The Hydrochemical Characteristics Evolution and Driving Factors of Shallow Groundwater in Luxi Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. The Absolute Principal Component Score–Multiple Linear Regression Receptor Model
2.4. Water Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in the Study Area
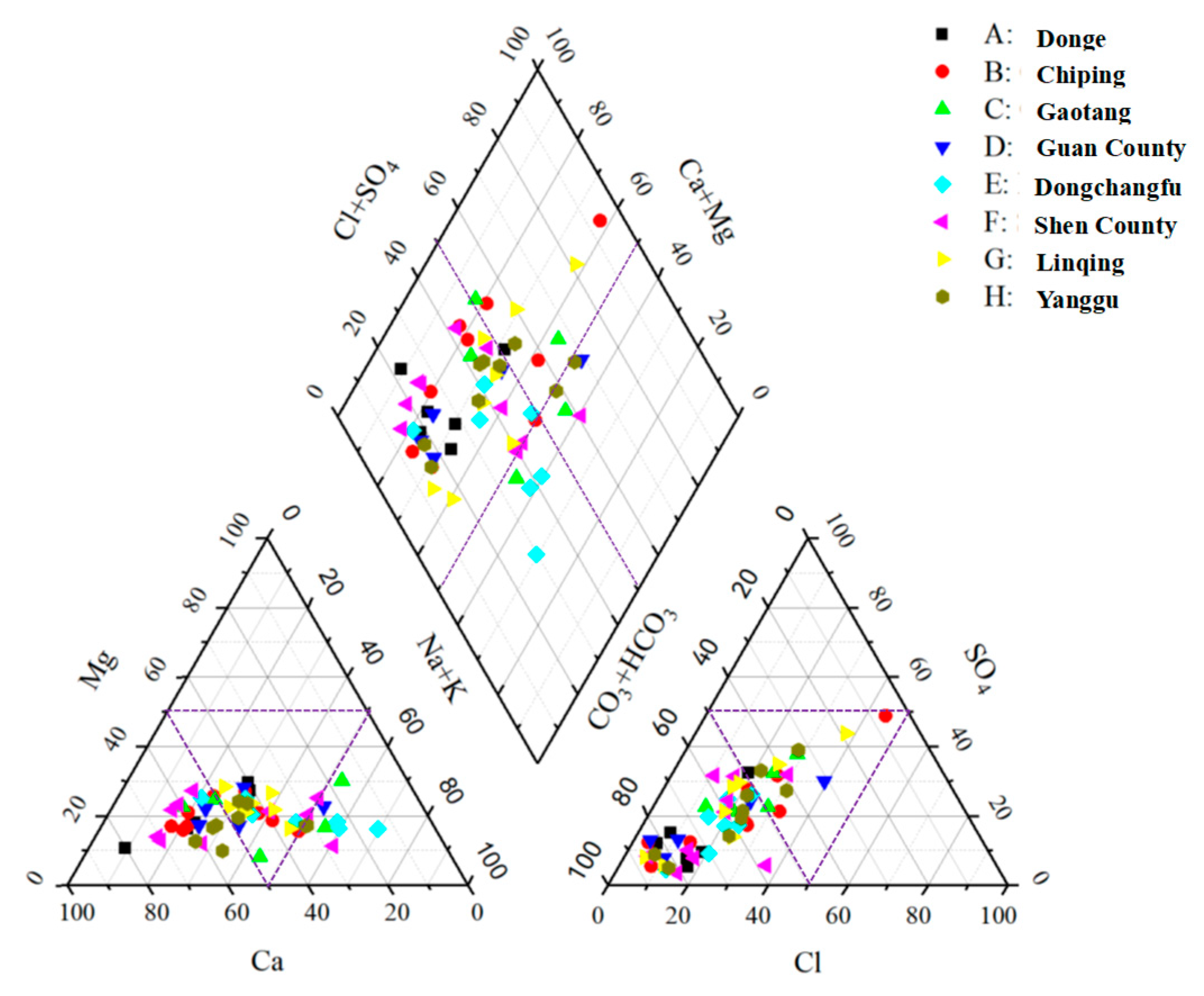
3.2. Types of Groundwater Chemistry in the Study Area
3.3. Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment
3.4. Analysis of Major Ion Sources and Driving Factors
3.4.1. Different Ion Contributions
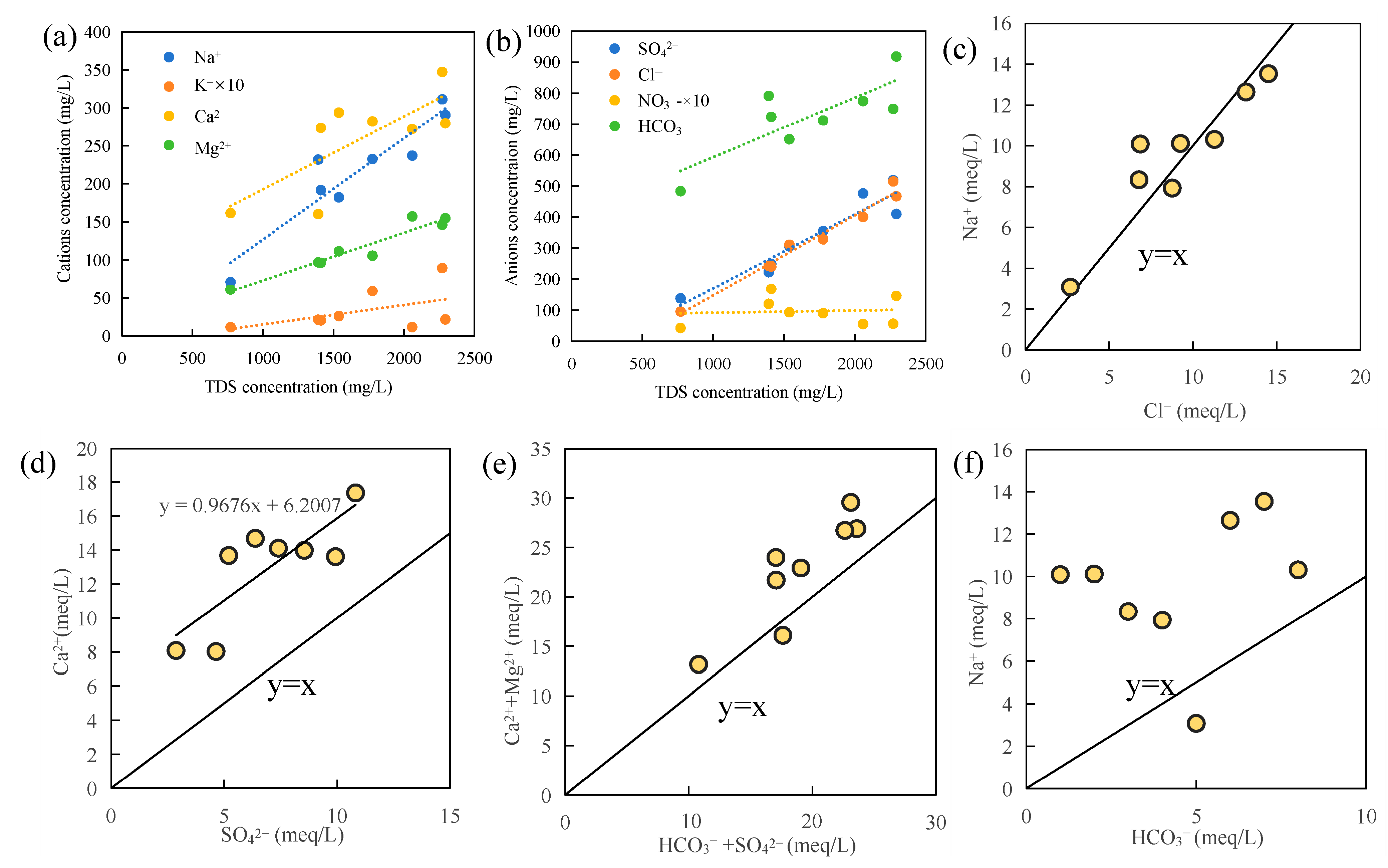
3.4.2. Relationships Between Main Ions
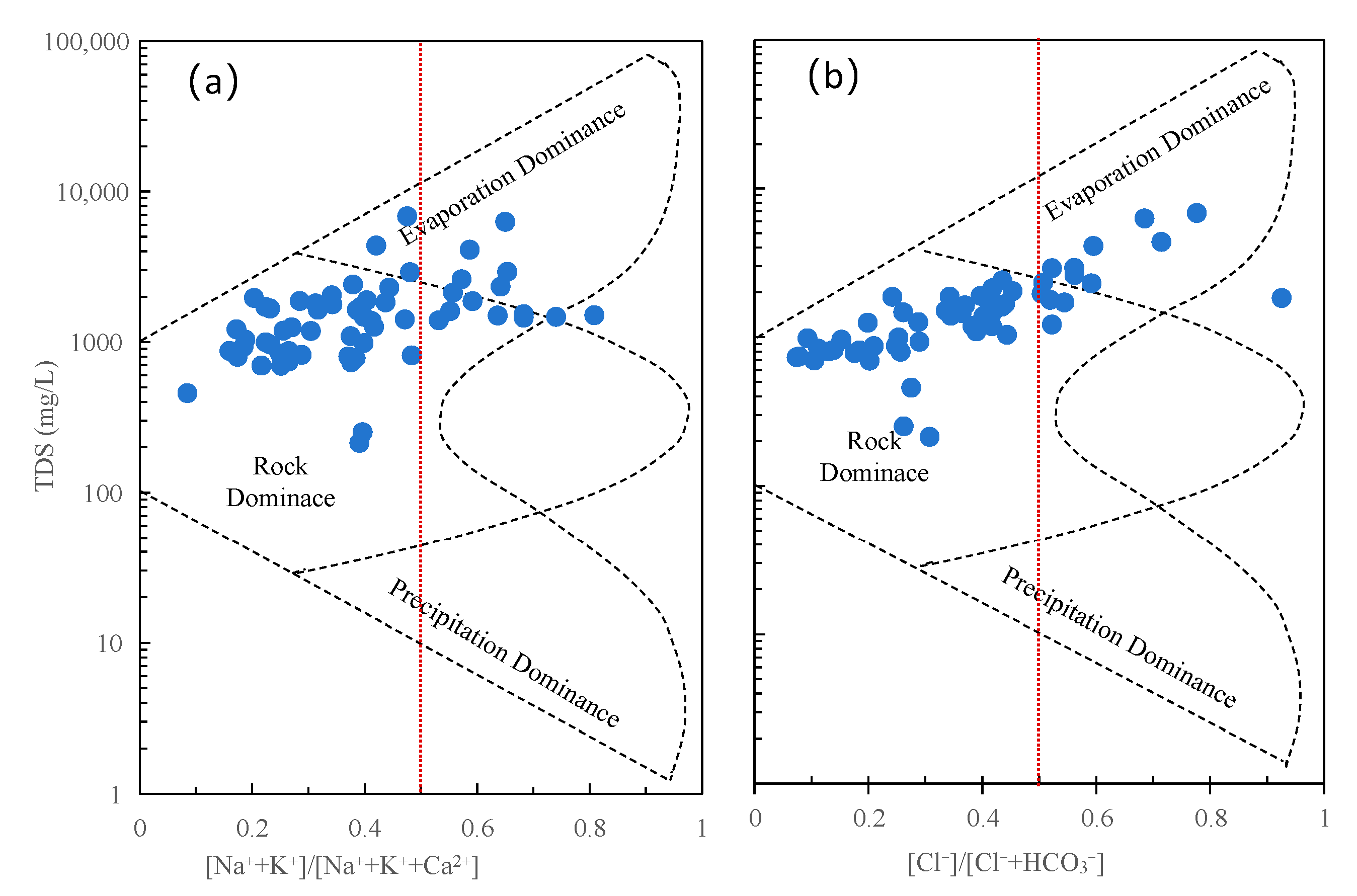
3.4.3. Rock Weathering
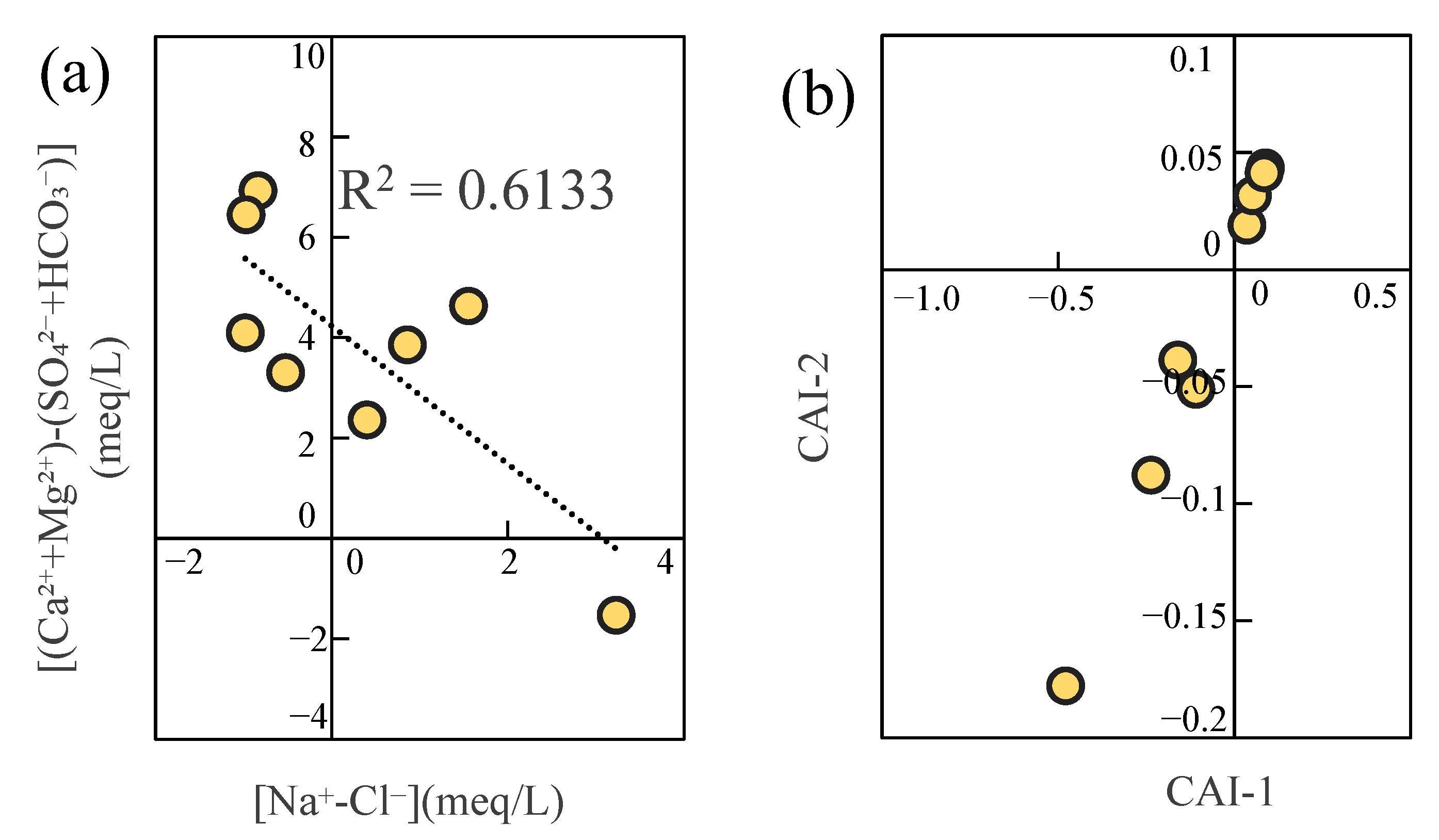
3.4.4. Cation Exchange Adsorption
3.4.5. Anthropogenic Influences on Groundwater Chemistry
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mthembu, P.P.; Elumalai, V.; Senthilkumar, M.; Wu, J. Investigation of geochemical characterization and groundwater quality with special emphasis on health risk assessment in alluvial aquifers, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3711–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, Y.; Ubomba-Jaswa, E.; Dippenaar, M.A. Potential SARS-CoV-2 contamination of groundwater as a result of mass burial: A mini-review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natishah, A.J.; Samuel, M.S.; Velmurugan, K.; Showparnickaa, S.R.; Indumathi, S.M.; Kumar, M. Contamination of groundwater by microorganisms and risk management: Conceptual model, existing data, and challenges. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 29, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, R.S.; Aswal, R.S.; Negi, J.S.; Prasad, M.; Joshi, A.; Ramola, R.C. Distribution and risk estimation of potentially toxic elements in potable groundwater of Kumaun Himalaya, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Nandimandalam, J.R.; Pant, D.; Chatterjee, S.; Ram, P. Environmental isotope constraints and hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in the semi-arid national capital environs of Delhi, India. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewusi, A.; Sunkari, E.D.; Seidu, J.; Coffie-Anum, E. Hydrogeochemical characteristics, sources and human health risk assessment of heavy metal dispersion in the mine pit water-surface water-groundwater system in the largest manganese mine in Ghana. Environ. Technol. Innvo. 