Scheduling and Routing of Device Maintenance for an Outdoor Air Quality Monitoring IoT
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Air Quality Monitoring IoT in Taiwan
2.2. Maintenance Scheduling Policies
- A.
- Corrective Maintenance (CM)
- B.
- Preventive Maintenance (PM)
2.3. Maintenance Scheduling Methodologies
- A.
- Mathematical Programming
- B.
- Artificial Intelligence
- C.
- Multi-Objective Approaches
- D.
- Others
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Studied Problem
3.2. Maintenance Programming Framework
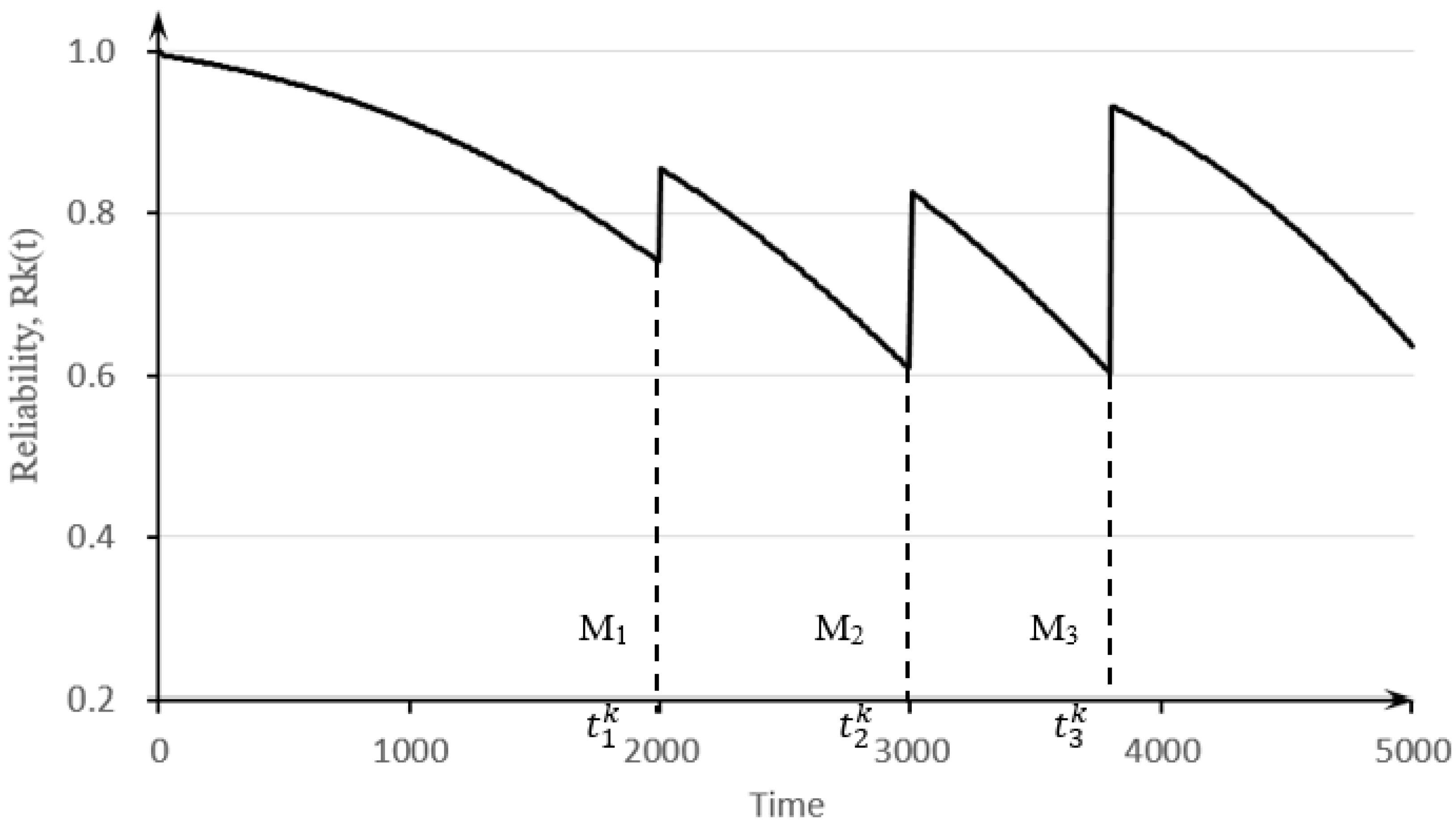
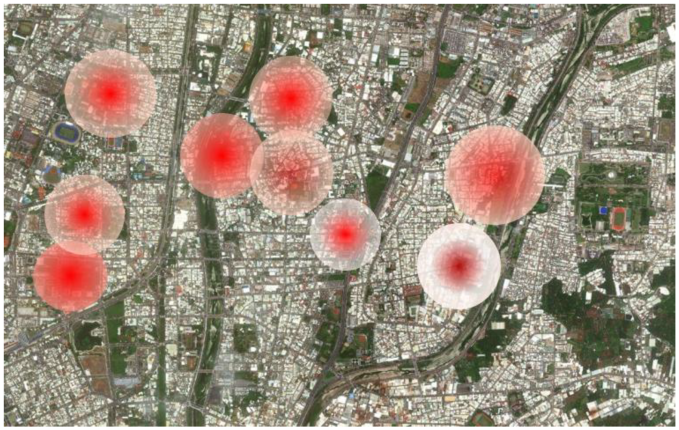
3.2.1. Reliability Evaluation of Microsites Prior to Maintenance
3.2.2. Reliability Evaluation of Microsites Between Maintenance Cycles
3.2.3. IoT Availability Evaluation
3.2.4. Scheduling and Routing of IoT Maintenance
3.2.5. Maintenance Programming Model
- A.
- Maintenance Cost
- B.
- Transportation Cost
- C.
- CO2 Emissions
- D.
- Labor Hours
3.2.6. Optimization Algorithms
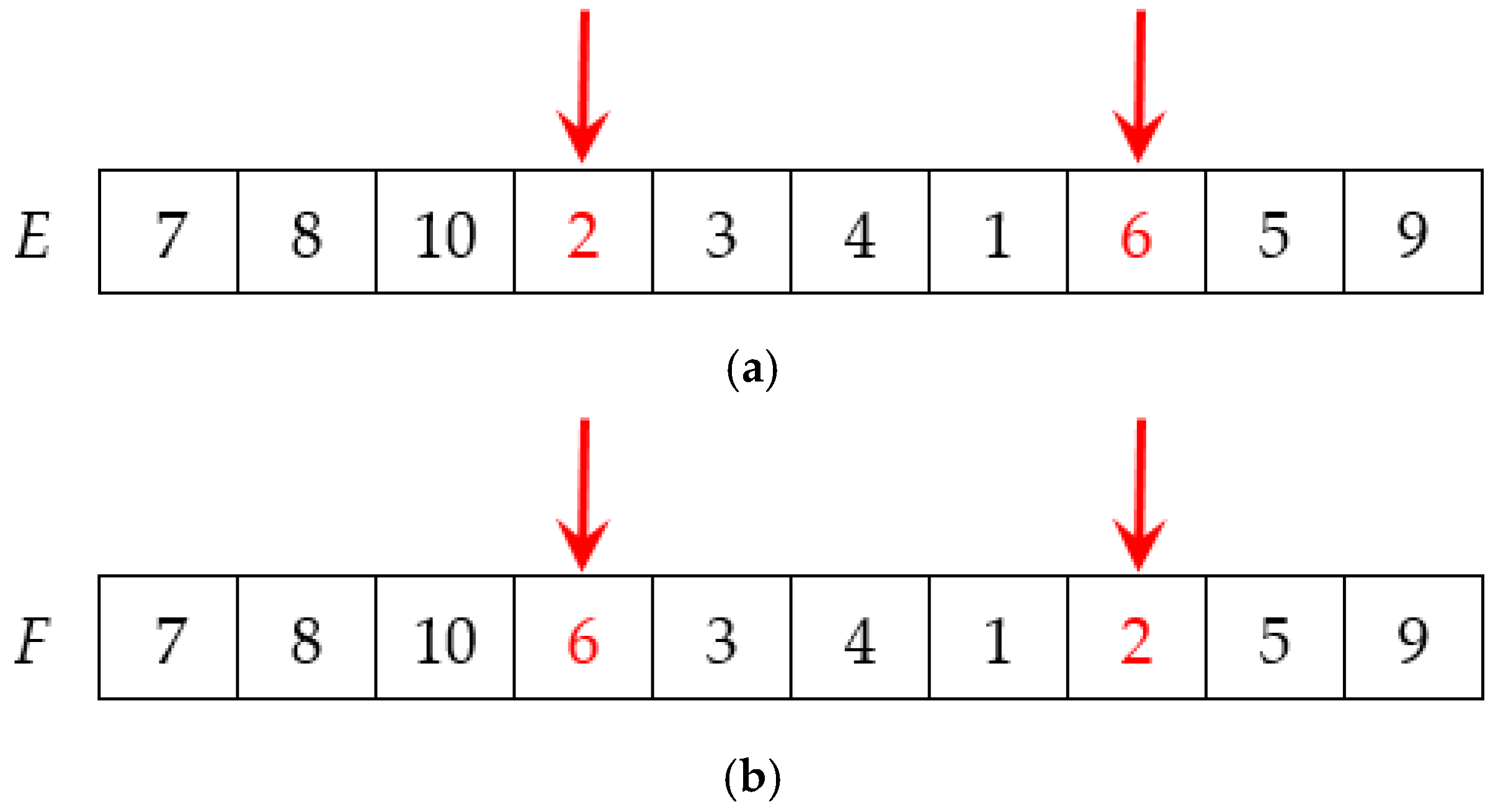
Heuristics for Batch Maintenance Scheduling
GA for Maintenance Vehicle Routing
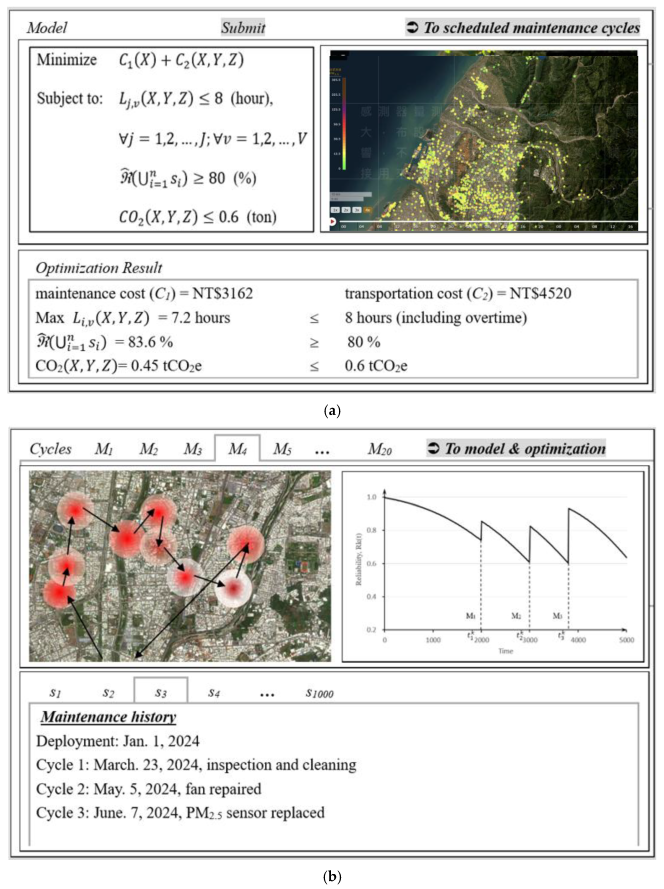
3.2.7. Dashboard for Maintenance Programming and Visualization
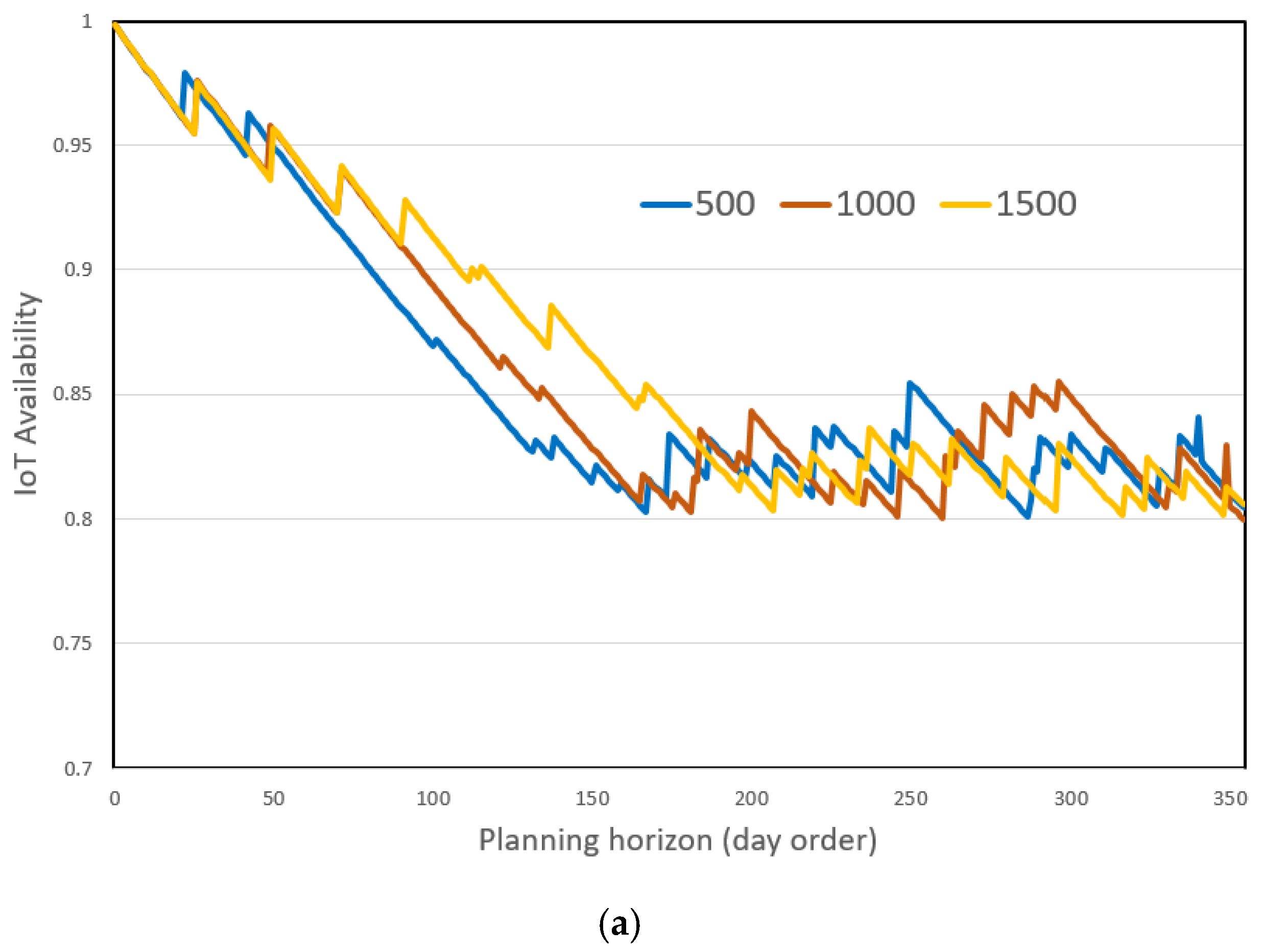
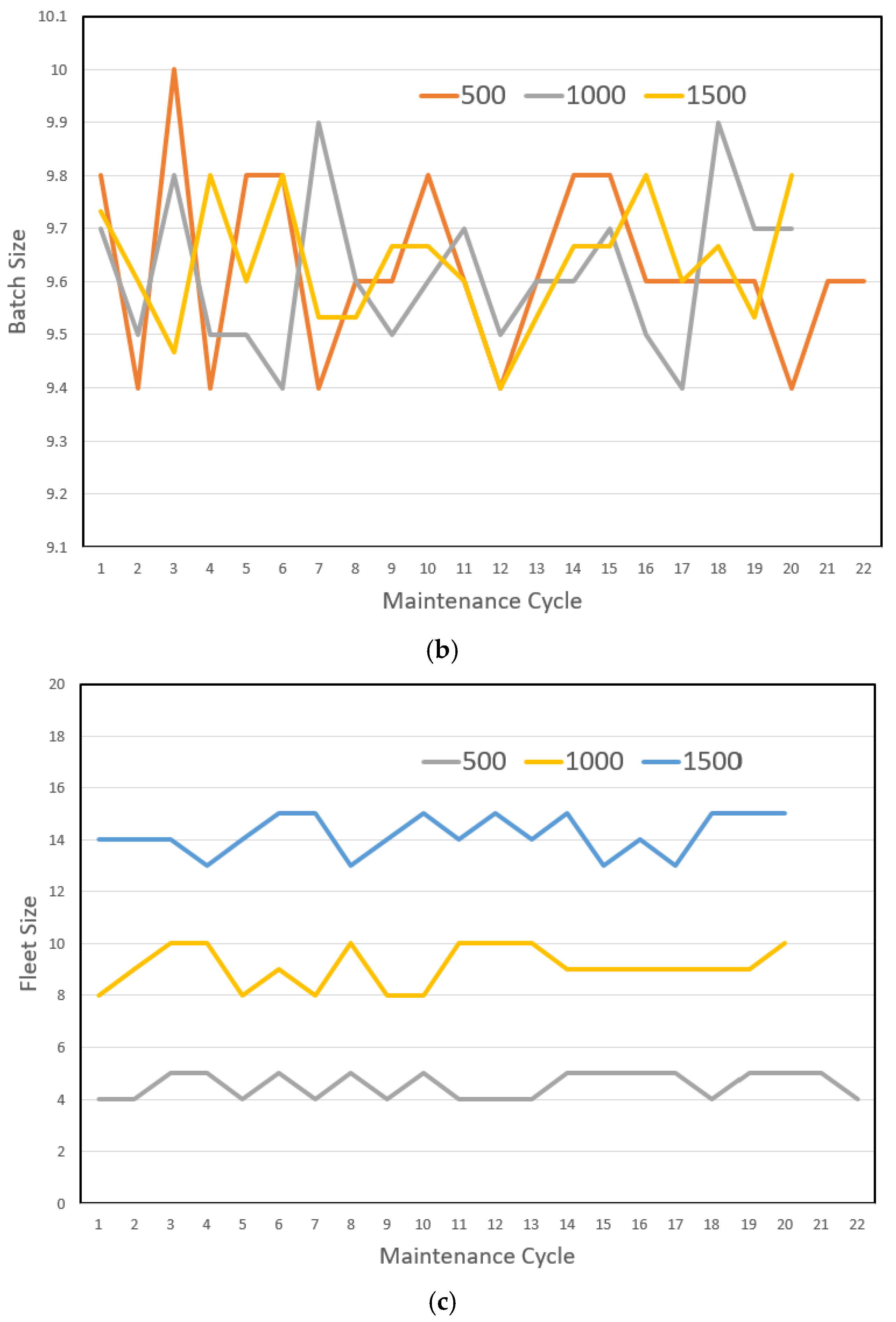
4. Experimental Results
4.1. IoT Microsite Datasets and Research Limitations
4.2. Illustration of Maintenance Programming Simulations
4.3. Scalability and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hwang, S.-L.; Lin, Y.-C.; Guo, S.-E.; Chi, M.-C.; Chou, C.-T.; Lin, C.-M. Emergency room visits for respiratory diseases associated with ambient fine particulate matter in Taiwan in 2012: A population-based study. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; He, J.; Wu, L.; Jin, T.