Abstract
Students are rapidly losing interest in STEM education due to the minimal incorporation of media into learning and the complexity of teaching methods, which ultimately results in a lack of motivation. However, despite these challenges, incorporating active learning methods in STEM can ultimately reignite students’ interest in STEM education. This paper reports a case study presenting the effects of simulation games on enhancing the learning experiences of civil engineering students through an intervention method. It develops a framework for enhancing learning through game-based learning. Intervention included the following two groups: a control group exposed to conventional teaching methods and an experimental group introduced to the simulation game. Following the learning sessions, a survey was conducted to gauge students’ perceptions about the proposed framework. Results indicated a strong positive response from students toward the game-based learning approach. They expressed satisfaction with its effectiveness in improving their understanding. Independent t-tests found that the mean score (4.13) for entertainment via the game exceeded that of traditional teaching methods (3.72). Furthermore, 85% of students acknowledged the game’s utility in reinforcing civil engineering concepts, compared to 67% for traditional methods. Many students suggested expanding the game to cover a wider range of topics in future versions to enable a more comprehensive learning experience.
1. Introduction
Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) play an important role in the development of a country, as they have a major contribution to improving the economy [1]. However, over time, most students are losing interest in STEM education [2]. It has been observed that only 40% of students in the US take an interest in STEM education, while only 20% finish with 57a STEM degree [3]. According to the National Science Foundation (2016), there has been a drop in STEM graduation rates. Just half of the students who started with STEM majors stayed in STEM fields, while the remaining either left college or changed to a non-STEM major [4]. Fear and reluctance in students’ learning are significantly influenced by the minimal utilization of media and the complicated teaching methods employed by educators during lectures [5]. Additionally, students may lack motivation due to lack of aspiration to perform an activity and may consider learning activities as unpleasant [6]. Moving toward non-traditional teaching methods can largely help in solving these problems [7], and with the use of new techniques, the skill levels of the students will eventually increase [8]. By using active learning techniques, students’ interest in STEM education can be increased [9]. Active learning is the combination of engaging participants, creating an effective infrastructure, and using technologies effectively [10]. Active learning is a student-centered learning approach that directly involves the learner in the process, with learners being the main players of the learning process by performing activities and engaging in critical thinking [11]. Therefore, there is a need to adopt more effective active learning techniques in STEM education. Educational games are one of the most successful methods of active learning, as they can greatly help increase the learning experience and reduce misconceptions [12].
Gamification involves the application of video game mechanics to non-game processes to enhance user engagement, leading to increased user retention and interaction [13]. While computer games are typically enjoyed in free time, their educational potential is often neglected. Studies suggest that when games are used for educational purposes, they engage students more effectively than traditional lecture methods, making them more alert, active, and involved [14]. When games are incorporated into STEM education, students report markedly improved learning outcomes, heightened motivation, and observable behavioral changes compared to those in traditional classrooms [15]. Unlike lectures, games can adjust to the user’s pace and present information through multiple visual and auditory modes, accommodating diverse learning styles. Additionally, games excel at delivering information gradually by dividing complex tasks into manageable parts [16]. Digital games act as powerful learning environments, fostering active and critical learning while complementing traditional teaching methods. It has been widely demonstrated that engaging in gameplay enables students to develop their cognitive recognition abilities and experience satisfaction, along with a sense of achievement. Among numerous available strategies, gaming stands out as a tool proven to significantly enhance teaching and learning effectiveness [17]. For game development, game engines are an integral part of the toolkit of researchers and developers as they offer pathways to achieve immersion, ubiquity, and rapid game content development. Among these engines, Unity emerges as the clear preference, with a notable 57% of developers opting it for in their work. This preference is attributed to its robust functionality, multi-platform compatibility, no-cost availability, and seamless integration with major 3D tools and file formats [18].
To improve the STEM learning experience, this study aims to introduce gaming into one of the STEM subjects, civil engineering. This research aims to conduct a comparative study in a case study setting to investigate the effectiveness of gaming in enhancing active learning among civil engineering students and to observe how students react to this active learning technique. By addressing structural engineering concepts through simulation games, student interest can be effectively increased, further reinforcing their understanding of structural engineering concepts. This study has the following objectives: (a) examine and identify the limitations of conventional teaching methods in a classroom setting through a case study; (b) develop an interactive game to effectively translate classroom concepts, integrating it within the case study framework; and (c) observe and evaluate the preliminary findings of the game-based learning approach on student engagement and understanding within the context of the case study.
1.1. Active Learning Techniques
Students are becoming increasingly disengaged from STEM education, experiencing a lack of motivation [6]. Minimal utilization of media and the intricate teaching methods employed by educators during lectures are significantly increasing fear and reluctance in students’ learning [5]. Different active learning techniques have been used across the world to increase student’s engagement in lectures [19]. Active learning techniques, such as transform, interact, learn, and engage (TILE) teaching spaces, utilize specially designed classrooms equipped with round tables capable of seating nine students each. These spaces feature a control station, glass boards, whiteboards, laptops, an LCD screen, and a wireless mouse per table [20]. The main advantage of TILE teaching spaces is that students gain a sense of responsibility for their education. They cannot stay disengaged in these classrooms and must actively participate in the learning process [21]. TILE classrooms at the University of Iowa revealed several benefits. Students reported increased engagement and interaction, particularly appreciating round tables for face-to-face communication, and felt more responsible and collaborative, focusing more on group performance than grades. While it does offer potential benefits to enhancing students’ learning, its effectiveness may depend on various factors, such as the high cost of technological infrastructure and students’ willingness for collaborative learning [22]. The flipped classroom is another active learning technique, in which video-based lectures are recorded and sent to students to study before coming to class. Classroom hours are completely dedicated to addressing questions and engaging in group-based discussions on real-world problems relevant to the lecture [23]. Student satisfaction and increased entertainment levels are the advantages of the flipped classroom technique [24]. McCabe [25] utilized flipped learning in civil engineering modules at the National University of Ireland, Galway. The results show that students found the approach more convenient, engaging, and effective. Two main limitations of the flipped classroom technique are students’ discomfort with group work, as many prefer working alone [20], and the challenge for teachers to verify individual students’ engagement with video lectures [10].
McCarthy and Anderson [26] discussed an Activity-based learning method, in which students were grouped into teams of three to five and tasked with a series of questions. They reviewed materials from textbooks, lectures, and other sources, and then each group shared their answers in class the following week. While this method enhanced collaborative learning, its success mainly depended on students’ motivation to participate in the activity [27]. Hernández-de-Menéndez et al. [20] discusses technology-enabled active learning (TEAL), in which advanced technologies are used in an active learning environment to enhance students’ effective interactions and problem-solving abilities. Additionally, integrating technology with traditional teaching methods can enhance students’ technical skills and overall learning experience [28]. Hassan et al. [29] validated TEAL among undergraduate students at a university. TEAL application in practical learning significantly aided in improving understanding, creativity, and innovativeness. The study found a moderate relationship between TEAL application and enhanced student creativity and innovativeness. The problem with this method is the initial cost of infrastructure, which may not be financially viable for many institutions [30]. Fioravanti et al. [31] experimented with project-based learning to connect theoretical concepts with practical applications and promote learning. Tseng et al. [32] consider the project-based learning technique as the major tool for improving student’s interest and motivation in engineering. However, learning quality is affected by the time allocated to the project-based learning and teamwork environment [33].
Role-play is another effective active learning technique, in which students take on different assigned roles [34]. The role-play technique brings realism by directly involving learners in the activity and teaching them how to react in real-world situations [35]. The effect of role-playing in engineering was realized through a study conducted by the authors at Technological University Dublin. The results indicated that role-playing enhanced students’ understanding of complex scenarios and the social factors influencing engineering decision-making [36]. However, the effective adoption of this technique might be hindered by students’ low motivation caused by shyness and the absence of a systematic method for evaluating the quality of role-play [37]. Computer games are another effective active learning tool having the traits to be used for educational purposes [14]. As the current generation grew up in technology era, gaming can engage students more effectively than traditional methods [38], offering satisfaction and confidence through a sense of achievement [39].
