Coupling Coordination of Carbon Cutting, Pollution Reduction, and Economic Growth in China: Spatiotemporal Evolution, Regional Differences, and Influence Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Relationship Between Economic Growth and Environmental Pollution
2.2. Relationship Between Economic Growth and Carbon Cutting
2.3. Synergy Between Carbon Cutting and Pollution Reduction
2.4. Relationship Among CC, PR, and EG
3. Theoretical Analysis and Research Design
3.1. Theoretical Analysis
3.2. Research Area
3.3. Evaluation Indicators and Data Sources
3.3.1. Evaluation Indicators
3.3.2. Data Sources
3.4. Research Method
3.4.1. Data Treating
3.4.2. Entropy Weight Method
3.4.3. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
3.4.4. Cold and Hot Spot Analysis
3.4.5. Dagum Gini Coefficient
3.4.6. Geographically Weighted Regression Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Spatial–Temporal Evolution Characteristics of CCD
4.1.1. Temporal Characteristic Analysis of CCD
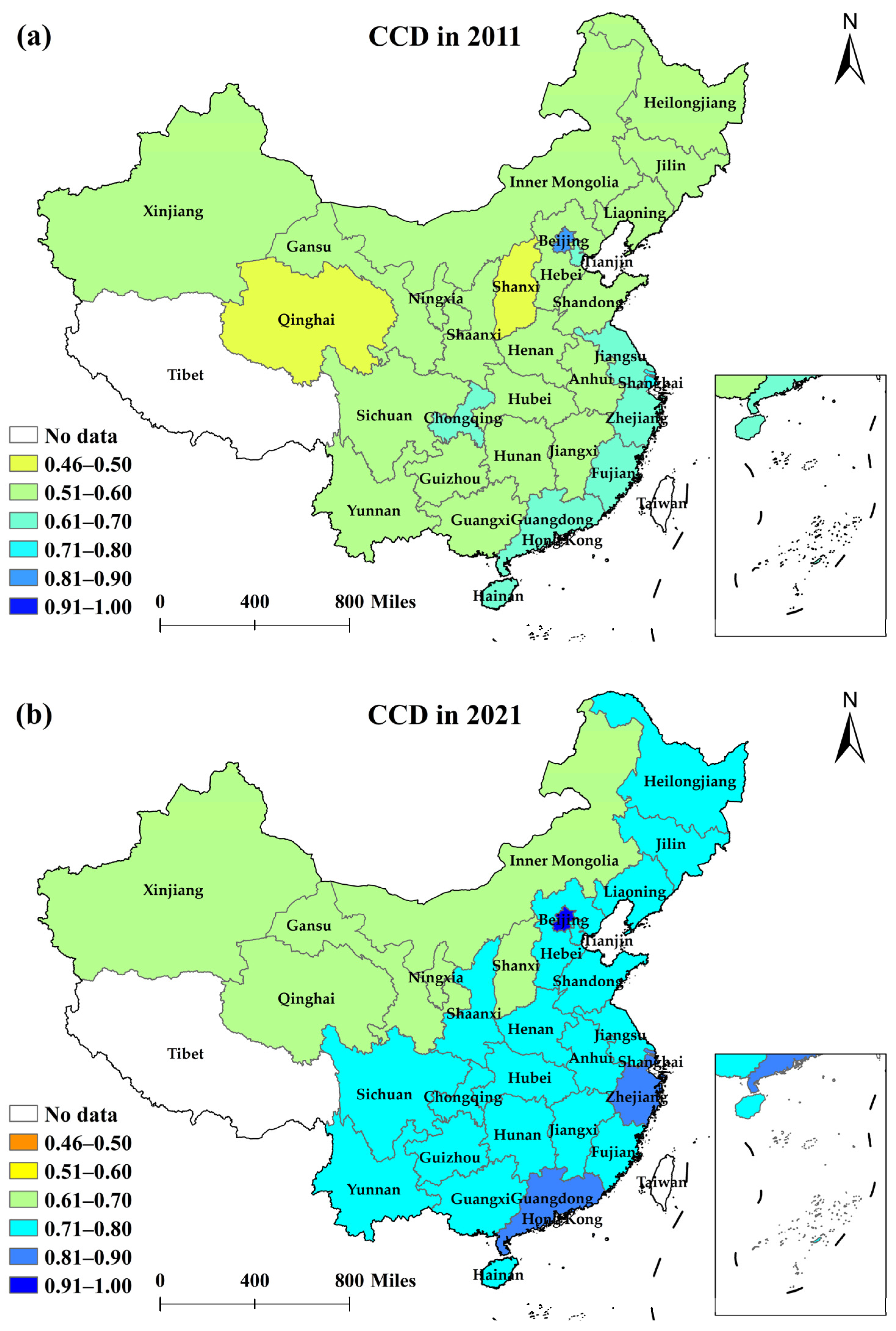
4.1.2. Spatial Distribution Analysis of CCD
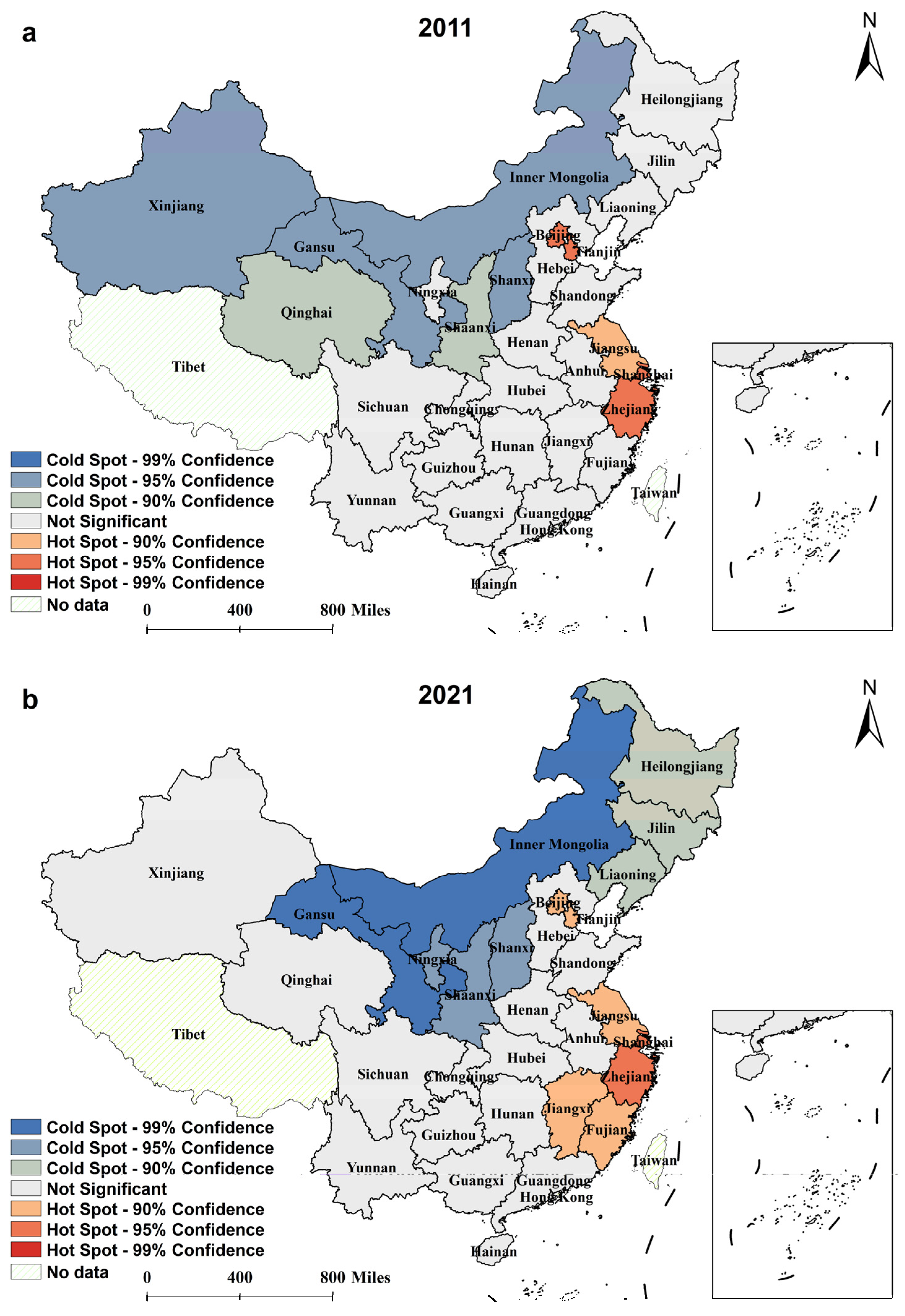
4.2. Spatial Agglomeration Characteristics of CCD
4.3. Regional Differences in CCD
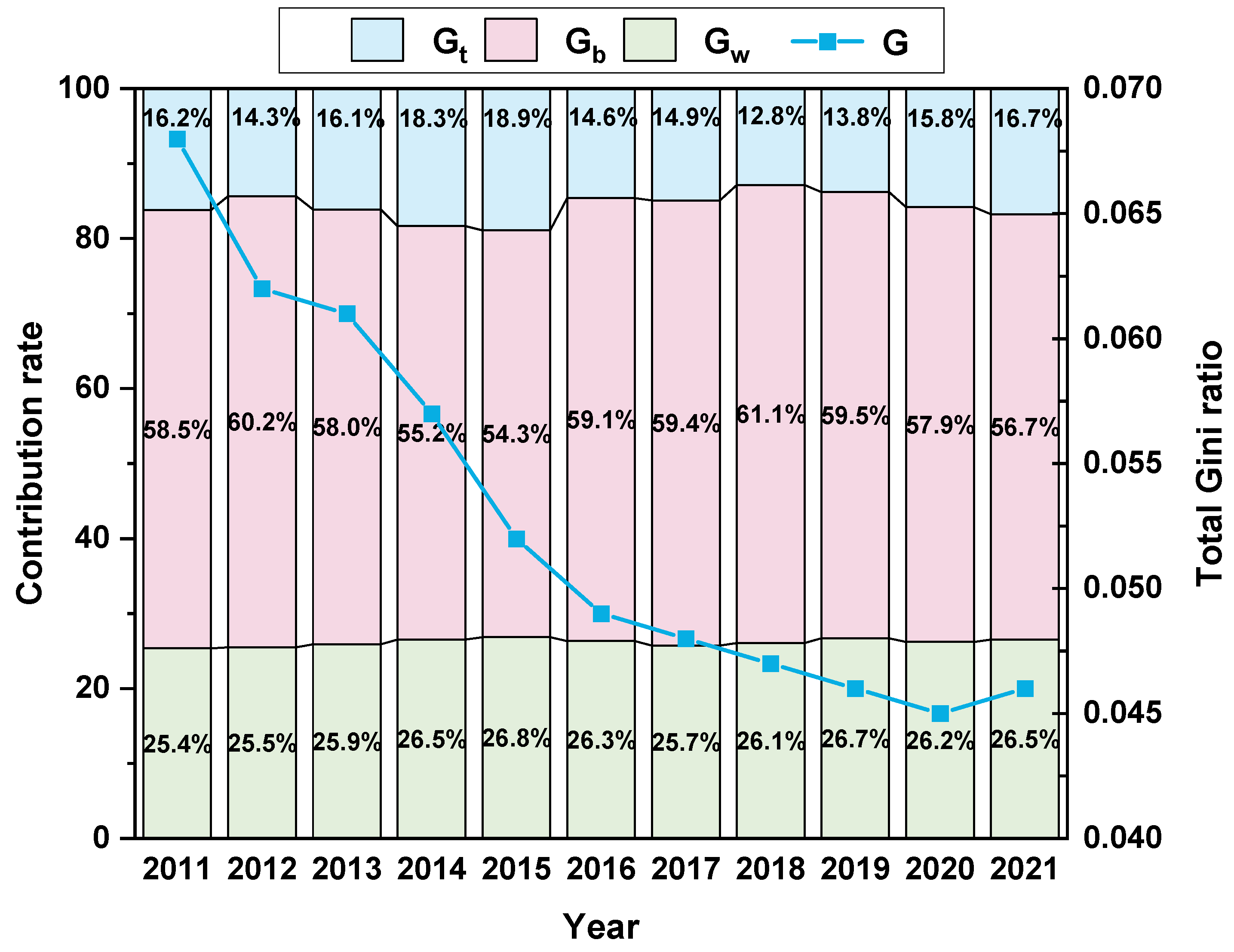
4.3.1. The Total Difference and Its Sources
4.3.2. Intra-Regional Differences
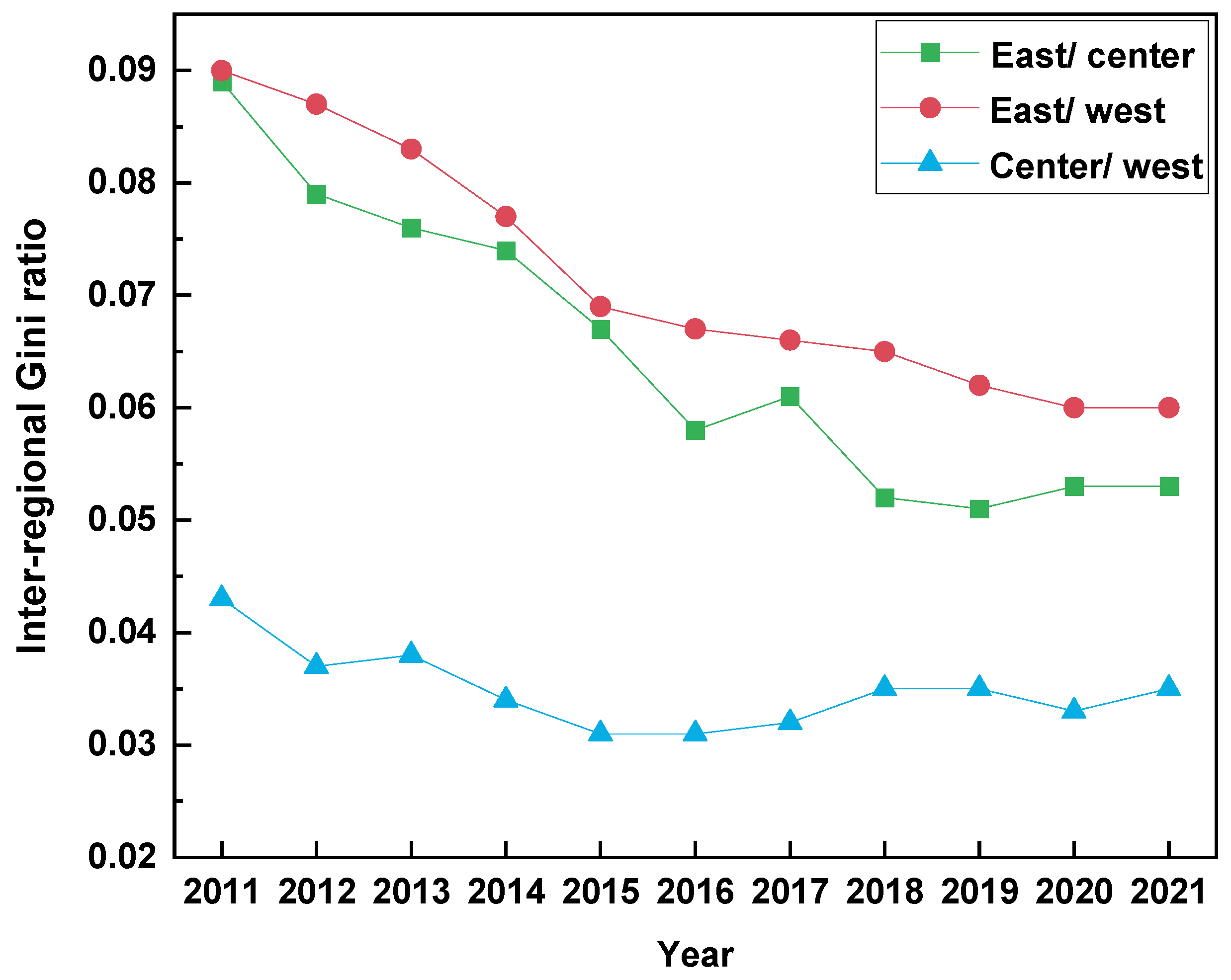
4.3.3. Inter-Regional Differences
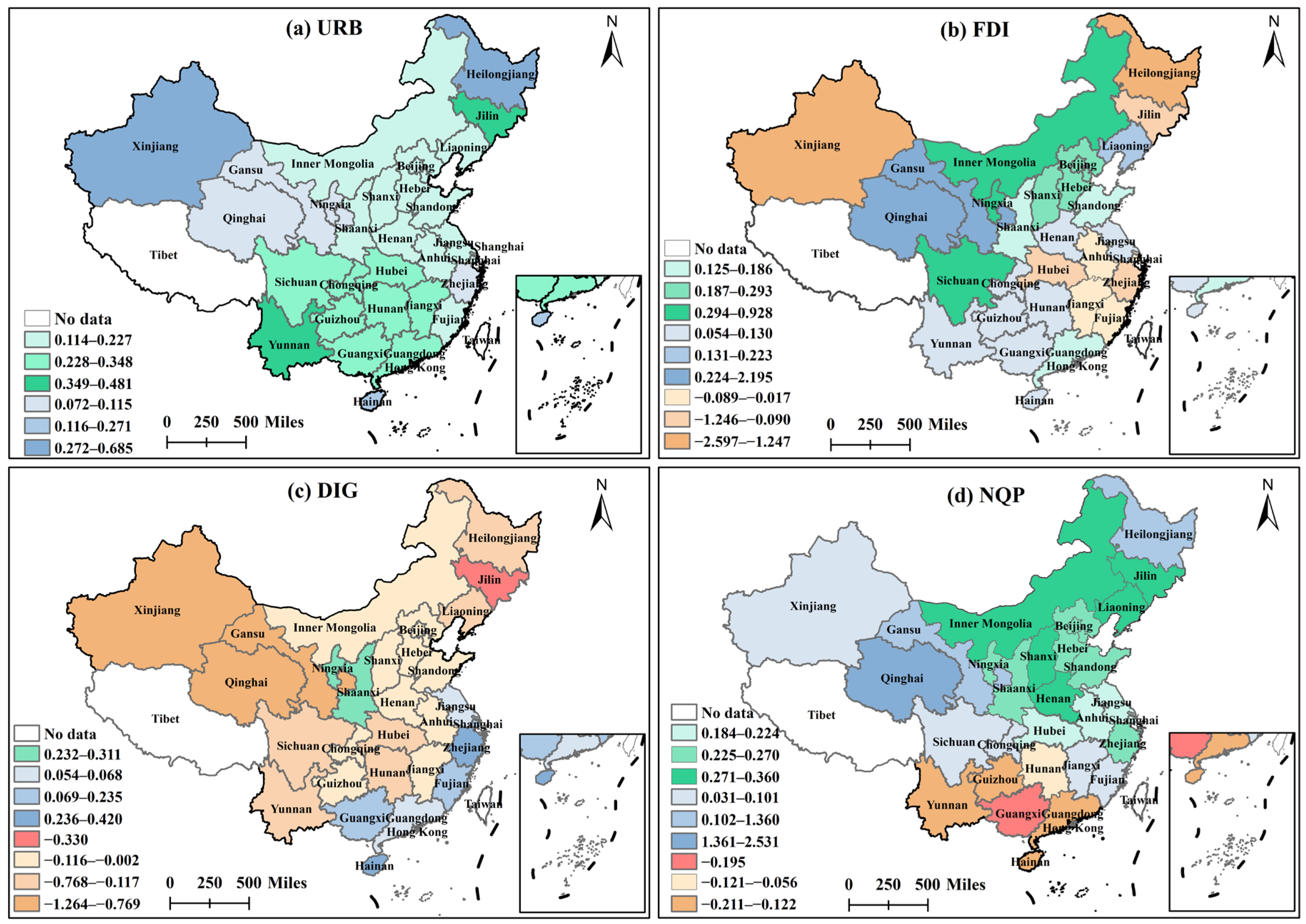
4.4. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis of Influencing Factors
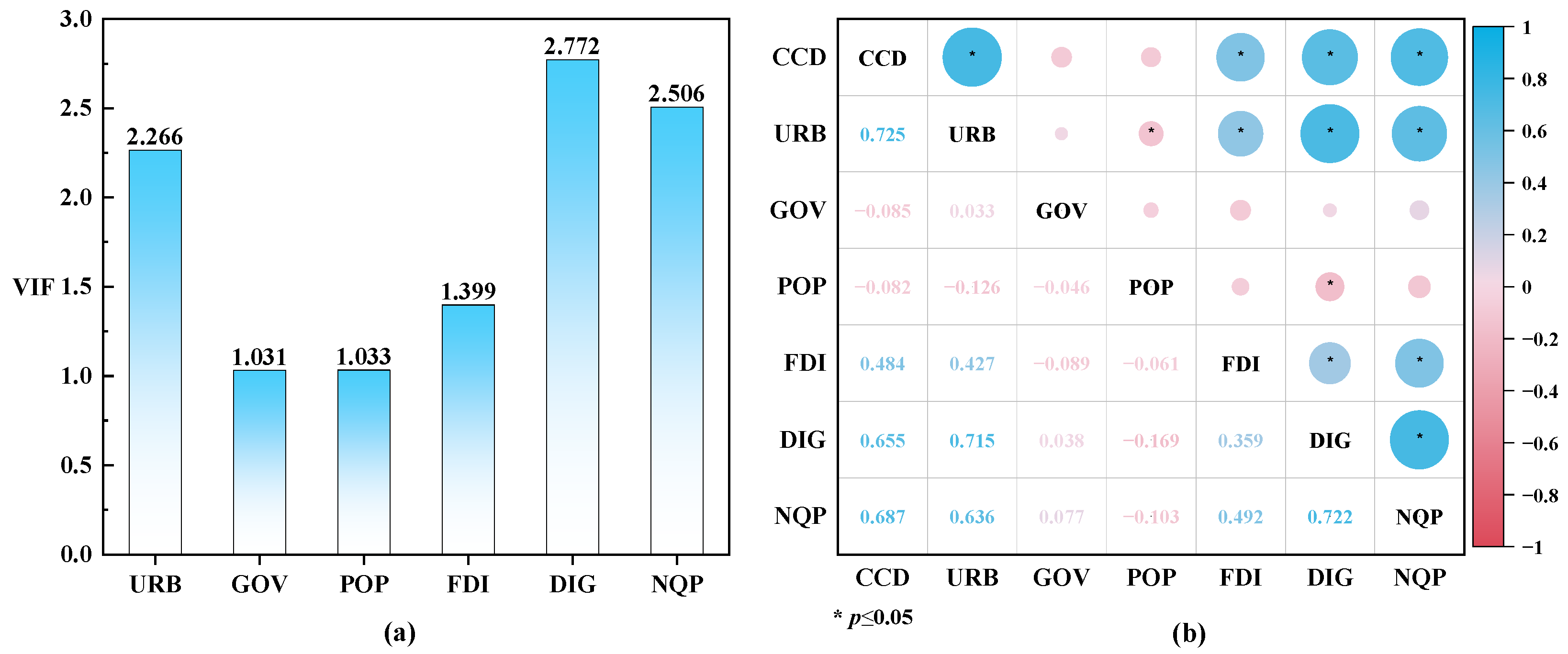
4.4.1. Explanatory Variable Selection
4.4.2. Regression Result
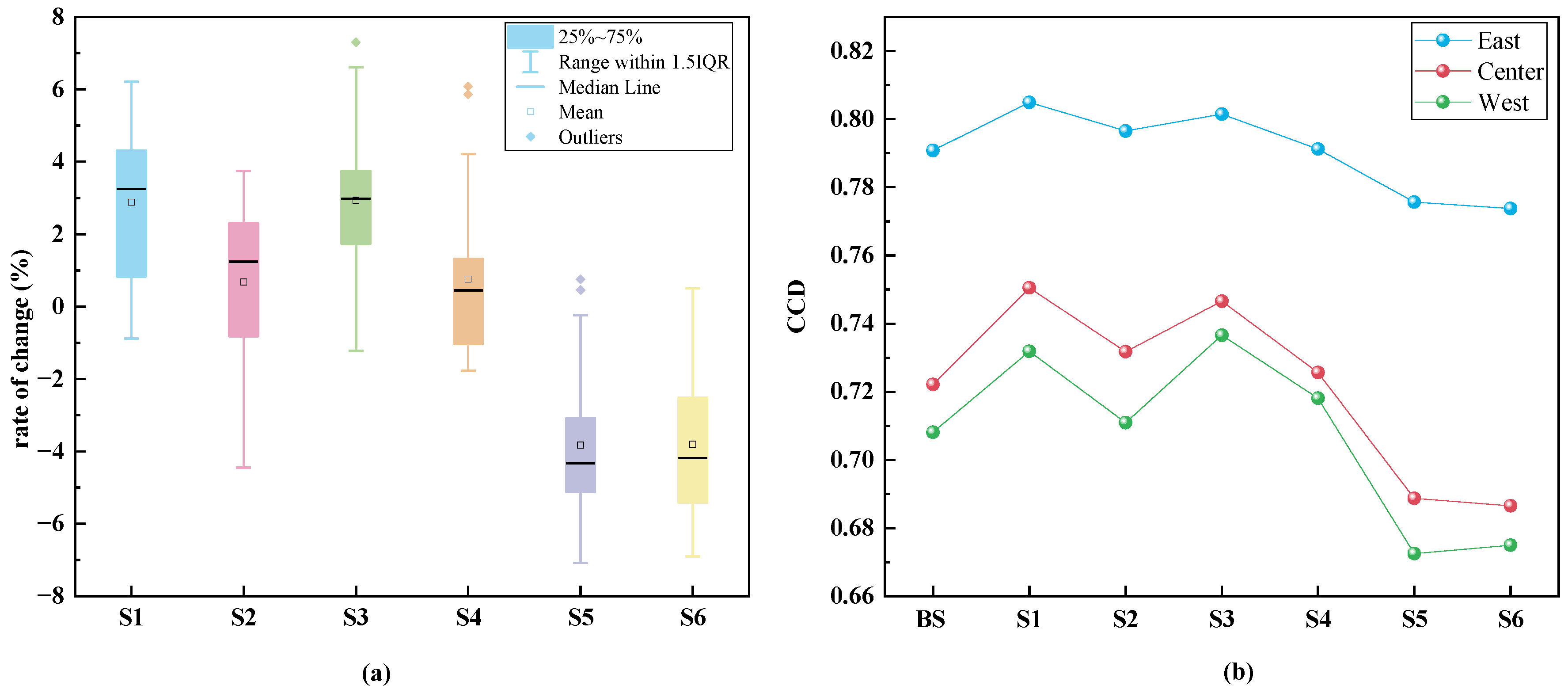
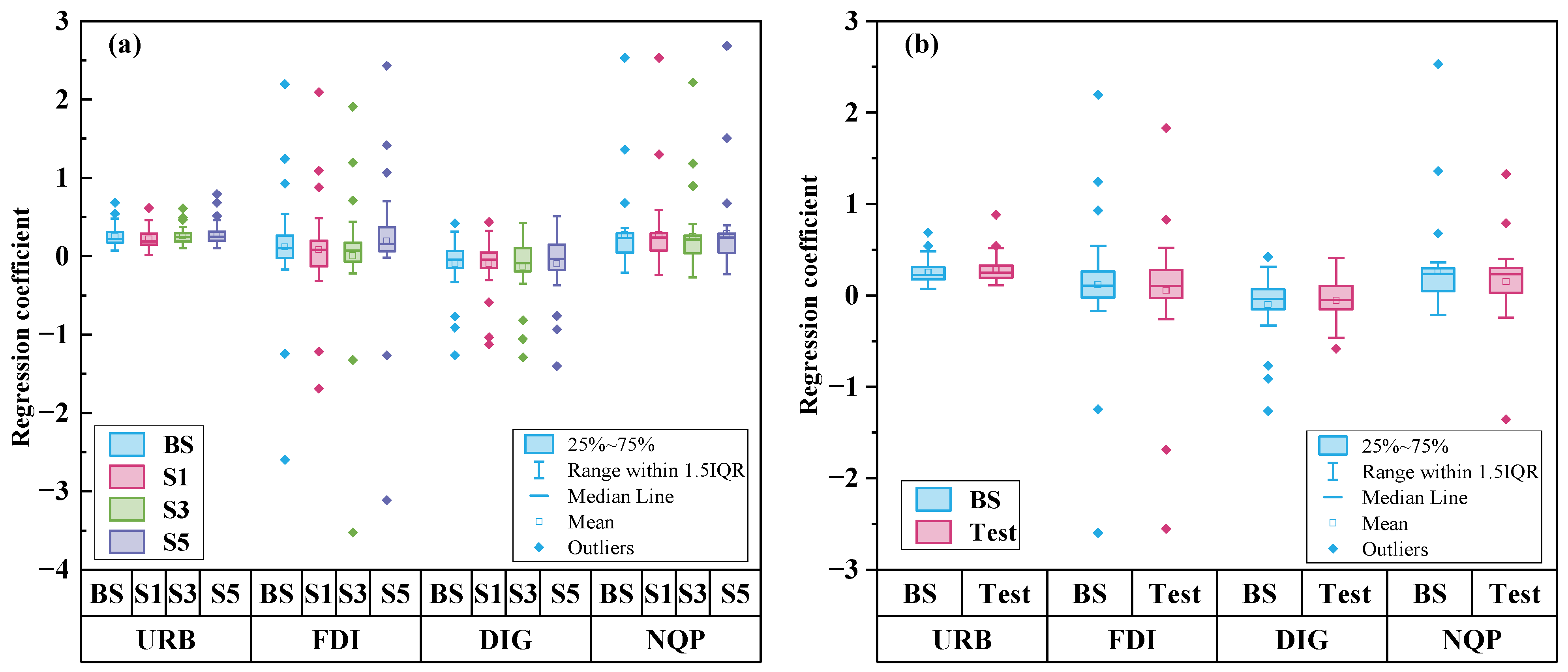
4.5. Robustness Test
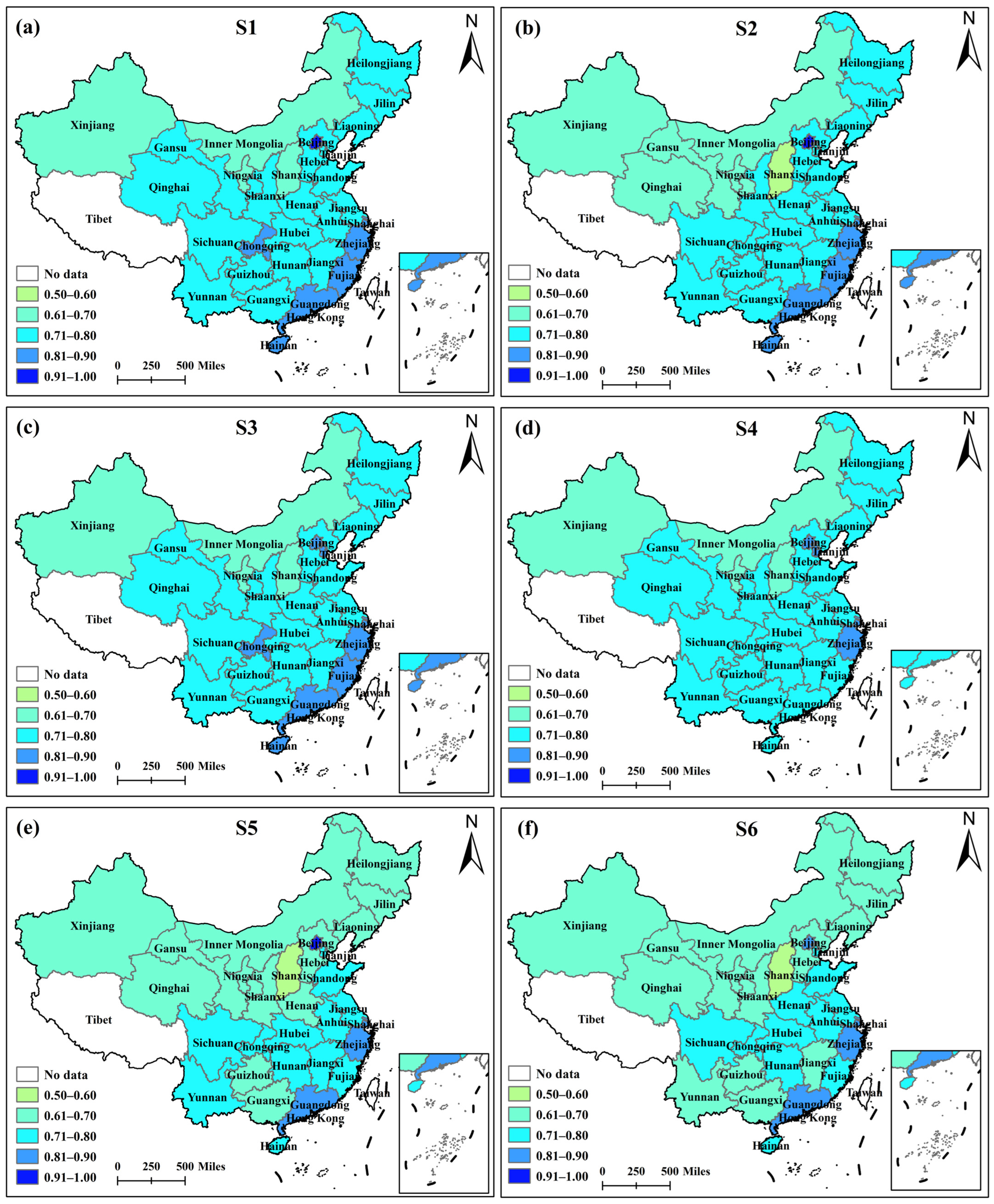
4.5.1. Robustness Test of the CCD Model
4.5.2. Robustness Test of the GWR Model
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CC | Carbon cutting |
| PR | Pollution reduction |
| EG | Economic growth |
| CCD | Coupling coordination degree |
References
- Wang, E.; Liu, B.; Dai, C. China’s energy Consumption, Carbon Emissions and Economic Growth Coordinated Development Evaluation Indicating System and Its Application. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, B.; Jiang, M.; Wang, K.; Chevallier, J.; Wang, P.; Wei, Y.-M. On the road to China’s 2020 carbon intensity target from the perspective of “double control”. Energy Policy 2018, 119, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkodie, S.A.; Ozturk, I. Investigating the Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis in Kenya: A multivariate analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 109481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Wang, W.; Yu, J. Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve in China: A spatial dynamic panel data approach. Energy Econ. 2021, 104, 105600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Zhang, X. Summary about the Critique of Environmental Kuznets Curve. