Innovations in Clay-Based Irrigation Technologies—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Identify existing clay-based irrigation technologies and related available evidence in terms of characteristics, operation principles, and investigated subject matter;
- (2)
- Analyze the reported findings and determine the applicability of the studied technologies;
- (3)
- Identify gaps in knowledge on this topic to inform future research efforts.
2. Materials and Methods
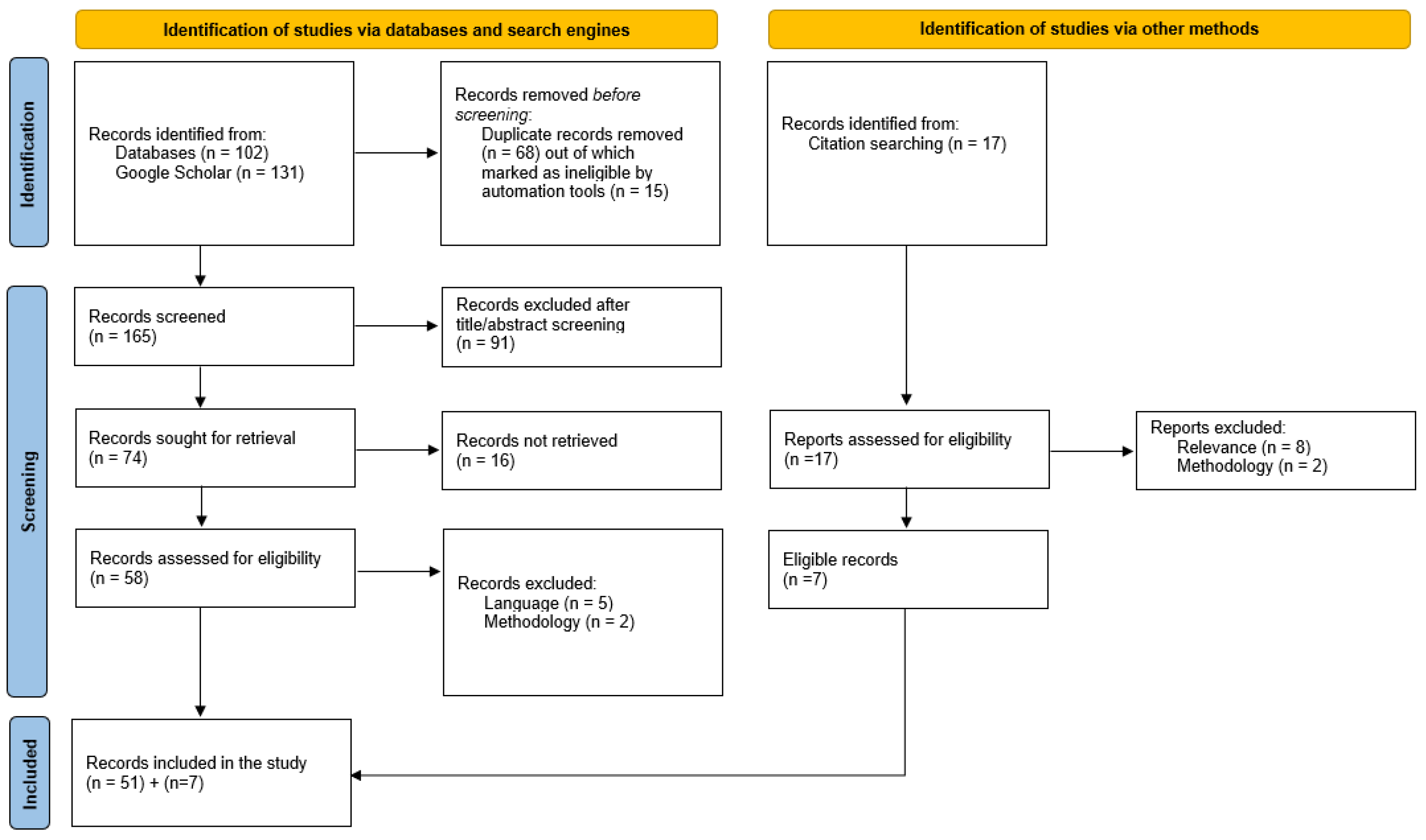
2.1. Systematic Search and Information Sources
2.2. Eligibility Criteria, Screening, and Data Selection
- Articles focusing on irrigation systems that report on clay-based materials and components integrated in the irrigation system or method;
- Articles from Agricultural Sciences with a strong focus on irrigation;
- Articles written in English;
- Articles presenting application studies on various crops, reporting findings with regard to yield, water consumption and saving, energy and labour use, and environmental impact;
- Articles not published in English (as an exception, one research report written in German was identified and included due to the limited number of publications available in English on Self-Regulating Low-Energy Clay-Based Irrigation (SLECI) technology [11]).
