Artificial Intelligence Technology Applications and Energy Utilization Efficiency: Empirical Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Hypotheses
2.1. AI Technology Applications and Energy Utilization Efficiency
2.2. The Mediating Role of Technological Effects
2.3. The Mediating Role of Scale Effects
2.4. The Moderating Role of Environmental Regulations
2.5. The Moderating Role of Digital Infrastructure
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Benchmark Regression Model
3.2. Variable Selection
3.2.1. Explained Variable
3.2.2. Explanatory Variable
3.2.3. Control Variables
3.3. Sources of Data and Preliminary Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Benchmark Regression Tests
4.2. Endogeneity Test
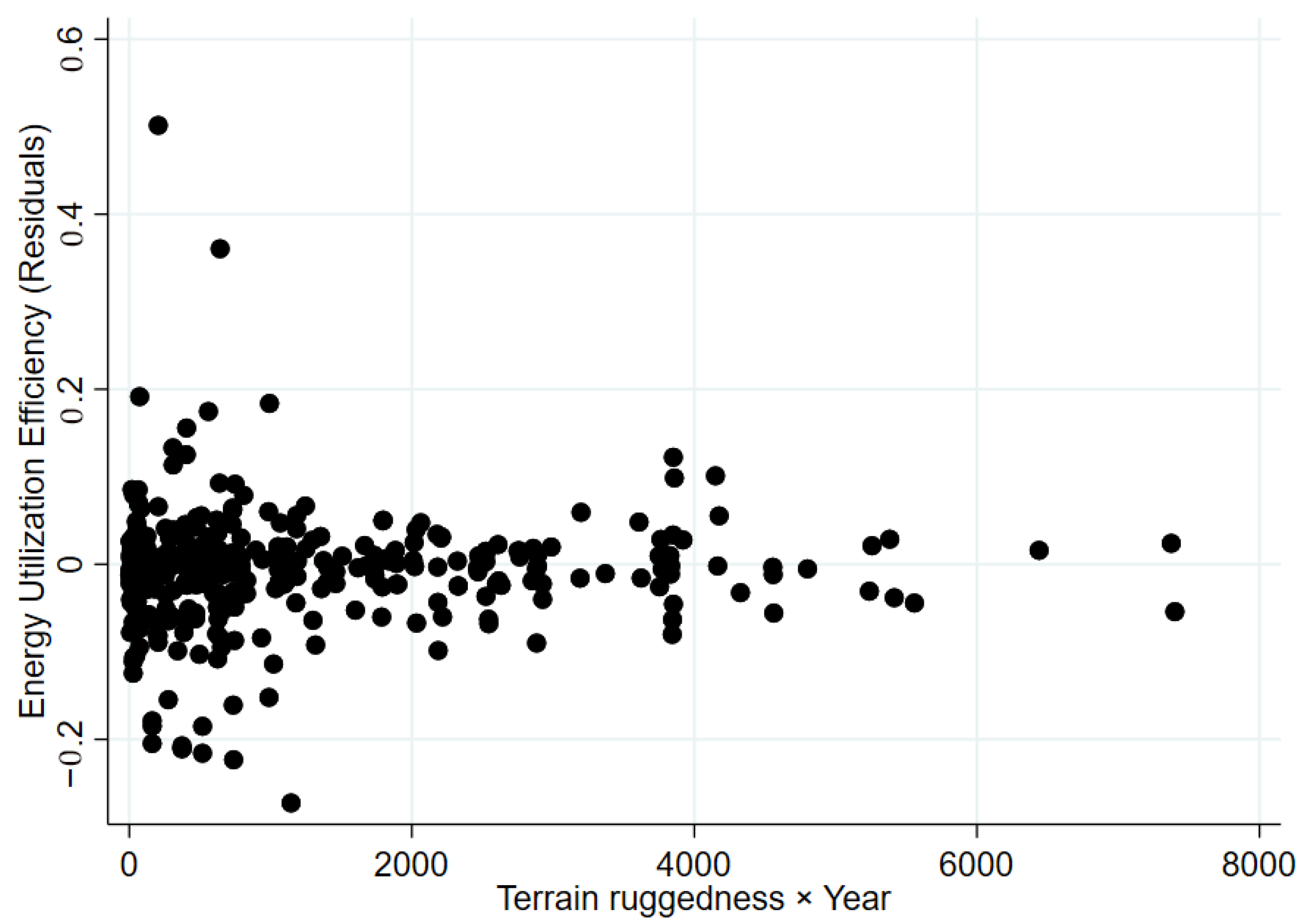
4.2.1. Instrumental Variable Method
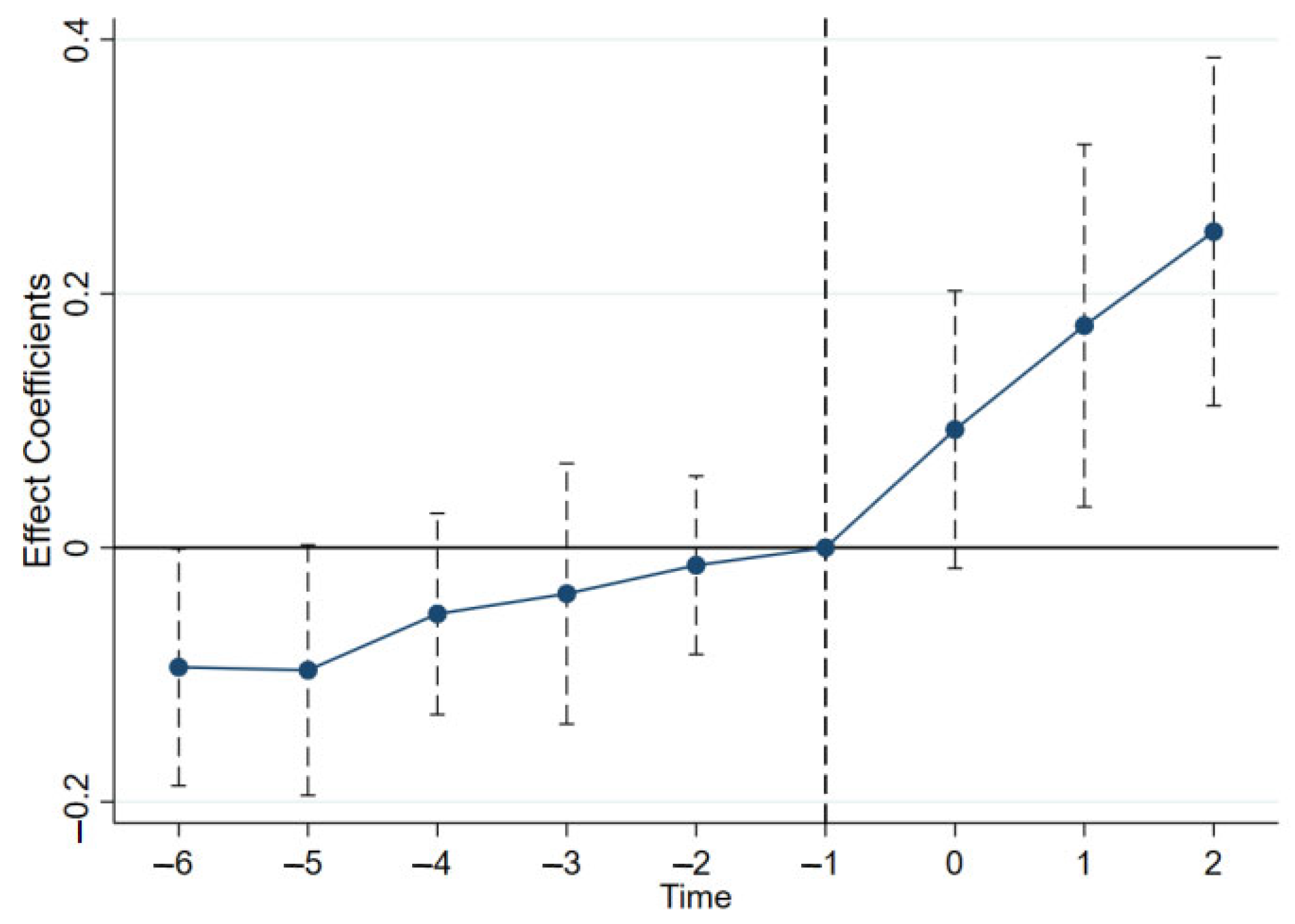
4.2.2. DID Method
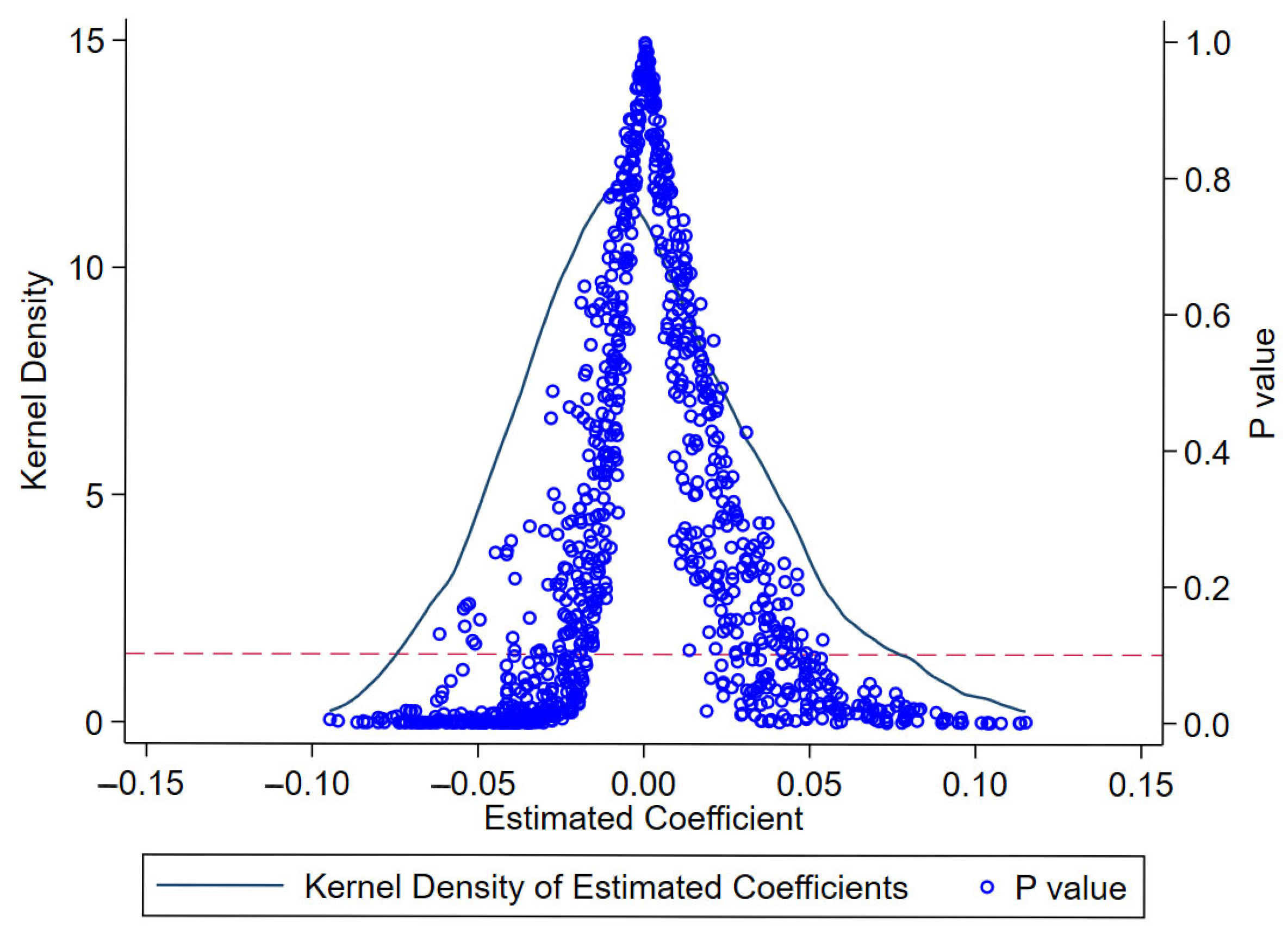
4.3. Robustness Tests
4.4. Mechanisms
4.4.1. Technological Effects Mechanism
4.4.2. Scale Effects Mechanism
4.4.3. Analysis of the Mechanistic Effects of Input Variables and Output Variables
Analysis of the Mechanistic Effects of Input Factors
Analysis of the Mechanistic Effects of Output Factors
4.5. Moderating Effects
4.5.1. Moderating Effects of Environmental Regulation
4.5.2. Moderating Effect of Digital Infrastructure
4.6. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.6.1. Heterogeneity of Geographical Location
4.6.2. Heterogeneity of Urban Types
5. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moriarty, P.; Honnery, D. Can renewable energy power the future? Energy Policy 2016, 93, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, W.; Cheng, J. Effects of urbanization on energy efficiency in China: New evidence from short run and long run efficiency models. Energy Policy 2020, 147, 111858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Chen, B.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B. Sustainability-based economic and ecological evaluation of a rural biogas-linked agro-ecosystem. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wu, H.; Geng, S. Heterogeneity and threshold effects of environmental regulation on health expenditure: Considering the mediating role of environmental pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngarambe, J.; Yun, G.Y.; Santamouris, M. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) methods in the prediction of thermal comfort in buildings: Energy implications of AI-based thermal comfort controls. Energy Build. 