Assessment of Organic Matter Content of Winter Wheat Inter-Row Topsoil Based on Airborne Hyperspectral Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
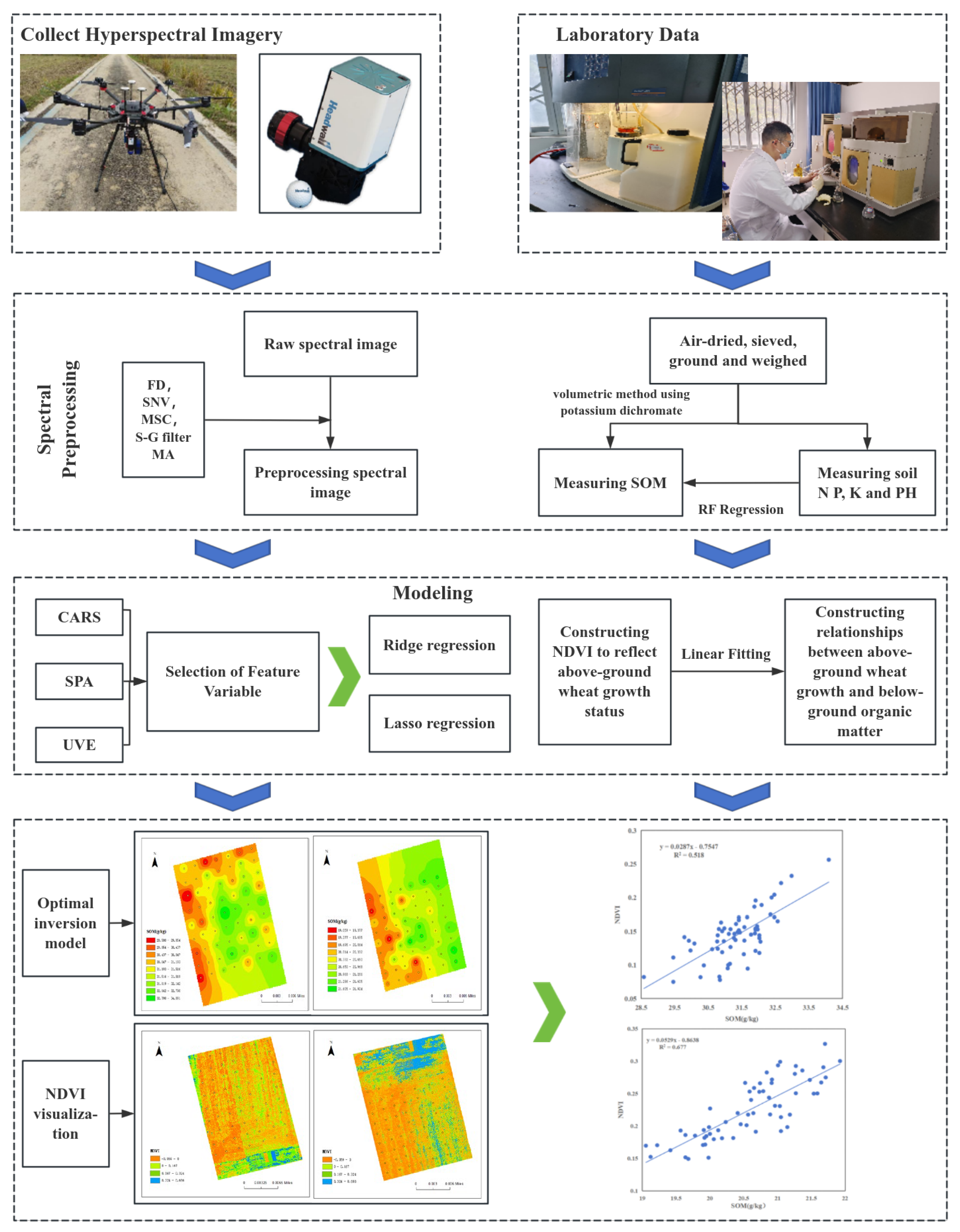
2.1. Research Technology Process
2.2. Study Area and Experimental Design
2.3. Hyperspectral Data Acquisition
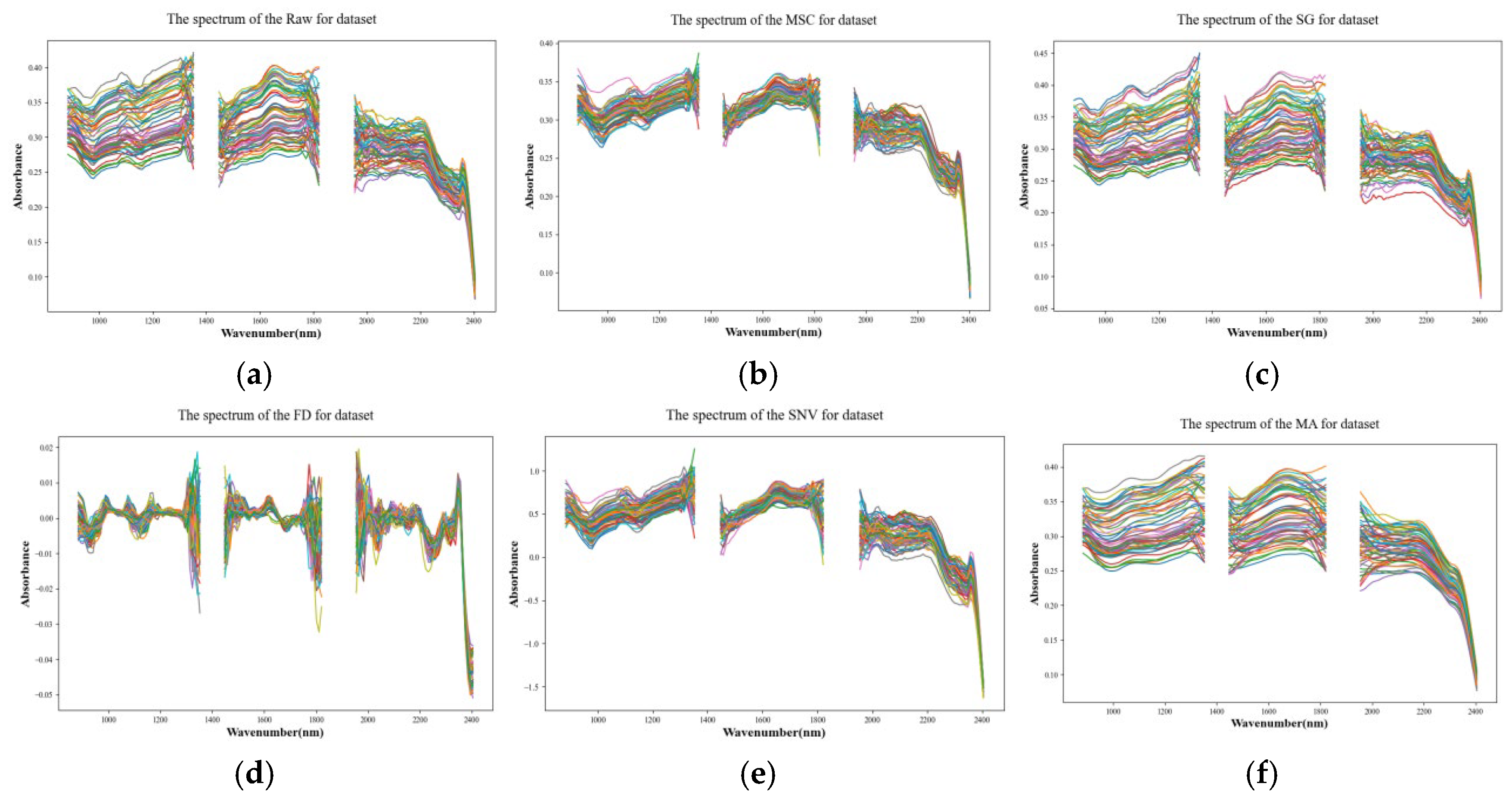
2.4. Spectral Data Preprocessing
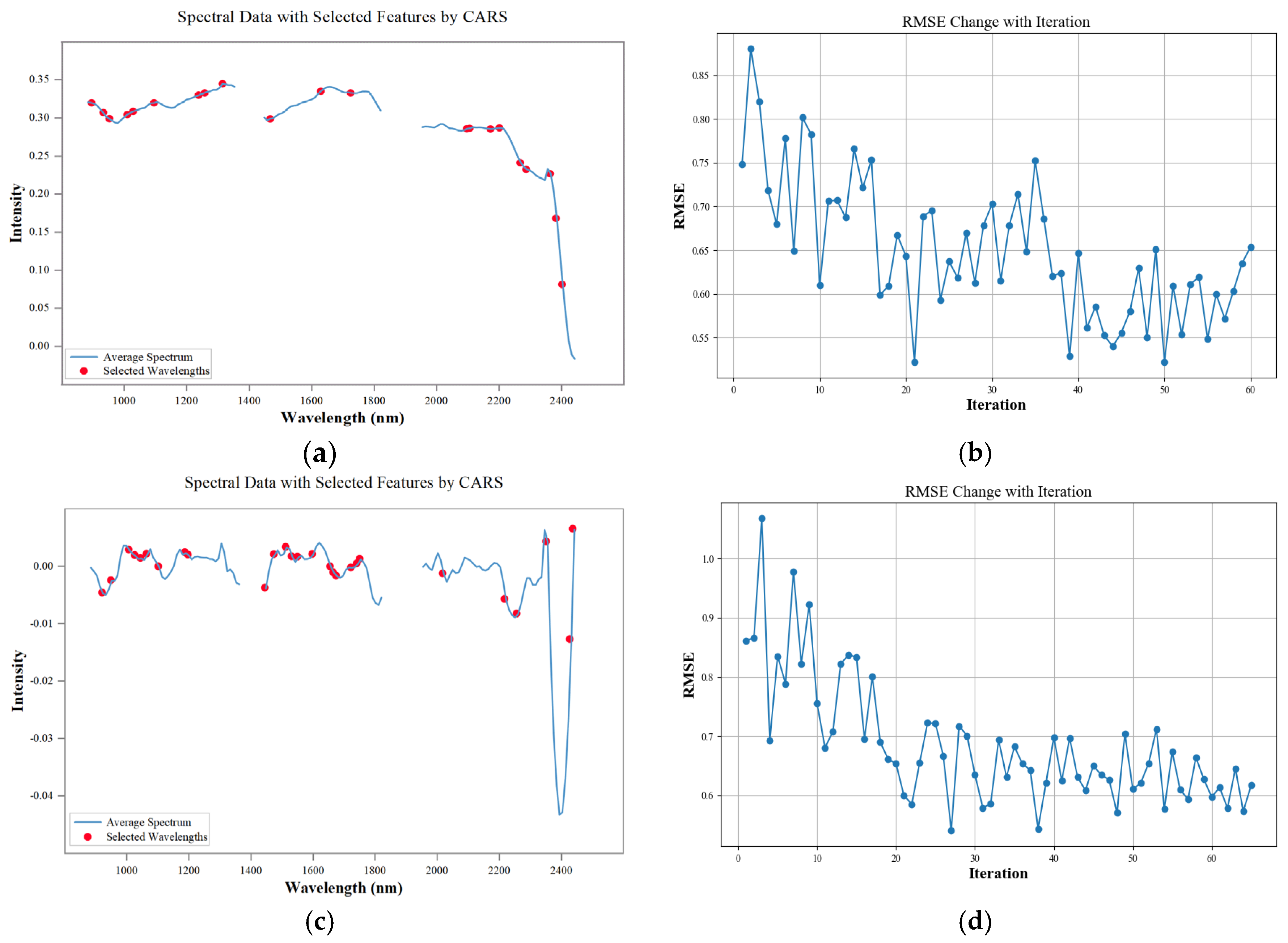
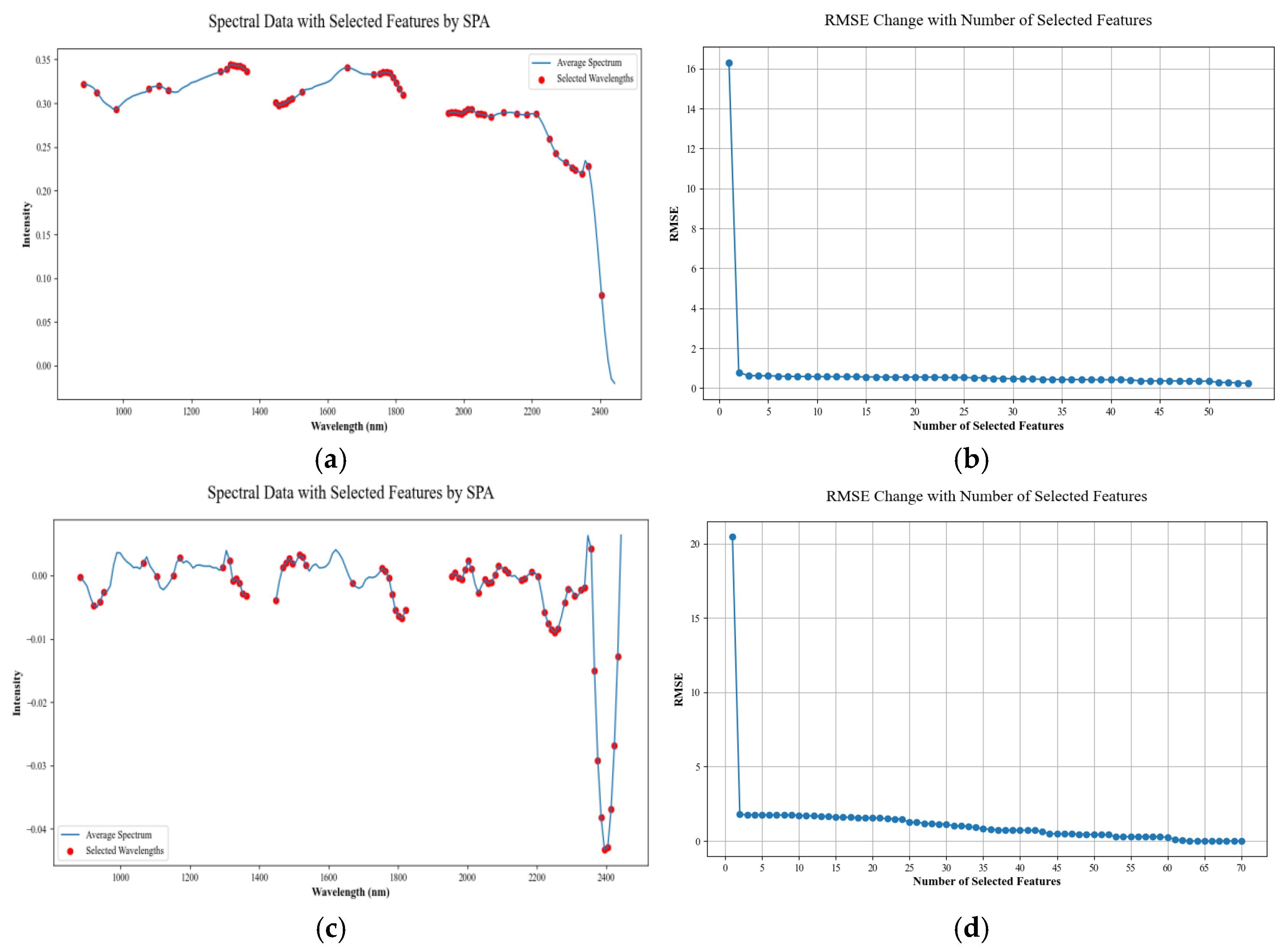
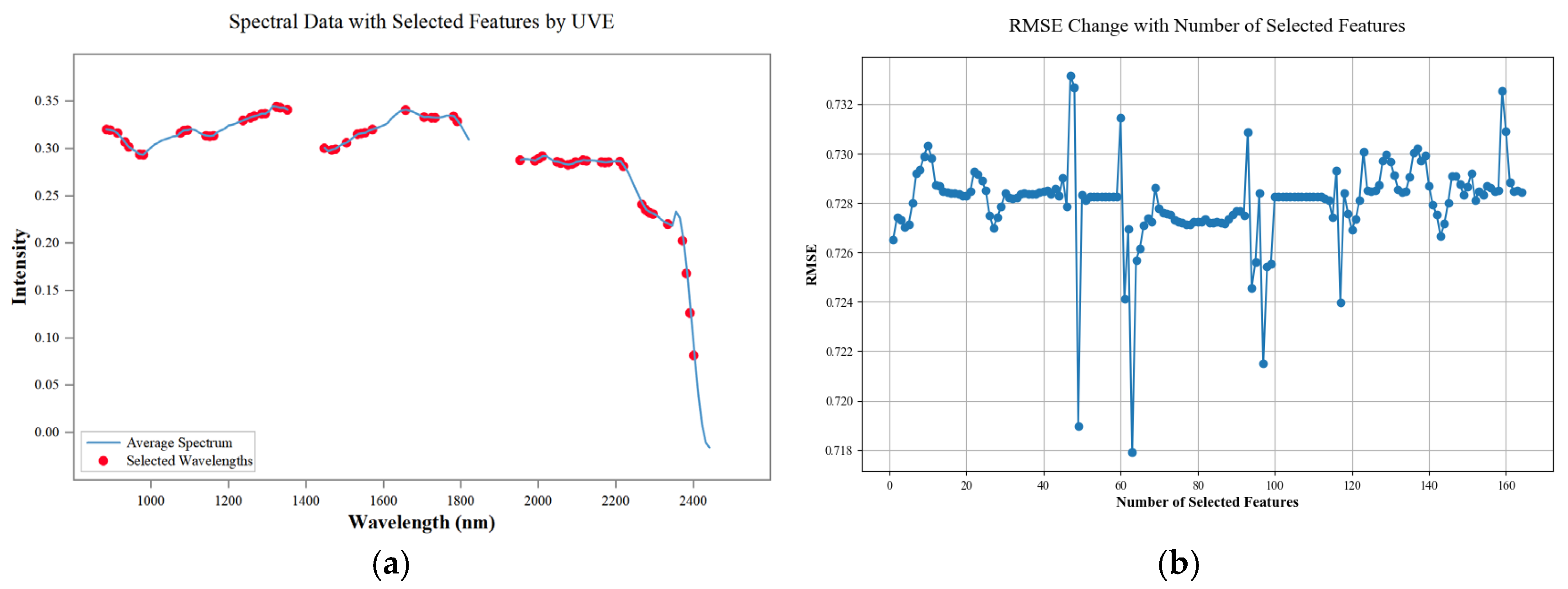
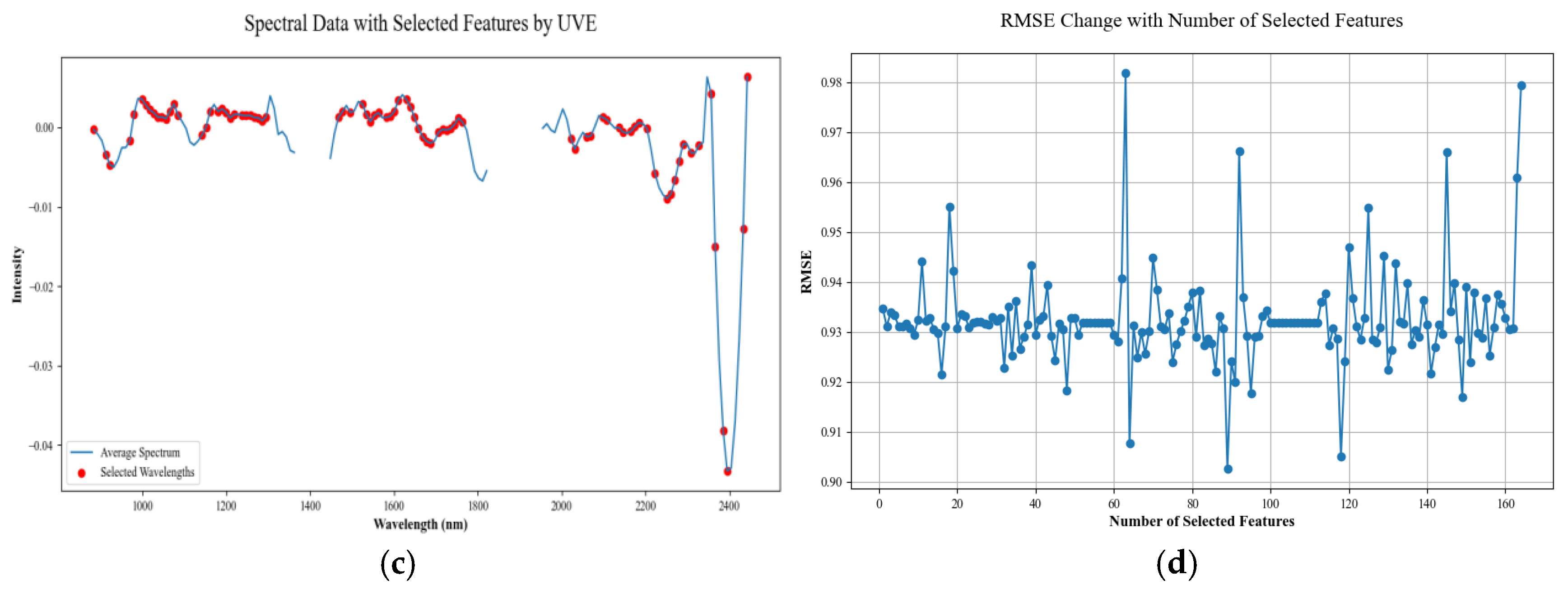
2.5. Extraction of Characteristic Bands
2.5.1. Competitive Adaptive Reweighted Sampling Algorithm
2.5.2. Successive Projections Algorithm
2.5.3. Uninformative Variables Elimination Algorithms
2.6. Model Construction and Evaluation
2.6.1. Ridge Regression Model
2.6.2. Lasso Regression Model
2.6.3. Model Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Spectral Pre-Processing
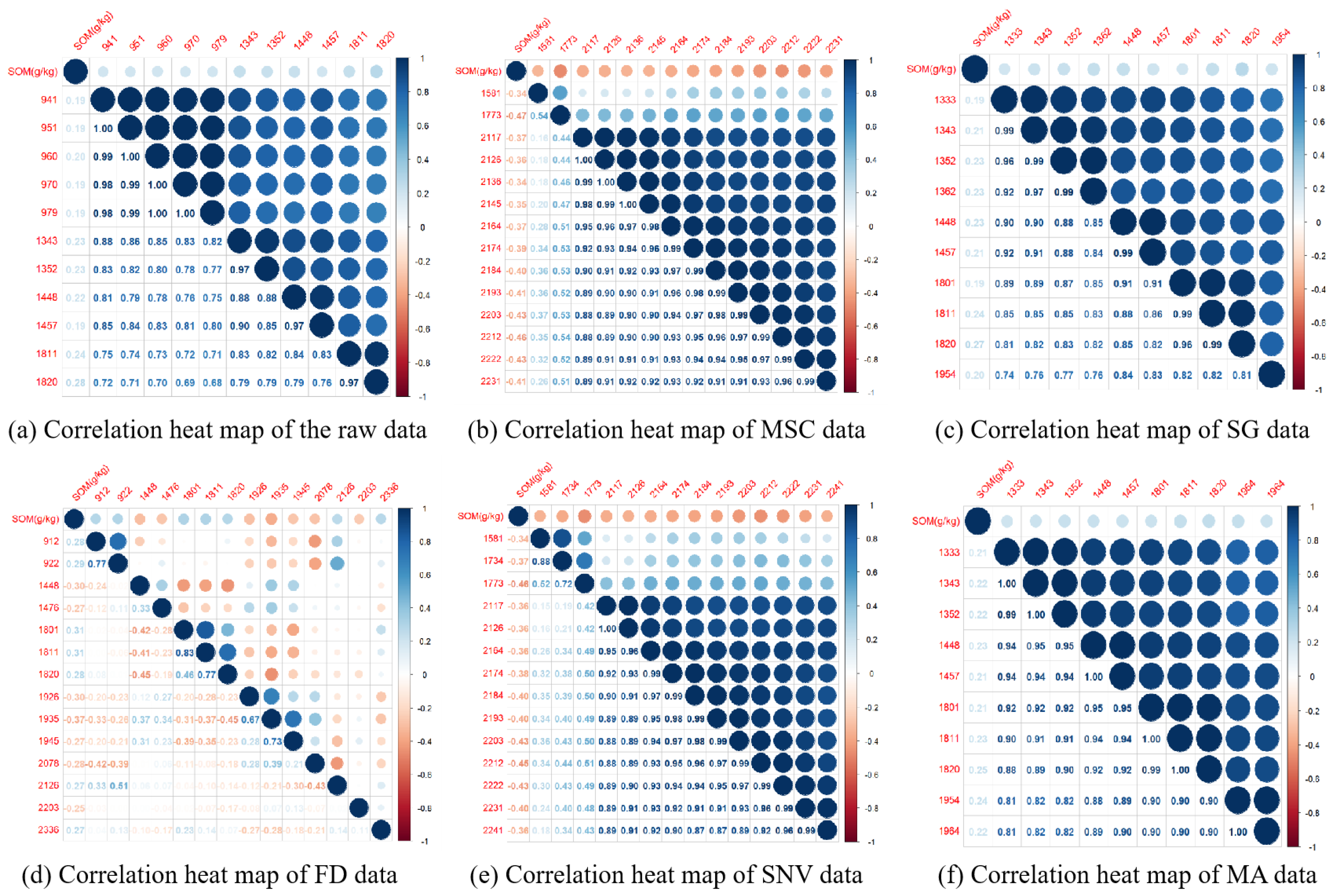
3.2. Correlation Analysis
3.3. Feature Band Extraction Analysis
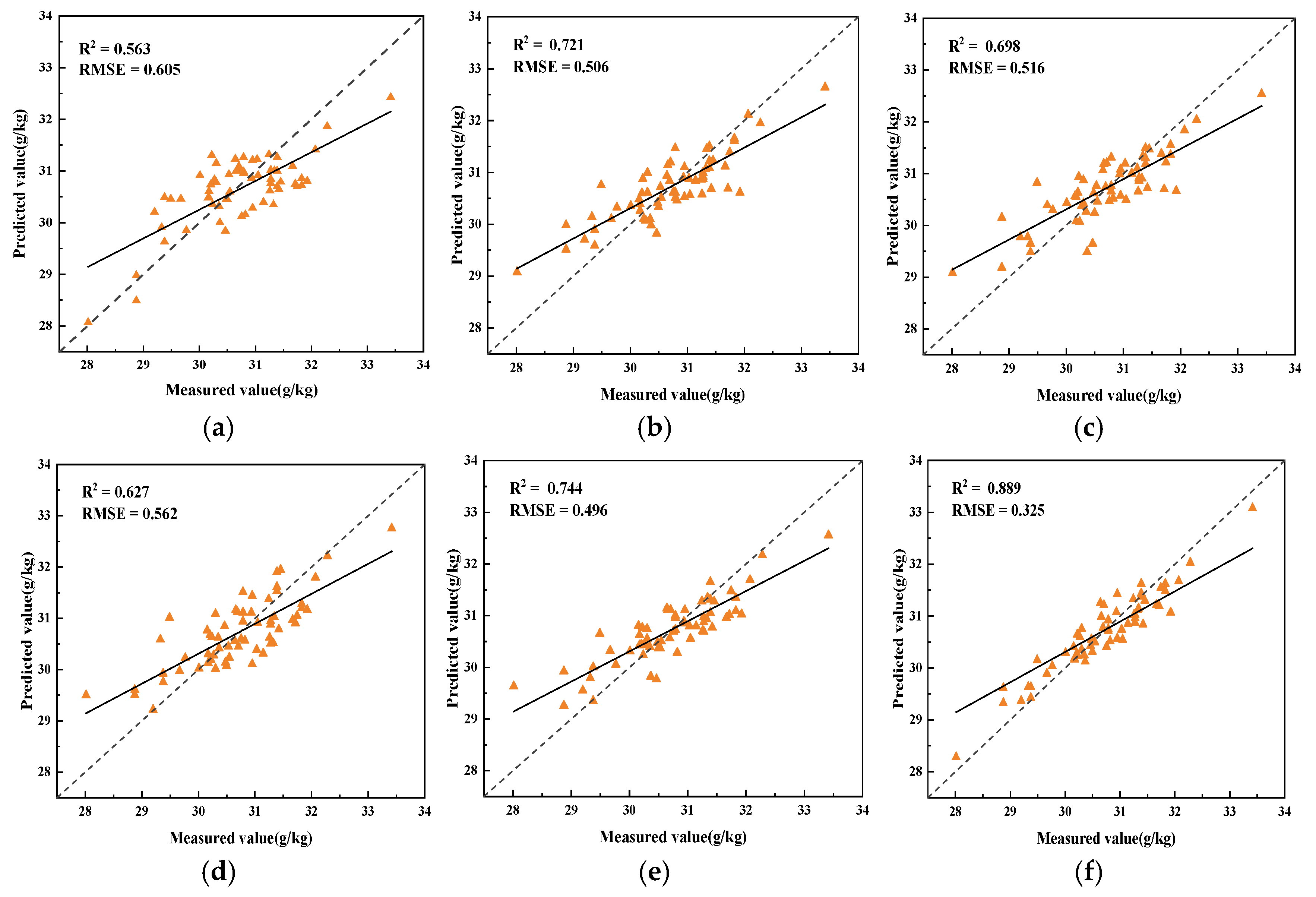
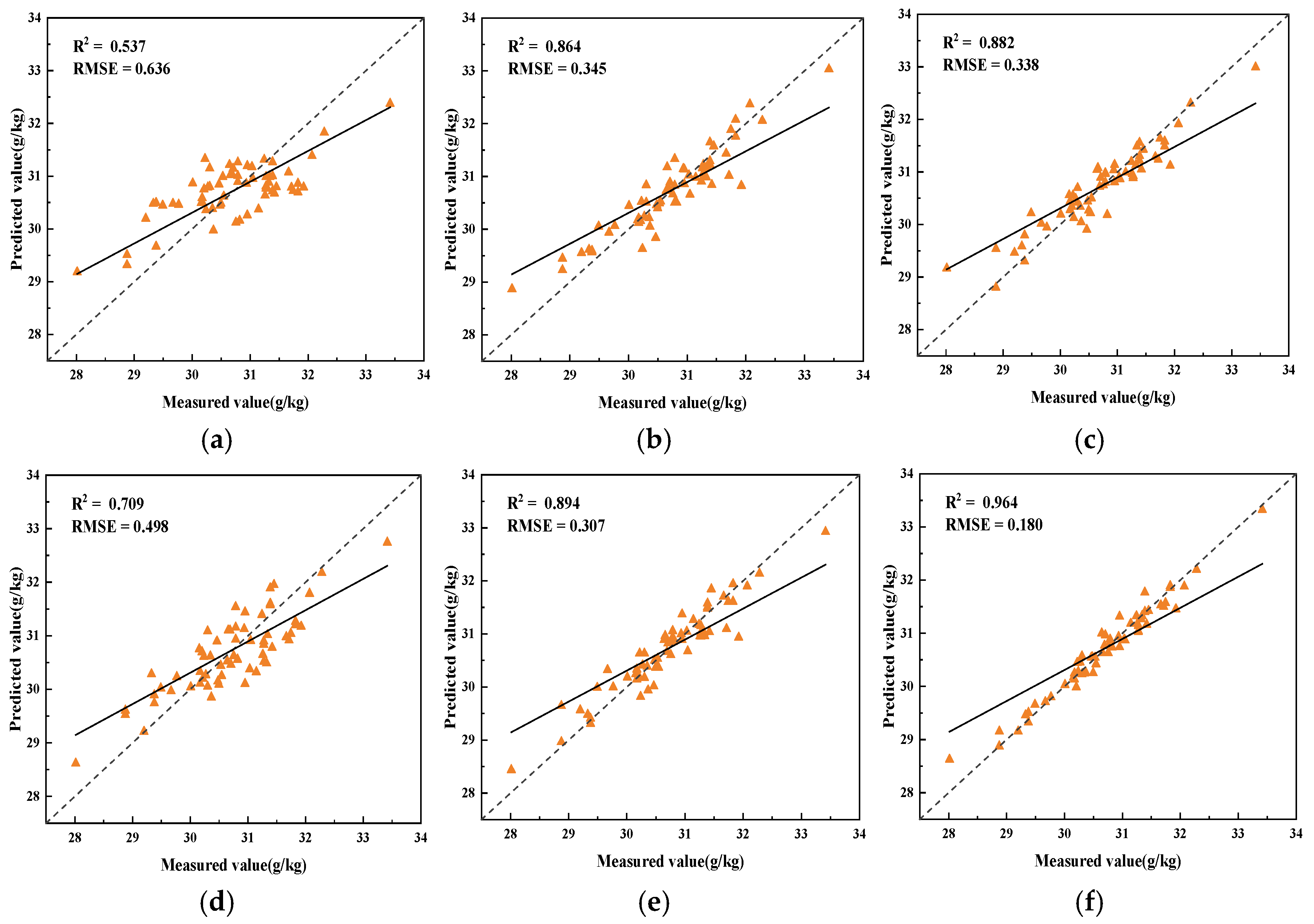
3.4. Regression Model Analysis
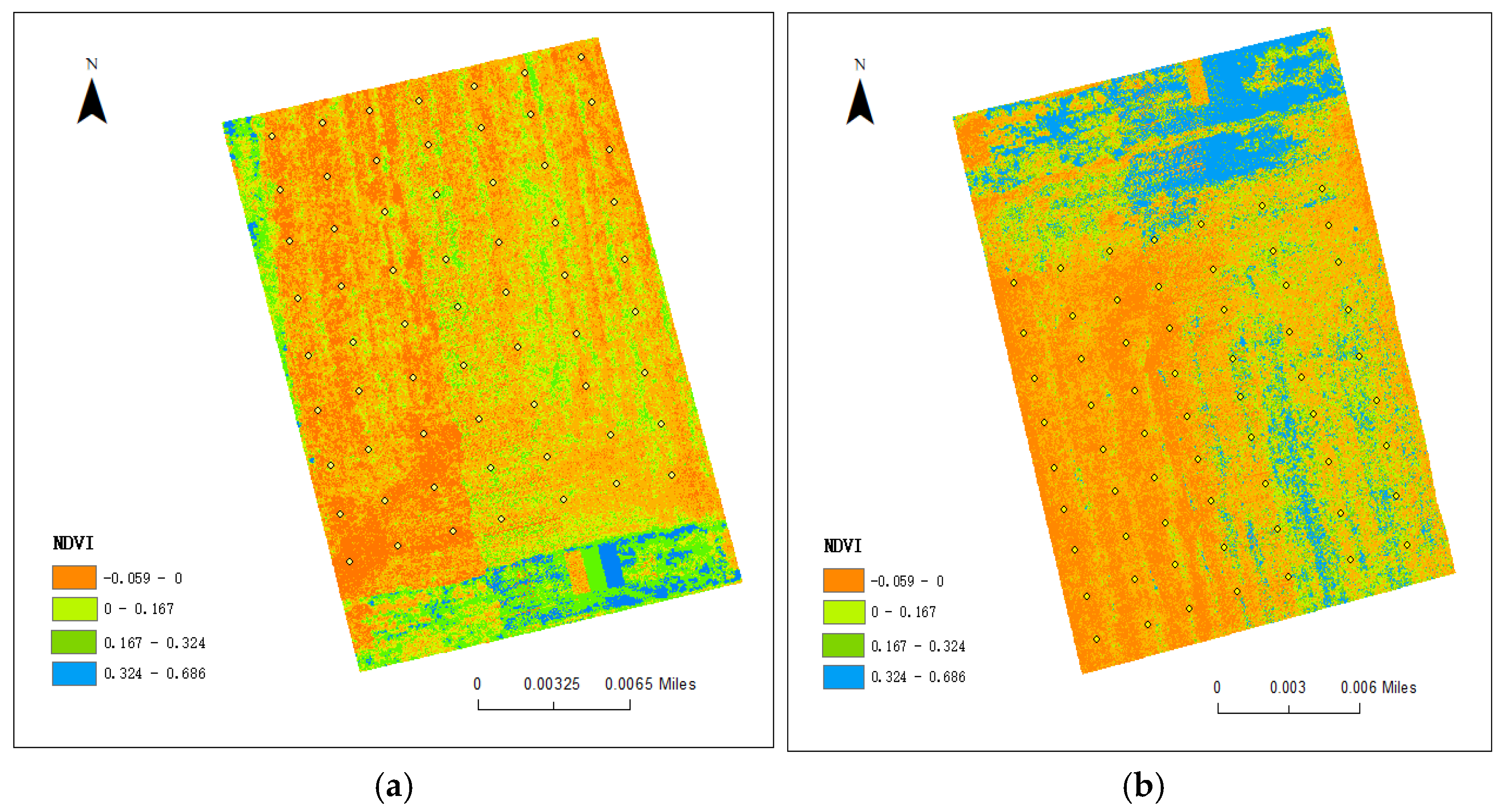
3.5. Analysis of the Relationship Between Below-Ground Organic Matter and Above-Ground Crop Growth
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristic Band Analysis
4.2. Model Selection and Evaluation
4.3. Analysis of the Impact of Other Factors
4.4. Interactions Between Soil and Crops
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The use of spectral data preprocessing methods can reduce data noise, improve the correlation between spectral data and SOM content, and reduce the multicollinearity between spectral data. The three feature extraction algorithms, CARS, SPA, and UVE, each have their own advantages, and for the problem of the existence of redundant features in the hyperspectral data in this paper, the UVE algorithm has the best extraction effect.
- (2)
- Ridge regression and Lasso regression models have significant advantages in dealing with the multicollinearity problem of hyperspectral data, the model that obtains the optimal results based on ridge regression is FD-UVE-Ridge (R2 = 0.889, RMSE = 0.325), and the model that obtains the optimal results based on Lasso regression is FD-UVE-Lasso (R2 = 0.961, RMSE = 0.180).
- (3)
- There was a positive correlation between SOM content and above-ground crop growth, in which the accuracy of fitting the above-ground NDVI values to the below-ground SOM content was 0.518 for field 1, and the accuracy of fitting the above-ground NDVI values to the below-ground SOM content was 0.677 for field 2. Fertilizing operations could significantly increase soil SOM content, thus promoting wheat growth.
- (4)