1.2. Game-Based Learning
Fatahi and Khabbaz [39] used the “BACK TO BEDROCK” game, utilizing PLAXIS software, to test soil behavior and design infrastructure among undergraduate geotechnical students. The study results showed that students were more engaged and had fun while learning. They enjoyed the computer game-based assessment tasks and were unaware that they were learning various aspects of soil testing and earth structure design. Another study demonstrated the detailed integration of game and simulation aspects in infrastructure planning. A UPTown game was developed at the University of Pretoria, South Africa, in which students simulated the actions of both public-sector planners and private-sector real estate developers [40]. The outcomes of this study indicated that students achieved much higher learning outcomes than before. Another study was conducted in which teachers and students of civil engineering from Wentworth Institute of Technology conducted a study on the “Design of Educational Game for Fluid Mechanics”, employing Unity 3D and C# programming. They solved fluid mechanics problems like head loss, pump power, and buoyancy by applying power output and the equation of energy conservation [38].
A study by Jacobs et al. [41] found that implementing game-based learning apps tailored to engineering students’ needs enhances engagement and supports effective learning by promoting the transfer of knowledge through perceptual learning tasks. Most students positively rated the app while indicating that it was successful in meeting educational goals and improving their learning experience. Meksophawannagul [42] found that the developed online games were effective learning materials for engineering students. The study results showed that students’ vocabulary knowledge improved, and they felt positive about learning in an enjoyable, interactive environment. Similarly, another study found that using game-based applications among engineers significantly improved students’ engagement, motivation, enjoyment, and learning outcomes compared to traditional paper-based methods. By including games into lectures on mechanics, students in the game-based group showed higher levels of interest and performance compared to traditional method-based group [43].
As evident, games are one of the most effective techniques in active learning and have been previously utilized in STEM education. However, their application in civil engineering remains limited, with their implementation in structural engineering concepts being minimal, and there has been insufficient observation of students’ responses within this specific domain. The most prevalent methodology in game-based learning studies is the development of a game application and testing it in an educational setting. The studies typically divide participants into two groups and compare their results through a questionnaire survey or quiz to validate the effectiveness of the game-based learning approach. [12,14,40,43]. Following a similar approach, this study aims to conduct a comparative analysis to investigate the effectiveness of gaming in enhancing active learning among structural engineering students and observe their response to this technique.
2. Method
This research carried out an intervention study to examine the impact of introducing gaming on student learning. The intervention group received game-based training, while the control group received traditional method-based training. This study aimed to understand the perspectives of two groups and compare them to identify differences and similarities. One advantage of an intervention study is its ability to establish causality, allowing us to determine whether intervention strategies cause changes in selected outcomes [44].
2.1. Case Study
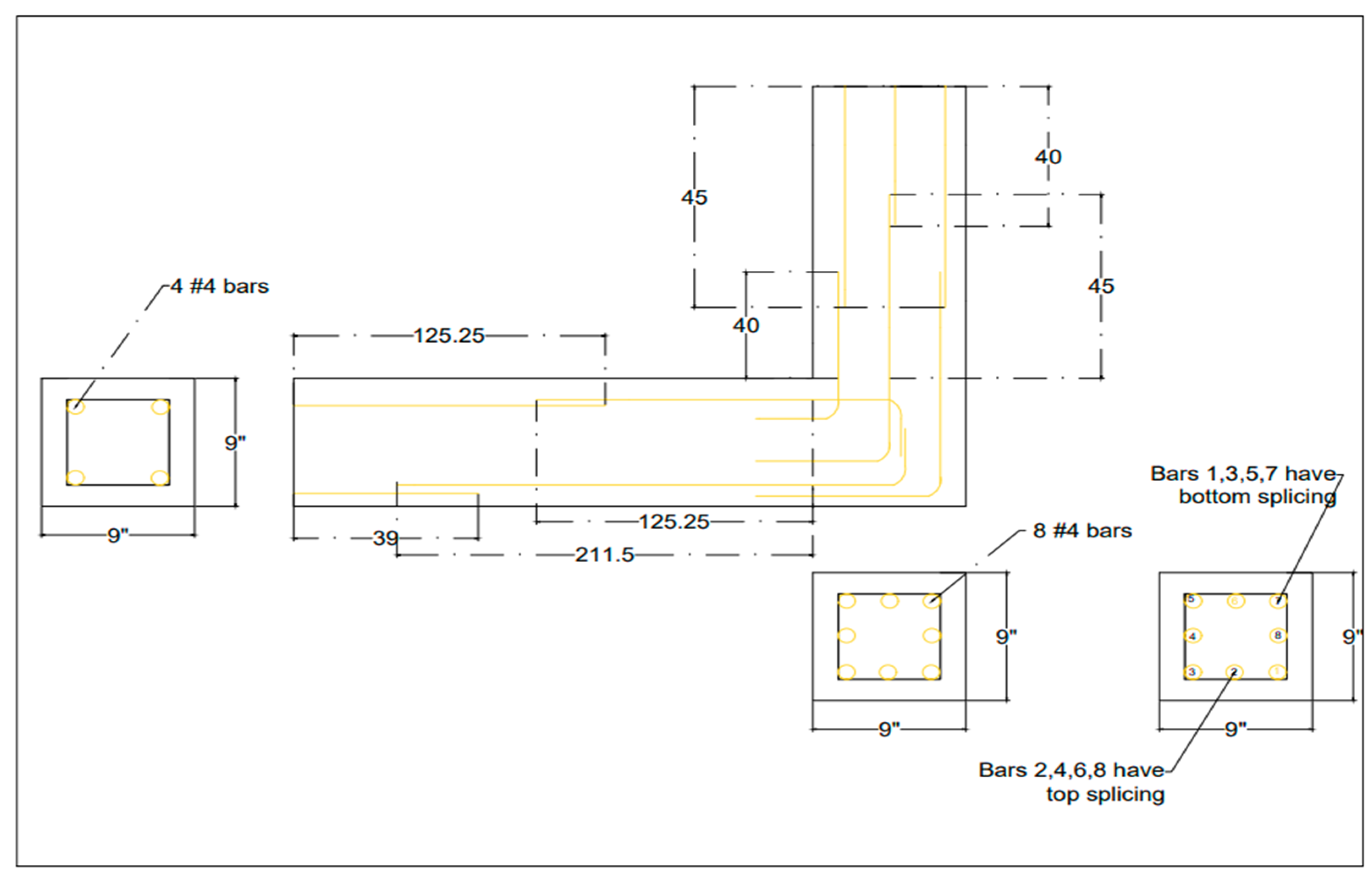
The case study approach consisted of final-year civil engineering students at the University of Engineering and Technology (UET), Peshawar. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of game-based learning compared to traditional teaching methods in understanding structural engineering concepts, specifically development length and lap splices. Development length is the minimum length that a reinforcing bar must be embedded in concrete to ensure proper bonding and load transfer. Lap splices connect reinforcing bars to distribute stress across concrete members. Compliance with code requirements ensures safety and durability, minimizing risks such as premature failure or corrosion [45]. A beam-column section being tested in the structural laboratory of the National University of Science and Technology, Islamabad, was selected as a prototype for teaching students about development length and lap splices. The beam-column section is shown in Figure 1.
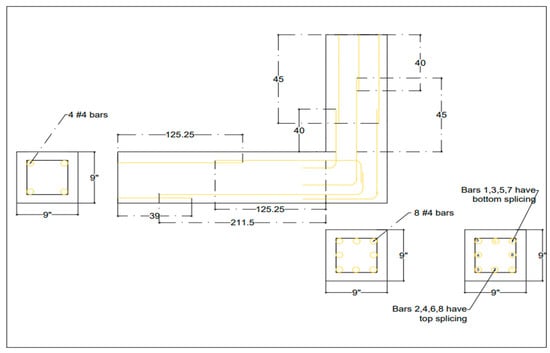
Figure 1.
Beam-column section.
The intervention group used a Unity 3D game for an interactive learning experience, allowing them to visualize and manipulate structural elements. The control group received traditional lecture-based instruction. Data were collected through a questionnaire survey, assessing entertainment, engagement, perceived difficulty, and the reinforcement of concepts. This approach provides an analysis of the educational impact of different teaching methods on complex engineering topics. The data obtained through the questionnaire were analyzed using a statistical method. The results of both groups will be compared to report the observed differences. The subsequent sections provide detailed explanations about different aspects of the study.