- Research articles without an explicit focus on clay-based materials used in the irrigation systems and the corresponding methods;
- Articles on other sub-surface irrigation systems (e.g., Moistube, porous pipe irrigation, subsurface drip);
- Irrigation methods explicitly tailored to potted plants or closed systems.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection and Limitations
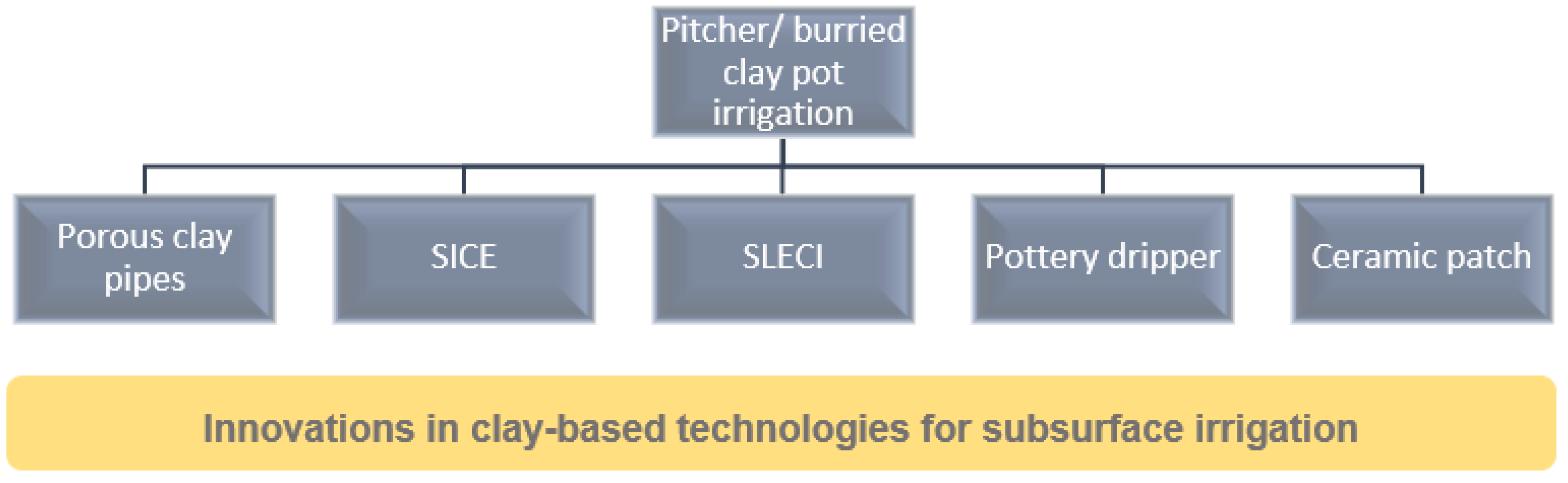
3.2. Results of Individual Studies on Clay-Based Irrigation Technologies—Types, Main Characteristics, and Operation Principles
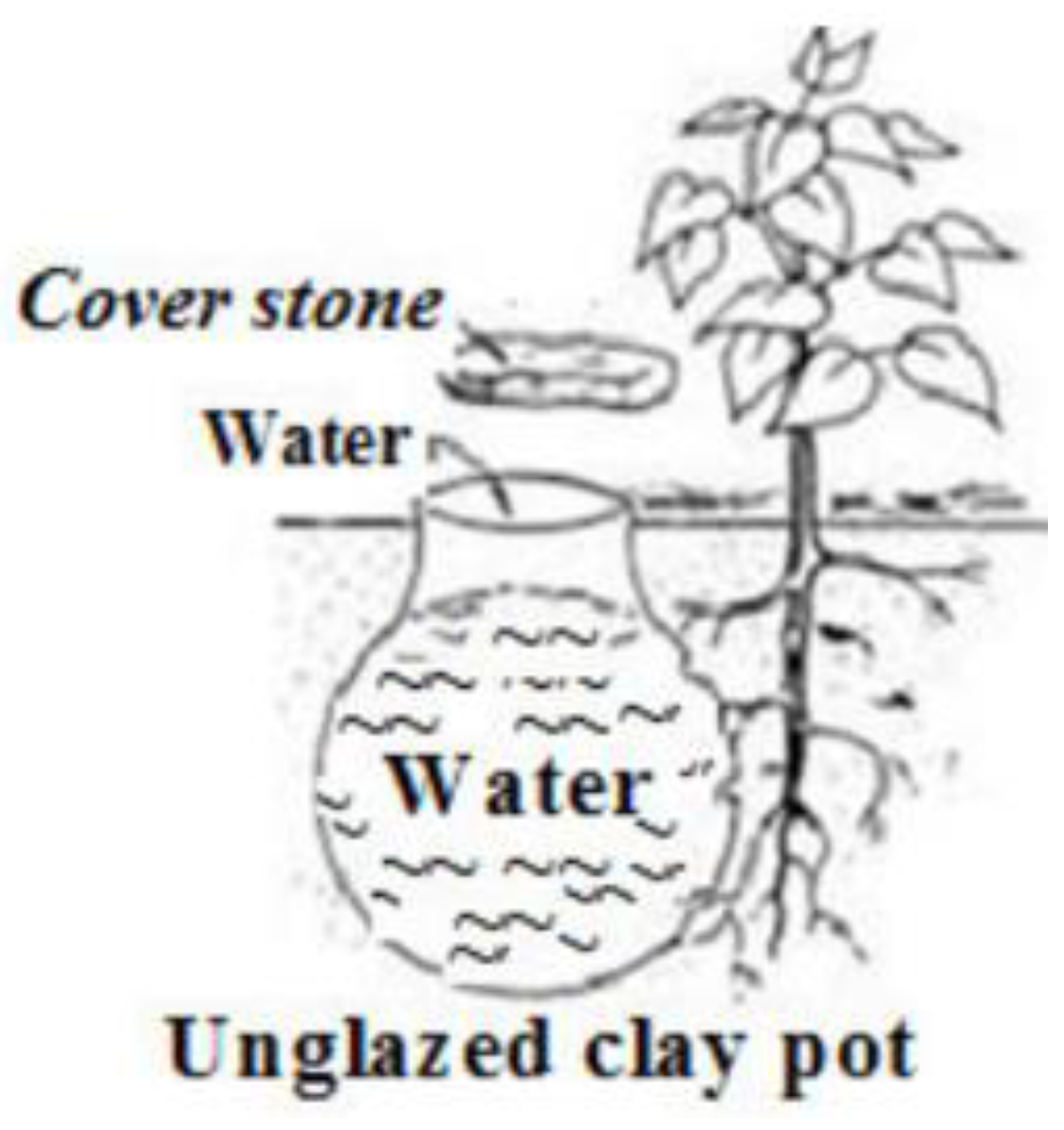
3.2.1. Clay Pot Irrigation
- (a)
- History and process mechanism
- (b)
- Case studies
- Arid regions characterised by annual rainfall of less than 500 mm [43];
- Areas where access to sufficient water is a challenge due to scarcity or financial constraints [45];
- Areas characterized by uneven or sloping terrain, wherein levelling the soil for traditional irrigation methods is challenging, ensuring water distribution remains consistent and efficient [25];
- Regions with light or sandy soils that face moisture retention challenges, as clay pot irrigation conserves water by delivering it directly to a plant’s roots [45];
- Situations where the available water supply is limited and cannot cover a wide area [44];
- For the initial establishment of horticulture [25]
- (c)
- Advantages
- (d)
- Disadvantages
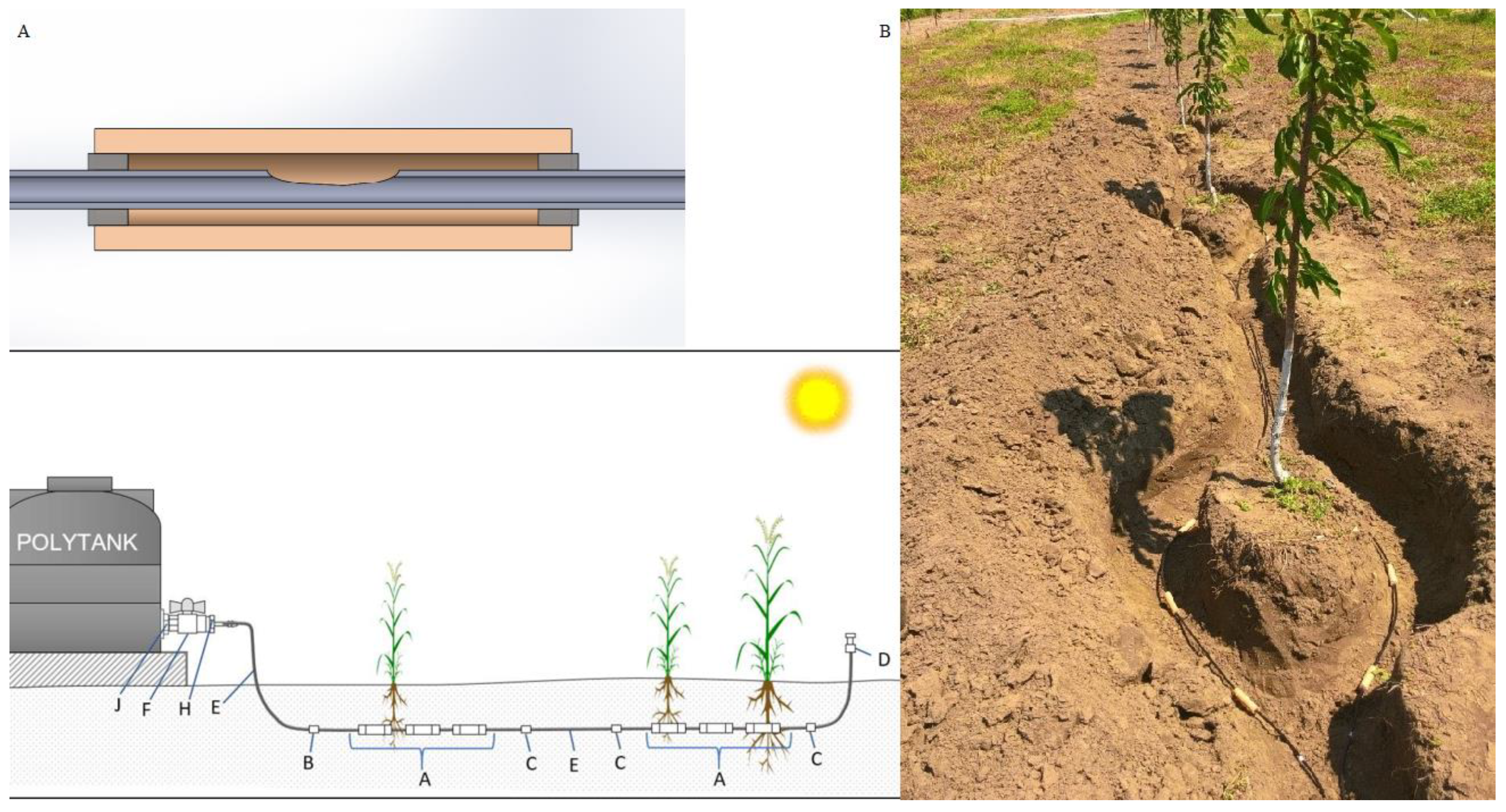
3.2.2. Subsurface Irrigation with Ceramic Emitters
- (a)
- Process mechanism
- (b)
- Case studies
- (c)
- Advantages
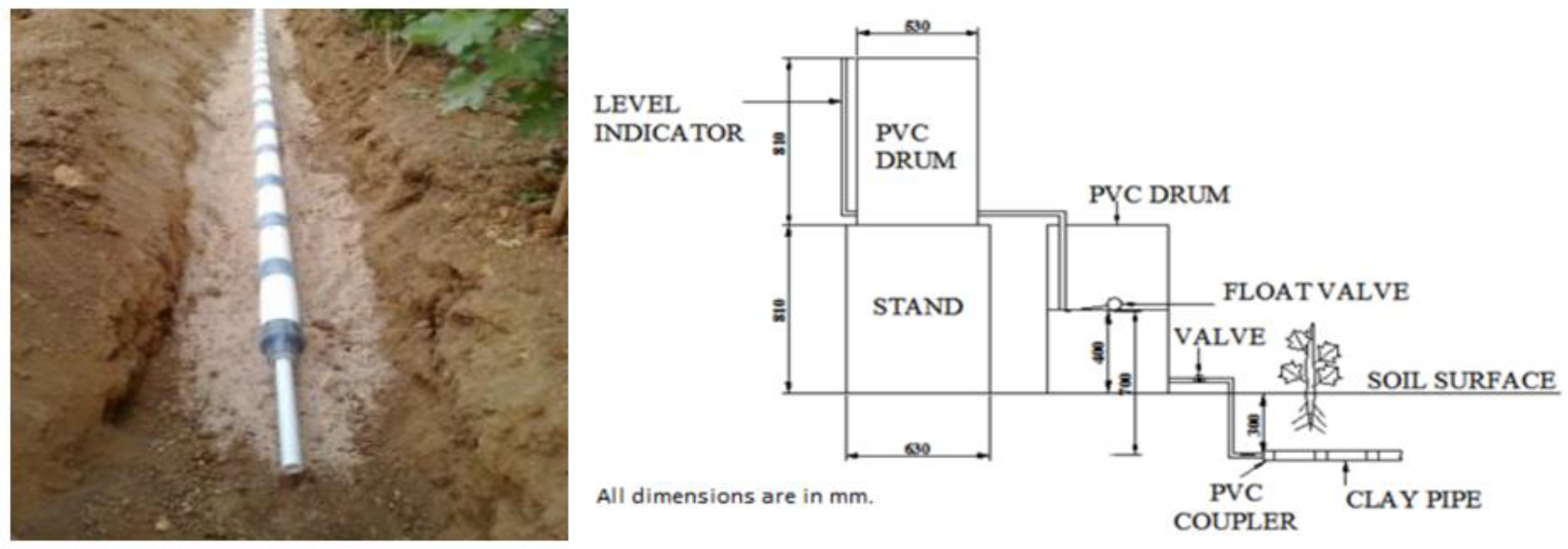
3.2.3. Self-Regulating, Low Energy, Clay-Based Irrigation
- (a)
- Process mechanism
- (b)
- Advantages and disadvantages
3.2.4. Porous Clay Pipe Irrigation
- (a)
- Process mechanism
- (b)
- Advantages
- (c)
- Disadvantages
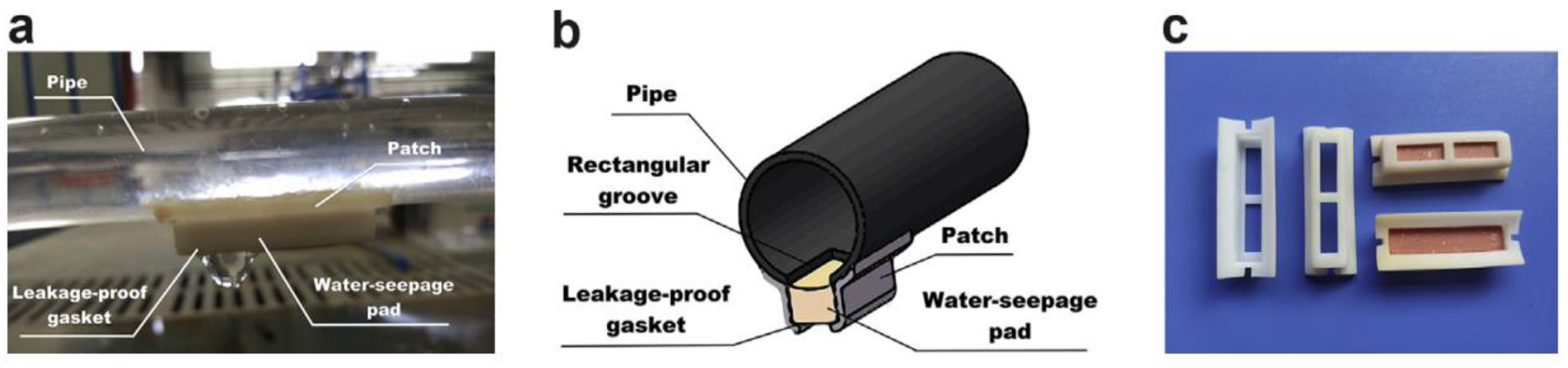
3.2.5. Ceramic-Patch-Type Subsurface Drip Irrigation Line (CP-SDIL)
3.2.6. Pottery Dripper
3.3. Results of Syntheses
3.3.1. Hydraulic Characteristics and Soil Water Dynamics
3.3.2. Application Studies—Water Use Efficiency and Yield Response
3.3.3. Comparison Studies
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Facts and Figures. Managing Water under Uncertainty and Risk. 2012. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000215492 (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Rost, S.; Gerten, D.; Bondeau, A.; Lucht, W.; Rohwer, J.; Schaphoff, S. Agricultural green and blue water consumption and its influence on the global water system. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. AQUASTAT. 2012. Available online: http://www.fao.org/aquastat (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Grant, M.J.; Booth, A. A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2009, 26, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, A.; Noyes, J.; Flemming, K.; Gerhardus, A.; Wahlster, P.; van der Wilt, G.J.; Mozygemba, K.; Refolo, P.; Sacchini, D.; Tummers, M.; et al. Guidance on choosing qualitative evidence synthesis methods for use in health technology assessments of complex interventions. Soc. Soc. Med. 2016, 70, 10–20. Available online: https://esquiresheffield.pbworks.com/w/file/fetch/111070576/Guidance-on-choosing-qualitative-evidence-synthesis-methods-for-use-in-HTA-of-complex-interventi.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- Gessler, M.; Siemer, C. Umbrella review: Methodological review of reviews published in peer-reviewed journals with a substantial focus on vocational education and training research. Int. J. Res. Vocat. Educ. Train. 