2022, 26, 102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folarin, G.M.; Badmus, B.S.; Akinyemi, O.D.; Idowu, O.A.; Oke, A.O.; Badmus, G.O. Groundwater quality assessment using physico-chemical parameters and pollution sources apportionment in selected farm settlements of Southwestern Nigeria. Int. J. Energy Water Resour. 2023, 7, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X.; Deng, W.; He, Y.; Ramis, S. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution laws of groundwater in Songnei Plain, Northeast China. Adv. Water Sci. 2006, 17, 20–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ustaoglu, F.; Tepe, Y.; Tas, B. Assessment of stream quality and health risk in a subtropical Turkey river system: A combined approach using statistical analysis and water quality index. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H. Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, South India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanidhi, D.; Aravinthasamy, P.; Deepali, M.; Subramani, T.; Bellows, B.C.; Li, P. Groundwater quality evolution based on geochemical modeling and aptness testing for ingestion using entropy water quality and total hazard indexes in an urban-industrial area (Tiruppur) of Southern India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18523–18538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, W.M.; Healy, R.W.; LaBaugh, J.W.; Reilly, T.E. Flow and storage in groundwater systems. Science 2002, 296, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Lv, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, F.; Wang, Q. Spatial–temporal changes in shallow groundwater quality with human health risk assessment in the Luxi Plain (China). Water 2023, 15, 4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.; Liu, X.Z.; Zhang, G.Y. Exploration and management of shallow groundwater over-exploitation area in Luxi Plain. Groundwater 2010, 4, 24–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5749–2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. Inspection and Quarantine of the P.R. China. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese)