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2010, 20, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jin, F.; Song, Z.; Liu, Y. Spatial coupling analysis of regional economic development and environmental pollution in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Cui, N. Spatiotemporal analysis of the coordination of economic development, resource utilization, and environmental quality in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahtebay, J.; Zhang, F.; Ariken, M.; Chan, N.W.; Tan, M.L. Evaluation of the coordinated development of urbanization-resources-environment from the incremental perspective of Xinjiang, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Chen, J.; Tao, F.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M. On the Coupling and Coordination Development between Environment and Economy: A Case Study in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhou, Q. Study on coupling coordination and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment of cities along the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6898–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, Q.; Wu, K.; Xu, Z.; Liu, P. Spatial-temporal patterns and evolution characteristics of the coordinated development of industrial economy, natural resources and environment in China. Resour. Policy 2022, 75, 102463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; Dai, L. Coupling coordination relationship between tourism economy-social welfare-ecological environment: Empirical analysis of Western Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Mu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Evaluating the level of coordinated development of fisheries economic growth and environmental quality in selected Chinese regions. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 89, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qu, J.; Zhao, K. Is China’s development conforms to the Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis and the pollution haven hypothesis? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K. Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: Testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, X. Spatial economic dependency in the Environmental Kuznets Curve of carbon dioxide: The case of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Lei, H.; Ali, I.; Ji, X.; Sharif, A.; Elkhrachy, I.; Khan, I. Striving for carbon neutrality and economic prosperity in the top ten emitting countries: Testing N shape Kuznets curve hypothesis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 429, 139641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Venevsky, S.; Shi, X.; Wang, L.; Wright, J.S.; Wu, C. Econometrics of the environmental Kuznets curve: Testing advancement to carbon intensity-oriented sustainability for eight economic zones in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, N. Coupling coordination between new urbanisation and