2020, 7, 91–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddington, H.; White, H.T.; Tugwell, P. How to do a good systematic review of effects in international development: A tool kit. J. Dev. Eff. 2012, 4, 359–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015, 349, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pussegoda, K.; Turner, L.; Garritty, C.; Mayhew, A.; Skidmore, B.; Stevens, A.; Boutron, I.; Sarkis-Onofre, R.; Bjerre, L.M.; Hróbjartsson, A.; et al. Systematic review adherence to methodological or reporting quality. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansmann, H.; Siering, J. Verhinderung des Algenbefalls von Saugsystemen aus Ton zur Bewässerung von Nutzpflanzen in Tropischen Gebieten der Sahel-Zone am Beispiel Ghanas [Preventing Algae Infestation of Clay Suction Systems for Irrigating Crops in Tropical Areas the Sahel Zone Using Ghana as an Example]. German Research Report on Agricultural Innovations. 2018. Available online: https://edocs.tib.eu/files/e01fn20/1690620927.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2024).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: Updated guidelines for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Skaggs, T.H. Solute transport in a loamy soil under subsurface porous clay pipe irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 121, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zreig, M.M.; Atoum, M.F. Hydraulic characteristics and seepage modelling of clay pitchers produced in Jordan. Can. Biosyst. Eng. 2004, 46, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Zreig, M.M. The auto-regulative capability of pitcher irrigation system. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, T.M. Evaluation of clay pots for irrigation in semi-arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 1997, 34, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. Preparation technology optimization of diatomite porous ceramic irrigation emitter. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2015, 31, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malchev, S.; Hansmann, H. Innovative clay-based micro-irrigation system “SLECI” (self -regulating, low energy, clay-based irrigation) preliminary results from cherry orchard trials. J. Agric. Food Environ. Sci. 2022, 76, 45–55. Available online: https://journals.ukim.mk/index.php/jafes/article/view/1892 (accessed on 19 June 2023). [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Leitao JC, C.; Gaspar, P.D.; Fael, C.; Falorca, I. Exploring Irrigation and Water Supply Technologies for Smallholder Farmers in the Mediterranean Region. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Lin, L. Ceramic patch type subsurface drip irrigation line: Construction and hydraulic properties. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 182, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hagarey, M.E.-S. Design and Manufacture of Pottery Dripper for the Use of Saline Water in Irrigation Systems. IOSR J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2014, 7, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, A.; Martorano, L.G.; Girma, A.; Habtu, S.; Tesfay, S.Z. Comparative efficiency evaluation of different clay pots versus bucket irrigation system under Swiss chard (Beta vulgaris subsp. cicla) growers condition in Ethiopia. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2015, 14, 25–33. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311196581_Comparative_Efficiency_Evaluation_of_Different_Clay_Pots_Versus_Bucket_Irrigation_System_Under_Swiss_Chard_Beta_vulgaris_subsp_cicla_Growers_Condition_in_Northern_Ethiopia (accessed on 24 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, D.A. Buried clay pot irrigation: A little known but very efficient traditional method of irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 48, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, D.A. Alternative irrigation systems for arid land restoration. Ecol. Restor. 2002, 20, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, D.A. Super-Efficient Irrigation with Buried Clay Pots; United States International University, Environmental Studies Program: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Available online: http://works.bepress.com/david_a_bainbridge/22/ (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Babiker, A.E.; Maria, H.E.; Abd Elbasit, M.A.M.; Abuali, A.I.; Abu-Zerig, M.; Liu, G. Potential of low-cost subsurface irrigation system in maize (Zea mays L.) production in high water scarcity regions. AgricEngInt CIGR J. 2021, 23, 42–51. Available online: http://www.cigrjournal.org (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Daka, A.E. Chapter 7 Clay Pot Sub-Surface Irrigation as Water-Saving Technology for Small-Farmer Irrigation in Development of a Technological Package for Sustainable Use of Dambos by Small-Scale Farmers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2001. Available online: https://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/handle/2263/27777/Complete.pdf?sequence=11 (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Tesfaye, T.; Kindie Tesfaye, K.; Woldetsadik, K. Clay pot irrigation for tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) production in the north east semiarid region of Ethiopia. J. Agric. Rural. Dev. Trop. Subtrop. 2011, 112, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, R.C. Farming with a pitcher: A technique of water conservation. World Crops 1974, 26, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, R.C.; Dubey, S.K.; Gupta, S.K. Subsoil irrigation by saline water using earthen pitcher. Indian Agric. 1988, 25, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.C.; Dubey, S.K.; Gupta, S.K. Use pitchers when water for irrigation is saline. Indian Agric. 1992, 36, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kefa, C.C.; Kipkorir, E.C.; Kwonyike, J.; Kubowon, P.C. Comparison of water use savings and crop yields for clay pot and furrow irrigation methods in Lake Bogoria, Kenya. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 3439. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255796208_Comparison_of_Water_Use_Savings_and_Crop_Yields_for_Clay_Pot_and_Furrow_Irrigation_Methods_in_Lake_Bogoria_Kenya (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Soomro, S.A.; Siyal, A.A.; Siyal, A.G. Performance of pitcher irrigation with saline water under high evapotranspiration rates. J. Chin. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 46, 61–69. Available online: http://www.cswcs.org.tw/AllDataPos/JournalPos/VOL46/NO1/jcswc46(1)061-069_07.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Woldu, Z. Clay pot pitcher irrigation: A sustainable and socially inclusive option for homestead fruit production under dryland environments in Ethiopia (A partial review). J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2015, 5, 157–167. Available online: https://soilhealth.ucdavis.edu/application/files/4515/4223/2421/Clay_Pot_Pitcher_Irrigation-A_Sustainable_and_Socially_Inclusive_Option_for_Homestead_Fruit_Production_under_Dryland_Environments_in_Ethiopia_A_Partial_Review.