Abstract
The swift adoption of digitalization and transformation within enterprises and their operations had commenced prior to the onset of COVID-19, characterized by the shift towards Industry 4.0 and subsequently progressing towards Industry 5.0. However, mandated restrictions significantly amplified the necessity and drive to utilize digital tools for both businesses and consumers. New opportunities previously not utilized have arisen yet are hand in hand with several risks linked to the use of these new digital tools. The bioeconomy sector is not an exception. The study aims to consider the sector representatives’ opinions on the significance of the risks related to digitalization. The empirical results of this study stem from a survey of enterprises in the bioeconomy sector carried out in 2020 and 2021 in Latvia. The research results prove that there are many factors influencing the development of digitalization. The results notably affirm that both entrepreneurs and employees in SMEs recognize the considerable importance of these risks, particularly emphasizing the significance of security and technology risks. While the Chi-Square Test of Independence indicates a notable association between risk evaluation scores and the education level of respondents before the COVID-19 outbreak in 2020, this association diminishes in 2021. Contrary to the hypothesis that individuals with higher education levels are more attentive to risks, the evidence shows inconsistency in their perception, particularly regarding professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools and other risk categories. However, the relationship between higher education levels and the significance of risks pertaining to security risks, technology risks, and the skills of the clients to use digital tools is partly affirmed.
1. Introduction
Digitalization had started well before COVID-19, described as a transition to Industry 4.0 and later on to Industry 5.0, but COVID-19 had led to more rapid digitalization processes as a response to social distancing measures [1]. The use of new tools and the change in customer behaviour has led to adapting new business models in many enterprises.
“Digitalization” originally refers to the continuous evolution and change in particular processes and procedures based on digital technologies [2] to transform and enhance business operations, services, or processes. It involves leveraging digital tools, technologies, and data to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and create new opportunities for innovation and growth.
Digitalization as a process is strongly linked with the concepts of Industry 4.0 and 5.0. Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, represents a significant shift in manufacturing and production processes driven by the integration of digital technologies [3]. It builds upon the previous industrial revolutions and leverages advancements in areas such as automation, data exchange, Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and cyber-physical systems [4]. A theoretical continuation of Industry 4.0 is Industry 5.0—an evolving concept that seeks to complement the technological advancements of Industry 4.0 with a stronger emphasis on human collaboration and integration. While Industry 4.0 laid the foundation for the digital transformation of industries, emphasizing automation and interconnectedness, Industry 5.0 builds upon this foundation by recognizing the importance of human skills, creativity, and collaboration in conjunction with advanced technologies to drive innovation and productivity. Both Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0 aim to revolutionize manufacturing, albeit with different focal points: Industry 4.0 emphasizes technological integration and automation, while Industry 5.0 seeks to combine technological advancements with a more prominent role for human workers in the manufacturing process. Innovation related to the technological advances of entrepreneurship is essential in Industry 4.0, and the symbiosis of technological and human-oriented advances are at the heart of Industry 5.0 [4,5,6].
Internationalization, digitalization, and sustainability are three key growth paths for enterprises [7]. A higher degree of digitalization in new ventures’ product/service offerings and their processes can lead to a faster entering time in the market and the ability to rapidly scale the business [8]. Digitalization can accelerate, for instance, data management, knowledge generation, and innovation processes to achieve the transition to a more efficient and sustainable production [9].
Digitally connected global firms reap the benefits of many new opportunities, but business leaders cannot underestimate the associated risks [10]. Digital technologies can help reduce costs and save time and resources [11], yet smaller manufacturers need particular competencies like change management and strategic planning for digitalization to achieve a certain level of maturity in information, digital, operational, and cyber aspects [12,13]. Despite the transformation of a digital business platform, many SMEs have stumbled in the middle road [14]. Although SMEs are aware and can benefit significantly from digital systems, the time, skills, and finances required to develop SME-specific systems are prohibitive [15].
At the same time, Amaral and Pecas [16] argued that not all types of digitalization are aligned with Industry 4.0-related measures; simply digitalizing processes (although relevant) might not be as impactful for the companies as re-engineering (the same) processes upon digitalization. For this, we defend that a process digitalization should encompass Industry 4.0 design principles and a human centric orientation to be considered an Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0 oriented digitalization.
In discussions about digital transformation, the focus tends to be on the integration of digital strategies and technology within the company. This can encompass a wide range of initiatives, including the introduction of new devices enabling remote work for employees, the development of mobile apps to enhance internal communication or paperless workflows, and the adoption of digital data collection solutions [17]. The kind of shift is, to a great extent, subject to risks that have been measured.
While the new coronavirus has devastated the organized world, it has also created an opportunity for new tides of transformation to emerge (…), namely the shift from offline to online digital media [18].
At the same time, there are many questions related to digitalization, e.g., Rajnai and Kocsis (2017) address an issue—are we facing a reduction in employment via automation, rendering the human workforce uncompetitive with the technologies used [19].
Risk signifies a probability of a negative occurrence caused by external or internal vulnerabilities that threaten business activities [10]. Recent research findings indicate that deficiencies in risk culture, as well as the strained market for IT experts, are the major obstacles with respect to the implementation of cyber risk management in SMEs and that these challenges are similar across countries [20].
Due to the resulting high risks, SMEs neglect the chances of digitalization and lose competitiveness. To start with, they need a maturity assessment model that can help them understand their level of readiness to implement aspects [21].