2020, 211, 109807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fu, F.; Liao, N. Exploring the path of carbon emissions reduction in China’s industrial sector through energy efficiency enhancement induced by R&D investment. Energy 2021, 225, 120208.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Edziah, B.K.; Kporsu, A.K.; Sarkodie, S.A.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Energy efficiency: The role of technological innovation and knowledge spillover. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 167, 120659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Wang, C.S.; He, Z.; Xing, W.W.; Wang, K. How does green finance affect energy efficiency? The role of green technology innovation and energy structure. Renew. Energy 2023, 219, 119417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, P.F. Digitization, digital twins, blockchain, and industry 4.0 as elements of management process in enterprises in the energy sector. Energies 2021, 14, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Pohl, J.; Santarius, T. Digitalization and energy consumption: Does ICT reduce energy demand? Ecol. Econ. 2020, 176, 106760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, K.T.; Lytras, M.D.; Visvizi, A. Energy sustainability in smart cities: Artificial intelligence, smart monitoring, and optimization of energy consumption. Energies 2018, 11, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brynjolfsson, E.; Hitt, L.M. Beyond computation: Information technology, organizational transformation, and business performance. J. Econ. Perspect. 2000, 14, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, D.; Jorgenson, A.K.; Longhofer, W. How organizational and global factors condition the effects of energy efficiency on CO2 emission rebounds among the world’s power plants. Energy Policy 2016, 94, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevini, B. Black boxes, not green: Mythologizing artificial intelligence and omitting the environment. Big Data Soc. 2020, 7, 2053951720935141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslid, R.; Okubo, T.; Ulltveit-Moe, K.H. Why are firms that export cleaner? International trade, abatement, and environmental emissions. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 91, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivanco, D.F.; Kemp, R.; Van Der Voet, E. How to deal with the rebound effect? A policy-oriented approach. Energy Policy 2016, 94, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Li, C.; Yin, H.; Zeng, M. Green innovation and China’s CO2 emissions–the moderating effect of institutional quality. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2022, 65, 877–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D.; Restrepo, P. Robots and jobs: Evidence from US labor markets. J. Political Econ. 2020, 128, 2188–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Sun, T. Artificial Intelligence Development and Carbon Emission Intensity: Evidence from Industrial Robot Application. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Impact of industrial robots on environmental pollution: Evidence from China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, C.N.; Long, X.; Dauda, L.; Boamah, K.B.; Salman, M.; Appiah-Twum, F.; Tachie, A.K. Technological innovation and green growth in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S.; Lyytinen, K.; Majchrzak, A.; Song, M. Digital Innovation Management: Reinventing Innovation Management Research in a Digital World. MIS Q. 2017, 41, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Rasool, Z.; Nazar, R.; Anser, M.K. Towards a greener future: How green technology innovation and energy efficiency are transforming sustainability. Energy 2024, 290, 129891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, K.; Dou, J. Effects of economic agglomeration on energy saving and emission reduction: Theory and empirical evidence from China. J. Manag. World 2019, 35, 36–60+226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wu, T.; Hu, X. The effect of spatial diffusion of directed technical change in China. China Ind. Econ. 2017, 35, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Fan, M.; Yang, L. Economic restructuring, green technical progress, and low-carbon transition development in China: An empirical investigation based on the overall technology frontier and spatial spillover effect. J. Manag. World 2022, 38, 46–69+4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.Y.; Li, K.; Qu, J. The path of technological progress for China’s low-carbon development: Evidence from three urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.M.; Ferrándiz, E.; Medina, J. The diffusion of energy technologies: Evidence from renewable, fossil, and nuclear energy patents. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 178, 121566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, D.T.; Helpman, E. International R&D spillovers. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1995, 39, 859–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhao, L.; Yunfang, L.; Wang, W. Can enterprise green technology innovation performance achieve “corner overtaking” by using artificial intelligence?