Comparing Different Strategies for Cr(VI) Bioremediation: Bioaugmentation, Biostimulation, and Bioenhancement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The CSS Samples
2.2. Microorganisms and Medium
2.3. Bioremediation Experiments
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Detection of Physicochemical Properties
2.4.2. Total Chromium, Cr(VI), and Cr(III) Determination
2.4.3. The Chemical Fraction of Chromium Determination by Sequential Extraction
2.5. The Leaching Toxicity Experiments after Bioremediation
2.6. Analysis of Microbial Community Structure
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The CSS Samples Characterization
3.2. Comparison of the Variation of pH and Eh in Different Bioremediation Systems
3.3. Comparison of the Removal of Cr(VI) in Two Bioremediation Systems
3.4. The Distribution of Chromium Fractions in Different Bioremediation Periods
3.5. The Leaching Toxicity in the CSS after Bioremediation
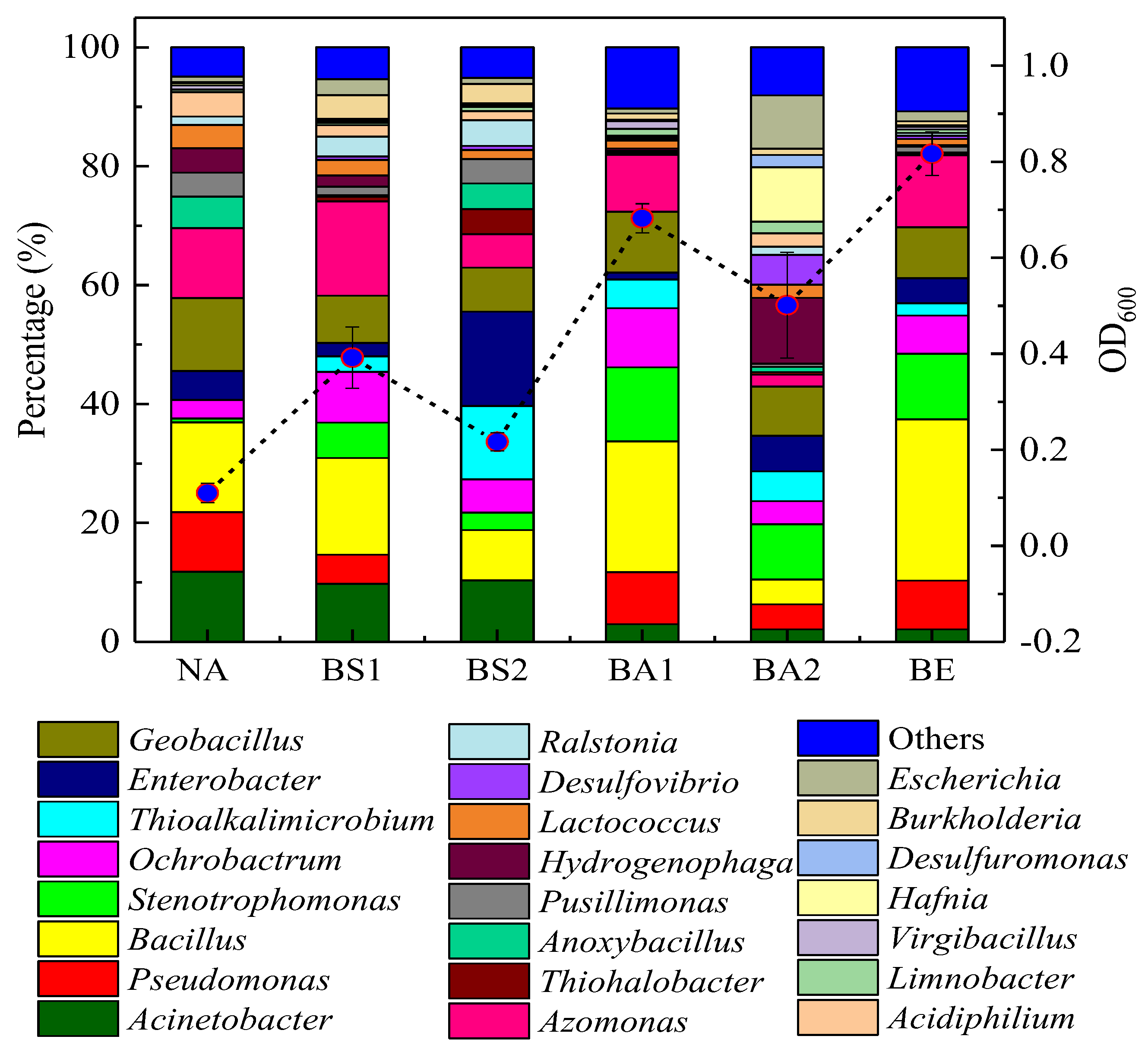
3.6. The Variation of Microbial Community Structure during Bioremediation Process
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Bioremediation Effects from Different Strategies
4.2. The Perdurable Stability of Chromium after Bioremediation
4.3. The Feasibility of the Bioremediation Cr(VI) from the CSS
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, I.G.; Terra, N.M.; Cardoso, V.L.; Batista, F.R.; Reis, M.H. Photoreduction of chromium (VI) in microstructured ceramic hollow fibers impregnated with titanium dioxide and coated with green algae Chlorella vulgaris. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120837. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Ding, C.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Shi, Y. Multi-omics response of Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB to hexavalent chromium. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, V.; Pakshirajan, K.; Chaturvedi, R. Chromium tolerance, bioaccumulation and localization in plants: An overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 715–730. [Google Scholar]
- Ishak, A.F.; Karim, N.A.; Ahmad, W.A.; Zakaria, Z.A. Chromate detoxification using combination of ChromeBac™ system and immobilized chromate reductase beads. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.M.; Viñarta, S.C.; Bernal, A.R.; Cruz, E.L.; Figueroa, L.I. Bioremediation strategies for chromium removal: Current research, scale-up approach and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Shamshad, S.; Rafiq, M.; Khalid, S.; Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C.; Rashid, M.I. Chromium speciation, bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 513–533. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Meng, F.; Li, L.; Wu, S. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by different surface-modified biochars: Acid washing, nanoscale zero-valent iron and ferric iron loading. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Sathvika, T.; Balaji, S.; Chandra, M.; Soni, A.; Rajesh, V.; Rajesh, N. A co-operative endeavor by nitrifying bacteria Nitrosomonas and zirconium based metal organic framework to remove hexavalent chromium. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 879–889. [Google Scholar]
- Vendruscolo, F.; da Rocha Ferreira, G.L.; Antoniosi Filho, N.R. Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by microorganisms. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobby, R.; Jha, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Desai, N. Biosorption and biotransformation of hexavalent chromium [Cr (VI)]: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Wang, Q.; Lv, M.; Chen, L. Microorganism remediation strategies towards heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Wu, C.F.; Yang, C.F.; Lin, C.W. Evaluation use of bioaugmentation and biostimulation to improve degradation of sulfolane in artificial groundwater. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.-B.; Shen, Y.; Huang, Y.-M.; Hu, N. A comparative study of aeration, biostimulation and bioaugmentation in contaminated urban river purification. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 11, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, E.E.; Saez, J.M.; Aparicio, J.D.; Fuentes, M.S.; Benimeli, C.S. Coupling of bioaugmentation and biostimulation to improve lindane removal from different soil types. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Cao, J.; Ma, X.; Ping, J.; Zhang, C.; Ke, T.