Sustainability Effects of Free Trade Zones: Evidence from Water Pollution in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on Water Pollution
2.2. Research on the Policy Effects of FTZs
2.3. Summary
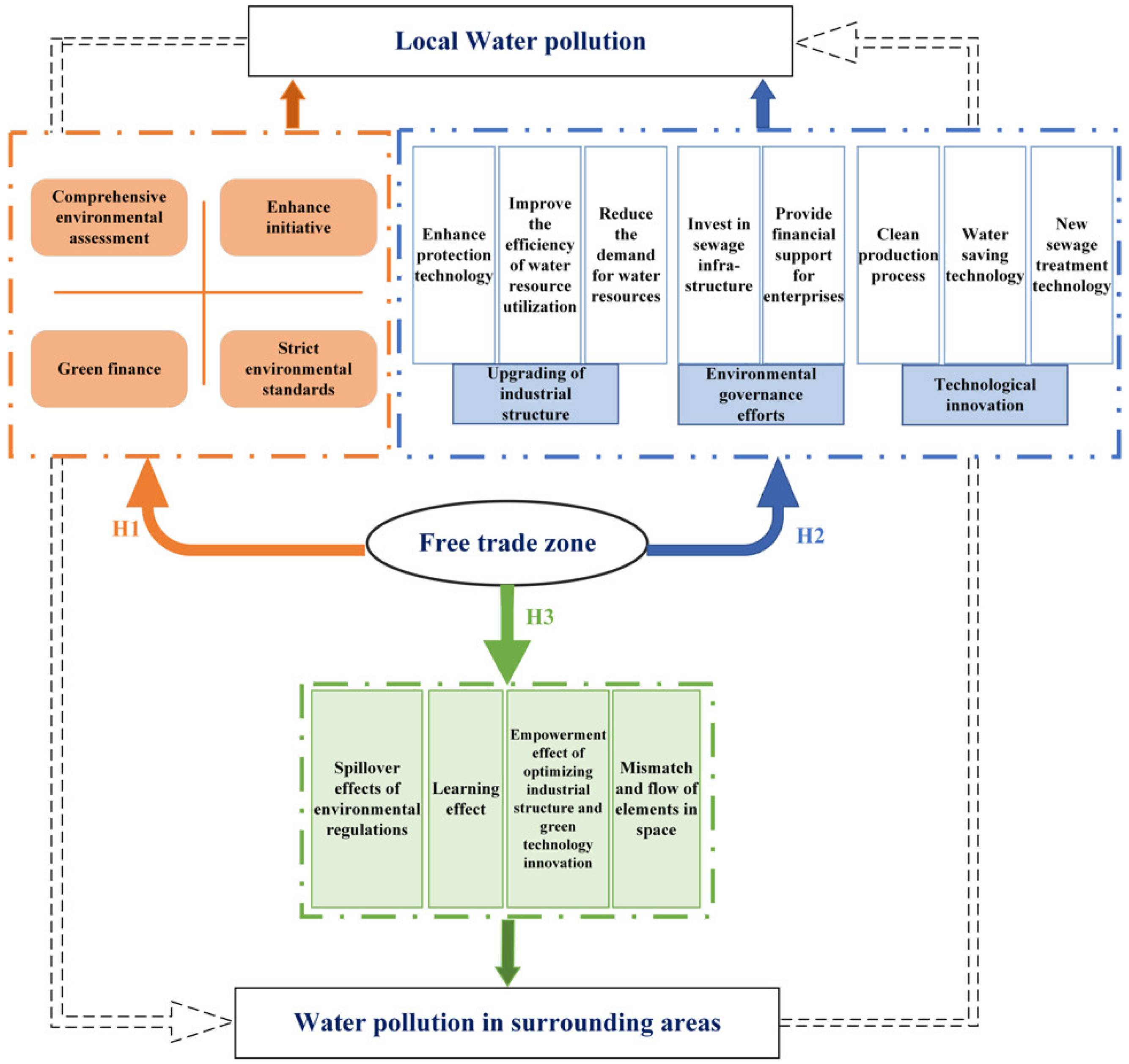
3. Theoretical Mechanism and Research Hypothesis
3.1. Direct Impact
3.2. Indirect Mechanism
3.2.1. FTZs Reduce Water Pollution by Facilitating Industrial Structure Upgrading
3.2.2. FTZs Reduce Water Pollution by Fostering Technological Innovation
3.2.3. FTZs Reduce Water Pollution by Enhancing Government Environmental Governance
3.3. Spatial Effects
4. Methodology
4.1. Variables
4.1.1. Dependent Variable
4.1.2. Independent Variable
4.1.3. Mediator Variables
4.1.4. Control Variables
4.2. Model
4.2.1. Basic Model
4.2.2. Spatial Effect Model
4.2.3. Influence Mechanism Model
4.3. Sample Selection and Data Sources
5. Empirical Results
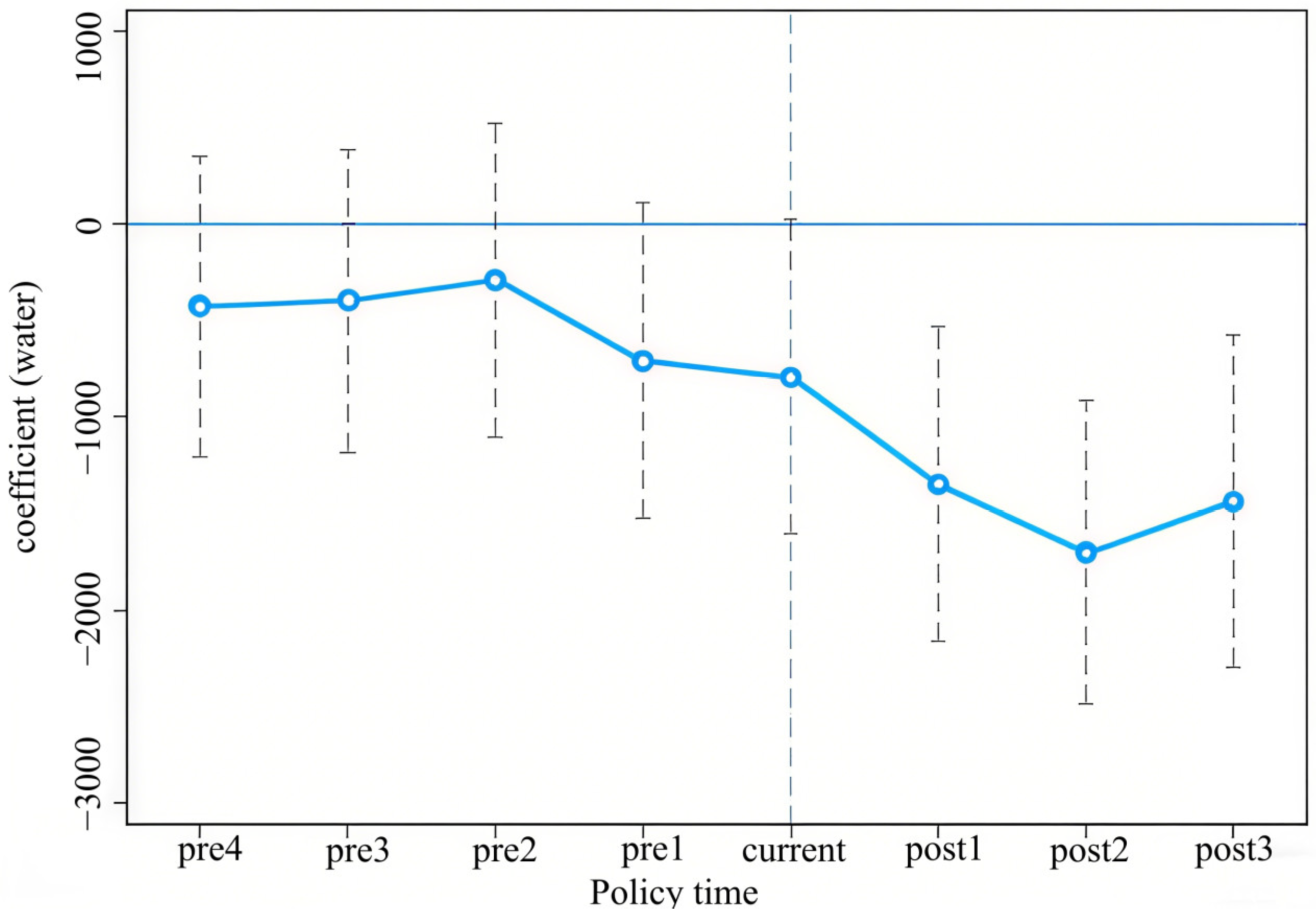
5.1. Parallel Trend Test
5.2. Regression Results
5.2.1. Benchmark Regression
5.2.2. Decomposition of Spatial Effects
5.3. Robustness Test
5.3.1. Placebo Test
5.3.2. PSM-DID Test
5.3.3. Eliminate the RCS’s External Interference
5.3.4. Change Methods
5.3.5. Replace Spatial Matrix
5.4. Analysis of Influence Mechanism
6. Discussion
6.1. Interpretation of Findings
6.2. Policy Implications
6.2.1. Strengthen the Concept of Green Development and Institutional Innovation in FTZs
6.2.2. Promote Industrial Structure Upgrading, Technological Innovation, and Environmental Governance in FTZs
6.2.3. Construct a Regional Collaborative Governance Network of Water Pollution
6.3. Limitations and Prospects
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| The Abbreviation of the City Name | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sjz | as | hh | mas | fz | ny | sg | hc | xa |
| ts | fs | sh | hb | sr | sq | sz | hk | tc |
| qhd | bx | nj | tl | jn | xy | zh | sy | bj |
| hd | dd | wx | aq | qd | zk | st | cd | xy |
| xt | jz | xz | hs | zb | zmd | fs | zg | wn |
| bd | yk | cz | cz | zz | wh | jm | pzh | ya |
| zjk | fx | sz | fy | dy | hs | zj | zz | hz |
| cd | ly | nt | sz | yt | sy | mm | dy | yl |
| cz | pj | lyg | la | wf | yc | zq | my | ak |
| lf | tl | ha | zz | jn | ez | hz | gy | sl |
| hs | cy | yc | cz | ta | jm | mz | sn | lz |
| ty | hld | yz | xc | wh | xg | sw | nj | jyg |
| dt | cc | zj | fz | rz | jz | hy | ls | jc |
| yq | jl | tz | xm | ly | hg | yj | nc | by |
| cz | sp | sq | pt | dz | xn | qy | ms | ts |
| jc | ly | hz | sm | lc | sz | dz | yb | ww |
| sz | th | nb | qz | bz | cs | zs | ga | zy |
| jz | bs | wz | zz | hz | zz | cz | dz | pl |
| yc | sy | jx | np | zz | xt | yf | ya | jq |
| xz | bc | hz | ly | kf | hy | nn | bz | xn |
| lf | heb | sx | nd | ly | sy | lz | zy | yc |
| hhht | qqhe | jh | nc | pds | yy | gl | gy | szs |
| bt | jx | zz | jdz | ay | cd | wz | lps | wz |
| wh | hg | zs | px | hb | zjj | bh | zy | gy |
| cf | sys | tz | jj | xx | yy | fcg | as | wlmq |
| tl | dq | ls | xy | jz | cz | qz | km | klmy |
| eeds | yc | hf | yt | zy | yz | gg | qj | |
| hlbe | jms | wh | gz | xc | hh | yl | yx | |
| sy | qth | bb | ja | zh | ld | bs | bs | |
| dl | mdj | hn | yc | smx | gz | hz | zt | |
References
- Zhou, X.F.; Cao, G.Z.; Yu, F.; Liu, Q.; Ma, G.; Yang, W. Risk zoning of acute water pollution in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2020, 1, 334–342. [Google Scholar]