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Ren, P.; Zhang, L.; Mao, H. Health burden attributable to ambient PM2.5 in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chiang, H.-C.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Yang, T.-T.; Lin, T.-Y.; Chen, M.-J.; Chen, N.-T.; Wu, Y.-S. Ambient PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Changhua County, central Taiwan: Seasonal variation, source apportionment and cancer risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C.; Day, R.-F.; Tung, C.-Y.; Bhanu, B. Ensemble learning of model hyperparameters and spatiotemporal data for calibration of low-cost PM2.5 sensors. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 6858–6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.-Y.; Day, R.-F.; Lin, Y.-C.; Hu, C.-Y. Improving PM2.5 concentration forecast with the identification of temperature inversion. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.-Y.; Yen, A.-Y.; Chao, S.-E.; Day, R.-F.; Bhanu, B. A machine learning-based ensemble framework for forecasting PM2.5 concentrations in Puli, Taiwan. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.-Y. A novel spatiotemporal analysis framework for air pollution episode association in Puli, Taiwan. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Peltier, W.-R.; von Schneidemesser, E. Low-Cost Sensors for the Measurement of Atmospheric Composition: Overview of Topic and Future Applications; Research Report; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, P.-Y. Mining associations between air quality and natural and anthropogenic factors. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkateb, S.; Métwalli, A.; Shendy, A.; Abu-Elanien, A.E.B. Machine learning and IoT–based predictive maintenance approach for industrial applications. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 88, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, P.; Vigo, D. (Eds.) The Vehicle Routing Problem; Monographs on Discrete Mathematics and Applications; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2022; Volume 9, ISBN 0-89871-579-2. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwan MOENV. Taiwan Air Quality Monitoring Network. Available online: https://airtw.moenv.gov.tw/CHT/EnvMonitoring/Central/spm.aspx (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Han, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, M.; Bai, Z. Gravimetric analysis for PM2.5 mass concentration based on year-round monitoring at an urban site in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Aggarwal, S.-G. A technical overview on beta-attenuation method for the monitoring of particulate matter in ambient air. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 220195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.-F.; Yin, P.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C.; Yu, C.-H. Concentration-temporal multilevel calibration of PM2.5 low-cost sensor. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, E.-I.; Abdul Razak, I.-H.; Ab-Samat, H.; Kamaruddin, S. Preventive maintenance (PM) planning: A review. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2017, 23, 114–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.-J.; Emmanouilidis, C.; Tomiyama, T.; Tiwari, A.; Roy, R. Intelligent decision support for maintenance: An overview and future trends. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2019, 32, 936–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilotti, L.; Kurscheidt, R.; Loures, E.; Portela, E.; Freire, R. A review of maintenance scheduling methods in the context of Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Production Research—Americas. ICPR 2023; Deschamps, F., Pinheiro de Lima, E., Gouvêa da Costa, S.E.G., Trentin, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, M.