Abstract
This article presents an innovative approach as a potential alternative for the reuse of discarded green mussel shells from the fishing and food sectors. This technique entails the use of harmless chemicals and the consumption of energy in an efficient manner to generate shell powder of different dimensions. The shell powder was categorized into three distinct sizes to investigate changes after heat treatment. SEM-EDS was used to analyze particle sizes before calcination and examine the microstructure of heated shell powder. FTIR spectroscopy was conducted to assess the purity of all sizes before and after calcination, showing excellent cleanliness suitable for practical applications. XRD spectroscopy was used to examine the crystal structure, while thermal characteristics and surface color changes during heat treatment were also analyzed due to their impact on final product quality. The variety in particle size enhances the potential for diverse industrial applications. Each size may be suitable for different artificial sand uses, as noted in the conclusion. The proposed method provides both environmental and economic advantages by converting shell waste into a sustainable substitute for artificial sand. It utilizes low-cost, readily available materials and aligns with circular economy principles by reducing shell waste accumulation and dependence on natural aggregates.
1. Introduction
Thailand is renowned for its abundant food resources and is one of the leading countries globally in terms of food production and export, notably in the seafood industry [1,2]. Nevertheless, the primary challenge of seafood production and export lies in appropriate waste management, particularly in tourist and industrial regions, where the handling of seafood waste continues to be troublesome. Worldwide, mollusk shells (oysters, clams, scallops, and mussels) generate over 10 million tons of waste annually [3,4]. In Thailand’s context, the green mussel industry produced approximately 51,000 tons in 2022. Given that shells comprise 65–70% of the total weight, this volume translates to roughly 35,000–40,000 of shell waste per year in Thailand. This figure demonstrates the significance of local shell waste accumulation relative to the global scale of the problem. In these regions, effective waste management is required due to the occurrence of unpleasant odors from spoiling seafood trash when it is not properly managed over long periods of time. Typically, this trash is allowed to undergo natural decomposition, hence exacerbating the destruction of the environment [5]. Concurrently, the construction industry faces significant environmental challenges from conventional aggregate extraction. The mining of natural aggregates (sand, gravel, limestone, and crushed stone) leads to habitat destruction, soil erosion, water pollution, and depletion of natural resources [6,7]. Additionally, the process generates substantial greenhouse gas emissions, contributes to global warming, causes air pollution, and results in noise pollution [7]. Therefore, developing sustainable alternatives that can simultaneously address shell waste accumulation and reduce dependency on natural aggregate extraction presents a dual environmental benefit through circular economic principles. In addition, this approach to shell waste management aligns with several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), by promoting resource efficiency and circular use of seafood waste. It also supports SDG 13 (Climate Action) through energy-efficient processing that reduces environmental impact and SDG 14 (Life Below Water) by minimizing marine pollution from shell waste accumulation. Additionally, it contributes to SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) by offering potential community-based solutions for waste reduction and sustainable material innovation.
The eastern regions of Thailand, such as Chonburi, Rayong, Chanthaburi, and Trat, are coastal areas where many residents engage in seafood harvesting and processing. These places are also notable tourist sites, drawing a large number of visitors from all over the globe, resulting in a substantial demand for seafood. Shellfish is highly sought after for its delectable flavor and exceptional nutritional advantages. Mussel is a highly popular shellfish due to its widespread availability and versatility in culinary preparations. This gives rise to the issue of accumulated mussel shell waste. Presently, the disposal of trash generated by the seafood industry, particularly mussel shells, presents a substantial obstacle (Figure 1). After consuming the meat, an estimated 5 million tons of shells are discarded annually, mostly through landfill, which is improper as it causes soil and water pollution, reduces soil porosity and fertility, and impedes water absorption [8,9]. Shells require a maximum of 10 years to undergo decomposition and are not biodegradable. Moreover, the expense associated with appropriately disposing of shell trash is substantial. Local restaurant owners and shell processors stated in interviews that trash disposal often entails burying the shells. Disused shells are frequently abandoned in residential or public spaces to undergo natural decomposition, leading to olfactory pollution, causing disruptions in communities, and serving as breeding sites for disease-causing microorganisms, which could potentially affect public health. Nevertheless, because of the irregular nature of this gathering, the trash gradually builds up, resulting in unpleasant smells and problems with air pollution. In addition, the decomposition of shell debris in acidic settings results in the release of carbon dioxide, which has a substantial impact on global warming [10,11].

Figure 1.
Seashell waste from fishing and food industries.
Due to the significant impact of shell waste on shellfish growers, sellers, and consumers, both in terms of practicality and economics, numerous research efforts have been made to convert shell waste into sustainable materials [12,13,14]. The scientific literature documents the utilization of several kinds of seashells for the creation of innovative biomaterials. The shells of bivalve mollusks are primarily composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), which is a key component in many materials. These shells have the potential to be valuable raw material for various uses. CaCO3 is widely recognized in various industries for its versatile uses, such as being a fluxing agent in the steel industry, a filler in the polymer business, and a raw ingredient for producing mortars, plasters, refractories, glasses, and additives [14,15,16]. The compound CaCO3 can undergo decomposition and be converted into calcium oxide (CaO) by a process called calcination [11,14,17,18,19]. The outcome is contingent upon the temperature at which calcination occurs and the characteristics of the compounds prior to the shell’s calcination. On the other hand, CaO has been used as a primary substance in the manufacturing of essential chemicals, including sodium carbonate, calcium carbide, calcium sulfite, calcium hydroxide, among others [14,15,16]. Both materials have garnered considerable attention in various applications.
The primary focus of most shellfish-based research is the investigation of the conversion of CaCO3 to CaO through the process of fire at various temperatures. The study focused on investigating the thermal decomposition of CaCO3 and analyzing the relationship between temperature and other factors, including lattice constants, thermal expansion coefficients, lattice strain, and crystallite size. The primary method for pre-treating seashells to obtain CaO is rinsing the shells with tap water. Subsequently, acetone or mild acids were employed to eliminate organic substances from the shell. Hence, certain chemicals used in manufacturing processes may have an impact on the environment. Subsequently, the shell was subjected to boiling for a duration of 30–60 min or followed by heating for 1–4 h at 105–120 °C and finally pulverized to obtain CaCO3 powder [14,17,20]. Once CaCO3 is acquired, the conventional approach to handling CaCO3 entails subjecting it to CaO use in high-temperature incineration prior to its utilization in other goods or small-scale industries [14,21,22]. This process necessitates the use of kilns and entails substantial energy and time consumption, yielding shell powder consisting of minute CaO particles. Consequently, it is not feasible for the local community to manage vast quantities of discarded shells independently [21,22,23,24,25].