- The current study lacks continuous observation data from the irrigating stage to the maturity stage of winter wheat, which may weaken the predictive stability of the model in the later stages of the crop growth; in future research, we want to collect In the future, we want to collect the growth data of the whole life cycle of winter wheat to establish an adaptive inversion model with applicability to the whole life cycle.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, K.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X. A Hyperspectral Feature Selection Method for Soil Organic Matter Estimation Based on an Improved Weighted Marine Predators Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 63, 5500411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.I.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A.C.; et al. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ju, W.; Song, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, M. Soil organic matter content prediction based on two-branch convolutional neural network combining image and spectral features. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Liu, Y. Rapid identification of soil organic matter level via visible and near-infrared spectroscopy: Effects of two-dimensional correlation coefficient and extreme learning machine. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Hou, J.; Zhao, J.; Clarke, N.; Kempenaar, C.; Chen, X. Predicting Soil Organic Matter, Available Nitrogen, Available Phosphorus and Available Potassium in a Black Soil Using a Nearby Hyperspectral Sensor System. Sensors 2024, 24, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Jia, C.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Cui, T.; He, X. A rapid detection method for soil organic matter using a carbon dioxide sensor in situ. Measurement 2023, 208, 112471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Jin, X. Hyperspectral approaches for rapid and spatial plant disease. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Wei, C.; Cao, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, D. Assessing water quality environmental grades using hyperspectral images and a deep learning model: A case study in Jiangsu, China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 84, 102854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Ke, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, B.; Yu, H.; Li, H.; Feng, H. Estimation of the soil arsenic concentration using a geographically weighted XGBoost model based on hyperspectral data. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Ding, S.; Liu, S. Effects of hyperspectral data with different spectral resolutions on the estimation of soil heavy metal content: From ground-based and airborne data to satellite-simulated data. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bec, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Pfeifer, F.; Siesler, H.W.; Huck, C.W. Rapid on-site analysis of soil microplastics using miniaturized NIR spectrometers: Key aspect of instrumental variation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, N.