What Are the Disparities in Spatiotemporal Patterns Between Urban and Rural Well-Being? Evidence from a Rapidly Urbanizing Region in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
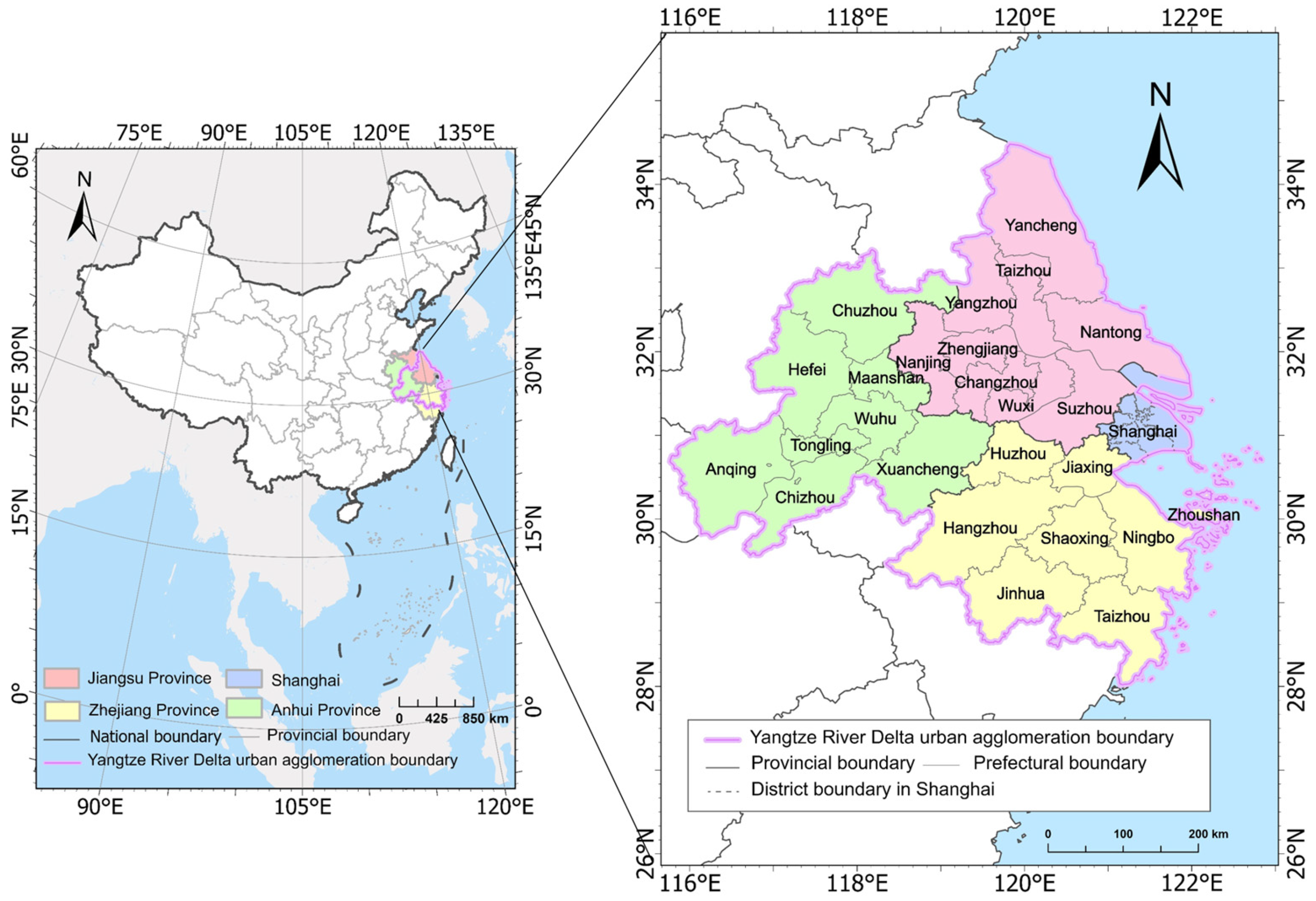
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
3. Methods
3.1. Quantification of the HDI
3.2. Quantifying the Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urban and Rural Well-Being
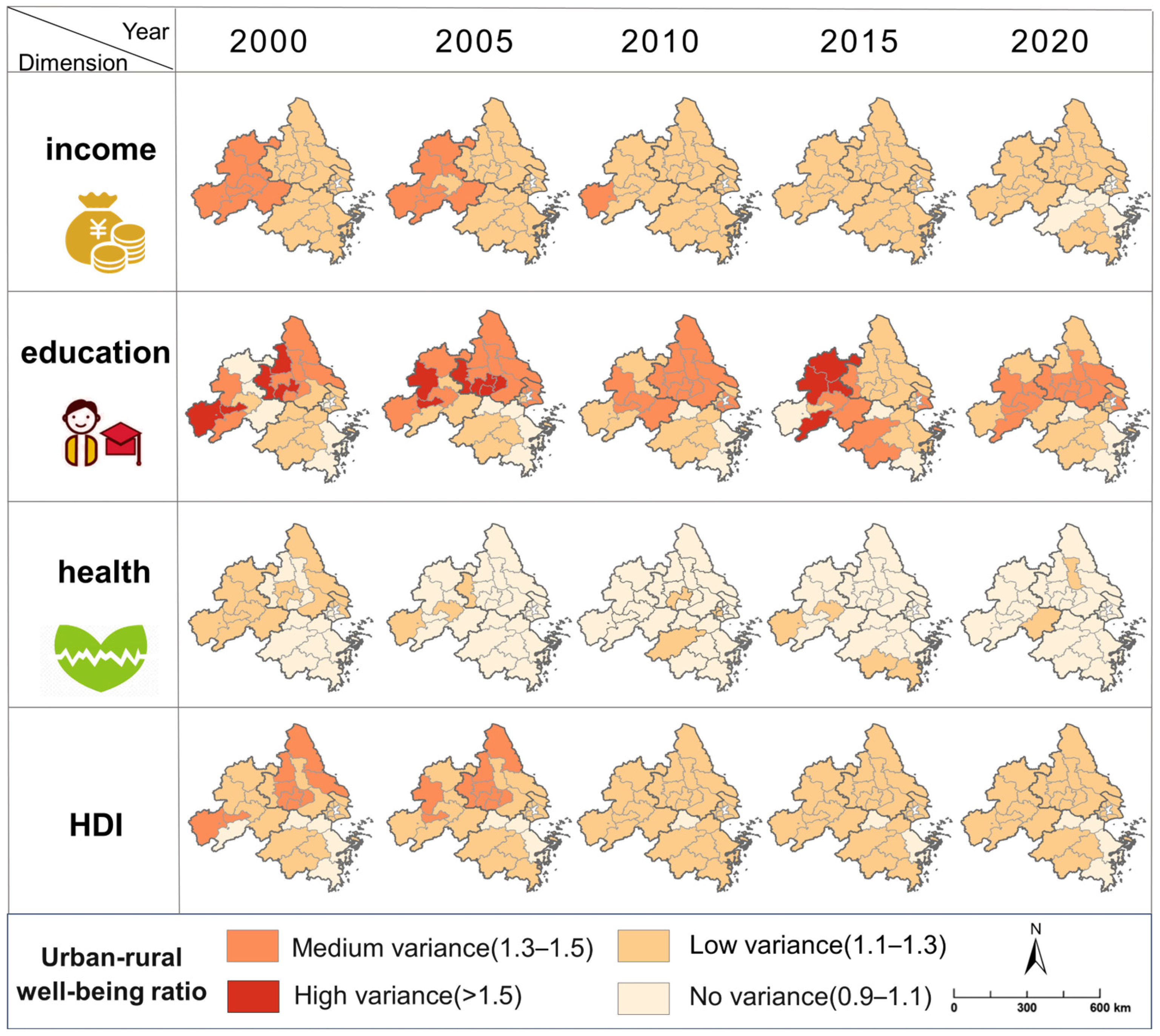
3.3. Quantifying Disparities in Well-Being Between Urban and Rural Residents
4. Results
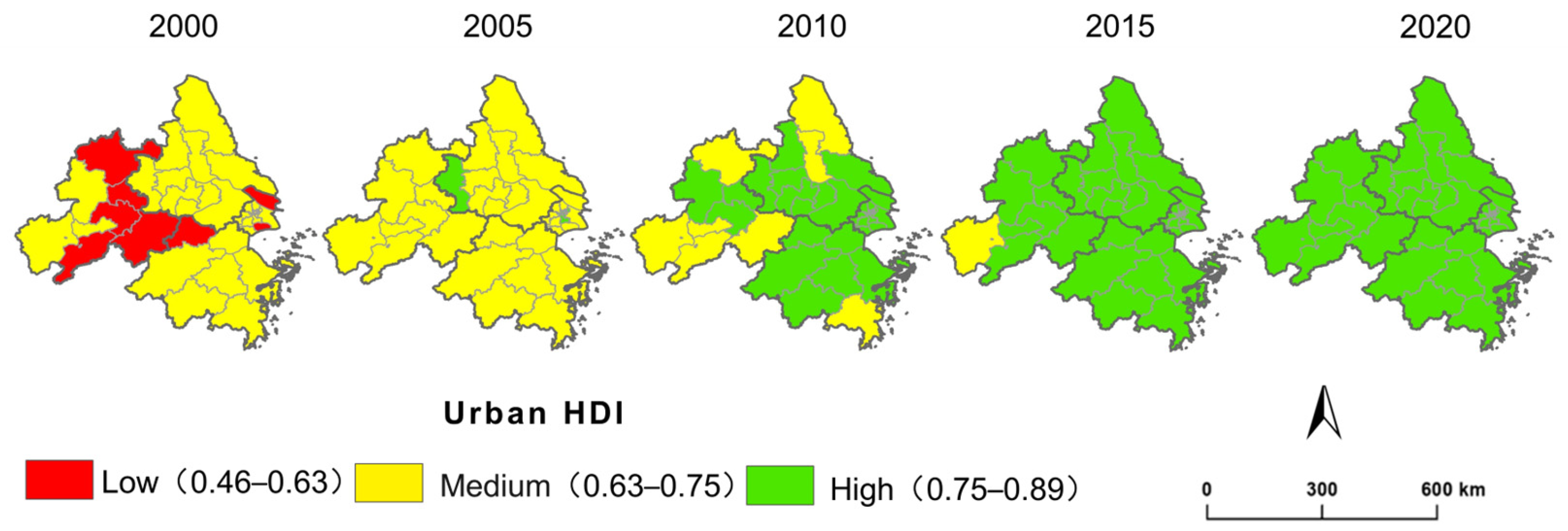
4.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urban HDI from 2000 to 2020
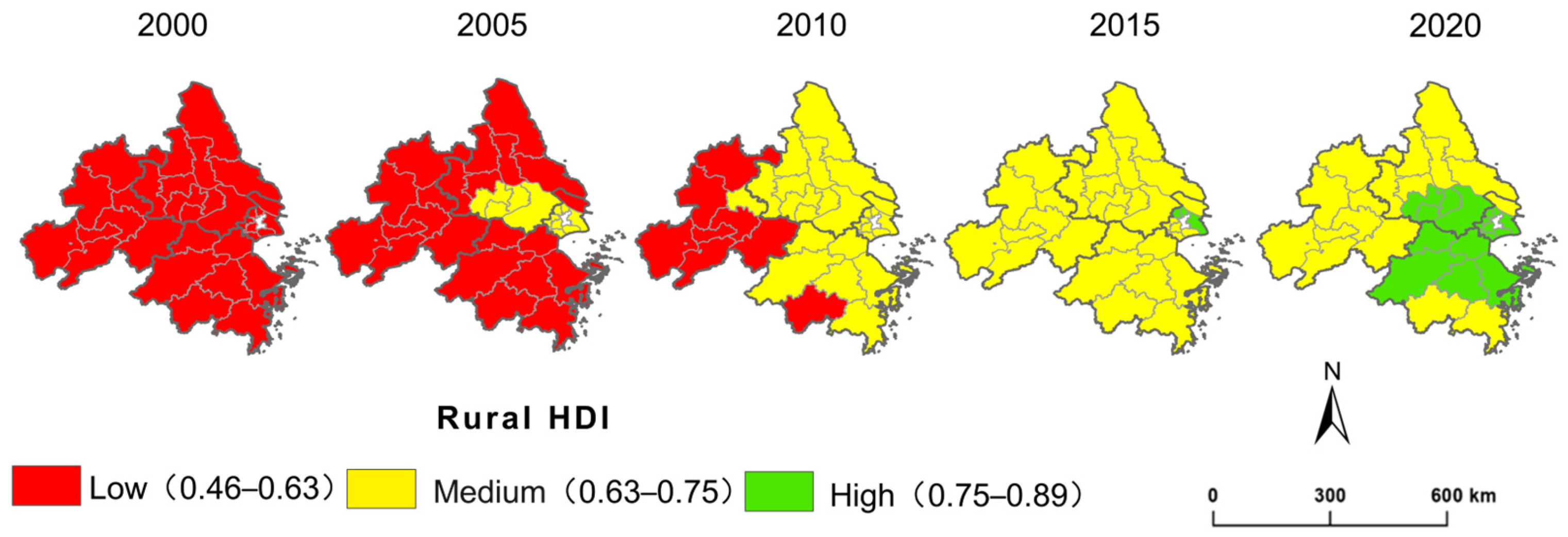
4.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Rural HDI from 2000 to 2020
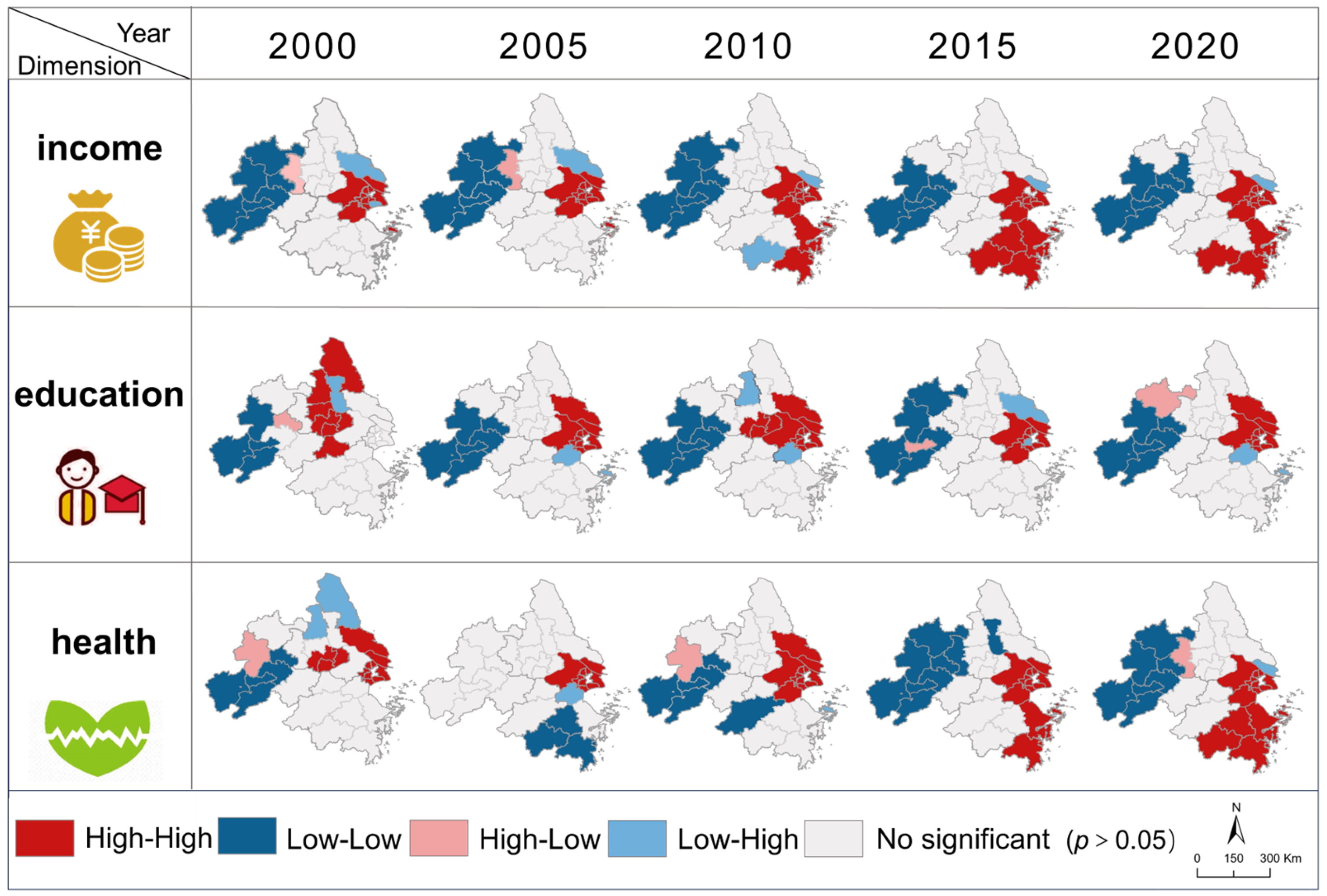
4.3. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urban–Rural HDI Disparities from 2000 to 2020
5. Discussion
5.1. The Well-Being of Urban and Rural Residents (Especially Income) in the YRD Urban Agglomeration Has Been Significantly Improved
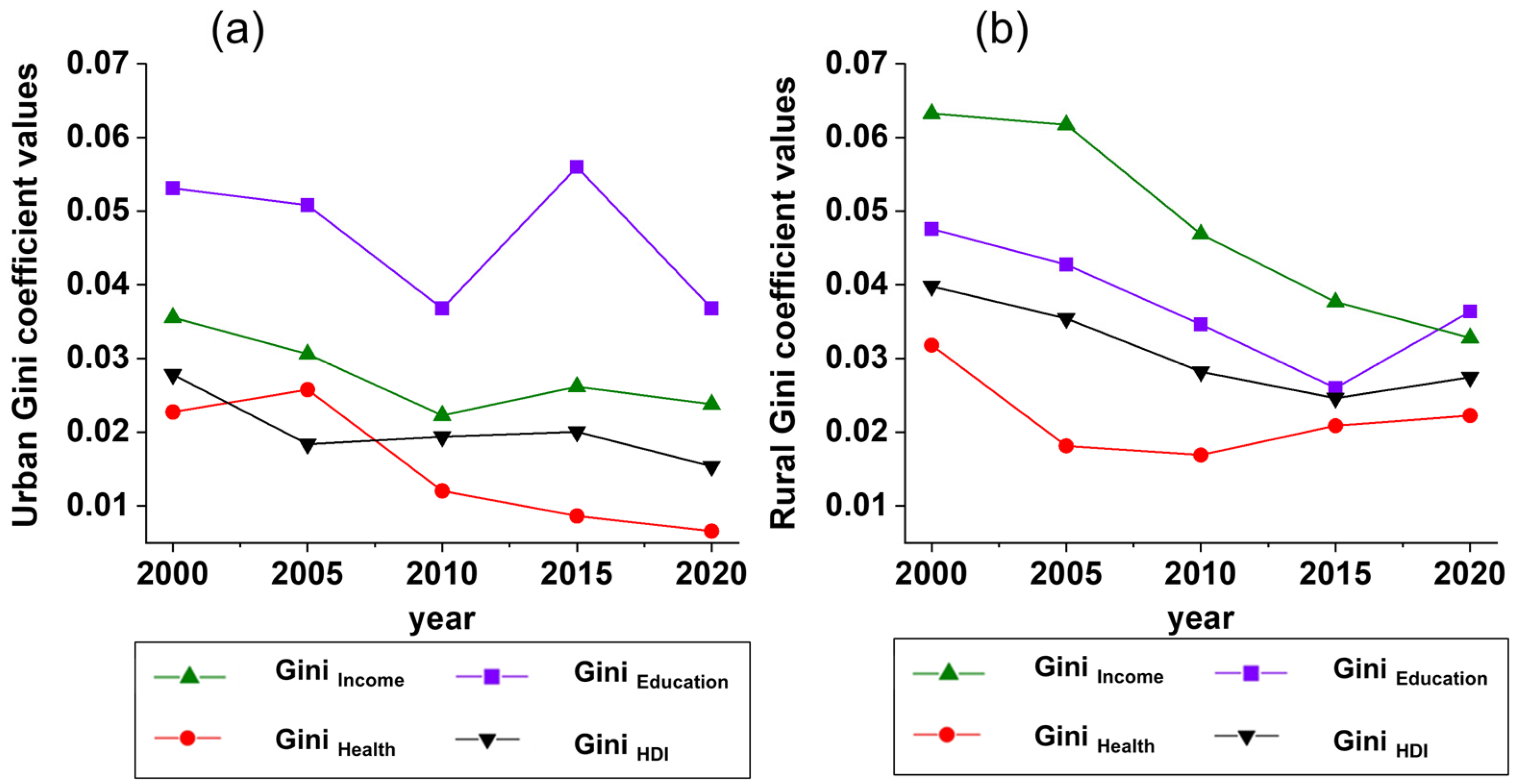
5.2. Inequality in Both Urban Education and Rural Income Within the YRD Urban Agglomeration Remains Prominent
5.3. Although Disparities Existed Between Urban and Rural Well-Being, the Urban–Rural Gap Narrowed, with Rural Health Well-Being Even Better than That of Urban Residents
5.4. Limitations and Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciftcioglu, G.C. Assessment of the relationship between ecosystem services and human wellbeing in the social-ecological landscapes of Lefke Region in North Cyprus. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.K.; Smith, L.M.; Case, J.L.; Linthurst, R.A. A review of the elements of human well-being with an emphasis on the contribution of ecosystem services. AMBIO 2012, 41, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, E.; Oishi, S.; Tay, L. Advances in subjective well-being research. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2018, 2, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, A.J.; Wu, S. Objective Confirmation of Subjective Measures of Human Well-Being: Evidence from the U.S.A. Science 2010, 327, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, A.B.; Stone, A.A. Progress in measuring subjective well-being. Science 2014, 346, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layard, R. Measuring Subjective Well-Being. Science 2010, 327, 534–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dade, M.C.; Bonn, A.; Eigenbrod, F.; Felipe-Lucia, M.R.; Fisher, B.; Goldstein, B.; Holland, R.A.; Hopping, K.A.; Lavorel, S.; le Polain de Waroux, Y.; et al. Landscapes—A lens for assessing sustainability. Landsc. Ecol. 2025, 40, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, J. The emerging “pattern-process-service-sustainability” paradigm in landscape ecology. Landsc. Ecol. 2025, 40, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.