Abstract
In recent decades, the use of pesticides has become fundamental to agricultural growth. However, the persistent and toxic nature of pesticides has led to significant concerns regarding their ecological and human health consequences. Therefore, for a better understanding of pesticide contamination and its potential risks, here we assessed the levels of five emerging pesticides—acetochlor, imidacloprid, MCPA, atrazine, and allethrin—in soil samples from ponds used for irrigation and in drinking water samples from nearby areas in Lahore, Pakistan. Our findings revealed that 100% of the samples were contaminated, posing substantial ecological and human health risks. Based on the toxic units (TUsum), all the soil samples showed higher toxic pressure, exceeding acute and chronic toxicity thresholds for earthworms, while 100% of water samples posed chronic toxicity risks to crustaceans and 10% to algae. Pollution index (PI) analysis further classified 100% of the soil samples and 10% of the water samples as highly polluted. These findings show high-pesticide residues in both soil and water and highlight immediate risk assessment and mitigation measures to protect non-target organisms. This preliminary information can be used to adopt risk assessment monitoring programmes and help higher authorities in making policies and guidelines to mitigate the escalating risk for ecology and humans.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, emerging pesticides have been considered as major contributors to improving both the quality and quantity of food. Farmers have steadily increased pesticide application to meet the demands of growing populations [1]. In agricultural countries like Pakistan, where a large population is linked to agriculture, pesticide usage has also been on the rise [2,3,4,5]. According to a previous survey, it was estimated that pesticide consumption increased from 254 metric tons/year in 1954 to over 300 times in 2003 [6]. Furthermore, the use of emerging pesticides is not only limited to better crop production but are also used for controlling vector-borne diseases [7,8]. However, monitoring data and information on the ecological effects of environmental pollution are very scarce in Pakistan. In contrast, sufficient pollution data are available for Europe, China, Australia, and other high-income countries [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17].
Unfortunately, only a small fraction of the applied pesticides reaches the target, while the remaining is lost to the environment, where they can travel long distances through environmental mediums due to their persistence and bio-accumulative nature [18,19,20]. Common sources of pesticide contamination include runoff and the dumping of excessive (thousands of kg) or illegally produced pesticides in nearby environments [21].
Despite the benefits of pesticides, their intensive use poses serious threats to human health and ecology and can cause long-term environmental problems [1,15,22,23]. Several studies provide strong evidence of the significant impacts of pesticides on the ecological status of water bodies [15,22,23,24,25]. Pesticide contamination can cause negative impacts on the structure and functions [26,27] of freshwater communities and may lead to a decline in the biodiversity of aquatic macroinvertebrates [15,28] and terrestrial organisms [29,30]. Aquatic organisms, including fish, experience noticeable changes even at the molecular level [31]. It is suggested that the consumption of contaminated fish can cause both carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic effects in humans due to the bio-magnification process [32,33]. Moreover, high levels of pollution in soil can contaminate the food chain, restrict plant growth, and impact the population of soil biota.
Many pesticides that can pose significant risks to the environment are banned in developed countries. For instance, imidacloprid, acetochlor, and atrazine are banned in Europe due to their risks to aquatic ecosystems and non-target organisms. In contrast, these pesticides continue to be used without any strict regulations in Pakistan, leading to their significant presence in different environmental compartments in Pakistan, as reported in previous studies [6,34,35]. We selected five emerging pesticides (acetochlor, imidacloprid, MCPA, atrazine, and allethrin), as they have been reported in different parts of Pakistan and are still excessively used in Pakistan due to illegal production, poor management policies, and insufficient knowledge about potential risks [36,37]. Meanwhile, scientists are working to find effective treatment solutions to minimize the risks associated with pesticide pollution. As an alternative to chemical pesticides, the use of biopesticides appears to be a promising approach, while bioremediation is considered one of the best methods for controlling pollution [38]. However, the detection and quantification of pesticide residues remain crucial in identifying sustainable solutions and implementing measures to reduce the overburden of pollutants in soil and water.
In the present study, we aimed to quantify the contamination level of five emerging pesticides and their potential risks to non-targeted organisms. For this, we collected sediments from the ponds and drinking water of nearby areas of Lahore, which is the second largest city of Pakistan. It is the most populous city and among the top 20 populated cities in the world, with a population density of 6300 persons/km2 [39]. For the ecological effects of pesticides, we conducted risk assessments for soil-dwelling organisms and sensitive aquatic species (algae, fish, and crustaceans). We also aimed to calculate the risk quotient (RQ) for the overall soil biotic community based on the predicted no-effect concentration (PNEC). Additionally, human health risks were calculated based on the health risk index (HRI) for oral and dermal exposure routes. To assess the overall environmental health, a pollution index for soil and water samples was also calculated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Sampling Sites and Sample Preparations
The current study was designed to evaluate the residual levels of emerging pesticides in ponds located in the vicinity of Lahore and drinking water samples from nearby areas. These ponds are deep and shallow depressions that collect water from their surroundings through surface runoff, drainage water, and rainfall. They are used for irrigation and as a water source for animals. However, most of these ponds have been filled with soil and sand to avoid unhygienic conditions and are used for growing crops.
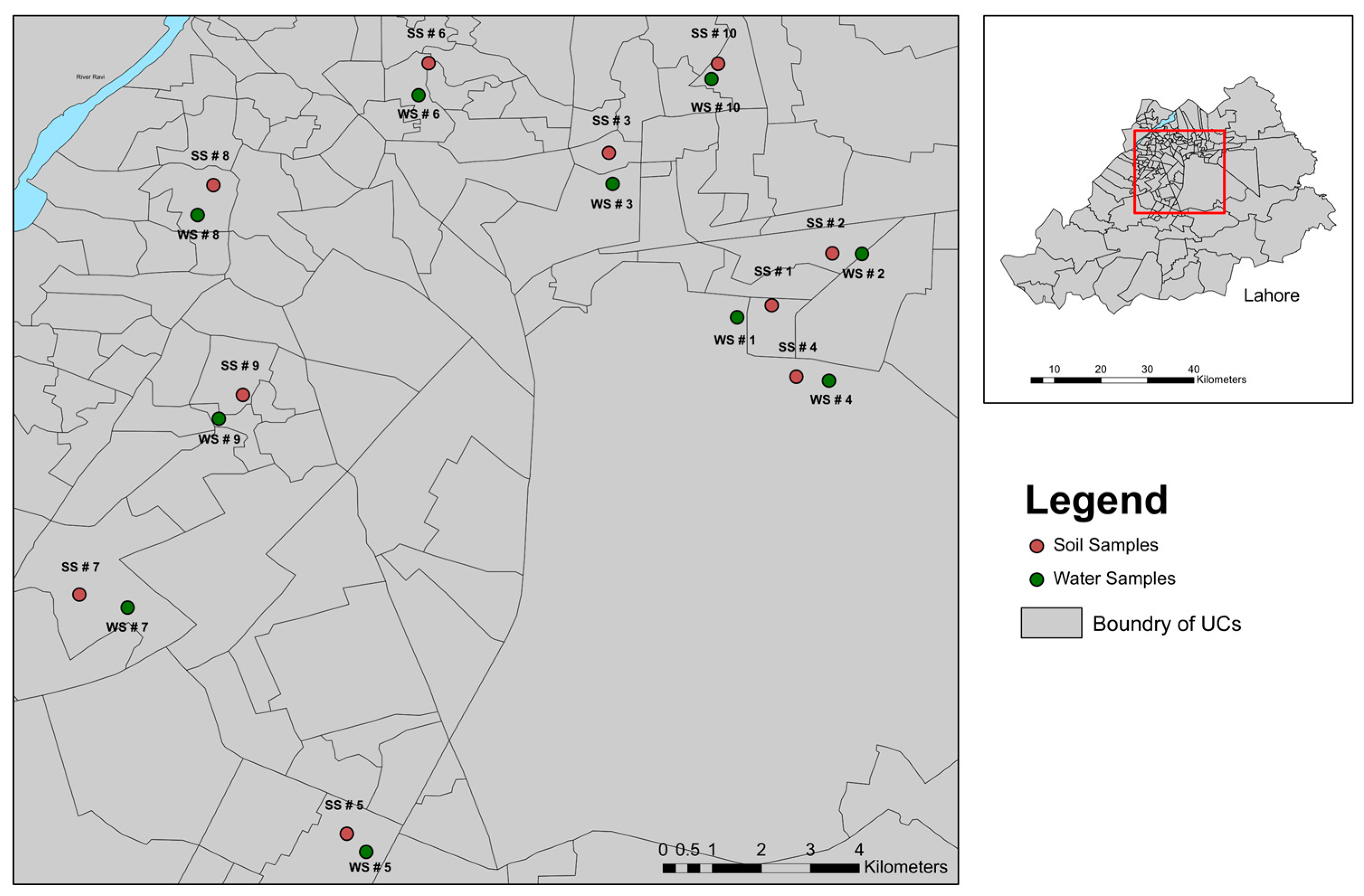
A preliminary survey was conducted to select the sampling sites based on estimated sources of pollution and accessibility. Lahore is divided into 10 towns, and one pond was selected from each town. The sampling locations were recorded using a GPS device (eTrax 20, Garmin, Olathe, USA), and the sampling locations were marked (Figure 1, Supporting Information Table S1). For the soil samples, we collected six random samples (0–100 cm of depth) in a zigzag pattern from each site, combined them into composite samples, and transferred them into zip-lock bags using a pre-washed glass pipe. Similarly, six drinking water samples were collected from nearby areas of ponds (within 5 km) and combined to create representative samples. After proper labelling, samples were placed in cool boxes to prevent degradation and transported to the College of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of the Punjab, and stored in a freezer at –4 °C until further analysis.