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; et al. Combing transfer learning with the OPtical TRApezoid Model (OPTRAM) to diagnosis small-scale field soil moisture from hyperspectral data. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 298, 108856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenal, A.; Hüging, H.; Ahrends, H.E.; Bolten, A.; Bongartz, J.; Bareth, G. Investigating the Potential of a Newly Developed UAV-Mounted VNIR/SWIR Imaging System for Monitoring Crop Traits—A Case Study for Winter Wheat. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendor, E.; Banin, A. Near-infrared analysis as a rapid method to simultaneously evaluate several soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, R.C.; Henry, R.J. Simultaneous determination of moisture, organic carbon, and total nitrogen by near infrared reflectance spectrophotometry. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.A.V.; Behrens, T. Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2010, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, B. Effects of soil sample pretreatments and standardised rewetting as interacted with sand classes on Vis-NIR predictions of clay and soil organic carbon. Geoderma 2010, 158, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lai, J.; Tan, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Ding, J. Development of a soil heavy metal estimation method based on a spectral index: Combining fractional-order derivative pretreatment and the absorption mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 151882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Ma, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Du, Q.; Du, P.; Yan, B.; Liu, R.; Li, R. Estimating the distribution trend of soil heavy metals in mining area from HyMap airborne hyperspectral imagery based on ensemble learning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Du, Q.; Du, P.; Pan, C. Estimation of the spatial distribution of heavy metal in agricultural soils using airborne hyperspectral imaging and random forest. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 120987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabtai, I.A.; Wilhelm, R.C.; Schweizer, S.A.; Hoeschen, C.; Buckley, D.H.; Lehmann, J. Calcium promotes persistent soil organic matter by altering microbial transformation of plant litter. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, V.; Ardejani, F.D.; Yousefi, S.; Aryafar, A. Monitoring soil lead and zinc contents via combination of spectroscopy with extreme learning machine and other data mining methods. Geoderma 2018, 318, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Estimation of soil organic matter content using selected spectral subset of hyperspectral data. Geoderma 2022, 409, 115653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Ustin, S.; Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Guan, H.; Qi, B.; Liu, H. A regional-scale hyperspectral prediction model of soil organic carbon considering geomorphic features. Geoderma 2021, 403, 115263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jin, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z. Spatial Upscaling of Sparse Soil Moisture Observations Based on Ridge Regression. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaks, M.; Staudinger, I.; Homeister, L.; Di Biase, B.; Steinkraus, B.R.; Spiess, A.-N. Local microbial yield-associating signatures largely extend to global differences in plant growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 177946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, K.-O.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S. Machine learning identification of edible vegetable oils from fatty acid compositions and hyperspectral images. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Zu, J.; Cai, W.; Wang, J.; Su, H.; Yang, J. Fine-Scale Mangrove Species Classification Based on UAV Multispectral and Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Using Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavlas, N.-C.; Porre, R.; Meng, L.; Elhakeem, A.; van Egmond, F.; Kooistra, L.; Deyn, G.B.D. Cover crop impacts on soil organic matter dynamics and its quantification using UAV and proximal sensing. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 9, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coucheney, E.; Katterer, T.; Meurer, K.H.E.; Jarvis, N. Improving the sustainability of arable cropping systems by modifying root traits: A modelling study for winter wheat. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2024, 75, e13524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, W. Rhizosphere priming effect: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 111, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.P.; Yu, L.; Lu, W.H.; Jiang, H. Study on the relationship between ground biomass and soil nutrient in the mixed grassland. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2009, 46, 592–596. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.F.; Liu, X.T.; Chen, J.W. Correlation analysis between aboveground biomass and soil organic matter and nitrogen of Ula moss grass (Carex meyeriana) in gully swamp wetland of Changbai Mountain. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2007, 14, 356–359. [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield, E.E.; Bradford, M.A.; Wood, S.A. Global meta-analysis of the relationship between soil organic matter and crop yields. Soil 2019, 5, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iheshiulo, E.M.A.; Larney, F.J.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G.; Luce, M.S.; Chau, H.W.; Liu, K. Soil organic matter and aggregate stability dynamics under major no-till crop rotations on the Canadian prairies. Geoderma 2024, 442, 116777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Ying, D.; Tian, S.; Zhao, G.; Ye, D.; Cheng, C.; Wu, C.; et al. Assessing the Alteration of Soil Quality under Long-Term Fertilization Management in Farmland Soil: Integrating a Minimum Data Set and Developing New Biological Indicators. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonobe, R.; Hirono, Y. Applying Variable Selection Methods and Preprocessing Techniques to Hyperspectral Reflectance Data to Estimate Tea Cultivar Chlorophyll Content. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahani, T.; Kashaninejad, M.; Ziaiifar, A.M.; Golzarian, M.; Akbari, N.; Soleimanipour, A. Effect of selected pre-processing methods by PLSR to predict low-fat mozzarella texture measured by hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 5060–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Rao, Z.; Ji, H. Determination of moisture content in barley seeds based on hyperspectral imaging technology. Spectrosc. Lett. 2020, 53, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, T.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Gou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Du, X.; Yuan, C.; Li, B. The life Prediction of PEMFC based on Group Method of Data handling with Savitzky-Golay Smoothing. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Hu, D.; Niu, G. Rapid and Non-Destructive Prediction of Moisture Content in Maize Seeds Using Hyperspectral Imaging. Sensors 2024, 24, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, M.; Li, Z.; He, X.; Ren, Z.; Dong, H. The identification of aged-rice adulteration by support vector machine classification combined with characteristic wavelength variables. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 110032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.A.; Khvalbota, L.; Onca, L.; Machynakova, A.; Spanik, I. Handling multiblock data in wine authenticity by sequentially orthogonalized one class partial least squares. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Feng, A.; Shi, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zou, Z.; Ma, W.; et al. Study on detection method of microplastics in farmland soil based on hyperspectral imaging technology. Environ. Res. 2023, 232, 116389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.C.U.; Saldanha, T.C.B.; Galvao, R.K.H.; Yoneyama, T.; Chame, H.C.; Visani, V. The successive projections algorithm for variable selection in spectroscopic multicomponent analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 57, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Lian, J.; Wu, Z.; Ye, W.; Wu, Z. Robust hyperspectral estimation of eight leaf functional traits across different species and canopy layers in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaf forest. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Hong, W.; Cui, W. Identification and sorting of impurities in tea using spectral vision. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 205, 116519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, M.J.C.; Galvao, R.K.H.; Araújo, M.C.U.; Nogueira, P.; Moreira, T.; Neto, O.D.P.; Saldanha, T.C.B. The successive projections algorithm for spectral variable selection in classification problems. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2005, 78, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Gao, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, S. Quantitative analysis of chlorophyll content in tea leaves by fluorescence spectroscopy. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2021, 58, 0830001. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Sui, Y. Prediction of anthocyanin content in purple-leaf lettuce based on spectral features and optimized extreme learning machine algorithm. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Jeng, D.S.; Wang, Y. Predictions of runoff and sediment discharge at the lower Yellow River Delta using basin irrigation data. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 78, 102385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Cheng, X.; Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Ren, Z. Apple firmness detection method based on hyperspectral technology. Food Control. 2024, 166, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B-Stat. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.J.; Zhang, C.; Bian, X.; An, J.; Wang, Y.; Ou, X.; Kamruzzaman, M. Improved prediction of vitamin C and reducing sugar content in sweetpotatoes using hyperspectral imaging and LARS-enhanced LASSO variable selection. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 132, 106350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Shi, Z. On LASSO for high dimensional predictive regression. J. Econom. 2024, 242, 105809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.A.V.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; McBratney, A.B.; Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 2006, 131, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.; Tan, K.; Lai, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. Semi-supervised DNN regression on airborne hyperspectral imagery for improved spatial soil properties prediction. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Lei, T.; Wang, S.; Li, K. An Improved Vis-NIR Estimation Model of Soil Organic Matter Through the Artificial Samples Enhanced Calibration Set. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 4626–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, Q.; Peng, J.; Ji, W.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Rossel, R.A.V. Development of a national VNIR soil-spectral library for soil classification and prediction of organic matter concentrations. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenDor, E.; Inbar, Y.; Chen, Y. The reflectance spectra of organic matter in the visible near-infrared and short wave infrared region (400-2500 nm) during a controlled decomposition process. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Biancolillo, A.; Roger, J.M.; Marini, F.; Rutledge, D.N. New data preprocessing trends based on ensemble of multiple preprocessing techniques. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 116045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Xie, M.; Hu, B.; Luo, D.; Wan, C.; Peng, J.; Shi, Z. Estimation of Soil Organic Carbon Using Vis-NIR Spectral Data and Spectral Feature Bands Selection in Southern Xinjiang, China. Sensors 2022, 22, 6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiodun, E.O.; Alabdulatif, A.; Abiodun, O.I.; Alawida, M.; Alabdulatif, A.; Alkhawaldeh, R.S. A systematic review of emerging feature selection optimization methods for optimal text classification: The present state and prospective opportunities. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 15091–15118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morra, M.J.; Hall, M.H.; Freeborn, L.L. Carbon and Nitrogen Analysis of Soil Fractions Using Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidêncio, P.H.; Poppi, R.J.; de Andrade, J.C. Determination of organic matter in soils using radial basis function networks and near infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 453, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasques, G.M.; Grunwald, S.; Sickman, J.O. Comparison of multivariate methods for inferential modeling of soil carbon using visible/near-infrared spectra. Geoderma 2008, 146, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; O’Connor, D.; Shi, Z.; Hou, D. VIRS based detection in combination with machine learning for mapping soil pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.; Tegegn, M.; Sarin, J.S.; Pal, S.; Rubin, J. It Is All about Data: A Survey on the Effects of Data on Adversarial Robustness. Acm Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, J.; Peng, Z.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Men, M. Accuracy analysis of remote sensing index enhancement for SVM salt inversion model. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 2406–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Huang, T.; Liu, Z.; Bao, L.; Guo, B.; Yu, Z.; Men, M. Improving Forest Above-Ground Biomass Estimation Accuracy Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing and Optimized Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator Variable Selection Method. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ji, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Pan, R.; Liu, X.; Yin, J.; Duan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, X.; et al. Mining sensitive hyperspectral feature to non-destructively monitor biomass and nitrogen accumulation status of tea plant throughout the whole year. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 225, 109358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, D.G.P. An Assessment of the Site-Specific Nutrient Management (SSNM) Strategy for Irrigated Rice in Asia. Agriculture 2020, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, B.