Abstract
In the ever-evolving era of technological advancements, generative artificial intelligence (GAI) emerges as a transformative force, revolutionizing education. This review paper, guided by the PRISMA framework, presents a comprehensive analysis of GAI in education, synthesizing key insights from a selection of 207 research papers to identify research gaps and future directions in the field. This study begins with a content analysis that explores GAI’s transformative impact in specific educational domains, including medical education and engineering education. The versatile applications of GAI encompass assessment, personalized learning support, and intelligent tutoring systems. Ethical considerations, interdisciplinary collaboration, and responsible technology use are highlighted, emphasizing the need for transparent GAI models and addressing biases. Subsequently, a bibliometric analysis of GAI in education is conducted, examining prominent AI tools, research focus, geographic distribution, and interdisciplinary collaboration. ChatGPT emerges as a dominant GAI tool, and the analysis reveals significant and exponential growth in GAI research in 2023. Moreover, this paper identifies promising future research directions, such as GAI-enhanced curriculum design and longitudinal studies tracking its long-term impact on learning outcomes. These findings provide a comprehensive understanding of GAI’s potential in reshaping education and offer valuable insights to researchers, educators, and policymakers interested in the intersection of GAI and education.
1. Introduction
In an era where technological advancements are redefining human existence, there is one revolutionary force that stands out among the rest: artificial intelligence (AI). AI has permeated every corner of our lives, quietly and profoundly transforming the way we work, communicate, and navigate the world. The rise of AI was sparked in November 2022, when U.S. company OpenAI (San Francisco, CA, USA) released ChatGPT [1], an AI program that draws upon a large language database to generate responses from text-based inputs entered by humans [2]. Since its launch, it has skyrocketed in popularity, becoming one of the fastest-growing consumer applications ever with an estimated 100 million active users every month [3]. Following the successful release of ChatGPT, other tech companies have come out with their own AI-powered products, such as Google’s Bard [4] and GitHub’s Copilot [5].
AI has infused various domains of our lives, revolutionizing industries such as finance, education, engineering, healthcare, and many more. According to Hadi et al. [6], AI has transformed practices in the financial sector, such as algorithmic trading, market prediction, and financial reporting. Hadi et al. [6] further argue that education has seen the integration of AI in automated essay grading, intelligent tutoring systems, and personalized learning. In engineering, AI drives advancements in code generation, software testing, and document generation. In addition, in the healthcare sector, AI assists in radiologic decision-making, patient care, and medical education. These various use cases demonstrate the extensive reach and transformative power that AI can deliver across these diverse domains.
More notably, the field of education is experiencing a transformative revolution, driven by the emergence of GAI. According to Baidoo-Anu and Owusu Ansah [7], GAI is an unsupervised or partially supervised machine learning framework that seamlessly generates artificial creations by analyzing existing digital content like videos, images/graphics, text, and audio. The impact of GAI has been felt across a diverse range of educational fields. In education, GAI finds versatile applications in assessment and evaluation, student performance prediction, intelligent tutoring systems, and learning management [8]. In the medical field, the application of GAI, such as ChatGPT, extends to medical education, where it offers realistic case scenarios and instantaneous feedback to medical students on their diagnostic and treatment decisions [9]. Moreover, GAI proves instrumental in providing simplified explanations of complex medical and pharmaceutical concepts, facilitating students’ understanding [9,10]. In the field of computer science, AI tools demonstrate tremendous potential in coding education, as evidenced by GPT-3’s ability to generate diverse code explanations [11].
AI’s impact has triggered a wide array of discussions encompassing diverse topics, ranging from its potential in transforming learning and teaching methods [12] to its role in aiding research endeavors and to the crucial considerations of ethics and academic integrity in its implementation [13]. In the domain of teaching, GAI showcases promising opportunities for lesson planning, personalized learning support, rapid assessment and evaluation, and addressing learners’ queries [12]. Furthermore, Markel et al. [14] have introduced a novel AI tool called “GPTeach”, which is specifically designed for teacher training, enabling aspiring educators to practice teaching with simulated students powered by GPT. As the transformative influence of AI in education continues to unfold, these discussions will undoubtedly shape the future of how we impart knowledge and foster learning in an ever-evolving educational landscape.
This transformative technology has opened up new avenues for personalized instruction, enhanced feedback, and tailored learning experiences, ultimately paving the way for a more efficient, inclusive, and engaging educational environment. GAI is reshaping the way we teach and learn by offering innovative solutions to longstanding challenges and opening up new possibilities for improving educational experiences for learners of all ages. As GAI continues to advance, it is crucial to investigate its applications, implications, and the challenges it poses to further explore its role in shaping the future of education.
The scope of this review encompasses a wide range of topics, delving into the applications of GAI in various educational contexts, the tools and techniques utilized, the effectiveness of GAI in supporting teaching and learning, the impact on student outcomes, and the potential challenges and ethical considerations associated with its implementation. By examining multiple dimensions of GAI in education, this review aims to provide a holistic overview of the field. This paper aims to analyze and consolidate a compilation of existing reviews on GAI in specific fields of education. By thoroughly examining a diverse range of papers in this domain, this study offers a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the current state of research in this field. Through synthesizing and summarizing key findings, methodologies, and recommendations from multiple papers, this study provides a valuable resource for researchers, educators, and policymakers who are keenly interested in exploring the transformative intersection of GAI and education.
This review paper contributes to the field in various ways. Firstly, it provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of research on GAI in education, allowing researchers to identify the prevailing themes and research directions within the field. Secondly, it synthesizes the findings and insights from multiple review papers, providing a holistic perspective on the effectiveness and potential of GAI in educational contexts. Additionally, this review identifies research gaps and areas that require further investigation, guiding future research endeavors. The subsequent sections of this paper will, therefore, present the methodology employed in selecting and analyzing the research papers, followed by a comprehensive content analysis and synthesis of the findings and insights. Key themes, trends, and recommendations will be presented, allowing readers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the existing knowledge base. Subsequently, a comprehensive bibliometric analysis will be conducted, examining prominent AI tools, research focus, geographic distribution, and interdisciplinary collaboration in detail. Finally, this review will conclude by highlighting the implications of the synthesized findings and suggesting future research directions to advance the field of GAI in education.
2. Methodology
The methodology employed in this research follows a systematic approach to gather and analyze literature concerning the integration of GAI in education. It involves four key steps, as described below:
- Literature retrieval—This step entails selecting appropriate search terms and keywords to comprehensively capture pertinent publications related to the intended topic representing the initial and pivotal phase of the data collection process. We retrieved a compilation of pre-existing articles and publications in the domain of GAI in education from the Scopus database. By utilizing a combination of the following keywords, “Education”, “GAI”, “Generative Artificial Intelligence”, “GPT-4”, “ChatGPT”, “AlphaCode”, “GitHub Copilot”, and “Bard”, the authors conducted a targeted search across titles, abstracts, and keyword fields. This process resulted in the enlistment of a total of 437 papers, spanning the years 2018 to 2023.
- Literature screening—The literature screening process for this study drew inspiration from the PRISMA statement, which is widely recognized as a rigorous and transparent approach for conducting systematic reviews and meta-analyses (Figure 1). PRISMA provides a structured framework to ensure the systematic identification, selection, and evaluation of the relevant literature, promoting the reliability and reproducibility of the review process [15]. Initially, a total of 437 papers were retrieved. Following the removal of duplicates, 312 papers remained. After observingly reviewing each publication, all articles that were deemed irrelevant to our research focus were discarded. We narrowed the list down to 217 reviews, papers, and publications that spanned from the years 2018 to 2023. The chronological growth of the papers (in the context of the topic) in the above-mentioned spanned years is depicted in Figure 2.
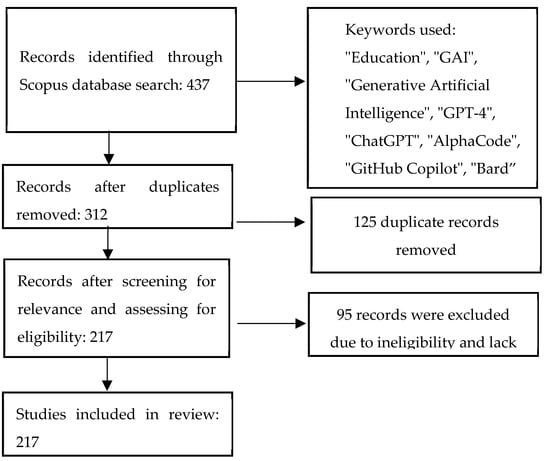 Figure 1. Literature screening approach.
Figure 1. Literature screening approach.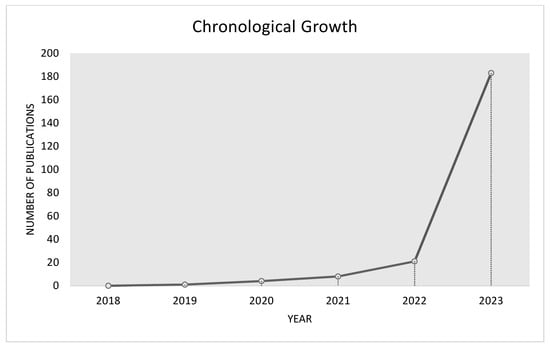 Figure 2. The number of papers and publications in relation to GAI in education (2018–2023).
Figure 2. The number of papers and publications in relation to GAI in education (2018–2023).
The figure above depicts a substantial number of papers available from our compiled list, specifically published in the year 2023. Notably, there is a significant and exponential growth in the field of GAI from 2018 to 2023, indicating a growing amount of research interest in the topic. This surge in research can be attributed to the recent emergence of popular GAI tools, such as ChatGPT, which have garnered considerable attention and sparked innovation within the education domain. The increasing research activity, therefore, suggests that GAI is perceived as a promising area for innovation in education and that researchers and educators are increasingly recognizing the potential benefits of integrating AI technologies into educational settings.
- c.
- Content analysis—This step entails carefully studying a large amount of information, like research publications, and organizing it in a meaningful way. This helps researchers see common themes and patterns in the information. In this case, the content analysis focused on how GAI is being used in education. The methodology involved categorizing and classifying the research papers into different themes and sub-themes. This organization helps researchers understand the different ways GAI is impacting education, making it easier to draw conclusions and insights from the collected information.
- d.
- Bibliometric analysis—It serves the purpose of systematically evaluating academic literature, typically through analyzing citations and references in research papers. This methodology helps researchers understand the influence, trends, and relationships among different academic works. By examining patterns of citations, co-authorships, and keywords, bibliometric analysis allows for the identification of key authors, influential papers, emerging areas of study, and collaborative networks within a particular field. This approach aids researchers in gaining insights into the evolution of research topics, identifying leading scholars.