This research aims to propose an alternative approach involving the extraction and refinement of CaCO3 from green mussel shells (GMSs), which are the predominant form of shellfish waste in the seafood sector. The method involves creating shell powder of different sizes through an eco-friendly chemical approach to obtain CaCO3 and CaO. It utilizes an alkaline solution to eliminate organic impurities, which may be safely discharged into the environment upon completion of the process without causing any harm to the local community. The production process is straightforward, energy-efficient, and does not necessitate heating for several hours. By employing grinding techniques, the particle size of the shell powder may be regulated, rendering it appropriate for various industrial uses. It is possible to create distinct products that are suitable for each size. Producing alternate types of different-sized CaCO3 products could be a viable method to handle shellfish waste without resorting to incineration. Therefore, before undergoing the calcination process, the properties of CaCO3 of each size were researched. Furthermore, we performed an analysis of the seashells’ color both prior to and during thermal treatment, as the color of the seashells significantly influences the results of the diverse products [26,27]. Moreover, it indicates the level of purity and cleanliness of the processed shells.
As an alternative to converting CaCO3 powder into CaO, our research also investigates the calcination of various sizes of processed CaCO3 to CaO at a temperature of 800 °C. This temperature range was determined based on the calcination temperature of CaCO3 shells, which is typically between 700 and 900 °C. Additionally, 800 °C is commonly utilized in many applications of CaCO3. Additionally, the purity of the processed shell powder, both non-calcined and calcined GMS powder, was analyzed by FTIR spectroscopy, and the crystal structures of the shells were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques. Furthermore, we investigated the effect of temperature on the combustion of shells of varying sizes using thermogravimetry and differential thermal analysis (TG/DTA). This research yields useful insights that can be applied in diverse industries. In this study, we utilized waste shells for the purpose of sustainable application of artificial sand. Specific examples of the use of artificial sand made from GMS smash are also mentioned in the last section of the article.
2. Materials and Methods
The trash mussel shells were acquired from Bang Pra, Chonburi Province, Thailand. The shells were subjected to a washing process using tap water to remove any external debris and impurities. The production of GMS powder entailed submerging the discarded shells in a 3.00 M potassium hydroxide solution at room temperature (25 ± 2 °C) without stirring based on a previous study [28], which demonstrated its effectiveness in softening mollusk shells by partially dissolving the protein matrix. This procedure was conducted to efficiently eradicate organic debris, decomposing compounds, and detrimental bacteria found on the outer layer of the shells. After the soaking process, the used KOH solution was neutralized with dilute hydrochloric acid before disposal, following standard safety and environmental protocols. Subsequently, they were cleansed and dried in the atmosphere. A laboratory rollerball mill was employed to grind the crushed seashells into a finely powdered form for 10 min at 400 rpm to ensure fine and consistent particle size. Afterwards, the crushed shell powder underwent filtration using mesh with pore diameters of 200, 60, and 20 μm to separate and collect the sections with different particle sizes that were used in this investigation. Figure 2 depicts the thorough preparation process. The figure exhibits color photographs of waste GMS and finely powdered GMS powder. In order to examine the effects of different sizes of calcined crushed shell powder on appearance and structural changes, the powder was passed through various sizes of sieves and then exposed to calcination at a temperature of 800 °C for 1 h using an electric furnace. The non-calcined and calcined samples underwent investigation utilizing Scanning Electron Microscope and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometer (SEM-EDS), TG-DTA, XRD spectroscopy, UV-Visible spectroscopy, and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy.
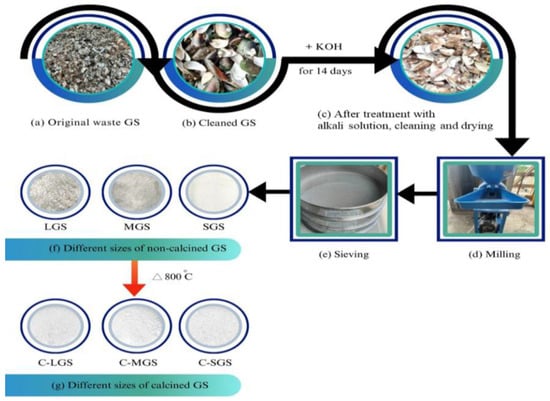
Figure 2.
The pre-treatment procedure for green mussel shell (GMS) powder.
The Shimadzu 2600 UV-Visible spectrophotometer (Kyoto, Japan) was used to analyze the reflectance spectra of the samples. The measurements were conducted using reflection mode with a wavelength range of 350 nm to 800 nm. The color variations in the samples were examined using the CIE L*a*b* color measurement. Each color index can be individually interpreted. L* represents the numerical value of brightness, ranging from 0 (representing black) to 100 (representing white). There is no specific numerical limit for the variables a* and b*. The colors will intensify as the magnitudes of a* and b* grow. Red represents positive a*, whereas green represents negative a*. Similarly, yellow represents positive b*, while blue represents negative b*.
The scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) technique was used to investigate the surface morphology of various sizes of crushed GMS using the JEOL JSM-6510 A instrument (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). To determine the crystalline phases present in the GMS powder, X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were obtained for each of the shells of various sizes. X-ray examinations were conducted to determine the mineralogical phases present in the GMS at both room temperature and after being heated to 800 °C. In order to achieve this objective, a Bruker D8 X-Ray Diffractometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) was utilized. The thermal profile measurement and weight loss during heating were measured using a simultaneous thermogravimetric analyzer (STA Instrument, NETZSCH STA 449C model, Dresden, Germany).