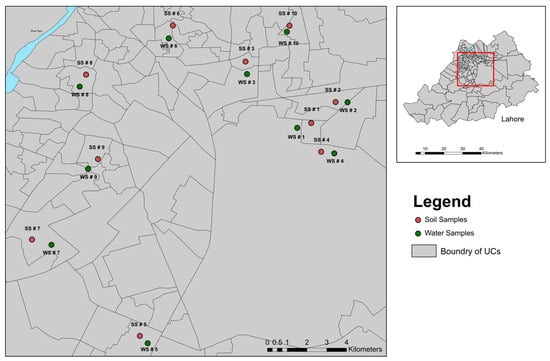
Figure 1.
The locations of the sampling sites around the city of Lahore. Red points represent soil samples collected from ponds, while green points indicate water sampling sites.
Soil samples were air-dried at a temperature of 20–25 °C in a closed airtight glass compartment. Any foreign particles, such as leaves, biological remains, plastic, or metallic objects were removed. Subsequently, the dried soil was sieved using a sieve size of 2 mm and the mixture was homogenized according to international standards [40]. Furthermore, each sample was divided into two sub-samples, one for a physico-chemical analysis and the other for a residual assessment of pesticides. The mixture of soil was prepared by mixing soil and water in a 1–10 ratio. The mixture was stirred continuously for 5–10 min and then allowed to settle for 30–40 min. The supernatant was filtered, and the filtrate was used to assess physico-chemical parameters such as pH, conductivity, nitrates, sulphates, and chloride content [41].
For water samples, 1000 mL of water was collected from each site using a glass container and filled in 2 mL glass vials, with five replicates of each sample. Physico-chemical parameters including pH, EC, and TDS were measured on-site using CyberScan PC510 (EUTECH, Singapore). The samples were frozen and transported to the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research, UFZ, for pesticide analysis.
2.2. Sample Analysis
Samples were analyzed in four different laboratories including the College of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Pakistan Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (PCSIR), Lahore College for Women University (for soil samples), and the Helmholtz Centre (for Environmental Research—UFZ) for the pesticide analysis of water samples. To check soil pH, we used a CyberScan PC510 multi-meter (EUTECH, Singapore), which was calibrated before each sample measurement. Chloride content was determined via the gravimetric method using AgNO3 for precipitation [42]. For sulphates, 10 mL of soil extract was mixed with HCl, glycerol, and a 0.03 BaCl2 solution, and absorbance was measured with a spectrophotometer following the detailed procedure outlined in a previous study [40]. Furthermore, nitrates were measured with the sodium salicylate method, as described in a previous study [43].
For the residual assessment of pesticides in soil, extraction was conducted according to the standard procedure described earlier [42,44,45]. Briefly, methanol was used as an extraction solvent. Subsequently, the solvent containing the extracts of pesticides was filtered and concentrated at 40 °C. For further purification, the extract was cleaned up using a Florasil-packed column, and eluate was concentrated and re-dissolved in 5 mL acetonitrile. The prepared samples containing pesticide residues were subjected to a nitrogen stream to concentrate the extract. Acetonitrile containing the elute was used as a mobile phase in HPLC. The samples were analyzed through high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Specifically, for the detection and quantification of pesticides, a C18 column (250 × 4.6 mm internal diameter) with a 5 µm particle size was used as a reverse phase in HPLC. During analysis, the temperature was maintained at 28 °C and pressure was about 20 MPa (megapascal). Standard reference materials for quality assurance were obtained from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and some pesticide standards, including acetochlor, MCPA, and imidacloprid, were purchased from Ali Akbar Group of Industries with 99.9% purity. For water analysis, 100 µL of the water sample was directly injected into LC-HRMS following the procedure described in a previous study [13].
2.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
The ecological risk assessment was conducted based on toxic units (TUs) for both soil and water samples. For soil, toxic pressure was calculated for soil-dwelling organisms, such as earthworms. For water, TUs were calculated at three trophic levels, using sensitive species such as algae, crustaceans, and fish [46]. The toxic unit is the ratio between the measured concentration of a pollutant (in this case, pesticide residues) and the mean lethal (LC50) and mean effect concentration (EC50) Equation (1).
where TUsum is the sum of the effect of n pesticides detected at each location, Ci = concentration (ng/L) of each pesticide “i”, and LC50i is the lethal concentration of the pesticide for each organism.
Terrestrial ecotoxicology under the Council’s directive defined toxicity as 0.1 (threshold level) for soil-dwelling organisms. For water samples, acute risk (0.1) for all three organisms (algae, crustaceans, and fish) and chronic risk for algae (0.02), crustaceans (0.001), and fish (0.01) were also calculated [47]. Reference values for LC50 and EC50 were retrieved from the ECOTOX database and some previous studies [9,48,49] (further details in Supporting Information Table S2).
The risk quotient (RQ) was calculated to determine the overall ecological risk for all aquatic organisms. It is defined as the ratio between the concentration of pollutants (residue of pesticide detected) and the predicted no-effect concentration (PNEC), as shown in Equation (2). The reference values were obtained from the NORMAN network [50] (Supporting Information Table S2).
where RQsum is the sum of the risk of the n number of detected pesticides, MECi is the measured concentration of pesticide “i”, and PNEC represents the predicted no-effect concentration of the respective pesticide “i” at each location. If RQsum is below 1, it indicates that the studied sample is adequately safe.
2.4. Pollution Index (PI)
To check the overall pollution regardless of any specific species, the pollution index (PI) was calculated by dividing each pesticide by its permissible limit and then taking an average of all detected pesticides, as shown in Equation (3).
In the above equation, PI is classified as low pollution (0 > PI ≤ 1), moderate pollution (1 < PI ≤ 3), and high pollution (PI > 3) [51].
2.5. Human Health Risk Assessment
A human health risk assessment was calculated by considering two pathways (oral and dermal exposure). The potential risk of each pesticide was calculated by chronic daily intake (CDI) and the risk quotient (RQ), with equations recommended by the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, 2005.
All the parameters used in the equations above were in accordance with the previous literature [52,53], and are listed with a complete description of units and values in the Supporting Information, Table S3. Moreover, non-carcinogenic effects on humans were calculated by using the hazard quotient, HQ, described in Equation (6) as described in previous studies [53,54,55,56,57,58].
Details about reference doses are provided in the Supporting Information, Table S4. If the HQ value is greater than 1, the pollutants have the potential to cause adverse health effects, including cancer in exposed organisms.
To calculate the health risk index (HRI), we added up all hazard quotients (HQs), as given in Equation (7). The HRI was calculated separately for two age groups, namely youth (less than 18 years of age) and adults (above 18 years of age), for both dermal and oral routes.
2.6. Data Analysis
The data analysis illustration was performed using Microsoft Excel 2010, R Studio (version 2024.4.1.748) [36], and R (version 4.4.0) [59]. Moreover, concentrations below the method detection limit were considered zero. Due to variations in the concentration of compounds, data were log-transformed and scaled to minimize the skewness before data analysis. ArcGIS (ver. 10.8.2) from ESRI was used to display the sampling locations and to show the distribution of pesticides on the map.
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters of Soil and Water
The analysis of physico-chemical parameters of the soil samples revealed several key insights into the health and composition of the soil. The pH levels of the soil samples ranged from 7.2 to 8.9, with 50% of the sites exceeding the permissible limits set by the World Health Organization (WHO), which recommends a pH range of 6 to 7.5 for optimal plant growth. This indicates an overall alkaline nature of the soil, which can affect the availability of nutrients and the microbial community. High-pH soils tend to be deficient in essential nutrients and often favour bacterial dominance over fungi and algae. In water samples, the pH ranged from 7.24 to 9.91, with an average value of 7.76. The highest value was observed in the groundwater of Nishtar Town within the premises of Quaid-e-Azam Industrial Estate, Lahore.