The remaining part of this paper presents a content analysis and a bibliometric analysis while adhering to the methodological steps described in this section.
3. Content Analysis
The integration of GAI in education has become a subject of considerable interest, opening up new possibilities and challenges for educational practices. GAI models, such as ChatGPT, have been extensively explored across various academic disciplines, presenting transformative opportunities in teaching, learning, and research. This section seeks to provide a thorough content analysis of the use of GAI in education.
3.1. Application of GAI in Computer Science
This study explores a collection of research papers focusing on the intersection of GAI and computer science education and assesses various aspects of GAI technologies and their implications for teaching and learning programming concepts (Table 1).

Table 1.
The applications of GAI in computer science.
The findings from the above publications reveal several key insights. Firstly, researchers highlight the transformative potential of generative machine learning in creative programming education, indicating that GAI can significantly impact how programming concepts are taught and learned. Secondly, crucial considerations are raised regarding AI-generated code, pointing to the need for careful examination of the quality and reliability of code produced by AI systems. Moreover, the potential of large language models (LLMs) in providing explanations for programming concepts is showcased, suggesting that AI can enhance the understanding of complex programming principles. Additionally, practical insights are offered into the implications of AI-powered code generation tools, like Copilot, shedding light on the benefits and challenges of using such technologies in educational settings.
These findings, therefore, provide valuable insights into GAI in computer science education, highlighting a lack of in-depth exploration of drawbacks and ethical concerns. While the spotlight is often on the positive outcomes of AI-generated code, it is crucial to acknowledge the possible drawbacks, like an excessive dependence on automated coding and its potential to undermine students’ algorithmic comprehension. Furthermore, the studies focus on short-term improvements in performance and motivation without fully considering long-term effects on problem-solving skills and holistic learning. Future research should, therefore, balance the positive and negative aspects of GAI integration, addressing academic integrity, assessment challenges, and innovative methods for incorporating AI-generated code into programming curricula.
3.2. Application of GAI in Engineering Education
This section delves into a collection of research papers that explore the impact of GAI in various disciplines within engineering education. The papers are, therefore, categorized into three groups, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The application of GAI in engineering education.
GAI presents transformative benefits in engineering education, as evident from various studies. Indeed, its integration enhances active learning and problem-solving skills and streamlines educational processes through advanced chatbots and text generation models. The potential to foster creative engagement in design and collaboration further empowers students to generate innovative solutions. Cloud-based frameworks amplify social robots’ intelligence and accessibility in engineering education, providing new opportunities for interactive learning experiences.
Taking a critical view of these studies, while they undoubtedly showcase the positive implications of GAI for fostering active learning, honing problem-solving skills, and streamlining design processes, they also unveil crucial issues that demand careful consideration. These concerns encompass the potential erosion of lateral competencies due to overreliance on GAI, challenges in human–AI collaboration, and the necessity for a pedagogical framework that seamlessly incorporates GAI tools without diluting the essence of education. While these research papers accentuate the transformative potential of GAI in revolutionizing the educational landscape, they simultaneously underscore the urgency for judicious implementation, particularly within dynamic domains, like design and social robots. To address these issues, future work must refine GAI integration and assess long-term impacts to ensure its benefits are maximized while mitigating potential challenges.
3.3. Application of GAI in Higher Education
This section explores the potential, applications, challenges, and implications of GAI tools in specifically higher education. Table 3 shows the classification of these papers and their main focus.

Table 3.
The application of GAI in higher education.
The studies in this section offer insights into various aspects of GAI integration in higher education. They delve into the integration of GAI tools, such as ChatGPT and large language models, exploring their potential impact on teaching and learning practices. Student acceptance and usage of GAI technology are examined, revealing factors that influence their adoption. The applications of AI and machine learning in higher education are explored, particularly in predicting academic performance and employability. Furthermore, the impact of ChatGPT on learning outcomes and academic integrity is assessed, prompting discussions on assessment methodologies. Ethical and pedagogical considerations of GAI are discussed, highlighting both potential benefits and concerns related to originality and critical thinking.
These studies provide valuable insights into the potential of GAI tools in enhancing higher education. However, there are certain areas that could be more comprehensive, whereby the tendency to highlight the positive aspects of GAI integration could benefit from a more balanced exploration of potential challenges and unintended consequences. For instance, while the impact of tools like ChatGPT on student learning is explored, a deeper investigation into how such tools might affect critical thinking skills and originality in academic work could provide a more holistic understanding. Additionally, while the studies touch on students’ acceptance of GAI technology, a deeper analysis of the socio-cultural factors influencing students’ attitudes and perceptions is warranted. By addressing these critical perspectives, future research in this area can provide a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of the role and impact of GAI in higher education.
3.4. Application of GAI in Medical Education
This section aims to provide an overview of research papers that discuss the integration of GAI tools in healthcare, as shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
The application of GAI in medical education.
The research papers in this section reveal a range of findings regarding the integration of GAI tools in medical education and practice. Notably, ChatGPT and GPT-4 showcase potential benefits, including personalized learning, improved comprehension of medical concepts, and effective translation of radiology reports. However, concerns about data privacy, potential bias, and impacts on critical thinking are brought to light. In clinical education, these tools exhibit promise in enhancing decision-making and supporting surgical training, although occasional random or oversimplified responses are identified as areas of caution. Specialized medical fields, such as neurosurgery and parasitology, show potential for GAI integration, but validation and context-specific refinement are crucial. The application of GAI in health education for individuals with Down syndrome highlights its significance in cognitive development and social interaction. Moreover, GAI’s role in pandemic response and shaping future medicine proves noteworthy, with AI models contributing to mitigating COVID-19 spread and suggesting new research directions. Ethical considerations emerge as a common theme, emphasizing responsible usage and preventing misuse of GAI tools in healthcare.
A critical perspective reveals that these papers sometimes tend to overlook significant concerns such as data privacy, biases, and the risk of undermining critical thinking. Consequently, future work should prioritize establishing ethical guidelines and governance frameworks to address data privacy, bias, and transparency. Rigorous validation processes are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of GAI-generated information. Continuous research and development efforts are needed to enhance GAI capabilities for more complex medical scenarios. Interdisciplinary collaboration can promote responsible and effective integration of GAI in medical practices and education.
3.5. Application of GAI in Nursing Education
In this section, we explore a few research papers that delve into the implications of ChatGPT in nursing education (Table 5).

Table 5.
The application of GAI in nursing education.
The research papers in this section focus on the potential benefits of integrating GAI into nursing education. These studies explore how AI can enhance patient care, information literacy, and critical thinking skills among nursing students. The papers emphasize the importance of balancing AI integration with human interaction for comprehensive learning experiences and address ethical considerations. They delve into topics such as AI’s impact on clinical judgment, broader implications in nursing practice, personalized learning, and clinical decision-making. Frameworks are introduced to equip nursing students with critical thinking skills for responsible AI engagement.
Future work in this domain is needed to address critical issues such as data privacy, biases, and the potential threat of compromising human-centered nursing practices. This can be achieved by establishing robust ethical guidelines and governance frameworks for the integration of AI in nursing education. Additionally, rigorous validation processes are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of AI-generated content.
3.6. Application of GAI in Communication
In this section, we explore a collection of research papers that delve into the applications and implications of GAI in communication education. These studies shed light on how GAI models are revolutionizing research, education, journalism, and social media in the context of communication, as shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
The application of GAI in communication.
These studies showcase the effectiveness of GAI in improving machine translation accuracy and its transformative potential in journalism and media education. Furthermore, the impact of AI on streaming media is explored, providing an understanding of GAI’s role in communication education.
The small number of papers provide a restricted view of the challenges and ethical issues linked to biases and human interaction. These papers predominantly accentuate the positive impacts of GAI. This highlights the need for further research to gain a holistic understanding of GAI’s impacts on communication and strike a balance between technological advancements and maintaining authentic human engagement. Future research could focus on developing and assessing AI-powered tools for communication skills, as well as examining ethical implications and potential biases in GAI model implementation in communication and journalism.
3.7. Application of GAI in Academia
This section examines a collection of research papers focusing on GAI’s impact on research and its potential applications in different fields, as summarized in Table 7 below.

Table 7.
The application of GAI in academia.
This section highlights the transformative impact of GAI in academia, showcasing its potential benefits for higher education, research, and library services. The discussion covers the advantages of AI technologies, natural language processing techniques, and large language models in various domains. However, it also stresses the need to address ethical concerns, algorithmic biases, and maintain academic integrity. Strategies to ensure integrity and accuracy are explored to address these challenges. Additionally, the section sheds light on the implications of GAI in library science.
Moving forward, future research should take a critical and interdisciplinary approach to GAI integration in academia, considering a wide array of potential benefits and risks. It is imperative to delve deeper into the ethical implications, potential biases, and algorithmic transparency associated with GAI tools. Moreover, a more in-depth investigation into the long-term effects of GAI on academic integrity, learning experiences, and research methodologies is warranted.
3.8. Application of GAI in General Education
In this section, we delve into the general applications of GAI in education. While earlier sections have explored the use of GAI in specific domains, such as medical education, higher education, engineering education, and more, this section broadens the scope to encompass the wider applications of GAI in education. To provide a structured analysis of this topic, the content is divided into several subsections. This section, therefore, covers a review of a wide range of applications and considerations regarding the integration of GAI in education, as discussed in Table 8 below:

Table 8.
Application of GAI in general education.
The remaining part of this section synthesizes and discusses the applications of GAI in general education across each subcategory of papers outlined in Table 8.
Technology Adoption and Integration in Education—The findings demonstrate improved learning outcomes, enhanced student engagement, and the potential for personalized learning experiences. However, ethical considerations, responsible usage, and addressing limitations are crucial. Future work necessitates a more critical perspective in developing nuanced guidelines and policies, cautiously navigating interdisciplinary collaboration and fostering genuinely informed critical thinking skills. This is imperative to ensure that AI integration in education addresses complex challenges effectively and ethically. Additionally, an in-depth exploration of the lasting repercussions of AI technologies on education is crucial, surpassing superficial assessments and delving into their potential to reshape fundamental educational dynamics.
Classroom Design and Learning Environment—The papers in this category highlight the significance of incorporating technology and GAI in creating effective learning environments. The research demonstrates the potential of AI models to automate classroom design, optimize learning spaces, and enhance the learning experience through interactive dialogue systems and gamified environments. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the potential pitfalls, like algorithmic biases and copyright concerns. Moving forward, there is a pressing need to prioritize the promotion of AI interactions that are inclusive and culturally sensitive. Moreover, the development of AI-powered solutions tailored to resource-limited educational contexts should be a key focus of future endeavors.
