Polarization or Equilibrium: Spatial and Temporal Patterns and Divergent Characteristics of Rural Restructuring in Unevenly Developed Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Constructing the Indicator System
2.3.2. Entropy-Weighted TOPSIS Method
2.3.3. Measurement of Rural Restructuring Intensity Index
2.3.4. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
2.3.5. Driver Analysis Method and Variable Setting
3. Results
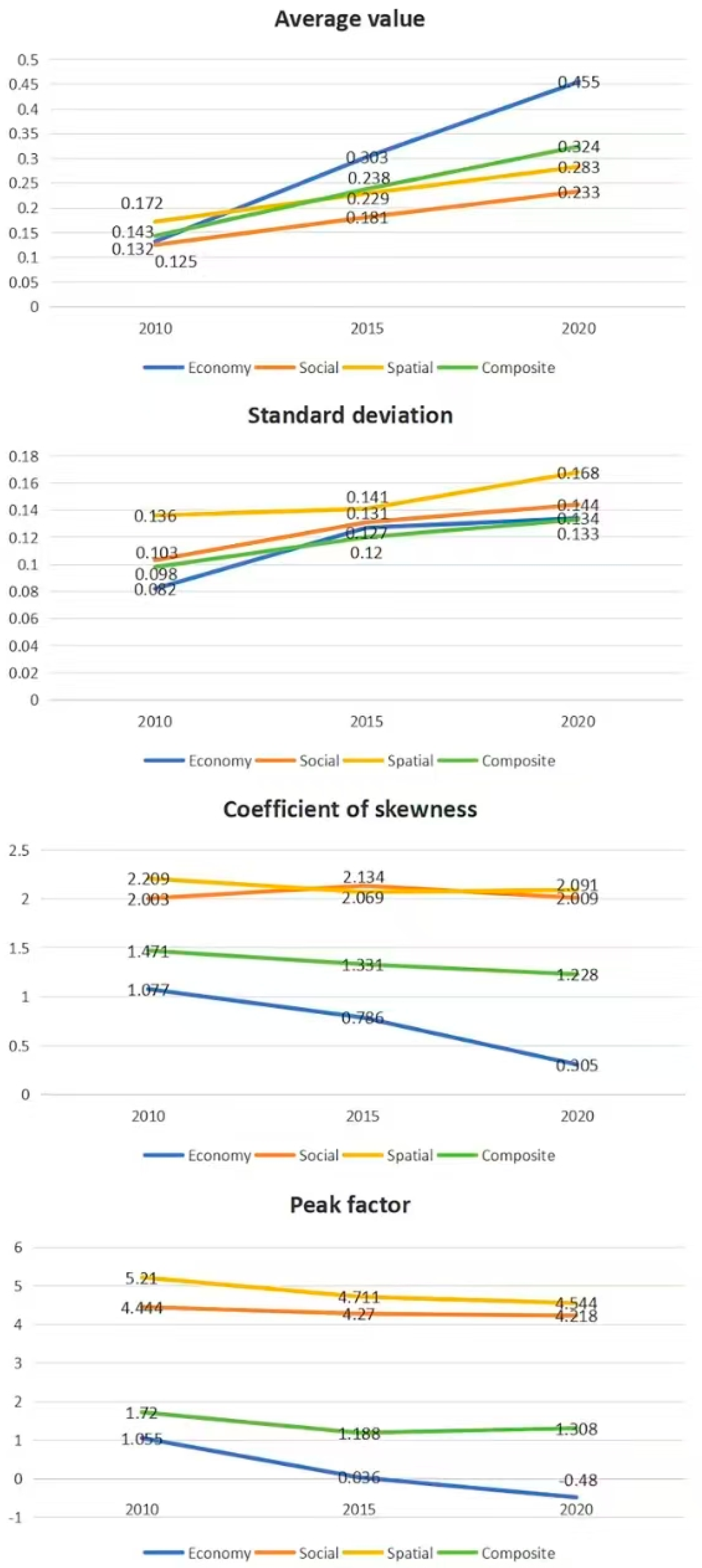
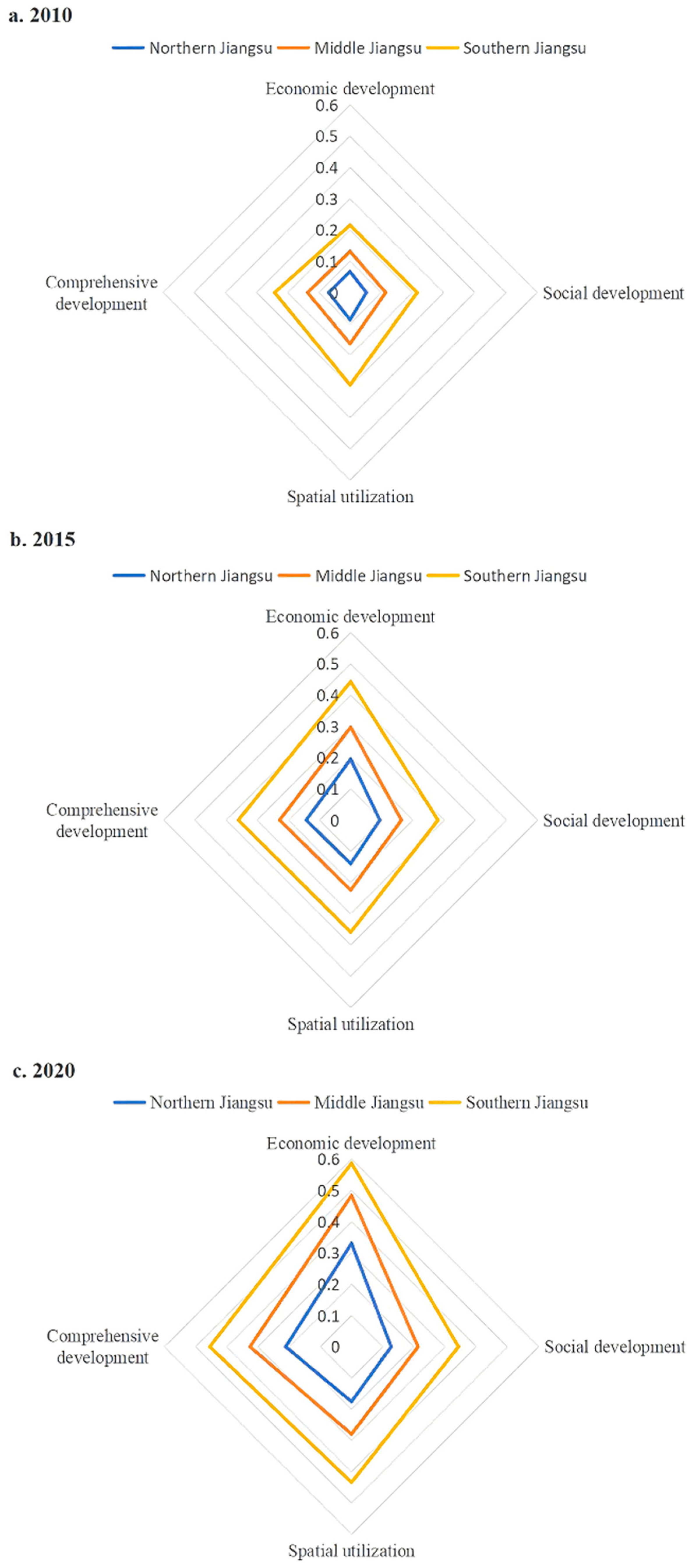
3.1. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Rural Development Level in Jiangsu Province
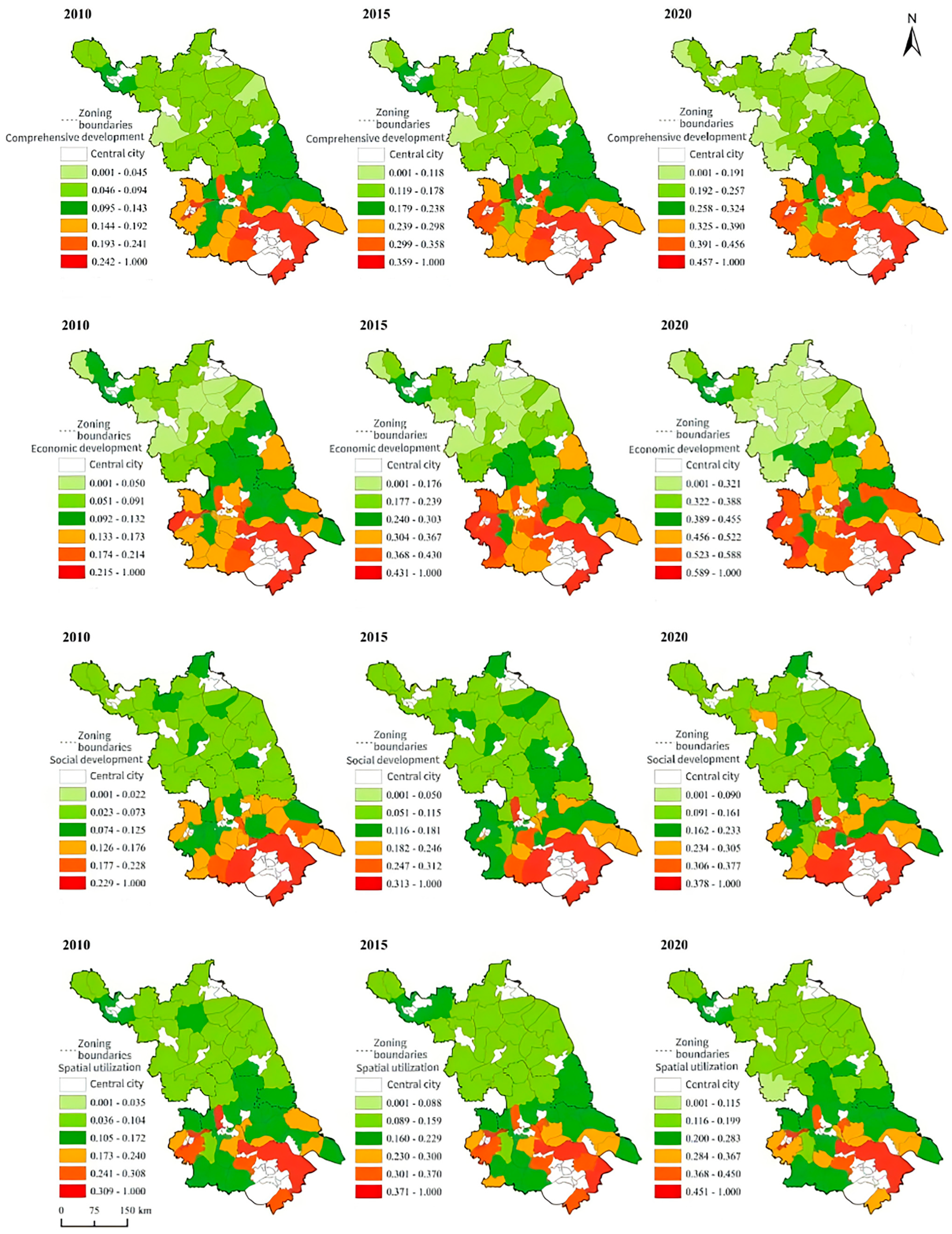
3.2. Spatial–Temporal Differentiation of Rural Development in Counties of Jiangsu Province
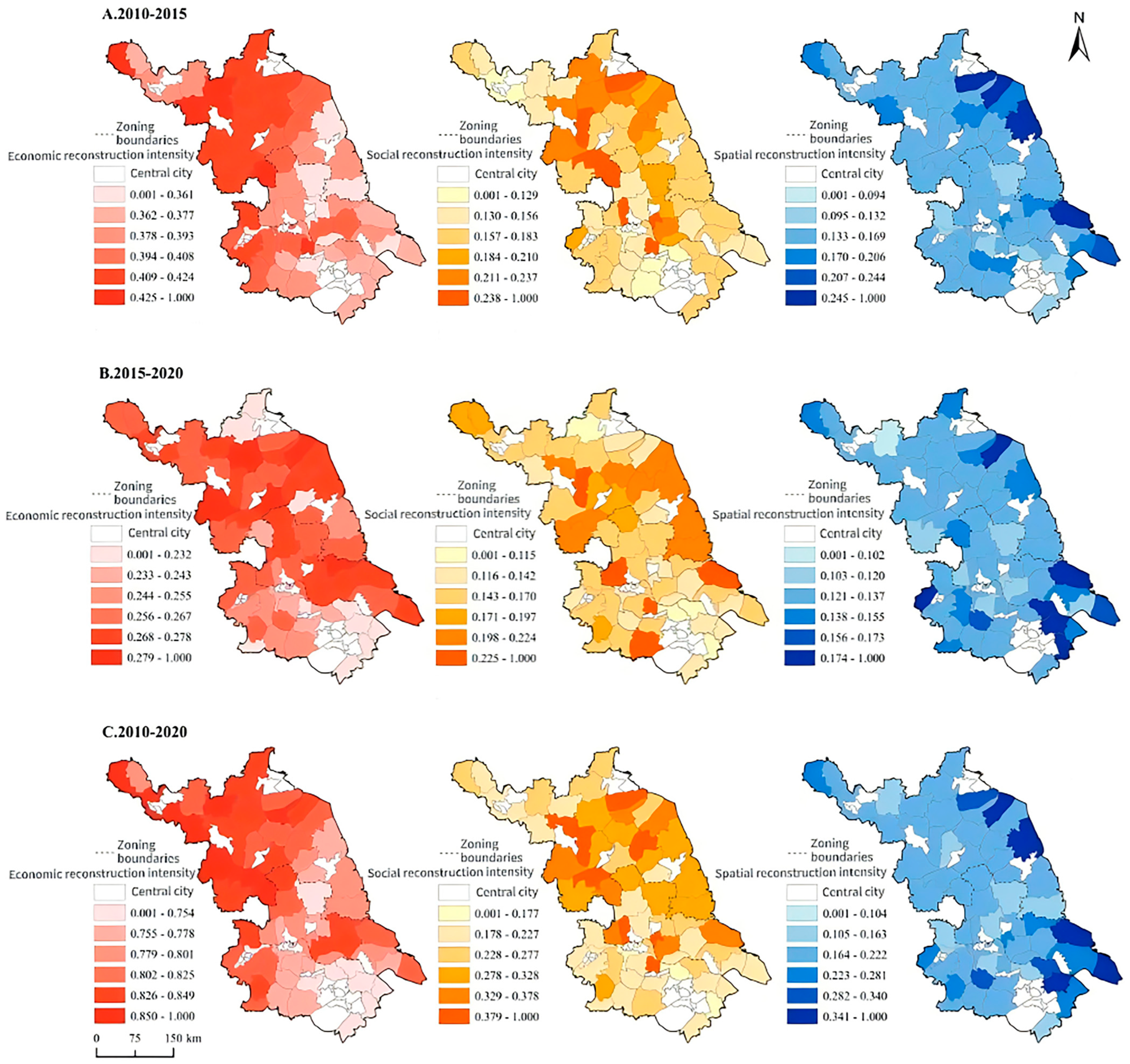
3.3. Pattern Characteristics of Rural Restructuring Intensity in Each County of Jiangsu Province
3.4. Analysis on the Coupling Coordination Pattern of Rural Restructuring in Various Counties of Jiangsu Province
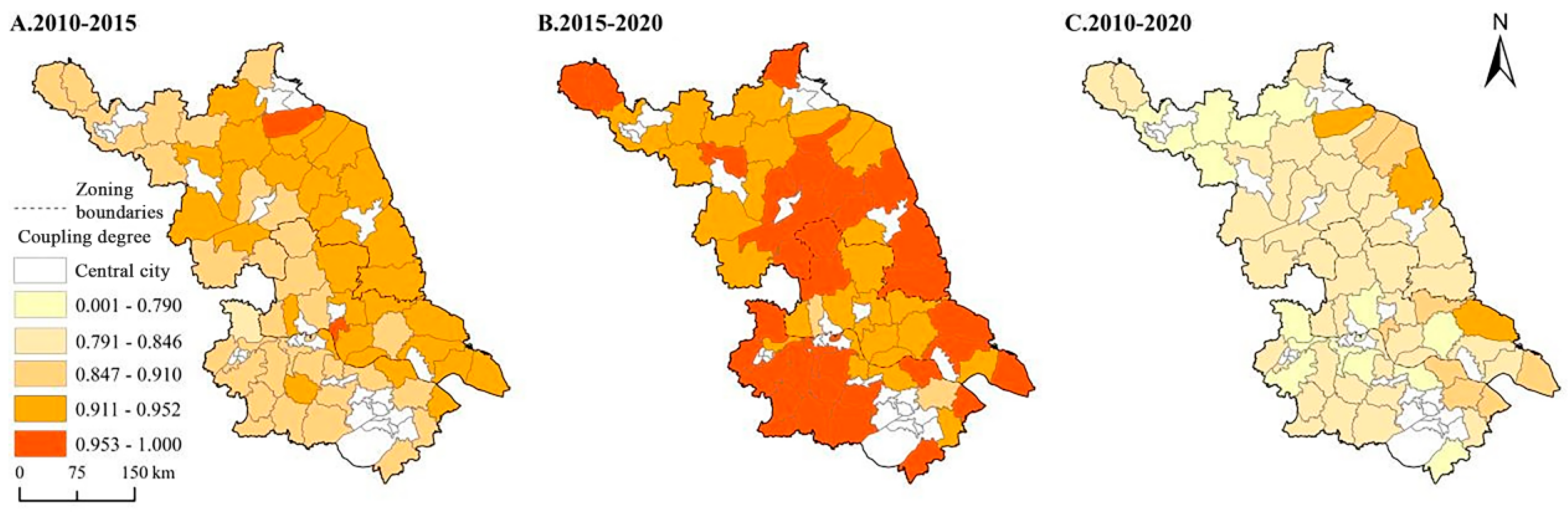
3.4.1. Analysis on the Coupling Degree of Rural Restructuring in Each County of Jiangsu Province
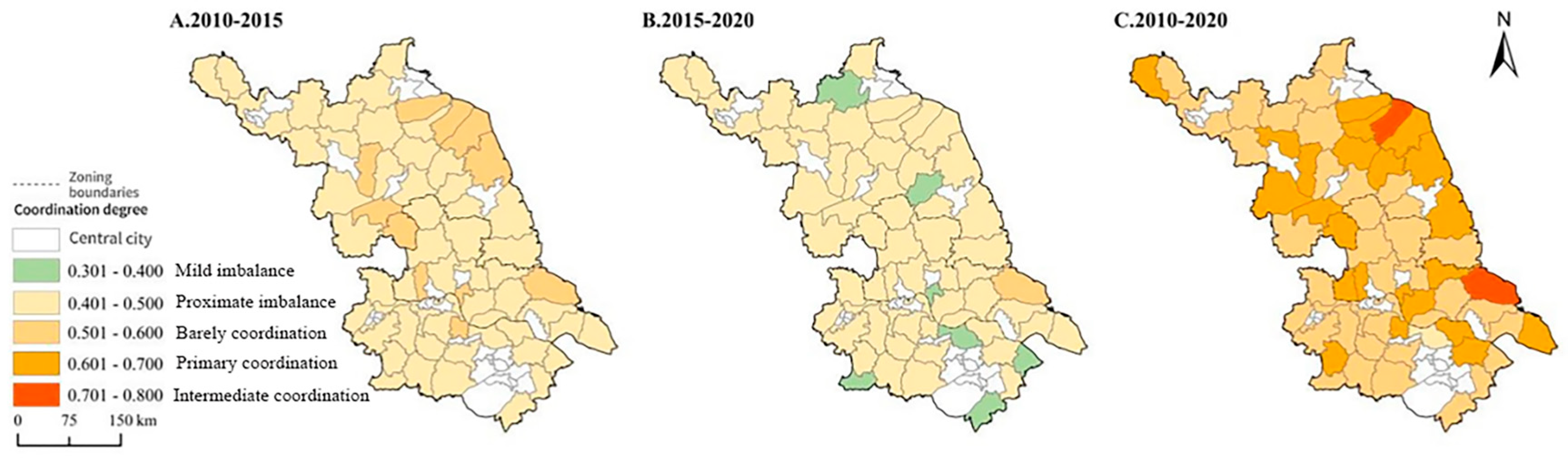
3.4.2. Analysis of Coordination Degree of Rural Restructuring in Counties (Districts) of Jiangsu Province
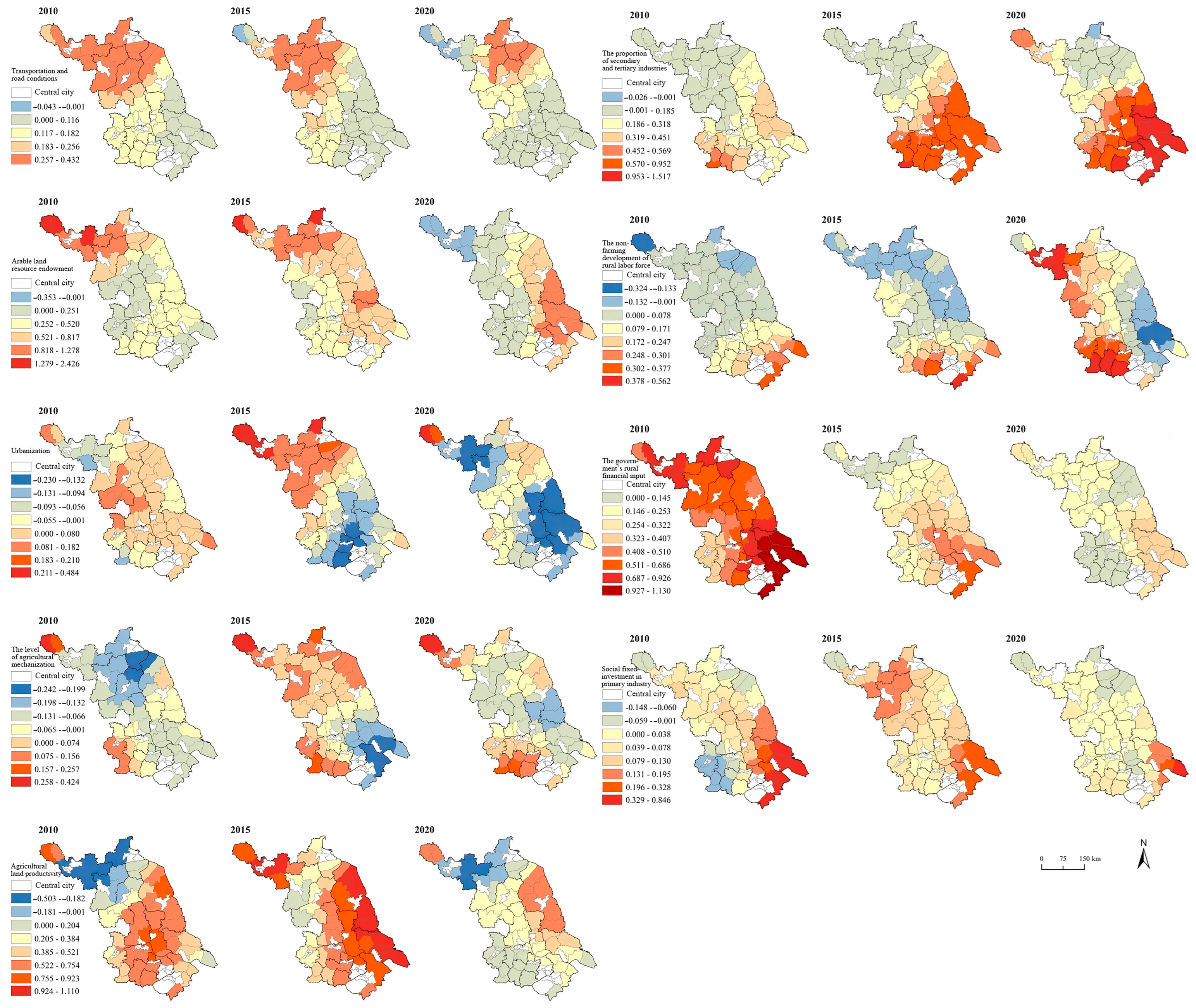
3.5. Drivers of Rural Reconstruction in Jiangsu Province
4. Discussion
4.1. Deepening Intra-Regional Imbalances in the Process of Rural Reconfiguration
4.2. Multidimensional Sources of Heterogeneity in the Deepening of Regional Imbalances
4.3. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation of Driving Forces in Rural Restructuring
4.4. Limitations and Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TOPSIS | Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution |
References
- Tu, S.; Long, H. Rural restructuring in China: Theory, approaches and research prospect. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 1169–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Li, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, R.; Du, S. A quantitative review of nature-based solutions for urban sustainability (2016–2022): From science to implementation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J. Landscape sustainability and land sustainability: A bibliometric analysis. Land Use Policy 2024, 147, 107374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Tu, S.; Ge, D.; Li, T.; Liu, Y. The allocation and management of critical resources in rural China under restructuring: Problems and prospects. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 47, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, B.; Chen, R.; Liang, J.; Khan, N.; Ray, R.L. Government Intervention on Cooperative Development in Poor Areas of Rural China: A Case Study of XM Beekeeping Cooperative in Sichuan. Land 2023, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Geng, H.; Yue, L.; Li, K.; Huang, L. Spatial Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Mechanism of Rural Settlements Transformation in the Metropolis: A Case Study of Pudong District, Shanghai. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 755207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Evolution and transformation mechanism of the spatial structure of rural settlements from the perspective of long-term economic and social change: A case study of the Sunan region, China. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 93, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Ni, H.; Sang, X. How land use functions evolve in the process of rapid urbanization: Evidence from Jiangsu Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ou, X.; Xu, Y. Study on Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Public Service Facilities in County Towns of Jiangsu Province. Areal Res. Dev. 2024, 43, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, G.; Hans, G. Rural Development and Transformation in the Federal Republic of Germany since the 1950s. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 12, 1644–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P. Rural restructuring in the American West: Land use, family and class discourses. J. Rural Stud. 2001, 17, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, O. Rural restructuring and agriculture-rural economy linkages: A New Zealand study. J. Rural Stud. 1995, 11, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobnjaković, M.; Steinfürer, A. Re-thinking rurality: Towards a new research approach and rural-urban spatial gradient establishment in Serbia. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 163, 103195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, M.; Qiong, H. Research on the Rural Revitalization Process Driven by Human Capital: Based on Farmers’ Professionalization Perspective. SAGE Open 2024, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.; Yang, Q. The spatial production of rural settlements as rural homestays in the context of rural revitalization: Evidence from a rural tourism experiment in a Chinese village. Land Use Policy 2023, 128, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, B.; Henry, M.S. Size and growth of urban centers in French labor market areas: Consequences for rural population and employment. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2000, 30, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, R. Rurality, Locality and Industrial Change: A Micro-scale Investigation of Manufacturing Growth in the District of Leominster. Geoforum 1996, 27, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D. The restructuring of local government in rural regions: A rural development perspective. J. Rural Stud. 2005, 21, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Han, Z.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H. Mechanisms of Rural Sustainable Development Driven by Land Use Restructuring: A Perspective of “Scale-Space” Interactions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Ye, L. Reconstructing Rural Settlements Based on Structural Equation Modeling—Taking Hongshanyao Town of Jinchang City as an Example. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perc, M. The Matthew effect in empirical data. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balci, E.; DİNÇER, İ. A cultural geography review on understanding the mechanisms of transformation in rural settlements: The case of İzmit district. Megaron 2024, 19, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falťan, Ľ. Socio-spatial transformations of rural settlements in slovakia at the beginning of the 21st century-sociological reflection. Sociologia 2019, 51, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Liu, Y.; Zou, J. Assessment of Rural Development Types and Their Rurality in Eastern Coastal China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 426–434. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, C.; You, L. Engaging Smallholders in Flower Agribusiness for Inclusive Rural Development: The Case of Yunnan, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, H. Spatial pattern evolution of rural settlements from 1961 to 2030 in Tongzhou District, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, H. Effect Mechanisms of Peasant Relocation Decision-making Behaviours in the Process of Rural Spatial Restructuring: The case of Hotan region, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Rao, Y.; Luo, F.; Yi, C.; Du, P.; Liu, H.; Wu, P.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Y. Evolution of rural settlements and its influencing mechanism in the farming-pastoral ecotone of Inner Mongolia from a production-living-ecology perspective. Habitat Int. 2024, 151, 103137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, L.; Qi, Z. The spatiotemporal variation of farmland use transition and its critical influential factors in coordinated urban-rural regions: A case of Chongqing in western China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 70, 102921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Heilig, G.K.; Li, X.; Zhang, M. Socio-economic development and land-use change: Analysis of rural housing land transition in the Transect of the Yangtse River, China. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S. Betting on the strong: Local government resource allocation in China’s poverty counties. J. Rural Stud. 2014, 36, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Zou, Y.; Yi, C.; Luo, F.; Song, Y.; Wu, P. Optimization of rural settlements based on rural revitalization elements and rural residents’ social mobility: A case study of a township in western China. Habitat Int. 2023, 137, 102851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pan, M. Emerging rural spatial restructuring regimes in China: A tale of three transitional villages in the urban fringe. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 93, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Shang, Y. Spatial optimization of rural settlements in ecologically fragile regions based on a multi-agent model: Evidence from different types of towns. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, R.; Long, H.; Lin, Y.; Ge, Y. Rural spatial restructuring in suburbs under capital intervention: Spatial construction based on nature. Habitat Int. 2024, 150, 103112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Qiu, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, Y. Study on the mechanism of livelihood behavior decision of rural residents in ethnic tourism villages in Western Sichuan. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lin, Y. Research on High-Quality Urbanization Development and Optimization Pathways Based on the Coupling Coordination Perspective of “Population–Land–Economy–Environment”: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province, China. Land 2025, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhong, J.-L.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Xiang, X.; Huang, H. Exploring the coupling coordination and key factors between urbanization and land use efficiency in ecologically sensitive areas: A case study of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 86, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D. Study on the coupling coordination and barrier factors between agroecological security and rural green development in China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhou, W.; Jing, C.; Zhaxi, D. Mapping and measuring urban-rural inequalities in accessibility to social infrastructures. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 5, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, M. Unpacking the ‘supply-utilization-demand’ interplay: Keys to multifunctional sustainability in rural China. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 5, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Fan, H. Reciprocal regulation between rural settlement expansion and human-elephant conflict in China’s wild elephant range. Geogr. Sustain. 