Soil conductivity ranged from 984 to 4994 μS/cm. The average concentrations of chlorides, nitrates, and sulphates were 16.88 mg/g, 31.7 mg/g, and 83.9 mg/g, respectively (Supporting Information, Table S5). In drinking water samples, the electrical conductivity (EC) ranged from 222 to 1439 µS/cm, with an average value of 630.66 µS/cm.
3.2. Residual Assessment of Pesticides in Soil and Water
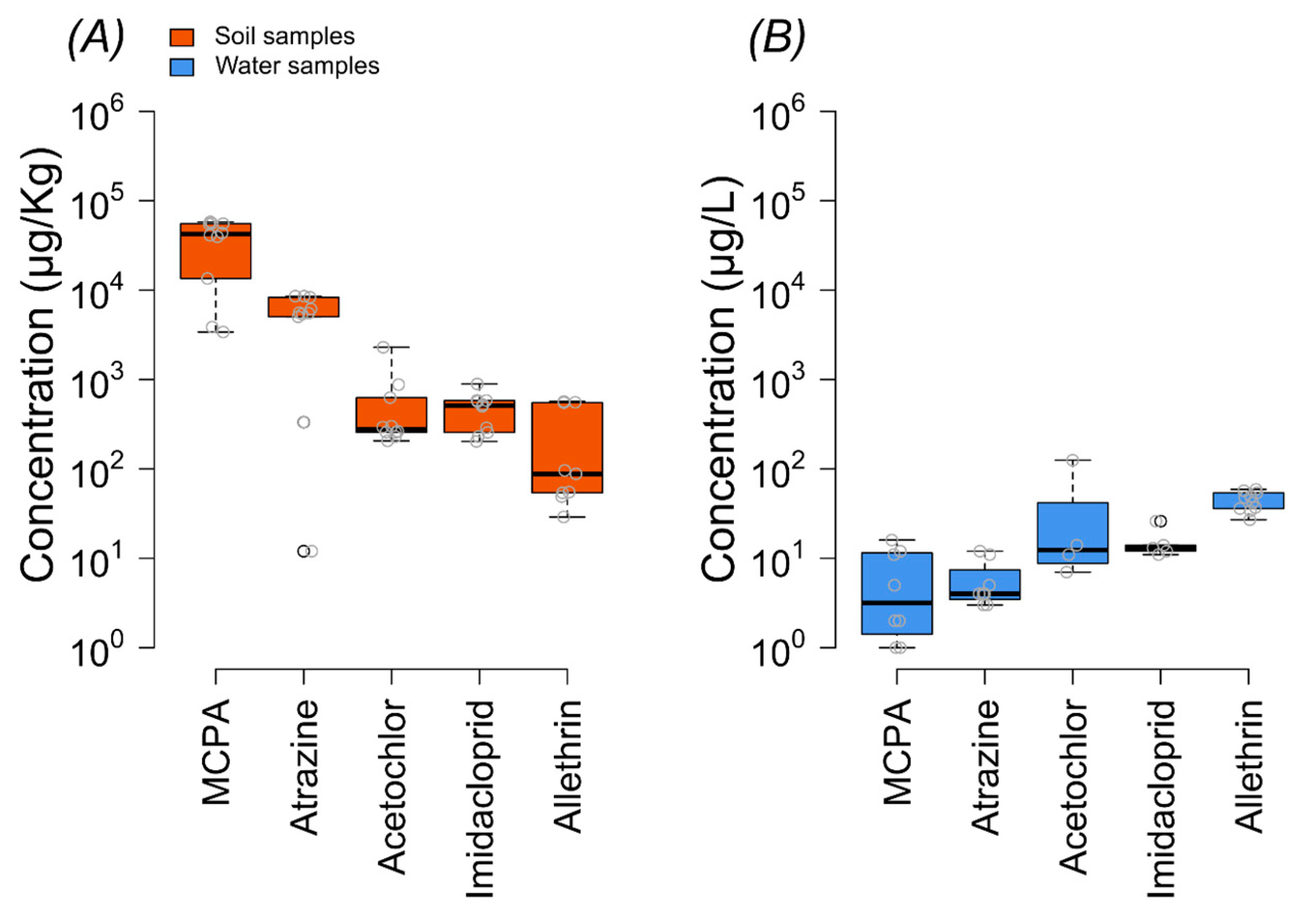
Residues of five emerging pesticides including acetochlor, imidacloprid, MCPA, atrazine, and allethrin were detected in the soil and water samples. In soil samples, all pesticides were detected in 100% of the samples except for allethrin, which was detected in 90% of the samples. The highest concentration was observed for MCPA, with an average concentration of 36928 µg/kg, exceeding the WHO’s permissible limit of 2000 µg/kg (Figure 2). Atrazine, another herbicide, was found at an average concentration of 5344 µg/kg. Among insecticides, imidacloprid and allethrin were detected at concentrations ranging from 203 to 891 µg/kg and 204 µg/kg on average, respectively.
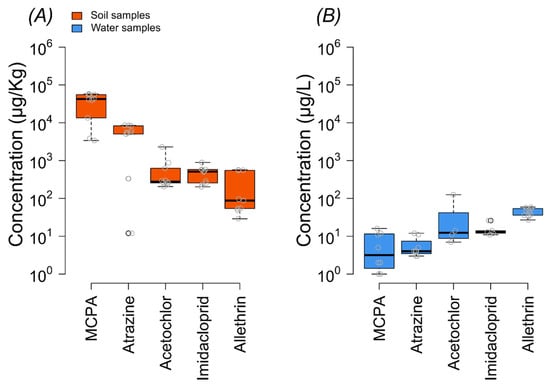
Figure 2.
Concentrations of different pesticides in soil (A) and water samples (B). The border lines of the box are the 25th and 75th percentiles; the horizontal line shows the median value; and the whiskers of the boxplot correspond to the minimum and maximum values. The red dashed line indicates the threshold level.
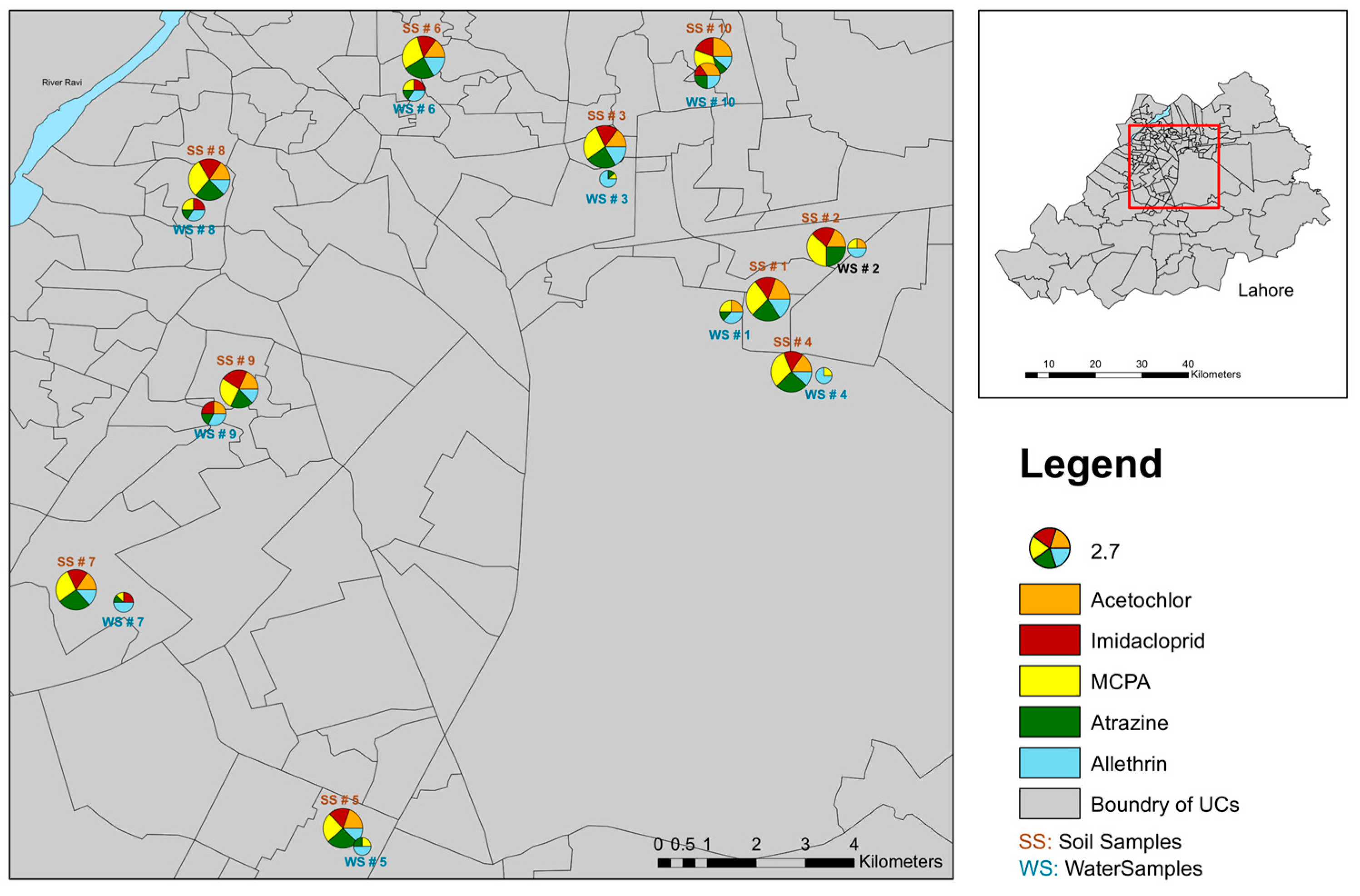
Key results from the concentration variability show that MCPA exhibited the highest concentration among the pesticides analyzed, consistently appearing in higher levels across many sites (Figure 2 and Figure 3). This was followed by atrazine, which also showed significant concentrations, particularly in certain hotspots (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
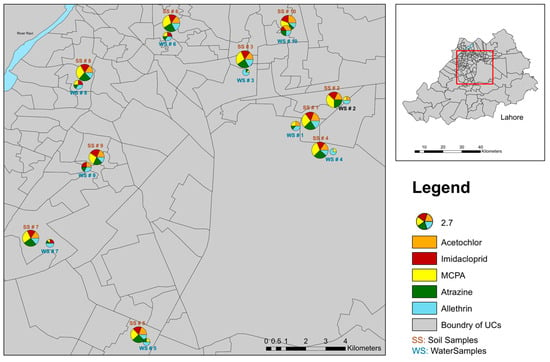
Figure 3.