Assessment Practices and Academic Integrity—The research highlights the superior performance of AI chatbots, such as ChatGPT, in subject-specific exams and the potential of natural language processing techniques to enhance peer feedback processes. However, concerns regarding authenticity, credibility, systematic errors, and the risk of plagiarism are raised, underscoring the need for caution and the responsible integration of AI tools in educational assessments. While the papers touch on the importance of updating assessment strategies, policy implementation, instructor training, and student awareness about AI’s impact on evaluations, a more in-depth analysis of these measures’ efficacy is warranted. To advance, it is crucial to fine-tune AI models for assessment precision, tackle biases and accuracy concerns, and establish robust guidelines and ethical standards to govern AI’s role in educational assessments.
Language Instruction—The publications demonstrate how integrating AI chatbots into language instruction can offer personalized support, optimize learning experiences, and address diverse language proficiencies. However, a more critical viewpoint uncovers the apprehensions surrounding the preservation of academic integrity and equitable learning experiences. While the potential gains are evident, the unexplored territory of AI’s potential biases and fairness concerns necessitates not only policy frameworks but also a deep reevaluation of instructional strategies.
Ethics and Responsible GAI Use—These papers highlight the importance of ethical considerations and the responsible use of AI systems, particularly chatbots like ChatGPT, in education and research. These works shed light on the merits, shortcomings, obstacles, and debates surrounding such technologies. Looking ahead, it is imperative that forthcoming efforts concentrate on interdisciplinary investigations to confront ethical difficulties, integrate conscientious AI education into academic curricula, and promote collaborative endeavors aimed at formulating comprehensive regulations and principled directives.
Subject-Specific Education and Skills Development—The reviewed research papers shed light on the potential applications of GAI in specific educational domains, including sustainability education, digital skills development, chemistry education, biology and environmental science, and construction education. The findings indicate that GAI technologies, such as ChatGPT, have the ability to simplify complex tasks, expedite education and research processes, enhance hazard recognition capabilities, promote safety management practices, and facilitate interdisciplinary approaches. However, the papers also acknowledge the limitations and potential risks associated with the utilization of GAI, such as concerns about data privacy, biases, and the need for human engagement. Moving forward, future work should focus on the seamless integration of sustainability education into AI learning frameworks, a dedicated commitment to addressing issues of equity and accessibility to ensure that the benefits of GAI are universally accessible, and a diligent pursuit of strategies to maximize the advantages that GAI offers while concurrently taking proactive steps to mitigate the inherent risks that come with its implementation.
Learning Outcomes and Student Engagement—The papers highlight the positive impact of GAI, such as AI chatbots and virtual instructors, on students’ learning outcomes and engagement. The findings demonstrate improvements in learning outcomes, motivation, and engagement when utilizing AI chatbots, like ChatGPT. However, a more discerning analysis beckons for heightened scrutiny in various aspects. This includes the imperative refinement of AI chatbot design, probing into alternative assessment strategies, enhancing the interaction between AI and educators, and undertaking an in-depth exploration into the long-term impact of AI on student motivation and engagement.
Challenges and Considerations in AI Integration—The related papers shed light on the obstacles and considerations associated with integrating GAI, such as ChatGPT, into education. These studies emphasize the importance of addressing concerns related to AI-generated misinformation, ensuring the secure integration of AI in education, and promoting responsible implementation practices. The findings underscore the need for raising learners’ awareness about the potential influence of AI on their learning and further research to ensure the conscientious and secure integration of AI technologies, like ChatGPT, in educational settings. The future trajectory in this field involves developing comprehensive strategies and guidelines to address challenges while conducting further research on AI integration’s impact on student learning outcomes. This avenue of exploration aims to formulate effective approaches to counter challenges and rigorously investigate how AI integration influences students’ academic achievements.
Pedagogical Approaches and Teaching Methods—The papers shed light on innovative instructional practices and frameworks that integrate AI technologies into education. The findings offer insights into teaching ethics in AI courses, enhancing peer feedback processes through natural language processing techniques, addressing challenges in teaching quantitative literacy alongside language-based AI systems, and showcasing the integration of AI to support student learning. The papers also emphasize the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration. Future endeavors could dedicate their focus to meticulously refining and substantially expanding the currently presented pedagogical methodologies. Delving deeper, a crucial area of investigation could encompass understanding the enduring effects of AI integration on the overall learning achievements of students, shedding light on potential shifts in learning dynamics, cognitive development, and critical thinking skills over the long term. Furthermore, it becomes imperative to navigate the intricate field of ethical considerations, delving into the multifaceted implications of AI technologies within educational contexts.
To sum-up the findings in this section, Figure 3 provides a comprehensive visualization and categorization of the diverse applications of GAI in the field of education. This spider graph employs a two-tier structure to present the information effectively. The initial tier highlights the primary themes that have been central to a majority of applications. The proportional sizing of the circles reflects the prevalence of these themes, representing the number of applications and associated publications in each domain. Furthermore, within each thematic category, a secondary layer delineates specific keywords, encapsulating the nuances of each area. The size of these sub-circles corresponds to the prominence of these keywords, which are characterized by their density and the number of related research publications. This elaborate spider graph succinctly encapsulates the breadth and depth of GAI’s influence in education, providing an illuminating snapshot of the ongoing research endeavors and practical implementations in this field.
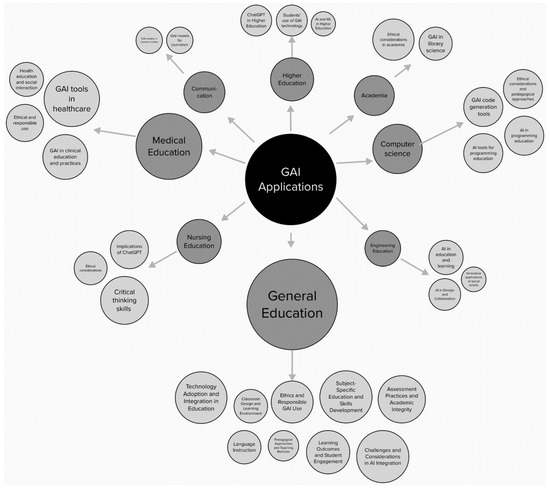
Figure 3.
Summary of GAI research and applications in education.
4. Bibliometric Analysis
In this section, we embark on a comprehensive bibliometric analysis that delves into the field of GAI within the context of education. By examining a vast collection of existing articles and publications retrieved from the Scopus database, we seek to provide a deeper understanding of the current state of research and innovation in this evolving field. Through systematic literature screening and data analysis, we aim to uncover valuable insights, trends, and implications surrounding GAI’s integration and impact on teaching and learning in educational settings. This exploration will shed light, for example, on the interdisciplinary nature of GAI research, key AI tools employed, the geographic distribution of contributions, and the diverse fields within education where GAI finds its applications. As we navigate through the findings and visualizations, we uncover the growth trajectory of GAI research, observe patterns of co-occurrence between terms, and ascertain the prominent applications of GAI tools, like ChatGPT, in educational settings.
To provide an in-depth analysis of the current state of GAI in education, we utilized VOSviewer to generate five types of visualization maps. These maps are designed to provide a comprehensive analysis of the topic. Each map consists of circles that represent different items such as publications, researchers, or terms. The size of the circle and the font within it indicate the level of activity associated with that item. A larger circle and a bigger font size indicate a higher level of activity, whereas a smaller circle and a smaller font size suggest less activity. The distance between any two terms in the diagram reflects the degree of association between them. A shorter distance signifies a stronger correlation, whereas a longer distance indicates a weaker correlation [151].
4.1. Co-Occurrence Map Based on Text Data
The relevant and frequently occurring terms were identified by analyzing the text data of the 217 selected publications. The analysis of text data looks to extract relevant terms from the titles and abstracts of the selected articles and constructs a network of co-occurrence links between them [151]. This analysis enables us to detect any emerging developments and identify impactful terms within the field of GAI in education. A total of 4408 terms were generated, out of which 102 terms meet the minimum threshold of 10 occurrences. To further narrow down the selection of terms, VOSviewer calculated a relevance score for each term, and the top 60% most relevant terms were selected, resulting in the 61 terms that were displayed in the network seen in Figure 4. Terms with a high relevance score represent more specific topics covered by the text data, while terms with a low relevance score tend to be of a general nature [151]. A thesaurus was created and uploaded to VOSviewer for the standardization of keywords and the elimination of duplicate terms [152].
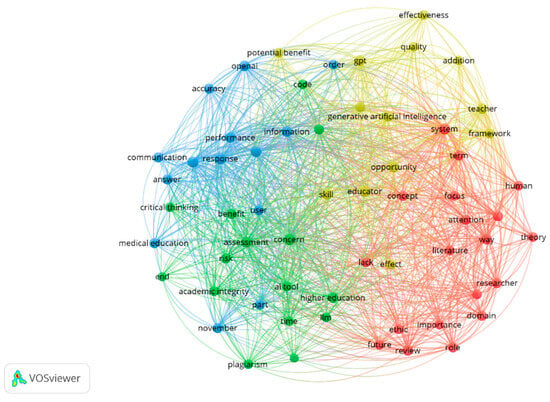
Figure 4.
Co-occurrence map of text data.
The findings in Figure 4 demonstrate the diverse range of research and exploration within the field of GAI in education. The interconnected web of key terms suggests that the research on GAI has encompassed the areas of assessment, teaching, research, higher education, academic integrity, and ethics. The findings also highlight GAI’s revolutionary potential with the appearance of terms such as “opportunity” and “effectiveness”. Additionally, the terms that are directly linked with GAI are shown in Figure 5.
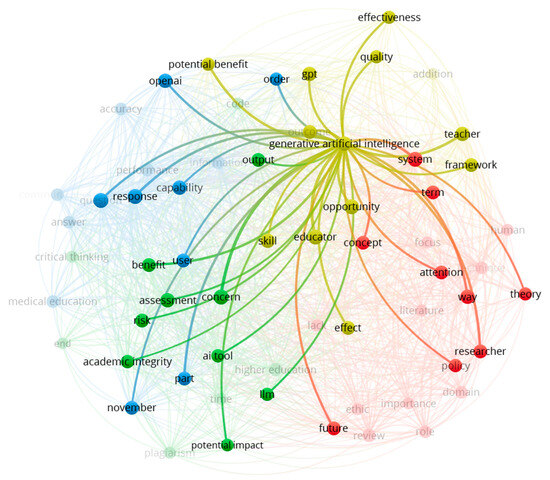
Figure 5.
Terms directly connected with “Generative Artificial Intelligence”.
