Enhanced Recognition of Sustainable Wood Building Materials Based on Deep Learning and Augmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Wood Identification Approaches
1.2. Machine Learning-Assisted Wood Recognition Approaches
1.3. Summary
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Augmentation Strategy for Training Images
2.1.1. Geometric and Photometric Augmentation for Feature Diversity
2.1.2. Systematic Implementation of Augmentation Pipeline
2.1.3. Validation-Set Augmentation with Controlled Transformations
2.1.4. Error Handling and Quality Control
2.1.5. Training Dynamics and Generalization Enhancement
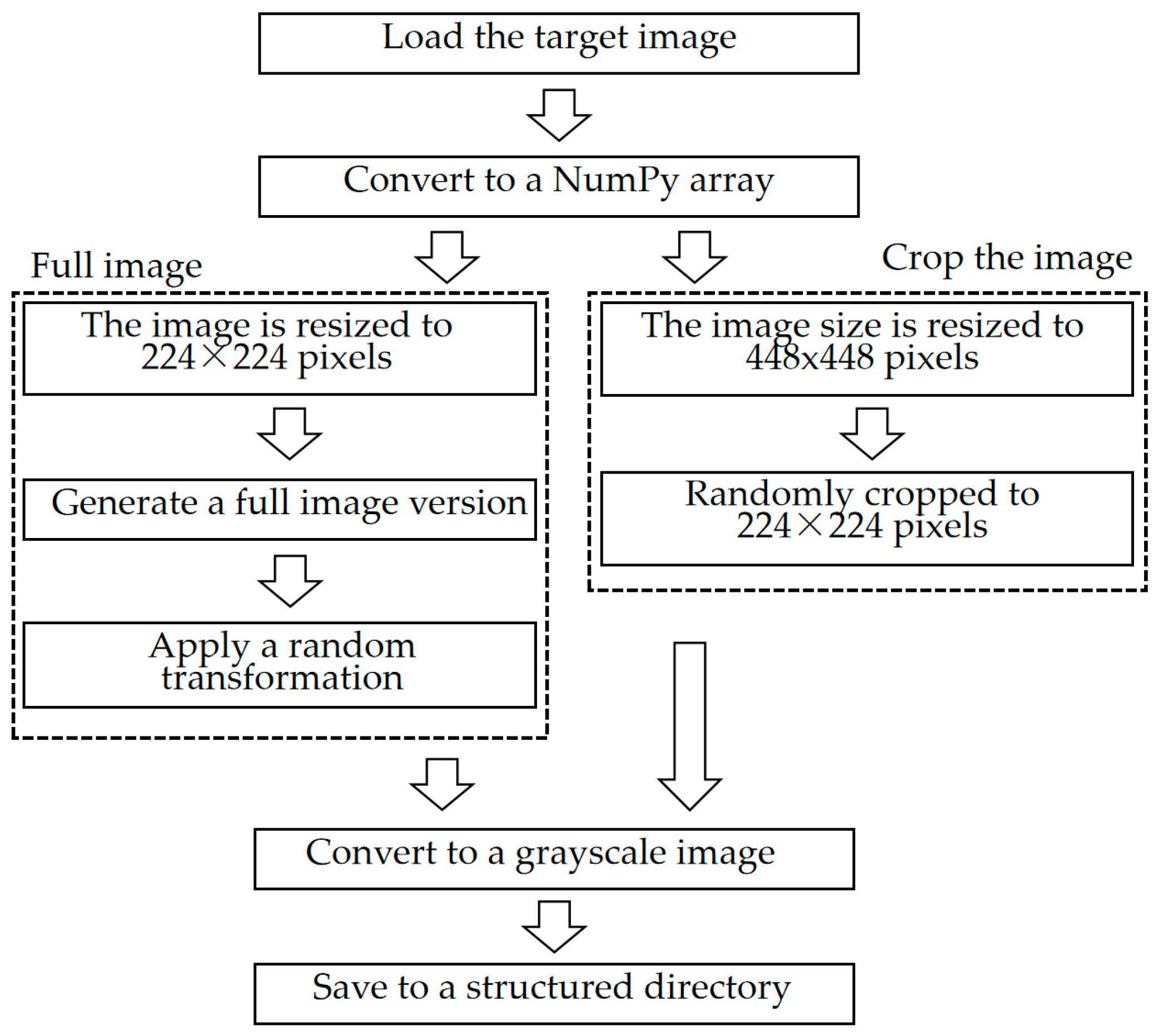
2.2. Preprocessing Pipeline for Target Images
2.2.1. Full Image Preprocessing
2.2.2. Cropped Image Preprocessing
2.2.3. Grayscale Conversion
2.2.4. Implementation and Data Augmentation
2.3. EfficientNet-Based Architecture for Wood Pattern Classification
2.3.1. Model Selection and Fine-Tuning Strategy
2.3.2. Data Augmentation and Transformations
2.3.3. Loss Function and Optimization
2.3.4. Training, Early Stopping, and Inference Configuration
2.4. Prediction Function for Wood Pattern Recognition
2.4.1. Prediction Process and Top-n Predictions
2.4.2. Output and Interpretability
2.4.3. Utility in Real-World Applications
3. Results Analysis
3.1. Results of the Augmentation
3.2. Preprocessing Outcomes and Enhanced Feature Preservation
3.3. Prediction Performance and Verification
3.4. Summary of Prediction Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion of the Results
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Research Potentials and Relation to Sustainability
4.4. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NN | Neural Network |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| GS-GM | Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry |
| NIR | Near-Infrared |
| IAWA | International Association of Wood Anatomists |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| SSIM | Structural Similarity Index |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Bai, X.; Lischinski, D.; Cohen-Or, D.; Huang, H. Non-Stationary Pattern Synthesis by Adversarial Expansion. ACM Trans. Graph. 2018, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Galerne, B.; Gousseau, Y.; Morel, J.-M. Random phase patterns: Theory and synthesis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Shi, S.; Yu, H. WTSM-SiameseNet: A Wood-Pattern-Similarity-Matching Approach Based on Siamese Networks. Information 2024, 15, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ge, Z.; Zheng, H.; Yang, X.; Qin, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y. Arnet: Research on wood CT image classification algorithm based on multi-scale dilated attention and residual dynamic convolution. Wood Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpoutis, P.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Barboutis, I.; Grammalidis, N.; Lefakis, P. Wood Species Recognition through Multidimensional Pattern Analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 144, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, M.; Abitha, J.; Mal Mathan Raj, R.; Ramar, K. Wood Species Classification Based on Local Edge Distributions. Optik. 2015, 126, 2884–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, E.A.; Baas, P. Wood Identification-A Review. IAWA J. 1998, 19, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zeng, Y.L.; Qin, J.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Yang, Q. Building of Digital Timber Specimens Retrieval System. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2013, 33, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Akhmetzyanov, L.; Copini, P.; Sass-Klaassen, U.; Schroeder, H.; De Groot, G.A.; Laros, I.; Daly, A. DNA of Centuries-Old Timber Can Reveal Its Origin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguilloux, M.; Pemonge, M.; Petit, R. Novel Perspectives in Wood Certification and Forensics: Dry Wood as a Source of DNA. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isak, I.; Newson, H.L.; Singh, J. Wood Species Differentiation: A Comparative Study of Direct Analysis in Real-Time and Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Forests 2025, 16, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Sun, X.M. HPLC and Pattern Recognition for the Identification of Four Species of Hongmu. Sci. Silvae. Sin. 2012, 48, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Tsuchikawa, S. Estimation of Wood Stiffness and Strength Properties of Hybrid Larch by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.M.; Zhang, H.P.; Feng, H.L. Feature Extraction and Recognition of Wood Micrograph Based on FFT and ICA. J. Zhejiang For. Coll. 2010, 27, 826–830. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Purusatama, B.D.; Savero, A.M.; Prasetia, D.; Jang, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, N.H. Convolutional neural network performance and the factors affecting performance for classification of seven Quercus species using sclereid characteristics in the bark. BioResources 2024, 19, 510–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahimi, S.; Avramidis, S. Online species identification of green hem-fir timber mix based on near infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Wood Wood Prod. 2019, 78, 1–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hafemann, L.G.; Oliveira, L.S.; Cavalin, P. Forest Species Recognition Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fabijańska, A.; Danek, M.; Barniak, J. Wood Species Automatic Identification from Wood Core Images with a Residual Convolutional Neural Network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 181, 105941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Poyatos, D.; Poyatos, A.H.; Soldado, R.M.; De Palacios, P.; Esteban, L.G.; Iruela, A.G.; Fernández, F.G.; Herrera, F. Deep Learning Approachology for the Identification of Wood Species Using High-Resolution Macroscopic Images. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Yokohama, Japan, 30 June 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Trieu, M.N.; Thinh, N.T. A Novel Approach in Wood Identification Based on Anatomical Image Using Hybrid Model. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 47, 2381–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.R.D.; Deklerck, V.; Baetens, J.; Bulcke, J.V.D.; De Ridder, M.; Rousseau, M.; Bruno, O.M.; Beeckman, H.; Acker, J.V.; De Baets, B.; et al. Improved Wood Species Identification Based On Multi-View Imagery of The Three Anatomical Planes. Plant Approaches 2022, 18, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Lens, J.J. Understand Potential Ramifications of Ruling Involving NCAA Show-cause Orders. Coll. Athl. Law 2020, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ergun, H. Wood Identification Based on Macroscopic Images Using Deep and Transfer Learning Approaches. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kılıç, K.; Kılıç, K.; Doğru, İ.A.; Özcan, U. WD Detector: Deep Learning-Based Hybrid Sensor Design for Wood Defect Detection. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2025, 83, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ma, D.; Lv, J.; Li, J. ACTL: Asymmetric Convolutional Transfer Learning for Tree Species Identification Based on Deep Neural Network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 13643–13654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Guo, F.; Xiao, Z. YOLOv7-MA: Improved YOLOv7-Based Wheat Head Detection and Counting. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Wang, R.; Liang, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, B. SiM-YOLO: A Wood Surface Defect Detection Approach Based on the Improved YOLOv8. Coatings 2024, 14, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Teng, X.; Sun, P. FDD-YOLO: A Novel Detection Model for Detecting Surface Defects in Wood. Forests 2025, 16, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Razzaq Malik, K.; Ur Rehman, A.; Safdar Malik, T.; Alajmi, M.; Haider Khan, A.; Haider, A.; Hussen, S. Leveraging Two-Dimensional PreTrained Vision Transformers for Three-Dimensional Model Generation via Masked Autoencoders. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Fu, F.; Zheng, J.; Yang, H.; Zou, F.; Linghua, K. Intelligent Wood Inspection Approach Utilizing Enhanced Swin Transformer. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 16794–16804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Li, K.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, T. Leveraging Visible-near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Machine Learning to Detect Nickel Contamination in Soil: Addressing Class Imbalances for Environmental Management. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, D.; Mishra, J. Perspectives on Deep Learning for Near-Infrared Spectral Data Modelling. NIR News 2022, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodytek, P.; Bodzas, A.; Bilik, P. A Large-Scale Image Dataset of Wood Surface Defects for Automated Vision-Based Quality Control Processes. F1000Research 2022, 10, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, J.W.; Yeh, I.H. Cspnet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1571–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, M.D.A.; Marcato, J.; Martins, J.A.C.; Zamboni, P.; Costa, C.S.; Siqueira, H.L.; Araújo, M.S.; Gonçalves, D.N.; Furuya, D.E.G.; Osco, L.P.; et al. A Deep Learning-Based Mobile Application for Tree Species Mapping in RGB Images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtisham, R.; Qayyum, W.; Plevris, V.; Mir, J.; Ahmad, A. Classification and Computing the Defected Area of Knots in Wooden Structures using Image Processing and CNN. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Evolutionary and Deterministic Approaches for Design, Optimization and Control, Chania, Greece, 1–3 June 2023; Institute of Structural Analysis and Antiseismic Research National Technical University of Athens: Athens, Greece, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.; Chang, J.; Shi, H.; Xiao, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Strip Steel Defect Classification Using the Improved GAN and EfficientNet. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 1887–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Wang, B.; Lu, K.; Zhang, J.; Chen, P.; Pan, L.; Zhu, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, W. Multiple classification network of concrete defects based on improved EfficientNetV2. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2023, 14087, 603–614. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Kim, Y.; Jang, H.; Ha, N.; Sohn, K. Multi-Task Learning Framework for Motion Estimation and Dynamic Scene Deblurring. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 8170–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charpiat, G.; Hofmann, M.; Schölkopf, B. Advanced intelligent Computing Technology and Applications. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Zhengzhou, China, 10–13 August 2023. lClC 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ulu, A.; Yildiz, G.; Dizdaroğlu, B. MLFAN: Multilevel Feature Attention Network With Pattern Prior for Image Denoising. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 34260–34273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Yu, Z. Improved ResNet-50 Model for Identifying Defects on Wood Surfaces. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 3119–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Lu, Y.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yin, Y. Developing Deep Learning Models to Automate Rosewood Tree Species Identification for CITES Designation and Implementation. Holzforschung 2020, 74, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Peers, P.; Tong, X. Modeling Surface Appearance from a Single Photograph Using Self-Augmented Convolutional Neural Networks. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.T.; Abarghouei, A.A.; Bonner, S.; Breckon, T.; Obara, B. Style. Augmentation: Data Augmentation via Style Randomization. Workshop 2019, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]










| Identification Method | Time | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Identification [6,7] | 1931 | Prone to misjudgment, low efficiency |
| Dichotomous Key Identification [8] | 1938 | Complicated compilation, low efficiency |
| DNA Identification [9,10] | 2002 | Long testing period, high cost, difficult to popularize due to technical challenges |
| Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Identification [11] | 2006 | The chemical composition of wood is complex, and the experimental accuracy is low. |
| Near-infrared Spectroscopy Identification [13] | 2007 | Relies on equipment and environmental conditions, susceptible to moisture content interference, requires many samples for training |
| Basic Machine Image Processing Identification [14] | 2010 | High image quality requirements, limited generalization ability, limited capability to handle complex textures |
| Chemical Fingerprinting [12] | 2019 | Lack of theoretical foundation, requires further exploration |
| Case-01 | Case-02 | Case-03 | Case-04 | Case-05 | Case-06 | Case-07 | Case-08 | Case-09 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FH164 | FH53 | F183 | F241 | HF30 | FW176 | HC1 | HW10 | HD83 |
| 28.23% | 55.90% | 63.38% | 82.76% | 8.30% | 59.87% | 57.74% | 53.86% | 29.08% | |
| 2 | FH31 | H458 | FH47 | H434 | F194 | SW1 | HW28 | F222 | FH352 |
| 9.01% | 2.40% | 10.36% | 7.42% | 6.88% | 11.55% | 18.41% | 2.77% | 7.94% | |
| 3 | FW3 | SH14 | H175 | SC1 | H40 | H67 | FS1 | SW1 | SH19 |
| 8.98% | 2.18% | 1.60% | 0.87% | 4.08% | 6.32% | 13.41% | 2.51% | 6.66% | |
| 4 | FS3 | FH12 | SW1 | SH6 | FH136 | FHD1 | FW3 | F25 | H17 |
| 4.75% | 1.95% | 1.11% | 0.40% | 4.32% | 1.78% | 1.84% | 1.80% | 3.73% | |
| 5 | FH15 | FH1 | FHD1 | FH305 | FM8 | S225 | FH164 | FD8 | H236 |
| 4.54% | 1.64% | 1.03% | 0.25% | 4.22% | 1.27% | 0.63% | 1.55% | 3.63% | |
| 6 | F21 | FS14 | SH36 | SH8 | S31 | SH51 | FHD1 | FD61 | H129 |
| 3.24% | 2.75% | 1.27% | 0.25% | 3.58% | 0.79% | 0.28% | 1.36% | 2.45% | |
| 7 | FS1 | FM8C | HW10 | FHD79 | SH19 | H146 | HW10 | FW10 | F241 |
| 2.75% | 1.27% | 0.68% | 0.19% | 2.51% | 0.78% | 0.25% | 1.26% | 1.94% | |
| 8 | FC1 | F67 | HD70 | H349 | HC1 | H2 | FD72 | H236 | HD71 |
| 1.68% | 1.14% | 0.61% | 0.15% | 2.12% | 0.74% | 0.24% | 1.14% | 1.76% | |
| 9 | FC3A | FH224 | HF37 | H458 | FH41 | H236 | H9 | FW59 | SH27 |
| 1.56% | 1.09% | 0.53% | 0.13% | 1.70% | 0.54% | 0.21% | 0.96% | 1.51% | |