This study focuses on the digitalization of enterprises working in the sectors of the bioeconomy. Bioeconomy can be defined as an economy where the fundamental components for materials, chemicals, and energy originate from renewable biological resources [22]. Empowered by digital solutions, bioeconomy has made substantial advancements in recent years towards realizing the enduring objective of transitioning from a conventional fossil-fuel-based economy to one founded on a circular bioeconomy [23].
Bioeconomy includes agriculture, forestry, fisheries and aquaculture, food industry, and wood industry, as well as parts of chemical, biotechnological, and energy sectors. These sectors serve as the bedrock for national economic development, bolster rural sustainability, and hold considerable potential for generating well-paying employment opportunities [24].
Digitalization in the bioeconomy has shifted onwards during COVID-19 [25], yet there are still many issues to be researched, especially concerning the risks related to digitalization.
The information available in the risk mitigation strategy literature is generally descriptive rather than specific but is still useful for bioeconomy. Also, McCormik (2013) states that in order to facilitate an understanding of the existing bioeconomy and the transition to an advanced bio-based economy, it is necessary to examine it more in-depth [23]. There is increasing interest in the potential opportunities for digitalization at a broader bioeconomy scale; however, there is limited knowledge of the potential barriers to a digital bioeconomy [26]. The previously analyzed research papers have not concentrated on evaluating the risks related to digitalization in the bioeconomy sector, especially from the employers’ perspective. Also, there is no research found on evaluating the digital risk perception from the age and education level perspective. Therefore, the paper fills the research gaps identified to promote a clear understanding of the risk perception among entrepreneurs in the bioeconomy sector.
The aim of the study is to group the factors influencing the development of digitalization in the bioeconomy sector and to consider the sector representatives’ opinions on the significance of the risks related to digitalization.
Based on the findings arising from the previous research works, policy documents, and statistical analysis, the authors introduced the following research questions:
RQ1: What are the main factors influencing the development of digitalization?
RQ2: What are the main risks that the entrepreneurs and employees of the SMEs consider?
To address the research questions, four hypotheses were set. They were based on the recent literature studies without finding answers to these issues. Therefore, the authors considered it interesting to research the following aspects:
H1.
Entrepreneurs and employees of SMEs consider the risks related to digitalization significant;
H2.
Security and Technology risks are considered to be the most significant;
H3.
People with higher education levels tend to consider the risks to be more significant;
H4.
Older people consider the risks related to digitalization to be more significant. The following limitations have been set for the research.
2. Materials and Methods
This study analyzes the results of a survey aimed at assessing the process of digitalization in the enterprises of the bioeconomy sector and the risks related to it. The survey was carried out in Latvia in 2 phases, in 2020 (n = 150) and 2021 (n = 171), of entrepreneurs and employees of the enterprises working in the sector of bioeconomy, which allows for the identification of the digitalization tools used by these enterprises, their motivation in moving towards the digital transformation, and the risks they have encountered. The study involves a literature review supplemented with an analysis of secondary data obtained from the Eurostat database. There are around 124,58 thousand people in Latvia employed in the bioeconomy sector; thus, the sample size was defined to cover a representative sample of the SME employers and employees involved in management activities in the bioeconomy sector in the survey different age groups were represented.
Education level was divided into three groups—secondary education, higher education (bachelor), and masters’ degree (no representative sample was reached regarding the persons with primary education or Ph.D. degree, yet this target group was also not intended to be specifically researched). From all respondents (in 2020 and 2021), 53 had secondary education; 145 had higher education; and 119 had a master’s- or Ph.D.-level education. Considering the age groups, from all respondents, 16 were below 25 years old; 59 were from 26 to 35 years old; 56 were 36 to 45 years old; 66 were 46 to 55 years old; 30 were 56 to 65 years old; and 3 respondents were above 65 years of age.
The data were gathered electronically and represent the overall range of enterprises in Latvia related to the bioeconomy. The surveys about the importance of digitalization of the bio-based enterprises in Latvia in 2020 and 2021 were the same, yet a section of COVID-19-related questions was added for the survey of 2021.
Taking into account the risks assessed with the survey, it is considered that the results can be applied to other countries having the same development level in digitalization.
A cross-tabulation analysis was performed to evaluate the risks by their significance. The Chi-Square Test of Independence was used to determine if there is a significant association or relationship between two categorical variables (risks and education level). The Chi-Square Test of Independence is a nonparametric test that determines whether there is an association between categorical variables (i.e., whether the variables are independent or related) [27]. And the correlation analysis was carried out to assess relations between education and age and the analyzed risk groups using Kendall’s rank correlation and Spearman’s rank correlation. Kendall’s rank correlation coefficient and Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient are both non-parametric methods used to measure the strength and direction of association between two variables. They are used when the data are in the form of ranked or ordinal variables or when the assumptions of parametric correlation methods like Pearson’s correlation cannot be met.
The performed analysis allowed for testing the hypotheses set for the research.
3. Results and Findings
The current research findings respond to the overall suggestions that risks in digitalization are very important. There is a necessity to evaluate the perception of risks concerning the age and education level of respondents. Risk can be understood as uncertainty, either regarding the probability of the occurrence of certain facts that may directly or indirectly affect the company or regarding the moment when such facts may manifest themselves [28].
Following research question 2, “What are the main risks the entrepreneurs and employees of the SMEs consider?” among questions regarding the digitalization status of the enterprises, questions about the risks encountered and their significance were asked to the respondents. The limitations were set, and the risks were divided into five groups:
Technological risks:
- Security risks;
- Technology risks;
Social risks:
- 3.
- Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools;
- 4.
- Skills of the clients to use digital tools;
Other risks’ categories:
- 5.
- Other risks.
The risk groups were identified based on the theoretical analysis, taking into account that the security risks and the technology risks were among the most often mentioned. Cybersecurity plays a critical role in digital transformation, safeguarding enterprises from cyber threats while shifting to digital processes. The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the necessity of strong cybersecurity measures, given the increased risks posed by rapid digitalization. Organizations embracing digital transformation need to prioritize cybersecurity to ensure a smooth transition and protect against disruptions caused by cyber-attacks [29,30,31].
In addition, the researchers noted that social risks should be considered, especially the professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees in using digital tools [32] and the skills of the clients in using digital tools. Since the challenges to using digital tools and the skills in using digital tools might be related to the age and education level of the respondents, these two factors were also considered in the survey. A category of “Other risks” was also placed in the survey in order not to limit the answers.
The risks were assessed on a 5-point Likert scale from highly significant to insignificant. To estimate the risk perception with respect to the education level and the age of the respondents, a cross-tabulation analysis was carried out (Table A1, Table A2, Table A3 and Table A4 in Appendix A).
To test the hypotheses, the results of the survey were analyzed within the evaluated risk groups and the significance levels (Table 1); the total number of risks was assessed as “Significant”, or a sum of risks in the groups “Highly significant”, “Significant”, and “Moderately significant” was calculated. This calculation provides an overall measure of the level of significance across the different risk groups. In 2020, the “Total significant” percentage for security risks was 80.5%. This means that the percentages of “Highly significant” (28.9%), “Significant” (30.9%), and “Moderately significant” (20.8%) categories were added together to give the “Total significant” value.

Table 1.
The evaluation results of risks by their significance, %.
In 2021, the “Total significant” percentage for security risks was 81.2%, technology risks had a “Total significant” percentage of 84.7%, professional challenges related to digital tools had a “Total significant” percentage of 78.8%, and the skills of clients to use digital tools had a “Total significant” percentage of 80.0%.
Overall, technology risks had the highest level of significance in both years, while security risks and professional challenges also remained significant. The skills of clients to use digital tools showed relatively consistent significance levels between the two years. Thus, these results indicate that H1 and H2 can be approved. More information is reflected in Table 1.
Figure 1 reflects cross-tabulation analysis for the evaluation results of security risks with respect to the education level of the respondents, thus aiming to test H3: People with higher education levels tend to consider the risks more significant.
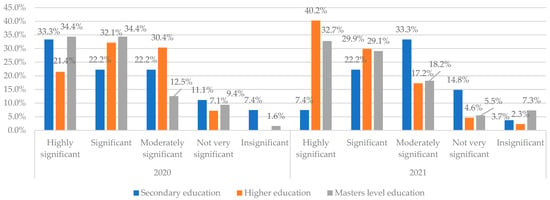
Figure 1.
Consideration of Security risks referring to the education level in 2020 and 2021. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
The results reflect changes between the evaluation results in 2020 and 2021—in 2021, the security risks are assessed as “Highly significant”, especially by the group of respondents with higher education and master’s degrees. It may indicate that in 2020, many enterprises did not face the security risks that arrived with intensified digitalization during the COVID-19 period 2020. A different tendency can be observed for the respondents with secondary education—in 2020, 33.3% of respondents considered security risks to be “Highly significant”, while in 2021, only 7.4% of respondents considered security risks at this education level to be “Highly significant”, which might be linked to the digital tools they use in their work and the level of responsibility they take in the enterprise.
Figure 2 provides insights into how the perceived level of security risks varies across different levels of education. The percentages are given separately for 2020 and 2021, allowing for a comparison of changes over time. A majority of the respondents assessed technological risks as “Significant” from 2020 to 2021; there seems to be a change in the risk perception in the group with secondary education. Overall, they consider such risks as less significant, but the % of respondents determining this risk group as “Highly significant” increased in the group with higher education from 21.4% to 35.6%.
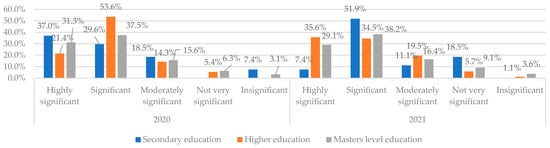
Figure 2.
Consideration of Technology risks referring to the education level in 2020 and 2021. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
The risk of professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools is assessed in Figure 3, which reflects that “Significant” professional challenges have been encountered in the group of respondents with secondary education—51.9% assessed these risks as “Significant” compared to 29.6% in 2020. This could be linked to new digital tools introduced in 2020 and 2021, and there could be challenges for this group of those of lower education levels to master new tools since their digital skills might not be sufficient. Yet they do not consider this risk to be “Highly significant”, perhaps indicating that the digital skills could be a hindering and not a limiting factor for them to use digital tools.
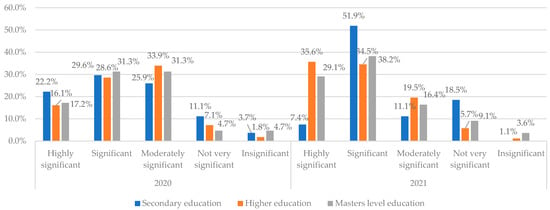
Figure 3.
Consideration of Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools referring to the education level in 2020 and 2021. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
More than 50% of the respondents of all groups (leading to more than 66% of the respondents with higher education) consider that the skills of the clients in using digital tools are highly significant or significant (Figure 4).
