhanna, R., Zinoveev, D., Konyukhov, Y., Li, K., Maslennikov, N., Burmistrov, I., Kargin, J., Kravchenko, M., & Mukherjee, P. S. (2025). Extraction of Alumina and Alumina-Based Cermets from Iron-Lean Red Muds Using Carbothermic Reduction of Silica and Iron Oxides. Sustainability, 17(15), 6802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156802