FTIR spectroscopy was carried out using a Thermo Scientific Nicolet Summit X FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The spectra were obtained using Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) techniques. The ATR-FTIR spectra were acquired via the Smart Everest ATR attachment. The spectra were obtained in the mid-infrared range from 500 to 4000 cm−1. Each spectrum was collected using 64 accumulations with a spectral resolution of 4 cm−1. The various dimensions of the GMS crush were positioned on a diamond IRE, and meticulous measures were implemented to ensure accurate contact. Before further examination, baseline correction was performed on the observed spectra.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Appearance and Color
The particle sizes were not only solely based on standard sieve mesh sizes but also selected based on observable differences in surface appearance and morphology, as shown in Table 1. During the process of grinding and sieving the shell, it was observed that the largest crushed green mussel shell (LGS) retained a noticeable iridescent quality from the inner layer of the shell. The LGS displays a blend of brownish-gray and yellow tones, mixed with white, which signifies that an alkaline environment can degrade proteins into tiny peptides, resulting in the formation of brown-colored substances [29,30]. The medium grain size (MGS) group consisted of fine but visibly shiny flakes, showing iridescent sparkle. These were particles mostly passing through a 200-mesh but retained on a 325-mesh sieve, exhibiting partial aragonite reflectivity and suggesting crystalline fragments in the submicron range. The small grain size (SGS) group included extremely fine particles with no visible luster, resembling talc-like powder. These particles were collected from the fine residue that had a dull and non-reflective appearance. Table 1 provides comprehensive comparisons of the crushed shells before and after being subjected to calcination at a temperature of 800 °C. After calcination at a temperature of 800 °C, all three shell sizes exhibited a white powdery residue that lacked iridescence and had a white appearance with a subtle yellowish-gray hue.

Table 1.
Appearance and color values of different-sized GMSs.
Table 1 demonstrates that the L* values of all calcined samples exhibited an increase in appearance and color. Furthermore, the a*b* values of the calcined shells shift towards a neutral value, indicating a lighter shade and transition to a white color. This change corresponds to the visual appearance of the shell powder obtained from all calcined samples. The L*a*b* values demonstrate the color alteration effects prior to and following the application of heat, as depicted in Figure 3. The graph shows a rise in the luminosity, or L* value, of each sample (Figure 3a), along with movement towards greater negative values in the a* and b* values (Figure 3b). The calcined GMS had the palest hue and the closest similarity to the white reference after calcination at 800 °C. The alteration in hue of the specimen pertains to the phenomenon of CaCO3 calcination. The study conducted by N. Suwannasingha et al. [14] discovered that subjecting marine shell debris to calcination at a temperature of 700 °C produces a gray hue, which progressively transitions to a lighter shade of yellow at 900 °C. The transformation of CaCO3 into CaO can be achieved. These data exhibited a comparable pattern to our observation. Furthermore, our discovery demonstrates that exposing shells of different sizes and initial flake characteristics to a temperature of 800 °C can uniformly transform them into CaO powder, regardless of their size.
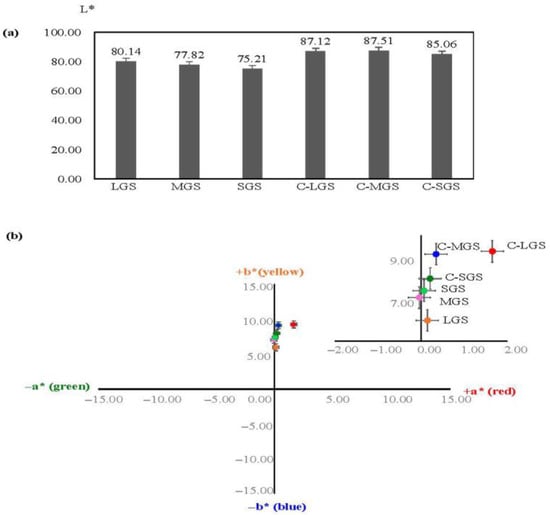
Figure 3.
Color values of different-sized non-calcined and calcined GMSs: (a) L* and (b) a*b* diagram, with enlarged areas shown above for better visibility. L* indicates lightness (higher = brighter); a* indicates red (+) to green (−); b* indicates yellow (+) to blue (−). Dot colors represent sample types: orange = LGS, pink = MGS, light green = SGS, red = C-LGS, blue = C-MGS, dark green = C-SGS.
Figure 4 presents the reflection spectra of the samples. The calcined crushed shells of SGS and MGS exhibit a higher reflection percentage compared to the non-calcined crushed shells. The reflectance of calcined crushed shells (C-SGS) is 1.2 times more than that of non-calcined crushed shells, while the reflectance of calcined mixed grain shells (C-MGS) is 1.8 times greater. Computation was performed using the percent reflectance value at a wavelength of 550 nm. The observed outcomes could potentially be attributed to the increased surface area of calcined crushed shells, resulting in enhanced light scattering. However, LGS has the highest reflectance due to its strong angular reflection, as mentioned by reference Lertvachirapaiboon [28]. Such an effect ultimately results in a higher overall reflection value.
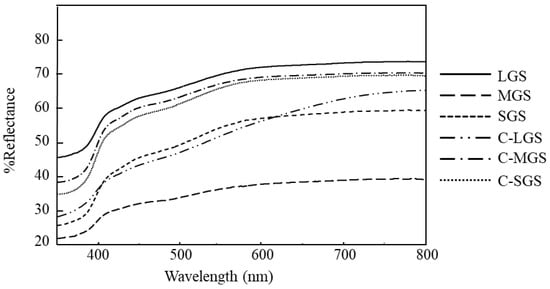
Figure 4.
Reflectance spectra of different-sized non-calcined and calcined GMSs.
The color transformation observed during calcination presents significant implications for material applications. For products such as artificial sand and decorative materials, chromatic properties and light reflectance characteristics directly influence esthetic value and commercial viability. The achievement of uniform white coloration following thermal treatment enhances material suitability for decorative applications, including ceramic composites, architectural finishes, and ornamental concrete products. These findings enable the optimization of processing parameters to satisfy specific esthetic and functional requirements across diverse applications.
3.2. Morphology Observation by SEM-EDS
A Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) was used to analyze the structure and shape of crushed GMSs of different sizes, as depicted in Figure 5. The Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) pictures shown in Figure 5a illustrate the LGS particles that have a plate-like structure with a size that ranges from around 1800 to 2000 microns. SEM images of MGS and SGS are depicted in Figure 5b and Figure 5c, respectively. The shells have average diameters of approximately 400 microns and 200 microns, respectively. The SEM pictures in Figure 5d–f depict the surface of fragmented shells. The diagram illustrates the preserved structure of the mussel shell, which consists of stacked layers of plate-shaped CaCO3. This enables the crushed shells to possess exceptional light-reflecting characteristics [28,31]. Small fragments of aragonite plates are present on the surface of the crushed shells. The SEM images of calcined crushed shells are depicted in Figure 5g–i. Following the calcination process, CaCO3 underwent decomposition, resulting in the release of CO2 and subsequent decomposition of the organic matrix present in the crushed shell. The relevant data may be found in the thermal profile section. The results indicated that the crushed shell underwent fragmentation into smaller particles, whereas the surface between the CaCO3 plates experienced sintering and fusing together [19,32]. Subsequently, shrinking of the CaCO3 plates was observed.
