Abstract
Integrating sustainability into STEAM education is crucial for fostering environmental awareness among students. The Erasmus+ project Clean Environment–Clean School Climate with Creative Environmental Practices in School Education—Clean&Creative aims to develop environment-themed curriculum content that seamlessly integrates into ten different STEAM school disciplines. This initiative enhances multidisciplinary learning by connecting scientific knowledge with creative environmental practices, equipping students with the skills and mindset needed for sustainable problem solving. This paper presents the project’s key findings, highlighting innovative pedagogical approaches that merge sustainability with STEAM and humanities-based education. By incorporating hands-on, creative activities into school curricula, the project fosters active student engagement and a deeper understanding of environmental challenges. The results demonstrate how multidisciplinary strategies can bridge the gap between scientific principles and real-world sustainability issues, reinforcing the role of education in shaping eco-conscious citizens. Furthermore, the study discusses the challenges and opportunities in implementing these practices, providing insights into their long-term impact on students and educators. The findings contribute to the ongoing discourse on sustainability education, offering practical solutions for integrating environmental themes into diverse educational contexts. Ultimately, this research underscores the importance of creative, inter- and multidisciplinary methods in promoting sustainability within STEAM and humanistic education.
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Context
The 21st century presents a unique array of challenges that profoundly impact the health and well-being of the humanity and the planet. Climate change, resource depletion, biodiversity loss, and public health crises are just a few of the interconnected issues shaping our global landscape. Future generations must be equipped not only to navigate these challenges but also to make informed, ethical, and effective decisions that contribute to sustainable solutions. Central to this preparation is a reimagined educational framework, one that prioritizes the integration of sustainability in the curricula to empower both students and educators with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes required for a resilient future. Education for global sustainability requires dynamic curricula underpinned by cutting-edge research, interdisciplinary perspectives, and actionable insights. Educators play a pivotal role in translating this evidence into impactful learning experiences, equipping students with the tools to analyze, adapt, and innovate in response to rapidly changing global circumstances. Equally, students must be encouraged to become active participants in their learning journeys, developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills that extend beyond the classroom. Fostering sustainability-related competencies includes systems thinking, ethical reasoning, collaboration, and adaptive leadership—all essential for addressing multifaceted challenges in diverse contexts. For instance, systems thinking enables learners to understand the interconnectedness of ecological, social, and economic systems, while ethical reasoning fosters a commitment to equity and justice. By emphasizing these competencies, educators can inspire a sense of agency and responsibility in their students, empowering them to drive meaningful change [1,2,3,4,5].
Moreover, personalized and experiential learning allows students to engage with real-world sustainability challenges in authentic and meaningful ways; immersive experiences foster a deep sense of environmental responsibility [6,7]. From community-based projects to simulations and case studies, learners can apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, gaining a deeper understanding of the implications of their decisions [8]. This experiential focus not only enhances learning outcomes but also builds resilience, adaptability, and a proactive mindset—qualities indispensable for navigating an uncertain future [9].
Recent research underscores the critical importance of professional development for educators/teachers, who must themselves be well versed in the principles of sustainability. Providing educators with access to the latest evidence-based resources, training opportunities, and collaborative networks is essential for fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation in teaching [10]. Such programs positively influence teachers’ confidence and promote the development of transformative pedagogies for sustainability education [11]. Teachers of all subjects should have access to flexible professional development opportunities, including online and in-person workshops, free resources, and collaborative networks. By equipping educators with the necessary tools and support through targeted professional development, school administrators can ensure that they are prepared to guide their students toward mastering competencies related to sustainability and developing sustainable solutions [12,13].
1.2. The European Educational Project Opportunities
Erasmus+ projects, particularly the KA220-SCH (Cooperation Partnerships in School Education), are uniquely positioned to address the pressing need for preparing young generations to respond to a world facing multifaceted global challenges. These projects, designed to foster collaboration, innovation, and knowledge exchange across educational institutions, can significantly contribute to equipping students and educators with the competencies required to make informed decisions that promote human health and well-being in the next century [13,14,15,16,17,18]. One of the key strengths of KA220-SCH projects is their emphasis on transnational cooperation, which exposes participants to diverse perspectives and cultural contexts. By engaging in collaborative initiatives, students develop critical global competencies such as intercultural understanding, systems thinking, and ethical reasoning. These skills are crucial for addressing interconnected challenges like climate change, resource depletion, and public health crises. For instance, students participating in sustainability-themed Erasmus+ projects can explore real-world solutions to environmental issues, learn from best practices across countries, and cultivate a sense of global responsibility. Furthermore, Erasmus+ projects encourage inclusive education by bringing together students and educators from diverse backgrounds. This inclusivity helps break down barriers and promotes equity, ensuring that all participants, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographical location, have access to high-quality education and opportunities for personal growth. By fostering a culture of collaboration and mutual respect, these projects contribute to building a resilient and cohesive global community [13,18].