2025, 6, 100238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Understanding rural system with a social-ecological framework: Evaluating sustainability of rural evolution in Jiangsu province, South China. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 86, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, Y. Assessing rural revitalization potential through rural transformation degree and sustainability: A quantitative study of 460 case villages in Lingbao, China. Habitat Int. 2024, 153, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.V.S.-R.B.I.; Serrano, M.V.D.; Pozas, B.M. SDG monitoring framework for rural settlements mapping interactions with the Spanish Urban Agenda. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 93, 104514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Li, T.; Yu, Z.; Meng, H. Assessment of Rural Development Level and Mechanism Analysis Based on MicroPerspective—A Case Study of the Demonstration Area of Urban-Rural Intergration in Gaoling County of Shaanxi Province. Econ. Geogr. 2013, 33, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiming, Z.; Li, Z.; Hong, Z.; Yunchang, H.; Yonghui, D. Construction and Application of Evaluation Index System for Agricultural Green Development. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 34, 21–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, W. Analysis of Rural Tourism Competitiveness and Obstacle Factors in Shandong Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhou, G.; Tang, C.; Peng, P. Evaluation of rural transformation development in Hunan Province based on major function oriented zoning. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Cui, Y. Rural Vitalization and DevelopmentEvaluation Index System, Regional Disparity and Spatial Polarization. Issues Agric. Econ. 2021, 5, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Li, T. Construction and Application of County Urban-Rural Correlation Evaluation Index System—A Case Study of the Region of Xi’an. Hum. Geogr. 2010, 25, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Fan, L. Research on Rurality at Village Scale and Rural Development ModelA Case of Jintan City, Jiangsu Province. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 37, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Zou, J.; Li, T.; Liu, Y. Study on the characteristics and territorial types of rural transformation development: The case of “Southern Jiangsu-Northern Shaanxi” transect. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 495–506. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Long, H. Spatial pattern and influencing factors of the coordination development of industrialization, informatization, urbanization and agricultural modernization in China: A prefecture level exploratory spatial data analysis. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Luo, Q.; Li, T.; Li, T.; Long, D. Evalution on the Coupling of Water Resources and Rural Development System in theSemiarid Area: A Case Study of Tongliao City. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G. Rural development in metropolitan areas and implications for rural vitalization strategy. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. The Evaluation of Coordinated Development Level between Urban and Rural and Its Spatial-Temporal Pattern in Yangtze River Economic Zone. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 60–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, C. Evaluation of Provincial Digital Inclusive Finance and Rural Revitalization and Its Coupling Synergy Analysis. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 187–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y. Characteristics and Mechanism of Rural Settlements Spatial Reconstruction in Developed Areas—A Case Study of Southern Jiangsu. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K. Evaluation index system and empirical analysis of rural revitalization level. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Long, H.; Wan, S.; Liang, X.; Wang, W. Spatio-temporal pattern of rural development and restructuring and regional path of rural vitalization in Guangxi, China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuo, R.; Zeng, J. Characteristics and regional model of rural restructuring in main agricultural production regions in Central China: A case study of Jianghan Plain. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 2063–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xu, G.; Yu, H. Spatio-Temporal Pattern, Influencing Mechanismsand Optimization Strategies of Rural Restructuring From The Perspective of Territorial Spatial Governancea Case of Guizhou Province. Hum. Geogr. 2023, 38, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, X. Spatial–Temporal Differentiation and the Driving Mechanism of Rural Transformation Development in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, B.; Ao, Y.; Bahmani, H.; Chai, B. The coupling and coordination degree of urban resilience system: A case study of the Chengdu–Chongqing urban agglomeration. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 101, 107145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Kong, H.; Miao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, J. Spatial Coupling Coordination Evaluation between Population Growth, Land Use and Housing Supply of Urban Agglomeration in China. Land 2022, 11, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wei, Y.D.; Huang, X.; Chen, B. Economic transition, spatial development and urban land use efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 63, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Kang, X. Market-Driven Rural Construction—A Case Study of Fuhong Town, Chengdu. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dimension | Indicator Layer | Calculation Method and Unit | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic development | Regional per capita economic aggregate | Gross regional product/resident population (yuan) | + |
| Level of farmers’ income | Per capita net income of rural residents (yuan) | + | |
| Engel coefficient of rural permanent residents | Consumption expenditure on food as a proportion of total consumption expenditure by rural permanent residents (%) | − | |
| Agricultural labor productivity | Gross output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery/total number of people employed in agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery (yuan/person) | + | |
| Social development | Medical and health facilities | Number of beds in medical institutions/resident population × 1000 (beds/per thousand people) | + |
| Level of communication facilities | (Number of fixed and mobile telephone households + Internet broadband subscribers)/Total population | + | |
| Level of rural electrification | Rural electricity consumption/rural resident population (kwh/person) | + | |
| Road network density | Total regional road mileage/county land area (km/km2) | + | |
| Spatial utilization | Agricultural land use efficiency | Grain yield/grain sown area (tons/hectare) | + |
| Rural housing per capita | Per capita housing area of peasant families (square meters) | + | |
| Land use efficiency in the second and third industries | Value added of the second and third industries/(urban construction land + other construction land such as industry, mining and transport) (billion yuan/km2) | + | |
| Regional heterogeneity | Urban industrial and mining land area/county land area (%) | + |
| Driving Force Type | Criterion Level | Indicator Level | Calculation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endogenous Drivers | Location Conditions | Transportation Condition | Total road mileage/Total area (km2) |
| Natural Resource Endowment | Arable Land Resource Endowment | Arable land area/Rural agricultural workers (hm2/person) | |
| Urbanization | Urban Development Level | Urban population/Total population (%) | |
| Exogenous Drivers | Industrialization and Marketization | Industrial Structure | Secondary and tertiary industries output/Regional GDP (%) |
| Non-agricultural Employment in Rural Areas | Rural non-agricultural workers/Rural population (%) | ||