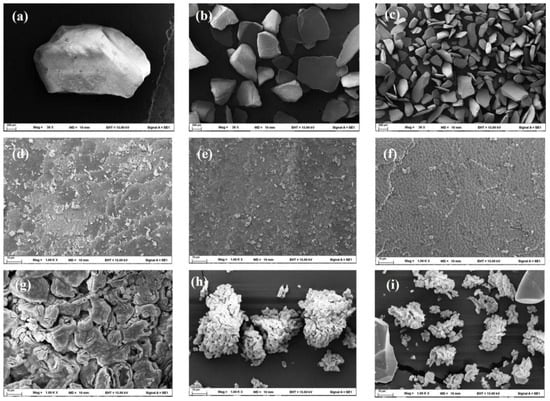
Figure 5.
SEM images of ground shell powder: (a–c) particle size comparison of LGS, MGS, and SGS (200 μm scale); (d–f) surface textures of uncalcined powder (10 μm scale); (g–i) morphological changes after calcination showing particle agglomeration (10 μm scale).
The elemental analysis conducted with Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) indicated that both crushed shells and calcined crushed shells consist of calcium (Ca), carbon (C), oxygen (O), and sodium (Na) content, as shown in Table 2. Moreover, XRD analysis reveals a comprehensive composition analysis of crushed shells and calcined crushed shells. This finding is consistent with previous studies on biogenic carbonates, including foraminiferal calcite, which suggest that Na can be incorporated in both primary and secondary phases of CaCO3 [33]. In addition to the SEM-EDS results, structural and compositional analyses of ground and calcined green mussel shells were further performed using XRD, as shown in Figure 6.

Table 2.
The composition of elements in crushed shells and calcined crushed shells was measured by SEM-EDS analysis.
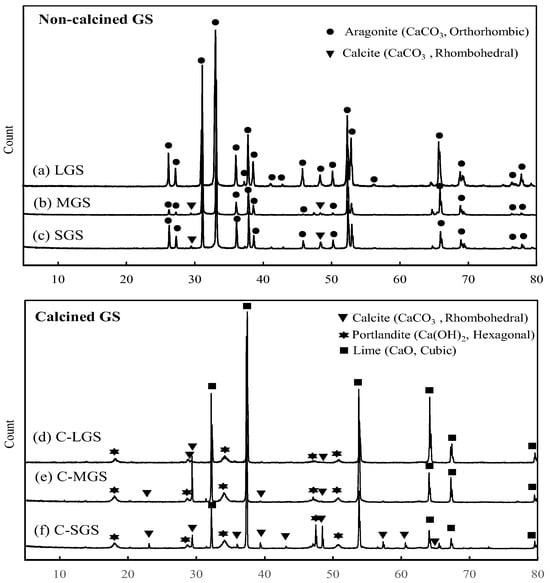
Figure 6.
XRD spectra of different-sized non-calcined and calcined GMSs: (a) LGS; (b) MGS; (c) SGS; (d) C-LGS; (e) C-MGS; and (f) C-SGS.
3.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
The XRD spectrum of LGS, as shown in Figure 6a, unequivocally demonstrates the presence of the aragonite polymorph with a purity of 100%. Figure 6b,c displays the XRD spectra of MGS and SGS, respectively. The experimental results indicate that the shells, which vary in size from moderate to small, consist of a combination of calcite and aragonite polymorphs of CaCO3. This occurrence can be attributed to the thermal energy generated during the grinding and erosion of the shell during processing, resulting in the creation of small amounts of different crystal forms of calcite within the CaCO3 structure. Figure 6d–f displays the X-ray diffraction spectra of the calcined powder from all three shell sizes at a temperature of 800 °C. Figure 6d illustrates the results of the LGS after undergoing the most thorough calcination process. The presence of lime (CaO) appears to exist, whereas only a small quantity of CaCO3 in the form of calcite is present. In addition, the presence of portlandite (Ca(OH)2) is indicated at trace levels, which are less than 1%. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of medium- and small-sized shells after calcination, as shown in Figure 6e,f, reveal higher concentrations of CaO and Ca(OH)2 compared to the larger shells. The difference can be attributed to the larger surface area of smaller broken shells, which enables them to efficiently release heat energy and decompose at a faster rate [34,35]. Furthermore, if an atmosphere with oxidizing properties is present during the calcination process, there is an increased likelihood of CaO, carbon dioxide, or water undergoing a reaction, leading to a greater production of Ca(OH)2 in comparison to larger shells.
These experimental findings offer useful information regarding material application, as the variation in aragonite-to-calcite ratios across different particle sizes enables targeted material selection for optimal product performance. Aragonite provides superior mechanical strength and hardness, making aragonite-rich fractions ideal for high-strength structural applications. Conversely, calcite exhibits higher chemical reactivity with cement matrices, enhancing bonding performance and making calcite-dominant materials suitable for chemically reactive composite systems. These polymorphic differences also influence particle morphology, surface characteristics, workability, and packing density. Understanding these size-dependent polymorphic compositions allows for tailored material selection based on specific application requirements.
3.4. Thermal Profile
To comprehensively investigate the thermal degradation of shells of different sizes, the organic component content was measured using TG/DTA. Figure 7 exhibits the thermogravimetric (TG) and differential thermal analysis (DTA) curves for different sizes of GMS powder. All samples exhibit two distinguishable thermal transitions in their DTA diagrams, which are endothermic transition and exothermic transition. The DTA curve of LGS powder displayed endothermic peaks of heat absorption at around 275 °C and 453 °C. This peak corresponds closely to the temperature at which the organic substance on the shell undergoes fusion [14,30]. On the other hand, there is a clear exothermic process occurring at approximately 817 °C, which is linked to the thermal decomposition of CaCO3 into CaO. Figure 7b,c presents the TG/DTA results for MGS and SGS powder. An exothermic reaction was seen at temperatures of about 269 °C and 450 °C, indicating the decomposition of the organic component on the surface of the LGS powder. Furthermore, a thermally induced reaction occurred with a slight decrease in mass at the maximum recorded temperature of 811 °C for MGS powder and 804 °C for SGS powder. This reaction involves the decomposition of CaCO3 into CaO. The results indicated that the decomposition temperature of these powder had a slight fluctuation.