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Vasudevan, P.; Thapliyal, A.; Davies, P.; Dastidar, M.G.; Sen, P.K. Pitcher or clay pot irrigation for controlled water flow. In Proceedings of the 36th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics and Fluid Power, College of Engineering, Pune, India, 17–19 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Zreig, M.; Abo-Izreik, A.; Abd Elbasit, M.A. Water seepage rate from clay emitters. In Proceedings of the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers Annual International Meeting (ASABE 2012), Dallas, TX, USA, 29 July–1 August 2012; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatungimana, J.C.; Niyigaba, J.B.; Kwitonda, T.S.; Mutwarasibo, F. Water saving and water productivity under buried clay pot and drip irrigation systems for cabbage in Rwanda. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2023, 23, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elavarasan, K.; Govindappa, M.; Hareesh, S.B. Clay pot irrigation of young coffee seedling under Pulney hills of Tamil Nadu, India. J. New Biol. Rep. 2014, 3, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Gebru, A.A.; Araya, A.; Habtu, S.; Wolde-Georgis, T.; Teka, D.; Martorano, L.G. Evaluating water productivity of tomato, pepper, and Swiss chard under clay pot and furrow irrigation technologies in semi-arid areas of northern Ethiopia. Int. J. Water 2018, 12, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, A.; Mondal, A.; Pal, A.; De, S.K. Pitcher irrigation and surface cover management on bitter gourd (Momordica charantia) production in alfisols. Int. J. Bot. Stud. 2021, 6, 897–901. Available online: www.botanyjournals.com (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Naik, B.S.; Panda, R.K.; Nayak, S.C. Impact of pitcher material and salinity of water used on flow rate, wetting front advance, soil moisture, and salt distribution in soil in pitcher irrigation: A laboratory study. Irrig. Drain. 2013, 62, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Adhikary, R.; Bera, M.; Garanayak, R.; De Kumar, S. Pitcher Irrigation Technology for Crop Cultivation in Arid Region. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2020, 13, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Rajshekar, C.B.; Armstrong, B. Enhancing the performance of clay pot irrigation using water retaining granules. J. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 33, 644–655. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, S.K.; Sharma, B.; Meena, S.K. Pitcher irrigation system: A water saving approach. Indian Farmer. 2017. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319504730_Pitcher_Irrigation_System_A_Water_Saving_Approach (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Adhikary, R.; Pal, A. Clay Pot Irrigation—A Review Study. Asian Plant Res. J. 2020, 5, 37–42. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342243138_Clay_Pot_Irrigation-A_Review_Study (accessed on 20 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Martínez de Azagra Paredes, A.; Zapata, N.; Faci, J.M. Pitcher irrigation: Some theoretical and practical aspects. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 68, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Skaggs, T.H. Measured and simulated soil wetting patterns under porous clay pipe sub-surface irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A. Porous clay pipe irrigation: A tool for sustainable agriculture under arid conditions. In Proceedings of the Conference: International Perspective on Water Resources and the Environment (IPWE-2011) at National University of Singapore, Singapore, 4–6 January 2011; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275965227_Porous_clay_pipe_irrigation_A_tool_for_sustainable_agriculture_under_arid_conditions (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Siyal, A.A.; Siyal, A.G.; Siyal, P.; Solangi, M.; Khatri, I. Pitcher irrigation: Effect of pitcher wall properties on the size of soil wetting front. Sci. Int. 2016, 28, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, N.; Kanzariya, B.; Motiani, A.; Pandit, B. An experimental investigation on pitcher irrigation technique on alkaline soil with saline irrigation water. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Innov. Technol. 2013, 2, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, N.J. Experimental investigations on localized porous clay pipe irrigation technique for sustainable agriculture: A new paradigm for soil and water management in rainfed areas. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Dev. 2017, 4, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bhople, B.S.; Adhikary, K.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Singh, G. Sub-Surface Method of Irrigation-Clay Pipe Irrigation System. J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2014, 7, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, C.; Lovell, C.; Murata, M. Simple microirrigation techniques for improving irrigation efficiency on vegetable gardens. Agric. Water Manag. 1996, 32, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Mondal, R.C. Pitcher irrigation technique for arid and semi-arid zones. Dry Land Resour. Technol. 1991, 6, 137–177. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Wu, S.; Zhao, X. Simulation of soil water movement under subsurface irrigation with porous ceramic emitter. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 192, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Wu, S.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Dong, Z. Prediction of flow characteristics and risk assessment of deep percolation by ceramic emitters in loam. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Chen, J. Effect of Soil Texture on Water Movement of Porous Ceramic Emitters: A Simulation Study. Water 2019, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, X.; Ge, M.; Song, X.; Wu, Y.; Dai, Z. Subsurface irrigation with ceramic emitters: An effective method to improve apple yield and irrigation water use efficiency in the semiarid Loess Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 313, 107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yao, C.; Wu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Du, Y. Effectiveness of a subsurface irrigation system with ceramic emitters under low-pressure conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, P.; Gao, X.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Dai, Z.; Chau, H.W.; Zhao, X. Subsurface irrigation with ceramic emitters: Evaluating soil water effects under multiple precipitation scenarios. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 272, 107851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Yang, F.; Han, M.; Yao, S. Subsurface irrigation with ceramic emitters: Optimal working water head improves yield, fruit quality and water productivity of greenhouse tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, X.; Zhang, L. Simplified method for estimating discharge of microporous ceramic emitters for drip irrigation. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 219, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, W. Clogging formation and an anti-clogging method in subsurface irrigation system with porous ceramic emitter. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.-y.; Zhang, L. Study on Yield Increasing Mechanism of Greenhouse Tomato under Subsurface Irrigation with Ceramic Emitters Based on Water Consumption and Photosynthetic Characteristics. Water Sav. Irrig. 2022, 7, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Long, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cai, B.; Liu, W. Effects of different irrigation management parameters on cumulative water supply under negative pressure irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 224, 105743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wei, Q.; Xu, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, P.; Guo, H.; Liao, L.; Zhao, X.; Min, Z. Matching water requirements of Chinese chives planted at different distances apart from the line emitter under negative pressure irrigation subsurface system. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yao, C. Hydraulic performance and parameter optimisation of a microporous ceramic emitter using computational fluid dynamics, artificial neural network and multi-objective genetic algorithm. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 189, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, S.; Zhou, M. The Clogging Rules of Ceramic Emitter in Irrigation Using Saline Water with Different EC. Agronomy 2019, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Qi, F.; Ji, X.; Peng, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Peng, Q. Effect of different irrigation levels on quality parameters of ‘Honeycrisp’ apples. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 3316–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.S. Fan Sheng-Chih Shu: An Agriculturist Book of China; Written by Fan Sheng-Chih in the First Century BC; Science Books: Beijing, China, 1974; pp. 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Anon. Clay pot irrigation water conservation in Iran. J. Aust. Inst. Hort. 1974, 2, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Olguín, P.C. Riego por succión. Descripción del método y avances enla investigación. In Memorias del 1er Seminario Nacional de Riego porGoteo; Tomo II: Hermosillo, Mexico, 1975; pp. 165–181. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Stein, T.M. Grundlagen und Technik der Gefäßbewässerung. Z. Für Bewässerungswirtschaft 1994, 29, 62–94. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Al Maimuri, N.M.L.; Abood, K.F.; Hussian, A.A. Optimum water management of pitcher irrigation under extreme climatic changes. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 592–602. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Subsurface irrigation with ceramic emitters improves wolfberry yield and economic benefits on the Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Arid Land 2023, 15, 1376–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Kukal, S.S.; Bhowmik, A.; Dubey, R.K. Performance evaluation of different mulching materials for water conservation and yield improvement of summer squash under drip and pitcher irrigation. J. Appl. Hortic. 