The purpose of this paper is to present the European project KA220-SCH “Clean Environment-Clean School Climate with Creative Environmental Practices in School Education-Clean & Creative” project “Clean & Creative” to a wide educational audience, reporting and discussing the activities and the results of the first 18 months of activity of the project. We have successfully implemented an inclusive action plan centered on environmental education as a key strategy in addressing environmental and climate challenges. This plan has been designed to foster a comprehensive and interdisciplinary approach, ensuring that sustainability principles are seamlessly integrated into school curricula. As part of this initiative, we have developed specialized environment-themed curriculum content that can be incorporated into ten different subjects. This integration should enhance students’ understanding of environmental issues while strengthening the connection between scientific knowledge, creativity, and real-world sustainability challenges. For this reason, we expect that sharing the project’s outcomes with educators, teachers, and key stakeholders is of paramount importance. By discussing our findings and methodologies, we aim to inspire and equip educational communities with innovative tools and strategies that promote environmental awareness and action. Engaging a broad network of educators and policymakers will not only facilitate the adoption of these practices in diverse educational settings but also contribute to a collective effort to foster a more sustainable future. Encouraging collaboration and knowledge exchange among educational institutions will amplify the project’s impact, ensuring long-term benefits for students and society as a whole.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Project
The European project KA220-SCH “Clean Environment-Clean School Climate with Creative Environmental Practices in School Education-Clean & Creative” holds immense potential to inspire and educate future generations about the importance of sustainability. The project outcomes marked the initial step in a collaborative effort to incorporate the principles of sustainability into educational systems. Through active educator participation, creative methodologies, and a commitment to sustainability, the curricula aim to create a lasting impact on both students and the broader community, ensuring a cleaner and more sustainable future for all. Environmental consciousness and creative solutions can also be promoted to waste management through artistic applications. The project “Clean & Creative” has been funded for 24 months (starting from September 2023) in the first round of the Call for Proposals 2023 Programme: ERASMUS+, Key Action 2, Action: Cooperation partnerships in school education (KA220-SCH). The Coordinating Organization is the Valdres Vidaregåande Skule in Leira (Norway); the partners of the Consortium are:
- -
- Department of Physics and Chemistry of the University of Palermo (UNIPA)—Palermo (Italy);
- -
- Çağdaş ve Yenilikçi Eğitimciler Derneği—Trabzon (Turkey);
- -
- 1o Geniko Lykeio Kaisarianis—Athens (Greece);
- -
- Colegiul Economic “Virgil Madgearu”—Galati (Romania);
- -
- Srednja skola—Valpovo (Croatia);
- -
- Bildungsanstalt für Elementarpädagogik der Kongregation der Schwestern vom göttlichen Erlöser—Wien (Austria).
The main objectives of the project are related to an inclusive action plan based on environmental education in the fight for the environment and against climate change. In particular, the project aims to (i) transform the amount of waste in schools and social-life centers into useful products; (ii) develop environment-themed curriculum contents that can be integrated into the curricula of 10 different subjects; and (iii) increase the impact of environmental awareness and make it sustainable with the project’s web portal/digital games/mobile application.
Figure 1 displays the project’s logo, which was selected through a competition involving students from all Consortium partners.

Figure 1.
Clean&Creative project logo.
The logo is visually appealing, meaningful, and well aligned with the project’s goals. It effectively conveys themes of environmental awareness, sustainability, and collaboration. The central image of two arms embracing the Earth symbolizes protection, care, and a collective effort toward a cleaner environment. The choice of watercolor-style art gives it a natural, creative, and harmonious feel, aligning well with the project’s focus on sustainability and artistic practices. The text “Clean Environment, Clean School Climate” emphasizes the project’s commitment to improving both environmental conditions and educational spaces. The inclusion of the word “creativity” and the Erasmus and EU logos further reinforces the idea that this is a collaborative, international initiative promoting innovation in sustainability.
As shown in Figure 2, the project is articulated in five work packages:
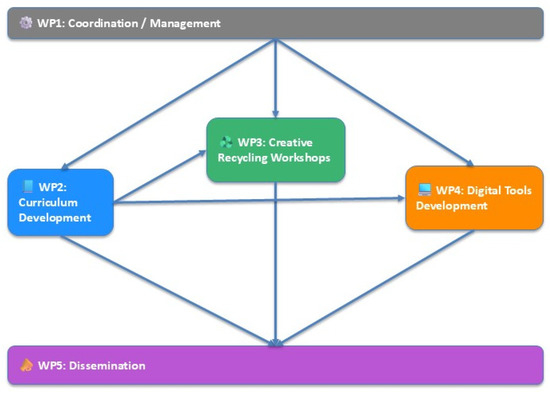
Figure 2.
Clean&Creative project visual flowchart.
WP1: Project management;
WP2: Interdisciplinary educational practices: environment and climate-themed curriculum contents (it includes the development of environmental-themed curriculum content for 10 different education disciplines);
WP3: Aesthetic transformation and exhibition of wastes: creative applications for the transformation of solid wastes (glass, plastic, packaging, etc.) into products as raw materials in artistic applications (it includes the staff and student mobilities, as well as local and transnational art workshops about the transformation of waste into artistic products);
WP4: Environmental and climate-themed educational and awareness-raising digital contents: A web portal that will support the fight for the environment and against climate change will be created with innovative digital tools such as digital pedagogical games and mobile applications.
WP5: Dissemination (It includes three Transnational Project Meetings (TPMs), the final conference, events, and other sharing and promotion strategies, with which all project achievements and outputs will be disseminated nationally and internationally).
The work packages implemented using the inductive methodology aim to significantly enhance the waste management skills of participants, including students, teachers, members of civil society, and other key stakeholders. These improvements will be evident across various aspects of social life, with particular emphasis on educational institutions. By fostering better waste management practices within schools, the initiative is expected to contribute to a noticeable reduction in the overall amount of waste generated. The key component of this approach is the integration of curriculum content into formal education, ensuring that waste management principles become an essential part of students’ learning experiences. Furthermore, the development of waste management skills will be reinforced through artistic practices, allowing participants to engage creatively with sustainability concepts. In addition, the incorporation of digital tools will serve to strengthen these competencies, making learning more interactive and accessible.
By combining educational, artistic, and technological approaches, this initiative will cultivate a long-lasting and deeply rooted environmental awareness among participants. This, in turn, will contribute to the promotion of sustainable habits and responsible waste management practices that extend beyond schools into the broader community, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship for future generations.