carbon emissions in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, X.; Cudjoe, D. Coordination between economic growth and carbon emissions: Evidence from 178 cities in China. Econ. Anal. Policy 2024, 81, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, H. Coupling analysis and driving factors between carbon emission intensity and high-quality economic development: Evidence from the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Guo, L. Road to sustainable development of China: The pursuit of coordinated development between carbon emissions and the green economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lou, Y.; Ye, G.; Wong, S.-W. Improved coupling analysis on the coordination between socio-economy and carbon emission. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Qie, X.; Ning, Y. Measurement and analysis of the comprehensive emission intensity and coupling coordination relationship of carbon dioxide emissions and pollutant emissions in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheung, A.; Qu, X. Can digital financial inclusion promote the coupling coordination between pollution reduction and low-carbon development? Evidence from China. Econ. Anal. Policy 2024, 82, 1113–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Lee, C.-C. Synergy of pollution control and carbon reduction in China: Spatial–temporal characteristics, regional differences, and convergence. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 101, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Meng, Q.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Shen, W. Spatial patterns and evolution trend of coupling coordination of pollution reduction and carbon reduction along the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Walker, T.R.; Adams, M.; Dong, H. Spatio-temporal patterns and spillover effects of synergy on carbon dioxide emission and pollution reductions in the Yangtze River Delta region in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 107, 105419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Zhao, L.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, P. How to achieve synergy between carbon dioxide mitigation and air pollution control? Evidence from China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 78, 103609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W. Research on the difference in air pollution and carbon dioxide reduction and regional economic development levels in China. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2022, 12, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Di, Q.; Jia, W.; Hou, Z. Spatial correlation network of pollution and carbon emission reductions coupled with high-quality economic development in three Chinese urban agglomerations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 94, 104552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Cheng, W.; Tang, X.; Liu, W. Measurement of the Degree of Coordination in Regard to Carbon Emissions, Economic Development, and Environmental Protection in China. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tan, Z.; Mu, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; He, X. Synergy level of pollution and carbon reduction in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and driving factors. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhang, M.; Wu, W.; Zhu, B. Synergistic efficiency in pollution and carbon reduction: Measurement, evolution, and pathways in Chinese cities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 113, 107879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.Y. A techno-economic review on carbon capture, utilisation and storage systems for achieving a net-zero CO2 emissions future. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 3, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Khishgee, S.; Alimujiang, A.; Dong, H. Cost-effective approaches for reducing carbon and air pollution emissions in the power industry in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhao, H. Analysis of collaborative emission reduction of air pollutants and greenhouse gases under carbon neutrality target: A case study of Beijing, China. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2024, 26, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Huang, C.; Ren, W. Performance evaluation and driver analysis of pollution control and carbon reduction in China: Based on a new analytical framework. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 84368–84385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zhang, H. Spatiotemporal characteristics and strategies of synergistic effect of pollution and carbon reduction in China. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2025, 15, 465–473. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Moosavian, S.F.; Zahedi, R.; Hajinezhad, A. Economic, environmental and social impact of carbon tax for Iran: A computable general equilibrium analysis. Energy Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pang, J.; Teng, F.; Gong, R.; Springer, C. The environmental co-benefit and economic impact of China’s low-carbon pathways: Evidence from linking bottom-up and top-down models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 136, 110438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Liu, H. Measurement and Driving Factors of Carbon Emissions from Coal Consumption in China Based on the Kaya-LMDI Model. Energies 2022, 16, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, P. Carbon sequestration potential of forest vegetation in China from 2003 to 2050: Predicting forest vegetation growth based on climate and the environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Geng, Q.; Si, X.; Kan, L. Coupling and coordination analysis of urbanization, economy and environment of Shandong Province, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 10397–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q. Coupling coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment in Chinese provincial capital cities-assessment and policy implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q. Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment—Empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khan, S.U.; Swallow, B.; Liu, W.; Zhao, M. Coupling coordination analysis of China’s water resources utilization efficiency and economic development level. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Long, R.; Chen, H.; Li, Q. Coupling coordination degree and spatial dynamic evolution of a regional green competitiveness system—A case study from China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Ge, Y.; Xu, S.; Ma, X. Measurement and prediction of coupling coordination level of economic development, social stability and ecological environment in Qinghai—Thoughts on sustainable societal safety. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Zhang, R.; Jin, X.; Yu, L. Research and optimization of the coupling and coordination of environmental regulation, technological innovation, and green development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhong, K.; Liao, Y.; Xiong, R.; Wang, F.; Pang, M. Coupling coordination degree of environment, energy, and economic growth in resource-based provinces of China. Resour. Policy 2023, 81, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Lin, X.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of household consumption carbon emissions in China from a spatial perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Ding, T.; Nie, L.; Hao, Z. Agricultural eco-efficiency loss under technology heterogeneity given regional differences in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagum, C. Decomposition and interpretation of Gini and the generalized entropy inequality measures. Statistica 1997, 57, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Bai, H.; Zhong, S.; Wu, Z. Prediction of CO2 emission peak and reduction potential of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Xiang, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Geng, G.; Zheng, J. District level decoupling analysis of energy-related carbon dioxide emissions from economic growth in Beijing, China. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Lin, R.; Sun, J.; Wang, F.; Wu, W. Dynamically evaluating technological innovation efficiency of high-tech industry in China: Provincial, regional and industrial perspective. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 2021, 74, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, M. A comparative study on decoupling relationship and influence factors between China’s regional economic development and industrial energy–related carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Hua, H.; Dong, Z.; Hao, C. Environmental Performance Index at the Provincial Level for China 2006–2011. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Yin, Q. Multidimensional measurement of the High-Quality development of city Clusters: Dynamic Evolution, regional differences and trend forecasting--based on the basic connotation of Chinese-style modernization. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 111989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, P.; Lin, H.; Cai, Z.; Huang, H.; Long, J. Synergic emissions reduction effect of China’s “Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan”: Benefits and efficiency. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lee, C.-C. Does technological innovation reduce CO2 emissions? Cross-country evidence. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, J.; Yang, T.; Ding, T. Spatial and temporal evolution characteristics and spillover effects of China’s regional carbon emissions. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, F. Examining the effects of urbanization and industrialization on carbon dioxide emission: Evidence from China’s provincial regions. Energy 2017, 125, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Xia, X. Spatio-Temporal evolution and spatial heterogeneity of influencing factors of SO2 Emissions in Chinese cities: Fresh evidence from MGWR. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, S.; Huo, Y.; Lee, C.-C. Assessing the role of globalization on renewable energy consumption: New evidence from a spatial econometric analysis. Renew. Energy 2023, 215, 118974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, X. Does foreign direct investment lead to lower CO2 emissions? Evidence from a regional analysis in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Liu, R.; Dwivedi, R. Digital economy, structural deviation, and regional carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Chen, X.; Di, Q. Path to pollution and carbon reduction synergy from the perspective of the digital economy: Fresh evidence from 292 prefecture-level cities in China. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 119050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, Z. Study on the Promotional Effect and Mechanism of New Quality Productive Forces on Green Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Song, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Xie, Q. Coupling coordination between carbon emissions and the eco-environment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C. Spatial-temporal multi-factor decomposition and two-dimensional decoupling analysis of China’s carbon emissions: From the perspective of whole process governance. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 103, 107291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jin, K.; Duan, Z.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gao, C. Spatial-temporal differentiation and influencing factors of carbon emission trajectory in Chinese cities—A case study of 247 prefecture-level cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B. Economic growth effects of industrial restructuring and productivity improvement: Analysis of dynamic spatial panel model with Chinese city data. China Ind. Econ. 2015, 12, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Object Level | Criterion Level | Indicator Level | Property | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon cutting (CC) | Carbon emissions | Carbon dioxide emission | − | 0.081 |