—Evidence from Chinese manufacturing enterprises. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 194, 122732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Jia, R.; Li, D.; Li, H. The rise of robots in China. J. Econ. Perspect. 2019, 33, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Lei, W.; Hou, P. Impact of artificial intelligence technology innovation on total factor productivity: An empirical study based on provincial panel data in China, Natl. Account. Rev 2024, 2, 172–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockburn, I.M.; Henderson, R.; Stern, S. The impact of artificial intelligence on innovation. In The Economics of Artificial Intelligence: An Agenda; Agrawal, A., Gans, J., Goldfarb, A., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018; pp. 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marku, E.; Castriotta, M.; Di Guardo, M.C.; Loi, M. Mapping innovation in the digital transformation era: The role of technology convergence. In Research Anthology on Digital Transformation, Organizational Change, and the Impact of Remote Work; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 761–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y. Artificial Intelligence, Technological Innovation, and Employment Transformation for Sustainable Development: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Gans, J.; Goldfarb, A. Economic policy for artificial intelligence. Innov. Policy Econ. 2019, 19, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyytinen, K.; Yoo, Y.; Boland, R.J. Digital product innovation within four classes of innovation networks. Inf. Syst. J. 2016, 26, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varian, H.R. Computer-mediated transactions. Am. Econ. Rev. 2010, 100, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, E.T.; Nijkamp, P. Externalities in urban sustainability: Environmental versus localization-type agglomeration externalities in a general spatial equilibrium model of a single-sector monocentric industrial city. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 40, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, A.; Hall, R.E. Productivity and the Density of Economic Activity; National Bureau of Economic Research: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Xie, R.; Fang, J. Urban agglomeration economies and industrial energy efficiency. Energy 2018, 162, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lin, B. Will agglomeration improve the energy efficiency in China’s textile industry: Evidence and policy