- Meng, L.; Zuo, R.; Wang, J.S.; Yang, J.; Teng, Y.G.; Shi, R.T.; Zhai, Y.Z. Apportionment and evolution of pollution sources in a typical riverside groundwater resource area using PCA-APCS-MLR model. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 218, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, M.; Wu, S.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. A modified receptor model for source apportionment of heavy metal pollution in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 354, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, G.D.; Spengler, J.D. A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston. Atmos. Environ. 1985, 19, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Fang, W.; Shafi, M.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhong, B.; Ma, D.; Liu, D. Source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil with application of APCS-MLR model: A pilot study for restoration of farmland in Shaoxing City Zhejiang, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14848–2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. Inspection and Quarantine of the P.R. China. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Albi, L.S.; Kartohardjono, S. The combined process of coagulation flocculation and membrane separations to treat wastewater from Tofu industry. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2230, 030010. [Google Scholar]
- Ngwese, S.N.; Mouri, H.; Akoachere, R.A.I.; McKinley, J.; Candeias, C. Assessment of potentially harmful elements in surface and groundwater from the granito-gneissic aquiferous formations in Bertoua city and environs, East Region, Cameroon, Central Africa: Effects on human health. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 29, 101420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Ma, C.; He, Z.; Hu, X.; Gao, L. Lithium and its isotopes as tracers of groundwater salinization: A study in the southern coastal plain of Laizhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.Y. Feasibility Assessment of River Bank Filtration Along the Second Songhua River and Yinma River. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Ding, Q.Z.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Zhou, J.L. Analysis of groundwater hydrochemical variation and its source during the low water level period in the southern oasis area of Gaochang District, Turpan City. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 227–238. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.H.; Wu, B.; Wu, G.; Gao, F.; Du, M.L.; Cao, W. Evolution and mechanism analysis of groundwater chemical characteristics in the context of overexploitation—A case study of Qitai County, eastern part of Changji Prefecture, Xinjiang. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2024, 44, 168–178. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Qian, H. Groundwater nitrate contamination and associated health risk for the rural communities in an agricultural area of Ningxia, northwest China. Expos. Health 2016, 8, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Xiao, J.; Li, S.; Li, Z. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and their controlling factors in the Fen River of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, S. Extreme precipitation accelerates the contribution of nitrate sources from anthropogenetic activities to groundwater in a typical headwater area of the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, T.; Sheik Farid, N.S.; Swathi, K.V.; Sowmya, A.; Ramani, K. Sustainable biological system for the removal of high strength ammoniacal nitrogen and organic pollutants in poultry waste processing industrial effluent. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2020, 70, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounslow, A.W. Water Quality Data: Analysis and Interpretation; CRC Press: Florida, BR, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Biddau, R.; Dore, E.; Da Pelo, S.; Lorrai, M.; Botti, P.; Testa, M.; Cidu, R. Geochemistry, stable isotopes and statistic tools to estimate threshold and source of nitrate in groundwater (Sardinia, Italy). Water Res. 2023, 232, 119663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qian, H.; Xu, P.; Li, W.; Feng, W.; Liu, R. Effect of hydrogeological conditions on groundwater nitrate pollution and human health risk assessment of nitrate in Jiaokou irrigation district. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 795–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Z. Hydrochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of groundwater in Dingbian county of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaga, A.C.; Soler, J.M.; Ganor, J.; Burch, T.E.; Nagy, K.L. Chemical weathering rate laws and global geochemical