2.2. Experimental Procedure for Data Collection and Evaluation Criteria
The “Clean Environment-Clean School Climate” project aims to improve environmental education in schools, focusing on the integration of digital tools in the teaching process and through interdisciplinary activities. In this endeavor, several studies, reports and questionnaires were carried out or will be administered at the end of the project, aiming to evaluate how students and teachers perceive and apply ecological principles in the school setting. A pre-test was administered to 244 students based on their expectations. Following the project’s completion, the same participants will take a post-test to assess their engagement in the project activities. The difference between the pre-test and post-test results will be analyzed to measure the impact level. The feasibility and sustainability of the web portal and mobile application created will be evaluated with a pilot application and a report will be prepared for this research. The number of visitors, followers, comments, and likes on the social media accounts of our project on the web page are collected. A technical analysis of the psychomotor development of students’ artistic skills is performed during the project and accompanied by expert opinions. The pre-test and post-test will be conducted to measure the foreign language practices of staff, teachers, and students.
In the final stage of the project, several evaluation tasks will be undertaken to assess its overall impact and effectiveness. Questionnaires will be administered to measure students’ environmental awareness within the school context, focusing on success rates. To evaluate the project’s broader outcomes, a “Curriculum Eligibility Assessment Survey” will be conducted with teachers, complemented by the use of a Likert scale to gauge responses. Additionally, quantitative data will be collected on the reduction in waste generated in schools and the proportion of this waste that has been converted into useful products. The aesthetic quality of items repurposed from waste materials will be assessed by art educators to determine their creative value. Furthermore, user engagement with the project’s digital platforms will be measured by tracking the number of comments on the web portal content and the number of downloads of the mobile application.
2.3. Survey Analysis
The documents created in the project provide an overview of the current state of ecological education in pre-university education and highlight the role of digital resources in increasing student awareness and involvement. Currently, ecological education is mainly integrated at the traditional curriculum level (Geography, Biology, Chemistry), but it also extends to subjects such as Mathematics, Literature, History, or Philosophy. At the same time, school remains the main source of information for students, but there is an increased interest in didactic methods that can combine theory with interactive tools: applications, online platforms, and educational games. The main trends identified by our needs analysis are the following: (i) the increasing role of digital resources (mass media, social networks, and online games are considered channels through which students can attractively access environmental information); (ii) the need for interdisciplinarity (traditional subjects can be enriched by interdisciplinary approaches, so that students can form a holistic vision of ecological issues); (iii) the continuous teacher training (many teachers signal the need for specific support and training to effectively use digital platforms and ecological applications in the teaching process). These trends confirm that classical teaching approaches are increasingly complemented or even replaced by technology-based methods, with an emphasis on interactivity and practical involvement.
The data collected in the studies carried out at the start of the project show that over 80% of students consider school as the main resource for ecological training, followed by mass media and social networks. However, only a smaller percentage (under 15%) declares themselves “very well informed”, suggesting that there is room for improvement in deepening environmental topics. According to the responses to the questionnaires, students appreciate online games with ecological themes, mentioning that they can increase interest and motivation for the subject, although some emphasize that their simple use, without further discussion, does not ensure a profound behavior change. Students and teachers indicated that subjects such as Geography and Biology are the easiest to correlate with environmental education, but Mathematics, Language and Literature, Philosophy, or History can also integrate ecological notions, especially through examples and interdisciplinary projects. Most respondents believe that practical activities (volunteering, recycling campaigns, field projects) have a greater impact on the formation of responsible behaviors than exclusively theoretical or online exposure.
The current state of environmental education in schools participating in the project reveals a growing interest among students and teachers in innovative methods, especially digital tools. However, success depends on the coherent integration of these tools into the curriculum and practical activities, continuous training of teachers and the provision of technological resources, the correlation of theory with concrete examples and projects applied in the community.
2.4. Activities on Sustainability During the Learning/Teaching/Training (LTT) Mobilities
Environmental projects and sustainability activities during LTTs are essential for promoting a culture of environmental responsibility and empowering students and educators to become agents of change. By integrating sustainability into the curriculum and fostering collaboration, schools can play a vital role in creating a more sustainable future. All the LTTs of this project are part of the WP3: Creative applications for the transformation of solid wastes (glass, plastic, packaging, etc.) into products as raw materials in artistic applications. Each school partner attended the transnational mobilities with 2 teachers and 4 students. In the first 18 months of project activity, three student mobilities have been implemented, which involved 30 teachers and 60 students belonging to the five partner schools.
The first student mobility of the project took place in Athens, Greece, from April 2nd to 5th, 2024, with 1o Geniko Lykeio Kaisarianis serving as the host school. The central event of this mobility was the Art Workshop on “Recycling of Packaging Waste”, where students explored creative ways to repurpose discarded materials. During their stay, participants visited the Niarchos Foundation, a state-of-the-art sustainable building that operates using renewable energy. There, they attended an insightful workshop on the building’s sustainability features and green design principles. Another engaging activity was a hands-on workshop on creating art from metal packaging, promoting the idea of reducing waste through artistic expression. Additionally, students conducted research on the use and management of packaging waste in their respective countries, utilizing the multimedia equipment available at the hosting school. They then presented their findings in a collaborative session, fostering knowledge exchange. The mobility concluded with a visit to BlueCycle, an innovative model center equipped for the utilization of marine plastic waste, where students learned about sustainable recycling processes and their impact on ocean conservation.