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Participants
This study was conducted on a group of 92 students from the University of Engineering and Technology (UET), Peshawar. This sample size is considered sufficient for intervention research [46,47]. Participants were final-year civil engineering students in their 7th semester, chosen because of their prior exposure to complex civil engineering concepts. Their ages ranged from 21 to 23 years. Out of 92 students, 10 were female, and 82 were male. Students were asked to agree to take part in this study, and consent forms were completed. The total participants were divided into the following two groups: the intervention group and the control group, with each group comprising 46 students. One group was exposed to traditional teaching methods, while the other was exposed to game-based learning.
2.2.2. Instrument
To gather students’ responses on both methods, a questionnaire survey was conducted face-to-face in the classroom with both groups. Before conducting it, the survey was validated by two academic experts. Past research has also often involved a limited number of experts to validate theoretical assumptions before conducting a questionnaire survey [48,49]. The questionnaire was divided into two sections, comprising a total of five items. The first section required each group to rate their extent of agreement with three measures on a 5-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 (very low) to 5 (very high). Participants were asked, “How entertaining did you find the method used in this study?”, “How engaged did you feel during the learning process with this method?”, and “How difficult was it for you to understand the concepts presented using this method?”. These questions aimed to measure entertainment [38,39,50], engagement [43,51], and the perceived difficulty level of both techniques to understand [52,53]. How entertaining did you find the method used in this session? How engaged did you feel during the learning process with this method? How difficult was it for you to understand the concepts presented using this method? The second section consisted of two yes/no questions that were included to determine whether the method was helpful in reinforcing concepts [38,54] and to assess motivation to use this method for future learning [43,55]. Participants were asked, “Did you find the method helpful in reinforcing concepts?” and “Are you motivated to use this method for future learning?”. Internal consistency was measured using Cronbach’s alpha, which was 0.721. Values ≥0.70 are considered reliable [56].
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Traditional Teaching Method
The traditional passive approach to education typically involves a lecture-style classroom where the focus is on the professor, with minimal interaction between teachers and students. In this learning mode, the professor assumes an authoritative role in imparting knowledge to the students, while the students primarily act as passive listeners. Traditional teaching methods are teacher-centered methods that lack cooperation and communication opportunities among students [57]. All the students have the same environment for learning, motivation depends on the teacher’s method and style [58], and the physical presence of both teachers and students is necessary in the classroom in the traditional teaching method [59]. The control group was exposed to traditional teaching methods, in which students were taught the topics of development length and lap splices in a lecture-style classroom, where a teacher delivered the lesson using a whiteboard. Following the end of the lecture, the control group was asked to complete the questionnaire survey to gather their feedback regarding the teaching method.
2.3.2. Game-Based Learning Method
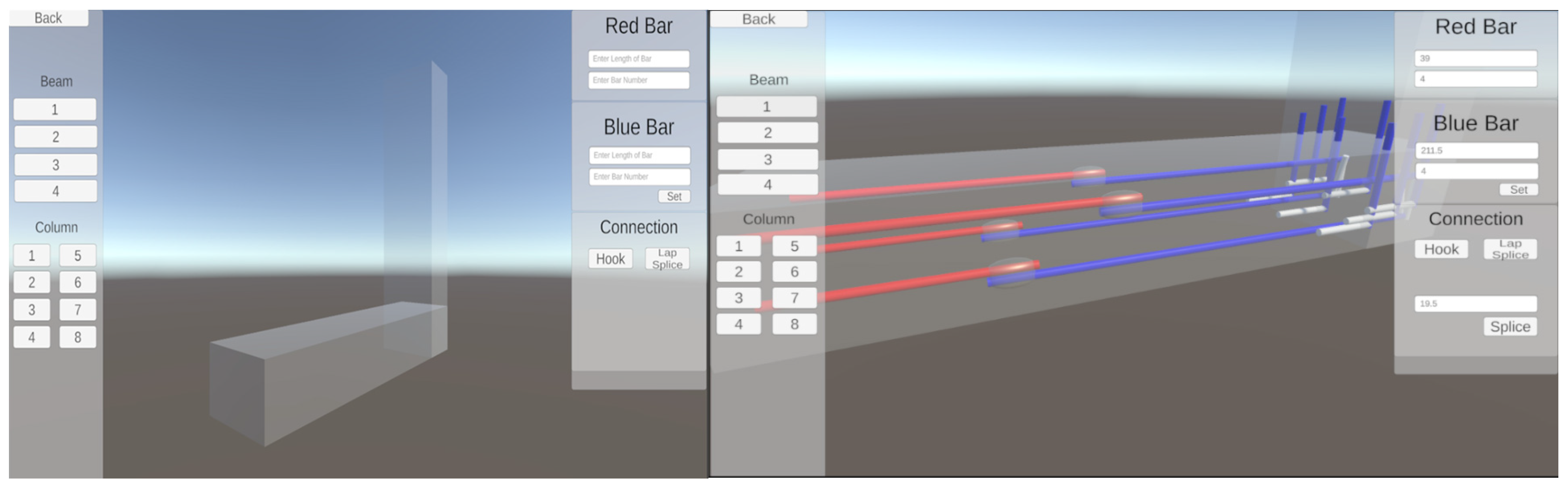
The intervention group was exposed to a game made in Unity 3D. Unity is a versatile game engine designed to develop 2D and 3D video games, simulations, and applications across various platforms, including computers, virtual reality, consoles, and mobile devices. Developed by Unity Technologies, it is commercial software that offers extensive capabilities for three-dimensional manipulation and simulation through programming languages like C#, JavaScript, and Boo. Unity 3D enables the development of high-quality games and 3D social network gaming platforms [60]. Unity’s Graphical User Interface (UGUI) is a robust UI system introduced in Unity versions 4.6 and above. It enables the creation of immersive 3D environments for showcasing and managing virtual elements, such as objects, text, and audio prompts. UGUI offers several advantages, including flexibility, efficiency, visualization, ease of use, and expandability [61]. In a similar manner to the questionnaire, the game was also validated by the same academic experts.
Unity 3D includes various objects, such as cylinders and capsules, utilized for bars, splices, and hooks. The game inputs are the length of bars, diameter of bars, splicing length of bars, and hook lengths. The game outputs include visualizations of bar splicing and development lengths, representing hooks in beam and column bars. The game works as follows: The process begins with the user selecting a bar number within the “Beam” or “Column” category. The camera moves toward the selected bar, and the user is prompted to input the lengths and diameters of the red and blue bars. The red and blue bars are labeled in the game for clarity (see Figure 2 for the game interface, with the left displaying the start of the game with only the beam and column, while the right showcases the bars installed). Upon entering the values, the user is prompted again to input the hook and splicing length for the selected bar. The splicing length is determined using the following formula: Splicing length = 1.3 × development length (dL). Hook lengths are entered for each beam and column bar. Additionally, the game restricts splicing for bars number exceeding 11, in accordance with ACI(318-14) [62] (25.5.1.1) regulations. Finally, the game generates visual representations of the bar splicing and hooks, providing a comprehensive view of the structural elements. The lengths are measured in inches within the game.
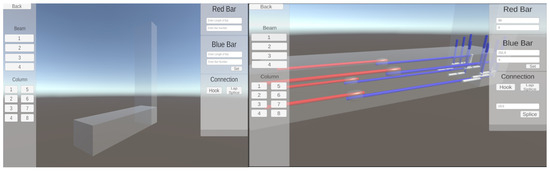
Figure 2.
Game interface.
2.3.3. Data Analysis
The data collected from the questionnaire were analyzed using an independent t-test, as there were no common members between the two groups. The independent t-test was used to compare the mean values of the two sample groups [63]. The mean was calculated for the measures in the questionnaire for both groups, and then the difference between the means was calculated to compare them.