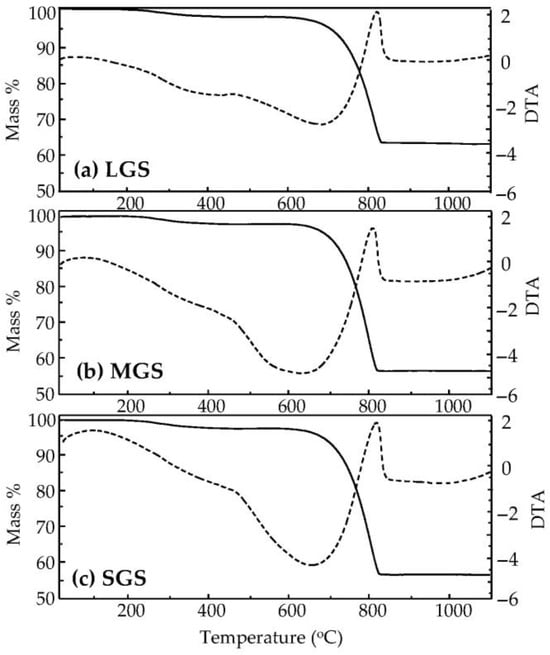
Figure 7.
TG-DTA diagrams illustrate various GMS sizes. (a) LGS; (b) MGS; and (c) SGS.
The average weight loss of all samples, due to organic decomposition, from room temperature to around 450 °C, is approximately 2.6%. Additionally, thermal analysis conducted on all variations in GS revealed that the decomposition of calcite takes place between the temperature range of 700 °C to 800 °C. The weight loss range observed in the TG curve, notably ranging from 35% to 42%, is attributed to the liberation of gaseous carbon dioxide (CO2) [11,18,35]. TG analysis reveals that the weight loss percentage in LGS is 35.78%, which is comparatively lower than that of MGS (41.25%) and SGS (41.33%). The DSC curve has an endothermic form between 700 °C and 800 °C, indicating that the thermal breakdown initiated slowly and then increased significantly when the temperature exceeded 750 °C. The analysis of X-ray diffraction (Figure 6) further confirms this observation. The X-ray diffractograms unequivocally illustrate the creation of CaO and the total absence of calcite at around 800 °C, showing the culmination of thermal degradation. The results correspond to the quantity of CaO and Ca(OH)2 produced during the decomposition of CaCO3, as seen in Figure 6e,f. The relationship between temperature and composition during the thermal conversion of calcite demonstrates a noticeable shift in composition or an accelerated rate of conversion at 800 °C from CaCO3 to CaO and Ca(OH)2 (Figure 6e,f). The differences observed between LGS, MGS, and SGS are primarily attributed to the surface area-to-volume ratio and diffusion kinetics during thermal decomposition. Finer particles (SGS and MGS) possess a higher surface area, which facilitates faster and more uniform thermal degradation of organic matter and volatile components. As a result, these samples tend to exhibit slightly higher and more complete weight loss compared to LGS during TGA. In contrast, the coarser LGS particles may retain more structural water or residual organics in their interior due to limited diffusion, leading to slightly lower or more gradual weight loss profiles.
3.5. FT-IR Spectroscopy
The study employed ATR-FTIR spectroscopy to evaluate the purity of GMS after a green chemical procedure and to characterize the changes in functional groups in GMS after calcination. Figure 8 exhibits the ATR spectra of different dimensions of crushed GMS. Figure 7a shows the particular wavenumbers at which the absorption peaks of LGS powder are observed: 700, 712, 854, 1080, 1240, 1414, 1473, 1635, and 1785 cm−1 [14]. The presence of the aragonite phase is responsible for the observed peaks, as supported by the XRD data presented in Figure 6a. A band detected within the 1400–1470 cm−1 range indicates the stretching of the C-O bonds in carbonate. The shell displays a prominent absorption in this area, which is a distinctive characteristic of aragonite. In addition, the LGS spectra display a carbonate out-of-plane bending vibration at 854 cm−1 and an in-plane bending vibration at 700–712 cm−1 in its FTIR spectrum. Aragonite has a prominent double peak at 700 and 712 cm−1, with greater absorbance at 700 cm−1 compared to 712 cm−1. The spectra of GMS exhibited an absorption peak at 1080 cm−1, which suggests the existence of aragonite. This unique band is undetectable within the calcite structure. This result confirms the existence of aragonite in the GMS, which corresponds to the results of the XRD examination. Furthermore, the spectra display a clearly defined, narrow peak at 1780 cm−1, indicating the elongation of the C=O bond. In addition, there is minimal absorption of triplet bands within the range of 2500–2650 cm−1 and 2800–2950 cm−1 that correspond to the brownish-gray color in their appearance (Table 1). These bands are caused by the existence of residual organic molecules in the broken shell. In addition, a weak band at 3300 cm−1, which indicates the absorption of OH groups, was seen. This observation provides convincing evidence of the dimensions of the non-calcined shell.
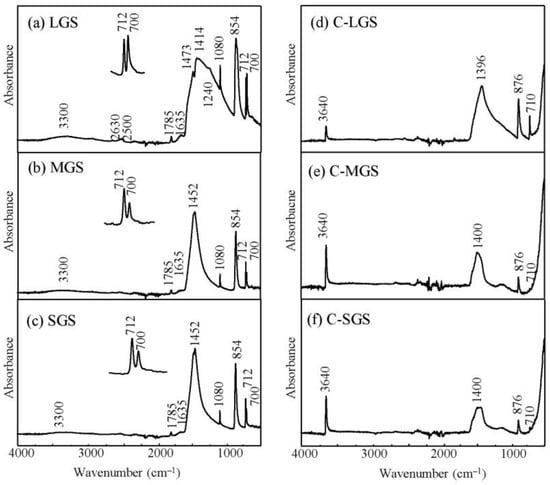
Figure 8.
FTIR spectra of different-sized non-calcined and calcined GMSs: (a) LGS; (b) MGS; (c) SGS; (d) C-LGS; (e) C-MGS; and (f) C-SGS.