-L.; Zou, J. Rural Transformation and Development during Rapid Urbanization in China. J. Soochow Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 32, 97–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Long, H.L. The process and driving forces of rural hollowing in China under rapid urbanization. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Yang, R.; Li, Y.H. Potential of land consolidation of hollowed villages under different urbanization scenarios in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Duan, H.; Zhuang, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, B. Global effects of progress towards Sustainable Development Goals on subjective well-being. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhong, Z.; Fang, X. How Do Changes in Ecosystem Services Multifunctionality Influence Human Wellbeing? Evidence From the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration in China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 5224–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, Z.; Ren, J.; Lu, N.; Fan, W.; Zhang, P.; Dong, X. Linking ecosystem services supply, social demand and human well-being in a typical mountain–oasis–desert area, Xinjiang, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, K.D.; Summers, J.K.; Smith, L.M.; Harwell, L.C. Application of the Human Well-Being Index to Sensitive Population Divisions: A Children’s Well-Being Index Development. Child Indic. Res. 2018, 11, 1249–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakócai, C. How sustainable is happiness? An enquiry about the sustainability and wellbeing performance of societies. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2023, 30, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, C.M.; Poudel, R.; Stitzel, K.; Khan, Y. Current and Future Perceptions of Well-being are Associated With General Health Status in Adults: Results From the Gallup National Health and Well-being Index, 2018. Circulation 2020, 141 (Suppl. S1), AP393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Lepinteur, A.; D’Ambrosio, C. Life Satisfaction and the Human Development Index Across the World. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 2021, 54, 002202212110447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, S.; Armanmehr, V.; Nematollahi, S.; Rezaeian, S.; Khazaei, S. Suicide rate in relation to the Human Development Index and other health related factors: A global ecological study from 91 countries. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2017, 7, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, Z.; Mazaheri, E.; Hasanpour-Dehkordi, A.; Pordanjani, S.R.; Naghibzadeh-Tahami, A.; Naemi, H.; Goodarzi, E. COVID-19 Pandemic in the World and its Relation to Human Development Index: A Global Study. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 15, e103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Taka, M.; Guillaume, J.H.A. Gridded global datasets for Gross Domestic Product and Human Development Index over 1990–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaei, Z.; Sohrabivafa, M.; Darvishi, I.; Naemi, H.; Goodarzi, E. Relation between obesity prevalence and the human development index and its components: An updated study on the Asian population. J. Public Health 2020, 28, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabaso, M.L.H.; Zama, T.P.; Mlangeni, L.; Mbiza, S.; Mkhize-Kwitshana, Z.L. Association between the Human Development Index and Millennium Development Goals 6 Indicators in Sub-Saharan Africa from 2000 to 2014: Implications for the New Sustainable Development Goals. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2018, 8, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çilingirtürk, A.M.; Koçak, H. Human Development Index (HDI) Rank-Order Variability. Soc. Indic. Res. 2018, 137, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rende, S.; Donduran, M. Neighborhoods in Development: Human Development Index and Self-organizing Maps. Soc. Indic. Res. 2013, 110, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghati, A.; Talebkhah, H.; Omrani, S. Analyzing The Role of Migration Phenomenon on The Human Development Index of The City, Case Study: Bojnord City. Int. J. Sustain. Constr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 14, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.A.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.F.; Wang, T.; Sui, P.; Sheng, J.; Gao, W.S.; Chen, Y.Q. Balancing the development and carbon emissions in rural areas of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 454, 142338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B. Urbanisation and human development in West Bengal: A district level study and comparison with inter-state variation. Econ. Political Wkly. 1998, 33, 3027–3032. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Jiang, Y. Urbanization and Socioeconomic Development in Inner Mongolia in 2000 and 2010: A GIS Analysis. Sustainability 2017, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Economic Perspectives on Human Development in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Bobkov, V.N.; Dolgushkin, N.K.; Odintsova, E.V. The Inequality of Human Potential in Urban and Rural Areas: Risks and Opportunities. Her. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2023, 93, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Y. Measurement and Differences of Urban and Rural Residents’ Well-being in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Trop. Geogr. 2021, 41, 327–339. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; He, B.; Sun, D.; Yin, D. Research on the Prediction of Per Capita Life Expectancy in Hainan Province from 2018 to 2022. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2024, 25, 1148–1151. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, W.H. 70 years of urban expansion across China: Trajectory, pattern, and national policies. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1970–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y. Regional differences of China’s urban expansion from late 20th to early 21st century based on remote sensing information. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.-G.; Shi, Z.-D.; Tang, X. China’s HDI Regional Disparity Continuously Decreases and Its Explanatory Factors (1982–2015). J. Xinjiang Norm. Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.), 2018; 47–55+2. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.; Wu, X.; Cao, G. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Human Development Levels in Different Regions of China. Chin. Popul. Sci. 2020, 41–52+127. (In Chinese). Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=i7m15r_oBqoQEO2HTZ39N94cZahYsGBPeXfSZ6RCNhHPnAW7-y5Z6vq4cbz6Pj6SzHKQkz_hrI7_fF13d1s8-zWvr1dn9t9BvnmdIr4tm8YA9wPYbTaMMiLJTG4ufBNTLne_LG9Ne2K7kNnNEMD08zoK2sAx6zMkoqWPav5pBlb9DJdfbZSkJA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Peng, G.; Liu, M. Urban–Rural Development Disparities at the Provincial Level in China: Measurement and Evolution Based on HDI. Stat. J. 2024, 5, 12–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Yu, S.; Hu, J. Development of a Simplified Life Table Excel Program and Its Application in Evaluating Residents’ Health Status. J. South. Med. Univ. 2012, 32, 627–630. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Yu, D.; Hou, Z. Analysis of Average Life Expectancy and Disease Influencing Factors. Popul. J. 2018, 40, 31–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vachon, P.J.; Sestier, F. Life Expectancy Determination. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 24, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Ma, H. An Estimation of Urban–Rural Disparity in China Using the Human Development Index. Econ. Res. J. 2004; 4–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Bi, G. A multidimensional investigation on spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors of China’s urban-rural income gap (URIG) since the 21st century. Cities 2024, 148, 104920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Cheng, G.Q. Targeted poverty alleviation narrowed China’s urban-rural income gap: A theoretical and empirical analysis. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 157, 103000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, T.; Das, A. Formulation of deprivation index for identification of regional pattern of deprivation in rural India. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 74, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.J.; Bao, Q.F. Evolutionary characteristics, regional differences and spatial effects of coupled coordination of rural revitalization, new-type urbanization and ecological environment in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1510867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Chen, X.M. A Spatiotemporal Evolution and Pathway Analysis of Rural Development Efficiency: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Delta. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, D.N.; Liang, R.; Song, J.B. Exploring Spatial Connection Networks in Metropolitan Areas Led by Megacities: A Case Study of the Shanghai Metropolitan Area. J. Urban Plann. Dev. 2023, 149, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, S.; Yang, S.; Chen, M. Assessment and analysis of regional economic collaborative development within an urban agglomeration: Yangtze River Delta as a case study. Habitat Int. 2019, 83, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Jia, J.; Qiao, X. Assessment on Radiant Ability of Regional Central City—A Case Study of Zhengzhou City. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 26, 266–272. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.D.; Nath, N.; Murayama, A.; Manabe, R. Transit-oriented development with urban sprawl? Four phases of urban growth and policy intervention in Tokyo. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G. Metropolitan governance and strategic planning: A review of experience in Manchester, Melbourne, and Toronto. Prog. Plan. 1999, 52, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.Q.; Lu, Z.L.; Wu, H.X. Current Situation of Rural Residents’ Tourism: A Case Study in Zhejiang Province in China. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2014, 19, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, C. Urban Compulsory Education Enrollment Threshold and Migrant Children’s Settlement Decisions: Optimizing Spatial Allocation of Educational Resources under New Population Mobility Trends. J. Educ. 2024, 20, 126–141. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Analysis of the Impact of New Urbanization on the Balanced Allocation of Urban and Rural Compulsory Education Resources and Countermeasures: A Case Study of Henan Province. Value Eng. 2013, 32, 240–242. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bo, X.; Wang, Y. Crossing the threshold: A study on school-choice strategies of migrant worker families’ children under the point-based admission policy. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.). 2025, pp. 1–17. (In Chinese). Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=i7m15r_oBqr3Lbo2MzJ3z9RHxToYRqFBuqprjZfgI0JYalhD6uNHkLcqVdZSR5mig1qDEUOoArpNK8KiQsw3enCsxYGSwh6ibcqs4CTRah14KJvgZFH1XlAgQS0LsnDnVbKPvZIEa_VRUrMTXSZ-UepJIBfuXpKH-QN2aZL4bhr6X_dV9oiWsg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Central Institute of Educational Sciences Research Team. Survey Report on the Educational Status of Migrant Workers’ Children Entering Cities. Educ. Res. 2008, 29, 13–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Q. Why Do Large Cities Face Compulsory Education Resource Carrying Capacity Issues? Res. Educ. Dev. 2019, 39, 8–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Duan, L.C.; Jiang, S.W. Research on Spatial Differences and Driving Effects of Ecological Well-Being Performance in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. Study on the Impact of Urban Coordinated Development in the Yangtze River Delta on the Urban-Rural Income Gap. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China, 2024. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Urban-Rural Income Gap: An Empirical Study of 16 Prefecture-Level Cities in the Yangtze River Delta. Shanghai Econ. Res. 2009; 15–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Song, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y. Study on the Impact of Rural Financial Development on Farmers’ Income Growth in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Value Eng. 2013, 24, 46–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, Z. Practice and Exploration of Regional Collaborative Innovation at the Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Shanghai Agric. J. 2018, 34, 107–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, P. Analysis of the Health Status of the Elderly Population in China. Popul. Econ. 2013; 3–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, B. Performance Analysis of the “Welfare-Risk” Model in the New Rural Cooperative Medical System: An Empirical Study Based on Yinzhou District, Zhejiang Province. Econ. Syst. Reform. 