3. Results
3.1. Independent t-Test
The independent t-test was utilized to determine the mean values for questionnaire responses. The mean value of various measures between the game-based and traditional teaching methods was calculated. Table 1 illustrates that the mean for entertainment was 4.13 in the game-based method, higher than the mean of 3.72 in the traditional teaching method, indicating that students found the game more entertaining. Similarly, the mean engagement was 0.93 in the game-based method, which was higher than the mean of 0.41 in the traditional teaching method. Additionally, the mean difficulty level was 2.65 in the game-based method, which was lower than the mean of 2.72 in the traditional teaching method, suggesting that students encountered less difficulty understanding the topic through the game. Moreover, the game was more effective in reinforcing concepts, with a mean of 0.85 compared to 0.67 in the traditional teaching method. Furthermore, for motivation to learn, the mean was 4.65 (p < 0.05) in the game-based method, which was higher than the mean of 2.89 (p < 0.05) in the traditional teaching method.

Table 1.
Independent t-test results.
3.2. Comparison of Measures
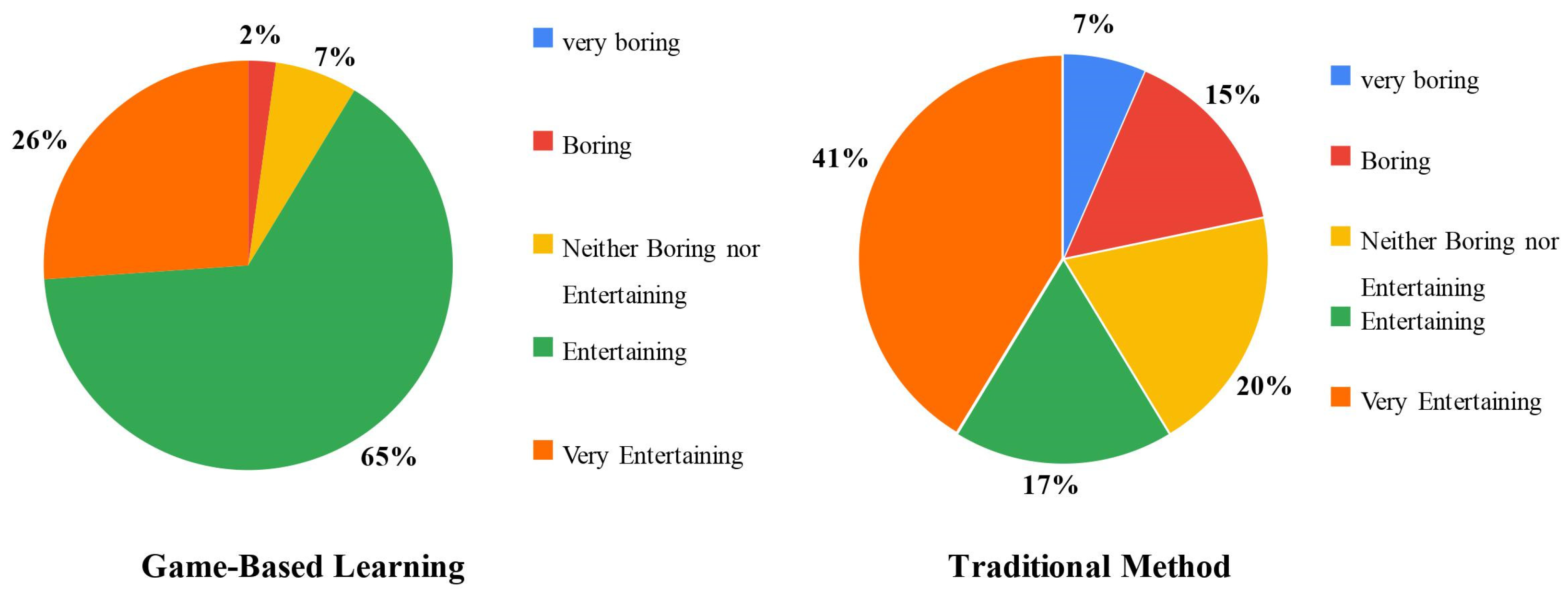
The questionnaire results obtained through the case study indicate that transitioning from traditional teaching methods to gaming techniques can lead to several significant improvements. Figure 3 provides a comparison between these two approaches in terms of their entertainment value. Remarkably, 91% of students found the gaming technique either entertaining or very entertaining, with only 2% finding it boring. In contrast, 58% of students found the traditional teaching method entertaining or very entertaining, while 22% found it boring or very boring.
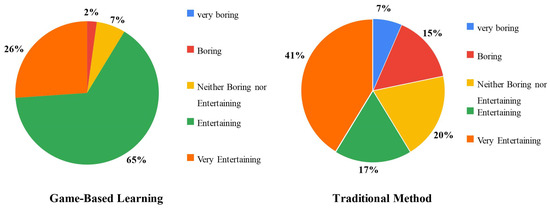
Figure 3.
Entertainment comparison between the two methods.
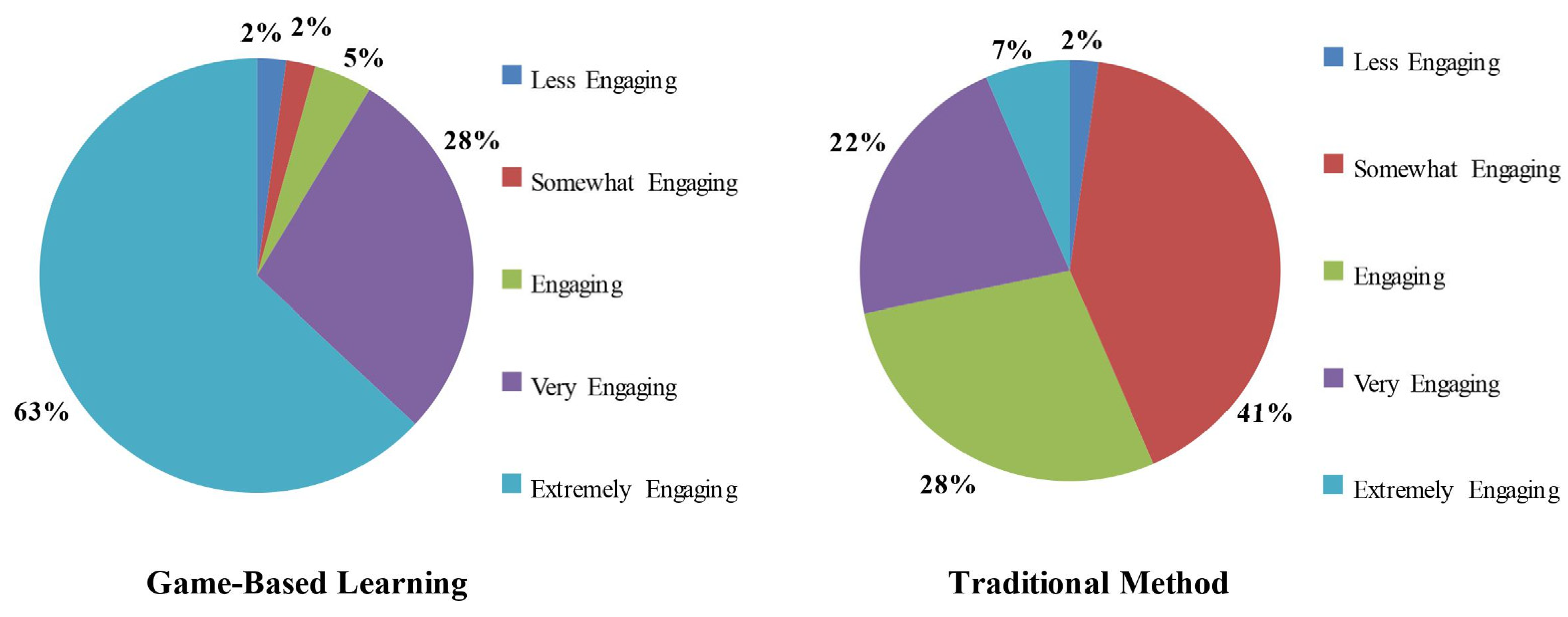
Figure 4 shows the comparison between the traditional teaching method and the gaming technique for engagement purposes. A total of 96% of the students found the gaming technique engaging, very engaging, or extremely engaging, while less than 5% of students found it somewhat engaging or less engaging. In contrast, only 57% of the students found the traditional teaching method engaging, very engaging, or extremely engaging, while 43% students found it somewhat engaging or less engaging. This results in a total of 39% increase in engagement by switching from traditional teaching methods to gaming techniques.