The findings in Figure 5 indicate a strong relationship between GAI and “Generative Pre-training Transformers” (GPT), which are a type of large language model (LLM). GPTs, such as ChatGPT, have emerged as foundational technologies in GAI and have demonstrated their capabilities in various applications. The integration of GPTs in educational contexts, particularly in the development of AI chatbots, has the potential to enhance learning experiences through personalized interactions, intelligent feedback, and adaptive learning pathways. This raises questions about the impact of GAI on student engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes. Additionally, the association between GAI and terms such as opportunity, question, response, and assessment highlight the diverse applications of GAI in educational contexts. GAI has the potential to support various aspects of teaching and learning, including generating questions, providing responses, and assessing student performance. The use of GAI in assessments raises concerns about the fairness and reliability of automated grading systems. It is crucial to examine the validity and equity of GAI-based assessment methods to ensure that they align with established educational standards and principles of fairness.
The ten most frequently occurring terms and their number of occurrences can be seen listed below in Table 9. Also listed in the table is the relevance score for each term. The relevance score for each term is calculated by VOSviewer. For each term, VOSviewer determines the distribution of (second order) co-occurrences over all terms and then compares it to the overall distribution of co-occurrences over terms. The larger the difference between the two distributions (measured using the Kullback–Leibler distance), the higher the relevance of a term [153]. Table 9 provides an insightful analysis of the key terms frequently encountered in the context of GAI in education. These terms shed light on the diverse aspects of GAI’s integration into educational practices. The term “System” suggests the broader framework within which GAI operates, emphasizing the need for systematic implementations. “Response” indicates the generation of AI-driven outputs, while “Question” signifies GAI’s potential to create queries and foster interactive learning environments. “Concern” highlights the importance of addressing ethical and practical considerations when employing GAI in education. “Opportunity” underscores the positive prospects that GAI offers in enhancing educational experiences and outcomes. The prominence of “Generative Pre-training Transformers (GPT)” demonstrates the pivotal role of advanced language models, like ChatGPT, in driving GAI applications. Terms like “Assessment” and “Capability” indicate GAI’s relevance in evaluating student performance and its potential to augment educational capabilities. This analysis unveils the nuanced facets of GAI in education, encompassing both its capabilities and the essential aspects that demand attention for responsible implementation.

Table 9.
Top 10 terms by occurrences.
4.2. Co-Occurrences Map Based on Keywords
The keywords that occur frequently were identified by analyzing the bibliographic data of the 217 selected publications. A total of 1204 keywords were found, out of which 50 were selected, where the minimum number of occurrences of those terms was limited to 6 (Figure 6). A thesaurus was also used in VOSviewer to standardize keywords and eliminate redundant duplicate terms. This analysis looks at all keywords, including both author keywords and index keywords. Author keywords are specific keywords chosen and provided by the authors of the articles themselves, while index keywords are keywords that have been assigned by indexers or databases to classify and categorize the articles for the purpose of information retrieval and indexing.
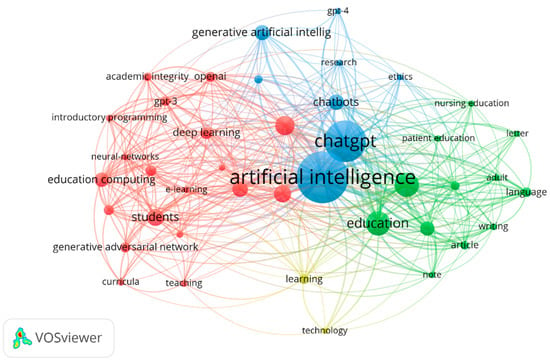
Figure 6.
Co-occurrence map of all keywords.
Some of the most common keywords identified include “Artificial intelligence”, “ChatGPT”, “Education”, and “Human”. A list of the ten most frequently used keywords, their occurrences, and their total link strength can be found in Table 10. The total link strength indicates the total strength of the co-occurrence links of a given keyword with other keywords [151].

Table 10.
Top 10 keywords by occurrences.
Table 10 presents a comprehensive analysis of the most frequently occurring keywords in the domain of GAI in education, offering valuable insights into the prominent themes and research areas. The top ten keywords are indicative of the central focus and key aspects of GAI’s integration into educational contexts. “Artificial intelligence” emerges as the most prevalent keyword, reflecting the overarching role of AI technologies in transforming educational practices. “ChatGPT” follows closely, showcasing the widespread recognition and utilization of this AI chatbot in educational applications. “Education” and “Human” hold significant positions, highlighting the significance of GAI in shaping learning experiences and considering human aspects in the educational process. “Education computing” signifies the intersection of computing technologies and education, while “Machine learning” underscores the pivotal role of ML algorithms in GAI applications. “Medical education” and “Natural language processing” reveal GAI’s potential in healthcare education and language-based learning environments. Lastly, “Students” emphasizes the focus on learners and their experiences, reflecting the student-centric approach that GAI-driven educational interventions strive to achieve. These keywords depict the breadth and depth of GAI research in education, with an emphasis on AI-driven technologies, human-centric design, and transformative potential in diverse educational settings.
To further the analysis, two additional keyword maps were generated. Firstly, a map of the most common author keywords was generated. The keywords were limited to a minimum of five occurrences, which resulted in a total of twenty-five author keywords in the network visualization (Figure 7). Similarly, a map of the most common index keywords was created. The keywords were also limited to a minimum of five occurrences, which resulted in a total of thirty-nine index keywords in the map (Figure 8).
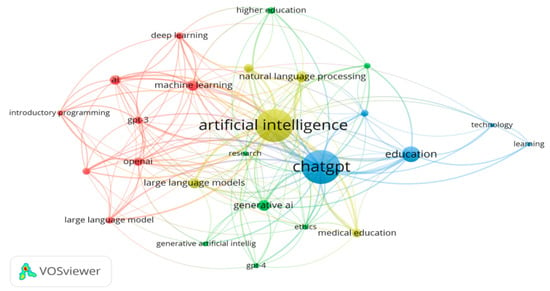
Figure 7.
Co-occurrence map of author keywords.
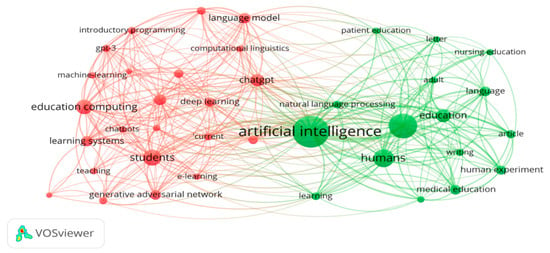
Figure 8.
Co-occurrence map of index keywords.
The analysis of keywords reveals the central focus of GAI research in education, with terms such as artificial intelligence, ChatGPT, and education featuring prominently. This emphasizes the significance of AI technologies in transforming educational practices and the need for collaborations between AI experts and educators. The inclusion of medical education-related keywords suggests potential applications of GAI in healthcare education. GAI has the potential to support medical training, enhance diagnostic processes, and improve patient care.
4.3. Co-Occurrence Map Based on Country of Co-Authorship
Furthermore, the data analysis enabled us to examine the geographic distribution of these publications. The visualization map was generated for the countries of co-authorship by setting the minimum number of documents of a country to five. Of the 69 countries with publications, 20 met the threshold, and the results are depicted in Figure 9.
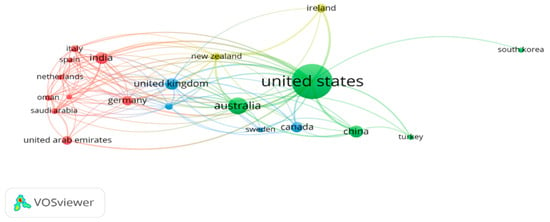
Figure 9.
Country of co-authorships.
Most publications appeared from English-speaking countries (USA, Australia, and the UK), followed by India, Germany, and China. The ten countries with the strongest links on the map are listed in Table 11.

Table 11.
Top 10 countries by link strength.
Table 11 presents the top 10 countries based on their contributions to GAI research in education. The United States leads the list, indicating its central role in GAI-related studies. Australia and the United Kingdom follow closely, showcasing their active engagement in the field. New Zealand, India, Germany, Hong Kong, Italy, Saudi Arabia, and Switzerland also feature, reflecting their emerging roles in GAI research within the educational context.
The geographical distribution of publications demonstrates widespread global interest and collaboration in exploring the potential of GAI in education. Moreover, the distribution indicates the dominance of English-speaking countries such as the United States, Australia, and the United Kingdom. This aligns with the global prominence of these countries in educational research and technological advancements. However, it is worth noting the increasing contributions from countries like India, Germany, and China, suggesting a broader global interest in GAI in education. Collaboration and knowledge sharing across countries and regions can further propel advancements and foster cross-cultural perspectives in GAI research.
4.4. Co-Occurrence Map Based on Authorship
A further analysis looks at investigating the authorship relations across the multitude of authors of the publications. The network visualization map was limited to authors with a minimum of five citations. Out of the 682 authors, 144 met the threshold, and the largest set of connected authors included 23 authors. The resulting network visualization, depicted in Figure 10, presents a complex web of links connecting these 23 authors.
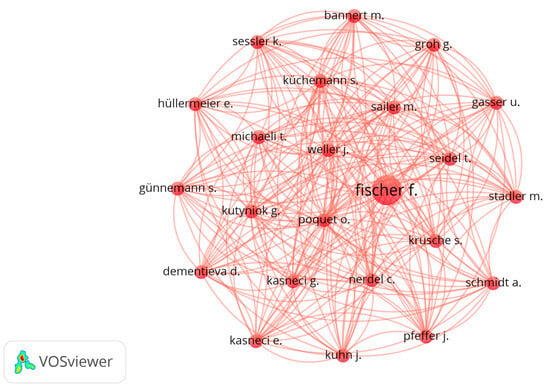
Figure 10.
Co-occurrence map of authors.
The network visualization consists of a large network of links connecting the authors, which showcases the collaborative and interdisciplinary nature of the research being conducted within the field of GAI in education. Moreover, it demonstrates how researchers from diverse backgrounds and institutions come together to advance knowledge and innovation in this area. By highlighting these connections, the visualization fosters a better understanding of the knowledge-sharing dynamics and the collective effort behind the advancements in GAI in education. This insight can prove invaluable in identifying key contributors, potential research trends, and opportunities for further collaboration and development within the field.
The top 10 authors in terms of documents produced and citations can be seen in Table 12 and Table 13, respectively. The total link strength in each table indicates the total strength of the co-occurrence links of a given author with other authors [151].

Table 12.
Top 10 authors by documents produced.

Table 13.
Top 10 authors by citations.
Table 12 depicts the key contributors of research in the domain of GAI in education. The relatively high number of documents, citations, and total link strength demonstrates the great influence and contribution of the authors.