The second student mobility took place in Vienna, Austria, in April 2024, hosted by Wien School. The focus of this mobility was the Art Workshop on “Recycling of Paper and Cardboard Waste”. Students explored different methods of repurposing paper-based materials and participated in creative exercises that highlighted the importance of sustainable paper use and responsible recycling habits. The third student mobility occurred in Valpovo, Croatia, from November 4th to 7th, 2024, with Valpovo High School as the host institution. The central theme of this mobility was “How to Reuse Textile Waste”. In this engaging workshop, students demonstrated their creativity by designing and crafting unique ties from discarded pieces of clothing. Under the expert guidance of Professors Marija Šimić and Jasna Vuković, they incorporated motifs representing their home countries, transforming waste textiles into wearable art.
These student mobilities provided invaluable educational and personal development opportunities for participants. While engaging in hands-on workshops, students gained practical skills in sustainable waste management, creative recycling techniques, and environmental responsibility. Exposure to diverse artistic methods encouraged them to think critically about waste reduction and explore innovative solutions to global sustainability challenges. Furthermore, working in international teams fostered cross-cultural communication, collaboration, and teamwork, enhancing their ability to interact with peers from different backgrounds. Beyond skill development, the mobilities also broadened students’ perspectives by immersing them in different cultures, educational systems, and sustainable practices. Visiting eco-friendly institutions and participating in expert-led workshops deepened their understanding of environmental conservation efforts at both local and global levels. These experiences not only inspired a lifelong commitment to sustainability but also empowered students to become active agents of change in their communities. Ultimately, the mobilities enriched their educational journeys, fostering creativity, responsibility, and a proactive attitude toward a greener future.
3. Project Results
3.1. Project Perspectives on Sustainability in Education
Our project, in contrast to traditional sustainability education models that primarily focus on STEM disciplines, integrates environment and climate-themed curriculum content across a wide range of subjects, intending to enhance student awareness and inspire actionable engagement in sustainability. Furthermore, embedding sustainability principles across multiple disciplines may offer a more comprehensive and impactful approach [19]. For this reason, in addition to the more commonly associated fields such as Biology, Chemistry, and Physics (Science), our approach extends to disciplines that are often overlooked in sustainability education, including Music, Sport, Literature, Philosophy, History, Geography, Visual Arts, Mathematics, and Foreign Languages. This inclusive strategy ensures that sustainability concepts are woven into diverse learning experiences, making them more accessible and relevant to students with varying academic interests [20,21]. A discipline-specific approach allows students to engage with sustainability in ways that are contextually relevant to each field. While integrating sustainability into ten distinct subject areas, students develop a more profound understanding and practical application of sustainability concepts.
Research highlights the importance of integrating sustainability into the humanities and arts, emphasizing that creative disciplines can serve as powerful tools for fostering environmental consciousness and ethical reflection [22]. For instance, in Art, students can explore eco-friendly materials and design practices [23], while in Geography, they can analyze climate-change patterns and urban planning for sustainability [24]. Teaching sustainability in a Foreign Language class can expose students to global perspectives on environmental policies, reinforcing the importance of cultural diversity in sustainable development, allowing for cross-cultural dialogue [25]. Similarly, Literature courses can highlight ecological themes in classic and contemporary works, fostering critical thinking about humanity’s relationship with nature [26]. History provides a lens to examine past environmental challenges and policy responses, helping students understand the evolution of sustainability movements [27]. Music can incorporate themes of environmental activism and the use of sustainable instruments, enhancing awareness through creative expression [28]. In Mathematics, sustainability can be integrated through statistical analysis of environmental data, fostering quantitative literacy on issues such as carbon footprints and resource depletion [29]. Science subjects naturally align with sustainability through topics like biodiversity conservation and renewable energy [30]. Physical Education and Sport can promote sustainability advocating for outdoor experiential learning as a means of connecting students with nature [31] and discussions on the ecological impacts of sports [32]. Finally, Philosophy encourages ethical reflections on human responsibility toward the planet, providing a critical foundation for sustainable decision making [33].
Our project fosters an interdisciplinary approach that equips students with the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to engage with environmental issues from multiple perspectives. This model aligns with current educational trends that advocate for a transdisciplinary approach to sustainability, bridging scientific inquiry with cultural, ethical, and artistic dimensions [34]. By expanding the scope of sustainability education beyond traditional STEM subjects, we empower students to become well-rounded, environmentally conscious global citizens.
3.2. The Curriculum Structure
How to bring environmental protection education to schools? In addition to including it as a compulsory subject, there are numerous activities related to climate change that can be carried out in schools. For example: nature activities related to environmental care such as cleaning, visits to farms and nurseries to learn first-hand how to care for animals and plants, recycling courses, and workshops. Whether as a separate subject or as an optional topic in the school curriculum, it is crucial to foster environmental values and knowledge among young people so that they can lead a more sustainable life. In order to stimulate their curiosity about the natural world and concern for the health of the planet, appropriate curricula must be promoted.
The academic partner of the Consortium provided support to other responsible institutions during the program development stages of the curricula. It prepared a common structure, evaluation, and recommendation reports for the contents to be developed in ten different disciplines. Table 1 shows the common structure of the Learning Units.

Table 1.
Common structure for the “Clean & Creative” Learning Units.
In the following, as an example, we discuss a significant case of integration of Environmental Education (EE) in the curriculum of Philosophy within the Learning Unit reported in Appendix A, identifying both the benefits and obstacles, and offering recommendations for enhancing the inclusion of environmental education in this subject.
All the ten curricula developed by the Consortium partners together with the feedback from teachers in the pilot studies are available upon request.