- Babuji, P.; Thirumalaisamy, S.; Duraisamy, K.; Periyasamy, G. Human Health Risks due to Exposure to Water Pollution: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.S.; Agapi, S. A dynamic evaluation of the effects of a free trade area of the Americas—An intertemporal, global general equilibrium model. J. Econ. Integr. 2001, 1, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.C.; Yu, D.F.; Zhai, Q.; Wang, D.; Niu, Z.Y. On the effect of China (Shanghai) pilot free trade zone on headquarters economic development in Shanghai. Foreign Econ. Manag. 2014, 4, 65–71+80. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.L.; Liu, D. Research on the “quality effect” of the construction of China’s pilot free trade zone. Economist 2021, 9, 58–68. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Hu, Y.N.; Cheng, H.F. Water pollution during China’s industrial transition. Environ. Dev. 2013, 1, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Q. Clean production and wastewater treatment technologies to reduce water pollution in the manufacturing sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; He, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ren, K. Evaluating the effect of Chinese environmental regulation on corporate sustainability performance: The mediating role of green technology innovation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 11, 6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Zhao, T.R. Has the pilot free trade zone promoted the upgrading of industrial structure: An empirical analysis based on China (Shanghai) pilot free trade zone. J. Cent. Univ. Financ. Econ. 2019, 8, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.X.; Yang, H.E.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.L. Research on the impact of construction of pilot free trade zones on corporate R&D investment: An analysis based on the moderating effect of marketability process. Sci. Res. Manag. 2024, 4, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, P.; Moretti, E. People, Places, and Public Policy: Some Simple Welfare Economics of Local Economic Development Programs. Annu. Rev. Econ. 2014, 1, 629–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeSage, J.P.; Dominguez, M. The importance of modeling spatial spillovers in public choice analysis. Public Choice 2012, 1, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Liu, Y.B. The effectiveness of “bottom-up” environmental policies: A comparative analysis of heterogeneity of the River Chief System Policy in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Sci. 2023, 7, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, B. Assessing the impact of China’s river chief system on enterprise pollution discharge. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1268473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.J.; Deng, Q.Z. River chief governance system: Policy instruments, hydro-engineering and system governance effectiveness. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 2, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Q.; Le, Z.; Xia, Y. Research on the influence of lake chief system on water environment treatment effect: Taking Wuhan city as an example. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2022, 5, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, S.W.; Zhang, J. Can Xin’anjiang river basin horizontal ecological compensation reduce the intensity of water pollution? China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 10, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.C.; Paudel, K.P.; Rupasingha, A. Role of income and policy in reducing water pollution: Evidence from the Mississippi river basin healthy watersheds initiative. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2024, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Liu, L.W. Evaluating the effect of water pollution governance policy in China: Evidence from the water ecological civilization city construction pilot. Reform 2023, 2, 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, L.J.; Kan, D.X.; Yao, W.Q.; Huang, W.C. Has China’s pilot policy of water ecological civilization city construction reduced water pollution intensity? Land 2022, 11, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.S.; Hu, M.L.; Yang, F.L. Efficiency and equity balanced water pollutant emission aggregate allocation for Jiangsu province. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 4, 833–843. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.B.; Yang, Y.W. Flattening reform of environmental monitoring and enforcement agencies and transboundary water pollution. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 4, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.R.; Li, L.; Zhai, H.Y. Outgoing audit of natural resource assets and water pollution control: Based on empirical data from water quality monitoring in major river basins in China. Jiangxi Soc. Sci. 2022, 5, 90–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Tian, G.L.; Li, J.W.; Xu, H.J. Research on the outgoing audit and evaluation of water resource assets of leadership cadres in city y. Sustainability 2023, 16, 12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yin, Y.; Chen, Y.F. Driving factors and scale effects of water pollutant discharge in the urban agglomeration. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 9, 2219–2235. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Q.; Shen, Z.Y.; Liu, G.W.C.; Jin, Z.T.; Liu, R.Z. The effect of social economy-water resources-water environment coupling system on water consumption and pollution emission based on input-output analysis in Changchun city, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Qi, B.C. The effects of environmental regulation on industrial transfer and upgrading and banking synergetic development: Evidence from water pollution control in the Yangtze River basin. Econ. Res. J. 2021, 2, 174–189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Li, F. Can the establishment of free trade zone promote the high-quality development of regional economy: Based on the analysis of free trade zones in central and western China. West Forum Econ. Manag. 2022, 06, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.T.; Wang, W.X. The spatial spillover effects of establishing free trade pilot zones on FDI: Empirical evidence from China. Heliyon 2023, 10, e20587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.P.; Tian, S.T.; Shi, N. The effects of pilot free trade zones on the regional advantages of and complementarity between four regions in China: Evidence from the Dendrinos-Sonis model. China Soft Sci. 2016, 11, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, Z.Y. Does the construction of the pilot free trade zones bring regional radiation effects empirical research based on the Yangtze River delta pearl river delta, and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei regions. J. Int. Trade 2020, 9, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Shi, H.L. The impact of the pilot free trade zone on regional financial development. China World Econ. 2022, 5, 154–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.L.; Wang, Y. Innovative performance promotion effect of free trade zone: Evidence from the quasi-experiment of the Shanghai free-trade zone. Res. Econ. Manag. 2018, 09, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.T.; Shen, R.