| Agricultural Modernization | Level of Agricultural Mechanization | Total power of agricultural machinery/Arable land area (kw/hm2) | |
| Land Productivity | Agricultural output/Arable land area (104 yuan/hm2) | ||
| External Investment | Government Investment in Rural Areas | Agri./Forestry/Water expenditure/Rural population (104 yuan/person) | |
| Fixed-asset Investment in Primary Sector | Total investment in primary industry (billion yuan) |
| Grade of Value Area | Statistical Standard |
|---|---|
| I Lowest | (0, mean value − 1 standard deviation] |
| II Lower | (mean value − 1 standard deviation, mean value − 0.5 standard deviation] |
| III Medium–low | (mean value − 0.5 standard deviation, mean value] |
| IV Medium–high | (mean value, mean value + 0.5 standard deviation] |
| V Higher | (mean value + 0.5 standard deviation, mean value + 1 standard deviation] |
| VI Highest | (mean value + 1 standard deviation, 1] |
| Time Period | 2010–2015 | 2015–2020 | 2010–2020 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Econ. | Soc. | Spat. | Comp. | Econ. | Soc. | Spat. | Comp. | Econ. | Soc. | Spat. | Comp. |
| Mean value | 0.393 | 0.183 | 0.169 | 0.248 | 0.255 | 0.170 | 0.137 | 0.187 | 0.801 | 0.277 | 0.222 | 0.434 |
| Standard deviation | 0.031 | 0.054 | 0.075 | 0.035 | 0.023 | 0.055 | 0.036 | 0.022 | 0.048 | 0.101 | 0.118 | 0.057 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, L.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q.; Fang, X. Polarization or Equilibrium: Spatial and Temporal Patterns and Divergent Characteristics of Rural Restructuring in Unevenly Developed Regions. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5989. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135989
Shao L, Zhou B, Li Y, Huang Q, Fang X. Polarization or Equilibrium: Spatial and Temporal Patterns and Divergent Characteristics of Rural Restructuring in Unevenly Developed Regions. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):5989. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135989
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Lin, Bochuan Zhou, Yeyang Li, Qiaoli Huang, and Xuening Fang. 2025. "Polarization or Equilibrium: Spatial and Temporal Patterns and Divergent Characteristics of Rural Restructuring in Unevenly Developed Regions" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 5989. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135989
APA StyleShao, L., Zhou, B., Li, Y., Huang, Q., & Fang, X. (2025). Polarization or Equilibrium: Spatial and Temporal Patterns and Divergent Characteristics of Rural Restructuring in Unevenly Developed Regions. Sustainability, 17(13), 5989. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135989