Environmental Education in Teaching Philosophy
Integrating Environmental Education (EE) into Philosophy enables students to critically analyze humanity’s relationship with nature through ethical, metaphysical, and existential inquiry. They examine key questions—such as nature’s intrinsic value, human moral obligations toward the environment, and our role in ecosystems—fostering deep reflection and a stronger philosophical foundation for sustainability.
A major advantage is Philosophy’s emphasis on ethical debate and critical reasoning, which helps students evaluate environmental responsibility. Discussions on anthropocentrism, biocentrism, and ecocentrism challenge them to assess whether nature holds inherent worth or merely instrumental value, refining their ethical perspectives and environmental awareness [35].
Environmental Philosophy encourages students to view sustainability through an ethical lens, analyzing the moral implications of consumption, resource depletion, and ecological harm. Key themes like intergenerational justice—whether present generations have a duty to preserve nature for the future—prompt deeper reflection. These discussions shift students’ focus beyond short-term consequences, cultivating a long-term, ethically grounded perspective on environmental responsibility [36].
Integrating EE into Philosophy helps students explore existential and metaphysical questions about humanity’s role in nature. By examining traditions like deep ecology, indigenous perspectives, and Eastern philosophies, students discover alternative views of environmental interconnectedness.
Philosophy also serves as a framework for analyzing environmental justice, revealing how ecological harms have an impact on marginalized groups. Through ethical discussions on fairness and equity, students grasp the social dimensions of sustainability, fostering a sense of global citizenship and advocacy for just solutions.
However, challenges include Philosophy’s abstract nature, which may feel detached from practical EE. Teachers may need specialized training, and students could struggle to connect theoretical debates (e.g., nature’s intrinsic value) to real-life contexts without concrete examples. Solutions involve using case studies (e.g., climate change, biodiversity loss) to ground philosophical concepts, interdisciplinary collaboration with sciences and ethics, and experiential learning (e.g., outdoor sessions, debates) to enhance engagement.
In summary, merging EE with Philosophy cultivates critical thinking and ethical environmental stewardship. Addressing abstraction and curriculum gaps can create programs that empower students as reflective, responsible ecological citizens.
3.3. The Impact of the Project on the School Environment
Research indicates that when sustainability is embedded in curricula beyond traditional science classes—such as in humanities, arts, and social sciences—students develop a more holistic understanding of sustainability issues [37] and are motivated to apply sustainable practices in real-world contexts [38]. Schools that implement sustainability projects demonstrate measurable improvements in campus operations (waste reduction, energy efficiency) [39], while interdisciplinary approaches boost both academic engagement and community environmental responsibility [40].
Cross-disciplinary integration of sustainability concepts significantly enhances education by fostering systemic thinking, responsible citizenship, and real-world problem-solving skills. Embedding sustainability across diverse subjects—from sciences to humanities—enables students to develop a holistic understanding of interconnected environmental, social, and economic systems [37]. This approach cultivates critical thinking as students examine sustainability challenges through multiple academic lenses [40], while project-based learning increases engagement by connecting studies to practical applications [38].
The model also promotes active citizenship, with students developing pro-environmental behaviors and ethical awareness [39]. Institutionally, it strengthens teacher collaboration and transforms schools into living laboratories through operational improvements like energy conservation and waste reduction. Furthermore, it equips students with future-ready competencies valued in green economy sectors [41].
Our project has led to tangible improvements in the school’s physical environment by promoting the creation of school gardens, implementing recycling programs, installing energy-efficient lighting, and developing composting systems. These changes have contributed to a greener and more sustainable school life. By actively participating in this project, students and staff became more aware of the importance of conservation and sustainable practices. This heightened awareness has translated into behavioral changes, such as reduced waste generation and increased energy efficiency.
Workshops and seminars on topics such as climate change, renewable energy, waste management, and biodiversity conservation provided participants with the knowledge and skills needed to implement sustainable practices in their own schools and communities. Getting acquainted with local environmental projects, recycling centers, renewable energy installations, or nature reserves provided participants with firsthand experience of sustainable practices in action. Collaborative projects between participating schools allowed students and teachers from different countries to work together on sustainability initiatives. This collaboration has fostered cross-cultural understanding and promoted the exchange of best practices. Developing and sharing educational materials on sustainability, such as lesson plans, activity guides, and multimedia resources around the world amplified the impact of the project.
4. Bridging Technology and Sustainability in Education
Today’s pressing environmental challenges require dynamic digital education tools. The Erasmus+ project Clean&Creative develops innovative web and mobile applications that transcend traditional e-learning approaches. Specifically designed for youth (14–19 years), our platform combines gamification strategies—interactive elements, reward systems—with accessible design to effectively promote sustainable behaviors. Research-confirmed engagement techniques ensure the platform not only educates but inspires lasting environmental action. A systematic literature review found that game-based learning approaches effectively engage users in climate-change topics [42]. Similarly, a study demonstrated that gamification enhances learning outcomes in Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) education [43]. Within the project, we deeply explored how visual design elements should be tailored to enhance engagement and comprehension in environmental and climate-themed digital applications, focusing on the interests and needs of different target age groups, since the effectiveness of digital applications depends significantly on the visual preferences and the cognitive and emotional development of the target audience. From colorful, animated content for young children to data-driven visual storytelling for adults, designers must tailor their approaches accordingly. The study developed within the project provides a framework for developing engaging, educational, and sustainable digital content focused on environmental and climate awareness, ensuring innovative and environmentally friendly solutions and providing a thorough analysis of visual design principles, usability, and interactivity tailored to maximize learning impact.
