Assessing Water Security and Coupling Coordination in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin for Sustainable Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Indicator System Construction Method
2.2.2. Indicator Weighting Method
2.2.3. Integrated Water Security Assessment Method
- (1)
- Single-index quantification
- (2)
- Comprehensive multi-index
- (3)
- Multi-criteria synthesis
2.2.4. Coupling Coordination Method
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Indicator Weighting Results
3.2. Comprehensive Assessment of Water Security in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin
3.3. Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Degree between Water Security Subsystems in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin
4. Discussion
4.1. Constraints to Water Security in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin
4.2. Differences in the Coupling and Coordination of Water Security Systems and Lagging Systems between Countries
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cramer, W.; Guiot, J.; Fader, M.; Garrabou, J.; Gattuso, J.; Iglesias, A.; Lange, M.A.; Lionello, P.; Llasat, M.C.; Paz, S. Climate change and interconnected risks to sustainable development in the Mediterranean. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q. Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment—Empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 244, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN-Water. Water Security and the Global Water Agenda: A UN-Water Analytical Brief; United Nations University—Institute for Water, Environment and Health: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2013; ISBN 92-808-6038-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nhamo, L.; Ndlela, B.; Nhemachena, C.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Mpandeli, S.; Matchaya, G. The water-energy-food nexus: Climate risks and opportunities in southern Africa. Water 2018, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.K.; Giupponi, C.; Wada, Y. Measuring global water security towards sustainable development goals. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 124015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D. Water for Food Water for Life: A Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture; Routledg: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.K.; Tortajada, C. Water crisis and water wars: Myths and realities. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2019, 35, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Van Beek, L.; Bierkens, M.F. Modelling global water stress of the recent past: On the relative importance of trends in water demand and climate variability. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 3785–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollah, S.B.H.S.; Sharafati, A.; Motta, D.; Yaseen, Z.M. River water quality index prediction and uncertainty analysis: A comparative study of machine learning models. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, L.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Ren, L. Planning for regional water system sustainability through water resources security assessment under uncertainties. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 3135–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhu, L.; Meng, J. Fuzzy evaluation of the ecological security of land resources in mainland China based on the Pressure-State-Response framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzani, M.; Karami, E. Agricultural water poverty index and sustainability. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C. Calculating a water poverty index. World Dev. 2002, 30, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhu, Y.Z. The measurement of water resources security: A study and challenge on water resources carrying capacity. J. Nat. Resour. 2002, 17, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, A.D.; Forum, A.W. Asian Water Development Outlook 2013: Measuring Water Security in Asia and the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Manila, Philippines, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S. Regional water resources stress and water resources security appraisement indicators. Prog. Geogr. 2002, 21, 538–545. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, D.B.; Gupta, H.V.; Mendiondo, E.M. A blue/green water-based accounting framework for assessment of water security. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7187–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, S.E.; Schuster-Wallace, C.J.; Newton, J.J. Water security assessment indicators: The rural context. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 1567–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Feng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, X.; Li, Y. Systematic evaluation of management measure effects on the water environment based on the DPSIR-Tapio decoupling model: A case study in the Chaohu Lake watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Wu, P.; Geng, Q.; Xu, L. Sustainability assessment of regional water resources under the DPSIR framework. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, F.; Elsawah, S.; Bagheri, A.; Nabavi, E.; Jakeman, A.J. Improved integrated water resource modelling by combining DPSIR and system dynamics conceptual modelling techniques. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, O.; Wu, H. Urban water security indicators: Development and pilot. Environ. Sci Policy 2018, 83, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Evaluating the ability of transformed urban agglomerations to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 6 from the perspective of the water planetary boundary: Evidence from Guanzhong in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ryu, J.; Won, J.; Park, H. Determination and application of the weights for landslide susceptibility mapping using an artificial neural network. Eng. Geol. 2004, 71, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wen, F.; Wang, K.; Li, L.; Singh, S. A fuzzy comprehensive evaluation and entropy weight decision-making based method for power network structure assessment. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, P.; Zuo, S.; Ren, Y.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Dai, S. Refined water security assessment for sustainable water management: A case study of 15 key cities in the Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.P.; Singh, S.; Jani, M.; Singh, K.A.; Pande, C.B.; Varade, A.M. Assessment of water quality index using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and GIS: A case study of a struggling Asan River. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R. A note on the use of the analytic hierarchy process for environmental impact assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 63, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, X.; Fernandez, I.C.; Guo, J.; Wilson, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wu, J. When to use what: Methods for weighting and aggregating sustainability indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, C.; Lian, J.; Xu, K.; Chaima, E. Urban flooding risk assessment based on an integrated k-means cluster algorithm and improved entropy weight method in the region of Haikou, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Yang, Q.; Liang, J.; Ma, H. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation with AHP and entropy methods and health risk assessment of groundwater in Yinchuan Basin, northwest China. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Comprehensive ecological risk assessment for semi-arid basin based on conceptual model of risk response and improved TOPSIS model—A case study of Wei River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wu, Y.; Zou, W.; Zhao, L.; Liu, W. A Rural Water Poverty Analysis in China Using the DPSIR-PLS Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 1933–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Liao, W.; Wang, C.; Lei, X.; Wang, H. An Assessment of Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Regional Water Resources Security in the DPSIR Framework in Jiangxi Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Osuna, V.R.; Cak, A.D.; Bhaduri, A.; Bunn, S.E.; Corsi, F.; Gastelumendi, J.; Green, P.; Harrison, I.; Lawford, R. Ecosystem-based water security and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2018, 18, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, P.; Cialani, C.; Ulgiati, S. A review on circular economy: The expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M. Energy, environment and sustainable development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 2265–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, C.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J. Evolution of coordination degree of eco-economic system and early-warning in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q. Coupling coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment in Chinese provincial capital cities-assessment and policy implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X. Investigation of a coupling model of coordination between urbanization and the environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, W.; Li, M.; Linlin, M. Coupling coordination degree of production, living and ecological spaces and its influencing factors in the Yellow River Basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; He, D.; Wang, H. Environmental consequences of damming the mainstream Lancang-Mekong River: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 146, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Campbell, I.; Roch, M.; Leinenkugel, P.; Tuan, V.Q.; Dech, S. Understanding the impact of hydropower developments in the context of upstream–downstream relations in the Mekong river basin. Sustain. Sci. 2013, 8, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Varis, O. Sediment-related impacts due to upstream reservoir trapping, the Lower Mekong River. Geomorphology 2007, 85, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pech, S.; Sunada, K. Population growth and natural-resources pressures in the Mekong River Basin. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2008, 37, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Brunier, G.; Besset, M.; Goichot, M.; Dussouillez, P.; Nguyen, V.L. Linking rapid erosion of the Mekong River delta to human activities. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannezhad, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, D. Influential climate teleconnections for spatiotemporal precipitation variability in the Lancang-Mekong River basin from 1952 to 2015. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020J–e33331J. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, L.P.; Lauri, H.; Kummu, M.; Koponen, J.; Van Vliet, M.T.; Supit, I.; Leemans, R.; Kabat, P.; Ludwig, F. Mekong River flow and hydrological extremes under climate change. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3027–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Hasson, S.; Pascale, S.; Lucarini, V.; Böhner, J. Seasonal cycle of precipitation over major river basins in South and Southeast Asia: A review of the CMIP5 climate models data for present climate and future climate projections. Atmospheric. Res. 2016, 180, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I.C. Integrated management in the Mekong River Basin. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2016, 16, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherbee, D.E. Cooperation and conflict in the Mekong River Basin. Stud. Confl. Terror. 1997, 20, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, J.; Lebel, L. Deliberation and scale in Mekong region water governance. Environ. Manag. 2010, 46, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, P.J.; Barlow, C.; Agostinho, A.A.; Baran, E.; Cada, G.F.; Chen, D.; Cowx, I.G.; Ferguson, J.W.; Jutagate, T.; Mallen-Cooper, M. Fish migration, dams, and loss of ecosystem services in the Mekong basin. AMBIO 2010, 39, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Yang, Z.; Cui, B.; Li, B.; Chen, H.; Bai, J.; Dong, S. Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 1763–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Impacts of Water Resources Management on Land Water Storage in the Lower Lancang River Basin: Insights from Multi-Mission Earth Observations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Z.; Kittel, C.M.; Yao, Z.; Druce, D.; Wang, R.; Tøttrup, C.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; et al. Flow regime changes in the Lancang River, revealed by integrated modeling with multiple Earth observation datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Liu, J.P.; Ge, Q. Changes in hydrology and sediment delivery of the Mekong River in the last 50 years: Connection to damming, monsoon, and ENSO. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2011, 36, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Lai, C. Reconstruction of annual runoff since CE 1557 using tree-ring chronologies in the upper Lancang-Mekong River basin. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Sridhar, V.; Mainuddin, M.; Trung, L.D. Future rice farming threatened by drought in the Lower Mekong Basin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Sridhar, V. A near-term drought assessment using hydrological and climate forecasting in the Mekong River Basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, E2497–E2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.; Tian, F.; Zhu, T.; Zohidov, B.; Ni, G.; Lu, H.; Liu, H. Exploring synergies in the water-food-energy nexus by using an integrated hydro-economic optimization model for the Lancang-Mekong River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 137996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smajgl, A.; Ward, J.; Pluschke, L. The water–food–energy Nexus–Realising a new paradigm. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, M.S.; Shinde, V.R.; Sharma, D.; Dang, N.M. Measuring water security: A vital step for climate change adaptation. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, S. Evaluation of water ecological security in Huaihe River Basin based on the DPSIR-EES-SMI-P model. Water Supply 2023, 23, 1127–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, K.; Cheng, Y. Ecological Security Warning Degree and Spatiotemporal Pattern in Shandong Province. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 35, 166–171+189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Ren, J. Ecological security early warning degree and spatiotemporal pattern in the Yellow River Delta region. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, F.; Jin, L.; Yang, Y.; Bilgaev, A. Quantitative analysis of the coupling coordination degree between urbanization and eco-environment in Mongolia. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z. An integrated approach to evaluating the coupling coordination between tourism and the environment. Tour. Manag. 2015, 46, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, W.; Liu, Y. Coupling coordination analysis of rural production-living-ecological space in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Research on the Coupling and Coordinated Development of Regional Economic Growth and Environment in China. Resour. Sci. 2008, 1, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, L.; Xue, M.; Hu, M. Dynamic simulation and assessment of the coupling coordination degree of the economy–resource–environment system: Case of Wuhan City in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, H.; Baoshan, C.; Shikui, D.; Hongjuan, Z.; Zhaoyang, L. Ecological water requirement (EWR) analysis of High Mountain and Steep Gorge (HMSG) river—Application to Upper Lancang–Mekong river. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Chen, X.; He, Y. Spatiotemporal analysis of water resources system vulnerability in the Lancang River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, W. Drought variability at various timescales over Yunnan Province, China: 1961–2015. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2019, 138, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boithias, L.; Choisy, M.; Souliyaseng, N.; Jourdren, M.; Quet, F.; Buisson, Y.; Thammahacksa, C.; Silvera, N.; Latsachack, K.; Sengtaheuanghoung, O. Hydrological regime and water shortage as drivers of the seasonal incidence of diarrheal diseases in a tropical montane environment. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S. Water quality prospective in Twenty First Century: Status of water quality in major river basins, contemporary strategies and impediments: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribolzi, O.; Cuny, J.; Sengsoulichanh, P.; Mousquès, C.; Soulileuth, B.; Pierret, A.; Huon, S.; Sengtaheuanghoung, O. Land use and water quality along a Mekong tributary in Northern Lao PDR. Environ. Manag. 2011, 47, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, T.S.; Saboori, B.; Rasoulinezhad, E. Economic growth and environmental pollution in Myanmar: An analysis of environmental Kuznets curve. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20487–20501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soe, P.S.; Kyaw, W.T.; Arizono, K.; Ishibashi, Y.; Agusa, T. Mercury pollution from artisanal and small-scale gold mining in Myanmar and other southeast asian countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, A.; Kawamura, G.; Zin, W.W. A local level relationship between floods and poverty: A case in Myanmar. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 42, 101348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.B.; Kawasaki, A. Quantitative assessment of flood risk with evaluation of the effectiveness of dam operation for flood control: A case of the Bago River Basin of Myanmar. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 50, 101707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheewala, S.H.; Silalertruksa, T.; Nilsalab, P.; Mungkung, R.; Perret, S.R.; Chaiyawannakarn, N. Water footprint and impact of water consumption for food, feed, fuel crops production in Thailand. Water 2014, 6, 1698–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheewala, S.H.; Silalertruksa, T.; Nilsalab, P.; Lecksiwilai, N.; Sawaengsak, W.; Mungkung, R.; Ganasut, J. Water stress index and its implication for agricultural land-use policy in Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Laphimsing, A.; Putthividhya, A. Dry season water allocation in the Chao Phraya River basin, Thailand. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2016, 32, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A. Agricultural transformation and the politics of hydrology in northern Thailand. Dev. Chang. 2003, 34, 941–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, D. Climate change and Thailand: Impact and response. Contemp. Southeast Asia 2011, 33, 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promchote, P.; Wang, S.S.; Johnson, P.G. The 2011 great flood in Thailand: Climate diagnostics and implications from climate change. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanvisitthpon, N.; Shrestha, S.; Pal, I. Urban flooding and climate change: A case study of Bangkok, Thailand. Environ. Urban. ASIA 2018, 9, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, L.E.; Gorelick, S.M. Closing the irrigation deficit in Cambodia: Implications for transboundary impacts on groundwater and Mekong River flow. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.; Irvine, K.; Sampson, M. The stress of climate change on water management in Cambodia with a focus on rice production. Clim. Dev. 2013, 5, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatappa, M.; Sasaki, N.; Han, P.; Abe, I. Impacts of droughts and floods on croplands and crop production in Southeast Asia—An application of Google Earth Engine. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, R.; Hien, N.X.; Hoanh, C.T.; Tuong, T.P. Sea level rise affecting the Vietnamese Mekong Delta: Water elevation in the flood season and implications for rice production. Clim. Chang. 2004, 66, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Aviso, K.B.; Kojima, N.; Tokai, A. Structural analysis of the interrelationship between economic activities and water pollution in Vietnam in the period of 2000–2011. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Minh Hanh, P.; Sthiannopkao, S.; The Ba, D.; Kim, K. Development of water quality indexes to identify pollutants in Vietnam’s surface water. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, P.L. Urbanization and water management in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam-issues, challenges and perspectives. GeoJournal 2007, 70, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.C.; Black, M.C.; Knuteson, S.L.; Roberts, A.P. Environmental Pollution, Management, and Sustainable Development: Strategies for Vietnam and Other Developing Countries. Environ. Manag. 2019, 63, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scussolini, P.; Tran, T.V.T.; Koks, E.; Diaz Loaiza, A.; Ho, P.L.; Lasage, R. Adaptation to sea level rise: A multidisciplinary analysis for Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 10841–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, X.; Tang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D. Impacts of climate change and reservoir operation on streamflow and flood characteristics in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Zhao, T.; He, Y.; Chen, X. Hydropower change of the water tower of Asia in 21st century: A case of the Lancang River hydropower base, upper Mekong. Energy 2019, 179, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Tang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Xiao, S.; Ji, D.; Yang, Z.; Liu, D. Using stable nitrogen and oxygen isotopes to identify nitrate sources in the Lancang River, upper Mekong. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Yao, Z. Climate change and its impact on water availability of large international rivers over the mainland Southeast Asia. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 3966–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuchird, R.; Sasaki, N.; Abe, I. Influencing factors of the adoption of agricultural irrigation technologies and the economic returns: A case study in Chaiyaphum Province, Thailand. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praneetvatakul, S.; Janekarnkij, P.; Potchanasin, C.; Prayoonwong, K. Assessing the sustainability of agriculture: A case of Mae Chaem Catchment, northern Thailand. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, E.L.; Saunders, M.A. The 2011 Thailand flood: Climate causes and return periods. Weather 2013, 68, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singkran, N. Flood risk management in Thailand: Shifting from a passive to a progressive paradigm. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 25, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrier, G.; Paul, R.; Sananikhom, P.; Kaul, S.; Luthi, R.; Katz, J.; Robino, M.; Khammanithong, P.; Brey, P.T. Strategic success for hydropower in Laos. Science 2011, 334, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakenridge, G.R.; Syvitski, J.; Niebuhr, E.; Overeem, I.; Higgins, S.A.; Kettner, A.J.; Prades, L. Design with nature: Causation and avoidance of catastrophic flooding, Myanmar. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 165, 81–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, A.; Ichihara, N.; Ochii, Y.; Acierto, R.A.; Kodaka, A.; Zin, W.W. Disaster response and river infrastructure management during the 2015 Myanmar floods: A case in the Bago River Basin. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017, 24, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Grote, U. Multiple shocks and households’ choice of coping strategies in rural Cambodia. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 167, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, V.N.; Cassells, S.; Holland, J. Economic impact upon agricultural production from extreme flood events in Quang Nam, central Vietnam. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 1747–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
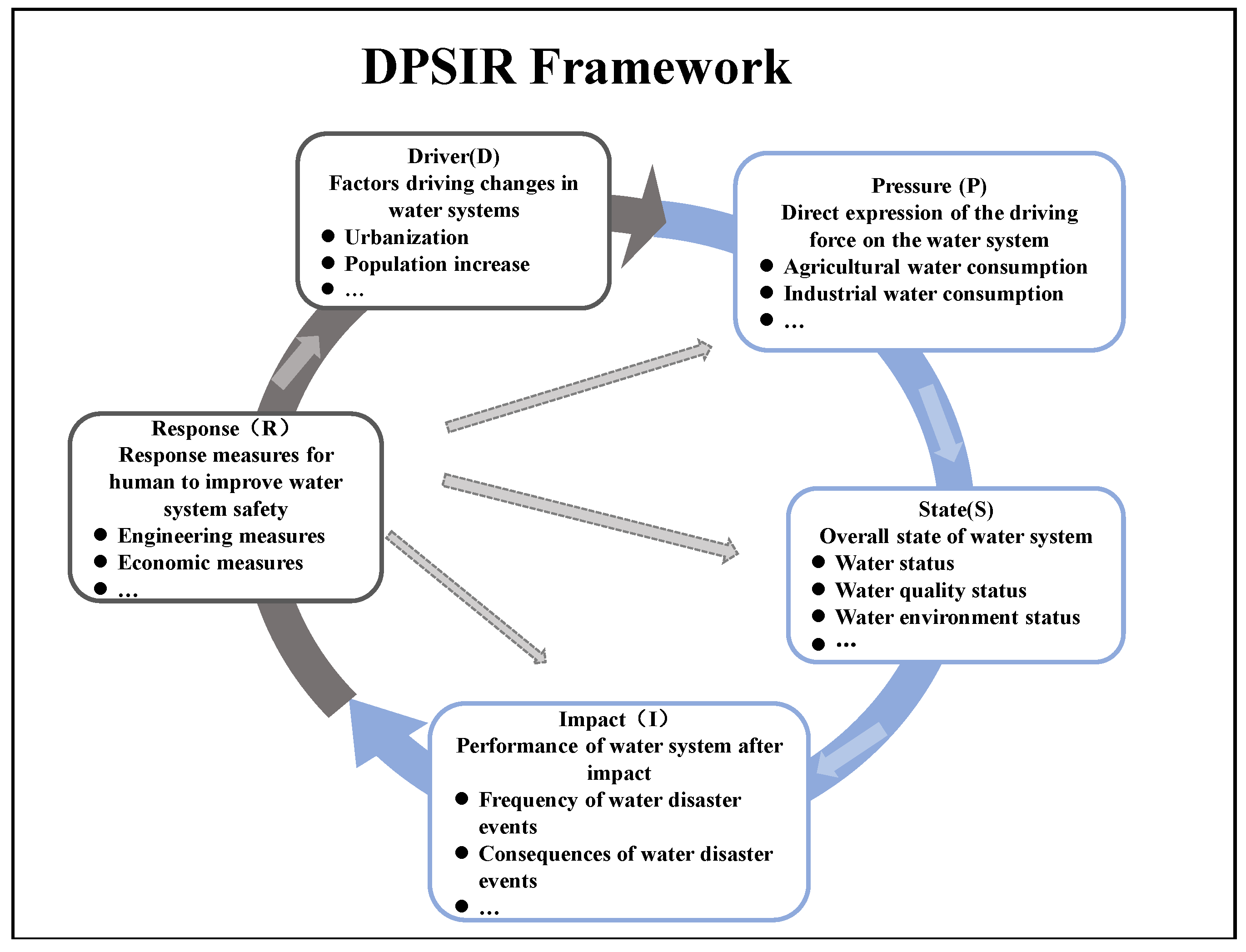
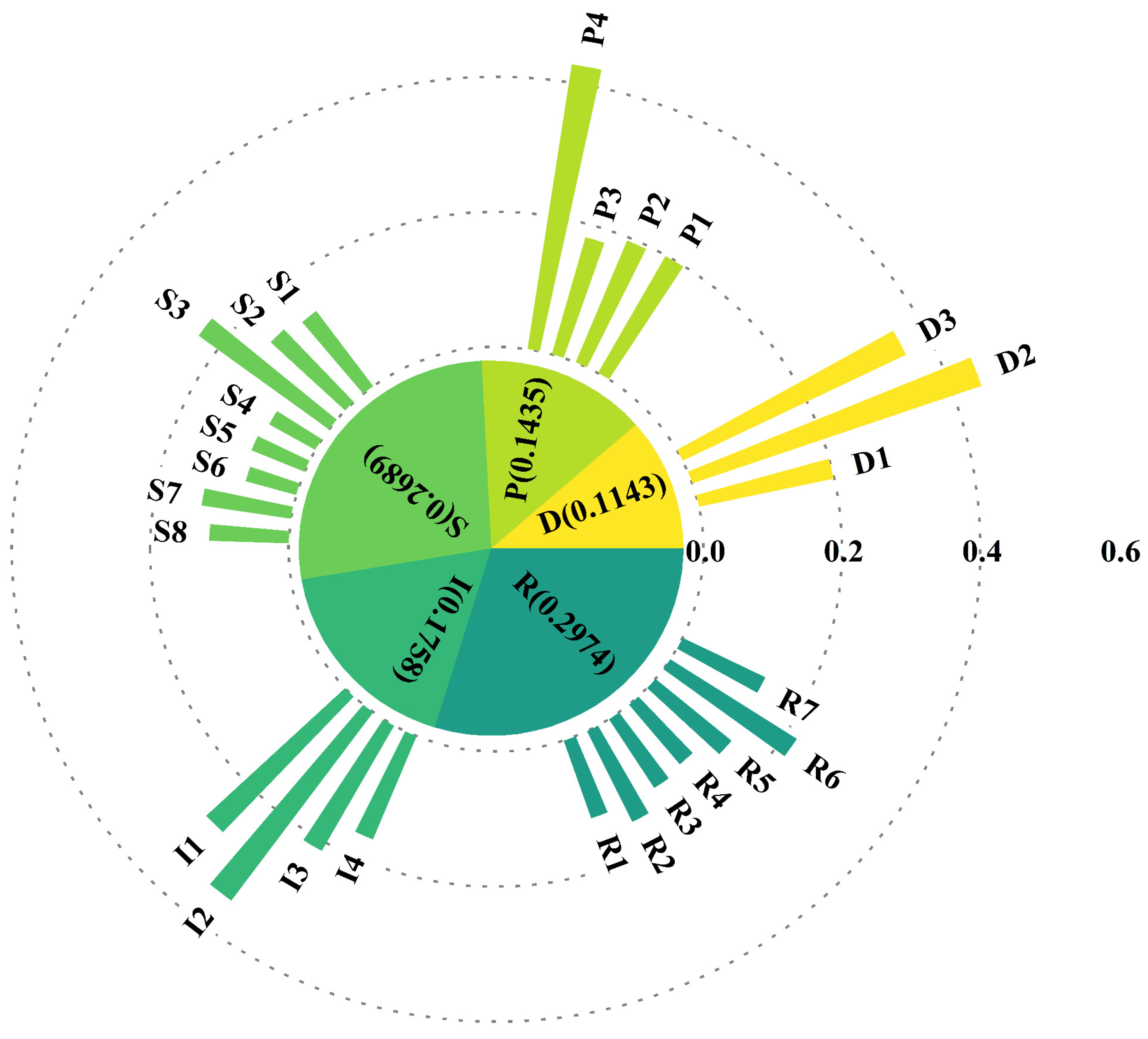
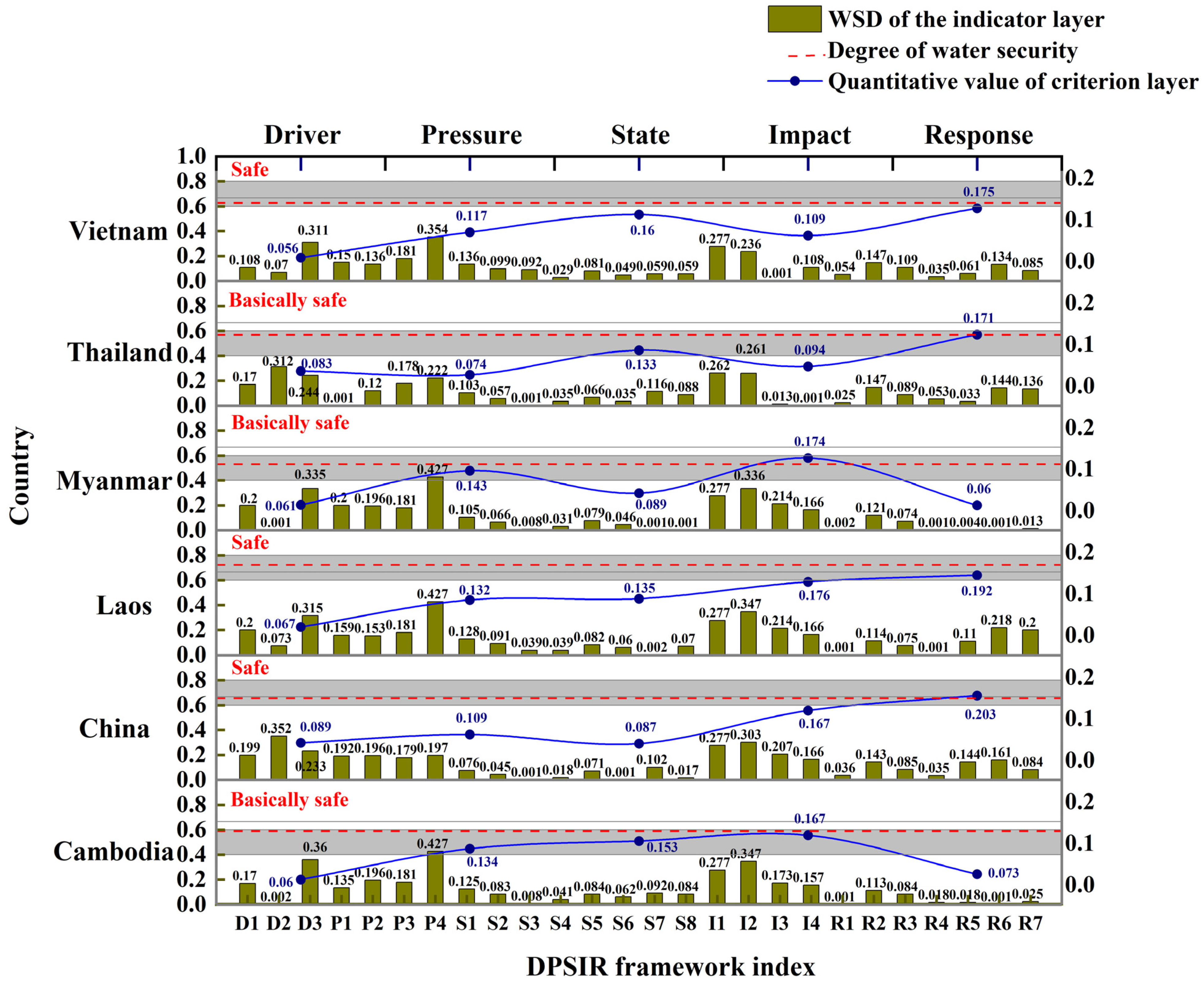
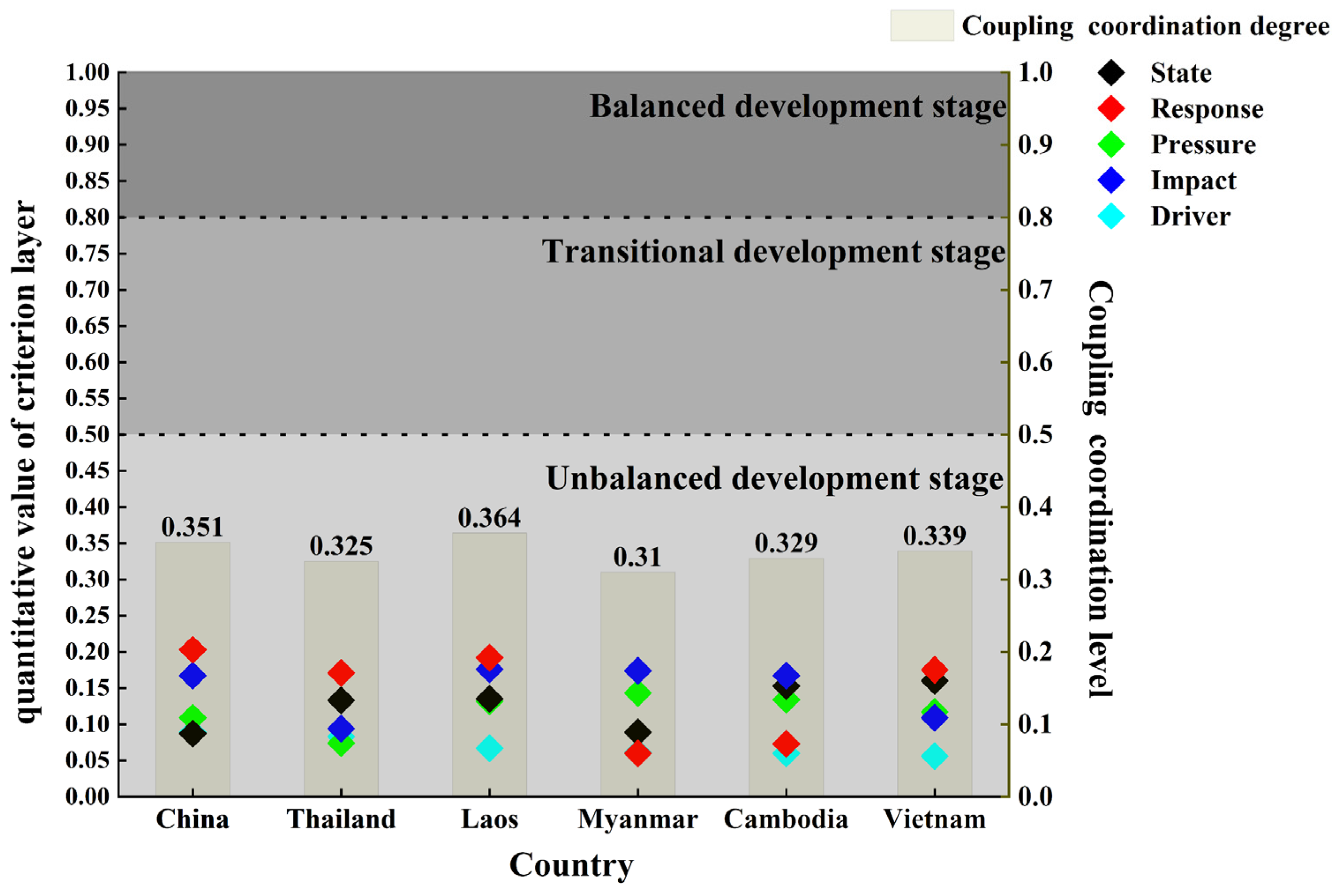
| Target | Criterion | Indicator | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water security Degree | Driver (D) | Population density (D1) | Gridded Population of the World Version 4 (GPWv4) (https://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/ accessed on 4 March 2022) |
| GDP per capita (D2) | World Bank (https://data.worldbank.org.cn/, accessed on 6 March 2022) | ||
| Urbanization rate (D3) | United Nations Population Division (https://www.un.org/, accessed on 22 April 2022) | ||
| Pressures (P) | Agricultural water consumption (P1) | Report <Research on the capacity building of water quality improvement in Lancang–Mekong River countries> | |
| Domestic water consumption (P2) | |||
| Industrial water consumption (P3) | |||
| Water pressure (P4) | Water Environment Partnership in Asia (WEPA) (https://wepa-db.net/, accessed on 19 March 2022) | ||