Geographic distribution of sampling sites with pesticide pollution. The map displays the locations of the sites with pie charts representing the relative concentrations of five emerging pesticides, namely acetochlor, imidacloprid, MCPA, atrazine, and allethrin. Each segment of the pie chart corresponds to the percentage contribution of each pesticide at that site, with the size of the chart proportional to the overall concentration detected.
On the other hand, the overall concentration of pesticides was lower in water samples than in soil samples (Figure 2 and Figure 3), and only allethrin was found with a 100% detection frequency. The highest concentration was found for acetochlor (125 µg/L), followed by allethrin > imidacloprid > MCPA > atrazine (Figure 2, Table S6, Supporting Information).
3.3. Ecological Risk Assessment (Toxic Unit, Risk Quotient, Pollution Index)
The ecological risk assessment was conducted by calculating toxic units (TUsum) according to the concept of concentration addition (CA). The acute and chronic toxicity thresholds were placed at 0.1 (logTU = −1) for all organisms, 0.02 (logTU = −1.67) for algae and earthworms, 0.01 (logTU = −2) for fish, and 0.001 (logTU = −3) for crustaceans, respectively.
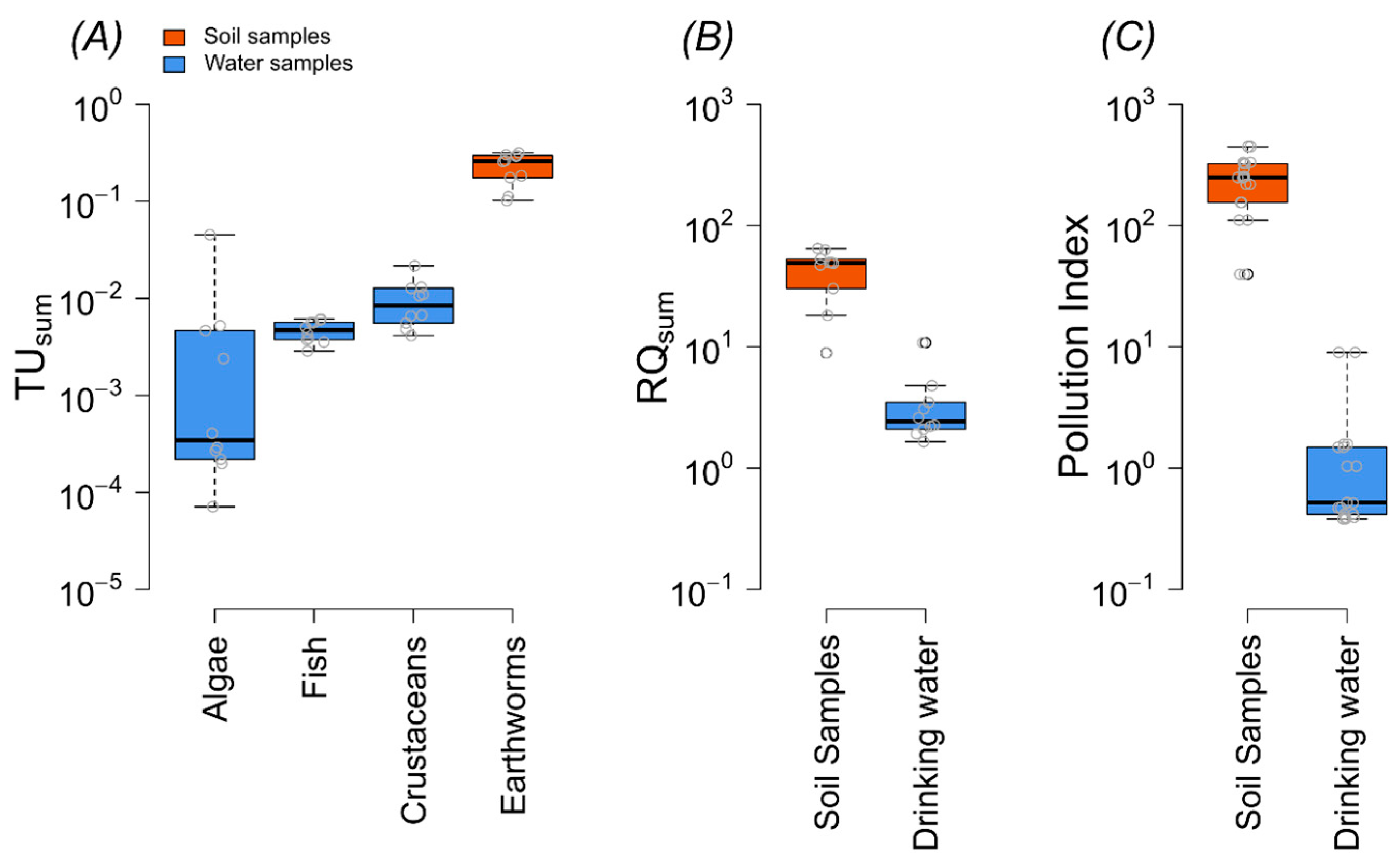
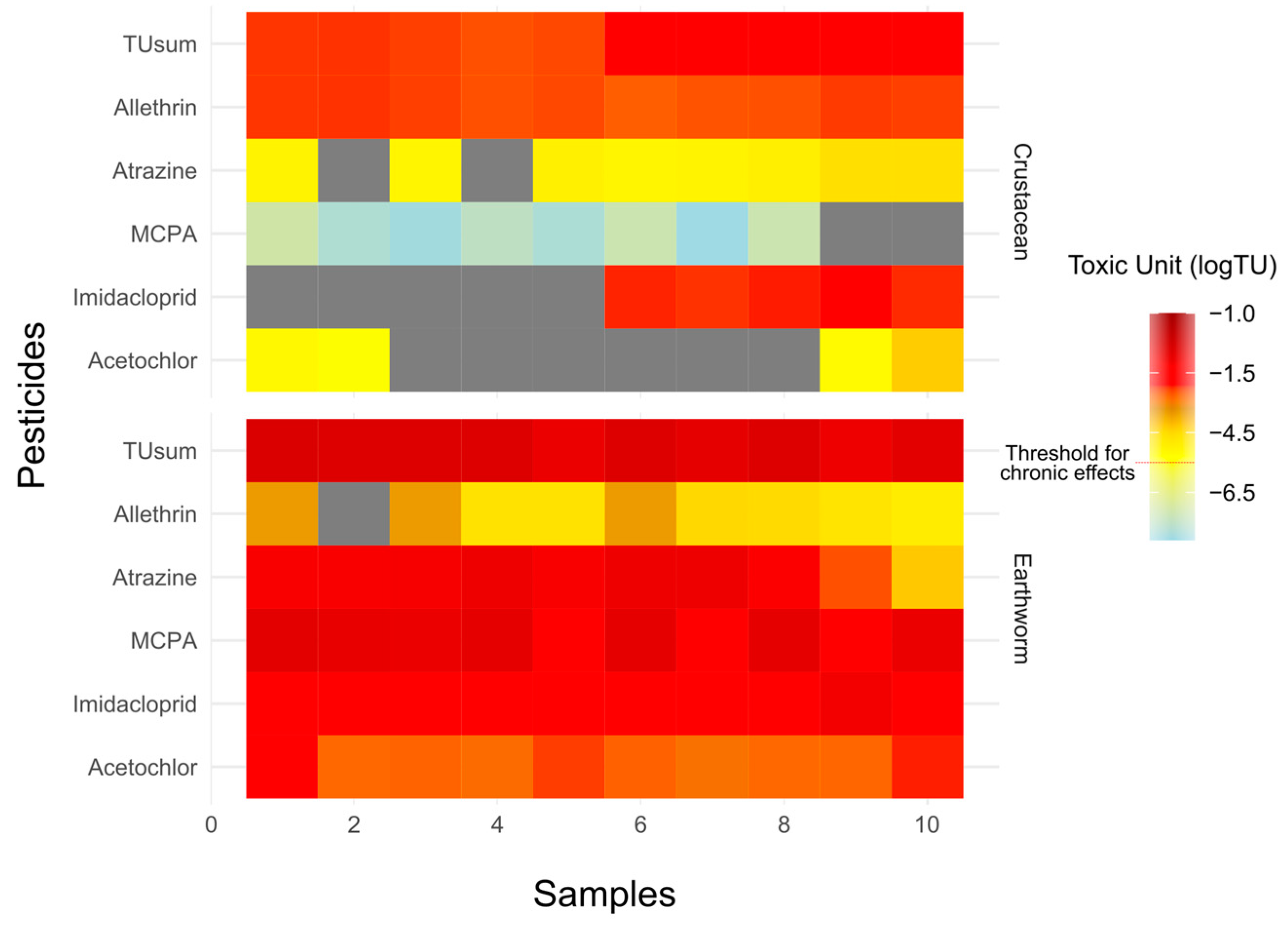
Results of the study showed that all soil samples exceeded the acute and chronic threshold limit for earthworms; 100% of water samples exhibited chronic risk for crustaceans, 10% of samples showed a chronic threshold for algae, and no significant risk was found for fish (Figure 4A, Table S7). In soil samples, MCPA was a highly toxic substance with an average logTU of −0.75 (Figure 5). The average logTUsum value of the soil samples was −0.5. In the case of water samples, the highest logTU was observed for imidacloprid (logTU = −1.8), and the average logTUsum value was −1.6 (Figure 5).