-A.; Khan, T.-A. Forecasting failure rate of IoT devices: A deep learning way to predictive maintenance. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 110, 108829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijailovic, V. Probabilistic method for planning of maintenance activities of substation components. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2003, 64, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-X. On preventive maintenance policy of a critical reliability level for system subject to degradation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2003, 79, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourelfath, M.; Nahas, N.; Ben-Daya, M. Integrated preventive maintenance and production decisions for imperfect processes. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 148, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.-H.; Tsai, H.-L. Flexible preventive maintenance planning for two parallel machines problem to minimize makespan. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2010, 16, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-T.; Wang, K.-S.; Teng, H.-Y. Optimizing preventive maintenance for mechanical components using genetic algorithms. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2001, 74, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, P.-D.; Vu, H.-C.; Barros, A.; Berenguer, C. Grouping maintenance strategy with availability constraint under limited repairmen. IFAC Proc. 2012, 45, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, M.-L.; Poorana, K.-S.; Vinodh, R.; Paul, R.-T. Preventive maintenance optimization of critical equipment in process plant using heuristic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 9–10 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Samrout, M.; Yalaoui, F.; Chatelet, E.; Chebbo, N. New methods to minimize the preventive maintenance cost of series–parallel systems using ant colony optimization. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2005, 89, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, D.-D.; Bose, G.-K.; Jana, D.-K.; Bose, D.; Mitra, S. Availability and cost-centered preventive maintenance scheduling of continuous operating series systems using multi-objective genetic algorithm: A case study. Qual. Eng. 2016, 28, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, M. Multi-objective optimization of parallel machine scheduling integrated with multi-resources preventive maintenance planning. J. Manuf. Syst. 2015, 37, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulkarim, A.-A.; Ball, P.-D.; Tiwari, A. Applications of simulation in maintenance research. World J. Model. Simul. 2013, 9, 14–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ab-Samat, H.; Jeikumar, L.-N.; Basri, E.-I.; Harun, N.-A.; Kamaruddin, S. Effective preventive maintenance scheduling: A case study. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Istanbul, Turkey, 3–6 July 2012; pp. 1249–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Shatz, S.-M.; Wang, J.-P.; Goto, M. Task allocation for maximizing reliability of distributed computer systems. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1992, 41, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Bhardwaj, N.; Kumar, V.; Parashar, B. Imperfect maintenance modeling for sequential corrective and preventive maintenance. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2357, 080006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiben, A.-E.; Smith, J.