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Hou, J.; Cao, R.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, W. Status and influential factors of soil nutrients and acidification in Chinese tea plantations: A meta-analysis. Soil 2025, 11, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ni, H.; Xie, M.; Li, H.; Wen, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Teng, H.; Bourennane, H.; Shi, Z. Mapping soil organic matter and identifying potential controls in the farmland of Southern China: Integration of multi-source data, machine learning and geostatistics. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 5468–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Bagchi, S.; Biederman, L.A.; Borer, E.T.; Brathen, K.A.; Bugalho, M.N.; Caldeira, M.C.; Catford, J.A.; Collins, S.L.; Eisenhauer, N.; et al. The positive effect of plant diversity on soil carbon depends on climate. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabloom, E.W.; Borer, E.T.; Hobbie, S.E.; MacDougall, A.S. Soil nutrients increase long-term soil carbon gains threefold on retired farmland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 4909–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.M.; Terrer, C.; Barriocanal, C.; Jackson, R.B.; Rosell-Mele, A. Soil organic carbon accumulation rates on Mediterranean abandoned agricultural lands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
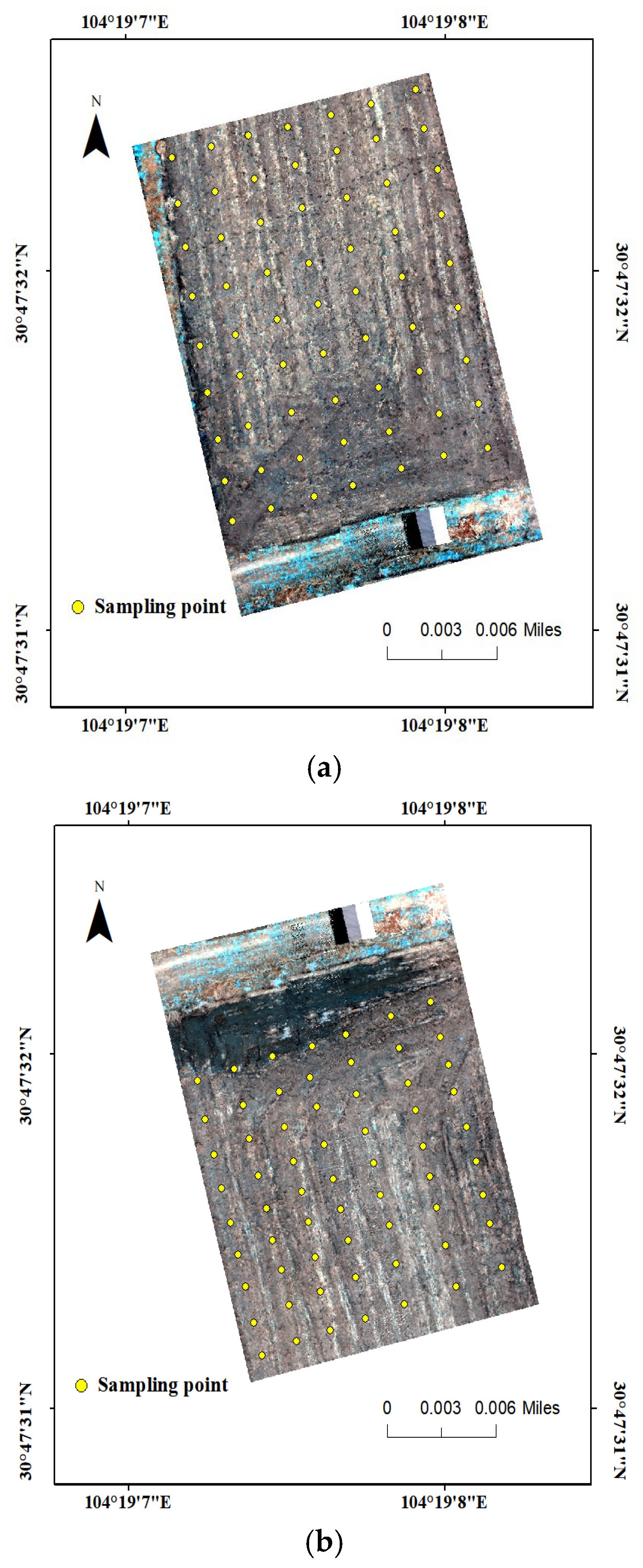
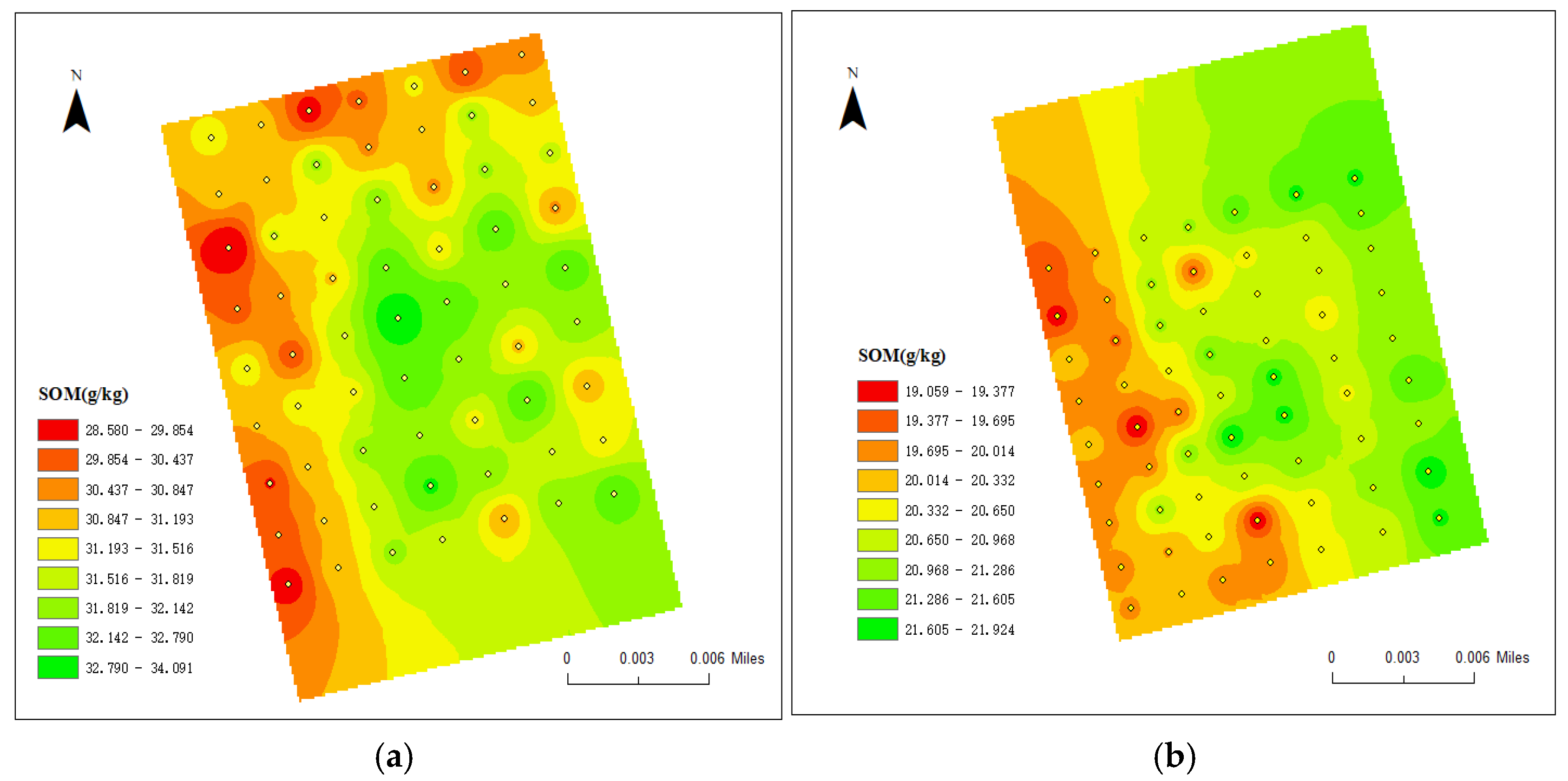
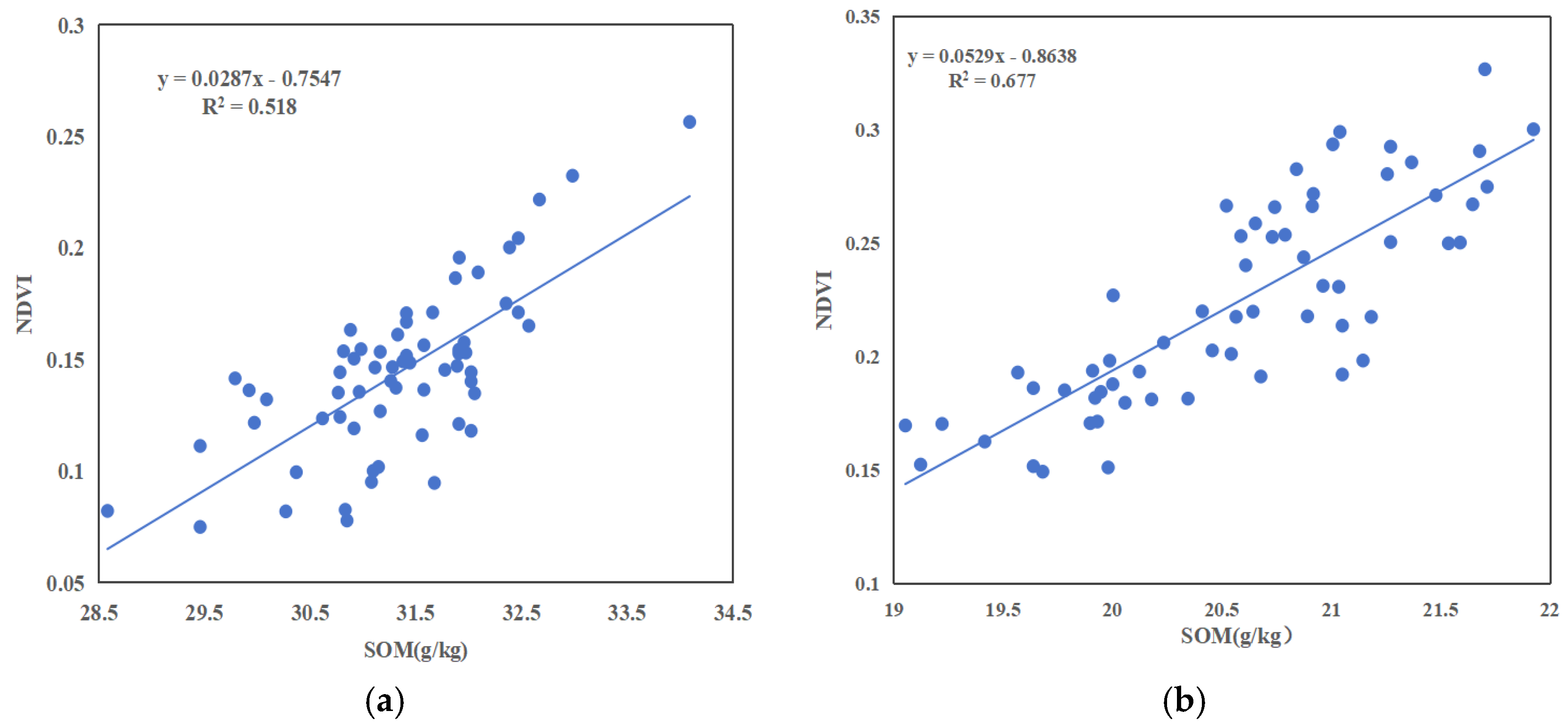
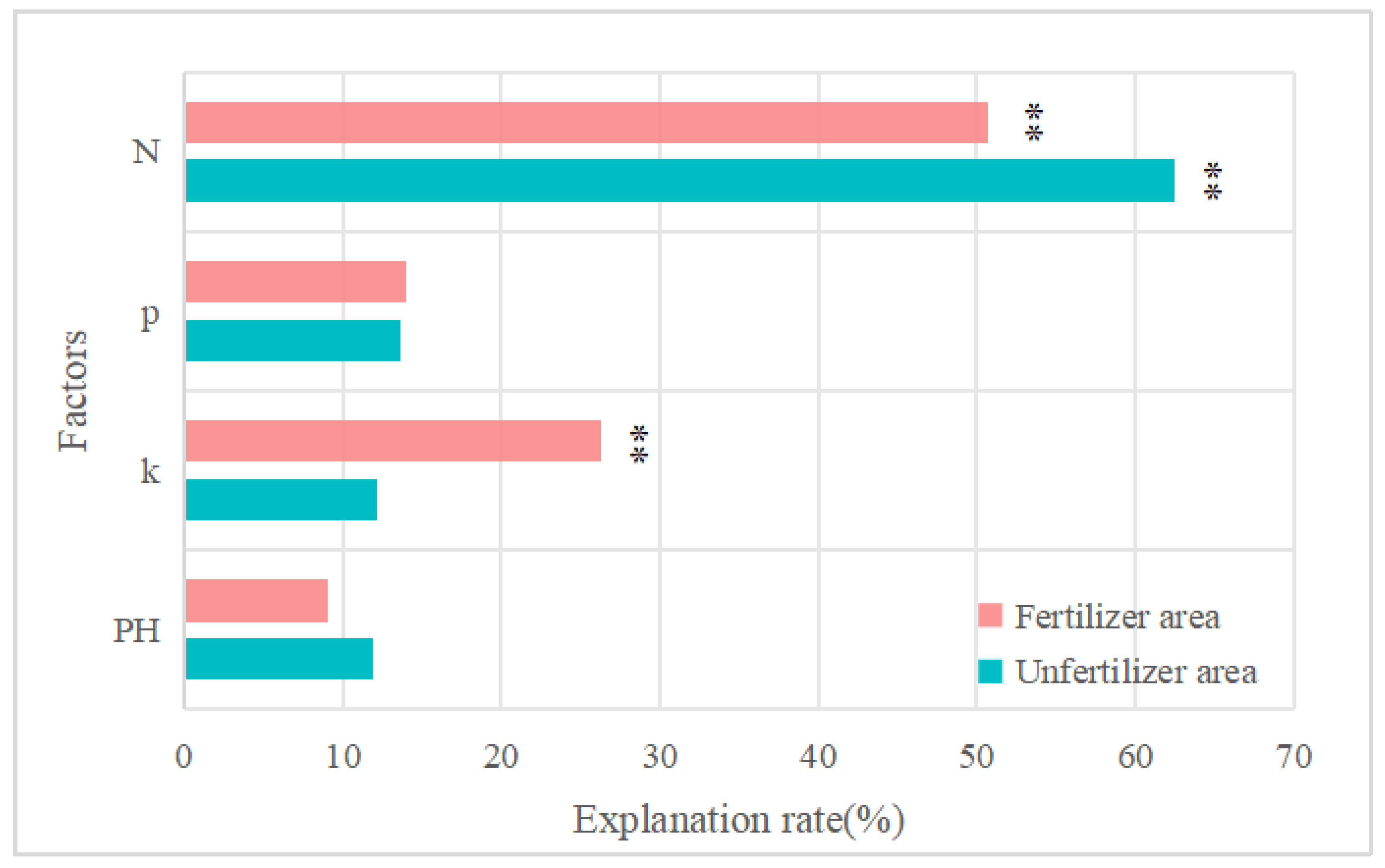
| Test Area | Max | Min | Average | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOM (g/kg) | Field 1 | 34.091 | 28.580 | 31.326 | 0.991 | 3.161% |
| Field 2 | 21.924 | 19.053 | 20.612 | 2.612 | 12.869% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Ma, W.; He, J. Assessment of Organic Matter Content of Winter Wheat Inter-Row Topsoil Based on Airborne Hyperspectral Imaging. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115160
He J, Ma W, He J. Assessment of Organic Matter Content of Winter Wheat Inter-Row Topsoil Based on Airborne Hyperspectral Imaging. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):5160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115160
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jiachen, Wei Ma, and Jing He. 2025. "Assessment of Organic Matter Content of Winter Wheat Inter-Row Topsoil Based on Airborne Hyperspectral Imaging" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 5160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115160
APA StyleHe, J., Ma, W., & He, J. (2025). Assessment of Organic Matter Content of Winter Wheat Inter-Row Topsoil Based on Airborne Hyperspectral Imaging. Sustainability, 17(11), 5160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115160