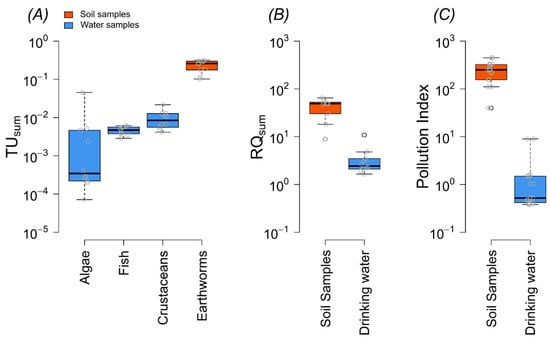
Figure 4.
Characterization of pesticide pollution in terms of toxic units (TUs), risk quotients (RQsum), and the pollution index (PI). For water samples, TUsum is presented for algae, crustaceans, and fish, whereas for soil samples, TUsum is based on LC50/EC50 values of earthworms (A). RQsum (B) and PI (C) are also shown for both water and soil samples.
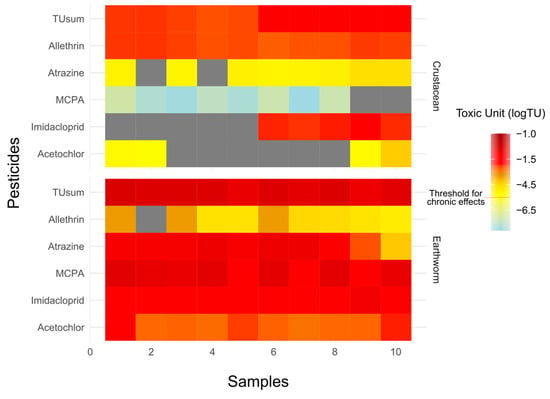
Figure 5.
Heatmap illustrating the toxic units (logTUs) of five emerging pesticides. The intensity of the colour represents the magnitude of the TUs, with darker shades indicating higher toxicity levels. The heatmap provides a comparative overview of the relative toxicity contribution of each pesticide to the total toxicity at different locations. Toxic units are presented only for crustaceans and earthworms.
Risk quotients (RQs) were calculated based on predicted no-effect concentrations (PNECs) to assess ecological risks, and the results showed that the RQ for all sites (water and soil) exceeded the threshold of one; this indicates a high ecological risk. For example, the RQsum of water ranged from 1.6 to 10 and that of soil from 9 to 64 (Figure 4B, Table S8).
According to the results of the pollution index, 10% of the water samples and 100% of the soil samples were classified as highly polluted. The pollution index values in drinking water ranged from 0.3 to 8.9 and in soil samples from 39 to 447 (Figure 4C). In the soil samples, all sites were ranked as highly polluted but in water samples, 60% of the sites were ranked as low-pollution sites, 30% as moderately polluted, and 10% as highly polluted sites.
3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
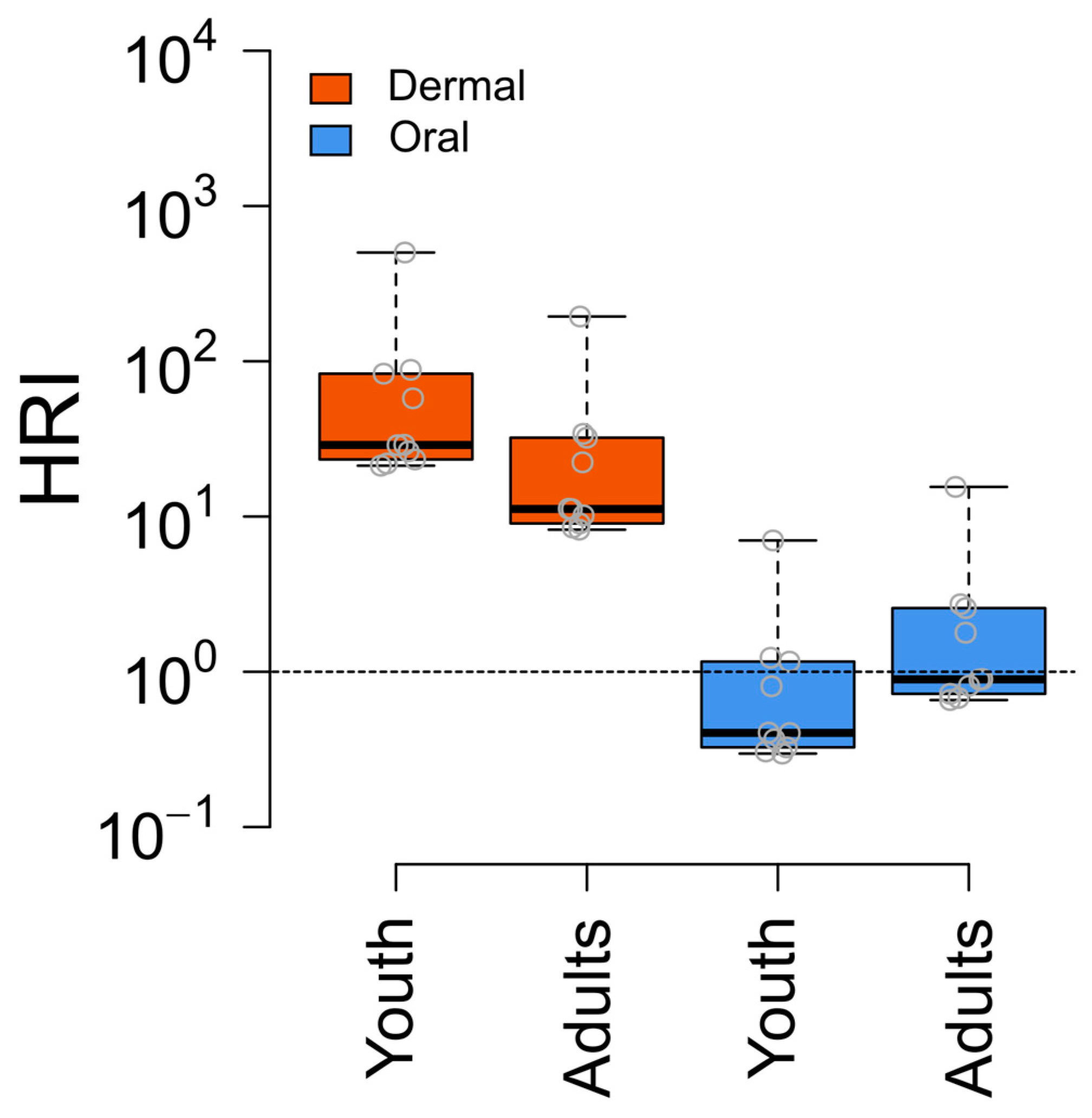
To perform a health risk assessment for dermal and oral exposure to pesticides through water, we calculated the health risk index (HRI). Overall, 100% of the water samples exceeded the threshold limit of one.