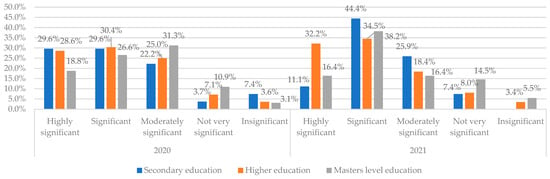
Figure 4.
Consideration of Skills of the clients to use digital tools referring to the education level in 2020 and 2021. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
Table 2 reflects The Chi-Square Test of Independence results to determine if there is a significant association or relationship between two categorical variables (risks and education level.

Table 2.
Consideration of the risk groups referring to the education level. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
The results of the test indicate (Table 2) that in 2020, the risk evaluation scores in the groups “Security risks”, “Technology risks”, and “Skills of the clients to use digital tools” are significantly associated with the education level of the respondents, but in 2021, none of the responses are associated with education level. Thus, H3: People with higher education levels tend to consider the risks to be more significant can be rejected for “Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools” and “Other” risk groups, and it can be partly approved for the “Security risks”, “Technology risks”, and “Skills of the clients to use digital tools” groups.
Since the data reflected differences in risk evaluation results concerning the education level, the authors concluded analysis on the differences considering the risks, taking into account the age groups of respondents and testing H4: Older people consider the risks related to digitalization to be more significant. Figure 5 reflects the result for the Security risks group—overall, more consideration for security risks is given by the respondents of higher age, especially in 2021, where the age groups of 45–55 and 56–65 year-olds assessed security risks as “Highly significant”.
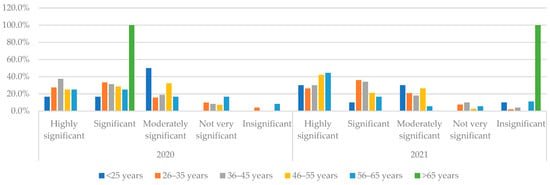
Figure 5.
Consideration of Security risks referring to the age of respondents in 2020 and 2021. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
Figure 6 reflects the results with respect to Technology risks that are considered especially high by the youngest group of respondents— “Significant” in 2020 by 66.7% of respondents under 25 years and “Highly significant” by 50% of respondents from this age group.
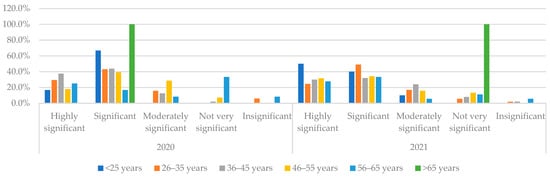
Figure 6.
Consideration of Technology risks referring to the age of respondents in 2020 and 2021. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
Professional challenges (Figure 7) are considered “Significant” and “Moderately significant” by most age groups, with an overall higher significance given to this group in 2021 by the age groups of 26–65 year-olds and less significance given to younger respondents.
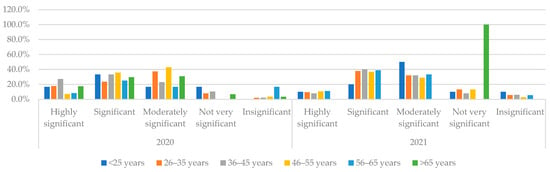
Figure 7.
Consideration of Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools referring to the age of respondents in 2020 and 2021. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
The consideration of the clients in using digital skills (Figure 8) was assessed as “Highly significant” by 40% of 46–55-year-olds in 2021 and “Significant” by the largest share of 26–45-year-olds.
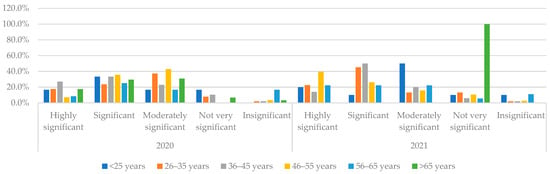
Figure 8.
Consideration of Skills of the clients to use digital tools referring to the age of respondents in 2020 and 2021. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
The results of the Chi-Square Test of Independence (Table 3) indicate that in 2020, all risk evaluation responses for the risk groups (except “Other”) are significantly associated with the age of the respondents. And in 2021, all but “Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools” and “Other” risks groups are associated with the age of the respondents.

Table 3.
Consideration of the risk groups referring to the age of respondents. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
H4: Older people consider the risks related to digitalization to be more significant can be partly approved as there is a statistically significant association between the age of the respondents and the evaluation results in most of the evaluated risk groups in 2020 and 2021. Also, the results of the correlation analysis (Table 4) indicate a moderate positive correlation between the age of respondents and education in both surveyed years and also with ‘Technological risks’ in 2020.

Table 4.
Correlation analysis for the survey results of 2020 and 2021. Source: authors’ calculations based on the survey results.
But the strongest correlation can be found among the risk groups, e.g., the ‘Security risk’ score correlates with ‘Technological risks’ and ‘Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools’ in both surveyed years, which also indicates the cultural background of the respondents and the differences in the perception of risk. What one culture considers a high-risk behaviour or situation may be viewed as relatively safe in another culture or for respondents of other ages or educational backgrounds. It can be observed that the respondents who start their evaluation by assessing ‘Security risks’ as significant also proceed to consider other risk groups as equally significant.