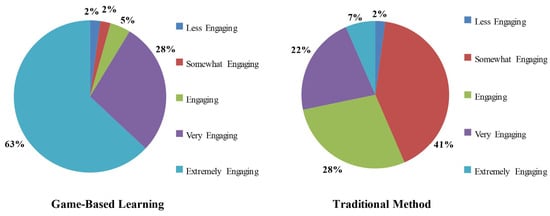
Figure 4.
Engagement comparison between the two methods.
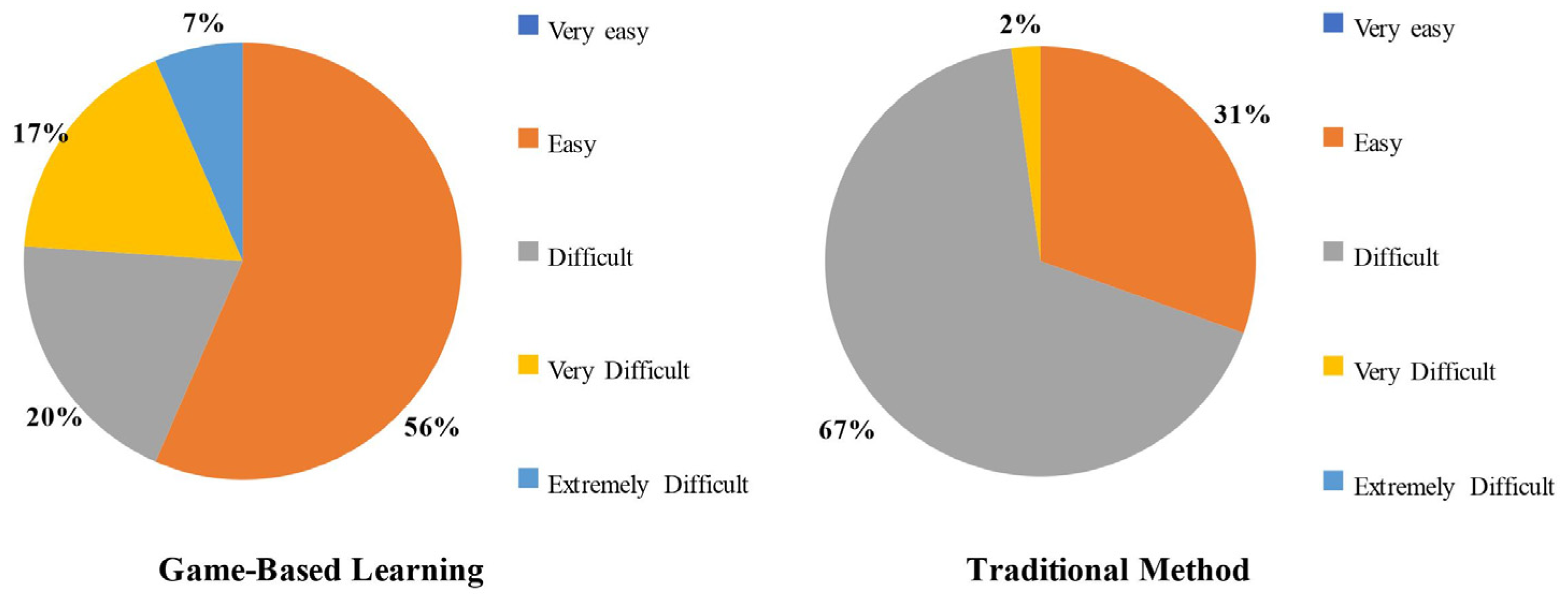
In response to the difficulty level of understanding through the game, one section of students found it easy, while the other section found it difficult. Specifically, 56% of students found the game easy and helpful in understanding the topic, while 44% found it difficult, very difficult, or extremely difficult to understand, as shown in Figure 5. In contrast, in the traditional teaching method, 69% of students found it difficult or very difficult to understand.
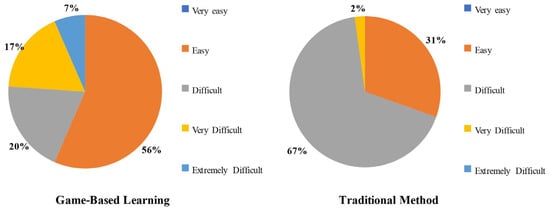
Figure 5.
Difficulty level comparison between the two methods.
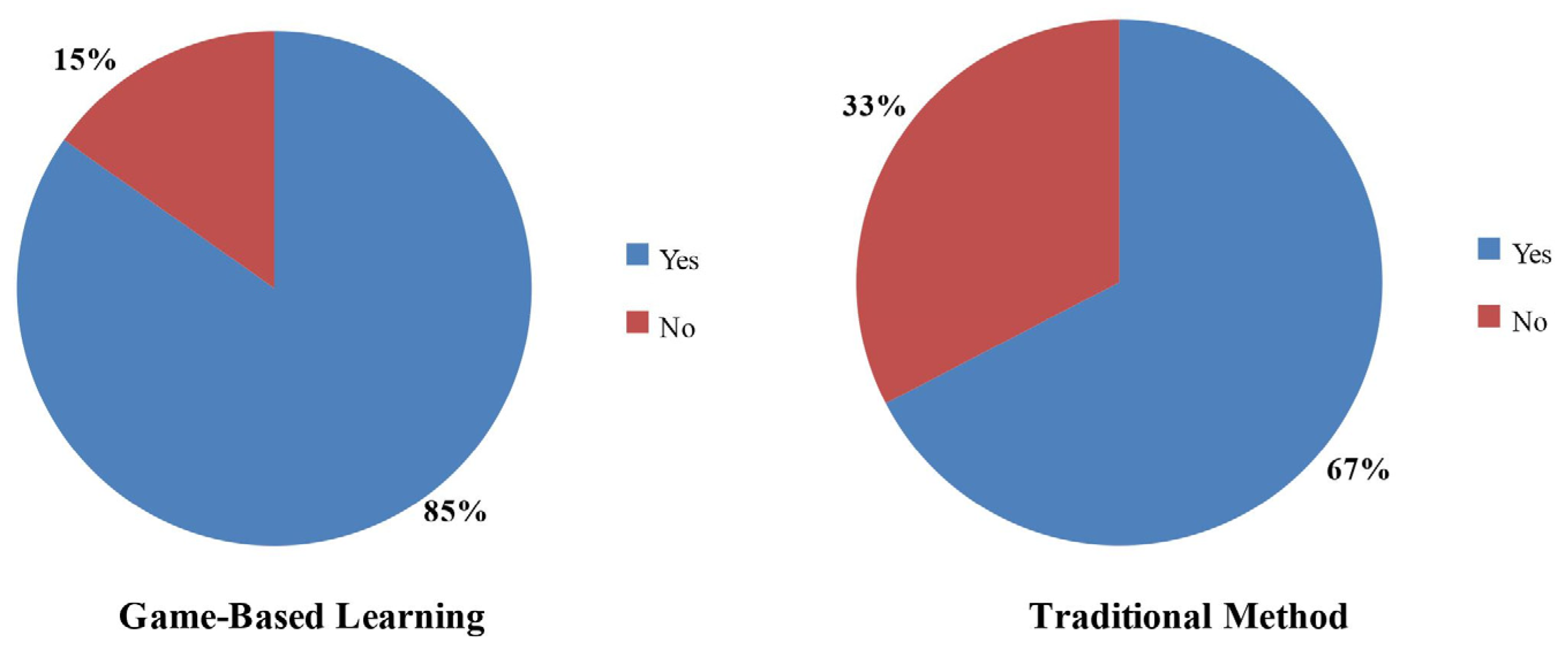
Figure 6 shows the comparison between traditional teaching methods and gaming techniques with regard to helping reinforce concepts. A total of 85% of students find the gaming technique helpful in reinforcing concepts, while 67% of students find traditional teaching methods helpful in the same regard. Therefore, a total of 18% of students found that the games helped more in reinforcing concepts compared to traditional teaching methods.