implications. Appl. Energy 2019, 237, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, E. Triumph of the City: How Our Greatest Invention Makes Us Richer, Smarter, Greener, Healthier, and Happier; Penguin: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, E.L.; Kahn, M.E. The greenness of cities: Carbon dioxide emissions and urban development. J. Urban Econ. 2010, 67, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Impacts of urbanization and industrialization on energy consumption/CO2 emissions: Does the level of development matter? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D.; Restrepo, P. Secular stagnation? The effect of aging on economic growth in the age of automation. Am. Econ. Rev. 2017, 107, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Scott, A.J. Industrial agglomeration and development: A survey of spatial economic issues in East Asia and a statistical analysis of Chinese regions. Econ. Geogr. 2003, 79, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Cai, Y. AI, accommodating capacity, and economic growth in China: The new “Solow paradox” and an empirical analysis using the AI patent data. Econ. Perspect. 2022, 39–57. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=ClyI0LvUrM-tpZUsISg-_lnxIM0FeBxpv3BrGoyEx0pjq9c9gIDiLbj4BRc_vQDhx9izHhQmFSAKasXYor_Ny8_ww2wMKcDQR3zfiClq6jQVb4LygUUNV1pE-YhFkoJHsQ0QvHDHmrwyjTKEOeeIOg==&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Wang, H.; Peng, G.; Du, H. Digital economy development boosts urban resilience: Evidence from China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, X.; Huang, S.; Cheng, T.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C. Assessment of green technology innovation on energy-environmental efficiency in China under the influence of environmental regulation considering spatial effects. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, Z.; Su, Y. New media environment, environmental regulation, and corporate green technology innovation: Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2023, 119, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Xiong, Y.; Xiang, G. Environmental regulation benefits for whom? Heterogeneous effects of the intensity of the environmental regulation on employment in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Peterson, S.R.; Portney, P.R.; Stavins, R.N. Environmental regulation and the competitiveness of US manufacturing: What does the evidence tell us? J. Econ. Lit. 1995, 33, 132–163. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2728912 (accessed on 10 October 2013).