Similarly, Table 13 identifies key contributors who have been influential through their publications within this domain. Notably, the top four authors, namely Hwang G.-J., Chen X., Xie H. and Zou D., all have an impressive citation count of 162. This exceptional citation count comes from their highly influential research paper titled “Application and theory gaps during the rise of Artificial Intelligence in Education”, which played a vital role in exploring the applications of AI in education in 2020, contributing significantly to the early development of the field [89].
4.5. Data Analysis on Article Sources
To investigate the different sources of the 217 publications, a list of all unique sources was created and then ordered from the highest number of articles to the lowest. A total of 152 unique sources were found. The sources with the highest number of publications were “Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence” and the “Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice”, with five publications each. A bar graph showcasing the top 10 sources by number of publications can be found in Figure 11.
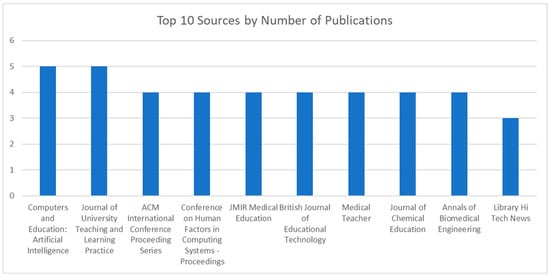
Figure 11.
Bar graph of the top 10 sources by number of publications.
The analysis of article sources, therefore, presents a compelling picture of the interdisciplinary nature of GAI research in education, drawing insights from various fields such as computer science, education, and even the medical field. The convergence of expertise from diverse disciplines underscores the significance of collaborative efforts in addressing the complex challenges associated with GAI implementation in education.
4.6. Data Analysis on Document Type, Fields, GAI Tools Used, and Research Types
In this section, we classified the 217 publications based on their type, field of study, GAI tools used, and paper types. Figure 12 presents an analysis of the occurrences of various document types from Scopus. Notably, the most common document type is “Article”, which appears 99 times, highlighting its preeminent role as the primary form of publication within the dataset. “Article” is followed by “Note”, with 23 occurrences, and “Conference Paper” and “Review”, with 20 and 18 occurrences, respectively. Moderately represented are “Letter” and “Editorial”, each occurring 17 and 11 times, respectively. Conversely, “Short Survey” is the least common, appearing only once. The dominance of scholarly articles in the dataset aligns with the typical composition of academic databases like Scopus, emphasizing their pivotal role as reliable sources of scientific information.
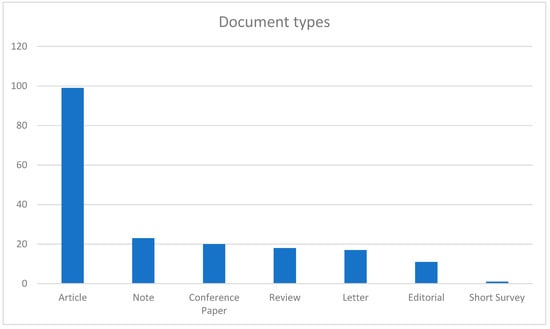
Figure 12.
Occurrences of document types.
Additionally, the analysis delves further into the field, revealing 21 distinct disciplines within the dataset, with the top 10 most prevalent fields illustrated in Figure 13. It is crucial to acknowledge that papers falling into multiple categories, such as higher education and academia, were individually counted as separate occurrences.
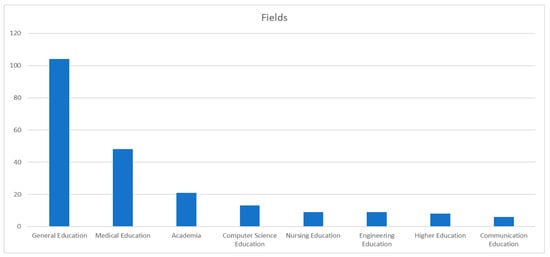
Figure 13.
Occurrences of unique fields in education.
As depicted in Figure 13, the majority of the papers encompass a broad scope of education and fall under the “general education” category, comprising 104 occurrences. Additionally, our analysis reveals the integration of GAI in various educational frameworks across different fields. Particularly noteworthy is the significant number of papers originating from the medical field, with 43 occurrences, indicating the growing adoption of GAI in both medical and educational contexts. Academia-related papers account for 21 occurrences, further highlighting the relevance of GAI in academic research. Moreover, we observed GAI’s intersection with specific disciplines, such as computer science education, nursing education, and engineering education, with thirteen, nine, and nine occurrences, respectively. Lastly, it is worth mentioning the representation of GAI in other fields, including higher education and communication education, with eight and six occurrences, respectively, showcasing the diverse applications and potential of this technology in various educational domains.
Moving forward, we conducted an analysis of the AI tools utilized in each paper, providing valuable insights into the tool landscape within the field of GAI in education (Figure 14). It is important to note that some papers utilize multiple AI tools, with each tool recorded as a distinct occurrence. Particularly noteworthy is the dominance of ChatGPT, which features in a significant number of papers, with a staggering 151 occurrences. This remarkable prevalence highlights the widespread recognition and adoption of ChatGPT within educational contexts, underlining its efficacy in generating coherent and contextually relevant responses for educational applications.
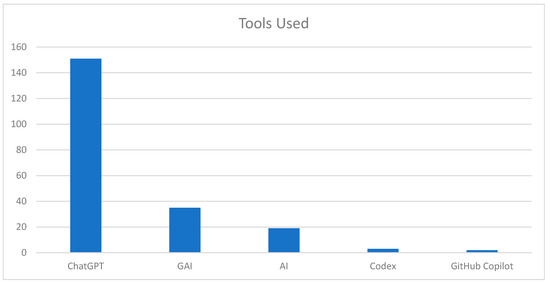
Figure 14.
Occurrences of AI tools.
AI-powered Chatbots, such as BlenderBot and LaMDA, and AI text generators (AITG) appear in the dataset, albeit with lower frequencies [73,110]. Tools such as Codex and GitHub Copilot, which translate natural language to code, appear in a limited number of papers [5,154]. BERT, a method of pre-training language representations, and Conditional GAN, a type of GAN that involves the conditional generation of images by a generator model, appear a few times in the dataset. Other unique tools with a low number of occurrences include EDU-AI, a model for generating adaptable and functional classroom layouts [94], MACHE—bot, an AI dialogue system [96], and Djehuty (AI), an AI-powered educational gamified environment [97]. Furthermore, several papers do not specify a particular tool and instead use more general terms, like “GAI” and “AI”, to describe the approaches they employed.
Then, we outlined the types of research in the context of GAI in education to gain valuable insights into the nature and focus of the scholarly work conducted in this field (Figure 15).
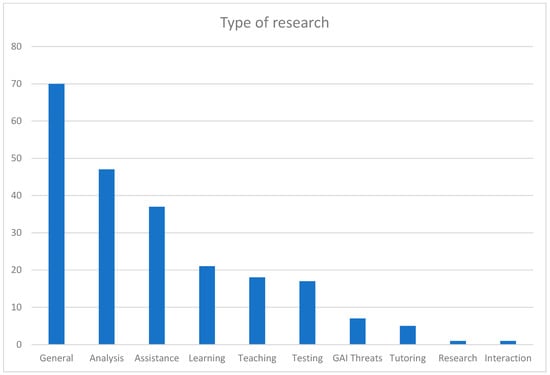
Figure 15.
Occurrences of research types in education.
The most prevalent type of research is “General”, with 70 occurrences. This suggests a broad range of papers that cover a wide array of topics, methodologies, and perspectives within the domain of GAI in education. Following general papers, “Analysis” emerges as the second most common type, appearing in 47 papers. This indicates a significant emphasis on examining and interpreting data, models, or educational contexts through analytical lenses, allowing for a deeper understanding of the implications and applications of GAI. “Assistance” is the third most frequent type, featured in 37 papers. This underscores the relevance of research aimed at developing AI systems that provide support and guidance to learners or educators. It suggests a strong interest in exploring how GAI can serve as an intelligent assistant in educational settings. “Learning”, “Teaching”, and “Testing” papers follow with 21, 18, and 17 occurrences, respectively. These types highlight the focus on investigating how GAI can enhance and optimize various aspects of the learning and assessment processes within educational environments. Moreover, “GAI Threats”, “Tutoring”, “Research”, and “Interaction” types make appearances in a more limited number of papers. These occurrences highlight specific areas of interest, such as addressing potential threats associated with GAI in education, exploring the use of AI systems in tutoring scenarios, conducting research studies, and examining interaction dynamics.
5. Conclusions and Future Research
AI has emerged as a revolutionary force in the era of rapid technological advancements, profoundly transforming various aspects of human life. In the field of education, the emergence of GAI has sparked a transformative revolution, influencing areas such as medical and engineering education. GAI’s versatile applications include assessment, personalized learning support, and intelligent tutoring systems. The integration of GAI in education has prompted discussions on ethics, academic integrity, and its potential to reshape teaching and learning methods. As GAI continues to advance, thorough research on its applications, implications, and challenges becomes essential in shaping the future of education. This review paper comprehensively analyzed the research on GAI in education, synthesized key findings and insights from 207 publications, and identified research gaps and future directions in the field.
The first step of this work was to conduct a comprehensive examination of the utilization of GAI in education through an in-depth study and content analysis of the literature in the field.
The content analysis has provided significant findings that highlight the transformative impact of GAI in education. Across various domains and contexts, the integration of GAI, including AI chatbots and virtual instructors, offers substantial opportunities for enhancing educational practices and improving learning outcomes. In computer science education, GAI has proven to be a powerful tool in teaching and learning programming concepts. The research papers revealed the potential benefits of AI technologies for creative programming education and the use of AI-powered code generation tools, like Copilot. Engineering education also benefits greatly from GAI’s integration, empowering students to generate innovative solutions through advanced chatbots and text-generation models. Cloud-based frameworks and social robots enhance interactive learning experiences, creating a technologically advanced and effective engineering education landscape. Medical education sees promising applications of GAI in fields like medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, and public health education. Nursing education benefits from ChatGPT in enhancing patient care and fostering critical thinking skills among nursing students. In communication education, GAI models showcase potential in journalism, media education, and healthcare communication. The studies demonstrate GAI’s effectiveness in enhancing translation accuracy, emphasizing the importance of educating students about responsible AI use and ethical considerations. In academia, GAI offers potential benefits in various academic fields, such as using AI technologies, natural language processing techniques, and LLMs for research. Furthermore, the subsection on “General Education” provided a comprehensive overview of GAI’s wider applications in the educational landscape. Diverse research papers explored technology adoption, classroom design, assessment practices, language instruction, ethics, subject-specific education, learning outcomes, student engagement, challenges in AI integration, and innovative pedagogical approaches.
