Climate Change Effects on Dates Productivity in Saudi Arabia: Implications for Food Security
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Data
2.2. Methods of Analysis
2.2.1. The Graphical Analysis Method
2.2.2. Co-Integration Tests: Testing the Long-Term Relationship
2.2.3. Error Correction Model (VECM)
2.2.4. Forecast Analysis (Date Productivity)
2.2.5. The Impact of Climatic Change on Saudi Arabia’s Food Security
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics Results
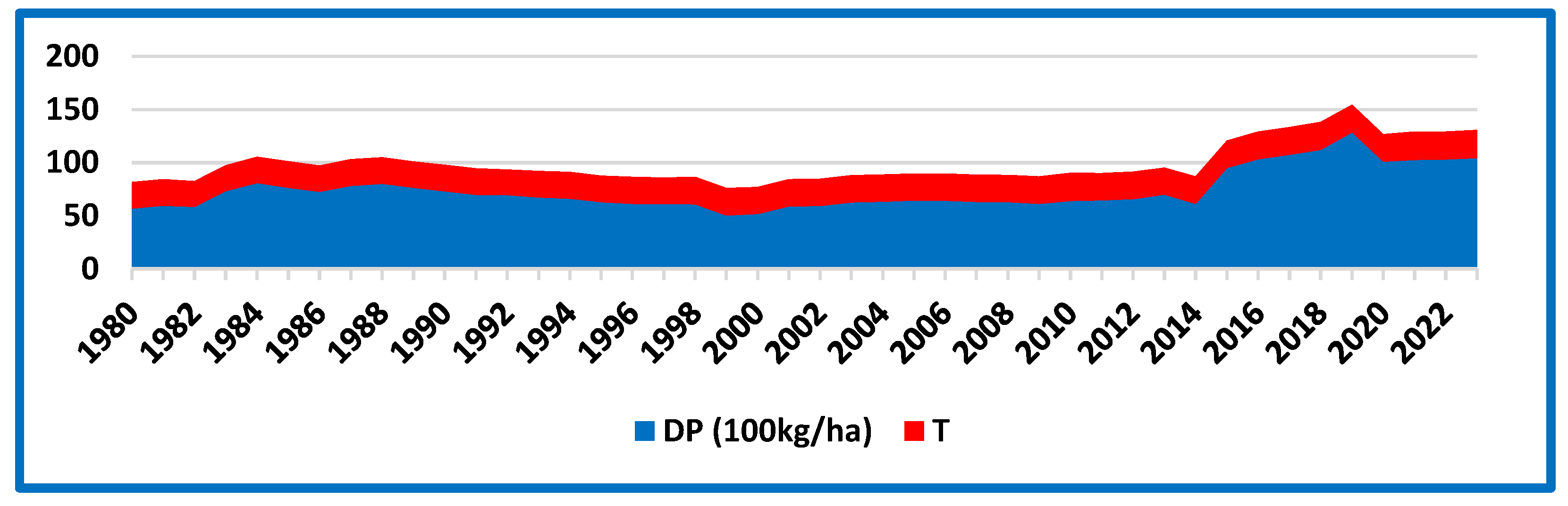
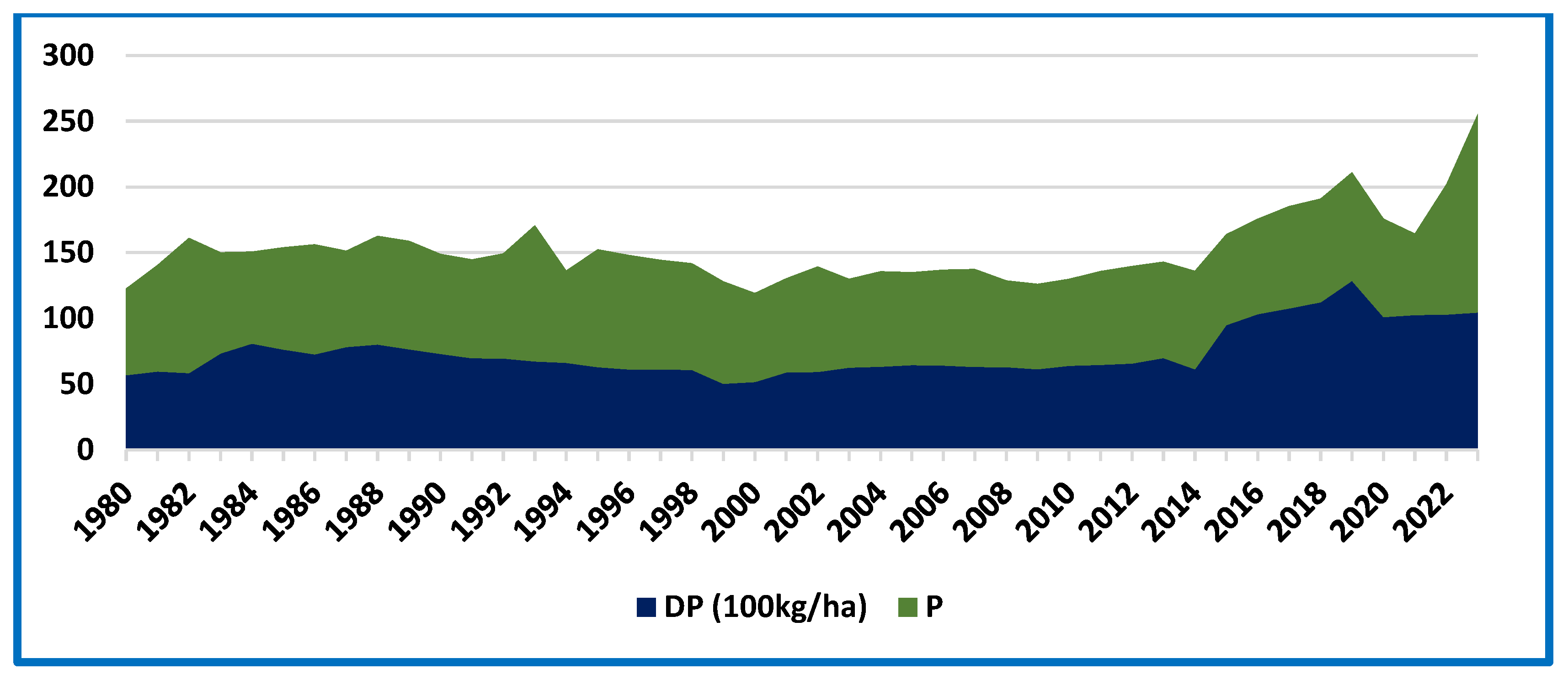
3.2. Graphical Analysis
3.3. Co-Integration Analysis Test (Date Productivity and Temperature)
3.3.1. Unit Root Test Results
3.3.2. Engle–Granger Test Results (Date Productivity and Temperature)
3.4. Results of VECM
3.5. The Results of the Engle–Granger Test (Date Productivity and Precipitation)
3.5.1. The Results of Unit Root Tests
3.5.2. Engle–Granger Test Results
3.6. Results of the VECM
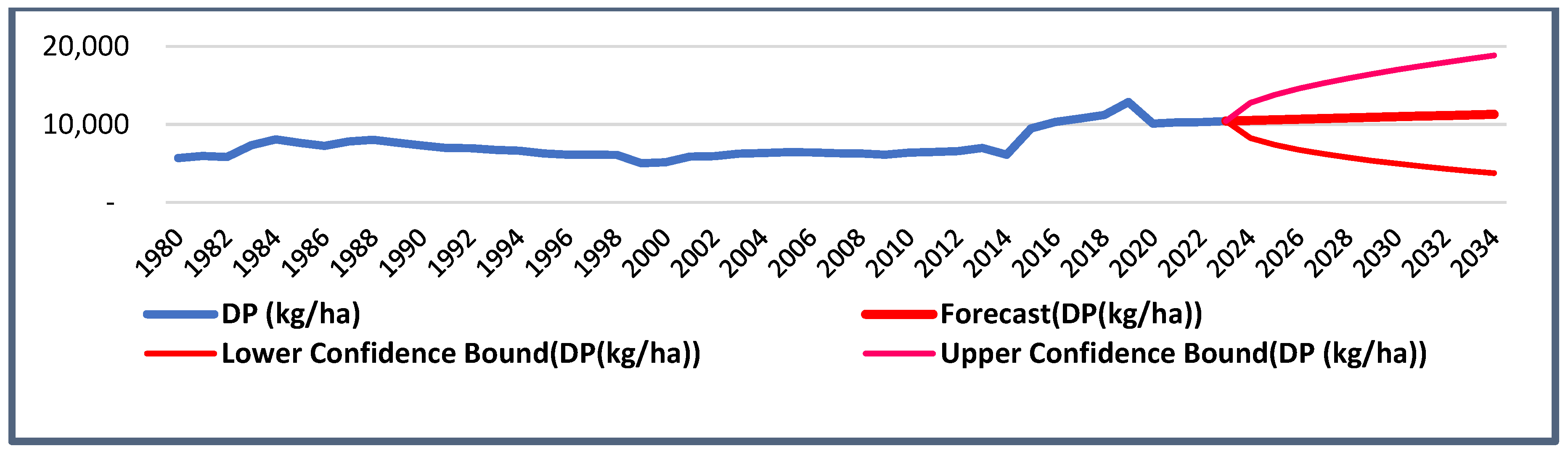
3.7. Forecast Results (Date Productivity)
3.8. The Impact of Climate Change on Saudi Arabia’s Food Security
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiba, S.; Anis, O. Literature survey on the relationships between energy, environment and economic growth. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 69, 1129–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbi, B. CO2 emissions reduction in road transport sector in Tunisia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroyehun, A.R.; Ugwuja, V.C.; Onoja, A.O. Determinants of melon farmers’ adaptation strategies to climate change hazards in south‒south Nigeria. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunnaike, M.G.; Oyawole, F.P.; Afolabi, O.I.; Olabode, J.O. Determinants of smallholder farmers adaptation strategy to climate change in Nigeria. NIU J. Soc. Sci. 2021, 7, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Droulia, F.; Charalampopoulos, I. Future climate change impacts on European viticulture: A review on recent scientific advances. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Reisinger, A. Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 2007, IPCC. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/ar4_syr_full_report.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- IPCC. Climate Change. Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. ISBN 978-92-9169-143-2. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/sr15/summary-for-policymakers/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Fatima, Z.; Ahmed, M.; Hussain, M.; Abbas, G.; Ul-Allah, S.; Ahmad, S.; Ahmed, N.; Ali, M.A.; Sarwar, G.; Haque, E.U.; et al. The fingerprints of climate warming on cereal crops phenology and adaptation options. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Parry, M.L. Potential impact of climate change on world food supply. Nature 1994, 367, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavalle, C.; Micale, F.; Houston, T.D.; Camia, A.; Hiederer, R.; Lazar, C.; Conte, C.; Amatulli, G.; Genovese, G. Climate change in Europe. 3. Impact on agriculture and forestry. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.V. Climate, grapes, and wine: Structure and suitability in a changing climate . In Proceedings of the XXVIII International Horticultural Congress on Science and Horticulture for People (IHC2010): International Symposium on the Citrus, Bananas and other Tropical Fruits Under Subtropical Conditions, Lisborn, Portugal, 22–27 August 2010; Volume 931, pp. 19–28. Available online: https://www.actahort.org/books/931/931_1.htm (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Emam, A.A. Saudi fertilizers and their impact on global food security: Present and future. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Food Summit. Declaration on World Food Security; World Food Summit: Rome, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- van Meijl, H.; Shutes, L.; Valin, H.; Stehfest, E.; van Dijk, M.; Kuiper, M.; Tabeau, A.; van Zeist, W.J.; Hasegawa, T.; Havlik, P. Modelling alternative futures of global food security: Insights from FOODSECURE. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 25, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 1996. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/w1358e/w1358e00.htm (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Guiné, R.D.P.F.; Pato, M.L.D.J.; Costa, C.A.D.; Costa, D.D.V.T.A.D.; Silva, P.B.C.D.; Martinho, V.J.P.D. Food Security and Sustainability: Discussing the Four Pillars to Encompass Other Dimensions. Foods 2021, 10, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C. Resilience of local food systems and links to food security–A review of some important concepts in the context of COVID-19 and other shocks. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 805–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrini, E.; Vigani, M. Technology adoption and the multiple dimensions of food security: The case of maize in Tanzania. Food Secur. 2016, 8, 707–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosratabadi, S.; Khazami, N.; Abdallah, M.B.; Lackner, Z.; Band, S.S.; Mosavi, A.; Mako, C. Social capital contributions to food security: A comprehensive literature review. Foods 2020, 9, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, A.R.; Nikolaus, C.J.; Ellison, B.; Nickols-Richardson, S.M. Food insecurity and food preparation equipment in US households: Exploratory results from a cross-sectional questionnaire. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 32, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houessou, M.D.; Cassee, A.; Sonneveld, B.G. The effects of the covid-19 pandemic on food security in rural and urban settlements in benin: Do allotment gardens soften the blow? Sustainability 2021, 13, 7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Du, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, H.-Z.; Hashmi, M.Z. Modelling the CO2 emissions and economic growth in Croatia: Is there any environmental Kuznets curve? Energy 2017, 123, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smutka, L.; Steininger, M.; Miffek, O. World agricultural production and consumption. Agris Line Pap. Econ. Inform. 