The FT-IR spectra of MGS and SGS show a similar pattern, which is characteristic of CaCO3 at specific wavenumbers of 700, 712, 840, 854, 1230, 1400, 1635, 1785, 2500, and 2630 cm−1 (Figure 8b,c) [14]. Unlike LGS (Figure 8a), these samples have a single peak at 1452 cm−1, which is indicative of calcite. Moreover, when analyzing the two peaks at 700 and 712 cm−1, it is evident that the absorbance at 712 cm−1, which represents the existence of calcite, is higher than the absorbance at 700 cm−1, which indicates the existence of aragonite. The MGS and SGS spectra both display an absorption peak around 1080 cm−1, which is comparable to the LGS spectra. This peak indicates the coexistence of aragonite and calcite in the structure. This discovery offers further substantiation of the existence of aragonite in the clam shells, confirming the outcomes derived from the XRD study.
Figure 8d–f shows the ATR spectra of all samples after calcination at a temperature of 800 °C. Every spectrum has an identical spectral pattern. The FT-IR spectra of the calcined powder indicated the presence of carbonate ions (CO32−) through the observation of C-O stretching bands, specifically at wavenumbers of 1400, 874, and 712 cm−1 [36]. The absence of the absorption peak at 700 cm−1 can be ascribed to the breakdown of aragonite. The peak at 853 cm−1 experiences a transition to 876 cm−1, indicating a unique vibration related to the conversion of CaO from the calcite phase to the calcite form of limestone. The conclusion was made based on the observation that the shell possessed bands with the same characteristics as limestone (CaO) at specific wavelengths: 1400 cm−1 (asymmetric stretching), 872 cm−1 (out-of-plane bending), and 712 cm−1 (in-plane bending) [14,37]. Moreover, the absorption peaks at 2800–2900 cm−1, 2600–2700 cm−1, and 3350 cm−1, which are caused by organic matter and the OH group of a little amount of water adsorbed on the surface, were completely removed after calcination. In all spectra, a distinct peak at 3640 cm−1 is detected, which corresponds to the O-H stretching of calcium hydroxide or portlandite. After thermal decomposition at high temperature, CaCO3 is converted into CaO. Portlandite (Ca(OH)2) is subsequently produced by the interaction of CaO with water or atmospheric moisture [38,39], as shown in Equations (1) and (2):
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
Following the process of calcination, the CaCO3 underwent a conversion into CaO and CO2. CaO can undergo a chemical reaction with water or moisture in the atmosphere, resulting in the formation of Ca(OH)2. These results are consistent with the previous data reports [40]. Therefore, the ATR-FTIR spectra demonstrate that all GMS crushes are characterized by cleanliness, and the main component of the calcined aragonite form of GMS produces calcium. The correlation between the XRD and FT-IR results verified that all samples achieved complete conversion of CaCO3 to CaO at the calcination temperature of 800 °C.
3.6. Potential Future Implementation
At present, there is a noticeable inclination towards adopting substitute materials for sand obtained from organic materials, namely recycling used resources. Artificial sand serves as a viable substitute for natural sand, finding application in diverse fields. As we have demonstrated in the above experimental results, all GMS particle sizes are clean and non-toxic. Various sizes are suitable for different applications. Larger particles of GMS display a robust, esthetically pleasing, and lustrous surface, rendering them well-suited for ornamental applications. Medium-sized GMS particles can be used as artificial sand, while the finest particles, although less glossy, have a soft texture that is non-irritating. Comprehensive FTIR and EDS analyses further confirmed the absence of hazardous substances and heavy metals in all particle size fractions. The calcined GMS powder was shown to be chemically inert and biocompatible, presenting minimal health risks for children and animals under standard exposure conditions [41,42]. These findings affirm the material’s safety and functional versatility, supporting its broader application in construction, decorative, and other human-contact uses as an eco-friendly replacement for silicon dioxide (SiO2) sand.
In certain cases, exotic pet care, which is continuously gaining popularity, can substitute medium- and large-sized GMSs in this article for SiO2. Some exotic animals might ingest SiO2 sand, which poses a risk because it is indigestible and may cause blockages in the digestive system, irregular defecation, fecal retention, and constipation [41], especially in animals with complex or sensitive digestive systems. For example, reptiles such as lizards and snakes, as well as amphibians like frogs and salamanders, may face digestive problems if they accidentally ingest SiO2 sand. Using CaCO3 powder from GMSs as a substitute for SiO2 sand is a safer option in some cases because CaCO3 is digestible in the digestive systems of certain animals, particularly those that require calcium, such as reptiles and amphibians. Calcium is also beneficial for building bones and eggshells. Many animals, including turtles and lizards, can break down CaCO2 in their digestive systems, thereby supplementing their bodies with calcium. CaCO2 does not carry the same risk of gastrointestinal obstruction as SiO2, which is not digestible and may cause blockages.
Our clean medium-sized GMS powder can serve as a substrate in terrariums, vivariums, and aquariums for aquaculture and decoration, thereby creating an environment that closely mimics the natural habitat of these animals. Cleanliness is also a key characteristic of artificial sand for aquaculture. This type of artificial sand helps balance pH, cleanliness, and safety for aquatic animals. Additionally, certain shades are designed to create a genuine atmosphere accurately. As synthetic sand of different sizes can be used for specific purposes, particles with a diameter of less than 1 mm can be utilized for aquatic plants and soft-bodied invertebrates, such as snails and shrimp.
In addition, our medium and large crushed GMSs can be used as artificial sand in small Zen gardens and can also be mixed into home decor products by incorporating them into concrete to produce raw concrete pots, vases, bricks, and other decorative materials. The large aragonite surface’s luster, which resembles glitter, will enhance the products’ shine.
Small-sized GMSs are suitable for use as a substitute material for artificial sand for children, which is mostly made from silica sand, including finely crushed limestone or marble. Gypsum or certain types of plaster used in children’s toys may cause allergic reactions in children, especially if there are additional chemicals that could trigger allergies, such as preservatives or synthetic dyes. Allergic symptoms may include itching rashes, swelling, or respiratory issues. For this application, GMS that is finely ground and free from chemical residues is suitable because it is non-toxic, has hygienic properties, and is available in various particle sizes. Finely ground GMS also provides very fine particles with a smooth surface, which is gentle on the skin, thereby reducing the likelihood of skin irritation in children.
We focus on the valorization of GMS waste, which constitutes a significant environmental challenge not only in Thailand but across multiple geographical regions globally. The transformation of this marine waste stream into value-added products offers a threefold benefit: (1) the remediation of accumulated waste, (2) a reduction in future waste generation, and (3) the creation of economic opportunities for local communities. Moreover, our methodology enables the production of sand with varying particle size distributions through a controlled mechanical grinding process, thereby facilitating diverse application potentials. This approach presents a sustainable circular economy solution for developing alternative construction materials, particularly artificial sand, addressing both environmental concerns and resource scarcity in the construction industry.