The Clean&Creative Innovative Products: Platform Development and Gamified Mobile Experience
The last months of the project will be devoted to the complete development of the digital educational platform, environmental digital games, and a mobile app. Thanks to the digital platform, the environmental education-themed digital games, and the mobile application developed within the last work package of the project, environmental awareness could be increased in line with our project goals, educational resources/content can be delivered to wider audiences, and users will be provided with environmentally friendly habits. The integration of digital technologies with environmental education will increase the permanence of the project and contribute to raising environmentally sensitive generations.
The Clean&Creative digital platform will finally serve as a centralized hub for environmental education content, offering age-appropriate resources with lasting accessibility beyond the project’s duration. This online environment will provide three key advantages: long-term access for educational institutions, teachers, and students ensures continued impact; expert contributions regarding environmental developments will be constantly updated; and international networking capabilities foster collaboration among educators, academics, and students across borders, ultimately supporting sustainable policy development and pedagogical innovation.
Complementing the platform, our digital environmental games revolutionize traditional learning by making sustainability education engaging and interactive. These web-based and mobile-compatible games serve multiple purposes: they transform students’ natural engagement with technology into productive learning, cultivate lasting ecological awareness and sustainable habits, and extend their reach beyond classrooms to families and environmental organizations. By integrating these gamified tools into both formal and informal educational settings, we create innovative resources that make environmental education both impactful and appealing to young learners.
The project’s mobile app provides on-demand access to environmental education resources and learning experiences. The potential impact of this mobile application is enormous; through our location-based gamified experience, users will be able to complete real-world sustainability challenges (e.g., waste audits, biodiversity mapping) integrated into their local environments, gaining practical experiences on topics such as recycling, energy saving, and sustainable consumption, and develop environmentally friendly habits in their daily lives. Unlike standard gamification models, the project mobile app uses real-time data tracking, collaborative scoring between schools across Europe, and dynamic environmental leaderboards to foster a sense of transnational eco-competitiveness. Moreover, the project employs student co-design workshops, allowing learners to co-create mini-games and digital storytelling modules, significantly boosting ownership and engagement. The application will allow users to reinforce their experiences even in their free time. In this way, it will contribute to the development of awareness about environmental education at all times and under all conditions. Up-to-date information about the environment, upcoming ecological activities and practical suggestions for sustainable living will be sent as notifications to the mobile device, with the aim of increasing the awareness of the app users.
5. Conclusions
In contemporary education, sustainability has emerged as a multidimensional concept that reaches far beyond traditional environmental awareness. While the environmental dimension remains vital, sustainability, as outlined in the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), encompasses complex ethical, social, economic, and political questions. It demands a transformative mindset capable of grappling with issues such as participatory governance, peacebuilding, responsible consumption, intergenerational equity, and the nuanced distinction between human needs and interests.
In this view, the European education practices reveal that sustainability education is most effective when integrated across curricula rather than treated as a standalone subject. Embedding sustainability concepts within diverse disciplines—from the sciences to the humanities—allows students to engage with them through varied lenses, fostering deeper comprehension and real-world applicability. This approach not only develops critical competencies like systems thinking and adaptive problem-solving but also equips learners to tackle sustainability’s interconnected challenges. Studies, including Tilbury’s (2011) work, demonstrate that discipline-specific integration improves both engagement and long-term retention of sustainability principles [44]. Thus, Europe’s cross-curricular model exemplifies how a multifaceted, context-driven strategy advances sustainability literacy more effectively than isolated programs—aligning with EU objectives for a green transition.
Transformative sustainability education emerges when theory intersects with action—evidenced by this Project and European models combining classroom learning with hands-on activities, community initiatives, and digital simulations. While technology (AI games, data apps, virtual labs) boosts engagement, its effectiveness depends on purposeful integration within pedagogical and social contexts. Examples include Finland’s digital ecosystem monitoring and Germany’s “Umweltschulen”, where technology enhances real-world applications like urban gardening, cultivating both skills and collective responsibility. This synergy between technology, curriculum, and community aligns with the EU’s GreenComp competencies, which emphasize action-oriented learning and systemic thinking.
This article challenges traditional environmentally centric perspectives by proposing a reconceptualization of sustainability. The Erasmus+ project Clean Environment–Clean School Climate with Creative Environmental Practices in School Education (Clean&Creative) utilizes environmental issues as an accessible and contextually relevant entry point, particularly within educational settings. However, its core objective extends beyond environmental awareness, aiming to cultivate cross-curricular connections that contribute to a more comprehensive, systemic understanding of sustainability. Rather than offering a definitive solution, the project introduces a pedagogical framework designed to promote critical thinking, participatory learning, and the creative application of sustainability principles across various disciplines. Preliminary findings from the project reveal a 40% increase in student-reported eco-conscious behaviors and a demonstrable enhancement in cross-cultural environmental literacy. These innovative features position the project as a progressive model for digital environmental education within the European context.
We recognize the limitations of this approach—especially the absence of dedicated curricula solely focused on sustainability theory—and argue for the long-term necessity of introducing such courses at both secondary and tertiary levels. In this light, this Erasmus+ project serves as both a practical intervention and a steppingstone toward deeper sustainability education.