cycles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1994, 58, 2361–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malov, A.I. The Conditions for the Formation of Strontium in the Water of Ancient Silicate Deposits Near the Arctic Coast of Russia. Water 2024, 16, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Luo, W.; Ma, T.; Wang, Y. Multiple isotope geochemistry and hydrochemical monitoring of karst water in a rapidly urbanized region. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 218, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, X.W.; Wan, L.; Han, G.; Guo, H. Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater flow systems in the discharge area of a river basin. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Wei, W.; Zhao, G.H.; Wang, X.D.; Huang, J.M. Hydrochemical characteristics and control factors of shallow groundwater in Anqing section of the Yangtze River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 1525–1538. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Shi, J.; Liu, J.; Gui, C. Combined use of multivariate statistical analysis and hydrochemical analysis for groundwater quality evolution: A case study in north chain plain. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 25, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, D.W.; Lei, K.; Lv, X.B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.B. Hydrochemical characteristics and impact factors in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River in the wet season. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 380–386. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, J. Hydrochemical evolution characteristics, controlling factors, and high nitrate hazards of shallow groundwater in a typical agricultural area of Nansi Lake Basin, North China. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.L.; Yang, R.B.; Ma, Y.Q.; Linghu, C.W.; Zhao, R.G.; He, C.Z. Characteristics and driving factors of hydrochemical evolution in Tuochangjiang River Basin, Western Guizhou Province. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 740–751. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Widory, D.; Kloppmann, W.; Chery, L.; Bonnin, J.; Rochdi, H.; Guinamant, J.L. Nitrate in groundwater: An isotopic multi-tracer approach. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 72, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameters | Units | Detection Limits | Chinese Standards [16] |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | - | 6.5–8.5 |