2009, pp. 106–110. (In Chinese). Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=i7m15r_oBqrGE3plDp_eRtqUv_4IcmqTrAhCs61zro9bGYGJlFOaNZq7ycjxsa3jY8TuRJB8GOZjRV_0DJGMJA0U3NVMYrbYmu6r6qDE9qhljrxtX1yeHQRXqVmYvKcPFQ0O7HVyVUtQ6HR2p12juItbDXHyCuIUvuOx7gZsIv0iPTZfADQx6w==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Zhao, W.; Jiang, C. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Dynamic Effects of Urban-Rural Integration Development in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Land 2022, 11, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Fu, B. The dual effects of digital inclusive finance on the urban-rural income gap: An empirical investigation in China’s Yangtze River Delta region. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 69, 106049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Yin, W. On the Formation of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Economic Circle and the Functional Positioning of Its Core City, Shanghai. Areal Res. Dev. 2001, 20, 27–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Xie, L.; Liu, J.; Geng, Y.; Liu, Z. The Spatial Correlation Network of China’s High-Quality Development and Its Driving Factors. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Agricultural Digital Transformation Efficiency Analysis and Response Strategies. Econ. Rev. 2020, 7, 106–113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- El Bilali, H.; Allahyari, M.S. Transition towards sustainability in agriculture and food systems: Role of information and communication technologies. Inf. Process. Agric. 2018, 5, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Luo, J.; Liu, H.; Tong, L.; Li, Y. Assessment and Promotion Strategy of Rural Resilience in Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, Q.; Mao, S. Addressing Rural Decline: China’s Practices in Rural Transformation and Farmers’ Income Growth. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dai, W.D. An Empirical Study on the Benefits Equity of the Medical Security Policy: The China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, H.L. From State Security Model to Selective plus Residual Security Model: Health care regime shift in urban China. Int. J. Soc. Welf. 2018, 27, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.M.; Zhang, N.J.; Ma, Q.; Li, J.W. How is human well-being related to