The highest HRI value for youth was 501 (mean: 88), whereas for adults, it was 195 (mean: 35). Additionally, approximately 40% of the water samples exceeded the threshold limits for the oral route. The highest HRI value for adults was 15 (mean: 2.6) and for youth, it was seven (mean: 1.2). Acetochlor was the primary contributor to the higher HRI values of the water samples (Figure 6, Table S9 Supporting Information).
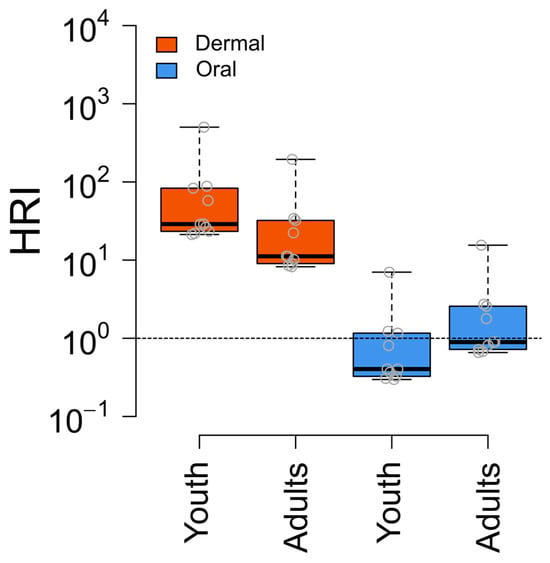
Figure 6.
Health risk for oral and dermal exposure to pesticides through water. The box plot visualizes the distribution of HRI values, where the box boundaries represent the interquartile range (IQR), showing the 25th and 75th percentiles.
4. Discussion
4.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters
In the present study, the physico-chemical parameters of soil and water were analyzed to evaluate the overall health of the soil and the condition of drinking water. Results indicated that 50% of the sites had pH levels exceeding permissible limits, which might be attributed to industrial discharge into the water bodies [60]. Additionally, high EC values, supported by the analysis of inorganic ions such as chlorides, nitrates, and sulphates, suggest high levels of fertilizers in soil, potentially due to runoff from heavily fertilized areas. In water samples, the higher concentration of chloride might be due to industrial, agricultural, and domestic waste. Similar findings have been reported in previous studies [61,62].
4.2. Concentration of Residues of Pesticides
In the present study, we detected elevated concentrations of all the studied pesticides in the soil and water samples. The highest average concentration was observed for MCPA (Figure 2 and Figure 3), a phenoxy acetic acid herbicide used to control broadleaf weeds in horticultural crops and arable lands [63]. MCPA is prone to surface and sub-surface runoff from soil into water, contributing to water quality degradation. According to the European Union (Drinking Water Directive 98/83/EC), the concentration of a single pesticide must not exceed 0.1 µg/L and the total sum of pesticides must not be beyond the limits of 0.5 µg/L [64,65]. However, MCPA is frequently detected in soil, water, and other environmental media, indicating the need for the proper treatment of water and soil to meet these permissible standard limits.
Atrazine (2-chloro-4-ethylamino-6-isopropylamino-1,3,5-triazine) showed the second highest average concentration (Figure 2 and Figure 3). This synthetic herbicide and used to control weeds in crops like corn and sugarcane [66] but poses health risks to humans and ecosystems [67,68]. Atrazine is a persistent organic pollutant with a half-life of 4–57, which affects soil microbial communities essential for maintaining soil health. Numerous studies highlight its harmful effects on soil microorganisms [69,70,71], underscoring the need to assess its ecological risks.
Among insecticides, imidacloprid and allethrin were detected at concentrations ranging from 203 to 891 µg/kg. Imidacloprid, a neonicotinoid, is known for its insecticidal properties [72]. In water and soil, it can undergo various physiological processes, with a half-life of around 40 days under favourable conditions. Microbial activity can also accelerate its degradation, sometimes producing metabolites more harmful than the parent compound [72,73]. In the water samples, the concentration of all pesticides was detected to be lower than in the soil samples.
4.3. Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment
Results of the present study revealed that the toxic unit based on TUsum for earthworms was high and posed acute and chronic toxicity (Figure 4a and Figure 5). The logTUsum ranged from –0.9 to –0.4. The highest TU was due to MCPA, followed by atrazine (Figure 5). MCPA is recognized as a harmful compound for different organisms including earthworms and fish; it is known to be genotoxic and mutates the DNA structure of fish [74].
In the water samples, elevated logTUsum for crustaceans was primarily due to imidacloprid, followed by allethrin. Imidacloprid is known as an extensively used insecticide around the globe [75], and different studies have been conducted to evaluate its risk for aquatic organisms including fish and crustaceans [76,77]. It has been reported that imidacloprid is more dangerous for crustaceans than fish [78]. Allethrin is a pyrethroid insecticide which is naturally present in chrysanthemum flowers [79,80]. It is suggested that excessive use of allethrin is very dangerous for human health and aquatic organisms [81,82].
For TUalgae, the logTUsum was high due to acetochlor, which may cause genotoxicity and is considered as an endocrine disrupter chemical [83]. Several studies have reported the occurrence, distribution, and degradation of acetochlor in water and soil [84,85]. Metabolites of acetochlor can be more toxic to green algae compared to the parent compound [86]. For earthworms, high toxic pressure was attributed to MCPA. Studies have shown that the absorption and degradation of MCPA are higher in earthworms compared to other soil organisms [87].
Risk quotients (RQs) were calculated to assess the overall ecological risk of all pesticides. Risk quotients greater than one indicate high risk. The present study shows that the RQsum of pesticides in all samples exceeded the threshold of one, indicating a high ecological risk to aquatic organisms in the study area. Additionally, the human health risk assessment for water revealed that water and soil samples have the potential to cause carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic effects. The risk index was higher in soil samples compared to water samples.
The findings of this study highlight the significant contamination of soil and water, with elevated physico-chemical parameters and pesticide residues, requiring targeted interventions to mitigate their impact. A combination of remediation strategies could be employed to address these issues. For soil, nature-based remediation solutions could effectively reduce pesticide levels and improve overall soil health, while liming can help neutralize the high pH levels observed. Similarly, for water, the implementation of constructed wetlands, bioreactors, or activated carbon filtration systems can help remove pesticide residues and ensure the water quality meets regulatory standards [88]. Additionally, promoting sustainable agricultural practises, such as integrated pest management (IPM) and organic farming, can reduce the reliance on harmful chemicals while encouraging biopesticides and less persistent alternatives. Regular monitoring and stricter regulations on pesticide usage, along with creating buffer zones between agricultural lands and water bodies, can further minimize contamination risks. These interventions not only support environmental protection but also contribute to the achievement of key Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 6 (Clean Water) and SDG 15 (Life on Land). Raising public awareness about the harmful effects of excessive pesticide use and educating farmers on sustainable practises will be essential for long-term environmental protection and improved public health outcomes.