- Geng, C.; Cui, Z. Analysis of spatial heterogeneity and driving factors of capital allocation efficiency in energy conservation and environmental protection industry under environmental regulation. Energy Policy 2020, 137, 111081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S. Digital entrepreneurship: Toward a digital technology perspective of entrepreneurship. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2017, 41, 1029–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkov, I.; Trump, B.D.; Poinsatte-Jones, K.; Florin, M.V. Governance strategies for a sustainable digital world. Sustainability 2018, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, T.J. Upgrading strategies for the digital economy. Glob. Strategy J. 2021, 11, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Dong, K.; Dong, X. How does the digital economy improve high-quality energy development? The case of China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 184, 121960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, R.; Gawer, A. Industry architecture as a determinant of successful platform strategies: A case study of the i-mode mobile Internet service. Eur. Manag. Rev. 2009, 6, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, K.; Bi, Y. Internet infrastructure construction, innovation drivers, and regional imbalance in China: Evidence from macro and micro data. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2023, 40, 46–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musacchio, A.; Lazzarini, S.G.; Aguilera, R.V. New varieties of state capitalism: Strategic and governance implications. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2015, 29, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, H.T.; Liu, J.Q.; Lei, J. Digital technology innovation and the high-quality development of Chinese enterprises: Evidence from enterprise’s digital patents. Econ. Res. J. 2023, 58, 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.; Li, S. Emissions trading system and energy use efficiency: Measurements and empirical evidence for cities at and above the prefecture level. China Ind. Econ. 2020, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolko, J. Broadband and local growth. J. Urban Econ. 2012, 71, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duflo, E.; Pande, R. Dams. Q. J. Econ. 2007, 122, 601–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pi, Y. Digital Technology, City Size and Gig Wage: An Empirical Study based on Big Data of Online Recruitment. Bus. Manag. J. 2022, 44, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.W.; Zhang, Y. Digital economy, declining demographic dividends and the rights and interests of low-and medium-skilled labor. Econ. Res. J. 2021, 56, 91–108. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Woods, D. The exogenous effect of geography on economic development: The case of Sub-Saharan Africa. Afr. Asian Stud. 2008, 7, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramcharan, R. Does Economic Diversification Lead to Financial Development? Evidence from Topography. IMF Work. Pap. 2006, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, C. Industry-research Compatibility and Innovation Spillovers from Public Research. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2025, 42, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.; Sant’Anna, P.H.; Bilinski, A.; Poe, J. What’s trending in difference-in-differences? A synthesis of the recent econometrics literature. J. Econom. 2023, 235, 2218–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, C. Can informal environmental regulation induce green innovation? Verification from the perspective of ENGOs. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, H. Local-neighborhood effect of green technology of environmental regulation. China Ind. Econ. 2019, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, S.J.; Shore, D.B.; Cortina, J.M. Review and recommendations for integrating mediation and moderation. Organ. Res. Methods 2017, 20, 686–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.K.; Gao, H.G.; Ding, Q.N.; Hu, Y.N. Impact of local environmental target constraint intensity on the quality of enterprise green innovation. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 32, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Fang, Y.; Quan, S.; Li, X. Leveraging the power of artificial intelligence toward the energy transition: The key role of the digital economy. Energy Econ. 2024, 135, 107654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraj, H.; Bahadori-Jahromi, A.; Amirkhani, S. Developing a Data-Driven AI Model to Enhance Energy Efficiency in UK Residential Buildings. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. dev | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | 3374 | 0.3365 | 0.1315 | 0.1026 | 1.1770 |
| AI | 3374 | 4.4864 | 4.3937 | 0.0126 | 25.9109 |
| Finance | 3374 | 2.4449 | 1.2390 | 0.5879 | 21.3018 |
| Finadp | 3374 | 0.4839 | 0.2241 | 0.0544 | 1.5413 |
| Govern | 3374 | 4.9704 | 2.1195 | 0.0526 | 17.1682 |
| Ind | 3374 | 0.4133 | 0.1028 | 0.1180 | 0.8387 |
| Structure | 3374 | 2.2964 | 0.1451 | 1.8312 | 2.8357 |
| Market | 3374 | 15.5843 | 1.0621 | 12.1008 | 19.0129 |
| Tecn | 3374 | 512.4795 | 1452.051 | 0.0000 | 22275 |
| EA | 3374 | 0.3472 | 0.8070 | 0.0013 | 15.3555 |
| ERI | 3374 | 80.2336 | 22.4102 | 0.4900 | 156.4500 |
| DI | 3374 | 0.1097 | 0.0997 | 0.0014 | 0.8647 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EU | EU | EU | |
| AI | 0.0032 *** | 0.0017 *** | 0.0036 *** |
| (0.0007) | (0.0005) | (0.0007) | |
| Finance | −0.0257 *** | 0.0058 ** | |
| (0.0048) | (0.0026) | ||
| Finadp | 0.1023 *** | 0.0170 | |
| (0.0181) | (0.0216) | ||
| Govern | −0.0064 *** | −0.0027 * | |
| (0.0012) | (0.0015) | ||
| Ind | 0.5860 *** | −0.4946 *** | |
| (0.0803) | (0.0823) | ||
| Structure | −0.3420 *** | 0.4605 *** | |
| (0.0522) | (0.0865) | ||
| Market | 0.0460 *** | −0.0264 *** | |
| (0.0041) | (0.0099) | ||
| Constant | 0.3223 *** | 0.2003 * | −0.1299 |
| (0.0034) | (0.1164) | (0.2063) | |
| City fixed | Yes | No | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | No | Yes |
| Observations | 3374 | 3374 | 3374 |
| R-squared | 0.6479 | 0.2046 | 0.6525 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| AI | EU | |
| Terrain ruggedness × Year | −0.1315 *** | |
| (0.0129) | ||
| AI | 0.0223 *** | |
| (0.0038) | ||
| Constant | 524.2929 *** | −0.4564 ** |
| (49.9756) | (0.1992) | |
| The first-stage F statistic | 104.6770 *** | |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk LM | 110.5960 *** | |
| Cragg–Donald Wald F | 124.6260 | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes |
| City fixed | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.8211 | 0.6125 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| EU | EU | |
| DID | 0.2724 *** | 0.2735 *** |
| (0.0454) | (0.0453) | |
| Constant | 0.3352 *** | −0.0266 |
| (0.0013) | (0.2047) | |
| Controls | No | Yes |
| City fixed | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.6646 | 0.6687 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| EU | EU | |
| DID_neighbor | −0.0032 | −0.0047 |
| (0.0139) | (0.0136) | |
| Constant | 0.3305 *** | −0.1019 |
| (0.0013) | (0.2043) | |
| Controls | No | Yes |
| City fixed | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.6650 | 0.6702 |
| Variable | Metrics Replacement | Tail Reduction Treatment | Reduce the Sample Size | Replace the Interpolation Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| EU | EU | EU | EU | LnEnc | EU | EU | EU | |
| Robotstock | 0.0007 *** | |||||||
| (0.0001) | ||||||||
| Company | 0.0014 *** | |||||||
| (0.0002) | ||||||||
| Patents1 | 0.0357 *** | |||||||
| (0.0034) | ||||||||
| Patents2 | 0.0347 *** | |||||||
| (0.0037) | ||||||||
| AI | −0.0268 *** | 0.0040 *** | 0.0036 *** | 0.0033 *** | ||||