ecosystem services at town and village scales? A case study from the Yangtze River Delta, China. Lands. Ecol. 2024, 39, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dimension | Indicator | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| A decent standard of living | Per capita disposable income (yuan) | Shanghai Statistical Yearbook (2001–2021) Zhejiang Statistical Yearbook (2001–2021) Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook (2001–2021) Anhui Statistical Yearbook (2001–2021) |
| Access to knowledge | Average years of schooling (year) | Census Yearbook 2000 Data from the 1% Population Sample Survey, 2005 Census Yearbook 2010 Data from the 2015 1% Population Sample Survey. 2020 Census Yearbook |
| A long and healthy life | Average life expectancy (year) | Census Yearbook 2000 Data from the 1% Population Sample Survey, 2005 Census Yearbook 2010 Data from the 2015 1% Population Sample Survey. 2020 Census Yearbook |
| Dimension | Indicator | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| A decent standard of living | Per capita disposable income (yuan) | 180 | 135,000 |
| Access to knowledge | Average years of schooling (year) | 0 | 15 |
| A long and healthy life | Average life expectancy (year) | 20 | 85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Ma, Q.; Huang, Y.; Sun, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, N.; Gao, J. What Are the Disparities in Spatiotemporal Patterns Between Urban and Rural Well-Being? Evidence from a Rapidly Urbanizing Region in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5682. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135682
Zhou Y, Ma Q, Huang Y, Sun X, Dong J, Zhang N, Gao J. What Are the Disparities in Spatiotemporal Patterns Between Urban and Rural Well-Being? Evidence from a Rapidly Urbanizing Region in China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(13):5682. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135682
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yihan, Qun Ma, Yuxi Huang, Xiaohui Sun, Jiayi Dong, Naijie Zhang, and Jun Gao. 2025. "What Are the Disparities in Spatiotemporal Patterns Between Urban and Rural Well-Being? Evidence from a Rapidly Urbanizing Region in China" Sustainability 17, no. 13: 5682. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135682
APA StyleZhou, Y., Ma, Q., Huang, Y., Sun, X., Dong, J., Zhang, N., & Gao, J. (2025). What Are the Disparities in Spatiotemporal Patterns Between Urban and Rural Well-Being? Evidence from a Rapidly Urbanizing Region in China. Sustainability, 17(13), 5682. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17135682