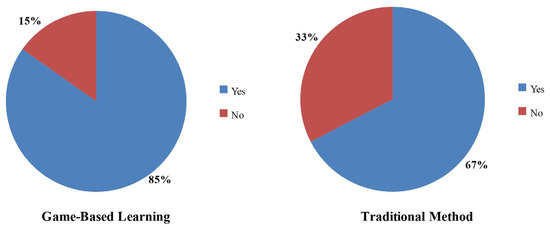
Figure 6.
Concept reinforcement comparison between the two methods.
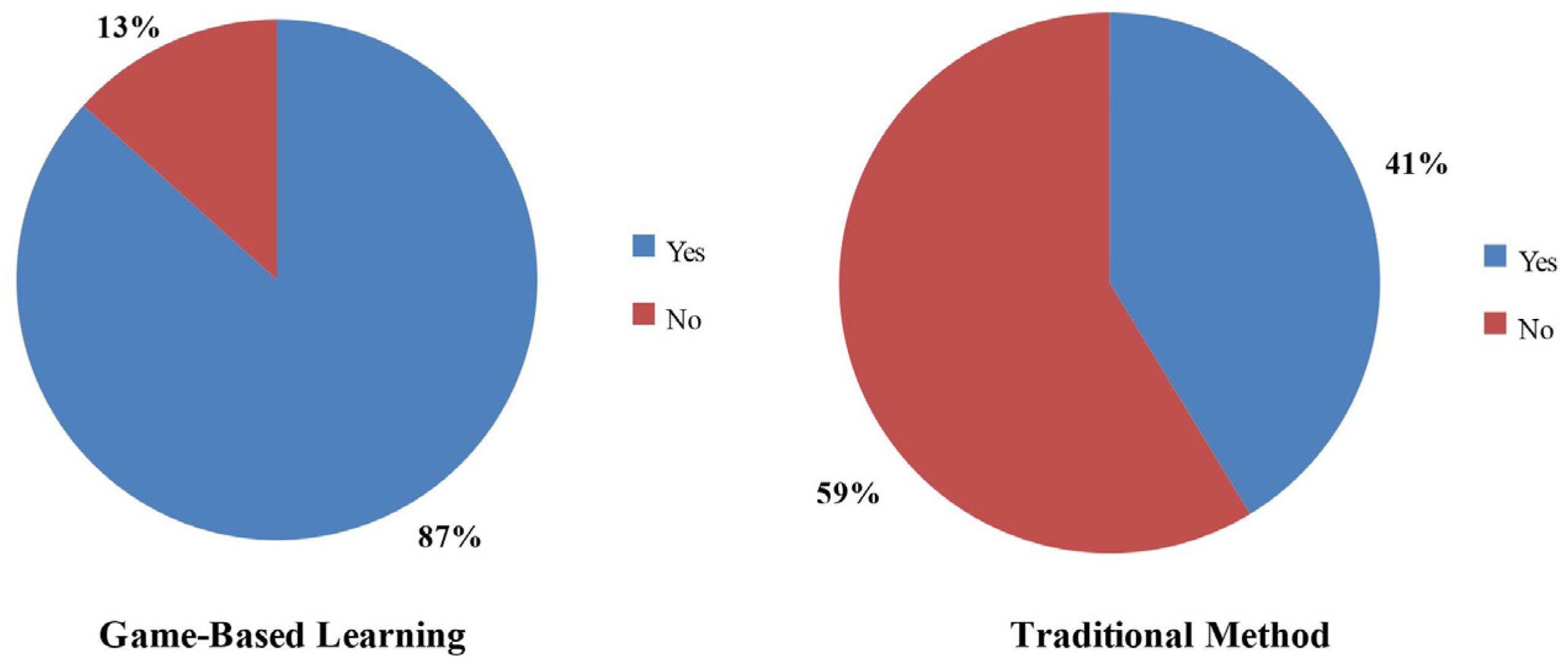
Figure 7 shows the comparison of the motivation levels to learn in the future using the traditional teaching method and the gaming technique. A total of 87% of the students were motivated to use gaming techniques for educational purposes in the future, while only 41% of the students were motivated to use traditional teaching methods.
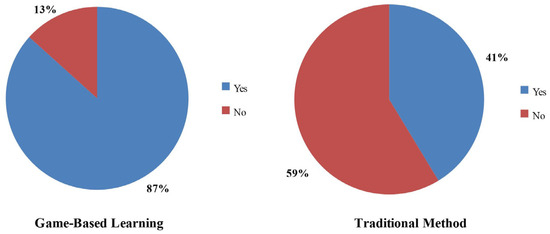
Figure 7.
Motivation level comparison between the two methods.
4. Discussion
Entertainment, which is an activity that captures attention [64], is a crucial element in both traditional teaching methods and gaming techniques. Entertainment value saw a 33% increase, as 91% of students found gaming techniques entertaining or very entertaining, compared to 58% for traditional methods. These findings are consistent with those of Fatahi and Khabbaz [39] and Kazemiroodsari and Folajimi [38]. Fatahi and Khabbaz [39] reported that 60% of participants found their educational game fun to play, while Kazemiroodsari and Folajimi [38] reported found that 73% of students found the games entertaining. This could be attributed to the fact that games have long been associated with leisure activities and have served as a primary source of entertainment in the past. Their integration into educational learning has brought about a significant increase in the entertainment factor [16]. Compared with conventional lecture-based methods, games enhance declarative knowledge, procedural knowledge, and knowledge retention. Entertainment video games are beneficial tools for academic learning, effectively implemented across various academic disciplines and grades. Their integration into classrooms can enhance cognitive skills and academic outcomes, making them a valuable alternative learning method [65].
The term “Engaging” can be defined as an increasing interest in incorporating new ideas into existing knowledge [66]. Engagement levels rose by 39%, with 96% of students finding gaming techniques engaging or very engaging, in contrast to 57% for traditional methods. This increase in engagement aligns with the findings of Hamari et al. [51], who found that educational video games effectively engage students by enhancing concentration, interest, and enjoyment. Their study showed that increasing challenges and skill levels during gameplay positively impacts learning. Similarly, Lashari et al. [43] observed increased engagement levels compared to traditional methods in their intervention study, in which the game-based group showed higher levels of engagement. This aligns with the fact that the introduction of gaming mechanics into educational results enhances user engagement, leading to increased user retention and interaction [13]. Game-based learning, when compared to lecture-based learning, leads to higher engagement for students. The current generation is different from previous generations, and today’s students are only engaged if they are learning through interaction, experience, and exploratory methods [14]. Integrating course content and assignments into video games effectively engages students, especially those from Generation Z and Generation Alpha, who have grown up in the technology era. Compared to conventional methods, educational video games create an interactive and engaging environment, leading to greater student engagement and productivity [38].
The difficulty level involves the effort required to solve the given problem. The difficulty level of understanding material was reduced, as 56% of students found the game easy to understand, compared to 31% with traditional methods, indicating a reduction in difficulty for many students. Martinez et al. [65] and Law [46], in their studies, highlighted that games can facilitate a better understanding of complex concepts compared to traditional methods. Generally, games facilitate learning by breaking down complex components into manageable sections, thus making it easier to comprehend educational concepts [16]. Therefore, students found it easier to understand the topics of development length and lap splicing through game-based learning. However, it is important to note that the difficulty level of the game can greatly affect factors such as entertainment, motivation, and concept reinforcement. Increasing difficulty in games can decrease motivation and immersion, as players may feel overwhelmed or frustrated when tasks become too challenging too quickly. Therefore, to maintain motivation and immersion, it is important to adapt to difficulty levels dynamically, ensuring tasks are neither too easy nor too hard, and to adjust gradually. Balancing the challenge can keep players engaged and motivated [53].
The effectiveness in reinforcing concepts increased by 18%, with 85% of students finding gaming techniques helpful, compared to 67% for traditional methods. Fatahi and Khabbaz [39], in their study of the game “Back-to-Bedrock”, found that game-based learning significantly improved learning outcomes and helped reinforce new concepts and methodologies much more effectively. Similarly, in the study by Lashari et al. [43], the game-based group displayed higher learning outcomes compared to a traditional classroom setting. Additionally, Riopel et al. [54], in their meta-analysis on the impact of serious games on science learning achievement, examined three learning outcomes, namely, declarative knowledge, knowledge retention, and procedural knowledge. They found that games were more beneficial than conventional instructional methods in reinforcing these outcomes. Given that playing video games can already enhance someone’s abilities to react, think, or understand quicker, games that heavily focus on educational purposes should aid students in excelling in school. Video games offer greater interactivity than a classroom setting and can particularly benefit hands-on learners who struggle with certain subjects. Integrating video games into classrooms can help students focus and comprehend concepts more clearly [38].