4. Conclusions
Digitalization plays an important role in our lives. There are shifts in digital tools used, e.g., automation rendering human work, the introduction of new devices that allow employees to work remotely, tools to improve internal communications, systems that allow work without paper, and artificial intelligence that fosters digital data collection solutions. Following the shifts in the use of digital tools, risks become an essential part of digitalization and their importance is acknowledged by the enterprises of the bioeconomy sector.
The research paper contributes to the problems identified concerning the consideration of risks related to digitalization. The research results prove that entrepreneurs and employees of SMEs consider the risks related to digitalization significant:
H1. Entrepreneurs and employees of the SMEs consider the risks related to digitalization significant—proved;
H2. The Security and Technology risks are considered the most significant—proved.
The results of the Chi-Square Test of Independence indicate that in 2020, the risk evaluation scores in the groups “Security risks”, “Technology risks”, and “Skills of the clients to use digital tools” are significantly associated with the education level of the respondents (before COVID-19), but in 2021, none of the responses are associated with the education level.
H3. People with higher education levels tend to consider the risks to be more significant—rejected for “Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools” and “Other” risk groups, and it can be partly approved for the “Security risks”; “Technology risks” and “ Skills of the clients to use digital tools” groups. This leads to the conclusion that there is still no clear evidence of people with higher education being more aware of risks.
H4. Older people consider the risks related to digitalization to be more significant–proved, as there is a statistically significant association between the age of the respondents and the evaluation results in most of the evaluated risk groups in 2020 and 2021.
The findings of this study highlight the pivotal role of digitalization in the contemporary business landscape, showcasing a shift in the utilization of various digital tools within enterprises, but as the concept of Industry 5.0 evolves, the role of the human becomes more centric, emphasizing the importance of human creativity, problem-solving skills, and innovation in conjunction with advanced technologies.
As digital tools evolve, the significance of associated risks becomes increasingly acknowledged by bioeconomy enterprises. This research enhances the current understanding by tackling the recognized issues associated with risks in the process of digitalization. The results notably affirm that both entrepreneurs and employees in SMEs recognize the considerable importance of these risks, particularly emphasizing the significance of “Security” and “Technology risks”.
While the Chi-Square Test of Independence indicates a notable association between risk evaluation scores and the education level of respondents before the COVID-19 outbreak in 2020, this association diminishes in 2021. Contrary to the hypothesis that individuals with higher education levels are more attentive to risks, the evidence shows inconsistency in their perception, particularly regarding the ‘Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools’ and ‘Other’ risk categories. However, the relationship between higher education levels and the significance of risks pertaining to ‘Security risks’, ‘Technology risks’, and ‘Skills of the clients to use digital tools’ is partly affirmed.
This suggests a lack of conclusive evidence regarding individuals with higher education levels being inherently more risk-aware. Perhaps with a higher education, the understanding of the risk mitigation measures also evolves; therefore, the risks are perceived as less significant. Additionally, the findings confirm that older individuals consider risks related to digitalization as more substantial. Statistical significance exists between respondents’ ages and evaluation results in various risk groups for both 2020 and 2021. This also indicates that perhaps younger generations have a better understanding of the nature of risks related to digitalization and their mitigation measures, but these claims would need to be studied further.
In conclusion, while there is a confirmed relationship between older age and the perception of digitalization risks, the link between higher education levels and risk awareness lacks consistency, thus indicating a need for future research studying the link between risk perception and education for the risks linked with digitalization. The particular study focuses on specific types of risks related to digitalization, but other potential risks associated with digitalization, e.g., regulatory compliance, economic implications or ethical issues, should also be studied further. The research limitations also include the sample size and timeframe of the study; also, external factors like the COVID-19 pandemic could have influenced perceptions and behaviours. Therefore, a longitudinal study tracking the same participants over time with a larger sample size might offer more robust insights into how risk perceptions regarding digitalization evolve. Addressing these limitations could lead to a more comprehensive understanding of the complexities surrounding the perceptions of risks related to digitalization among entrepreneurs and employees in the bioeconomy sector.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.R. and I.G.; methodology, S.Z.-R., software, P.R.; validation, S.Z.-R. and P.R.; formal analysis, I.B.; investigation, S.Z.-R.; resources, S.Z.-R.; data curation, S.Z.-R. and P.R.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z.-R. and I.B.; writing—review and editing, S.Z.-R.; visualization, S.Z.-R.; supervision, B.R.; project administration, B.R.; funding acquisition, B.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The article was made with the support of the National Research Programme “Latvian Heritage and Future Challenges for the Sustainability of the State” project “Latvian State and Society and the Solutions in International Context” (Interframe-LV).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
In the research, the following data from the Eurostat database were used: Internet purchases—goods or services (2020 onwards) (2023). Retrieved: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/ISOC_EC_IBGS__custom_6198465/default/table?lang=en (accessed on 17 May 2023). Internet purchases—problems encountered (2021 onwards) (2023). Retrieved: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/product/view/ISOC_EC_IPRB21 (accessed on 17 May 2023).
Acknowledgments
This article used data obtained within the project of the Post-doctoral Research Aid Program of the State Education Development Agency of Latvia, “Digitalisation of Enterprises of the Bioeconomy Sector for Increasing their Competitiveness and Exportability” grant number 1.1.1.2/VIAA/3/19/553.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Sandija Zeverte-Rivza and Ina Gudele was employed by the company Celteh Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Consideration of the risks referring to the education level, 2021.
Table A1.