| TDS | mg/L | 4 | 450 |
| THRD | mg/L | 5 | 1000 |
| COD | mg/L | 0.5 | 3 |
| K+ | mg/L | 0.03 | - |
| Na+ | mg/L | 0.02 | 200 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 0.002 | 200 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 0.02 | 150 |
| Mn2+ | mg/L | 0.05 | 0.1 |
| NH4+-N | mg/L | 0.025 | 0.5 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 0.1 | 250 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 0.1 | 250 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 5 | - |
| CO32− | mg/L | 5 | - |
| NO3−-N | mg/L | 0.1 | 10 |
| Districts | pH | THRD | TDS | Na+ | Mn2+ | SO42− | Cl− | NO3−-N | COD | NH4+-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | |
| Dognchangfu | 7.60 | 598 | 1392 | 232 | 0.30 | 223 | 243 | 12.0 | 1.80 | 0.18 |
| Yanggu | 7.59 | 732 | 1776 | 233 | 0.26 | 355 | 329 | 8.98 | 1.77 | 0.17 |
| Shen County | 7.51 | 662 | 1410 | 192 | 0.21 | 250 | 241 | 16.9 | 1.51 | 0.10 |
| Chiping | 7.58 | 795 | 1538 | 182 | 0.36 | 306 | 311 | 9.29 | 2.62 | 0.13 |
| Donge | 7.57 | 421 | 770 | 70.9 | 0.16 | 138 | 95.2 | 4.22 | 1.62 | 0.37 |
| Guan County | 7.64 | 898 | 2293 | 291 | 0.29 | 410 | 467 | 14.6 | 1.89 | 0.26 |
| Gaotang | 7.65 | 922 | 2271 | 311 | 0.42 | 519 | 515 | 5.60 | 2.00 | 0.26 |
| Linqing | 7.69 | 899 | 2058 | 237 | 0.28 | 476 | 401 | 5.51 | 1.55 | 0.18 |
| Districts | pH | THRD | TDS | Na+ | Mn2+ | SO42− | Cl− | NO3−-N | COD | NH4+-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | |
| Dognchangfu | 7.90 | 517 | 1206 | 193 | 0.58 | 108 | 161 | 0.33 | 1.55 | 0.43 |
| Yanggu | 7.57 | 709 | 1450 | 175 | 0.40 | 257 | 145 | 8.18 | 2.13 | 0.24 |
| Shen County | 7.65 | 617 | 1082 | 105 | 0.28 | 59.0 | 167 | 0.23 | 1.14 | 0.08 |
| Chiping | 7.69 | 805 | 2090 | 399 | 0.31 | 386 | 339 | 4.61 | 1.65 | 0.05 |
| Donge | 7.60 | 528 | 957 | 123 | 0.71 | 94.0 | 48.6 | 0.26 | 1.16 | 0.14 |
| Guan County | 7.25 | 770 | 1570 | 250 | 0.26 | 274 | 150 | 1.53 | 1.98 | 0.30 |
| Gaotang | 7.50 | 1180 | 2250 | 250 | 0.96 | 346 | 502 | 0.15 | 1.40 | 0.08 |
| Linqing | 7.27 | 745 | 1480 | 198 | 0.51 | 192 | 203 | 0.14 | 1.49 | 0.24 |
| Districts | pH | THRD | TDS | Na+ | Mn2+ | SO42− | Cl− | NO3− | COD | NH4+-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | |
| Dognchangfu | 7.42 | 541 | 1269 | 206 | 0.30 | 155 | 198 | 1.46 | 1.14 | 0.27 |
| Yanggu | 7.52 | 820 | 2167 | 392 | 0.12 | 451 | 482 | 10.2 | 1.39 | 0.06 |
| Shen County | 7.37 | 645 | 1239 | 113 | 0.39 | 93.9 | 243 | 3.27 | 0.77 | 0.11 |
| Chiping | 7.31 | 873 | 2650 | 546 | 0.29 | 612 | 592 | 5.03 | 1.17 | 0.02 |
| Donge | 7.17 | 463 | 932 | 134 | 0.50 | 97.5 | 38.5 | 1.31 | 1.02 | 0.05 |
| Guan County | 7.11 | 720 | 1605 | 255 | 0.19 | 313 | 203 | 0.94 | 0.80 | 0.24 |
| Gaotang | 7.02 | 1130 | 2150 | 231 | 0.71 | 355 | 505 | 1.67 | 0.76 | 0.02 |
| Linqing | 7.52 | 666 | 1338 | 188 | 0.21 | 198 | 190 | 0.73 | 1.21 | 0.09 |
| Parameters | Units | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | ||
| pH | — | 7.20 | 8.10 | 7.60 | 7.00 | 7.90 | 7.55 | 6.74 | 7.83 | 7.30 |
| TDS | mg/L | 214 | 6836 | 1689 | 791 | 3010 | 1511 | 817 | 5050 | 1689 |
| THRD | mg/L | 125 | 2363 | 741 | 450 | 1180 | 734 | 457 | 1290 | 732 |
| COD | mg/L | 0.81 | 7.26 | 1.85 | 0.75 | 3.04 | 1.55 | 0.14 | 2.17 | 1.07 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 19.2 | 901 | 215 | 64.6 | 690 | 212 | 81.8 | 1210 | 214 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 31.3 | 1654 | 318 | 46.8 | 546 | 209 | 38.5 | 1390 | 3089 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 20.8 | 1921 | 330 | 20.6 | 633 | 205 | 57.6 | 1420 | 302 |
| Year | Items | EWQI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | THRD | TDS | SO42− | Cl− | Mn2+ | COD | NH4+-N | ||
| 2020 | II | V | IV | IV | IV | IV | II | III | III |
| 2021 | II | V | IV | III | III | IV | II | IV | III |
| 2022 | II | V | IV | IV | IV | IV | II | III | III |
| Items | APCS1 | APCS2 |
|---|---|---|
| TDS | 0.99 | 0.12 |
| Na+ | 0.93 | 0.23 |
| K+ | 0.065 | −0.51 |
| Ca2+ | 0.83 | −0.19 |
| Mg2+ | 0.93 | 0.15 |
| SO42− | 0.97 | −0.16 |
| Cl− | 0.99 | 0.022 |
| NO3− | 0.017 | 0.89 |
| HCO3− | 0.73 | 0.66 |
| pH | THRD | TDS | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | SO42− | NO3− | Cl− | HCO3− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||||
| THRD | 0.70 | 1 | |||||||||
| TDS | 0.51 | 0.91 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| Na+ | 0.61 | 0.81 * | 0.88 ** | 1 | |||||||
| K+ | 0.17 | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 1 | ||||||