| Carbon emission intensities | − | 0.086 | ||
| Per capita carbon emissions | − | 0.082 | ||
| Energy consumption | Total energy consumption | − | 0.106 | |
| Energy intensity | − | 0.100 | ||
| Energy consumption per capita | − | 0.089 | ||
| Proportion of coal consumption | + | 0.131 | ||
| Carbon fixation | Forest coverage rate | + | 0.224 | |
| Coverage rate of afforestation in developed area | + | 0.101 | ||
| Pollution reduction (PR) | Air pollution | SO2 emissions | − | 0.102 |
| NOx emissions | − | 0.110 | ||
| PM emission | − | 0.090 | ||
| Water pollution | COD emissions | − | 0.128 | |
| NH3-N emissions | − | 0.100 | ||
| Environmental governance | Comprehensive utilization rate of solid wastes | + | 0.160 | |
| Decontamination rate of urban refuse | + | 0.093 | ||
| Proportion of environmental governance investment in GDP | + | 0.218 | ||
| Economic growth (EG) | Economic scale | GDP | + | 0.192 |
| Per capita GDP | + | 0.137 | ||
| Per capita disposable income | + | 0.133 | ||
| Industrial structure | Percentage of the secondary industry | − | 0.106 | |
| Percentage of the tertiary industry | + | 0.105 | ||
| Technological innovation | Proportion of R&D expenditure in GDP | + | 0.194 | |
| Patent application per R&D personnel | + | 0.133 |
| Variable | Abbreviation | Description | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanization | URB | Proportion of urban population in total population | Measuring the regional urbanization level and its environmental effects |
| Government intervention | GOV | Ratio of environmental protection input to fiscal expenditure | Reflecting the intensity of local government policy regulation in environmental governance |
| Population size | POP | Urban population density | Examining the impact of population agglomeration on environmental pressures |
| Foreign direct investment | FDI | Foreign direct investment | Assessment of technology spillovers from international economic and trade cooperation |
| Industry digitization | DIG | Ratio of information technology service revenue to GDP | Characterization of the degree of intelligent transformation of traditional industries |
| New quality productive forces | NQP | Ratio of value added of high-tech industries to industrial value added | Reflecting the level of green technology innovation and industrial upgrading |
| Year | China | East | Center | West |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 0.590 | 0.653 | 0.553 | 0.553 |
| 2012 | 0.612 | 0.672 | 0.582 | 0.573 |
| 2013 | 0.630 | 0.688 | 0.601 | 0.593 |
| 2014 | 0.645 | 0.699 | 0.616 | 0.611 |