| (0.0040) | (0.0008) | (0.0007) | (0.0007) | |||||
| Constant | −0.1169 | 0.0227 | −0.0821 | −0.0607 | −0.0121 | 0.0912 | −0.1645 | 0.0178 |
| (0.2031) | (0.2034) | (0.2041) | (0.2039) | (0.9380) | (0.2136) | (0.2066) | (0.2027) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.6538 | 0.6769 | 0.6985 | 0.6971 | 0.7338 | 0.6620 | 0.6555 | 0.6799 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| Tecn | EA | |
| AI | 0.0656 *** | 0.0379 *** |
| (0.0060) | (0.0038) | |
| Constant | −0.7391 | −0.7923 * |
| (0.9789) | (0.4343) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes |
| City fixed | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.6833 | 0.8441 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnKlstru | LnEc | LnLabor | GDP | UO | |
| AI | −0.014 *** | −0.0282 *** | 0.0062 *** | 0.0402 *** | −0.0269 *** |
| (0.0012) | (0.0041) | (0.0020) | (0.0031) | (0.0055) | |
| Constant | 10.9021 *** | 10.6623 *** | −0.9288 * | −1.1075 *** | 0.1955 |
| (0.4690) | (1.2186) | (0.4846) | (0.4737) | (0.7791) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.9828 | 0.8895 | 0.9449 | 0.9158 | 0.7970 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | EU | EU | EU | |
| AI | 0.0036 *** | 0.0034 *** | 0.0035 *** | 0.0003 |
| (0.0007) | (0.0007) | (0.0007) | (0.0012) | |
| LnERI | 0.0048 | 0.0076 | ||
| (0.0064) | (0.0063) | |||
| LnDI | −0.0126 * | −0.0062 | ||
| (0.0069) | (0.0069) | |||
| AI | 0.0029 *** | |||
| (0.0007) | ||||
| AI × LnDI | 0.0028 *** | |||
| (0.0008) | ||||
| Constant | −0.0981 | −0.0405 | −0.1640 | −0.2351 |
| (0.2051) | (0.2077) | (0.2067) | (0.2086) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.6525 | 0.6536 | 0.6530 | 0.6557 |
| Variable | East | Central | West | Northeast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | EU | EU | EU | |
| AI | 0.0038 *** | 0.0033 *** | 0.0039 *** | 0.0019 |
| (0.0014) | (0.0010) | (0.0012) | (0.0042) | |
| Constant | −0.4844 | −0.3207 | −0.2934 | −2.2362 |
| (0.5161) | (0.2658) | (0.3160) | (0.5903) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.5776 | 0.6527 | 0.7112 | 0.6165 |
| Variable | Resource-Based City | Non-Resource-Based City | Old Industrial Base City | Non-Old Industrial Base Cities | Key Environmental Protection City | Non-Key Environmental Protection City |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | EU | EU | EU | EU | EU | |
| AI | 0.0022 * | 0.0029 *** | −0.0007 | 0.0053 *** | 0.0032 ** | 0.0001 |
| (0.0012) | (0.0009) | (0.0008) | (0.0009) | (0.0013) | (0.0009) | |
| Constant | −0.0026 | −0.0201 | −0.5499 | −0.0212 | −0.5407 | −0.3282 |
| (0.2827) | (0.2987) | (0.3001) | (0.2709) | (0.5801) | (0.2084) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R-squared | 0.6635 | 0.6346 | 0.7540 | 0.6106 | 0.6860 | 0.6311 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Cheng, J.; Tan, X.; Li, J. Artificial Intelligence Technology Applications and Energy Utilization Efficiency: Empirical Evidence from China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6463. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146463
Xie H, Cheng J, Tan X, Li J. Artificial Intelligence Technology Applications and Energy Utilization Efficiency: Empirical Evidence from China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6463. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146463
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Hanjin, Jiahui Cheng, Xi Tan, and Jun Li. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence Technology Applications and Energy Utilization Efficiency: Empirical Evidence from China" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6463. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146463
APA StyleXie, H., Cheng, J., Tan, X., & Li, J. (2025). Artificial Intelligence Technology Applications and Energy Utilization Efficiency: Empirical Evidence from China. Sustainability, 17(14), 6463. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146463