| Ca2+ | 0.23 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.41 | 0.83 * | 1 | |||||
| Mg2+ | 0.69 | 0.91 ** | 0.88 ** | 0.76 * | 0.25 | 0.41 | 1 | ||||
| SO42− | 0.70 | 0.98 ** | 0.93 ** | 0.88 ** | 0.48 | 0.64 | 0.88 ** | 1 | |||
| NO3− | −0.67 | −0.095 | 0.095 | 0.048 | 0.18 | 0.048 | −0.071 | −0.12 | 1 | ||
| Cl− | 0.69 | 0.93 ** | 0.95 ** | 0.93 ** | 0.59 | 0.62 | 0.88 ** | 0.95 ** | −0.048 | 1 | |
| HCO3− | 0.23 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.71 * | 0.036 | −0.17 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 1 |
| Districts | γ | CAI-1 | CAI-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dognchangfu | −2.11 | −0.48 | −0.18 |
| Yanggu | 0.22 | −0.11 | −0.051 |
| Shen County | 0.34 | −0.24 | −0.088 |
| Chiping | −0.12 | 0.088 | 0.043 |
| Donge | 0.17 | −0.16 | −0.039 |
| Guan County | −0.16 | 0.036 | 0.019 |
| Gaotang | −0.15 | 0.051 | 0.032 |
| Linqing | −0.24 | 0.084 | 0.041 |
| Districts | NO3−/Cl− | Cl− | SO42−/Ca2+ | NO3−/Ca2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dognchangfu | 0.049 | 243 | 1.39 | 0.075 |
| Yanggu | 0.027 | 329 | 1.26 | 0.032 |
| Shen County | 0.070 | 241 | 0.91 | 0.062 |
| Chiping | 0.030 | 311 | 1.04 | 0.032 |
| Donge | 0.044 | 95.2 | 0.85 | 0.026 |
| Guan County | 0.031 | 467 | 1.47 | 0.052 |
| Gaotang | 0.011 | 515 | 1.49 | 0.016 |
| Linqing | 0.014 | 401 | 1.75 | 0.020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, N.; Han, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, F.; Wang, Q. The Hydrochemical Characteristics Evolution and Driving Factors of Shallow Groundwater in Luxi Plain. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146432
Yu N, Han Y, Liu G, Zhuang F, Wang Q. The Hydrochemical Characteristics Evolution and Driving Factors of Shallow Groundwater in Luxi Plain. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146432
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Na, Yingjie Han, Guang Liu, Fulei Zhuang, and Qian Wang. 2025. "The Hydrochemical Characteristics Evolution and Driving Factors of Shallow Groundwater in Luxi Plain" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146432
APA StyleYu, N., Han, Y., Liu, G., Zhuang, F., & Wang, Q. (2025). The Hydrochemical Characteristics Evolution and Driving Factors of Shallow Groundwater in Luxi Plain. Sustainability, 17(14), 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146432