Student motivation to learn in the future increased by 46%, with 87% of students being motivated by gaming techniques, compared to 41% by traditional methods. Arztmann et al. [15] conducted a meta-analysis on the effects of games in STEM education. Our results are consistent with their findings, indicating that game-based learning has beneficial effects on student motivation. Similarly, in the study by Lashari et al. [43], it was observed that motivation was higher in the game-based group compared to the traditional classroom. Lin et al. [67] reported similar findings, highlighting that increased student motivation is the most significant benefit of game-based learning, irrespective of the device/tool used, whether mobile phones or computers. Students may lack motivation due to a lack of aspiration to perform an activity and may consider learning activities as unpleasant [6]. Incorporating games into education has been shown to increase learning motivation [17]. When games are integrated into STEM education, students report markedly improved learning outcomes, heightened motivation, and observable behavioral changes compared to those in traditional classrooms [15]. The increased motivation compared to traditional methods can be attributed to the presence of a “flow” experience in games, in which players become fully immersed and engaged, losing track of time and external distractions. This state leads to enhanced concentration and enjoyment, ultimately leading to higher motivation [55].
The results of this study, although based on limited lectures, have important implications for both theory and practice in structural engineering. Key findings indicate that game-based learning in civil engineering can enhance student motivation and engagement; additionally, it can reinforce concepts effectively and reduce the difficulty level of complex topics. These benefits suggest that integrating educational games can significantly improve the learning experience and outcomes of engineering students.
5. Conclusions
Gamification involves the application of video game mechanics to non-game processes to enhance user engagement, leading to increased user retention and interaction [13]. This study investigated the impact of introducing gamification on student engagement and learning outcomes in civil engineering, a branch of STEM. For this purpose, a simulation game was developed using Unity 3D to teach the concepts of development length and lap splicing of reinforcement bars. The primary objective was to determine whether game-based learning could enhance student interest and understanding compared to traditional teaching methods. To validate the benefits of game-based learning in enhancing students’ learning, the game was tested in a classroom setting by students. The findings reveal that students found the game-based learning approach to be significantly more entertaining, engaging, effective in reinforcing concepts, motivating, and easier to understand compared to traditional teaching methods.
These preliminary findings suggest that incorporating interactive and gamified elements into the civil engineering curriculum can substantially improve student engagement, motivation, and understanding. Furthermore, the positive feedback from students highlights the need for a wider application of gamified learning tools in civil engineering education. Students expressed a strong preference for gamification and recommended expanding the game to cover additional topics in structural engineering. The practical application of this study is the incorporation of this game by teachers in the classroom, enabling students to apply their knowledge in a simulated real-world environment. This application helps students further improve their skills by dealing with real-world problems through game-based learning. Additionally, gamification will significantly reduce teachers’ efforts by allowing them to spend less time on lecture delivery.
This case study has certain limitations. Firstly, the validation was limited to one lecture. Secondly, there may be volunteer bias in the results, as a large group of participants were experiencing the educational game for the first time. Lastly, there may be observer bias due to the presence of the observer during the survey, potentially affecting participants’ behavior. Future studies may consider the implementation of gamification over an entire semester to generalize results better. Additionally, to enhance collaboration among students, games can be developed for multiple players, as the present study is limited to single-player mode. Given the positive response from students obtained through the survey, the game could cover more structural engineering concepts in the future. However, this study has certain limitations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.K., M.U.Z. and M.U.H.; methodology, M.A.K., M.U.Z. and M.U.H.; software, M.A.K., M.U.Z. and M.U.H.; validation, M.U.H., K.A. and T.A.; formal analysis, M.A.K.; investigation M.A.K., M.U.Z. and M.U.H.; resources, M.U.Z., K.A. and M.U.H.; data curation, M.A.K. and T.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.K., M.U.H., K.A. and M.U.Z.; writing—review and editing, M.U.Z., K.A. and T.A.; visualization, M.A.K. and T.A.; supervision, M.U.Z., K.A. and M.U.H.; project administration, M.U.H. and M.U.Z.; funding acquisition, M.U.Z. and M.U.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia (GRANT No. KFU 241390). The APC was funded by the same ”Grant No. KFU241390”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia (GRANT No. KFU241390). The authors extend their appreciation for the financial support that has made this study possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bacovic, M.; Andrijasevic, Z.; Pejovic, B. STEM education and growth in Europe. J. Knowl. Econ. 2022, 13, 2348–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, E.; Veermans, M.; Gegenfurtner, A.; Veermans, K. Individual Interest and Learning in Secondary School STEM Education. Frontline Learn. Res. 2020, 8, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N. Using computer simulation and animation to improve student learning of engineering dynamics. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 56, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.; Robbins, S.B.; Westrick, P. Predicting student enrollment and persistence in college STEM fields using an expanded P-E fit framework: A large-scale multilevel study. J. Appl. Psychol. 2014, 99, 915–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coman, C.; Țîru, L.G.; Meseșan-Schmitz, L.; Stanciu, C.; Bularca, M.C. Online teaching and learning in higher education during the coronavirus pandemic: Students’ perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, E.F.; Major, C.H. Student Engagement Techniques: A Handbook for College Faculty; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Harandi, S.R. Effects of e-learning on Students’ Motivation. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 181, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, R.M.; Felder, G.N.; Dietz, E.J. A longitudinal study of engineering student performance and retention. V. Comparisons with traditionally-taught students. J. Eng. Educ. 1998, 87, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobald, E.J.; Hill, M.J.; Tran, E.; Agrawal, S.; Arroyo, E.N.; Behling, S.; Chambwe, N.; Cintrón, D.L.; Cooper, J.D.; Dunster, G. Active learning narrows achievement gaps for underrepresented students in undergraduate science, technology, engineering, and math. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2020, 117, 6476–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehl, A.; Reddy, S.L.; Shannon, G.J. The flipped classroom: An opportunity to engage millennial students through active learning strategies. J. Fam. Consum. Sci. 2013, 105, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanberry, M.L. Active learning: A case study of student engagement in college calculus. Int. J. Math. Educ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 49, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, N. A Sample of Active Learning Application in Science Education: The Thema “Cell” with Educational Games. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 46, 2932–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Callaghan, M.; McShane, N.; Eguíluz, A.G. Using game analytics to measure student engagement/retention for engineering education. In Proceedings of the 2014 11th International Conference on Remote Engineering and Virtual Instrumentation (REV), Porto, Portugal, 26–28 February 2014; pp. 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimley, M.; Green, R.; Nilsen, T.; Thompson, D.; Tomes, R. Using computer games for instruction: The student experience. Act. Learn. High. Educ. 2011, 12, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arztmann, M.; Hornstra, L.; Jeuring, J.; Kester, L. Effects of games in STEM education: A meta-analysis on the moderating role of student background characteristics. Stud. Sci. Educ. 2023, 59, 109–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, E.; Esche, S.; Chassapis, C. Review of the State of the Art in Virtual Learning Environments Based on Multiplayer Computer Games. In American Society for Engineering Education. American Society for Engineering Education; American Society for Engineering Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 14.1032.1–14.1032.16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Peng, H.Y.; Chao, H.C. Examining the effects of learning motivation and of course design in an instructional simulation game. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2010, 18, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio Sandoval, C.; Koch, C.; Tizani, W. Computer Technology for Serious Games in Education: A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 24th EG-ICE International Workshop on Intelligent Computing in Engineering, Nottingham, UK, 10–12 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, M.; Wagner, M.J.; Poznanski, S.; Schiller, J.; Santen, S. Not another boring lecture: Engaging learners with active learning techniques. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 48, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-de-Menéndez, M.; Vallejo Guevara, A.; Tudón Martínez, J.C.; Hernández Alcántara, D.; Morales-Menendez, R. Active learning in engineering education. A review of fundamentals, best practices and experiences. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 2019, 13, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderdahl, P.A. Library classroom renovated as an active learning classroom. Libr. Hi Tech. 2011, 29, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Horne, S.; Murniati, C.; Gaffney, J.D.; Jesse, M. Promoting active learning in technology-infused TILE classrooms at the University of Iowa. J. Learn. Spaces 2012, 1, n2. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, F.S.; Kiray, S.A. Flipped classroom model in education. Res. Highlights Educ. Sci. 2016, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Akçayır, G.; Akçayır, M. The flipped classroom: A review of its advantages and challenges. Comput. Educ. 2018, 126, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, B.A. Flipped learning in a civil engineering module: Student and instructor experiences. Ir. J. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2019, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.P.; Anderson, L. Active learning techniques versus traditional teaching styles: Two experiments from history and political science. Innov. High. Educ. 2000, 24, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, F. Activity-Based Teaching, Student Motivation and Academic Achievement. J. Educ. Educ. Dev. 2019, 6, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.F.B.; Puteh, S.B.; Sanusi, A.B.M. Elements of technology enabled/enhanced active learning (TEAL) to enhance quality and employability of bachelor’s students. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 150, 05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.F.; Puteh, S.; Buhari, R. Student Understanding Through the Application of Technology Enabled Active Learning in Practical Training. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 204, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirker, J. The Virtual TEAL World-An Interactive and Collaborative Virtual World Environment for Physics Education. Master’s Thesis, Graz University of Technology, Graz, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fioravanti, M.L.; Sena, B.; Paschoal, L.N.; Silva, L.R.; Allian, A.P.; Nakagawa, E.Y.; Souza, S.R.; Isotani, S.; Barbosa, E.F. Integrating project based learning and project management for software engineering teaching: An experience report. In Proceedings of the 49th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education, Baltimore, MD, USA, 21–24 February 2018; pp. 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, K.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Lou, S.-J.; Chen, W.-P. Attitudes towards science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) in a project-based learning (PjBL) environment. Int. J. Technol. Des. Educ. 2013, 23, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilvonen, J.; Ovaska, P. Student Motivation in Project-Based Learning; International Conference on Engaging Pedagogy. 2010. Available online: http://icep.ie/wp-content/uploads/2011/02/Student-Motivation-in-Project-Based-Learning.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2024).
