A Reliability-Based Traffic Equilibrium Model with Boundedly Rational Travelers Considering Acceptable Arrival Thresholds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. TTB with Route Travel Time Boundary
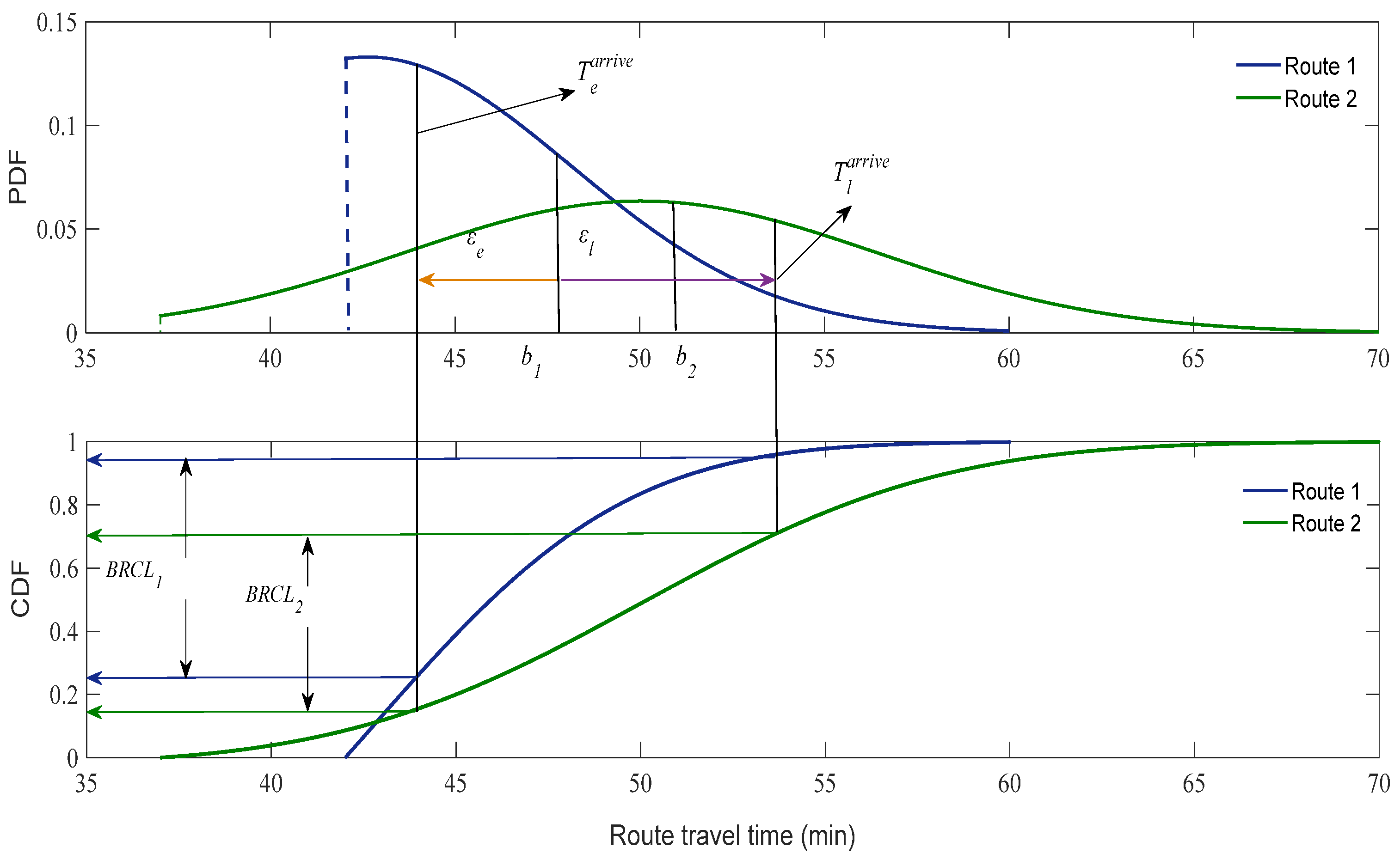
2.1. Truncated Route Travel Distribution
2.2. TTB with Lower Boundary
3. R-BRTE Model
3.1. Definition of BRCL
3.2. Threshold Estimation
3.3. Equilibrium Model and VI Formulation
4. Solution Algorithm
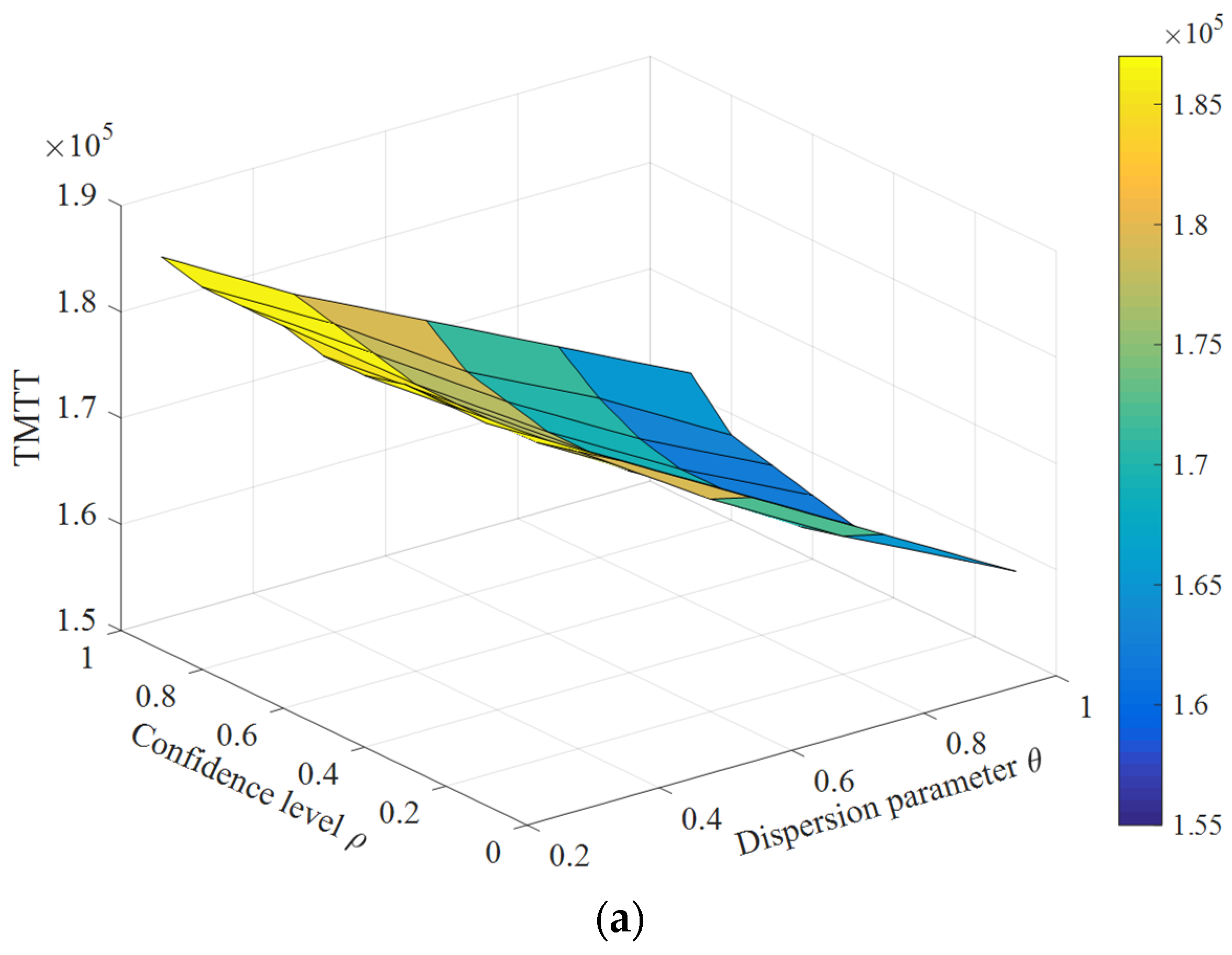
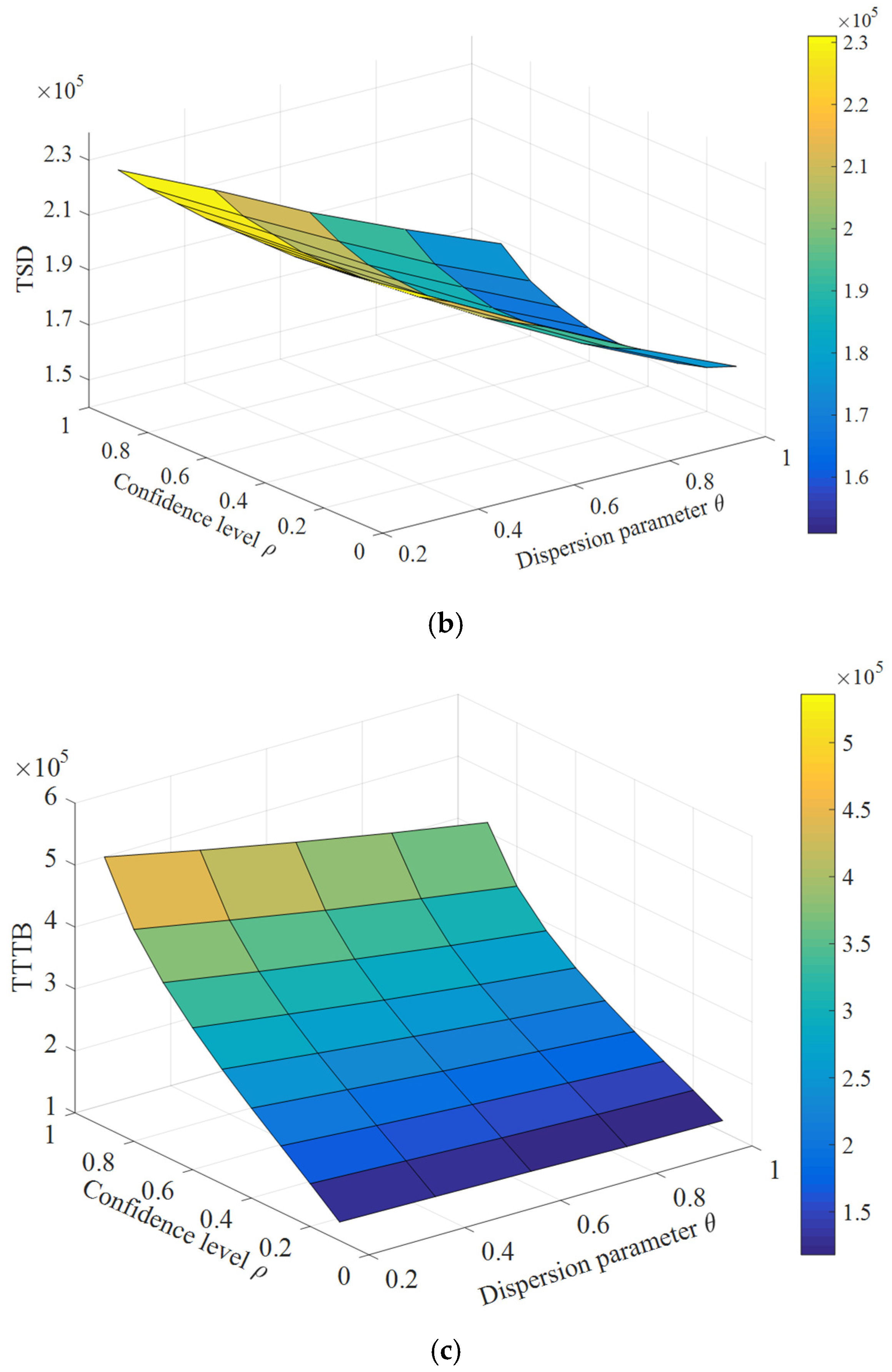
5. Numerical Example
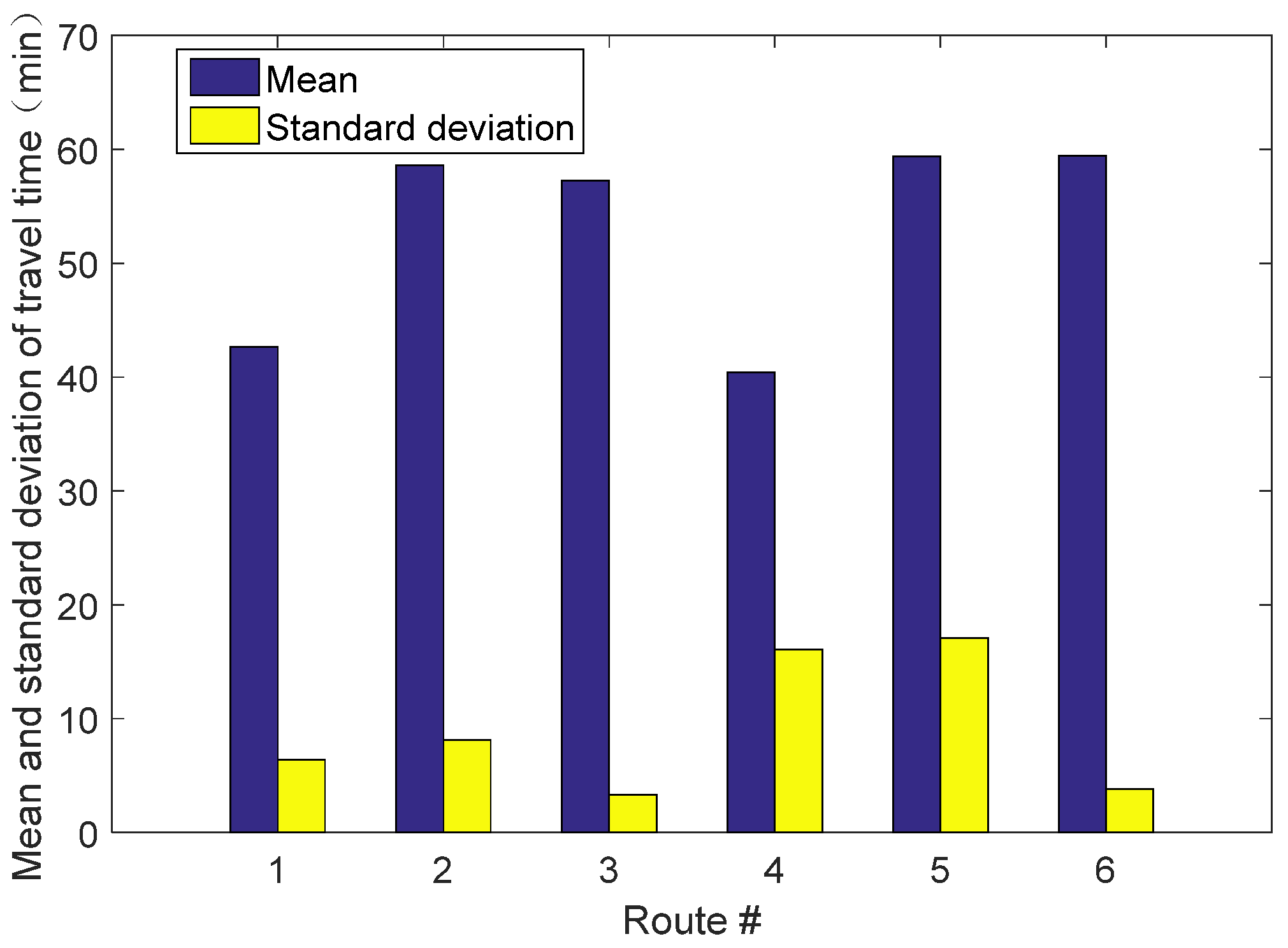
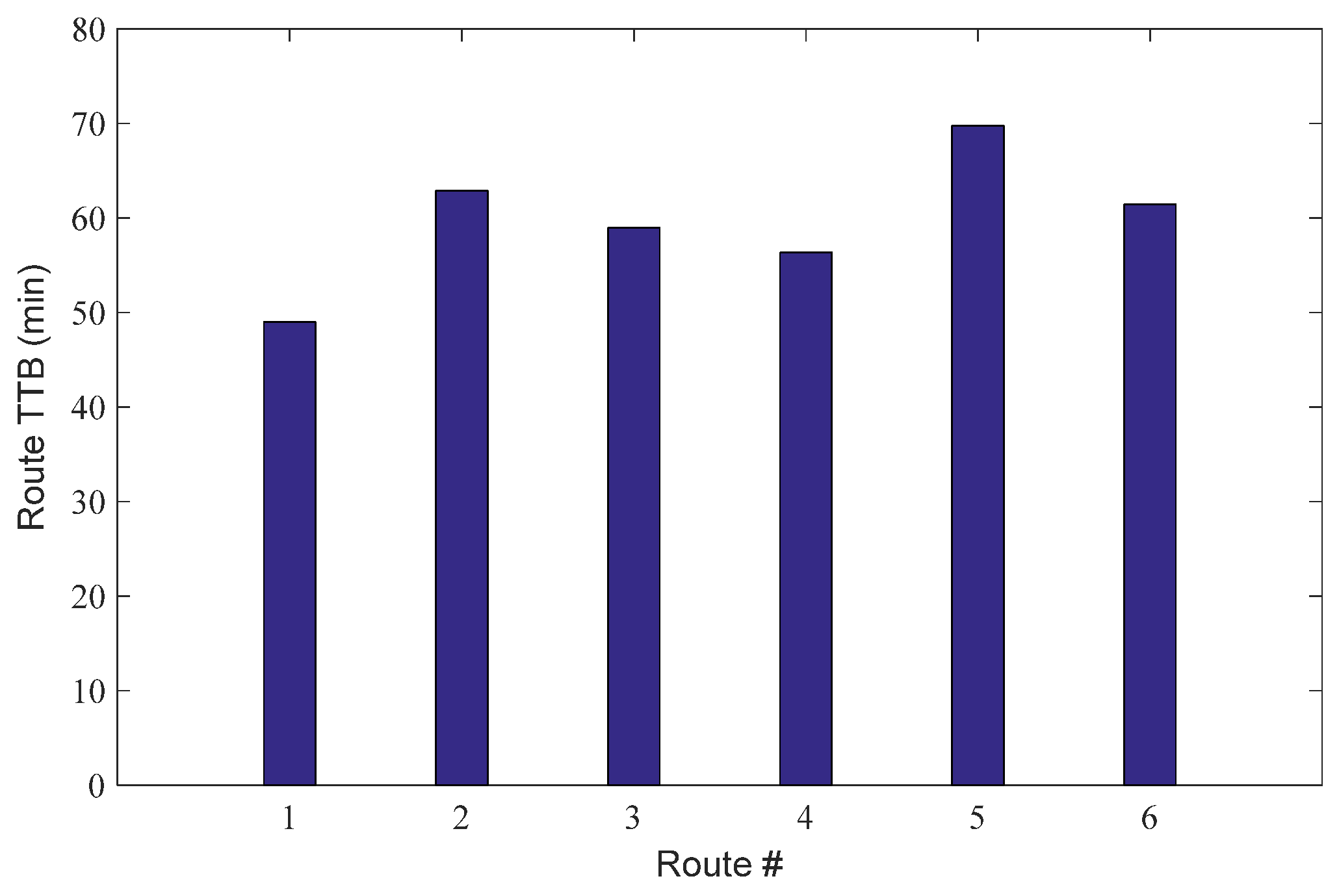
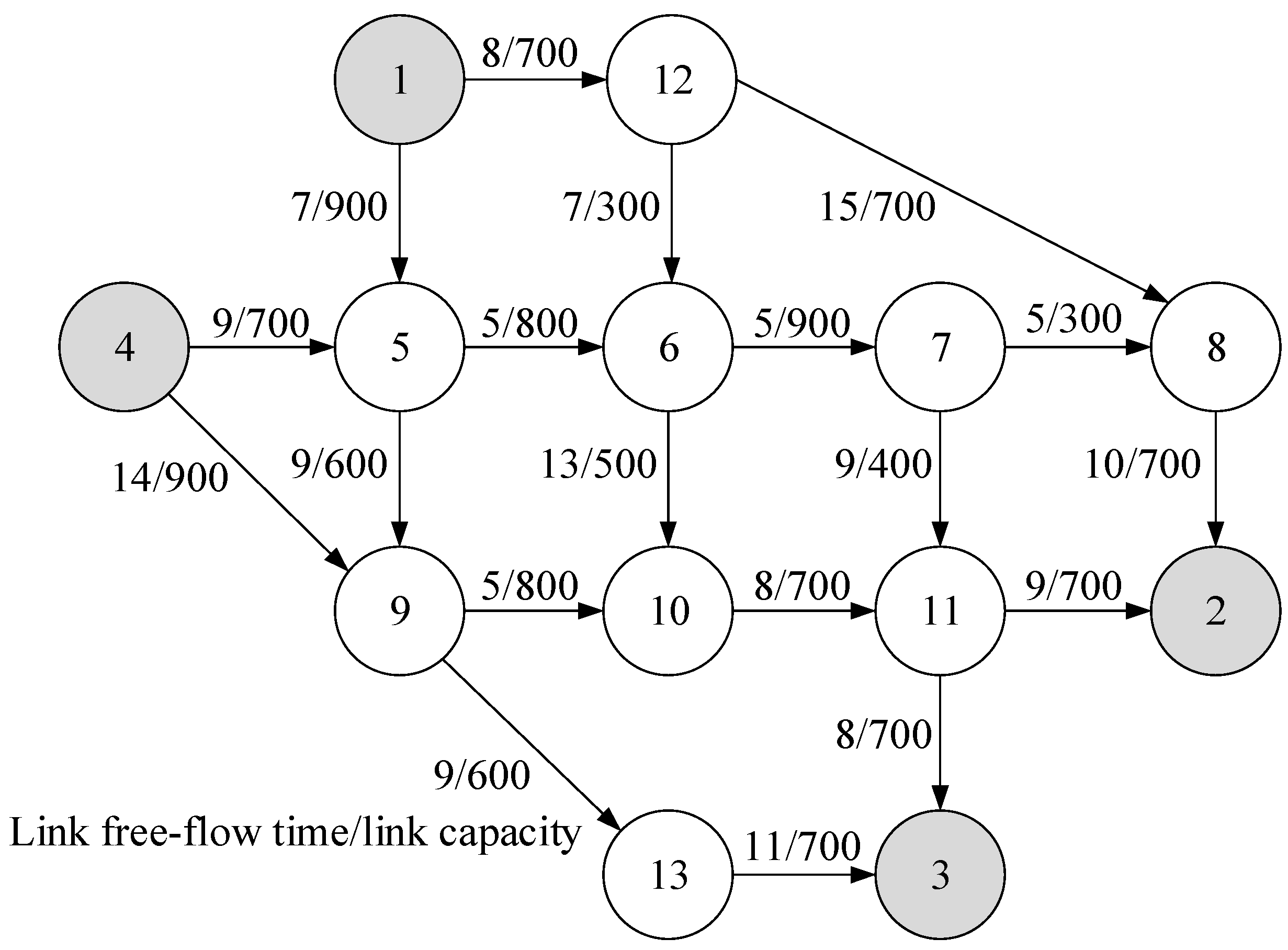
5.1. A Nine-Grid Transportation Network
5.2. Nguyen–Dupuis Transportation Network
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wardrop, J.G. Some theoretical aspects of road traffic research. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Part II 1952, 2, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huang, H. The multi-class, multi-criteria traffic network equilibrium and systems optimum problem. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2004, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Huang, H.; Gao, Z. A Cumulative Perceived Value-Based Dynamic User Equilibrium Model Considering the Travelers’ Risk Evaluation on Arrival Time. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2012, 12, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, H.; Zhou, J.; Yin, Y. A Route Choice Model with Context-Dependent Value of Time. Transp. Sci. 2017, 51, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, H.X. Bounded rationality and irreversible network change. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2011, 45, 1606–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Szeto, W.Y.; Friesz, T.L. Formulation, existence, and computation of boundedly rational dynamic user equilibrium with fixed or endogenous user tolerance. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2015, 79, 16–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S. Effect of providing traffic information estimated by a stochastic network equilibrium model with stochastic demand. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 70, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.C.; Small, K.A. The value of time and reliability: Measurement from a value pricing experiment. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2001, 37, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K.; Kato, T. A Simplified Network Model for Travel Time Reliability Analysis in a Road Network. J. Adv. Transp. 2017, 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.K.; Luo, X.W.; Siu, B.W.Y. Degradable transport network: Travel time budget of travelers with heterogeneous risk aversion. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2006, 40, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhou, Z. The α-reliable mean-excess traffic equilibrium model with stochastic travel times. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2010, 44, 493–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhou, Z.; Lam, W.H.K. Modeling stochastic perception error in the mean-excess traffic equilibrium model. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2011, 45, 1619–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, F.R.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lv, X.Y.; Wen, Z.L. A Reliability-Based Stochastic Traffic Assignment Model for Signalized Traffic Network with Consideration of Link Travel Time Correlations. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, M.; Bliemer, M.; Beck, M.J.; Hess, S.; van Lint, J. Stated choices and simulated experiences: Differences in the value of travel time and reliability. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2021, 128, 103145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, J.; Xu, W. A decision-making rule for modeling travelers’ route choice behavior based on cumulative prospect theory. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2011, 19, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Frejinger, E.; Ben-Akiva, M. Adaptive route choices in risky traffic networks: A prospect theory approach. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2010, 18, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhong, S.; Ma, S.; Jia, N. Prospect theory based estimation of drivers’ risk attitudes in route choice behaviors. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 73, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, H. A regret theory-based route choice model. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2017, 13, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guan, H.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Wu, X.B. A regret-based route choice model with asymmetric preference in a stochastic network. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, B. The impact of bounded rational differences in consumers on suppliers’ product pricing: A two-level popolation game model. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2022, 42, 144–154. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Xia, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z. Networked Decision-Making Dynamics Based on Fair, Extortionate and Generous Strategies in Iterated Public Goods Games. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 2450–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, A.; Lo, H.K.; Yang, C. Modeling the impacts of speed limits on uncertain road networks. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2017, 14, 66–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guan, H.Z.; Zhu, J.Z.; Wei, Y.F. A Reliability-Based Network Equilibrium Model with Adaptive Risk-Averse Travelers. J. Adv. Transp. 2018, 2018, 5294185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Jiang, R.; Gao, Z.; Shao, H. Effect of speed limits in degradable transport networks. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 56, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmassani, H.S.; Chang, G. On Boundedly Rational User Equilibrium in Transportation Systems. Transp. Sci. 1987, 21, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Lawphongpanich, S. Robust congestion pricing under boundedly rational user equilibrium. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2010, 44, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Liu, H.X.; Pang, J.; Ban, X.J. Boundedly Rational User Equilibria (BRUE): Mathematical Formulation and Solution Sets. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 80, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cantillo, V.; Heydecker, B.; Ortuzar, J.D. A discrete choice model incorporating thresholds for perception in attribute values. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2006, 40, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantillo, V.; Ortuzar, J.D.; Williams, H. Modeling discrete choices in the presence of inertia and serial correlation. Transp. Sci. 2007, 41, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Cheng, L.; Ma, J. Travel time reliability with boundedly rational travelers. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2017, 14, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Hongzhi, G.; Keke, L. Day-to-day dynamic evolution of network traffic folw under bounded rational view. Aacta Phys. Sin. 2016, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, H.G.; Leclercq, L.; Chiabaut, N.; Becarie, C.; Krug, J. Travel time and bounded rationality in travellers’ route choice behaviour: A computer route choice experiment. Travel Behav. Soc. 2021, 22, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.K.; Tung, Y. Network with degradable links: Capacity analysis and design. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2003, 37, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| OD Pair | Route # | Associated Link |
|---|---|---|
| 1-6 | 1 | 1-2-3-6 |
| 2 | 1-2-5-6 | |
| 3 | 1-5-5-6 | |
| 7-6 | 4 | 7-8-9-6 |
| 5 | 7-8-5-6 | |
| 6 | 7-4-5-6 |
| OD | Route | Route Flow (veh/h) | Shortest TTB (min) | Boundedly Rational Threshold | BRCL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Arrival Threshold (min) | Early Arrival Threshold (min) | |||||