To address the limitations of conventional shell treatment methods, we developed an environmentally friendly and energy-efficient approach using potassium hydroxide (KOH) soaking at ambient temperature. While traditional methods involving ketones or weak acids with thermal processing effectively remove organic matter, they often require high energy input and fume hoods and pose safety and environmental risks due to the volatility and corrosiveness of the chemicals involved. In contrast, our method eliminates the use of hazardous solvents and energy-intensive heating. The 14-day KOH soaking duration was optimized through preliminary testing, as shorter durations led to incomplete organic matter removal, confirmed by FTIR and SEM-EDS analyses. Although energy efficiency is qualitatively evident, this study acknowledges the lack of quantitative energy data, which should be addressed in future work through comprehensive energy monitoring and economic feasibility assessment.
We also evaluated the feasibility of scaling up the proposed process. The production method shows strong commercial viability due to the use of low-cost and readily available materials, such as mussel shells, water, and KOH, along with standard equipment like ball mills, sieves, and kilns, which are common in existing material processing industries. The process can be readily implemented under ambient pressure and manageable temperatures, supporting both batch and continuous production with commonly available equipment and without requiring specialized systems. These practical and economic advantages make the approach suitable for diverse operational scales—from small-scale community enterprises to large industrial systems—highlighting its potential for real-world deployment and contribution to sustainable circular economy practices.
4. Conclusions
The utilization of green mussel shells derived from seafood processing waste, subjected to chemical treatment protocols, facilitates the production of purified shell powder with controlled particle size distributions. The resulting powder exhibits pH neutralization properties, maintains high purity standards, and ensures safety compliance while requiring minimal energy input during manufacturing processes. Particle size modulation of the shell powder can be systematically controlled to meet specific application requirements. The developed method demonstrates environmental sustainability through its room temperature operation, eliminating the need for energy-intensive heating processes, drying ovens, or solvent evaporation commonly required in traditional synthesis approaches.
The optical reflectance characteristics of mussel shell powder demonstrate a positive correlation with particle size, exhibiting higher reflectance values for larger particles and progressively diminishing reflectance as particle dimensions decrease. Further analysis using FTIR and EDS confirmed that the shell powder obtained through this method possesses high purity and is safe for downstream applications. Differences in particle size influenced not only the optical properties but also the relative proportions of aragonite and calcite, as well as thermal behavior. These characteristics should be considered when selecting suitable particle sizes for specific applications, as discussed in the concluding section.
Upon calcination at 800 °C, all particle sizes underwent complete color transformation to white, and structural analysis revealed the conversion of aragonite and calcite phases into lime (CaO) and portlandite [Ca(OH)2], with no impurities detected post-treatment. The size-graded CaCO3 particles derived from GMS demonstrate versatility comparable to synthetic sand alternatives, finding applications across multiple industries including aquaculture systems, ornamental horticulture, specialized pet substrates, and therapeutic spa treatments. Furthermore, the CaO product obtained through 800 °C calcination maintains superior purity and whiteness characteristics, rendering it suitable for diverse industrial applications requiring high-grade calcium oxide.
These findings highlight both the environmental and economic benefits of upcycling seafood waste into high-value, sustainable materials. This indicates the value of continued research in developing sustainable materials from waste resources, as it plays a crucial role in supporting environmental conservation, resource efficiency, and long-term industrial innovation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.T., W.R. and C.L.; methodology, P.T. and C.L.; investigation, P.T. and C.L.; data curation, P.T. and C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, P.T.; writing—review and editing, C.L.; visualization, P.T. and W.R.; supervision, P.T.; project administration, C.L.; funding acquisition, P.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Thailand Science Research and Innovation (TSRI) and the National Science Research and Innovation Fund (NSRF) (Fundamental Fund: Grant No. 3.3/2568); the Science Innovation Facility, Faculty of Science, Burapha University (SIF-IN-49300011); and the Faculty of Science, Burapha University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data are presented in the main text. Any other data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by (i) Burapha University (BUU), (ii) Thailand Science Research and Innovation (TSRI), (iii) the National Science Research and Innovation Fund (NSRF) (Fundamental Fund: Grant no. 3.3/2568), and (iv) the Faculty of Science, Burapha University. The authors would like to thank the Science Innovation Facility, Faculty of Science, Burapha University (SIF-IN-49300011); the Microscopic Center at the Faculty of Science, Burapha University; and the Scientific and Technological Research Equipment Centre (STREC) at Chulalongkorn University for instrument support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GMS | Green mussel shell |
| LGS | Large-crushed green mussel shell |
| MGS | Medium-crushed green mussel shell |
| SGS | Smallest crushed green mussel shell |
References
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Thailand’s Food and Restaurant Trends in 2022; Report no. TH2022–0018; Global Agricultural Information Network: Washington, DC, USA, 10 March 2022.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Seafood Report; Report no. TH8067; Global Agricultural Information Network: Washington, DC, USA, 5 August 2018.
- Kaewprachu, P.; Jaisan, C. Physicochemical Properties of Chitosan from Green Mussel Shells (Perna viridis): A Comparative Study. Polymers 2023, 15, 2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topić Popović, N.; Lorencin, V.; Strunjak-Perović, I.; Čož-Rakovac, R. Shell Waste Management and Utilization: Mitigating Organic Pollution and Enhancing Sustainability. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V.; Sasidharan, A. Seafood industry effluents: Environmental hazards, treatment, and resource recovery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafu-Quvane, B.; Mlaba, S. Assessing the Impact of Quarrying as an Environmental Ethic Crisis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendouma, S.; Serradj, T.; Vapur, H. A case study of the life cycle impact of limestone quarrying on the environment. Int. J. Glob. Warm. 2020, 22, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives. Marine Fisheries Management Plan of Thailand 2020–2022; Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives: Bangkok, Thailand, 2022.
- Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives. Statistics of Marines Shellfish Culture Survey 2021; Report no. 5/2022, July; Fishery Statistics Group, Fisheries Development Policy and Planning Division: Bangkok, Thailand, 2022.