- Stevens, R. Role-play and student engagement: Reflections from the classroom. Teach. High. Educ. 2015, 20, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabsi, T.A. The effectiveness of role play strategy in teaching vocabulary. Theory Pract. Lang. Stud. 2016, 6, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.A.; Conlon, E.; Bowe, B. The role of role-play in student awareness of the social dimension of the engineering profession. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 2019, 44, 882–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Z.C. Role-playing in the problem-based learning class. Nurse Educ. Pract. 2012, 12, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemiroodsari, H.; Folajimi, Y. Video Game to Teach Fluid Mechanics (Work in Progress); 2022 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition. 2022. Available online: https://sftp.asee.org/video-game-to-teach-fluid-mechanics-work-in-progress (accessed on 4 May 2024).
- Fatahi, B.; Khabbaz, H. Based Computer Games to Train Civil Engineering Students to Be Lifelong Learners. In Proceedings of the 43rd SEFI Annual Conference 2015-Diversity in Engineering Education: An Opportunity to Face the New Trends of Engineering, SEFI 2015, Orléans, France, 29 June–2 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, C.J.; Coetzee, J. Interactive learning through gaming simulation in an integrated land use–transportation planning course. J. Prof. Issues Eng. Educ. Pract. 2014, 140, 04013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, E.; Garbrecht, O.; Kneer, R.; Rohlfs, W. Game-based learning apps in engineering education: Requirements, design and reception among students. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 2023, 48, 448–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meksophawannagul, M. The Development and Effectiveness of Game-Based Learning Prototypes for Daily Life Words at B1 Level: A Case Study of Engineering Students in Thailand. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2024, 17, 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, T.A.; Fiayaz, R.; Lashari, S.A.; Khan, I.; Sultana, S.; Afzal, T. Kahoot: A game-based web tool to assess motivation, engagement fun, and learning outcomes among engineers. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2024, 32, e22684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, B.M.; Morrison-Beedy, D. Setting the stage for intervention research: The “so what” factor. Interv. Res. Des. Conduct. Anal. Funding 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, M.N.; Al-Manaseer, A. Structural Concrete: Theory and Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Law, K.M. Teaching project management using project-action learning (PAL) games: A case involving engineering management students in Hong Kong. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2019, 11, 1847979019828570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatri, Z.G. Advantages and disadvantages of using information technology in learning process of students. J. Turk. Sci. Educ. 2020, 17, 420–428. [Google Scholar]
- Zahoor, H.; Chan, A.P.C.; Utama, W.P.; Gao, R.; Memon, S.A. Determinants of Safety Climate for Building Projects: SEM-Based Cross-Validation Study. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 05017005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.U.; Zhang, X. Hybrid Performance-Measurement Model of Elevators. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2020, 34, 04020013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesionkowska, J.; Wild, F.; Deval, Y. Active learning augmented reality for STEAM education—A case study. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamari, J.; Shernoff, D.J.; Rowe, E.; Coller, B.; Asbell-Clarke, J.; Edwards, T. Challenging games help students learn: An empirical study on engagement, flow and immersion in game-based learning. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 54, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Ruipérez-Valiente, J.A. Data-driven game design: The case of difficulty in educational games. In Proceedings of the Addressing Global Challenges and Quality Education: 15th European Conference on Technology Enhanced Learning, EC-TEL 2020, Heidelberg, Germany,, 14–18 September 2020; Proceedings 15. pp. 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, A.; McMullen, J.; Hannula-Sormunen, M.; Ninaus, M.; Kiili, K. The strength and direction of the difficulty adaptation affect situational interest in game-based learning. Comput. Educ. 2023, 194, 104694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riopel, M.; Nenciovici, L.; Potvin, P.; Chastenay, P.; Charland, P.; Sarrasin, J.B.; Masson, S. Impact of serious games on science learning achievement compared with more conventional instruction: An overview and a meta-analysis. Stud. Sci. Educ. 2019, 55, 169–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicia, P. Motivation in Games: A Literature Review. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Sport 2012, 11, 4. [Google Scholar]
- van Prooijen, J.-W.; van der Kloot, W.A. Confirmatory Analysis of Exploratively Obtained Factor Structures. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2001, 61, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. A comparative study on the effectiveness of traditional and modern teaching methods. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Humanities Education and Social Sciences (ICHESS 2022), Chongqing, China, 14–16 October 2022; pp. 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, S. E-learning environment compared to traditional classroom. In Proceedings of the 34th International Convention MIPRO, Opatija, Croatia, 23–27 May 2011; IEEE: Piscatway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1299–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, I.M. Can you see me now: Defining teaching presence in the online classroom through building a learning community. J. Leg. Stud. Educ. 2011, 28, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyuksalih, I.; Bayburt, S.; Buyuksalih, G.; Baskaraca, A.; Karim, H.; Rahman, A.A. 3D modelling and visualization based on the unity game engine–advantages and challenges. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 4, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, V.C.; Ren, H.X.; Nguyen, V.S. Using Unity3D to simulate VHF sailor 3520. In Proceedings of the 2017 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 13–16 December 2017; pp. 2920–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACI(318-14), Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete; Commentary on Building Code Requirements 663 for Structural Concrete (ACI 318R-14); American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2022.
- McCasland, R.L.; Moore, M.E. Prime submodules. Commun. Algebra 1992, 20, 1803–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, S. An Introduction to the Entertainment Industry; The Entertainment Industry: An Introduction; Peter Lang: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, L.; Gimenes, M.; Lambert, E. Entertainment video games for academic learning: A systematic review. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2022, 60, 1083–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Eddy, E.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.-C. Engaging in argumentation. Sci. Child. 2018, 56, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C.; Ho, J.-Y.; Lai, C.-H.; Jong, B. Mobile game-based learning to inspire students learning motivation. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Information Science, Electronics and Electrical Engineering, Sapporo, Japan, 26–28 April 2014; Volume 2, pp. 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).