Consideration of the risks referring to the education level, 2021.
| Level of Education | No Answer | Highly Significant | Significant | Moderately Significant | Not Very Significant | Insignificant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security risks | ||||||
| Secondary education | 18.5% | 7.4% | 22.2% | 33.3% | 14.8% | 3.7% |
| Higher education | 5.7% | 40.2% | 29.9% | 17.2% | 4.6% | 2.3% |
| Master’s level education | 7.3% | 32.7% | 29.1% | 18.2% | 5.5% | 7.3% |
| Technological risks | ||||||
| Secondary education | 11.1% | 7.4% | 51.9% | 11.1% | 18.5% | 0.0% |
| Higher education | 3.4% | 35.6% | 34.5% | 19.5% | 5.7% | 1.1% |
| Master’s level education | 3.6% | 29.1% | 38.2% | 16.4% | 9.1% | 3.6% |
| Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools | ||||||
| Secondary education | 11.1% | 7.4% | 51.9% | 11.1% | 18.5% | 0.0% |
| Higher education | 3.4% | 35.6% | 34.5% | 19.5% | 5.7% | 1.1% |
| Master’s level education | 3.6% | 29.1% | 38.2% | 16.4% | 9.1% | 3.6% |
| Skills of the clients to use digital tools | ||||||
| Secondary education | 11.1% | 11.1% | 44.4% | 25.9% | 7.4% | 0.0% |
| Higher education | 3.4% | 32.2% | 34.5% | 18.4% | 8.0% | 3.4% |
| Master’s level education | 9.1% | 16.4% | 38.2% | 16.4% | 14.5% | 5.5% |
| Other risks | ||||||
| Secondary education | 74.1% | 3.7% | 7.4% | 7.4% | 3.7% | 3.7% |
| Higher education | 82.8% | 3.4% | 1.1% | 4.6% | 1.1% | 6.9% |
| Master’s level education | 81.8% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 3.6% | 1.8% | 12.7% |

Table A2.
Consideration of the risks referring to the education level, 2020.
Table A2.
Consideration of the risks referring to the education level, 2020.
| Level of Education | No Answer | Highly Significant | Significant | Moderately Significant | Not Very Significant | Insignificant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security risks | ||||||
| Secondary education | 3.7% | 33.3% | 22.2% | 22.2% | 11.1% | 7.4% |
| Higher education | 8.9% | 21.4% | 32.1% | 30.4% | 7.1% | 0.0% |
| Master’s level education | 7.8% | 34.4% | 34.4% | 12.5% | 9.4% | 1.6% |
| Technological risks | ||||||
| Secondary education | 7.4% | 37.0% | 29.6% | 18.5% | 0.0% | 7.4% |
| Higher education | 5.4% | 21.4% | 53.6% | 14.3% | 5.4% | 0.0% |
| Master’s level education | 6.3% | 31.3% | 37.5% | 15.6% | 6.3% | 3.1% |
| Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools | ||||||
| Secondary education | 7.4% | 22.2% | 29.6% | 25.9% | 11.1% | 3.7% |
| Higher education | 12.5% | 16.1% | 28.6% | 33.9% | 7.1% | 1.8% |
| Master’s level education | 10.9% | 17.2% | 31.3% | 31.3% | 4.7% | 4.7% |
| Skills of the clients to use digital tools | ||||||
| Secondary education | 7.4% | 29.6% | 29.6% | 22.2% | 3.7% | 7.4% |
| Higher education | 5.4% | 28.6% | 30.4% | 25.0% | 7.1% | 3.6% |
| Master’s level education | 9.4% | 18.8% | 26.6% | 31.3% | 10.9% | 3.1% |
| Other risks | ||||||
| Secondary education | 55.6% | 0.0% | 3.7% | 14.8% | 0.0% | 25.9% |
| Higher education | 75.0% | 1.8% | 0.0% | 7.1% | 3.6% | 12.5% |
| Master’s level education | 78.1% | 3.1% | 1.6% | 4.7% | 1.6% | 10.9% |

Table A3.
Perception of risk and age group, 2021.
Table A3.
Perception of risk and age group, 2021.