| 1-6 | 1 | 566.32 | 48.99 | 14.21 | 8.59 | 0.88 |
| 2 | 456.35 | 0.45 | ||||
| 3 | 477.33 | 0.54 | ||||
| 7-6 | 4 | 597.28 | 56.38 | 14.49 | 8.95 | 0.40 |
| 5 | 621.97 | 0.48 | ||||
| 6 | 780.74 | 0.94 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H. A Reliability-Based Traffic Equilibrium Model with Boundedly Rational Travelers Considering Acceptable Arrival Thresholds. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6988. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086988
Wang L, Zhao L, Hu X, Zhao X, Wang H. A Reliability-Based Traffic Equilibrium Model with Boundedly Rational Travelers Considering Acceptable Arrival Thresholds. Sustainability. 2023; 15(8):6988. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086988
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liang, Lei Zhao, Xiaojian Hu, Xinyong Zhao, and Huan Wang. 2023. "A Reliability-Based Traffic Equilibrium Model with Boundedly Rational Travelers Considering Acceptable Arrival Thresholds" Sustainability 15, no. 8: 6988. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086988
APA StyleWang, L., Zhao, L., Hu, X., Zhao, X., & Wang, H. (2023). A Reliability-Based Traffic Equilibrium Model with Boundedly Rational Travelers Considering Acceptable Arrival Thresholds. Sustainability, 15(8), 6988. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086988