| State (S) | Average annual precipitation (S1) | Climatic Research Unit gridded Time Series (CRU TS) (https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/hrg/, accessed on 11 March 2022) | |
| Average annual runoff (S2) | Transboundary Waters Assessment Plan (TWAP) (http://www.geftwap.org/, accessed on 27 March 2022) | ||
| Proportion of wet season precipitation to annual precipitation (S3) | Climatic Research Unit gridded Time Series (CRU TS) (https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/hrg/, accessed on 11 March 2022) | ||
| Water biological oxygen demand (S4) | World Bank (https://data.worldbank.org.cn/, accessed on 14 April 2022) | ||
| Water conductivity (S5) | |||
| Water nitrate–nitrite concentration (S6) | |||
| Forest coverage (S7) | Global Forest Cover Map (GFCM) | ||
| Lake, reservoir, and wetland area (S8) | Global Lakes and Wetlands Database (GWLP) (https://www.worldwildlife.org/pages/global-lakes-and wetlands-database, accessed on 19 March 2022) | ||
| Impact (I) | Drought frequency (I1) | Emergency Events Database (EM-DAT) (https://www.emdat.be/, accessed on 27 March 2022) | |
| Flood frequency (I2) | |||
| Deaths caused by water disasters (I3) | |||
| Economic losses caused by water disasters (I4) | |||
| Response (R) | Government funding for water sanitation (R1) | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (https://www.oecd.org/, accessed on 15 March 2022) | |
| Proportion of population with access to improved drinking water (R2) | Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP) (https://washdata.org/, accessed on 6 April 2022) | ||
| Proportion of sanitation facilities receiving basic improvements (3) | |||
| Wastewater treatment capacity (4) | HydroSHEDS database (https://www.hydrosheds.org/, accessed on 13 April 2022) | ||
| Installed capacity of hydropower dam (R5) | Mekong River Commission (https://www.mrcmekong.org/, accessed on 23 April 2022) | ||
| Reservoir capacity (R6) | |||
| Hydropower dam density (R7) |
| Water Security Level | Value Range of the WSD |
|---|---|
| Very safe | 0.81–1.00 |
| Safe | 0.61–0.80 |
| Basically safe | 0.41–0.60 |
| Unsafe | 0.21–0.40 |
| Seriously unsafe | 0.00–0.20 |
| Coupling Coordination Degree | Type | Development Stage |
|---|---|---|
| Serious imbalance | Unbalanced development stage | |
| Moderate imbalance | ||
| Basic coordination | ||
| Moderate coordination | Transitional development stage | |
| Good coordination | Balanced development stage |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, W.; Lv, A. Assessing Water Security and Coupling Coordination in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16880. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416880
Zheng Y, He J, Zhang W, Lv A. Assessing Water Security and Coupling Coordination in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin for Sustainable Development. Sustainability. 2023; 15(24):16880. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416880
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yanting, Jing He, Wenxiang Zhang, and Aifeng Lv. 2023. "Assessing Water Security and Coupling Coordination in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin for Sustainable Development" Sustainability 15, no. 24: 16880. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416880
APA StyleZheng, Y., He, J., Zhang, W., & Lv, A. (2023). Assessing Water Security and Coupling Coordination in the Lancang–Mekong River Basin for Sustainable Development. Sustainability, 15(24), 16880. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416880