2009, 1, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smutka, L.; Steininger, M.; Maitah, M.; Škubna, O. The Czech Agrarian Foreign Trade—Ten Years after the EU Accession. In Agrarian Perspectives XXIV, Proceedings of the 24th International Scientific Conference, Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Faculty of Economics and Management, Prague, Czech Republic, 16–18 September 2015; Smutka, L., Rezbová, H., Eds.; CAB Direct: Glasgow, UK, 2015; pp. 385–392. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K. Food insecurity, income inequality, and the changing comparative advantage in world agriculture. Agric. Econ. 2013, 44, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegren, S.K.; Elvestad, C. Russia’s food self-sufficiency and food security: An assessment. Post-Communist Econ. 2018, 30, 565–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib-ur-Rahman, M.; Ahmad, A.; Raza, A.; Hasnain, M.U.; Alharby, H.F.; Alzahrani, Y.M.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Hakeem, K.R.; Ahmad, S.; Nasim, W.; et al. Impact of climate change on agricultural production; Issues, challenges, and opportunities in Asia. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 925548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Yu, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, C.; Huang, S.; Chen, H.; Ao, X. Impacts of global climate change on agricultural production: A comprehensive review. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A. Rukhsana. Climate change impact, agriculture, and society: An overview. In Climate Change, Agriculture and Society: Approaches Toward Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 3–13. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-28251-5_1 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Prajapati, H.A.; Yadav, K.; Hanamasagar, Y.; Kumar, M.B.; Khan, T.; Belagalla, N.; Thomas, V.; Jabeen, A.; Gomadhi, G.; Malathi, G. Impact of climate change on global agriculture: Challenges and adaptation. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2024, 14, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eekhout, J.P.; de Vente, J. Global impact of climate change on soil erosion and potential for adaptation through soil conservation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 226, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesk, C.; Coffel, E.; Winter, J.; Ray, D.; Zscheischler, J.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Horton, R. Stronger temperature–moisture couplings exacerbate the impact of climate warming on global crop yields. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägermeyr, J.; Müller, C.; Ruane, A.C.; Elliott, J.; Balkovic, J.; Castillo, O.; Faye, B.; Foster, I.; Folberth, C.; Franke, J.A.; et al. Climate impacts on global agriculture emerge earlier in new generation of climate and crop models. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Burney, J.; Chang, J.; Jin, Z.; Mueller, N.D.; Xin, Q.; Xu, J.; Yu, L.; Makowski, D.; Ciais, P. Warming reduces global agricultural production by decreasing cropping frequency and yields. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, A. Present and Future: Does agriculture affect economic growth and environment in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia? J. Agric. Econ. Czech Acad. Agric. Sci 2022, 68, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijerathna-Yapa, A.; Pathirana, R. Sustainable agro-food systems for addressing climate change and food security. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffiantini, G. Food Insecurity and Political Instability during the Arab Spring. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbow, C.; Rosenzweig, C.; Tubiello, F.; Benton, T.; Herrero, M.; Pradhan, P.; Barioni, L.; Krishnapillai, M.; Liwenga, E.; RiveraFerre, M.; et al. Chapter 5: Food Security. In IPCC Special Report on Land and Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aleid, S.M.; Al-Khayri, J.M.; Al-Bahrany, A.M. Date palm status and perspective in Saudi Arabia. In Date Palm Genetic Resources and Utilization; Al-Khayri, J.M., Jain, S.M., Johnson, D.V., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 49–95. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Palms and Dates, Report. 2022. Available online: https://ncpd.gov.sa/en/reports (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Mohammed, M.; Sallam, A.; Munir, M.; Ali-Dinar, H. Effects of deficit irrigation scheduling on water use, gas exchange, yield, and fruit quality of date palm. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Crops and Livestock Products. [Dataset]. Food and Agriculture Organization of the Nations (FAO). 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Alhamdan, A.; Alamri, Y.; Aljuhaim, F.; Kotb, A.; Aljohani, E.; Alaagib, S.; Elamshity, M. Economic Analysis of the Impact of Waste on the Production and Consumption of Dates in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xie, Z. Disclosing the future food security risk of China based on crop production and water scarcity under diverse socioeconomic and climate scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peseran, M.H.; Peseran, B. Working with Microfit 4.0: Interactive Econometric Analysis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Venujayakanth, B.; Swaminathan Dudhat, A.; Swaminathan, B.; Ardeshana, N.J. Price integration analysis of major groundnut domestic markets in India. Econ. Aff. 2017, 62, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Unit | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Date productivity (DP) | (kg/ha) | https://www.fao.org/faostat/ar/#data/QCL (accessed on 10 February 2025) |
| Annual average temperature | °C | https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/country/saudi-arabia (accessed on 10 February 2025) |
| Average precipitation | Millimeter |
| DP | T | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 7380.87 | 25.37 | 78.52 |
| Median | 6595.90 | 25.44 | 74.99 |
| Skewness | 1.23 | −0.06 | 3.12 |
| Kurtosis | 3.58 | 2.60 | 15.61 |
| Jarque–Bera | 11.78 | 0.32 | 362.49 |
| Probability | 0.003 | 0.85 | 0.000 |
| Observations | 44 | 44 | 44 |
| Time Series | Intercept | Intercept and Trend | Stationarity | Intercept | Intercept and Trend | Stationarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| at Level | at First Difference | |||||
| LDP | −1.22 | −1.59 | Non-stationary | −6.96 * | −6.9 * | Stationary |