| 2015 | 0.662 | 0.711 | 0.636 | 0.631 |
| 2016 | 0.688 | 0.738 | 0.667 | 0.653 |
| 2017 | 0.693 | 0.745 | 0.669 | 0.659 |
| 2018 | 0.715 | 0.765 | 0.699 | 0.677 |
| 2019 | 0.727 | 0.776 | 0.710 | 0.690 |
| 2020 | 0.732 | 0.781 | 0.710 | 0.699 |
| 2021 | 0.742 | 0.791 | 0.722 | 0.708 |
| Parameter | URB | FDI | DIG | NQP | Cons | R2 | Adjusted R2 | p-Value | AICc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | 0.034 *** | 0.011 *** | 0.009 ** | 0.023 *** | 0.676 *** | 0.627 | 0.622 | 0.000 | −1029.7 |
| Parameter | Moran’s I | Z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residuals | −0.033 | 0.058 | 0.460 |
| Variable | Regression Coefficient | Percentage of Provinces by Significance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | p < 0.05 (%) | Positive (%) | Negative (%) | |
| URB | 0.072 | 0.685 | 0.253 | 76.67 | 100 | 0 |
| FDI | −2.597 | 2.195 | 0.118 | 33.33 | 100 | 0 |
| DIG | −1.264 | 0.421 | −0.097 | 10.00 | 66.67 | 33.33 |
| NQP | −0.211 | 2.531 | 0.275 | 56.67 | 94.12 | 5.88 |
| Residual | −0.090 | 0.002 | −0.042 | |||
| Scenarios | Parameter Setting | Label | |
|---|---|---|---|
| α = β = δ | Baseline scenario | α = β = δ = 1/3 | BS |
| α > β > δ | Scenario 1 | α = 0.5, β = 0.3, δ = 0.2 | S1 |
| α > δ > β | Scenario 2 | α = 0.5, β = 0.2, δ = 0.3 | S2 |
| β > α > δ | Scenario 3 | α = 0.3, β = 0.5, δ = 0.2 | S3 |
| β > δ > α | Scenario 4 | α = 0.2, β = 0.5, δ = 0.3 | S4 |
| δ > α > β | Scenario 5 | α = 0.3, β = 0.2, δ = 0.5 | S5 |
| δ > β > α | Scenario 6 | α = 0.2, β = 0.3, δ = 0.5 | S6 |
| Parameter | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Residual Squares | AICc | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS | 0.870 | 0.869 | 0.289 | −1308.5 | 0.115 |
| S1 | 0.869 | 0.867 | 0.271 | −1329.7 | 0.115 |
| S3 | 0.850 | 0.848 | 0.281 | −1317.2 | 0.115 |
| S5 | 0.876 | 0.874 | 0.339 | −1255.6 | 0.115 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Cui, H. Coupling Coordination of Carbon Cutting, Pollution Reduction, and Economic Growth in China: Spatiotemporal Evolution, Regional Differences, and Influence Factors. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115052
Li Y, Cui H. Coupling Coordination of Carbon Cutting, Pollution Reduction, and Economic Growth in China: Spatiotemporal Evolution, Regional Differences, and Influence Factors. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115052
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yunyan, and Hua Cui. 2025. "Coupling Coordination of Carbon Cutting, Pollution Reduction, and Economic Growth in China: Spatiotemporal Evolution, Regional Differences, and Influence Factors" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115052
APA StyleLi, Y., & Cui, H. (2025). Coupling Coordination of Carbon Cutting, Pollution Reduction, and Economic Growth in China: Spatiotemporal Evolution, Regional Differences, and Influence Factors. Sustainability, 17(11), 5052. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115052