After conducting the content analysis, the next step involved a bibliometric analysis of GAI within the context of education. It included an examination of a total of 437 pre-existing articles and publications retrieved from the Scopus database. After conducting a literature screening and removing duplicates, the analysis comprised a list of 217 publications that focused on GAI in education.
The comprehensive bibliometric analysis of GAI in education yielded several key findings. The research on GAI experienced significant and exponential growth from 2018 to 2023, with a notable surge in papers published in 2023, which was likely due to the popularity and innovation sparked by tools like ChatGPT. In addition, ChatGPT emerged as the dominant AI tool in GAI research within educational contexts, indicating its widespread adoption for intelligent interactions and contextually relevant responses. The interdisciplinary nature of GAI research in education, spanning computer science, engineering education, and medical education, highlights the need for collaboration in addressing complex challenges and potential applications.
While highlighting the promising contributions of GAI integration in education, this review also delved into potential concerns associated with its implementation. This paper navigated the landscape of ethical implications, responsible GAI use, data privacy safeguards, biases, and academic integrity when exploring the assimilation of GAI within educational settings. These multifaceted concerns were considered in various sections of this review paper.
Based on the findings from this review paper, several future research directions can be suggested to advance the field of GAI in educational settings:
- Exploring Transparency: Future research should focus on enhancing the transparency of GAI models. Understanding how AI-generated outputs are generated and providing transparent explanations to users can increase user trust and acceptance of GAI tools in educational settings;
- Addressing Biases and Fairness: As GAI models learn from existing data, they may inherit biases present in the data, potentially leading to biased outputs. Future research should focus on addressing and mitigating biases in GAI tools, especially in educational contexts, to not perpetuate stereotypes or discriminate against certain groups of learners;
- Designing AI-Enhanced Curriculum: Researchers can explore the potential of GAI in generating adaptive and dynamic learning materials that cater to individual learners’ needs. AI-powered curriculum design can foster personalized and engaging learning experiences, promoting lifelong learning and skill development;
- GAI in Teacher Professional Development: Research can investigate how GAI tools can assist educators in improving their teaching practices, developing tailored instructional materials, and providing real-time feedback on their performance;
- Collaborative AI in Education: Research the potential of collaborative AI systems in education, where humans and AI work together to achieve educational goals;
- Longitudinal Studies: Conduct longitudinal studies to track the long-term effects of GAI integration in education. These studies can provide insights into the sustained impact of GAI on learning outcomes, retention rates, and academic performance over extended periods;
- Privacy and Data Security: Research should focus on developing robust data protection measures and ensuring that student data is handled responsibly and securely;
- Long-term Impact on Learning Outcomes: Investigate the long-term impact of GAI integration on learning outcomes, academic achievement, and students’ problem-solving skills;
- Ethical Considerations and Responsible AI: Further explore the ethical implications of using GAI in education, addressing concerns related to plagiarism, academic integrity, and the potential impact on students’ critical thinking skills. Develop guidelines and policies to ensure the responsible and ethical use of GAI technologies in educational settings;
- Student Acceptance and Adoption: Conduct research on students’ acceptance and adoption of GAI technology in the learning process. Understand factors influencing their attitudes toward AI-powered tools and identify strategies to enhance student engagement and acceptance;
- Interdisciplinary Collaborations: Foster interdisciplinary collaborations between educators, AI researchers, and policymakers to develop comprehensive frameworks for integrating GAI into education;
- Inclusivity and Accessibility: Explore ways to make GAI-powered educational tools more accessible to diverse learners, including those with disabilities or language barriers;
- AI in Assessment and Evaluation: Investigate the effectiveness of GAI in assessment practices, including essay grading, problem-solving evaluation, and personalized feedback;
- AI and Pedagogy: Investigate the implications of GAI for pedagogical practices, examining how it can complement and enhance traditional teaching methods.
This literature review revealed the immense potential of GAI in reshaping education across various disciplines. While GAI presents exciting opportunities for improving teaching, learning, and educational processes, responsible and ethical usage, as well as addressing potential biases and academic integrity, are crucial aspects that demand attention. The continued exploration of GAI’s potential, along with developing comprehensive guidelines and fostering critical thinking skills, will pave the way for a technologically advanced, inclusive, and effective educational landscape.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.B., C.A. and V.A.; methodology, Z.B., C.A. and V.A. and A.Z.; software, A.Z.; formal analysis, Z.B., C.A. and V.A.; investigation, Z.B., C.A. and V.A.; resources, Z.B. and C.A.; data curation, Z.B., C.A., V.A. and A.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.B., C.A., V.A. and A.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.B., C.A., V.A. and A.Z.; visualization, Z.B., C.A., V.A. and A.Z.; supervision, Z.B.; project administration, Z.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the support of the American University of Sharjah under the Open Access Program. This paper represents the opinions of the authors and does not mean to represent the position or opinions of the American University of Sharjah.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Melvern Moras, an undergraduate student, for his assistance in conducting the bibliometric analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- OpenAI ChatGPT. Available online: https://chat.openai.com (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Sullivan, M.; Kelly, A.; McLaughlan, P. ChatGPT in higher education: Considerations for academic integrity and student learning. J. Appl. Learn. Teach. 2023, 6, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrini, A.; Khamoshifar, M.; Abbasimehr, H.; Riggs, R.J.; Esmaeili, M.; Majdabadkohne, R.M.; Pasehvar, M. ChatGPT: Applications, opportunities, and threats. In Proceedings of the 2023 Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium (SIEDS), Charlottesville, VA, USA, 27–28 April 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Bard. Available online: https://bard.google.com/ (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Github Copilot. Available online: https://copilot.github.com/ (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Hadi, M.U.; Qureshi, R.; Shah, A.; Irfan, M.; Zafar, A.; Shaikh, M.B.; Akhtar, N.; Wu, J.; Mirjalili, S. A Survey on Large Language Models: Applications, Challenges, Limitations, and Practical Usage. TechRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidoo-Anu, D.; Owusu Ansah, L. Education in the Era of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI): Understanding the Potential Benefits of ChatGPT in Promoting Teaching and Learning. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4337484 (accessed on 28 July 2023).
- Crompton, H.; Burke, D. Artificial intelligence in higher education: The state of the field. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2023, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, M.; Salim, N.; Barakat, M.; Al-Tammemi, A. ChatGPT applications in medical, dental, pharmacy, and public health education: A descriptive study highlighting the advantages and limitations. Narra J. 2023, 3, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.; Chan, T.; Yu, C. Termbot: A Chatbot-Based Crossword Game for Gamified Medical Terminology Learning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNeil, S.; Tran, A.; Mogil, D.; Bernstein, S.; Ross, E.; Huang, Z. Generating diverse code explanations using the gpt-3 large language model. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM Conference on International Computing Education Research, Lugano, Switzerland, 7–11 August 2022; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Watanobe, Y. ChatGPT for education and research: Opportunities, threats, and strategies. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, C. Chatbots in education and research: A critical examination of ethical implications and solutions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markel, J.M.; Opferman, S.G.; Landay, J.A.; Piech, C. GPTeach: Interactive TA Training with GPT Based Students. In Proceedings of the Tenth ACM Conference on Learning @ Scale (L@S ‘23), Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Prisma Framework. Available online: http://www.prisma-statement.org/ (accessed on 6 August 2023).
- Jonsson, M.; Tholander, J. Cracking the code: Co-coding with AI in creative programming education. In Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Creativity and Cognition, Venice, Italy, 20–23 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnie-Ansley, J.; Denny, P.; Becker, B.A.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Prather, J. The robots are coming: Exploring the implications of openai codex on introductory programming. In Proceedings of the 24th Australasian Computing Education Conference, Virtual Event, 14–18 February 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, P.; Kumar, V.; Giacaman, N. Conversing with copilot: Exploring prompt engineering for solving cs1 problems using natural language. In Proceedings of the 54th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–18 March 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemitabaar, M.; Chow, J.; Ma, C.K.T.; Ericson, B.J.; Weintrop, D.; Grossman, T. Studying the effect of AI code generators on supporting novice learners in introductory programming. In Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 23–28 April 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelka, J.; Agarwal, A.; Bogart, C.; Sakr, M. Large language models (gpt) struggle to answer multiple-choice questions about code. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08033. [Google Scholar]
- Wermelinger, M. Using GitHub copilot to solve simple programming problems. In Proceedings of the 54th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–18 March 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.A.; Denny, P.; Finnie-Ansley, J.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Prather, J.; Santos, E.A. Programming is hard-or at least it used to be: Educational opportunities and challenges of AI code generation. In Proceedings of the 54th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education V. 1, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–18 March 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, L. Teaching CS-101 at the Dawn of ChatGPT. ACM Inroads 2023, 14, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, I.D.; Scheuerman, M.K.; Amironesei, R. You can’t sit with us: Exclusionary pedagogy in AI ethics education. In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Virtual Event, 3–10 March 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, R.; Yilmaz, F.G.K. The effect of generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based tool use on students’ computational thinking skills, programming self-efficacy and motivation. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 4, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortiñas-Lorenzo, K.; Lacey, G. Toward Explainable Affective Computing: A Review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023. accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, R.; Barrios, N.; Vera, R.E.; Mendez, M.E.; Tolosa, L.; Zambrano, F.; Li, Y. A perspective on the synergistic potential of artificial intelligence and product-based learning strategies in biobased materials education. Educ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 44, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphry, T.; Fuller, A.L. Potential ChatGPT Use in Undergraduate Chemistry Laboratories. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 1434–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ruiz, L.M.; Moll-López, S.; Nuñez-Pérez, A.; Moraño-Fernández, J.A.; Vega-Fleitas, E. ChatGPT Challenges Blended Learning Methodologies in Engineering Education: A Case Study in Mathematics. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, S.; Daniel, S.; Haque, R.; Belkina, M.; Hassan, G.M.; Grundy, S.; Lyden, S.; Neal, P.; Sandison, C. ChatGPT versus engineering education assessment: A multidisciplinary and multi-institutional benchmarking and analysis of this generative artificial intelligence tool to investigate assessment integrity. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 2023, 48, 559–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmeiner, F.; Yang, H.; Yao, L.; Holstein, K.; Martelaro, N. Exploring challenges and opportunities to support designers in learning to co-create with AI-based manufacturing design tools. In Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 23–28 April 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Olajoyegbe, T.O.; Morkos, B. The imminent educational paradigm shift: How artificial intelligence will reframe how we educate the next generation of engineering designers. In Proceedings of the 2020 ASEE Virtual Annual Conference Content Access, Virtual Event, 22–26 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdon, F.; Hall, A.; Ferrarello, L. Enhacing abductive reasoning in design and engineering education via probabilistic knowledge; a case study in ai. In Proceedings of the DS 110: 23rd International Conference on Engineering and Product Design Education (E&PDE 2021), VIA Design, VIA University, Herning, Denmark, 9–10 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaki, A.O.; Abduljabbar, M.; Ali, L.; Alnajjar, F.; Mehiar, D.; Marei, A.M.; Alhmiedat, T.; Al-Jumaily, A. Revolutionizing Social Robotics: A Cloud-Based Framework for Enhancing the Intelligence and Autonomy of Social Robots. Robotics 2023, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konecki, M.; Konecki, M.; Biškupić, I. Using artificial intelligence in higher education. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education, Prague, Czech Republic, 21–23 April 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eager, B.; Brunton, R. Prompting higher education towards AI-augmented teaching and learning practice. J. Univ. Teach. Learn. Pract. 2023, 20, 02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, I.S.; Sarwary, S.A.M.; El Refae, G.A.; Chabchoub, H. Time to Revisit Existing Student’s Performance Evaluation Approach in Higher Education Sector in a New Era of ChatGPT—A Case Study. Cogent Educ. 2023, 10, 2210461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskender, A. Holy or unholy? Interview with open AI’s ChatGPT. Eur. J. Tour. Res. 2023, 34, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecki, A. To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2023, 34, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, A. Learning with ChatGPT 3.5 as a more knowledgeable other: An autoethnographic study. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2023, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.S.; Abreu, A.; Costa, E.; Paiva, J. How Machine Learning (ML) is Transforming Higher Education: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Inf. Syst. Eng. Manag. 2023, 8, 21168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisberg, E.; Ong, J.; Masalkhi, M.; Kamran, S.A.; Zaman, N.; Sarker, P.; Lee, A.G.; Tavakkoli, A. GPT-4: A new era of artificial intelligence in medicine. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevgi, U.T.; Erol, G.; Doğruel, Y.; Sönmez, O.F.; Tubbs, R.S.; Güngor, A. The role of an open artificial intelligence platform in modern neurosurgical education: A preliminary study. Neurosurg. Rev. 2023, 46, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapeta, J. Are ChatGPT and other pretrained language models good parasitologists? Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, S. Are ChatGPT’s knowledge and interpretation ability comparable to those of medical students in Korea for taking a parasitology examination?: A descriptive study. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2023, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezal, J.M.; Wolk, R.; Hieromnimon, H.M.; Howard, F.M.; Srisuwananukorn, A.; Karpeyev, D.; Ramesh, S.; Kochanny, S.; Kwon, J.W.; Agni, M.; et al. Deep learning generates synthetic cancer histology for explainability and education. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalidis, I.; Cagnina, A.; Luangphiphat, W.; Mahendiran, T.; Muller, O.; Abbe, E.; Fournier, S. ChatGPT takes on the European Exam in Core Cardiology: An artificial intelligence success story? Eur. Heart J.-Digit. Health 2023, 4, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsello, A.; Santangelo, A. May Artificial Intelligence Influence Future Pediatric Research?—The Case of ChatGPT. Children 2023, 10, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Tan, J.; Zapadka, M.E.; Ponnatapuram, J.; Niu, C.; Wang, G.; Whitlow, C.T. Translating radiology reports into plain language using chatgpt and gpt-4 with prompt learning: Promising results, limitations, and potential. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.09038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Messih, M.S.; Kamel Boulos, M.N. ChatGPT in clinical toxicology. JMIR Med. Educ. 2023, 9, e46876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.; Choi, G.; Lee, W.Y. ChatGPT goes to the operating room: Evaluating GPT-4 performance and its potential in surgical education and training in the era of large language models. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2023, 104, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Bubeck, S.; Petro, J. Benefits, limits, and risks of GPT-4 as an AI chatbot for medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Por, L.Y.; Leong, M.C.; Ku, C.S. The Potential of ChatGPT in Assisting Children with Down Syndrome. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jia, S.; Li, Z.; Duan, Y.; Tao, G.; Zhao, Z. A Comprehensive Review of Artificial Intelligence in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 845305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascella, M.; Montomoli, J.; Bellini, V.; Bignami, E. Evaluating the feasibility of ChatGPT in healthcare: An analysis of multiple clinical and research scenarios. J. Med. Syst. 2023, 47, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Herzog, I.; Weisberger, J.; Chao, J.; Chaiyasate, K.; Lee, E.S. Utilization of ChatGPT for plastic surgery research: Friend or foe? J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 80, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, K. Ethical use of artificial intelligence in health professions education: AMEE Guide No. 158. Med. Teach. 2023, 45, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.P.H.; Lee, J.J.; Ho, M.; Kwok, J.Y.Y.; Lok, K.Y.W. Chatting or cheating? The impacts of ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence language models on nurse education. Nurse Educ. Today 2023, 125, 105796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.; Jones, D.; Fealy, S. What is ChatGPT and what do we do with it? Implications of the age of AI for nursing and midwifery practice and education: An editorial. Nurse Educ. Today 2023, 127, 105835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulai, A.; Hung, L. Will ChatGPT undermine ethical values in nursing education, research, and practice. Nurs. Inq. 2023, 30, e12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seney, V.; Desroches, M.L.; Schuler, M.S. Using ChatGPT to teach enhanced clinical judgment in nursing education. Nurse Educ. 2023, 48, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.K. The Impact of ChatGPT on the Nursing Profession: Revolutionizing Patient Care and Education. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, L.S. The CLEAR path: A framework for enhancing information literacy through prompt engineering. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2023, 49, 102720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Short sequence Chinese-English machine translation based on generative adversarial networks of emotion. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 3385477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santandreu-Calonge, D.; Medina-Aguerrebere, P.; Hultberg, P.; Shah, M. Can ChatGPT improve communication in hospitals? Prof. Inf. 2023, 32, e320219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlik, J.V. Collaborating with ChatGPT: Considering the implications of generative artificial intelligence for journalism and media education. J. Mass Commun. Educ. 2023, 78, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Poralla, P.; Dash, S.; Li, K.; Desai, V.; Qiu, M. The impact of chatgpt on streaming media: A crowdsourced and data-driven analysis using twitter and reddit. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 9th Intl Conference on Big Data Security on Cloud (BigDataSecurity), IEEE Intl Conference on High Performance and Smart Computing, (HPSC) and IEEE Intl Conference on Intelligent Data and Security (IDS), New York, NY, USA, 6–8 May 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, T.; Badreldin, H.A.; Alrashed, M.; Alshaya, A.I.; Alghamdi, S.S.; bin Saleh, K.; Alowais, S.A.; Alshaya, O.A.; Rahman, I.; Al Yami, M.S.; et al. The emergent role of artificial intelligence, natural learning processing, and large language models in higher education and research. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2023, 19, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotton, D.R.; Cotton, P.A.; Shipway, J.R. Chatting and cheating: Ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, G.M. Academic integrity and artificial intelligence: Is ChatGPT hype, hero or heresy? Semin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 53, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergaa, I.; Chamari, K.; Zmijewski, P.; Saad, H.B. From human writing to artificial intelligence generated text: Examining the prospects and potential threats of ChatGPT in academic writing. Biol. Sport 2023, 40, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, M. Academic Integrity considerations of AI Large Language Models in the post-pandemic era: ChatGPT and beyond. J. Univ. Teach. Learn. Pract. 2023, 20, 07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, S. Impact of artificial intelligence text generators (AITGs) on libraries. Libr. Hi Tech News 2023. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, D.E. ChatGPT: A viral data-driven disruption in the information environment. Libr. Hi Tech News 2023, 40, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ghatrifi, M.O.M.; Al Amairi, J.S.S.; Thottoli, M.M. Surfing the technology wave: An international perspective on enhancing teaching and learning in accounting. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 4, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerling, W.; Mateer, G.D.; Wooten, J.; Damodaran, N. ChatGPT has aced the test of understanding in college economics: Now what? Am. Econ. 2023, 05694345231169654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skavronskaya, L.; Hadinejad, A.; Cotterell, D. Reversing the threat of artificial intelligence to opportunity: A discussion of ChatGPT in tourism education. J. Teach. Travel Tour. 2023, 23, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnozahy, W.A.; El Khayat, G.A. Multi-lang question answering framework for decision support in educational institutes. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Computer Supported Education, Prague, Czech Republic, 21–23 April 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, N.; Erdem, O.A. A research on the new generation artificial intelligence technology generative pretraining transformer 3. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Informatics and Software Engineering Conference (IISEC), Ankara, Turkey, 15–16 December 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, G. Examining science education in chatgpt: An exploratory study of generative artificial intelligence. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2023, 32, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, W. Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: A framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Rev. Educ. 2023, 20965311231168423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, S.; Cherukuri, A.K. The Rise of Generative Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on Education: The Promises and Perils. Computer 2023, 56, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.; Ching, Y. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Education, Part One: The Dynamic Frontier. TechTrends 2023, 67, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mørch, A.I.; Andersen, R. Human-Centred AI in Education in the Age of Generative AI Tools. Available online: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3408/short-s2-08.pdf (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Gentile, M.; Città, G.; Perna, S.; Allegra, M. Do we still need teachers? navigating the paradigm shift of the teacher’s role in the AI era. Front. Educ. 2023, 8, 1161777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangjarat, K.; Kraiwanit, T.; Limna, P.; Sonsuphap, R. Public Perceptions Towards ChatGPT as the Robo-Assistant. Online J. Commun. Media Technol. 2023, 13, e202338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, A.; Shehata, B.; Adarkwah, M.A.; Bozkurt, A.; Hickey, D.T.; Huang, R.; Agyemang, B. What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learn. Environ. 2023, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, J.M.; Thompson, K.; Corrin, L. Mapping out a research agenda for generative artificial intelligence in tertiary education. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2023, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, H.; Zou, D.; Hwang, G. Application and theory gaps during the rise of artificial intelligence in education. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2020, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; He, H.; Liu, J.; Berson, I.R.; Berson, M.J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H. Aladdin’s Genie or Pandora’s Box for Early Childhood Education? Experts Chat on the Roles, Challenges, and Developments of ChatGPT. Early Educ. Dev. 2023, 2214181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasneci, E.; Seßler, K.; Küchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Gasser, U.; Groh, G.; Günnemann, S.; Hüllermeier, E.; et al. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2023, 103, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovianko, M.; Gryshko, S.; Terziyan, V.; Tuunanen, T. Responsible cognitive digital clones as decision-makers: A design science research study. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Bors, A.G. Lifelong teacher-student network learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 6280–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, I.; Güzelci, O.Z.; Alaçam, S. EDU-AI: A twofold machine learning model to support classroom layout generation. Constr. Innov. 2022, 23, 898–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartiainen, H.; Tedre, M. Using artificial intelligence in craft education: Crafting with text-to-image generative models. Digit. Creat. 2023, 34, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Wibowo, S.; Cowling, M. An innovative tool for education: An adversarial dialogue system embedded with humor, empathy and culture. In Proceedings of the 2023 11th International Conference on Information and Education Technology (ICIET), Fujisawa, Japan, 18–20 March 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarr, J.M.A.; Yannakakis, G.N.; Liapis, A.; Bah, A.; Cambier, C. Djehuty: A mixed-initiative handwriting game for preschoolers. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games, Bugibba, Malta, 15–18 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, E.; Greisel, M.; Kuznetsov, I.; Berndt, M.; Kollar, I.; Dresel, M.; Fischer, M.R.; Fischer, F. Using natural language processing to support peer-feedback in the age of artificial intelligence: A cross-disciplinary framework and a research agenda. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2023, 54, 1222–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhnia, M.; Banihashem, S.K.; Noroozi, O.; Wals, A. A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: Implications for educational practice and research. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.E.; Potgieter, P.H. What do telecommunications policy academics have to fear from GPT-3? Telecommun. Policy 2023, 102576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Khan, S.M. Advances in AI and machine learning for education research. In Computational Psychometrics: New Methodologies for a New Generation of Digital Learning and Assessment: With Examples in R and Python; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Asim, R.; Zaffar, F.; Rahwan, T.; Zaki, Y. Rethinking Homework in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2023, 38, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.; Dhamecha, T.I.; Mukhi, N. Improving short answer grading using transformer-based pre-training. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence in Education: 20th International Conference, AIED 2019, Chicago, IL, USA, 25–29 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.K. What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajevski, M.; Barker, K.; Gilbert, A.; Hardie, L.; Ryan, F. ChatGPT and the future of legal education and practice. Law Teach. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johinke, R.; Cummings, R.; Di Lauro, F. Reclaiming the technology of higher education for teaching digital writing in a post—Pandemic world. J. Univ. Teach. Learn. Pract. 2023, 20, 01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, D. Use of chatgpt in ESP teaching process. In Proceedings of the 2023 22nd International Symposium INFOTEH-JAHORINA (INFOTEH), East Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 15–17 March 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Song, T. Establishing a Fusion Model of Attention Mechanism and Generative Adversarial Network to Estimate Students’ Attitudes in English Classes. Teh. Vjesn. 2022, 29, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Deng, Y. The Design Model of English Graded Teaching Assistant Expert System Based on Improved B/S Three-Tier Structure System. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 4167760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, D.E. An analysis of three chatbots: BlenderBot, ChatGPT and LaMDA. Intell. Syst. Account. Financ. Manag. 2023, 30, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D. Impact of ChatGPT on learners in a L2 writing practicum: An exploratory investigation. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearman, M.; Ajjawi, R. Learning to work with the black box: Pedagogy for a world with artificial intelligence. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2023, 54, 1160–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, P. Through the looking glass: Envisioning new library technologies AI-text generators as explained by ChatGPT. Libr. Hi Tech News 2023, 40, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.P. ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh, A. ChatGPT: Systematic Review, Applications, and Agenda for Multidisciplinary Research. J. Chin. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2023, 21, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danry, V.; Leong, J.; Pataranutaporn, P.; Tandon, P.; Liu, Y.; Shilkrot, R.; Punpongsanon, P.; Weissman, T.; Maes, P.; Sra, M. AI-generated characters: Putting deepfakes to good use. In Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems Extended Abstracts, New Orleans, LA, USA, 29 April–5 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; DiPaola, D.; Lee, I.; Hong, J.; Breazeal, C. Exploring generative models with middle school students. In Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 8–13 May 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.; Jameel, S.M.; Goggins, J. Education for Sustainable Development: Mapping the SDGs to University Curricula. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emenike, M.E.; Emenike, B.U. Was This Title Generated by ChatGPT? Considerations for Artificial Intelligence Text-Generation Software Programs for Chemists and Chemistry Educators. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathokleous, E.; Saitanis, C.J.; Fang, C.; Yu, Z. Use of ChatGPT: What does it mean for biology and environmental science? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallsworth, J.E.; Udaondo, Z.; Pedrós-Alió, C.; Höfer, J.; Benison, K.C.; Lloyd, K.G.; Cordero, R.J.; de Campos, C.B.; Yakimov, M.M.; Amils, R. Scientific novelty beyond the experiment. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 1131–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, F.M.; Chen, Y.; Ferris, J.A.; Knoth, S.; Jones-Farmer, L.A. How generative AI models such as chatgpt can be (mis) used in spc practice, education, and research? an exploratory study. Qual. Eng. 2023, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S.; Soliman, M. Game of algorithms: ChatGPT implications for the future of tourism education and research. J. Tour. Futures 2023, 9, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergus, S.; Botha, M.; Ostovar, M. Evaluating academic answers generated using ChatGPT. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 1672–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siche, R.; Siche, N. El modelo de lenguaje basado en inteligencia artificial sensible-ChatGPT: Análisis bibliométrico y posibles usos en la agricultura y pecuaria. Sci. Agropecu. 2023, 14, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.J.; Albert, A.; Ovid, A.; Alsharef, A. Leveraging ChatGPT to Aid Construction Hazard Recognition and Support Safety Education and Training. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfert, R.; van Nederveen, S.; Binnekamp, R. Fit for Purpose Building Information Modelling and Systems Integration (BIMSI) for Better Construction Projects Management. J. Mod. Proj. Manag. 2022, 10, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yu, Z. Do AI chatbots improve students learning outcomes? Evidence from a meta-analysis. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, S.A.S.; Gayoso, G.G.; Huambo, A.C.; Tapia, R.D.C.; Incaluque, J.L.; Aguila, O.E.P.; Cajamarca, J.C.R.; Acevedo, J.E.R.; Rivera, H.V.H.; Arias-Gonzáles, J.L. Examining the Impacts of ChatGPT on Student Motivation and Engagement. Soc. Space 2023, 23, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, J.; Cowling, M.; Allen, K. Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). J. Univ. Teach. Learn. Pract. 2023, 20, 02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoufan, A. Exploring Students’ Perceptions of CHATGPT: Thematic Analysis and Follow-Up Survey. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 38805–38818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, D.E.; Giordano, A.N. The Challenges and Value of Undergraduate Oral Exams in the Physical Chemistry Classroom: A Useful Tool in the Assessment Toolbox. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemachandran, K.; Verma, P.; Pareek, P.; Arora, N.; Rajesh Kumar, K.V.; Ahanger, T.A.; Pise, A.A.; Ratna, R. Artificial Intelligence: A Universal Virtual Tool to Augment Tutoring in Higher Education. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1410448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limo, F.A.F.; Tiza, D.R.H.; Roque, M.M.; Herrera, E.E.; Murillo, J.P.M.; Huallpa, J.J.; Flores, V.A.A.; Castillo, A.G.R.; Peña, P.F.P.; Carranza, C.P.M.; et al. Personalized tutoring: ChatGPT as a virtual tutor for personalized learning experiences. Soc. Space 2023, 23, 293–312. [Google Scholar]
- Alnaqbi, N.M.; Fouda, W. Exploring the Role of ChatGPT and social media in Enhancing Student Evaluation of Teaching Styles in Higher Education Using Neutrosophic Sets. Int. J. Neutrosophic Sci. 2023, 20, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Lee, S. Large language models in education: A focus on the complementary relationship between human teachers and ChatGPT. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, R.; Genç, Z.; Kayal, S.; Kamps, J. Reading Comprehension Quiz Generation Using Generative Pre-Trained Transformers. 2022. Available online: https://intextbooks.science.uu.nl/workshop2022/files/itb22_p1_full5439.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Pataranutaporn, P.; Leong, J.; Danry, V.; Lawson, A.P.; Maes, P.; Sra, M. AI-generated virtual instructors based on liked or admired people can improve motivation and foster positive emotions for learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Uppsala, Sweden, 8–11 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; Doss, C.; Mondschein, J.; Kopecky, D.; Fitton-Kane, V.; Bush, L.; Tucker, C. A pilot study investigating STEM learners’ ability to decipher AI-generated video. In Proceedings of the 2021 ASEE Virtual Annual Conference, Virtual Event, 13–15 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wardat, Y.; Tashtoush, M.A.; AlAli, R.; Jarrah, A.M. ChatGPT: A revolutionary tool for teaching and learning mathematics. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2023, 19, em2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halaweh, M. ChatGPT in education: Strategies for responsible implementation. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2023, 15, ep421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.M.; Gunasekara, A.; Pallant, J.L.; Pallant, J.I.; Pechenkina, E. Generative AI and the future of education: Ragnarök or reformation? A paradoxical perspective from management educators. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2023, 21, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.; Chen, N. Editorial Position Paper. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2023, 26, xviii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, Y. Generative artificial intelligence empowers educational reform: Current status, issues, and prospects. Front. Educ. 2023, 8, 1183162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Kshetri, N.; Hughes, L.; Slade, E.L.; Jeyaraj, A.; Kar, A.K.; Baabdullah, A.M.; Koohang, A.; Raghavan, V.; Ahuja, M.; et al. “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2023, 71, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, R.T.; Nasir, O.; Borit, M.; Vanhée, L.; Zea, E.; Gupta, S.; Vinuesa, R.; Qadir, J. Get out of the BAG! Silos in AI ethics education: Unsupervised topic modeling analysis of global AI curricula. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2022, 73, 933–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaali, G. Artificial Intelligence, Basic Skills, and Quantitative Literacy. Numeracy 2023, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, G. Establishing a delicate balance in the relationship between artificial intelligence and authentic assessment in student learning. Chem. Educ. Res. Pract. 2023, 24, 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.; Muirhead, B. Where do we go from here? An interdisciplinary exploration of leveraging new technologies in education. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Society and Information Technologies (ICSIT0), Orlando, FL, USA, 8–11 March 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Álvarez, C.; Falcon, S. Students’ preferences with university teaching practices: Analysis of testimonials with artificial intelligence. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOSviewer Manual: Manual for VOSviewer Version 1.6.15; Centre for Science and Technology Studies (CWTS) of Leiden University: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Januszewski, A.; Żółtowski, D. Emerging ICT for Sustainable Development. Research Concept of Literature Analysis. In Proceedings of the Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS) 2023, Panama City, Panama, 10–12 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Text mining and visualization using VOSviewer. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1109.2058. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI Codex. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/openai-codex (accessed on 28 July 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).