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Cai, Y.F. Fostering regional innovation efficiency through pilot free trade zones: Evidence from China. Econ. Anal. Policy 2024, 81, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Xu, H.F.; Zeng, L.H. Does innovation in pilot free trade zone system improve export resilience? Reform Econ. Syst. 2023, 4, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.J.; He, K.; Yu, Y. Establishment of FTZ, trade development and capital flows based on the perspective of Shanghai free trade zone. J. Financ. Res. 2016, 10, 48–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.P.; Inmaculada, M. A panel data analysis of trade creation and trade diversion effects: The case of ASEAN–China free trade area. China Econ. Rev. 2014, 29, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.W. Research on the impact of the establishment of free trade zones on the total factor productivity of enterprises: Based on the mediating role of financing constraints. Mod. Bus. 2021, 23, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Z.K. The impact of the free trade zone on green total factor productivity: Evidence from the shanghai pilot free trade zone. Energy Policy 2021, 148, 112000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J.M.; Yang, Y. Does comprehensive bonded zone policy improve the transformation and upgrading of exporters? Stat. Res. 2022, 8, 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.L.; Liu, J.X. Can the establishment of pilot free trade zones promote enterprise innovation? Evidence from GEM listed companies. Stud. Int. Financ. 2021, 9, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Sui, G.J.; Yang, Y.C. Mechanisms and paths of the construction of the pilot free trade zone to promote the resilience of industrial chain and supply chain: Taking Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area as an example. Intertrade 2023, 6, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, S.S.; Chai, H.R.; Fang, Y.L.; Wang, B. Does the establishment of the pilot free trade zone improve the efficiency of financial services for the real economy? World Econ. Stud. 2021, 12, 3–21+132. [Google Scholar]
- Chauffour, J.P.; Maur, J.C. Preferential trade agreement policies for development: A handbook. World Bank Publ. 2011, 5, 662–687. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.K.; Li, Y. Has the establishment of free trade zones improved the atmospheric conditions? China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 2, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, P.Y.; Huang, L.Q.; Chen, Q. Construction of pilot free trade zone and regional industrial structure transformation and upgrading empirical analysis based on panel data of 286 cities in China. South China J. Econ. 2021, 4, 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.Z.; Sun, P.B.; Xuan, Y. Do constraints on local governments’ environmental targets affect industrial transformation and upgrading? Econ. Res. J. 2020, 8, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.X.; Chen, Z.M.; Zheng, X.Y. Influence of environmental externalities on export structure and trade policies. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 6, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.S.; Guo, R.; Tang, Y.E.; Peng, K.M.; Huang, X.F. Upgrading the industrial structure for optimizing water-energy-carbon nexus in regional trade network. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 469, 143231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Siddharth. Sustainable and eco-friendly approach for controlling industrial wastewater quality imparting succour in water-energy nexus system. Energy Nexus 2021, 3, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Weng, Z.X.; Liu, T.T.; Li, H.S. Research on fexible science and technology governance mechanisms for ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Prot. 2024, 7, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.M.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.X.; Liu, F.T. How to promote the sustainable development of strategic emerging industries: Evidence from Guangzhou. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.B.; Qi, S.Z. The effect of market-oriented and command-and-control policy tools on emissions reduction innovation: An empirical analysis based on China’s industrial patents data. China Ind. Econ. 2016, 6, 91–108. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, S.Z.; Lin, S.; Cui, J.B. Do environmental rights trading schemes induce green innovation? Evidence from listed firms in China. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 12, 129–143. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsen, A.; Mostafa, E.A.; Milad, H.C. Performance of the firms in a free-trade zone: The role of institutional factors and resources. Eur. Manag. Rev. 2019, 2, 363–378. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, I. Sustainable water management in urban areas: Integrating innovative technologies and practices to address water scarcity and pollution. Pharm. Chem. J. 2021, 1, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L. Innovative technologies for water pollution control and treatment in urban areas. Water Res. 2017, 120, 228–243. [Google Scholar]
- She, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, H. Is China’s river chief policy effective? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.R.; Jin, G.; Fang, X. Does environmental regulation cause pollution to transfer nearby. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 52, 44–59. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, L. Trade-off between economic development and environmental governance in China: An analysis based on the effect of river chief system. China Econ. Rev. 2019, 60, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Niu, X.T. Impact of social trust on the effectiveness of environmental regulations on carbon emission reduction: Based on panel data from 281 prefecture-level cities in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 4, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.G.; Li, J. Impact of environmental regulations on industrial structure upgrading: An empirical study on Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzini, R.; Piselli, P. The impact of R&D subsidies on firm innovation. Res. Policy 2016, 2, 442–457. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, J.H. Research on green bond promoting green innovation of enterprises. J. Financ. Res. 2022, 6, 171–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, T.; Hao, X.; Li, J. Effects of public participation on environmental governance in China: A spatial Durbin econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 25, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yan, L.; Chen, B.; Ding, W.; Wang, P. Environmental governance effects of local environmental protection expenditure in China. Resour. Policy 2022, 77, 102760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adina, D.; Ada-Iuliana, P.; Dumitru-Cristian, O. Government expenditure on environmental protection and environmental performance: Evidence from EU countries. Eur. Financ. Resil. Regul. 2023, 2023, 84–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, R.Z.; Li, X.M. Spatial effect of provincial-level free trade zone pilot policy on urban economic growth. Econ. Geogr. 