- Lagos, N.A.; Benítez, S.; Duarte, C.; Lardies, M.A.; Broitman, B.R.; Tapia, C.; Tapia, P.; Widdicombe, S.; Vargas, C.A. Effects of temperature and ocean acidification on shell characteristics of Argopecten purpuratus: Implications for scallop aquaculture in an upwelling-influenced area. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2016, 8, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsaenmai, S. Characterization of calcium oxide derived from cockle shells for carbon dioxide capture. SNRU J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 10, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, D. Review of shell waste reutilization to promote sustainable shellfish aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 14, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzcátegui, L.U.M.; Vergara, K.; Bordes, G.M. Sustainable alternatives for by-products derived from industrial mussel processing: A critical review. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwannasingha, N.; Kantavong, A.; Tunkijjanukij, S.; Aenglong, C.; Liu, H.-B.; Klaypradit, W. Effect of calcination temperature on structure and characteristics of calcium oxide powder derived from marine shell waste. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2022, 26, 101441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Lee, J.G.; Thriveni, T.; Baek, C.S.; Ahn, J.-W. Improving recycled fiber by applying in-situ aragonite calcium carbonate formation process. Mater. Trans. 2014, 55, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, S.; Subramanian, V.K.; Palanisamy, K. Aragonite–calcite–vaterite: A temperature influenced sequential polymorphic transformation of CaCO3 in the presence of DTPA. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilludin, A.J.; Dinatha, I.J.H.; Supii, A.I.; Partini, J.; Kusindarta, D.L.; Yusuf, Y. Chemical and morphological analysis of calcium oxide (CaO) powder from sea urchin (Diadema setosum) shell. Eng. Chem. 2023, 3, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinkin, A.M.; Kalinkina, E.V.; Zalkind, O.A.; Makarova, T.I. Chemical interaction of calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide with CO2 during mechanical activation. Inorg. Mater. 2025, 41, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.K.; Lin, S.C.; Yan, J.; Zhao, C.Y. Sintering mechanism of calcium oxide/calcium carbonate during thermochemical heat storage process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Peng, L.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, T.; Zhang, B. Improving the mechanical properties of mussel shell aggregate concrete by aggregate modification and mixture design. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.-I.; Kim, B.-J. Characteristics of mortar containing oyster shell as fine aggregate. Materials 2022, 15, 7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiri, M.Z.A.; Matori, K.A.; Zainuddin, N.; Abdullah, C.A.C.; Alassan, Z.N.; Baharuddin, N.F.; Zaid, M.H.M. The usability of ark clam shell (Anadara granosa) as calcium precursor to produce hydroxyapatite nanoparticle via wet chemical precipitate method in various sintering temperature. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Yin, Z.; Da, B.; Chen, D. Effect of waste oyster shell powder content on properties of cement-metakaolin mortar. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-Y.; Wu, H.-S.; Chou, C.-P. Study on engineering and thermal properties of environment-friendly lightweight brick made from Kinmen oyster shells & sorghum waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owuamanam, S.; Cree, D. Progress of bio-calcium carbonate waste eggshell and seashell fillers in polymer composites: A review. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.T.; Phan, N.H.; Luo, G.-F.; Lee, H.-Y.; Nguyen, D.Q.A. The application of calcium carbonate CaCO3 and titania TiO2 for color homogeneity and luminous flux enhancement in PC-LEDs. J. Adv. Eng. Comput. 2021, 5, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueli, A.; Bonfiglio, G.; Pasquale, S.; Troja, S.O. Effect of particle size on pigments colour. Color Res. Appl. 2016, 42, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertvachirapaiboon, C.; Parnklang, T.; Pienpinijtham, P.; Wongravee, K.; Thammacharoen, C.; Ekgasit, S. Selective colors reflection from stratified aragonite calcium carbonate plates of mollusk shells. J. Struct. Biol. 2015, 191, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Viñas, M.; Rodríguez-Seoane, P.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; Torres, M.D.; Díaz-Reinoso, B.; Moure, A.; Domínguez, H. Subcritical water for the extraction and hydrolysis of protein and other fractions in biorefineries from agro-food wastes and algae: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 14, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Adhikari, B. Modification of plant and algal proteins through the Maillard reaction and complex coacervation: Mechanisms, characteristics, and applications in encapsulating oxygen-sensitive oils. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024, 2, 567–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, G. Unique morphology and gradient arrangement of nacre’s platelets in green mussel shells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 52, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, N.; Tang, W.; Ke, J. Low-temperature sintering of calcium carbonate by a hydrothermal hot-pressing technique. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1992, 11, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.R.; Evans, D.; Henehan, M.; Weldeab, S.; Lea, D.W.; Müller, W.; Rosenthal, Y. Sodium incorporation in foraminiferal calcite: An evaluation of the Na/Ca salinity proxy and evidence for multiple Na-bearing phases. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 348, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.; Yusup, S.; Maitra, S. Decomposition study of calcium carbonate in cockle shell. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2012, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Karunadasa, K.S.P.; Manoratne, C.H.; Pitawalab, H.M.T.G.A.; Rajapakse, R.M.G. Thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate (calcite polymorph) as examined by in-situ high-temperature X-ray powder diffraction. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 134, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlena, C.; Maddu, A.; Hidayat, T. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite from green mussel shell with sol-gel Method. J. Kim. Val. 2022, 8, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, E.; Gamelas, J.A.F.; Coroado, J.; Monteiro, C.; Rocha, F. Exploring the potential of cuttlebone waste to produce building lime. Mater. Constr. 2020, 70, e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, B.S.; Wahyuni, D.; Asri, A.; Mustafa, U. Effect of calcination temperature on the powder of freshwater snail shells (Sulcospira testudinaria) properties. Positron 2023, 13, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaoui, M.; Hsissou, R.; Alami, M.; Assouag, M. Physico-chemical characterization of snail shells powder prepared by mechanochemical processes and thermal treatment. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2023, 33, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, V.; Jambulingam, R. Waste crab shell derived CaO impregnated Na-ZSM-5 as a solid base catalyst for the transesterification of neem oil into biodiesel. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017, 27, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mans, C. Clinical update on diagnosis and management of disorders of the digestive system of reptiles. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2013, 22, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mititelu, M.; Stanciu, G.; Drǎgǎnescu, D.; Ioniță, A.C.; Neacșu, S.M.; Dinu, M.; Stefan-van Staden, R.-I.; Moroșan, E. Mussel Shells, a Valuable Calcium Resource for the Pharmaceutical Industry. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