| Age | No Answer | Highly Significant | Significant | Moderately Significant | Not Very Significant | Insignificant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security risks | ||||||
| <25 years | 20.0% | 30.0% | 10.0% | 30.0% | 0.0% | 10.0% |
| 26–35 years | 7.5% | 26.4% | 35.8% | 20.8% | 7.5% | 1.9% |
| 36–45 years | 4.0% | 30.0% | 34.0% | 18.0% | 10.0% | 4.0% |
| 46–55 years | 7.9% | 42.1% | 21.1% | 26.3% | 2.6% | 0.0% |
| 56–65 years | 16.7% | 44.4% | 16.7% | 5.6% | 5.6% | 11.1% |
| >65 years | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% |
| Technological risks | ||||||
| <25 years | 0.0% | 50.0% | 40.0% | 10.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 26–35 years | 1.9% | 24.5% | 49.1% | 17.0% | 5.7% | 1.9% |
| 36–45 years | 4.0% | 30.0% | 32.0% | 24.0% | 8.0% | 2.0% |
| 46–55 years | 5.3% | 31.6% | 34.2% | 15.8% | 13.2% | 0.0% |
| 56–65 years | 16.7% | 27.8% | 33.3% | 5.6% | 11.1% | 5.6% |
| >65 years | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | 0.0% |
| Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools | ||||||
| <25 years | 0.0% | 10.0% | 20.0% | 50.0% | 10.0% | 10.0% |
| 26–35 years | 1.9% | 9.4% | 37.7% | 32.1% | 13.2% | 5.7% |
| 36–45 years | 6.0% | 8.0% | 40.0% | 32.0% | 8.0% | 6.0% |
| 46–55 years | 7.9% | 10.5% | 36.8% | 28.9% | 13.2% | 2.6% |
| 56–65 years | 11.1% | 11.1% | 38.9% | 33.3% | 0.0% | 5.6% |
| >65 years | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | 0.0% |
| Skills of the clients to use digital tools | ||||||
| <25 years | 0.0% | 20.0% | 10.0% | 50.0% | 10.0% | 10.0% |
| 26–35 years | 3.8% | 22.6% | 45.3% | 13.2% | 13.2% | 1.9% |
| 36–45 years | 8.0% | 14.0% | 50.0% | 20.0% | 6.0% | 2.0% |
| 46–55 years | 5.3% | 39.5% | 26.3% | 15.8% | 10.5% | 2.6% |
| 56–65 years | 16.7% | 22.2% | 22.2% | 22.2% | 5.6% | 11.1% |
| >65 years | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | 0.0% |
| Other risks | ||||||
| <25 years | 70.0% | 10.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 20.0% |
| 26–35 years | 79.2% | 5.7% | 1.9% | 3.8% | 1.9% | 7.5% |
| 36–45 years | 78.0% | 0.0% | 4.0% | 10.0% | 2.0% | 6.0% |
| 46–55 years | 84.2% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 2.6% | 2.6% | 10.5% |
| 56–65 years | 94.4% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 5.6% |
| >65 years | 100.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |

Table A4.
Perception of risk and age group, 2020.
Table A4.
Perception of risk and age group, 2020.
| Age | No Answer | Highly Significant | Significant | Moderately Significant | Not Very Significant | Insignificant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security risks | ||||||
| <25 years | 16.7% | 16.7% | 16.7% | 50.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 26–35 years | 9.8% | 27.5% | 33.3% | 15.7% | 9.8% | 3.9% |
| 36–45 years | 4.2% | 37.5% | 31.3% | 18.8% | 8.3% | 0.0% |
| 46–55 years | 7.1% | 25.0% | 28.6% | 32.1% | 7.1% | 0.0% |
| 56–65 years | 8.3% | 25.0% | 25.0% | 16.7% | 16.7% | 8.3% |
| >65 years | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Technological risks | ||||||
| <25 years | 16.7% | 16.7% | 66.7% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 26–35 years | 5.9% | 29.4% | 43.1% | 15.7% | 0.0% | 5.9% |
| 36–45 years | 4.2% | 37.5% | 43.8% | 12.5% | 2.1% | 0.0% |
| 46–55 years | 7.1% | 17.9% | 39.3% | 28.6% | 7.1% | 8.3% |
| 56–65 years | 8.3% | 25.0% | 16.7% | 8.3% | 33.3% | |
| >65 years | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Professional challenges of the entrepreneur and employees to use digital tools | ||||||
| <25 years | 16.7% | 16.7% | 33.3% | 16.7% | 16.7% | 0.0% |
| 26–35 years | 11.8% | 17.6% | 23.5% | 37.3% | 7.8% | 2.0% |
| 36–45 years | 4.2% | 27.1% | 33.3% | 22.9% | 10.4% | 2.1% |
| 46–55 years | 10.7% | 7.1% | 35.7% | 42.9% | 0.0% | 3.6% |
| 56–65 years | 33.3% | 8.3% | 25.0% | 16.7% | 0.0% | 16.7% |
| >65 years | 12.1% | 17.4% | 29.5% | 30.9% | 6.7% | 3.4% |
| Skills of the clients to use digital tools | ||||||
| <25 years | 16.7% | 16.7% | 33.3% | 16.7% | 16.7% | 0.0% |
| 26–35 years | 11.8% | 17.6% | 23.5% | 37.3% | 7.8% | 2.0% |
| 36–45 years | 4.2% | 27.1% | 33.3% | 22.9% | 10.4% | 2.1% |
| 46–55 years | 10.7% | 7.1% | 35.7% | 42.9% | 0.0% | 3.6% |
| 56–65 years | 33.3% | 8.3% | 25.0% | 16.7% | 0.0% | 16.7% |
| >65 years | 12.1% | 17.4% | 29.5% | 30.9% | 6.7% | 3.4% |
| Other risks | ||||||
| <25 years | 50.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 50.0% |
| 26–35 years | 66.7% | 2.0% | 0.0% | 9.8% | 3.9% | 17.6% |
| 36–45 years | 68.8% | 4.2% | 2.1% | 8.3% | 2.1% | 14.6% |
| 46–55 years | 85.7% | 0.0% | 3.6% | 7.1% | 0.0% | 3.6% |
| 56–65 years | 91.7% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 8.3% |
| >65 years | 100.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
References
- Butollo, F.; Flemming, J.; Gerber, C.; Krzywdzinski, M.; Wandjo, D.; Delicat, N.; Herzog, L. COVID-19 as a Jump Start for Industry 4.0? Motivations and Core Areas of Pandemic-Related Investments in Digital Technologies at German Firms. Science 2023, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, D.; Droste, N.; Allen, B.; Kettunen, M.; Lähtinen, K.; Korhonen, J.; Leskinen, P.; Matthies, B.; Toppinen, D. Green, circular, bio economy: A comparative analysis of sustainability avenues. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 716–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagermann, H.; Wahlster, W. Ten Years of Industrie 4.0. Science 2022, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhloul, A.; Kiss, E. Industry 4.0 as a Challenge for the Skills and Competencies of the Labor Force: A Bibliometric Review and a Survey. Science 2022, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; dos Santos, N. Neoindustrialization—Reflections on a New Paradigmatic Approach for the Industry: A Scoping Review on Industry 5.0. Logistics 2023, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alojaiman, B. Technological Modernizations in the Industry 5.0 Era: A Descriptive Analysis and Future Research Directions. Processes 2023, 11, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denicolai, S.; Zucchella, A.; Magnani, G. Internationalization, digitalization, and sustainability: Are SMEs ready? A survey on synergies and substituting effects among growth paths. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 166, 120650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, D.; Rosin, A.F.; Stubner, S.; Pinkwart, A. The influence of a digital strategy on the digitalization of new ventures: The mediating effect of digital capabilities and a digital culture. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2021, 0, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennings, M.; Burgsmüller, A.; Bröring, S. Convergence Towards a Digitalized Bioeconomy—Exploring Cross-Industry Merger and Acquisition Activities Between the Bioeconomy and The Digital Economy. Bus. Strategy Dev. 2023, 6, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y. A General Framework of Digitization Risks in International Business. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2022, 53, 344–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kergroach, S. Giving Momentum to SME digitalization. J. Int. Counc. Small Bus. 2020, 1, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M. Digital Transformation Success Under Industry 4.0: A Strategic Guideline for Manufacturing SMEs. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2021, 32, 1533–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gala, K.; Mueller, B.A. Acquihires by SMEs as a Strategic Response to Industry Digitalization. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2022, 0, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okfalisa, O.; Anggraini, W.; Nawanir, G.; Saktioto, S.; Wong, K. Measuring the Effects of Different Factors Influencing on the Readiness of SMEs Towards Digitalization: A Multiple Perspectives Design of Decision Support System. Decis. Sci. Lett. 2021, 10, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telukdarie, A.; Dube, T.; Matjuta, P.; Philbin, S. The Opportunities and Challenges of Digitalization for SME’s. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 217, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.; Pecas, P. SMEs and Industry 4.0: Two Case Studies of Digitalization for a Smoother Integration. Comput. Ind. 2021, 125, 103333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogavac, M.; Prigoda, L.; Cekerevac, Z. SMEs digitalization and the sharing economy. MEST J. 2020, 8, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emil, J.; Dhanabhakyam, M.M. Role of Digitalization Post-Pandemic for Development of SMEs. Res. Anthol. Bus. Contin. Navig. Times Crisis 2022, 21, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajnai, Z.; Kocsis, I. Labor Market Risks of Industry 4.0, Digitization, Robots and AI. In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Symposium on Intelligent Systems and Informatics (SISY), Subotica, Serbia, 14–16 September 2017; pp. 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, F.; Gatzert, N.; Gruner, P. Cyber Risk Management in SMEs: Insights From Industry Surveys. J. Risk Financ. 2021, 22, 240–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein-Pensel, F.; Winkler, H.; Brückner, A.; Wölke, M.; Jabs, I.; Mayan, I.J.; Kirschenbaum, A.; Friedrich, J.; Zinke-Wehlmann, C. Maturity assessment for Industry 5.0: A review of existing maturity models. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 66, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, K.; Niina, K. The Bioeconomy in Europe: An Overview. Sustainability 2013, 6, 2589–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, C.; Naveed, N.; Neittaanmäki, P. Digitalized bioeconomy: Planned Obsolescence-Driven Circular Economy Enabled by Co-Evolutionary Coupling. Technol. Soc. 2019, 56, 8–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Informative Report on the Latvian Bioeconomy Strategy 2030 Approved by the Government, Ministry of Agriculture of Latvia. 2017. Available online: https://www.zm.gov.lv/en/article/informative-report-latvian-bioeconomy-strategy-2030-approved-government?utm_source=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.com%2F (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Zeverte-Rivza, S.; Gudele, I. Digitalisation in Times of Covid-19—The Behavioural Shifts in Enterprises and Individuals in the Sector of Bioeconomy. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference Economic Science for Rural Development, Jelgava, The Republic of Latvia, 11–14 May 2021; pp. 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, C.; Turner, J.A.; Romera, A.; Selbie, D.; Henwood, R.; Espig, M.; Wever, M. A Review of Multi-Scale Barriers to Transitioning From Digital Agriculture to a Digital Bioeconomy. CABI Rev. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi-Square Test of Independence. Kent State University. Available online: https://libguides.library.kent.edu/spss/chisquare (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Chiara, V.; Venturini, K. Managing Risks in SMEs: A Literature Review and Research Agenda. J. Technol. Manag. Innov. 2013, 8, 186–197. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.; Altamimi, S.A.; Alkayyal, N.A.; Alshehri, E.; Alabbad, D.A. Digital Transformation and Cybersecurity Challenges for Businesses Resilience: Issues and Recommendations. Sensors 2023, 23, 6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AL-Dosari, K.; Fetais, N. Risk-Management Framework and Information-Security Systems for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): A Meta-Analysis Approach. Electronics 2023, 12, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudenko, R.; Pires, I.M.; Oliveira, P.; Barroso, J.; Reis, A. A Brief Review on Internet of Things, Industry 4.0 and Cybersecurity. Electronics 2022, 11, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencsik, A.; Hargitai, D.M.; Kulachinskaya, A. Trust in and Risk of Technology in Organizational Digitalization. Risks 2022, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).