-E. Recombination for permutation representation. In Introduction to Evolutionary Computing, 2nd ed.; Natural Computing Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buontempo, F. Genetic Algorithms and Machine Learning for Programmers: Create AI Models and Evolve Solutions, Pragmatic Works Inc Programmers; Pragmatic Bookshelf: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-J.; Ho, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-C.; Wu, H.-C.; Liu, H.-M.; Hsieh, H.-H.; Huang, Y.-T.; Lung, S.-C. An open framework for participatory PM2.5 monitoring in smart cities. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 14441–14454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| n | Number of microsites connected to the air quality monitoring IoT |
| J | Maximum number of maintenance cycles in the programming |
| k-th microsite | |
| Deployment time of microsite | |
| Failure rate of microsite within the j-th maintenance cycle | |
| Reliability of microsite by time t | |
| Improvement factor for the j-th maintenance cycle | |
| Availability of microsite | |
| Normalized availability of the IoT service | |
| Xi | Batch of visited microsites in the i-th maintenance cycle |
| Yi | Set of links between any ordered pairs of microsites from Xi |
| indicates that vehicle v passes through the link connecting and during the j-th maintenance cycle, and otherwise | |
| Amount of CO2 emitted from vehicle v passing through the link connecting and | |
| Fuel efficiency of vehicle v | |
| Mean speed of vehicle v | |
| Cost per liter of fuel | |
| PM cost for microsite in the j-th maintenance cycle | |
| CM cost for microsite in the j-th maintenance cycle | |
| Transportation cost for vehicle v passing through link | |
| Mean operational time for performing PM activities at a single site | |
| Mean operational time for performing CM activities at a single site |
| Name of Dataset | Number of Microsites | Size of Fleet | Northwest Location | Southeast Location | Diagonal Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoT-500 | 500 | 5 | 120.75, 24.18 | 120.60, 24.07 | 20 |