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Chen, L. The simultaneous removal of the combined pollutants of hexavalent chromium and o-nitrophenol by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Sukla, L.B.; Mishra, B.B.; Devi, N. Biosorption for removal of hexavalent chromium using microalgae Scenedesmus sp. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, C.; Zhang, D.; Song, M.; Cai, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, G. Autochthonous bioaugmentation-modified bacterial diversity of phenanthrene degraders in PAH-contaminated wastewater as revealed by DNA-stable isotope probing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2934–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Ye, W.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Xie, J.; Zhong, K.; Bao, M.; Yang, J.; Wen, H.; Li, S. Enhanced reduction of sulfate and chromium under sulfate-reducing condition by synergism between extracellular polymeric substances and graphene oxide. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.-B.; Li, Q.; Li, C.-c.; Chen, T.-h.; Wang, J. Component analysis and heavy metal adsorption ability of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from sulfate reducing bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 194, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Li, F.; Jin, Z.; Yang, Y. Acidic leaching of potentially toxic metals cadmium, cobalt, chromium, copper, nickel, lead, and zinc from two Zn smelting slag materials incubated in an acidic soil. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Peng, D.; Zeng, C.; Xu, H. Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by nano-FeS coated humic acid complex in combination with Cr-resistant microflora. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, E.E.; Saez, J.M.; Aparicio, J.D.; Fuentes, M.S.; Benimeli, C.S. Bioremediation of lindane-contaminated soils by combining of bioaugmentation and biostimulation: Effective scaling-up from microcosms to mesocosms. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111309. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, D.; Huang, X.; Yang, H. Bioaugmentation potential evaluation of a bacterial consortium composed of isolated Pseudomonas and Rhodococcus for degrading benzene, toluene and styrene in sludge and sewage. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320 Pt A, 124329. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Yun, H.; Kong, D.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Vangnai, A.S.; Wang, A. Bioaugmentation of triclocarban and its dechlorinated congeners contaminated soil with functional degraders and the bacterial community response. Environ. Res. 2020, 180, 108840. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Gong, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. Bioremediation of Cr (VI) contaminated groundwater by Geobacter sulfurreducens: Environmental factors and electron transfer flow studies. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Misra, A.; Chaudhury, S.; Dam, B. A Bacillus strain TCL isolated from Jharia coalmine with remarkable stress responses, chromium reduction capability and bioremediation potential. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldiris, R.; Acosta-Tapia, N.; Montes, A.; Hernández, J.; Vivas-Reyes, R. Reduction of hexavalent chromium and detection of chromate reductase (ChrR) in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Molecules 2018, 23, 406. [Google Scholar]
- GracePavithra, K.; Jaikumar, V.; Kumar, P.S.; SundarRajan, P. A review on cleaner strategies for chromium industrial wastewater: Present research and future perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Ma, D.; Tang, C.; Hu, X. Lab-scale evaluation of the microbial bioremediation of Cr(VI): Contributions of biosorption, bioreduction, and biomineralization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22359–22371. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, D.; Sukla, L.B.; Sawyer, M.; Rahman, P.K.S.M. Recent bioreduction of hexavalent chromium in wastewater treatment: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 55, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mala, J.G.S.; Sujatha, D.; Rose, C. Inducible chromate reductase exhibiting extracellular activity in Bacillus methylotrophicus for chromium bioremediation. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 170, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Xun, P.; Morris, S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Liu, K.; He, K. Chromium exposure and incidence of metabolic syndrome among American young adults over a 23-year follow-up: The CARDIA Trace Element Study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15606. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, B.; Xin, J. Occurrence and fractionation of Cr along the Loushan River affected by a chromium slag heap in East China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15655–15666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapulova, A.; Dampilova, B.V.; Bardamova, I.; Doroshkevich, S.G.; Smirnova, O. Heavy metals mobility associated with the molybdenum mining-concentration complex in the Buryatia Republic, Germany. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 24, 11090–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, S.; Villasenor, J.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Canizares, P. Biostimulation versus bioaugmentation for the electro-bioremediation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid polluted soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Huang, J.-C.; Zhou, C.; He, S.; Zhou, W. Mutual effects of selenium and chromium on their removal by Chlorella vulgaris and associated toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, L.; Guo, X.; Han, Z.; Ji, L.; He, Q.; Han, L.; Sun, K. Mechanism of biochar as a biostimulation strategy to remove polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from heavily contaminated soil in a coking plant. Geoderma 2020, 375, 114497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Sun, H. Differences in bacterial community structure and potential functions among Eucalyptus plantations with different ages and species of trees. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 149, 103515. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.-Y.; Li, B.-B.; Yang, Z.-C.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Liu, D.-F.; Yu, H.-Q. Mediation of functional gene and bacterial community profiles in the sediments of eutrophic Chaohu Lake by total nitrogen and season. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-N.; Min, D.; Liu, D.-F.; Cheng, L.; Qian, C.; Li, W.-W.; Yu, H.-Q. Formation mechanism of organo-chromium (III) complexes from bioreduction of chromium (VI) by Aeromonas hydrophila. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Liang, B.; Yun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Qi, M.; Ma, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, A. Combined bioaugmentation with electro-biostimulation for improved bioremediation of antimicrobial triclocarban and PAHs complexly contaminated sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahbub, K.R.; Krishnan, K.; Andrews, S.; Venter, H.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Bio-augmentation and nutrient amendment decrease concentration of mercury in contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattnaik, S.; Dash, D.; Mohapatra, S.; Pattnaik, M.; Marandi, A.K.; Das, S.; Samantaray, D.P. Improvement of rice plant productivity by native Cr (VI) reducing and plant growth promoting soil bacteria Enterobacter cloacae. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, N.; Feng, C. Chromium (VI) Bioreduction Behavior and Microbial Revolution by Phosphorus Minerals in Continuous Flow Experiment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, D.C.; Bolanos-Benitez, V.; Sivry, Y.; Gelabert, A.; Riotte, J.; Subramanian, S. Mechanistic studies on the bioremediation of Cr(VI) using Sphingopyxis macrogoltabida SUK2c, a Cr(VI) tolerant bacterial isolate. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 150, 107292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, N.; Li, M.; Feng, C. Microbial reduction fate of chromium (Cr) in aqueous solution by mixed bacterial consortium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharagava, R.N.; Mishra, S. Hexavalent chromium reduction potential of Cellulosimicrobium sp. isolated from common effluent treatment plant of tannery industries. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, A.; Rehman, A. Comparative behavior of two gram positive Cr6+ resistant bacterial strains Bacillus aerius S1 and Brevibacterium iodinum S2 under hexavalent chromium stress. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 21, e00307. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Ye, X.; Yang, X.; Li, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q. Effects of alternating wetting and drying versus continuous flooding on chromium fate in paddy soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohne, T.; Diaz-Bone, R.A.; Laing, G.D.; Rinklebe, J. Impact of systematic change of redox potential on the leaching of Ba, Cr, Sr, and V from a riverine soil into water. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 623–633. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, H.; Rinklebe, J.R.; Bolze, S.; Meissner, R. A scale-dependent approach to study pollution control processes in wetland soils using three different techniques. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Kamila, B.; Barman, S.; Joshi, S.; Mandal, T.; Halder, G. Interlining Cr (VI) remediation mechanism by a novel bacterium Pseudomonas brenneri isolated from coalmine wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xue, K.; Liang, Y.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; Stahl, D.A.; et al. Stochasticity, succession, and environmental perturbations in a fluidic ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E836–E845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Lisiecki, P.; Białas, W.; Owsianiak, M.; Piotrowska-Cyplik, A.; Wolko, Ł.; Ławniczak, Ł.; Heipieper, H.J.; Gutierrez, T.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Effect of bioaugmentation on long-term biodegradation of diesel/biodiesel blends in soil microcosms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatoi, H.; Das, S.; Mishra, J.; Rath, B.P.; Das, N. Bacterial chromate reductase, a potential enzyme for bioremediation of hexavalent chromium: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 383–399. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Wang, G.; Lou, L.; Lv, J. Physiological responses and tolerance of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) exposed to chromium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Gong, Y.; Gao, J.; Sun, T.; Liu, Y. The reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) mediated by environmentally relevant carboxylic acids: State-of-the-art and perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 365, 205–226. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; He, C.; Chen, X.; Liang, X.; Huang, T.; Yang, X.; Shang, H. Comparative study of remediation of Cr(VI)-contaminated soil using electrokinetics combined with bioremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17682–17689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, U.; Coronado-Apodaca, K.G.; Meza-Escalante, E.R.; Ulloa-Mercado, G.; Serrano, D. Two combined mechanisms responsible to hexavalent chromium removal on active anaerobic granular consortium. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Amor, K.; Galer, S.J.; Thompson, I.; Porcelli, D. Variations of stable isotope fractionation during bacterial chromium reduction processes and their implications. Chem. Geol. 2018, 481, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Motesharezadeh, B.; Hosseini, H.M.; Alikhani, H.; Zolfaghari, A.A. Geochemical fractions and phytoavailability of Zinc in a contaminated calcareous soil affected by biotic and abiotic amendments. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 40, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.K.; Bhattacharya, T. Mobility, Ecological risk and change in surface morphology during sequential chemical extraction of heavy metals in fly ash: A case study. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 13, 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Elahi, A.; Ajaz, M.; Rehman, A.; Vuilleumier, S.; Khan, Z.; Hussain, S.Z. Isolation, characterization, and multiple heavy metal-resistant and hexavalent chromium-reducing Microbacterium testaceum B-HS2 from tannery effluent. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2019, 31, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, K.; Gao, W.; Zheng, Y. Bioremediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by a bioleaching system with weak magnetic fields. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 128, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruko, R.; Selvarajan, R.; Ogola, H.; Edokpayi, J.; Odiyo, J. Contemporary and future direction of chromium tanning and management in sub Saharan Africa tanneries. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 133, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, J.; Lu, J.; Sun, Y. Study on the influence of soil microbial community on the long-term heavy metal pollution of different land use types and depth layers in mine. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Nasir, M.; Lv, J.; Dai, Y.; Gao, J. Understanding the variation of microbial community in heavy metals contaminated soil using high throughput sequencing. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mishra, J.; Das, S.K.; Pandey, S.; Rao, D.S.; Chakraborty, A.; Sudarshan, M.; Das, N.; Thatoi, H. Investigation on mechanism of Cr (VI) reduction and removal by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, a novel chromate tolerant bacterium isolated from chromite mine soil. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, P.A.; Wahid, S.; Khan, M.S.A.; Rafi, N.; Wahid, N. Investigation of the role of chromium reductase for Cr (VI) reduction by Pseudomonas species isolated from Cr (VI) contaminated effluent. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minari, G.D.; Saran, L.M.; Constancio, M.T.L.; da Silva, R.C.; Rosalen, D.L.; de Melo, W.J.; Alves, L.M.C. Bioremediation potential of new cadmium, chromium, and nickel-resistant bacteria isolated from tropical agricultural soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, G.; Raza, K. Potential of novel Dunaliella salina from sambhar salt lake, India, for bioremediation of hexavalent chromium from aqueous effluents: An optimized green approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 430–438. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, H.; Xiao, C.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, W.; Bai, R.; Ding, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, F. Proteomic analysis of the reduction and resistance mechanisms of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 under long-term hexavalent chromium stress. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Oxide | Mass Percentage (wt %) | Oxide | Mass Percentage (wt %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MgO | 30.08 | NiO | 0.15 |
| CaO | 26.06 | TiO2 | 0.11 |
| SO3 | 10.95 | Cl | 0.1 |
| Fe2O3 | 9.35 | P2O5 | 0.09 |
| Cr2O3 | 8.96 | V2O5 | 0.08 |
| SiO2 | 7.33 | Co3O4 | 0.03 |
| Al2O3 | 5.23 | ZnO | 0.03 |
| Na2O | 0.71 | K2O | 0.02 |
| Bioremediation Strategies | Medium (mL) | CSS (g) | Microorganism | Inoculation Size (v/v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NA | Deionized water (300) | 180 | - | - |
| BS1 | BMA (300) | - | - | |
| BS2 | BMB (300) | - | - | |
| BA1 | Deionized water (300) | 180 | native microbes | 10 |
| BA2 | Deionized water (300) | 180 | SRB | 10 |
| BE | BMA (300) | 180 | native microbes | 10 |
| Extraction Procedures | Extraction Conditions | Chemical Forms |
|---|---|---|
| 16 mL Deionized water | Oscillation140 rpm for 18 h | F1 |
| 16 mL of 1 mol/L MgCl2 (pH = 7) | Oscillation 140 rpm for 1.5 h | F2 |
| 16 mL of 1 mol/L NaOAc (pH = 5) | Oscillation 140 rpm for 6 h | F3 |
| 16 mL of 0.04 mol/L NH2OH·HCl dissolved in 25% (m/v) HOAc | Intermittent oscillation 120 rpm in a thermostatic equipment (97 °C) for 5 h | F4 |
| 10 mL of 0.01 mol/L HNO3 and 8 mL of 30% (m/v) H2O2, and adding 5 mL of 3.2 mol/L NH4OAc in the 20% HNO3 | Oscillation 120 rpm in a thermostatic equipment (87 °C) for 4 h, then, oscillation 120 rpm for 30 min | F5 |
| 15 mL HCl + 5 mL HNO3 + 2 mL H2SO4 | Digestion for 3 h | F6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, X.; Yan, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, G.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M. Comparing Different Strategies for Cr(VI) Bioremediation: Bioaugmentation, Biostimulation, and Bioenhancement. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612522
Yan X, Yan Z, Zhu X, Zhou Y, Ma G, Li S, Liu X, Zhang M. Comparing Different Strategies for Cr(VI) Bioremediation: Bioaugmentation, Biostimulation, and Bioenhancement. Sustainability. 2023; 15(16):12522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612522
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Xiao, Zhenghao Yan, Xuezhe Zhu, Yupin Zhou, Guoying Ma, Shuangquan Li, Xingyu Liu, and Mingjiang Zhang. 2023. "Comparing Different Strategies for Cr(VI) Bioremediation: Bioaugmentation, Biostimulation, and Bioenhancement" Sustainability 15, no. 16: 12522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612522
APA StyleYan, X., Yan, Z., Zhu, X., Zhou, Y., Ma, G., Li, S., Liu, X., & Zhang, M. (2023). Comparing Different Strategies for Cr(VI) Bioremediation: Bioaugmentation, Biostimulation, and Bioenhancement. Sustainability, 15(16), 12522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612522