2005, 7, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Seeda, M.A.; El-Aila, H.I.; Zohry, A.E.; El-Gindy, A.M.; Abou-El-Hassan, W.H. Evaluation and Optimization of Subsurface Irrigation (SDI) System: A Review. Middle East J. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 508–534. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Han, M.; Zhang, L. A new subsurface ceramic emitter for smallholders without pumps: Design, hydraulic performance, and field application. Irrig. Sci. 2023, 41, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Technology | Nr. of Articles Included | Author | Location | Crop |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay pot Pitcher | 26 | Araya et al. [22]; Bainbridge [23,24,25]; Babiker et al. [26]; Daka [27]; Tesfaye et al. [28]; Mondal [29,30,31]; Kefa et al. [32]; Soomro [33]; Woldu [34]; Vasudevan et al. [35]; Abu-Zreig and Atoum [14]; Abu-Zreig [15,36]; Hatungimana et al. [37]; Elavarasan, Govindappa, and Hareesh [38]; Gebru et al. [39]; Mahata et al. [40]; Naik, Panda, and Nayak [41]; Pal et al. [42]; Rajshekar and Armstrong [43]; Tripathi, Sharma, and Meena [44]; Adhikary, R., and Pal, A. [45]; Martínez de Azagra Paredes, Zapata, and Faci [46] | China, India, Pakistan, Malaysia, Indonesia, Iran, Jordan, Ethiopia, Zimbia, Mexico, Morocco, Kenya, Brazil, Rwanda, Iraq | Watermelon, tomato, corn, gourd, cauliflower, okra, sweet orange, avocado, apple, cucumber, eggplant, beans, citrus, cabbage |
| Porous clay pipe | 9 | Siyal et al. [47,48,49]; Bhatt, N. J. [50,51]; Bhople et al. [52]; Batchelor, Lovell, and Murata [53]; Dubey, Gapta, and Mondal [54] | India, Sudan, Pakistan | Maize, turnip, okra, eggplant |
| SICEs | 18 | Cai et al. [55,56,57,58,59,60]; Liu et al. [61,62]; Yao et al. [63,64]; Wang et al. [65,66]; Zhou et al. [67]; Chen et al. [68]; Huang et al. [69] | China | Tomato, apple, lettuce, wolfberry, persimmon, jasmine (Murraya paniculate) |
| SLECI | 3 | Malchev et al. [18]; Pereira et al. [19]; Hansmann and Siering [11] | Bulgaria, Morocco, Malta, Portugal | Sweet cherries, peaches, grapevines, citrus, olives |
| CP-SDIL | 1 | Cai et al. [20] | China | Lab-scale experiments |
| Pottery dripper | 1 | El-Hagarey [21] | Egypt | Lab-scale experiments |
| Clay Pot and Clay Pipe | SICE | SLECI |
|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes [28,32,39,54], maize [26,32], bitter gourd [40], pumpkin [42], watermelons [29,54], okra, cucumber, eggplants, coffee [38], cauliflower [54], Swiss chard [22,39], cabbage [37], pepper [39], bitter gourd [40,54] | Greenhouse tomatoes [61], apples [58], lettuce [55], wolfberry [75], persimmon [55] | Cherry trees [18] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahler, E. Innovations in Clay-Based Irrigation Technologies—A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167029
Mahler E. Innovations in Clay-Based Irrigation Technologies—A Systematic Review. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):7029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167029
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahler, Evgenia. 2024. "Innovations in Clay-Based Irrigation Technologies—A Systematic Review" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 7029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167029
APA StyleMahler, E. (2024). Innovations in Clay-Based Irrigation Technologies—A Systematic Review. Sustainability, 16(16), 7029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167029