2024, 2, 21–30+42. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Yao, W.Y.; Jiang, L.; Xue, Y.W. Impact of Chin’′s green finance reform and innovation pilot zone policies on urban pollution and carbon emission reduction and their mechanisms. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 61, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S.; Ge, L.M.; Zhu, J.L. How to achieve the harmony between humanity and nature: Environmental regulation and environmental welfare performance from the perspective of geographical factors. J. Manag. World 2024, 08, 119–146. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Liu, T.Z.; Liu, Y.H. Spillover effect of green finance on co, emissions from a spatial perspective: The Yangtze River economic belt as an example. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 6, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Miloš, K. Climate change in the EU: Analysis by clustering and regression. Serbian J. Manag. 2023, 1, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T. Mediating effects and moderating effects in causal inference. China Ind. Econ. 2022, 5, 100–120. [Google Scholar]
- Bardaka, E.; Delgado, M.S.; Florax, R.J.G.M. A spatial multiple treatment multiple outcome difference-in-differences model with an application to urban rail infrastructure and gentrification. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 121, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Q.; He, R.W. PM2.5 Pollution and health expenditures: Time lag effects and spatial spillovers. J. Saf. Environ. 2019, 1, 326–336. [Google Scholar]
- Alzahrani, F.; Collins, A.R.; Elham, E. Drinking water quality impacts on health care expenditures in the United States. Water Resour. Econ. 2020, 32, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.R.; Jin, G. The policy effects of local governments’ environmental governance in China: A study based on the evolution of the “River-Director” system. Soc. Sci. China 2018, 5, 92–115+206. [Google Scholar]

| Variable Type | Variables | Obs. | Mean | Std. Dev | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Water | 5586 | 2135.143 | 5010.378 | 0.090 | 1.09×105 |
| Independent variable | FTZ | 5586 | 0.194 | 0.396 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Control variable | Rate | 5586 | 0.507 | 0.177 | 0.058 | 1.000 |
| Pop | 5586 | 0.083 | 0.207 | 0.001 | 3.326 | |
| Pgdp | 5586 | 41,412.560 | 34,508.512 | 99.000 | 4.68 × 105 | |
| Scale | 5586 | 2.76 × 107 | 4.06 × 107 | 31,432 | 3.78 × 108 | |
| Pipe | 5586 | 1225.951 | 2205.890 | 5.000 | 43,249.360 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STA-DID | STA-DID | SDM-STA-DID | SDM-STA-DID | |
| FTZ | −888.1 *** | −916.6 *** | −878.3 *** | −894.7 *** |
| (213.7) | (209.0) | (208.8) | (203.8) | |
| W ∗ FTZ | −4211.9 ** | −4955.8 *** | ||
| (1798.7) | (1765.4) | |||
| City Fixed Time Fixed Control variables | Yes Yes No | Yes Yes Yes | Yes Yes No | Yes Yes Yes |
| N | 5586 | 5586 | 5586 | 5586 |
| R2 | 0.512 | 0.549 | 0.637 | 0.704 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| SDM-STA-DID | SDM-STA-DID | |
| Direct | −874.8 *** | −890.3 *** |
| (209.4) | (204.7) | |
| Indirect | −1074.0 ** | −1232.9 *** |
| (432.9) | (356.6) | |
| Total | −1948.8 *** | −2123.1 *** |
| (431.4) | (395.7) | |
| City Fixed | Yes | Yes |
| Time Fixed | Yes | Yes |
| Control variables | No | Yes |
| N | 5586 | 5586 |
| R2 | 0.637 | 0.704 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NN Matching | NN Matching | Caliper Matching | Caliper Matching | |