| IoT-1000 | 1000 | 10 | 120.82, 24.23 | 120.51, 24.01 | 40 |
| IoT-1500 | 1500 | 15 | 120.85, 24.26 | 120.46, 23.98 | 51 |
| Maintenance Activity | Drawn Probability | Improvement Factor | Maintenance Cost | Maintenance Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple PM | 0.7 | 0.3 | TWD 100 | 5 min |
| Complex PM | 0.3 | 0.7 | TWD 500 | 20 min |
| CM | 1.0 | TWD 1000 | 20 min |
| J | Max Mean Min | Max Mean Min | Max Mean Min Threshold | Max Mean Min Threshold | Max Mean Min Threshold | V Max Mean Min Threshold | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoT-500 | 22 | 6233 3898 2920 | 433.9 391.0 338.9 | 0.19 0.17 0.14 0.40 | 4.6 4.3 3.9 8.0 | 99.8% 85.7% 80.0% 80.0% | 5.0 4.5 4.0 5.0 |
| IoT-1000 | 20 | 8663 7555 6866 | 867.0 810.3 732.1 | 0.39 0.33 0.31 0.80 | 5.3 5.0 4.5 8.0 | 99.8% 86.3% 80.0% 80.0% | 10.0 9.1 8.0 10.0 |
| IoT-1500 | 20 | 16,006 14,527 13,487 | 1287.7 1203.3 1079.1 | 0.85 0.76 0.67 1.20 | 7.2 6.6 6.0 8.0 | 99.8% 86.6% 80.1% 80.0% | 15.0 14.2 13.0 15.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, P.-Y. Scheduling and Routing of Device Maintenance for an Outdoor Air Quality Monitoring IoT. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146522
Yin P-Y. Scheduling and Routing of Device Maintenance for an Outdoor Air Quality Monitoring IoT. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146522
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Peng-Yeng. 2025. "Scheduling and Routing of Device Maintenance for an Outdoor Air Quality Monitoring IoT" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146522
APA StyleYin, P.-Y. (2025). Scheduling and Routing of Device Maintenance for an Outdoor Air Quality Monitoring IoT. Sustainability, 17(14), 6522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146522