5. Conclusions
This study highlights significant pesticide contamination in the soil and water systems of Lahore, with MCPA showing higher concentrations in soil and acetochlor in water. Overall, results reveal severe ecological risks, with all soil samples exceeding toxicity thresholds for earthworms and water samples posing chronic risks to crustaceans and algae. The health risk index (HRI) also indicated substantial risks from both oral and dermal exposure, surpassing safety thresholds. This baseline study establishes a strong connection between the emerging pesticides and their effects on non-targeted aquatic and soil organisms, as well as risks to human health. Implementing effective monitoring programmes and regulatory policies is crucial to manage and reduce pesticide residues and protect ecological systems and human health. Therefore, we recommend further investigation with a larger number of pesticides using non-target screening techniques to enhance our understanding of pesticide residues and their potential impacts.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su16219257/s1, Table S1: Sampling locations and collection dates for soil and water samples. Table S2: Details of pesticides and reference values utilized for toxic unit (TU) and risk quotient (RQ) calculations. Table S3: Parameters and corresponding units for human health risk assessment. Table S4: Pesticides and corresponding reference values for calculating risk quotient (RQ). Table S5: Descriptive statistics of physico-chemical parameters from various sample sources. Table S6: Descriptive statistical summary of pesticide concentrations (µg/L) in water and soil samples. Table S7: Descriptive statistical summary of toxic units (TUs) calculated for water and soil samples across different organisms, including algae, fish, crustaceans, and earthworms. Table S8: descriptive statistical summary of risk quotient (RQ) for water and soil samples. Table S9: Descriptive statistical summary of hazard quotient (HQ) for oral and dermal exposure through drinking water. Table S10: Descriptive statistical summary of health risk index (HRI) for oral and dermal exposure of drinking water.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: H.H.I. and A.Q.; study design: H.H.I., A.Q. and M.A.R.; investigation: H.H.I.; chemical analyses: H.H.I., M.A.R. and A.R.; formal analysis: H.H.I. and N.S.; resources: S.R.A. and A.Q.; interpretation of results: H.H.I., N.S., M.A.R., M.A., A.R. and A.Q.; original draft: H.H.I.; review and editing: all, visualization: H.H.I. and N.S.; supervision: A.Q. and S.R.A.; funding acquisition: A.Q. and S.R.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Stolte, J.; Tesfai, M.; Oygarden, L.; Kvaerno, S.; Keizer, J.; Verheijen, F.; Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Hessel, R. Soil Threats in Europe: Status, Methods, Drivers and Effects on Ecosystem Services: Deliverable 2.1 RECARE Project. 2016. Available online: https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/content/soil-threats-europe-status-methods-drivers-and-effects-ecosystem-services (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Tariq, M.I.; Afzal, S.; Hussain, I. Pesticides in shallow groundwater of bahawalnagar, Muzafargarh, DG Khan and Rajan Pur districts of Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, J.; Syed, J.H.; Mahmood, A.; Ali, U.; Rehman, M.Y.A.; Malik, R.N.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Investigation of organochlorine pesticides from the Indus Basin, Pakistan: Sources, air-soil exchange fluxes and risk assessment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 497–498, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, A.K.; Kumar, A. Organochlorine pesticides in the surface waters from Sharda River Region, Uttar Pradesh-India. SIJ Trans. Adv. Space Res. Earth Explor. 2013, 1, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, M.A.; Naqvi, S.N.; Azmi, M.A.; Aslam, M. Effect of pesticide residues on health and different enzyme levels in the blood of farm workers from Gadap (rural area) Karachi-Pakistan. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, J.H.; Malik, R.N. Occurrence and source identification of organochlorine pesticides in the surrounding surface soils of the Ittehad Chemical Industries Kalashah Kaku, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, N.C.; Khan, K.; Uhllah, G.; Teglas, M.B. The emergence and maintenance of vector-borne diseases in the khyber pakhtunkhwa province, and the federally administered tribal areas of pakistan. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, F. Dengue Fever (DF) in Pakistan. Asia Pac. Fam. Med. 2011, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finckh, S.; Beckers, L.M.; Busch, W.; Carmona, E.; Dulio, V.; Kramer, L.; Krauss, M.; Posthuma, L.; Schulze, T.; Slootweg, J.; et al. A risk based assessment approach for chemical mixtures from wastewater treatment plant effluents. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Fang, W.; Krauss, M.; Brack, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, X. Screening hundreds of emerging organic pollutants (EOPs) in surface water from the Yangtze River Delta (YRD): Occurrence, distribution, ecological risk. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munz, N.A.; Burdon, F.J.; de Zwart, D.; Junghans, M.; Melo, L.; Reyes, M.; Schonenberger, U.; Singer, H.P.; Spycher, B.; Hollender, J.; et al. Pesticides drive risk of micropollutants in wastewater-impacted streams during low flow conditions. Water Res. 2017, 110, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschet, C.; Wittmer, I.; Simovic, J.; Junghans, M.; Piazzoli, A.; Singer, H.; Stamm, C.; Leu, C.; Hollender, J. How a complete pesticide screening changes the assessment of surface water quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5423–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finckh, S.; Carmona, E.; Borchardt, D.; Buttner, O.; Krauss, M.; Schulze, T.; Yang, S.; Brack, W. Mapping chemical footprints of organic micropollutants in European streams. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, G.F.; Drage, D.S.; Thompson, K.; Eaglesham, G.; Mueller, J.F. Emerging contaminants (pharmaceuticals, personal care products, a food additive and pesticides) in waters of Sydney estuary, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liess, M.; Liebmann, L.; Vormeier, P.; Weisner, O.; Altenburger, R.; Borchardt, D.; Brack, W.; Chatzinotas, A.; Escher, B.; Foit, K.; et al. Pesticides are the dominant stressors for vulnerable insects in lowland streams. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, B.; Ollivier, P.; Togola, A.; Baran, N.; Ghestem, J.P. Screening of French groundwater for regulated and emerging contaminants. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 518–519, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Laak, T.L.; Puijker, L.M.; van Leerdam, J.A.; Raat, K.J.; Kolkman, A.; de Voogt, P.; van Wezel, A.P. Broad target chemical screening approach used as tool for rapid assessment of groundwater quality. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 427–428, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, F.; Ou, J. Global pesticide consumption and pollution: With China as a focus. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 1, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.T. Sustaining the Earth, Thompson Learning. J. Inc. Pac. Grove Calif. 2004, 9, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shahawi, M.S.; Hamza, A.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Al-Saggaf, W.T. An overview on the accumulation, distribution, transformations, toxicity and analytical methods for the monitoring of persistent organic pollutants. Talanta 2010, 80, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Musstjab-Akber-Shah Eqani, S.; Malik, R.N.; Alamdar, A.; Faheem, H. Status of organochlorine contaminants in the different environmental compartments of Pakistan: A review on occurrence and levels. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.; Shahid, N.; Liess, M. Revealing the cascade of pesticide effects from gene to community. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 917, 170472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, N.; Becker, J.M.; Krauss, M.; Brack, W.; Liess, M. Adaptation of Gammarus pulex to agricultural insecticide contamination in streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemm, J.U.; Venohr, M.; Globevnik, L.; Stefanidis, K.; Panagopoulos, Y.; van Gils, J.; Posthuma, L.; Kristensen, P.; Feld, C.K.; Mahnkopf, J.; et al. Multiple stressors determine river ecological status at the European scale: Towards an integrated understanding of river status deterioration. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machate, O.; Dellen, J.; Schulze, T.; Wentzky, V.C.; Krauss, M.; Brack, W. Evidence for antifouling biocides as one of the limiting factors for the recovery of macrophyte communities in lakes of Schleswig-Holstein. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, R.B.; Bundschuh, M.; Rouch, D.A.; Szocs, E.; von der Ohe, P.C.; Pettigrove, V.; Schulz, R.; Nugegoda, D.; Kefford, B.J. Effects of pesticide toxicity, salinity and other environmental variables on selected ecosystem functions in streams and the relevance for ecosystem services. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 415, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, J.J.; Wiberg-Larsen, P.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Monberg, R.J.; Kronvang, B. Impacts of pesticides and natural stressors on leaf litter decomposition in agricultural streams. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 416, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beketov, M.A.; Kefford, B.J.; Schafer, R.B.; Liess, M. Pesticides reduce regional biodiversity of stream invertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11039–11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, T.G.; Bryant, D.M.; Cole, L.; Crick, H.Q.P. Linking agricultural practice to insect and bird populations: A historical study over three decades. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 39, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R. The decline of moths in Great Britain: A review of possible causes. Insect. Conserv. Diver. 2013, 6, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, M.L.; Rivetti, N.G.; Morillo, D.O.; Bertrand, L.; Ame, M.V.; Bistoni, M.A. Multi-biomarker responses in fish (Jenynsia multidentata) to assess the impact of pollution in rivers with mixtures of environmental contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.B.; Huang, H.; Chen, C.; Fu, Z.Q.; Xu, H.Q.; Tan, S.D.; She, W.; Liao, X.L.; Tang, J.W. Traditional symbiotic farming technology in China promotes the sustainability of a flooded rice production system. Sustain. Sci. 2017, 12, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauco, S.; Eguren, G.; Heinzen, H.; Defeo, O. Effects of herbicides and freshwater discharge on water chemistry, toxicity and benthos in a Uruguayan sandy beach. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 70, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, M.I.; Afzal, S.; Hussain, I.; Sultana, N. Pesticides exposure in Pakistan: A review. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eqani, S.A.; Malik, R.N.; Mohammad, A. The level and distribution of selected organochlorine pesticides in sediments from River Chenab, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2011, 33, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Rashid, W.; Tulcan, R.X.S.; Huang, H. Use, exposure, and environmental impacts of pesticides in Pakistan: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 43675–43689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Kalsoom; Khan, S.; Li, G.; Ali, M.; Nazneen, S.; Ali, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Samlullah; Ihsanullah. Exposure to multiple pesticides in drinking water and potential health risks: A case study of selected districts from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, S.M.; Ray, A.K.; Barghi, S. Water pollution and agriculture pesticide. Clean. Technol. 