| FTZ | −1002.6 *** | −981.3 *** | −998.1 *** | −977.0 *** |
| (260.4) | (260.6) | (260.8) | (260.9) | |
| City Fixed Time Fixed Control variables | Yes Yes No | Yes Yes Yes | Yes Yes No | Yes Yes Yes |
| N | 4210 | 4210 | 4208 | 4208 |
| R2 | 0.511 | 0.551 | 0.511 | 0.549 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STA-DID | STA-DID | SDM-STA-DID | SDM-STA-DID | |
| FTZ | −888.1 *** | −868.7 *** | −878.3 *** | −848.4 *** |
| (213.7) | (209.6) | (208.8) | (204.5) | |
| W ∗ FTZ | −4211.9 ** | −5186.7 *** | ||
| (1798.7) | (1771.7) | |||
| City Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Control variables | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| N | 5586 | 5586 | 5586 | 5586 |
| R2 | 0.514 | 0.554 | 0.638 | 0.745 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAR-STA-DID | SAR-STA-DID | SEM-STA-DID | SEM-STA-DID | |
| FTZ | −914.4 *** | −960.2 *** | −917.0 *** | −952.5 *** |
| (210.0) | (204.5) | (208.3) | (203.5) | |
| rho | −0.580 * | −1.126 *** | ||
| (0.329) | (0.338) | |||
| lambda | −1.090 *** | −1.428 *** | ||
| (0.363) | (0.379) | |||
| City Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Control variables | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| N | 5586 | 5586 | 5586 | 5586 |
| R2 | 0.621 | 0.685 | 0.633 | 0.692 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normalized Matrix | Normalized Matrix | Composite Matrix | Composite Matrix | |
| FTZ | −924.8 *** | −954.3 *** | −1024.1 *** | −1049.3 *** |
| (207.8) | (203.1) | (220.9) | (218.0) | |
| W ∗ FTZ | −9059.9 *** | −8998.9 *** | −232.4 *** | −257.6 *** |
| (2937.2) | (2871.2) | (49.92) | (49.31) | |
| City Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Control variables | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| N | 5586 | 5586 | 5586 | 5586 |
| R2 | 0.646 | 0.708 | 0.625 | 0.705 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industry | Water | Innovation | Water | Governance | Water | |
| FTZ | 0.441 *** | −1695.6 *** | 82.91 *** | −258.1 ** | 263.8 *** | −243.3 ** |
| (0.0109) | (209.2) | (24.81) | (107.0) | (29.68) | (108.1) | |
| Industry | −1166.4 *** | |||||
| (245.1) | ||||||
| Innovation | −0.303 *** | |||||
| (0.0686) | ||||||
| Governance | −0.151 *** | |||||
| (0.0575) | ||||||
| City Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time Fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4224 | 4224 | 4224 | 4224 | 4224 | 4224 |
| R2 | 0.292 | 0.551 | 0.477 | 0.562 | 0.698 | 0.577 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Dai, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Sustainability Effects of Free Trade Zones: Evidence from Water Pollution in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6013. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136013
Gao X, Sun J, Zhang X, Dai G, Liu Y, Zhang J. Sustainability Effects of Free Trade Zones: Evidence from Water Pollution in China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):6013. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136013
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xinyue, Junkai Sun, Xindan Zhang, Guilin Dai, Yuhao Liu, and Juyong Zhang. 2025. "Sustainability Effects of Free Trade Zones: Evidence from Water Pollution in China" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 6013. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136013
APA StyleGao, X., Sun, J., Zhang, X., Dai, G., Liu, Y., & Zhang, J. (2025). Sustainability Effects of Free Trade Zones: Evidence from Water Pollution in China. Sustainability, 17(13), 6013. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17136013