| LT | −0.65 | −5.95 * | Stationary | −5.651 * | −5.96 * | Stationary |
| LT | LDP | |
|---|---|---|
| LDP | −6.81 * | |
| LT | −6.81 * |
| Lag | LogL | LR | FPE | AIC | SC | HQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 105.38 | NA | 2.80 × 10−5 | −4.81 | −4.73 | −4.78 |
| 1 | 156.25 | 94.66 * | 3.16 × 10−6 * | −6.99 * | −6.74 * | −6.90 * |
| Long-Term Results: LDP (Dependent Variable) | Short-Term Results: LDP (Dependent Variable) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error Correction | Coefficient | t-Value Statistic | Coefficient | t-Value Statistic |
| CointEq1 | −0.08 | −1.22 | ||
| LT(−1) | −9.44 | −1.76 | ||
| D(LDP(−1)) | −0.04 | −0.27 | ||
| D(LT(−1)) | −0.98 | −0.97 | ||
| C | 21.63 | 0.02 | 0.94 | |
| - VECM residual serial correlation LM tests: | Lags LM-Stat | Prob | ||
| 1 | 7.20 | 0.13 | ||
| - VEC residual heteroskedasticity tests: | Chi-sq 14.99 | Prob. 0.66 | ||
| - VEC residual normality tests: | Chi-sq 0.58 | Prob. 0.75 | ||
| Time Series | Intercept | Intercept and Trend | Stationarity | Intercept | Intercept and Trend | Stationarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| at Level | at First Difference | |||||
| LDP | −1.22 | −1.59 | Non-stationary | −6.96 * | −6.91 * | Stationary |
| LP | −2.90 | −2.77 | Non-stationary | −6.70 * | −6.78 * | Stationary |
| LP | LDP | |
|---|---|---|
| LDP | −7.52 * | |
| LP | −7.23 * |
| LogL | LR | FPE | AIC | SC | HQ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 24.47 | NA | 0.0012 | −1.05 | −0.96 | −1.02 |
| 1 | 62.47 | 70.70 * | 0.00025 * | −2.63 * | −2.38 * | −2.54 * |
| Long-Term Results: LDP (Dependent Variable) | Short-Term Results: LDP (Dependent Variable) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error Correction | Coefficient | t-Value Statistic | Coefficient | t-Value Statistic |
| CointEq1 | −0.01 | −0.25 | ||
| LP(−1) | −5.10 | −3.05 | ||
| D(LDP(−1)) | −0.08 | −0.47 | ||
| D(LP(−1)) | −0.003 | −0.02 | ||
| C | 13.25 | 0.02 | 0.87 | |
| - VECM residual serial correlation LM tests: | Lags | LM-Stat | Prob. | |
| 1 | 8.46 | 0.08 | ||
| - VEC residual heteroskedasticity tests: | Chi-sq 40.96 | Prob. 0.51 | ||
| - VEC residual normality tests: | Chi-sq 0.58 | Prob. 0.75 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emam, A. Climate Change Effects on Dates Productivity in Saudi Arabia: Implications for Food Security. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4574. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104574
Emam A. Climate Change Effects on Dates Productivity in Saudi Arabia: Implications for Food Security. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4574. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104574
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmam, Abda. 2025. "Climate Change Effects on Dates Productivity in Saudi Arabia: Implications for Food Security" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4574. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104574
APA StyleEmam, A. (2025). Climate Change Effects on Dates Productivity in Saudi Arabia: Implications for Food Security. Sustainability, 17(10), 4574. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104574