In conclusion, embedding sustainability across the European school curriculum transcends traditional disciplinary boundaries, transforming classrooms into dynamic hubs of innovation and civic responsibility. This cross-curricular approach not only equips students with academic knowledge but cultivates the values, skills, and agency needed to navigate and address complex 21st century sustainability challenges. As demonstrated, when theoretical learning is reinforced through experiential activities, technological integration, and community engagement, environmental education becomes a powerful catalyst for behavioral change and systemic thinking. Building on these findings, our future research will quantitatively assess the impact of this integrated model through a detailed analysis of the pilot studies across participating European schools, offering empirical evidence to refine and scale these transformative educational practices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.P.A. and N.P.; methodology, D.P.A. and N.P.; software, Y.S.D.; validation, D.P.A., N.P., E.A.B., S.F.S., M.C., C.C., A.T. and Z.Š.; formal analysis, D.P.A., N.P., E.A.B., S.F.S., M.C. and C.C.; investigation, D.P.A. and N.P.; resources, D.P.A., N.P., E.A.B., S.F.S., M.C., C.C., A.T. and Z.Š.; writing—original draft preparation, D.P.A. and N.P.; writing—review and editing, D.P.A., N.P. and M.C.; visualization, D.P.A. and N.P.; supervision, D.P.A.; funding acquisition, D.P.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Erasmus+ Programme 2023: Key Action 2 Cooperation partnerships in school education (KA220-SCH) of the European Commission, grant number 2023-1-NO01- KA220-SCH-000159229. The APC was funded by the University of Palermo.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the fact the questionnaires were administered in full compliance with the principles of anonymity and voluntary participation. According to both EU and national regulations, this type of research does not require prior approval from an Ethics Committee or Institutional Review Board. In particular, the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR—Regulation (EU) 2016/679), Recital 26, clearly states that the principles of data protection do not apply to anonymous information, i.e., information which does not relate to an identified or identifiable natural person.
Informed Consent Statement
The research is based solely on the analysis of anonymous questionnaires voluntarily completed by students from partner schools within the framework of the Erasmus+ project. The questionnaires were administered in full compliance with the principles of anonymity and voluntary participation. No identifiable information was collected at any stage of the study, and respondents could not be re-identified.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting reported results can be found in the Google Drive generated during the project and are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Sustainability in Philosophy
- Lesson Title: Exploring Sustainability Through Ancient and Modern Philosophy
- Grade Level: Age range: 16–18 years (2nd Grade and 3rd Grade of Senior High School)
- Objective: Introduce students to philosophical perspectives on sustainability, encouraging them to critically examine human interaction with nature, ethical responsibilities, and societal organization. Foster skills such as critical thinking, empathy, and decision making through philosophical inquiry.
- Key Topics
- Nature and Philosophy in Ancient Thought
- -
- Explore Pre-Socratic philosophies on the harmony and forces of nature.
- -
- Understand Plato’s and Aristotle’s perspectives on the moral implications of environmental interaction.
- Stoic Philosophy and Sustainability
- -
- Examine Zeno’s principle of living in harmony with nature and its relevance to modern environmental ethics.
- -
- Discuss the Stoic values of simplicity, interconnectedness, and cosmopolitanism.
- Modern Philosophical Perspectives on Ecology
- -
- Analyze contemporary ecological philosophies, such as shallow vs. deep ecology.
- -
- Explore the integration of humanism and ecology in addressing environmental challenges
- Activities
- 1.
- Philosophical Text Analysis
- -
- Students read and analyze excerpts from philosophers such as Plato, Aristotle, Zeno, and contemporary thinkers like Barry Commoner.
- -
- Discuss key philosophical principles and their implications for sustainability.
- 2.
- Classroom Debates and Discussions
- -
- Facilitate debates on topics like anthropocentrism vs. ecocentrism and the ethics of resource consumption.
- -
- Encourage students to articulate and defend their positions using philosophical reasoning.
- 3.
- Creative Projects
- -
- Students create essays or multimedia presentations exploring philosophical solutions to modern environmental problems.
- -
- Develop arguments based on philosophical theories to address real-world issues.
- 4.
- Experiential Learning
- -
- Screen documentaries such as “Animated Philosophers” to connect philosophical ideas with current environmental challenges.
- -
- Organize interdisciplinary activities involving philosophy, art, and science to explore environmental ethics.
- Assessment
- 1.
- Class Participation
- -
- Assess engagement in discussions, debates, and group activities.
- 2.
- Analytical Essays
- -
- Evaluate students’ ability to critically analyze philosophical texts and articulate connections to sustainability.
- 3.
- Creative Outputs
- -
- Review multimedia or written projects for originality, depth of thought, and the application of philosophical principles.
- Conclusion: This lesson integrates the study of philosophy with contemporary environmental concerns, encouraging students to critically examine the moral and practical implications of sustainability. By exploring ancient and modern philosophical perspectives, students develop the skills and mindset needed to address ecological challenges as responsible and thoughtful global citizens.
- Teacher’s Feedback
“The students displayed great curiosity and critical engagement when exploring philosophical perspectives on sustainability. Discussions were particularly insightful, with students connecting ancient ideas to modern issues. The debates were lively and reflective, showcasing their growing ability to reason and argue effectively. One area for improvement would be fostering collaboration during group projects, as some students preferred individual work. Overall, this lesson successfully bridged philosophical inquiry with real-world environmental ethics, inspiring students to think deeply about their roles in sustainability.”