2022, 4, 1088–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakistan Bureau of Statistics. Brief Regarding Census-2017. Available online: https://www.pbs.gov.pk/content/brief-census-2017 (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Radojevic, M.; Bashkin, V.N. Practical Environmental Analysis; Royal Society of Chemistry: Edinburgh, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, S.R.; Shah, M.H.; Shaheen, N.; Khalique, A.; Manzoor, S.; Jaffar, M. Multivariate analysis of selected metals in tannery effluents and related soil. J. Hazard Mater. 2005, 122, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, P. Handbook of Environmental Analysis: Chemical Pollutants in Air, Water, Soil, and Solid Wastes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bartošová, A.; Michalíková, A.; Sirotiak, M.; Soldán, M. Comparison of two spectrophotometric techniques for nutrients analyses in water samples. Res. Pap. Fac. Mater. Sci. Technol. Slovak Univ. Technol. 2012, 20, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.; Shafiq, M.; Chotana, G. Distribution of Heavy Metals in the Soils Associated with the Commonly Used Pesticides in Cotton Fields. Scientifica 2016, 2016, 7575239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Guo, L.L.; Xu, W.H.; Li, X.D.; Lee, C.S.L.; Ding, A.J.; Wang, T. Organochlorine pesticides in the atmosphere of Guangzhou and Hong Kong: Regional sources and long-range atmospheric transport. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3889–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, J.B. Measurement of pollutant toxicity to fish. II. Utilizing and applying bioassay results. Water Res. 1970, 4, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaj, E.; von der Ohe, P.C.; Grote, M.; Kuhne, R.; Mondy, C.P.; Usseglio-Polatera, P.; Brack, W.; Schafer, R.B. Organic chemicals jeopardize the health of freshwater ecosystems on the continental scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9549–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandie, F.J.; Krauss, M.; Beckers, L.M.; Massei, R.; Fillinger, U.; Becker, J.; Liess, M.; Torto, B.; Brack, W. Occurrence and risk assessment of organic micropollutants in freshwater systems within the Lake Victoria South Basin, Kenya. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 714, 136748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckers, L.M.; Busch, W.; Krauss, M.; Schulze, T.; Brack, W. Characterization and risk assessment of seasonal and weather dynamics in organic pollutant mixtures from discharge of a separate sewer system. Water Res. 2018, 135, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NORMAN. Network of Reference Laboratories, Research Centres and Related Organisations for Monitoring of Emerging Environmental Substances. Available online: https://www.norman-network.net/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Nimick, D.A.; Moore, J.N. Prediction of Water-Soluble Metal Concentrations in Fluvially Deposited Tailings Sediments, Upper Clark Fork Valley, Montana, USA. Appl. Geochem. 1991, 6, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTDR. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Case Studies in Environmental Medicine. 1997. Available online: http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/HEC/CSEM/csem.html (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Naz, A.; Mishra, B.K.; Gupta, S.K. Human Health Risk Assessment of Chromium in Drinking Water: A Case Study of Sukinda Chromite Mine, Odisha, India. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhao, D.Y.; Jia, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Cheng, S.P. Preliminary risk assessment of trace metal pollution in surface water from Yangtze River in Nanjing Section, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.T.; Ara, J.; Muhammad, S.; Khan, S.; Tariq, S. Health risk assessment via surface water and sub-surface water consumption in the mafic and ultramafic terrain, Mohmand agency, northern Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 118, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Huang, H.; Xia, F.; Liu, Y.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Mei, K. Risk analysis of heavy metal concentration in surface waters across the rural-urban interface of the Wen-Rui Tang River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Khan, H.; Zakir, S.; Ihsanullah; Khan, S.; Khan, A.A.; Wei, L.; Wang, T. Health risks associated with heavy metals in the drinking water of Swat, northern Pakistan. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, Z. Risk assessment of dissolved trace metals in drinking water of Karachi, Pakistan. Bull. Environ. Contam Toxicol. 2011, 86, 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. 2024. Available online: http://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Naveed, S.; Bhatti, I.; Ali, K. Membrane technology and its suitability for treatment of textile waste water in Pakistan. J. Res. 2006, 17, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Aftab, T.; Shafiq, T.; Khan, B.; Chaudhry, M.N. Physicochemical properties, contamination and suitability of canal water for irrigation, Lahore branch Pakistan. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2011, 12, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A. Ecological studies of the river Padma at Mawa Ghat, Munshiganj. I. Physico-chemical properties. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2004, 7, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, D.; Shiu, W.-Y.; Lee, S.C. Handbook of Physical-Chemical Properties and Environmental Fate for Organic Chemicals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, S.; Reade, J.P.; Burn, A.; Zappala, S. Agricultural chemicals and the environment: Issues and potential solutions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 43, 45–93. [Google Scholar]
- CEC; CoTec. Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the quality of water intended for human consumption. Off. J. L 1998, 330, 32–54. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Fang, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Wang, Q.; Ma, W. Toxicological effects, environmental behaviors and remediation technologies of herbicide atrazine in soil and sediment: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Araújo, R.; Bernardes, R.C.; Martins, G.F. A mixture containing the herbicides Mesotrione and Atrazine imposes toxicological risks on workers of Partamona helleri. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasi, H.; Takdastan, A.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Babaei, A.A.; Tahmasebi Birgani, Y.; Cheraghian, B.; Saki, A.; Jorfi, S. Spatial distribution, ecological and health risk assessment and source identification of atrazine in Shadegan international wetland, Iran. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.H.; Yao, X.F.; Li, X.X.; Zhu, L.S.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, J. Responses of Soil Microbial Community to Herbicide Atrazine Contamination. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, C.L.; Rong, Q.; Li, C.Z.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.X.; Liu, X.T. Effect of two organic amendments on atrazine degradation and microorganisms in soil. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2020, 152, 103564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, A.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Qin, B.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Y. Impact of atrazine on soil microbial properties: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, K.K. Sorption and degradation of imidacloprid in soil and water. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2006, 41, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouchaud, J.; Gustin, F.; Wauters, A. Soil biodegradation and leaf transfer of insecticide imidacloprid applied in seed dressing in sugar beet crops. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 53, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokan, K.; Syberg, K.; Jensen, K.; Rank, J. Genotoxic potential of two herbicides and their active ingredients assessed with comet assay on a fish cell line, epithelioma papillosum cyprini (EPC). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2013, 76, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C. Insecticide Factsheet: Imidacloprid, Northwest Coalition for Alternatives to Pesticides/NCAP. J. Pestic. Reform 2001, 21, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Printes, L.B.; Callaghan, A. A comparative study on the relationship between acetylcholinesterase activity and acute toxicity in Daphnia magna exposed to anticholinesterase insecticides. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemec, A.; Drobne, D.; Tisler, T.; Trebse, P.; Ros, M.; Sepcic, K. The applicability of acetylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase in Daphnia magna toxicity test. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 144, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobne, D.; Blazic, M.; Van Gestel, C.A.; Leser, V.; Zidar, P.; Jemec, A.; Trebse, P. Toxicity of imidacloprid to the terrestrial isopod Porcellio scaber (Isopoda, Crustacea). Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatheyus, A.; Selvam, A.G. Synthetic pyrethroids: Toxicity and biodegradation. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 1, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, N. Discovery and development of pyrethroid insecticides. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2019, 95, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.K. Children’s exposures to pyrethroid insecticides at home: A review of data collected in published exposure measurement studies conducted in the United States. Int. J Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2964–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodidasu, A.; Satya, H.V.; Lavudi, K.; Thirunavukarasou, A.; Patnaik, S.; Penchalaneni, J. Effect of Probiotics on Allethrin Toxicity: An In Vivo Study Using Zebrafish Model. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 13, 431. [Google Scholar]
- Rollerova, E.; Gasparova, Z.; Wsolova, L.; Urbancikova, M. Interaction of acetochlor with estrogen receptor in the rat uterus. Acetochlor--possible endocrine modulator? Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2000, 19, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yokley, R.A.; Mayer, L.C.; Huang, S.B.; Vargo, J.D. Analytical method for the determination of metolachlor, acetochlor, alachlor, dimethenamid, and their corresponding ethanesulfonic and oxanillic acid degradates in water using SPE and LC/ESI-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3754–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnac, T.; Jeannot, R.; Mouvet, C.; Baran, N. Determination of oxanilic and sulfonic acid metabolites of acetochlor in soils by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 2002, 957, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Sheng, G.; Liu, W. Degradation and detoxification of acetochlor in soils treated by organic and thiosulfate amendments. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zaprasis, A.; Liu, S.J.; Drake, H.L.; Horn, M.A. The earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa stimulates abundance and activity of phenoxyalkanoic acid herbicide degraders. ISME J. 2011, 5, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Arslan, M.; Müller, J.A.; Shabir, G.; Islam, E.; Tahseen, R.; Anwar-ul-Haq, M.; Hashmat, A.J.; Iqbal, S.; Khan, Q.M. Floating treatment wetlands as a suitable option for large-scale wastewater treatment. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).