| 10 | FD323 | SH8 | FHS1 | FH284 | FW12 | FH53 | FH37 | FH114 | H9 |
| 1.39% | 1.03% | 0.48% | 0.12% | 1.69% | 0.43% | 0.19% | 0.90% | 1.08% | |
| 11 | SW13 | S17 | H263 | FH107 | HFD1 | FHS1 | SH27 | FH53 | HD50 |
| 1.16% | 0.96% | 0.43% | 0.11% | 1.51% | 0.41% | 0.19% | 0.87% | 0.87% | |
| 12 | FD251 | SH19 | FD35 | FW61 | HFD2 | FM8 | H458 | H458 | FH79 |
| 0.73% | 0.81% | 0.36% | 0.11% | 1.48% | 0.31% | 0.15% | 0.79% | 0.82% | |
| 13 | F37 | F26 | SH8 | FW135 | S12 | FHD57 | FW146 | SH85 | S5 |
| 0.64% | 0.77% | 0.30% | 0.10% | 1.40% | 0.29% | 0.15% | 0.77% | 0.73% | |
| 14 | HS20 | FHS1 | FH151 | FH151 | SH2 | FH98 | FHS1 | FH15 | FH70 |
| 0.62% | 0.71% | 0.30% | 0.09% | 1.29% | 0.28% | 0.13% | 0.66% | 0.63% | |
| 15 | FM1 | FC2 | H248 | FHM6 | FW3 | FHS1 | SH19 | SH27 | FH129 |
| 0.61% | 0.71% | 0.29% | 0.09% | 1.23% | 0.24% | 0.13% | 0.54% | 0.59% | |
| 16 | FHD1 | H236 | FHM6 | SH5 | FW17 | FWS61 | FS3 | F169 | SW1 |
| 0.59% | 0.71% | 0.28% | 0.09% | 1.16% | 0.21% | 0.12% | 0.50% | 0.55% | |
| 17 | FH1 | H394 | FW1 | H122 | HW1 | HD46 | H416 | FW3 | S17 |
| 0.58% | 0.68% | 0.27% | 0.09% | 1.14% | 0.20% | 0.12% | 0.49% | 0.55% | |
| 18 | FW146 | FD316 | FD245 | H451 | FH245 | FHC7 | H394 | FHM2 | F236 |
| 0.53% | 0.63% | 0.26% | 0.08% | 0.98% | 0.20% | 0.10% | 0.46% | 0.46% | |
| 19 | F227 | FD251 | F179 | FH227 | F37 | F179 | FD186 | HD83 | H338 |
| 0.42% | 0.59% | 0.25% | 0.08% | 0.88% | 0.19% | 0.10% | 0.46% | 0.42% | |
| 20 | H28 | FC41 | HW14 | FW3 | F224 | H429 | FW64 | F5 | H107 |
| 0.39% | 0.52% | 0.24% | 0.08% | 0.86% | 0.19% | 0.90% | 0.46% | 0.41% |
| Number | Case Name | Accuracy Rate | Prediction Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Case-01 | 28.23% | Succeed |
| 2 | Case-02 | 55.90% | Succeed |
| 3 | Case-03 | 63.38% | Succeed |
| 4 | Case-04 | 82.76% | Succeed |
| 5 | Case-05 | 8.30% | Fail |
| 6 | Case-06 | 59.87% | Succeed |
| 7 | Case-07 | 57.74% | Succeed |
| 8 | Case-08 | 53.86% | Succeed |
| 9 | Case-09 | 29.08% | Succeed |
| Number | Case Name | First Similarity Rate | Second Similarity Rate | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Case-01 | 28.23% | 9.01% | 19.22% |
| 2 | Case-02 | 55.90% | 2.40% | 53.5% |
| 3 | Case-03 | 63.38% | 10.36% | 53.02% |
| 4 | Case-04 | 82.76% | 7.42% | 75.24% |
| 5 | Case-05 | 8.30% | 6.88% | 1.42% |
| 6 | Case-06 | 59.87% | 11.55% | 48.32% |
| 7 | Case-07 | 57.74% | 18.41% | 39.33% |
| 8 | Case-08 | 53.86% | 2.77% | 51.09% |
| 9 | Case-09 | 29.08% | 7.49% | 21.59% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, W.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Peng, S.; Li, R.; Qiu, L.; Li, B.; He, Y. Enhanced Recognition of Sustainable Wood Building Materials Based on Deep Learning and Augmentation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156683
Gan W, Li S, Li J, Peng S, Li R, Qiu L, Li B, He Y. Enhanced Recognition of Sustainable Wood Building Materials Based on Deep Learning and Augmentation. Sustainability. 2025; 17(15):6683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156683
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Wei, Shengbiao Li, Jinyu Li, Shuqi Peng, Ruoxi Li, Lan Qiu, Baofeng Li, and Yi He. 2025. "Enhanced Recognition of Sustainable Wood Building Materials Based on Deep Learning and Augmentation" Sustainability 17, no. 15: 6683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156683
APA StyleGan, W., Li, S., Li, J., Peng, S., Li, R., Qiu, L., Li, B., & He, Y. (2025). Enhanced Recognition of Sustainable Wood Building Materials Based on Deep Learning and Augmentation. Sustainability, 17(15), 6683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17156683