References
- Barth, M.; Rieckmann, M.; Siegmund, A. Sustainability competencies: A systematic review of frameworks and assessment approaches. Int. J. Sust. Higher Ed. 2021, 22, 772–791. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, S.; Orr, D. Sustainability Education: Visions and Practice for a Sustainable Future; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2022; ISBN 9780367562031. [Google Scholar]
- Leicht, A.; Heiss, J.; Byun, W.J. Transforming Education for Sustainability: Contributions from UNESCO and Beyond; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; ISBN 9783030751778. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, R.; Barreiro-Gen, M.; Lozano, F.J. Competency-based learning for sustainability: Insights and challenges. Sustainability 2023, 15, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, H.; Hirsch, G. Systems Thinking for a Sustainable Future: Perspectives and Practices; Earthscan from Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2020; ISBN 9780367150344. [Google Scholar]
- Friman, H.; Banner, I.; Sitbon, Y.; Sahar-Inbar, L.; Shaked, N. Experiential learning for sustainability: A catalyst for global change. Educ. Admin. Theory Pract 2024, 30, 8508–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzolato, N.; Persano Adorno, D. Informal physics teaching for a better society: A mooc-based and context-driven experience on learning radioactivity. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1512, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Jabot, M.; Heath, C. (Eds.) Experiential Learning and Community Partnerships for Sustainable Development; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkinde, A.G. Experiential learning for sustainability. Conflux J. Educ. 2024, 12, 1–10. Available online: https://www.cjoe.naspublishers.com/2024/01/08/experiential-learning-for-sustainability-by-dr-anjali-g-kirkinde/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- British Council. Teacher Professional Development Imperative for Climate Change and Sustainability Education; British Council: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://www.britishcouncil.org/about/press/teacher-professional-development-imperative-climate-change-and-sustainability-education (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Murphy, C.; Smith, G.; Mallon, B.; Redman, E. Teaching about sustainability through inquiry-based science in Irish primary classrooms: The impact of a professional development programme on teacher self-efficacy, competence and pedagogy. Environ. Educ. Res. 2020, 26, 1112–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Stirling. Teacher Education Imperative for Climate Change and Sustainability Education; University of Stirling: Stirling, UK, 2023; Available online: https://www.stir.ac.uk/news/2023/12/teacher-education-imperative-for-climate-change-and-sustainability-education (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Persano Adorno, D.; Mallahnia, T.; Koch, V.; Zailskaitė-Jakštė, L.; Ostreika, A.; Urbaitytė, A.; Punys, V.; Pizzolato, N. The BioS4You European Project: An Innovative Way to Effectively Engage Z-generation Students in STEM Disciplines. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSF Report. Shaping the Future: New Expectations for Undergraduate Radication in Science, Mathematics, Engineering, and Technology; Education and Human Resources Directorate: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 96–139.
- Altbach, P.G.; Reisberg, L.; Rumbley, L. Trends in global higher education: Tracking an academic revolution. In Report for the UNESCO 2009 World Conference on Higher Education, Paris, France, 5–8 July 2009; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2009; pp. 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Roche, J.; Murphy, C. Changing Values in Science Education and the Emergence of Science Gallery. In Values in Science Education; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jeronen, E.; Palmberg, I.; Yli-Panula, E. Teaching Methods in Biology Education and Sustainability Education Including Outdoor Education for Promoting Sustainability—A Literature Review. Educ. Sci. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano Adorno, D.; Koliakou, I.; Bratitsis, T.; Komorek, J.; Pizzolato, N. Could Physics teaching and Sustainability challenges be linked? J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2025, 2950, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, S. Sustainability Education: Perspectives and Practice Across Higher Education; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gough, A. STEM policy and environmental education: A call for conversation. Environ. Educ. Res. 2016, 22, 757–764. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Education for Sustainable Development: A Roadmap; UNESCO Publishing: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Inwood, H.J.; Jagger, S. Earth art and sustainability education. Int. J. Educ. Through Art 2014, 10, 355–372. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, T.; Guyas, A.S. Earth education, interbeing, and deep ecology: Critical curriculum for sustainability in art education. Stud. Art Educ. 2012, 53, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M. Geography and Sustainability: Integrating Spatial Analysis and Environmental Science; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Boehnert, J. Design, Ecology, Politics: Toward the Ecocene; Bloomsbury Publishing: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Glotfelty, C.; Fromm, H. The Ecocriticism Reader: Landmarks in Literary Ecology; University of Georgia Press: Athens, GA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, J.R. Something New Under the Sun: An Environmental History of the Twentieth-Century World; W. W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pedelty, M. Ecomusicology: Rock, Folk, and the Environment; Temple University Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, S.; Maxey, L.; Luna, H. The Sustainable University: Progress and Prospects; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Orr, D.W. Ecological Literacy: Education and the Transition to a Postmodern World; SUNY Press: Albany, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørn, M.; Karlsen, H. Physical education and outdoor learning: Exploring sustainability education through movement. Environ. Educ. Res. 2022, 28, 412–428. [Google Scholar]
- Mullins, P.M. Environmental responsibility in physical education and sport. J. Phys. Educ. Recreat. Dance 2014, 85, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Naess, A. Ecology, Community and Lifestyle: Outline of an Ecosophy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wals, A.E.; Brody, M.; Dillon, J.; Stevenson, R.B. Convergence between science and environmental education. Science 2017, 356, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M. Challenges of environmental problems to the philosophy of education. Policy Futures Educ. 2015, 13, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C. “What do we talk about when we talk about climate change?”: Meaningful environmental education, beyond the info dump. J. Philos. Educ. 2023, 57, 457–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Education for Sustainable Development Goals: Learning Objectives; UNESCO Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, S. Sustainable Education: Re-Visioning Learning and Change; Green Books: Burnside, LA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Education for Sustainability (EfS). Standards and Practices for K-12 Sustainability Education; Cloud Institute: Austin, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wiek, A.; Withycombe, L.; Redman, C.L. Key competencies in sustainability: A reference framework for academic program development. Sustain. Sci. 2011, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. The Future of Education and Skills: Education 2030; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, L.; Dias, A.; Hamari, J. Gamification for climate change engagement: Review of corpus and future agenda. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 120, 84–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Enhancing ESG learning outcomes through gamification: The mediating role of psychological ownership and perceived importance. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1109571. [Google Scholar]
- Tilbury, D. Education for Sustainable Development: An Expert Review of Processes and Learning; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).